Combined Geophysical Methods in Extreme Environments—An Example from the Dead Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
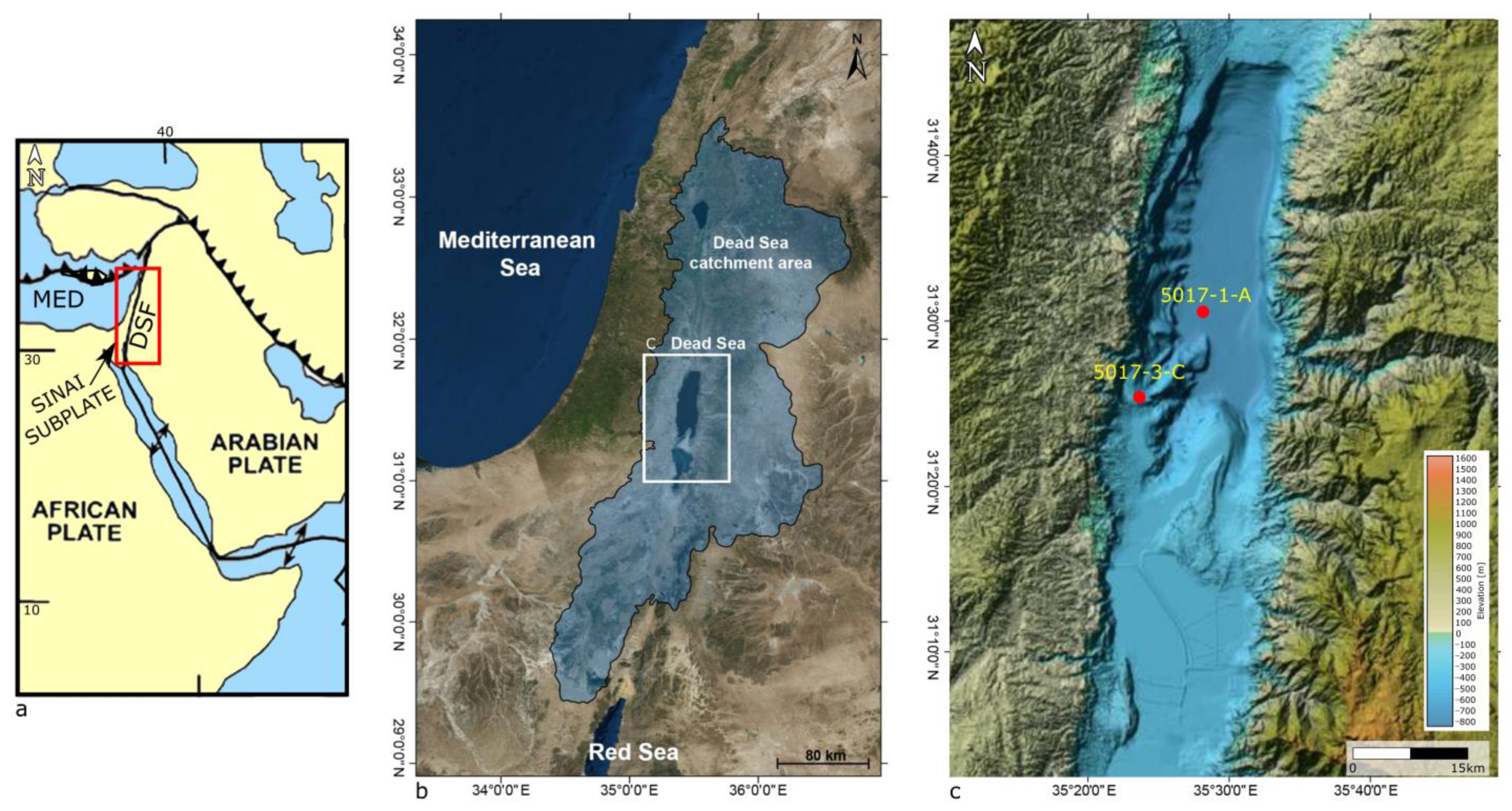
2. Geological Background
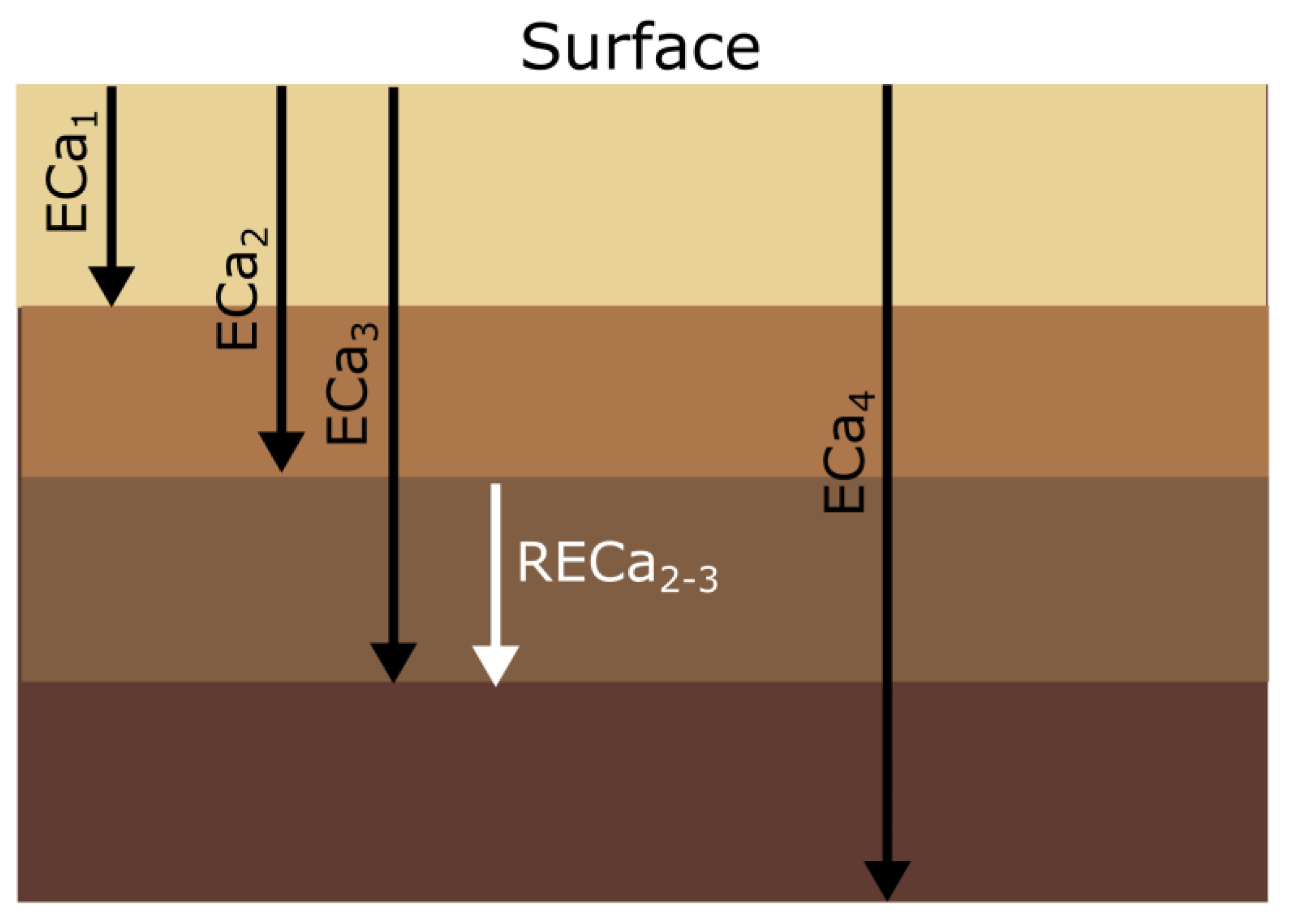
3. Materials and Methods
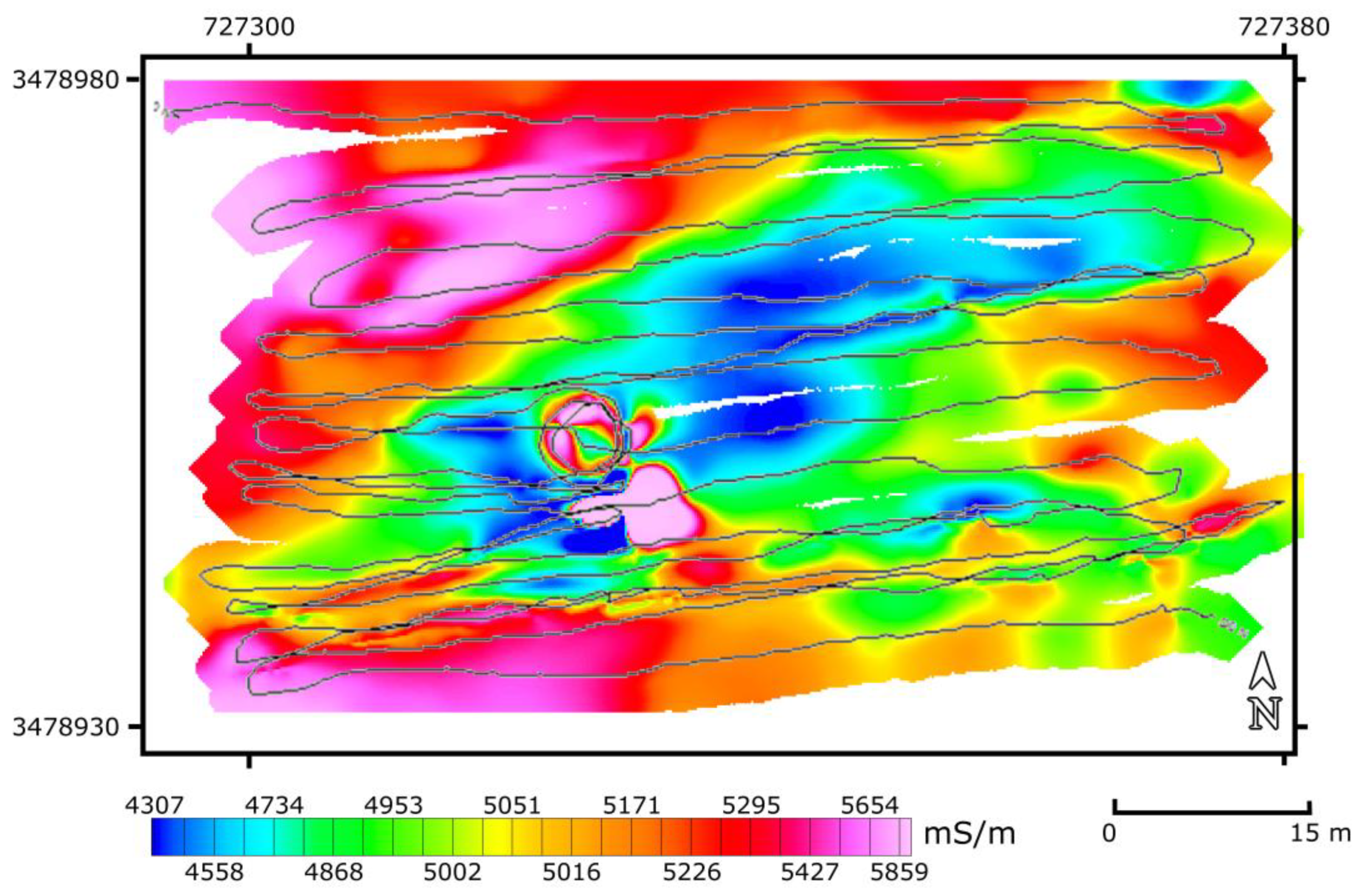
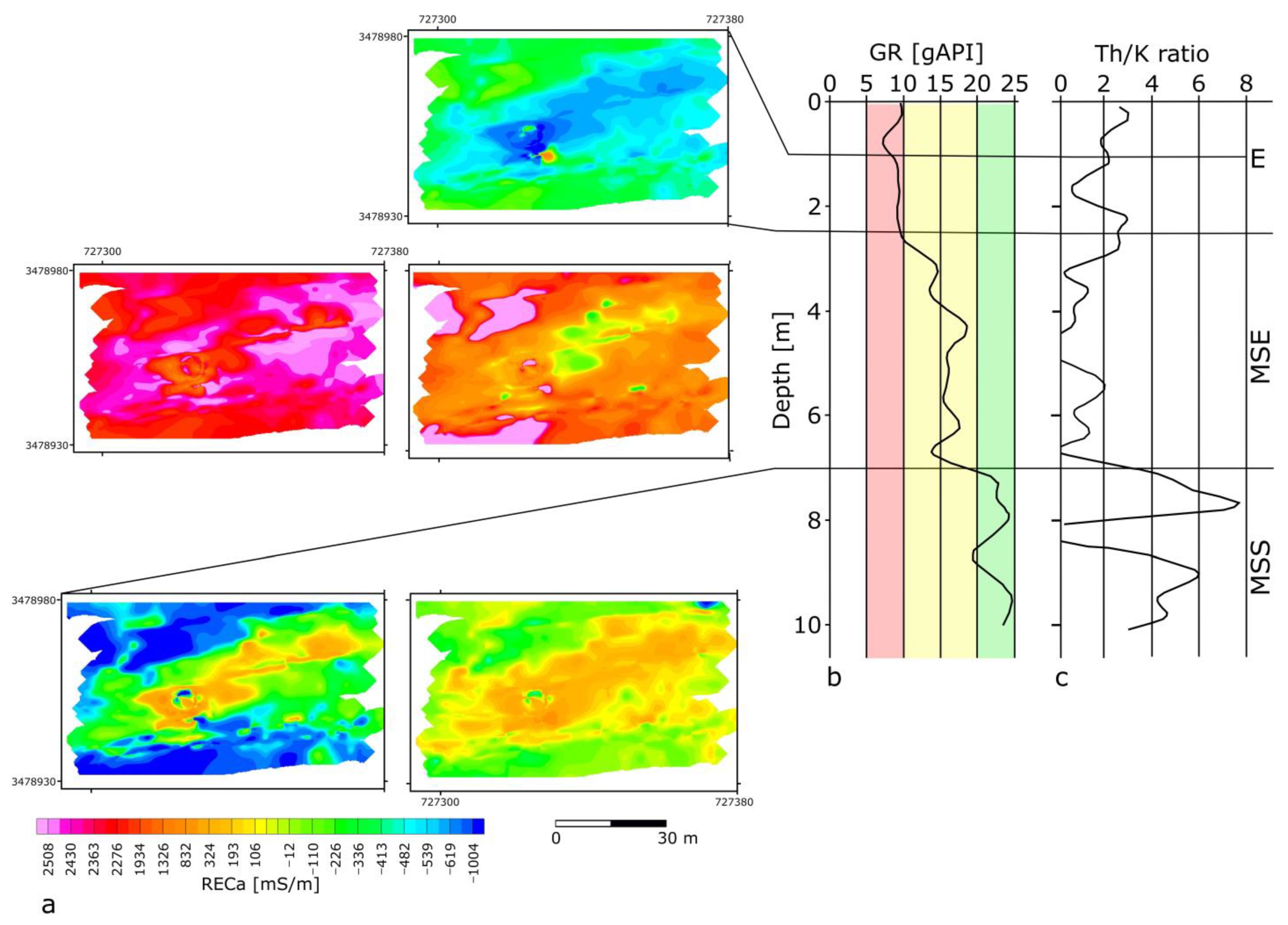
4. Results
5. Discussion

6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choudhury, K.; Saha, D.K. Integrated Geophysical and Chemical Study of Saline Water Intrusion. Groundwater 2004, 42, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obikoya, I.B.; Bennell, J.D. Geophysical Investigation of the Fresh-Saline Water Interface in the Coastal Area of Abergwyngregyn. J. Environ. Prot. 2012, 3, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costall, A.; Harris, B.; Pigois, J.P. Electrical Resistivity Imaging and the Saline Water Interface in High-Quality Coastal Aquifers. Surv. Geophys. 2018, 39, 753–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, C.S.; Jol, H.M. Ground Penetrating Radar in Sediments; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2003; ISBN 978-1-86239-459-9. [Google Scholar]
- Conyers, L.B. Ground-Penetrating Radar for Archaeology; Geophysical Methods for Archaeology; AltaMira Press: Walnut Creek, CA, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-0-7591-0773-1. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, M.; Leon, J.F.; Fisher, K.D.; Manning, S.W.; Sewell, D. Comparing Similar Ground-Penetrating Radar Surveys Under Different Moisture Conditions at Kalavasos-Ayios Dhimitrios, Cyprus. Archaeol. Prospect. 2012, 19, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezersky, M.; Eppelbaum, L.V.; Legchenko, A. Geophysical Methods Applied to the Sinkhole Investigation at the Dead Sea Coasts. In Applied Geophysics for Karst and Sinkhole Investigation: The Dead Sea and Other Regions; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ezersky, M.G.; Eppelbaum, L.V.; Al-Zoubi, A.; Keydar, S.; Abueladas, A.; Akkawi, E.; Medvedev, B. Geophysical Prediction and Following Development Sinkholes in Two Dead Sea Areas, Israel and Jordan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 