Investigation of Electromagnetic Scattering Mechanisms from Dynamic Oil Spill–Covered Sea Surface
Abstract
1. Introduction
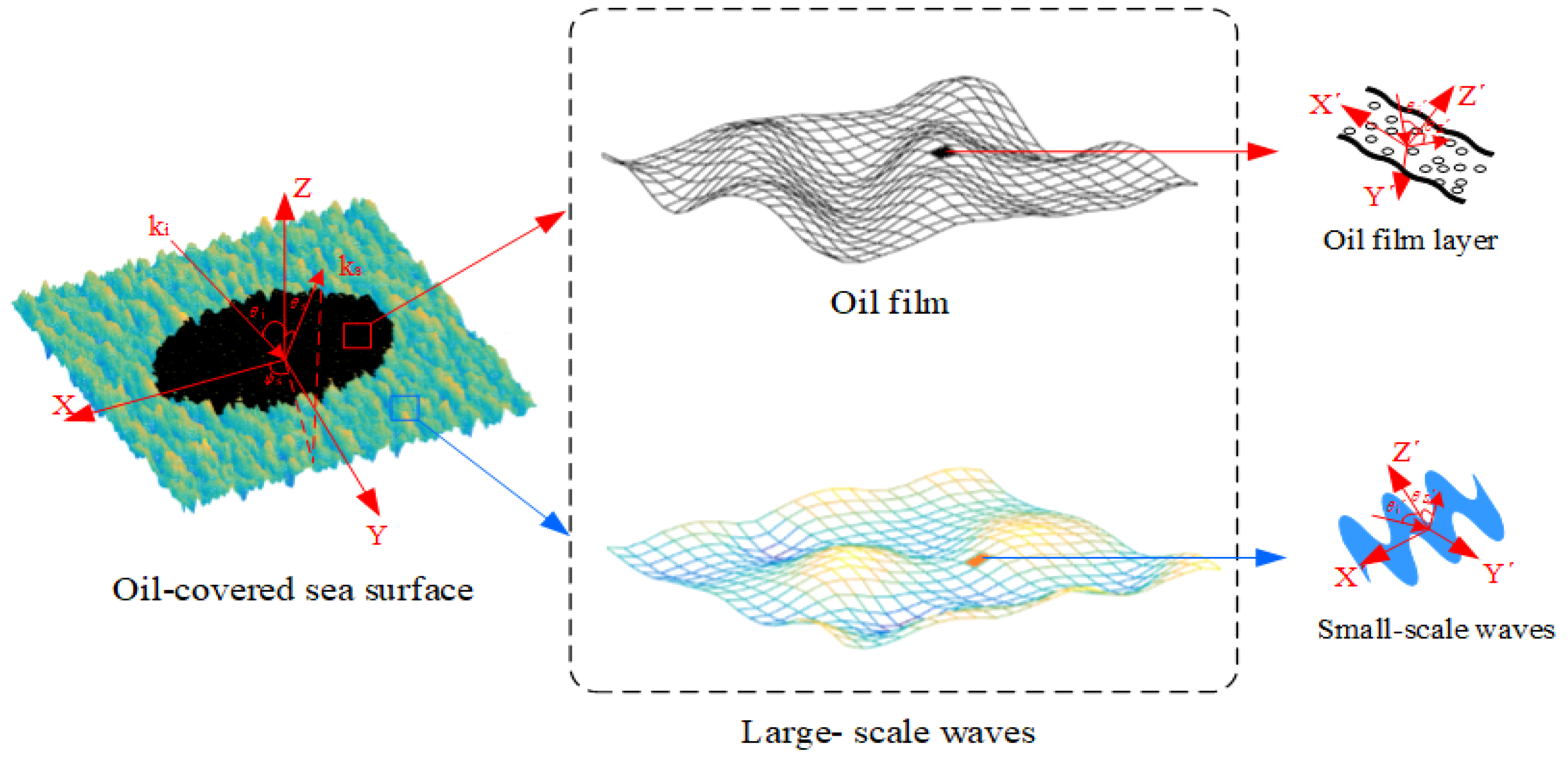
2. The 3D Geometric Model of Oil Spill–Covered Sea Surface Area
2.1. Sea Spectrum
2.2. Oil/Water Mixture
2.3. Oil Spill Diffusion
2.4. Sea Surface
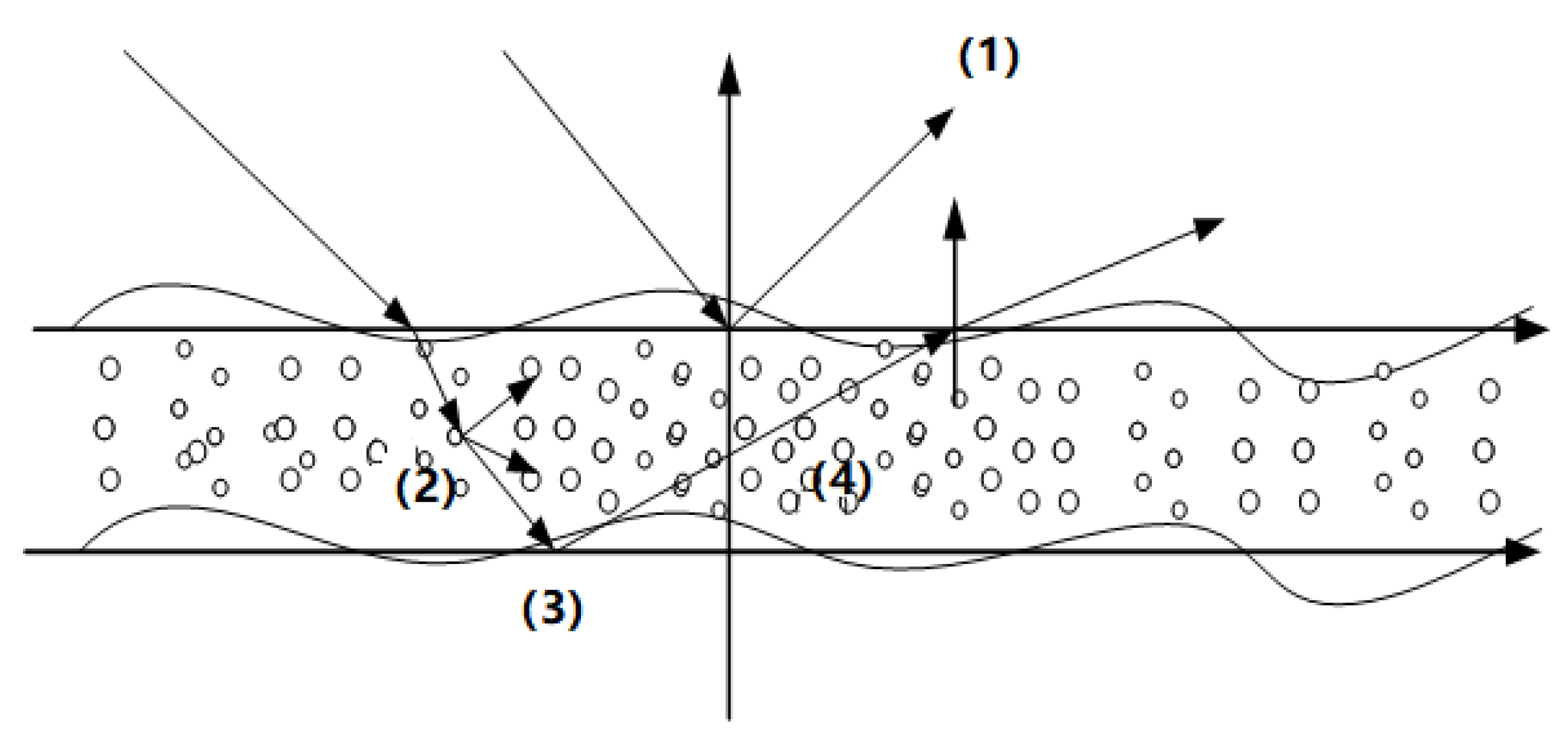
3. EM Scattering Model
3.1. The EM Scattering of Clean Sea
3.2. The EM Scattering of Oil Spill-Covered Sea
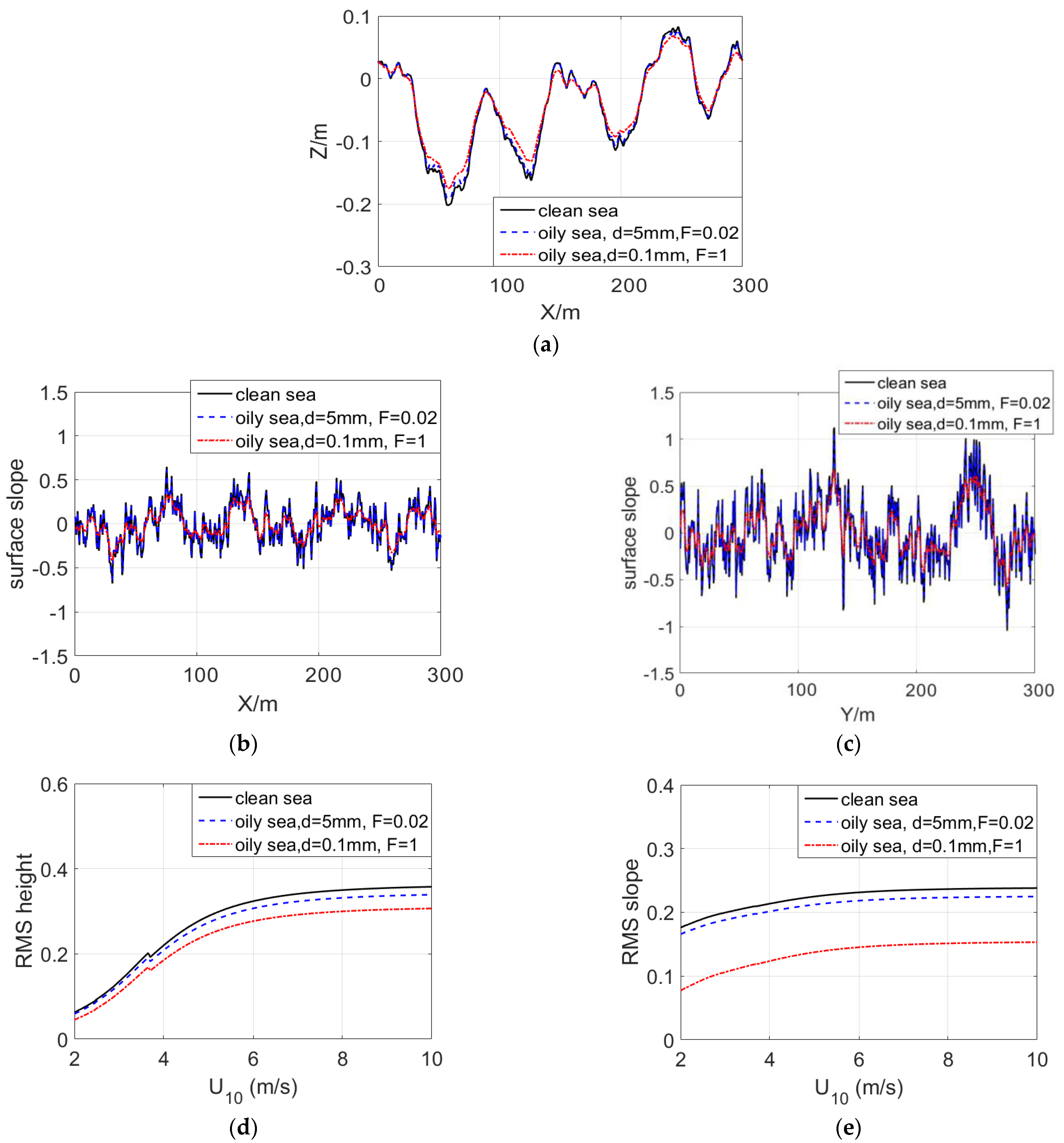
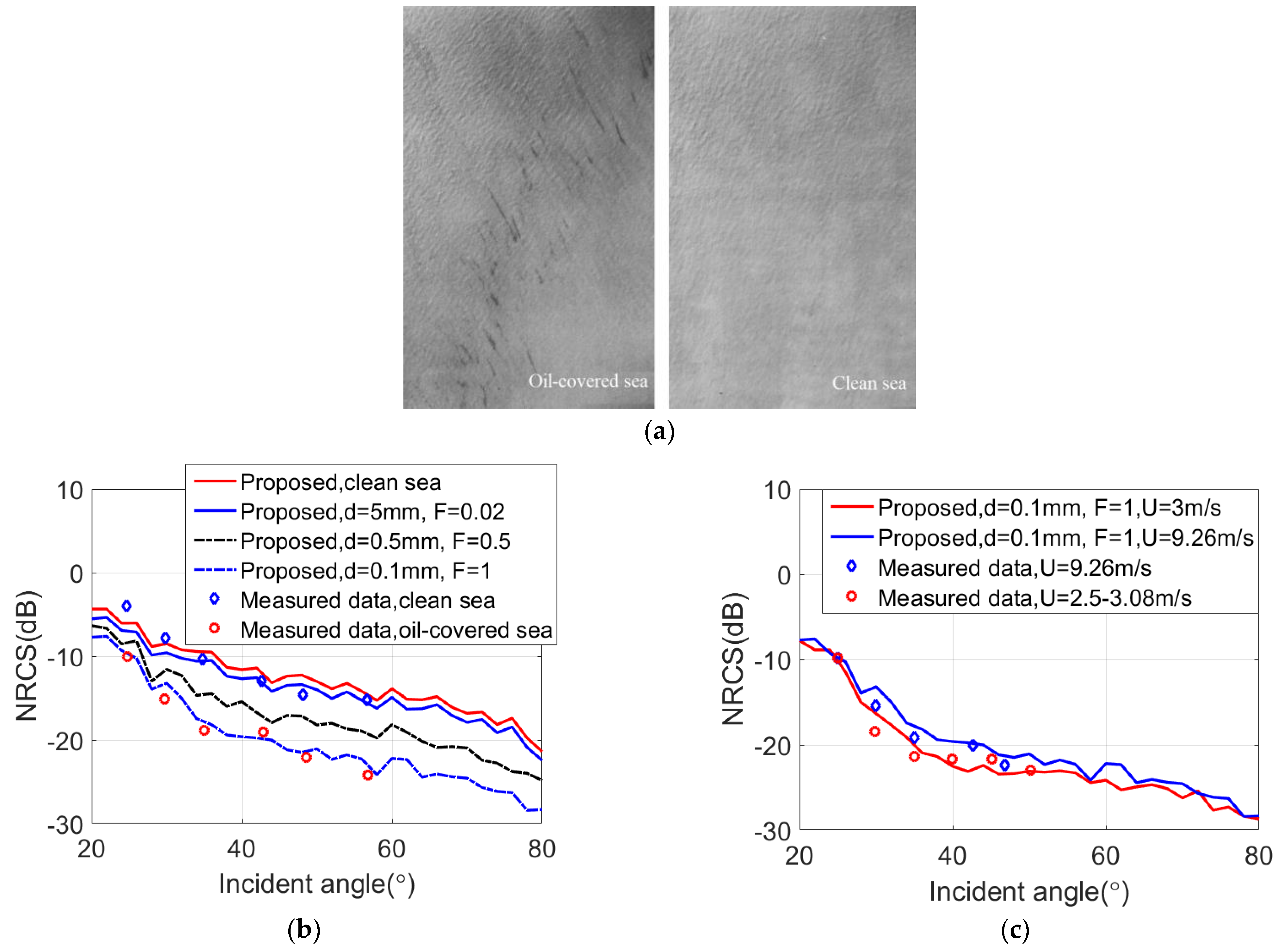
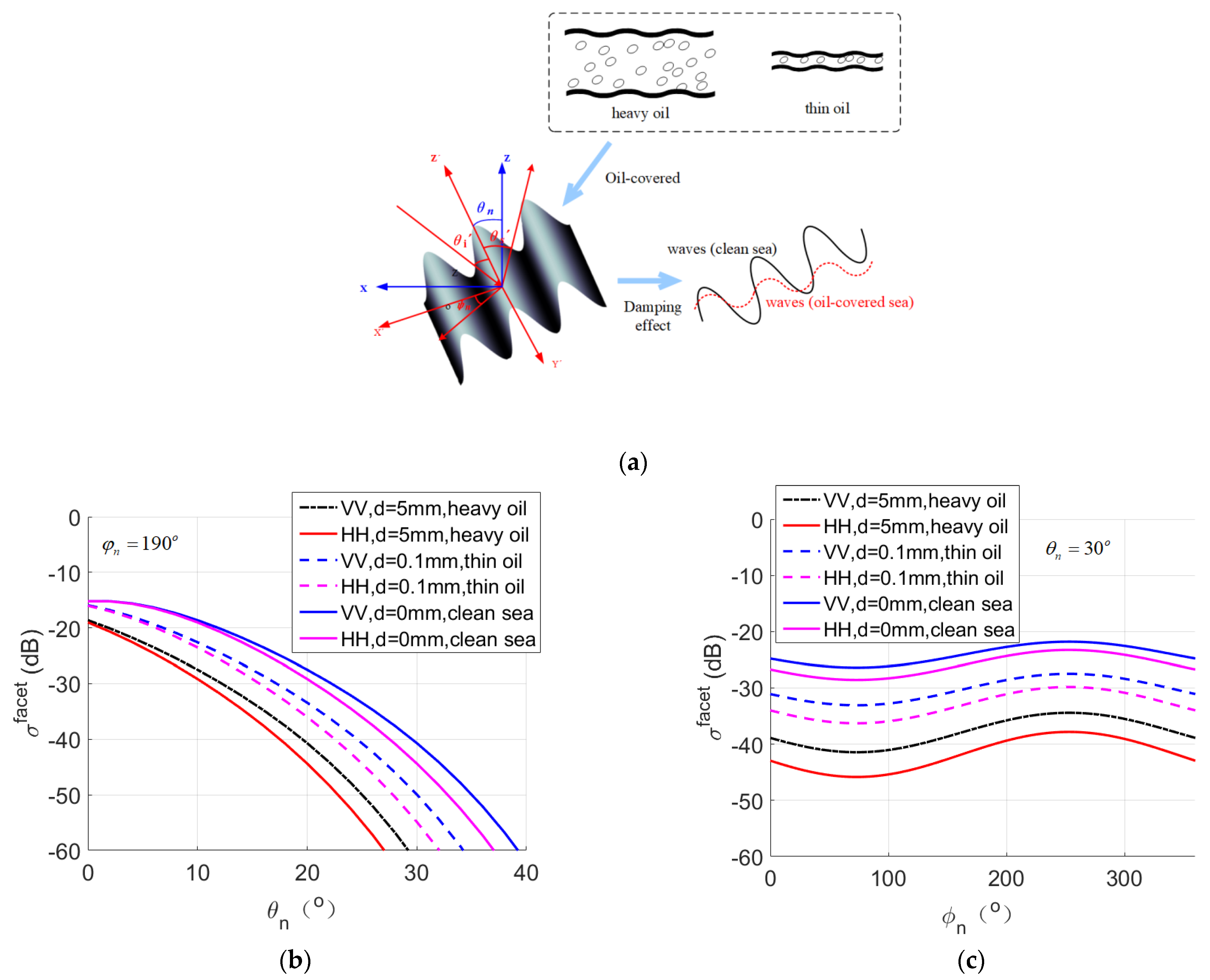
4. Results and Discussion
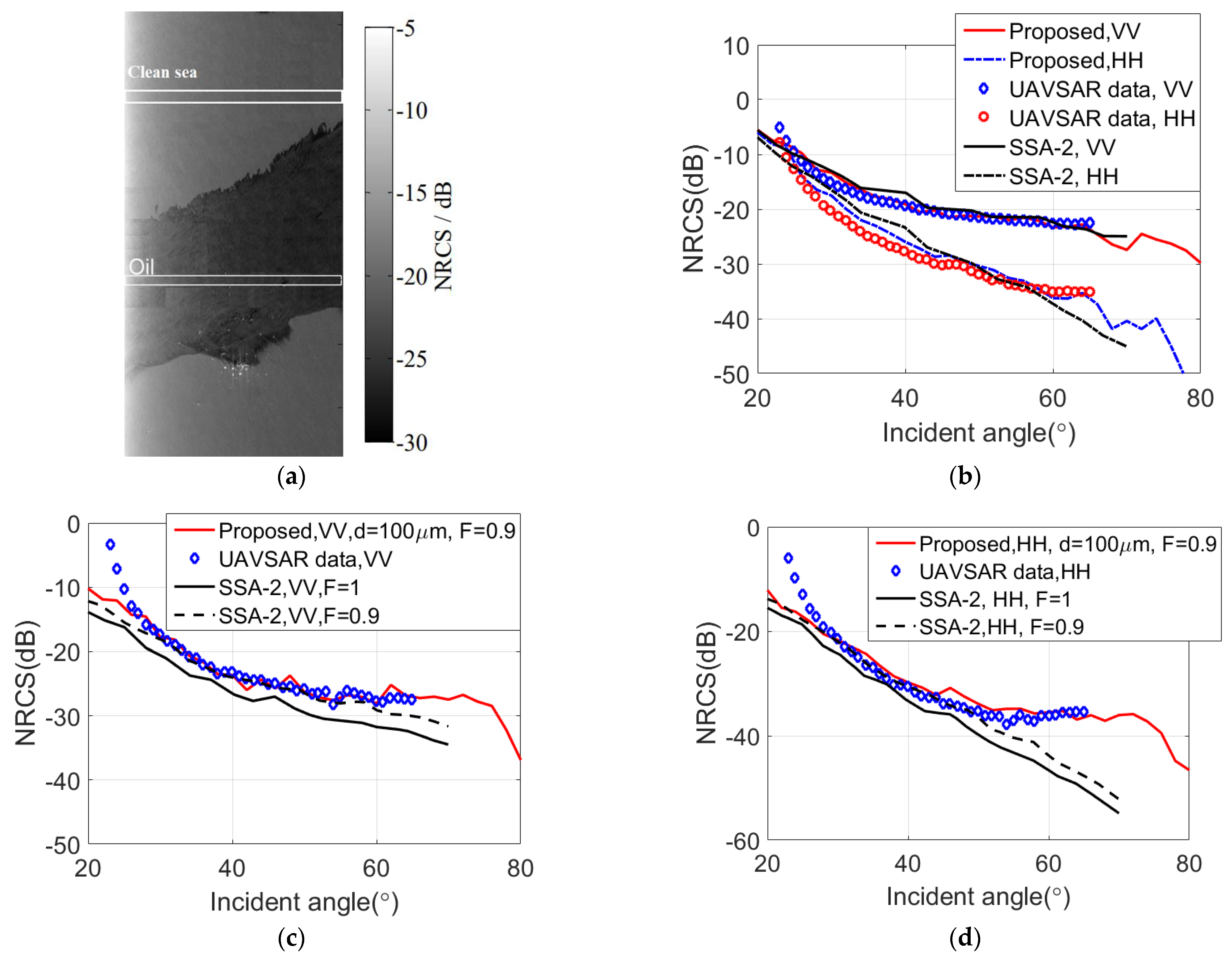
4.1. Comparison of Experimental Data and Simulation Results
4.2. Comparison of Hydrodynamic and Tilt Modulation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing: Active and Passive Volume III: Volume Scattering and Emission Theory, Advanced Systems, and Applications; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Pinel, N.; Dechamps, N.; Bourlier, C. Modeling of the bistatic electromagnetic scattering from sea surfaces covered in oil for microwave applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingas, M.; Brown, C. Review of oil spill remote sensing. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierson, J.W.; Moscowitz, L. A proposed spectral form for fully developed wind seas based on the similarity theory of S. A. kitaigorodsrii. J. Geophys. Res. 1964, 69, 