1463–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Closson, D.; Abou Karaki, N. Sinkhole Hazards Prediction at Ghor Al Haditha, Dead Sea, Jordan: “Salt Edge” and “Tectonic” Models Contribution—A Rebuttal to “Geophysical Prediction and Following Development Sinkholes in Two Dead Sea Areas, Israel and Jordan, by: Ezersky, M.G., Eppelbaum, L.V., Al-Zoubi, A.3, Keydar, S., Abueladas, A.-R., Akkawi, E., and Medvedev, B.”. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 2919–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legchenko, A.; Ezersky, M.; Camerlynck, C.; Al-Zoubi, A.; Chalikakis, K. Joint Use of TEM and MRS Methods in a Complex Geological Setting. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2009, 341, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Brink, U.S.; Ben-Avraham, Z. The Anatomy of a Pull-Apart Basin: Seismic Reflection Observations of the Dead Sea Basin. Tectonics 1989, 8, 333–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Brink, U.S.; Flores, C.H. Geometry and Subsidence History of the Dead Sea Basin: A Case for Fluid-Induced Mid-Crustal Shear Zone? J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2012, 117, B01406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neev, D.; Hall, J.K. Geophysical Investigations in the Dead Sea. Sediment. Geol. 1979, 23, 209–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pe’eri, S.; Zebker, H.A.; Ben-Avraham, Z.; Frumkin, A.; Hall, J.K. Spatially-Resolved Uplift Rate of the Mount Sedom (Dead Sea) Salt Diapir from InSAR Observations. Isr. J. Earth Sci. 2004, 53, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coianiz, L.; Schattner, U.; Lang, G.; Ben-Avraham, Z.; Lazar, M. Between Plate and Salt Tectonics—New Stratigraphic Constraints on the Architecture and Timing of the Dead Sea Basin during the Late Quaternary. Basin Res. 2020, 32, 636–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neev, D.; Emery, K.O. The Dead Sea: Depositional Processes and Environments of Evaporites; Geological Survey: Jeruslaem, Israel, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Begin, Z.B.; Begîn, Z.B.; Ehrlich, A.; Nathan, Y. Lake Lisan: The Pleistocene Precursor of the Dead Sea; Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Geological Survey: Jeruslaem, Israel, 1974.