5181–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselmann, K.; Barnett, T.P.; Bouws, E.; Carlson, H.; Cartwright, D.E.; Enke, K.; Ewing, J.A.; Gienapp, H.; Hasselmann, D.E.; Kruseman, P.; et al. Measurements of wind-wave growth and swell decay during the Joint North Sea Wave Project (JONSWAP). Deutches Hydrogr. Inst. 1973, 12, 1–95. [Google Scholar]
- Elfouhaily, T.; Chapron, B.; Katsaros, K. A unified directional spectrum for long and short wind-driven waves. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 15781–15796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardini, P.P.; Fiscella, B.; Trivero, P.; Cappa, C.; Garrett, W.D. Modulation of the Spectra of Short Gravity Waves by Sea Surface spills: Slick Detection and Characterization with a Microwave Probe. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1989, 6, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, A.D.; Jacobs, S.J. Wave damping by a thin layer of viscous fluid. Phys. Fluids 1997, 9, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakov, S.A.; Zujkova, A.M.; Panchenko, A.R.; Salashin, S.G.; Talipova, T.G.; Titov, V.I. Surface film effect on short wind waves. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 1986, 10, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinel, N.; Bourlier, C.; Sergievskaya, I. Unpolarized emissivity of thin oil spills over anisotropic Gaussian seas in infrared window regions. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, A.J.; Hurford, N.; Penn, C.J. Shear Diffusion and the Spreading of Oil—Slicks. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1986, 17, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoult, D.P. Oil Spreading on Sea. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1972, 4, 341–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.P. Turbulent diffusion of oil in the ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1972, 27, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.M.; Chew, W.C. Multilevel fast multipole algorithm for electromagnetic scattering by large complex objects. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1997, 45, 1488–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holliday, D. Resolution of a controversy surrounding the Kirchhoff approach and the small perturbation method in rough surface scattering theory. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1987, 35, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, S.O. Reflection of electromagnetic waves from slightly rough surfaces. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 1951, 4, 351–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J. A new model for sea clutter. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1968, 16, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhao, Z.; Qi, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Nie, Z. An Improved Two-Scale Model for Electromagnetic Backscattering from Sea Surface. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhao, Z. Facet-Based Hybrid Method for Electromagnetic Scattering from Shallow Water Waves Modulated by Submarine Topography. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 2004314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, A.K. Microwave Scattering and Emission Models and Their Applications; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Voronovich, A.G. Wave Scattering from Rough Surfaces; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Voronovich, A.G. Small-slope approximation in wave scattering from rough surfaces. Sov. Phys. JETP 1985, 62, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Mityagina, M.; Churumov, A. Radar backscattering at sea surface covered with oil spills. In Global Development in Environment Earth Observation from Space; Marcal, A., Ed.; Millpress: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 783–790. [Google Scholar]
- Ayari, M.Y.; Coatanhay, A.; Khenchaf, A. The influence of ripple damping on electromagnetic bistatic scattering by sea surface. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 25–29 July 2005; pp. 1345–1348. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Guo, L.; Jia, C. A semiempirical model for electromagnetic scattering from dielectric 1-D dielectric sea surface covered by oil spill. In Proceedings of the General Assembly and Scientific Symposium (URSI GASS), Beijing, China, 16–23 August 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Khenchaf, A.; Wang, Y.; Ghanmi, H.; Zhao, C. Investigation of EM Backscattering from Slick-Free and Slick-Covered Sea Surfaces Using the SSA-2 and SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.W.; Croswell, W.F. Characteristics of 13.9 GHz radar scattering from oil spills on the sea surface. Radio Sci. 1982, 17, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Gray, A.L.; Hawkins, R.K.; O’neil, R. The influence of surface oil on C- and Ku-band ocean backscatter. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1986, 24, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, M.; Alpers, W.; Huhnerfuss, H. On the reduction of the radar backscatter by oceanic surface spills: Scatterometer measurements and their theoretical interpretation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 52–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panfifilova, M.A.; Karaev, V.Y.; Guo, J. Oil slick observation at low incidence angles in Ku-band. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 1924–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montuori, A.; Nunziata, F.; Migliaccio, M.; Sobieski, P. X-band two-scale sea surface scattering model to predict the contrast due to an oil slick. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 4970–4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinel, N.; Bourlier, C.; Sergievskaya, I.; Longepe, N.; Hajduch, G. Asymptotic modeling of three dimensional radar backscattering from oil slicks on sea surfaces. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Nie, Z. A Modified Model for Electromagnetic Scattering of Sea Surface Covered with Crest Foam and Static Foam. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanmi, H.; Khenchaf, A.; Comblet, F. Numerical Modeling of Electromagnetic Scattering from Sea Surface Covered by Oil. J. Electromagn. Anal. Appl. 2014, 6, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, M. Imaging of biogenic and anthropogenic ocean surface spills by the multifrequency/multipolarization SIR-C/X-SAR. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 18851–18866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skou, N. Microwave Radiometry for Oil Pollution Monitoring, Measurements, and Systems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1986, GE–24, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhomenko, E.I. Electrical Properties of Rocks; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Meissner, T.; Wentz, J. The complex dielectric constant of pure and sea water from microwave satellite observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1836–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.; Khan, F.; Amyotte, P.; Sadiq, R. Multimedia fate of oil spills in a marine environment--An integrated modelling approach. Process Saf. Environ. Protect. 2008, 86, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay, J.A. The Spread of Oil Slick on a Calm Sea; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1969; pp. 53–63. [Google Scholar]