- Stein, M.; Starinsky, A.; Katz, A.; Goldstein, S.L.; Machlus, M.; Schramm, A. Strontium Isotopic, Chemical, and Sedimentological Evidence for the Evolution of Lake Lisan and the Dead Sea. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 3975–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, M. The Evolution of Neogene-Quaternary Water-Bodies in the Dead Sea Rift Valley. In Dead Sea Transform Fault System: Reviews; Garfunkel, Z., Ben-Avraham, Z., Kagan, E., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 279–316. ISBN 978-94-017-8872-4. [Google Scholar]
- Bartov, Y.; Goldstein, S.L.; Stein, M.; Enzel, Y. Catastrophic Arid Episodes in the Eastern Mediterranean Linked with the North Atlantic Heinrich Events. Geology 2003, 31, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bookman, R.; Enzel, Y.; Agnon, A.; Stein, M. Late Holocene Lake Levels of the Dead Sea. GSA Bull. 2004, 116, 555–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase-Schramm, A.; Goldstein, S.L.; Stein, M. U-Th Dating of Lake Lisan (Late Pleistocene Dead Sea) Aragonite and Implications for Glacial East Mediterranean Climate Change. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 985–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Vos, H.; Negendank, J.F.W.; Waldmann, N.; Goldstein, S.L.; Stein, M. Evidence from Lake Lisan of Solar Influence on Decadal- to Centennial-Scale Climate Variability during Marine Oxygen Isotope Stage 2. Geology 2004, 32, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, M.; Torfstein, A.; Gavrieli, I.; Yechieli, Y. Abrupt Aridities and Salt Deposition in the Post-Glacial Dead Sea and Their North Atlantic Connection. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2010, 29, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torfstein, A.; Goldstein, S.L.; Stein, M.; Enzel, Y. Impacts of Abrupt Climate Changes in the Levant from Last Glacial Dead Sea Levels. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2013, 69, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugebauer, I.; Brauer, A.; Schwab, M.J.; Waldmann, N.D.; Enzel, Y.; Kitagawa, H.; Torfstein, A.; Frank, U.; Dulski, P.; Agnon, A.; et al. Lithology of the Long Sediment Record Recovered by the ICDP Dead Sea Deep Drilling Project (DSDDP). Quat. Sci. Rev. 2014, 102, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiro, Y.; Goldstein, S.L.; Garcia-Veigas, J.; Levy, E.; Kushnir, Y.; Stein, M.; Lazar, B. Relationships between Lake-Level Changes and Water and Salt Budgets in the Dead Sea during Extreme Aridities in the Eastern Mediterranean. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 464, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Waldmann, N.; Nadel, D.; Marco, S. Increased Sedimentation Following the Neolithic Revolution in the Southern Levant. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2017, 152, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coianiz, L.; Ben-Avraham, Z.; Stein, M.; Lazar, M. Spatial and Temporal Reconstruction of the Late Quaternary Dead Sea Sedimentary Facies from Geophysical Properties. J. Appl. Geophys. 2019, 160, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coianiz, L.; Bialik, O.M.; Ben-Avraham, Z.; Lazar, M. Late Quaternary Lacustrine Deposits of the Dead Sea Basin: High Resolution Sequence Stratigraphy from Downhole Logging Data. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2019, 210, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torfstein, A.; Enzel, Y. Dead Sea Lake Level Changes and Levant Palaeoclimate. In Quaternary of the Levant; Enzel, Y., Bar-Yosef, O., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 115–126. ISBN 978-1-316-10675-4. [Google Scholar]
- Bookman, R. The Dead Sea and Its Deviation from Natural Conditions. In Large Asian Lakes in a Changing World: Natural State and Human Impact; Mischke, S., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–33. ISBN 978-3-030-42254-7. [Google Scholar]
- Migowski, C.; Stein, M.; Prasad, S.; Negendank, J.F.W.; Agnon, A. Holocene Climate Variability and Cultural Evolution in the Near East from the Dead Sea Sedimentary Record. Quat. Res. 2006, 66, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yechieli, Y.; Magaritz, M.; Levy, Y.; Weber, U.; Kafri, U.; Woelfli, W.; Bonani, G. Late Quaternary Geological History of the Dead Sea Area, Israel. Quat. Res. 1993, 39, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haliva-Cohen, A.; Stein, M.; Goldstein, S.L.; Sandler, A.; Starinsky, A. Sources and Transport Routes of Fine Detritus Material to the Late Quaternary Dead Sea Basin. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2012, 50, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelson, M.; Baer, G.; Shtivelman, V.; Wachs, D.; Raz, E.; Crouvi, O.; Kurzon, I.; Yechieli, Y. Collapse-sinkholes and Radar Interferometry Reveal Neotectonics Concealed within the Dead Sea Basin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 2003GL017103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, M.; Engoltz, K.; Basson, U.; Yasur-Landau, A. Water Saturated Sand and a Shallow Bay: Combining Coastal Geophysics and Underwater Archaeology in the South Bay of Tel Dor. Quat. Int. 2018, 473, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, M.; Basson, U.; Himmelstein, A.G.; Levy, T.E.; Arkin Shalev, E.; Yasur-Landau, A. The Door to Dor: Tracing Unseen Anthropogenic Impact in an Ancient Port. Geoarchaeology 2021, 36, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, I.J.; Keiswetter, D.A.; Fields, G.R.A.; Sutton, L.C. GEM-2: A New Multifrequency Electromagnetic Sensor. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 1996, 1, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Won, I.J. Real-time Resistivity Sounding Using a Hand-held Broadband Electromagnetic Sensor. Geophysics 2003, 68, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H. Depth of Investigation for Small Broadband Electromagnetic Sensors. Geophysics 2005, 70, G135–G142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudduth, K.A.; Kitchen, N.R.; Wiebold, W.J.; Batchelor, W.D.; Bollero, G.A.; Bullock, D.G.; Clay, D.E.; Palm, H.L.; Pierce, F.J.; Schuler, R.T.; et al. Relating Apparent Electrical Conductivity to Soil Properties across the North-Central USA. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2005, 46, 263–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spies, B.R. Depth of Investigation in Electromagnetic Sounding Methods. Geophysics 1989, 54, 872–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldshleger, N.; Basson, U.; Azaria, I.; Fastig, S. Using Combined Close-Range Active and Passive- Remote Sensing Methods to Detect Sinkholes. J. Remote Sens. GIS 2018, 7, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldshleger, N.; Basson, U. Utilization of Ground-Penetrating Radar and Frequency Domain Electromagnetic for Investigation of Sewage Leaks. In Environmental Applications of Remote Sensing; Marghany, M., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-953-51-2443-6. [Google Scholar]
- Goldshleger, N.; Shamir, O.; Basson, U.; Zaady, E. Frequency Domain Electromagnetic Method (FDEM) as a Tool to Study Contamination at the Sub-Soil Layer. Geosciences 2019, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, J.D. Electrical Conductivity of Soils and Rocks; Technical Note 5; Geonics LTD: Mississauga, ON, Canada, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Beamish, D. Low Induction Number, Ground Conductivity Meters: A Correction Procedure in the Absence of Magnetic Effects. J. Appl. Geophys. 2011, 75, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weymer, B.A.; Everett, M.E.; Houser, C.; Wernette, P.; Barrineau, P. Differentiating Tidal and Groundwater Dynamics from Barrier Island Framework Geology: Testing the Utility of Portable Multifrequency Electromagnetic Induction Profilers. Geophysics 2016, 81, E347–E361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Deszcz-Pan, M.; Smith, B. Limitations of Small EM Sensors in Resistive Terrain. In Symposium on the Application of Geophysics to Engineering and Environmental Problems Proceedings; The Environmental and Engineering Geophysical Society: Denver, CO, USA, 2008; pp. 163–180. [Google Scholar]
- Jadoon, K.Z.; Altaf, M.U.; McCabe, M.F.; Hoteit, I.; Muhammad, N.; Moghadas, D.; Weihermüller, L. Inferring Soil Salinity in a Drip Irrigation System from Multi-Configuration EMI Measurements Using Adaptive Markov Chain Monte Carlo. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 5375–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delefortrie, S.; Saey, T.; Van De Vijver, E.; De Smedt, P.; Missiaen, T.; Demerre, I.; Van Meirvenne, M. Frequency Domain Electromagnetic Induction Survey in the Intertidal Zone: Limitations of Low-Induction-Number and Depth of Exploration. J. Appl. Geophys. 