- Lehr, W.J.; Belen, M.S. A New Technique to estimate initial spill size using a modified Fay-Type spreading formula. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1984, 15, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carratelli, E.P.; Dentale, F.; Reale, F. On the effects of wave-induced drift and dispersion in the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Monitoring and Modeling the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill: A Record-Breaking Enterprise. Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 2011, 195, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Krishen, K. Detection of Oil Spills Using a 13.3-GHz Radar Scatterometer. J. Geophys. Res. 1973, 78, 1952–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.N.; Swayze, G.A.; Leifer, I.; Livo, K.E.; Kokaly, R.F.; Hoefen, T.; Lundeen, S.; Eastwood, M.; Green, R.O.; Pearso, N.; et al. A Method for Quantitative Mapping of Thick Oil Spills Using Imaging Spectroscopy; Open-File Report 1167; U.S. Geological Survey: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Minchew, B.; Cathleen, E.J.; Holt, B. Polarimetric Analysis of Backscatter From the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill Using L-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar. IEEE Trans. Geoscie Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3812–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Meng, J.; Zhang, X. THE damping model for sea waves covered by oil spills of a finite thickness. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2015, 34, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Physical Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Water density (ρ) | 1023 kg · m−3 |
| Oil density (ρ+) | 900 kg · m−3 |
| Surface viscosity (υs+) | 0 |
| Interfacial viscosity (υs−) | 0 |
| Kinematic viscosity of water(υ) | 10−6 m2 · S−1 |
| Kinematic viscosity of oil (υ+) | 10−4 m2 · S−1 |
| Surface elasticity (χ+) | 15 mN · m−1 |
| Interfacial elasticity (χ−) | 10 mN · m−1 |
| Surface tension (γ+) | 25 mN · m−1 |
| Interfacial tension (γ−) | 15 mN · m−1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, W.; Xue, Y. Investigation of Electromagnetic Scattering Mechanisms from Dynamic Oil Spill–Covered Sea Surface. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071777
Li D, Zhao Z, Ma W, Xue Y. Investigation of Electromagnetic Scattering Mechanisms from Dynamic Oil Spill–Covered Sea Surface. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(7):1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071777
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dongfang, Zhiqin Zhao, Wenying Ma, and Yajuan Xue. 2023. "Investigation of Electromagnetic Scattering Mechanisms from Dynamic Oil Spill–Covered Sea Surface" Remote Sensing 15, no. 7: 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071777
APA StyleLi, D., Zhao, Z., Ma, W., & Xue, Y. (2023). Investigation of Electromagnetic Scattering Mechanisms from Dynamic Oil Spill–Covered Sea Surface. Remote Sensing, 15(7), 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071777