2014, 100, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevnin, V.; Mousatov, A.; Ryjov, A.; Delgado-Rodriquez, O. Estimation of Clay Content in Soil Based on Resistivity Modelling and Laboratory Measurements. Geophys. Prospect. 2007, 55, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, H.L.; Hunter, J.A.; Olson, L.C.; Pugin, A.J.-M.; Russell, H.A.J. Borehole Geophysical Log Signatures and Stratigraphic Assessment in a Glacial Basin, Southern Ontario. Can. J. Earth Sci. 2018, 55, 829–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayal, J.R. Electrical and Gamma-Ray Logging in Gondwana and Tertiary Coal Fields of India. Geoexploration 1979, 17, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D. The Role of Downhole Measurements in Marine Geology and Geophysics. Rev. Geophys. 1997, 35, 315–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soua, M. Paleozoic Oil/Gas Shale Reservoirs in Southern Tunisia: An Overview. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2014, 100, 450–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, F.F.; Al-Rashed, A.R. Recognition of Lithostratigraphic Breaks in Undifferentiated Rock Units Using Well Logs: A Flow Chart. J. Geol. Geophys. 2015, 4, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, M.; Siebert, C. Out of Sight, out of Mind. Submarine Springs in the Dead Sea—An Underappreciated Phenomenon. Geomorphology 2023, 436, 108777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamir, G. The Active Structure of the Dead Sea Depression. In New Frontiers in Dead Sea Paleoenvironmental Research; Enzel, Y., Agnon, A., Stein, M., Eds.; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2006; Volume 401, ISBN 978-0-8137-2401-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzler, N.; Sagy, A.; Marco, S. The Association of Micro-Earthquake Clusters with Mapped Faults in the Dead Sea Basin. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2014, 119, 8312–8330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, M.; Ben-Avraham, Z.; Schattner, U. Formation of Sequential Basins along a Strike–Slip Fault–Geophysical Observations from the Dead Sea Basin. Tectonophysics 2006, 421, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagy, A.; Reches, Z.; Agnon, A. Hierarchic Three-Dimensional Structure and Slip Partitioning in the Western Dead Sea Pull-Apart. Tectonics 2003, 22, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartov, Y.; Sagy, A. Late Pleistocene Extension and Strike-Slip in the Dead Sea Basin. Geol. Mag. 2004, 141, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Closson, D.; Karaki, N.A. Salt Karst and Tectonics: Sinkholes Development along Tension Cracks between Parallel Strike-Slip Faults, Dead Sea, Jordan. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 1408–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
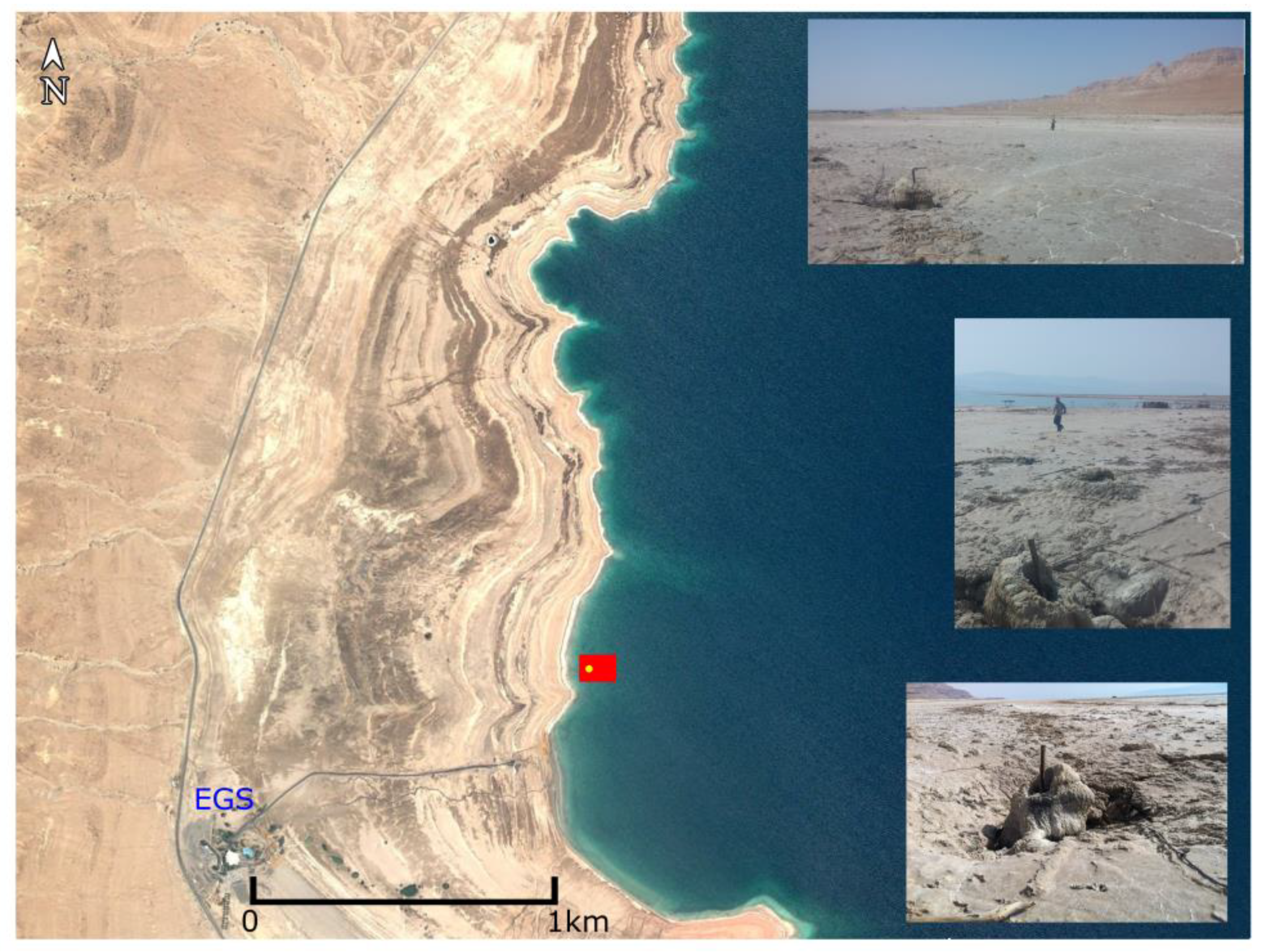

| Frequency (Hz) | Range of Effective Penetration (m) |
|---|---|
| 825 | 5.1–9.1 |
| 1925 | 4.6–7.7 |
| 4425 | 4.0–6.3 |
| 10,425 | 3.1–4.7 |
| 24,425 | 2.1–3.6 |
| 57,225 | 1.7–2.6 |
| Frequency (Hz) | Range of ECa (mS/m) |
|---|---|
| 825–1925 | −340–360 |
| 1925–4425 | −1360–450 |
| 4425–10,425 | −83–3500 |
| 10,425–24,425 | 1820–2520 |
| 24,425–57,225 | −630–−70 |
| 57,225 | 2295–2410 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lazar, M.; Cheng, L.; Basson, U. Combined Geophysical Methods in Extreme Environments—An Example from the Dead Sea. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16111978
Lazar M, Cheng L, Basson U. Combined Geophysical Methods in Extreme Environments—An Example from the Dead Sea. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(11):1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16111978
Chicago/Turabian StyleLazar, Michael, Linjing Cheng, and Uri Basson. 2024. "Combined Geophysical Methods in Extreme Environments—An Example from the Dead Sea" Remote Sensing 16, no. 11: 1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16111978
APA StyleLazar, M., Cheng, L., & Basson, U. (2024). Combined Geophysical Methods in Extreme Environments—An Example from the Dead Sea. Remote Sensing, 16(11), 1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16111978









