Extraction and Analysis of Radar Scatterer Attributes for PAZ SAR by Combining Time Series InSAR, PolSAR, and Land Use Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Geometric Attribute Extraction
2.1.1. Coherent Radar Scatterer Selection in Time Series InSAR
2.1.2. Spatial Reference Selection
- Spatial closeness and akin scattering mechanism [25];
- Nuance in deformation time series;
- Nearly stable temporal behavior.
2.2. Physical and Land-Use Attribute Extraction
2.2.1. Speckle Noise Removal
2.2.2. Polarimetric Features
2.2.3. IMP Classification in Terms of Scattering Mechanisms
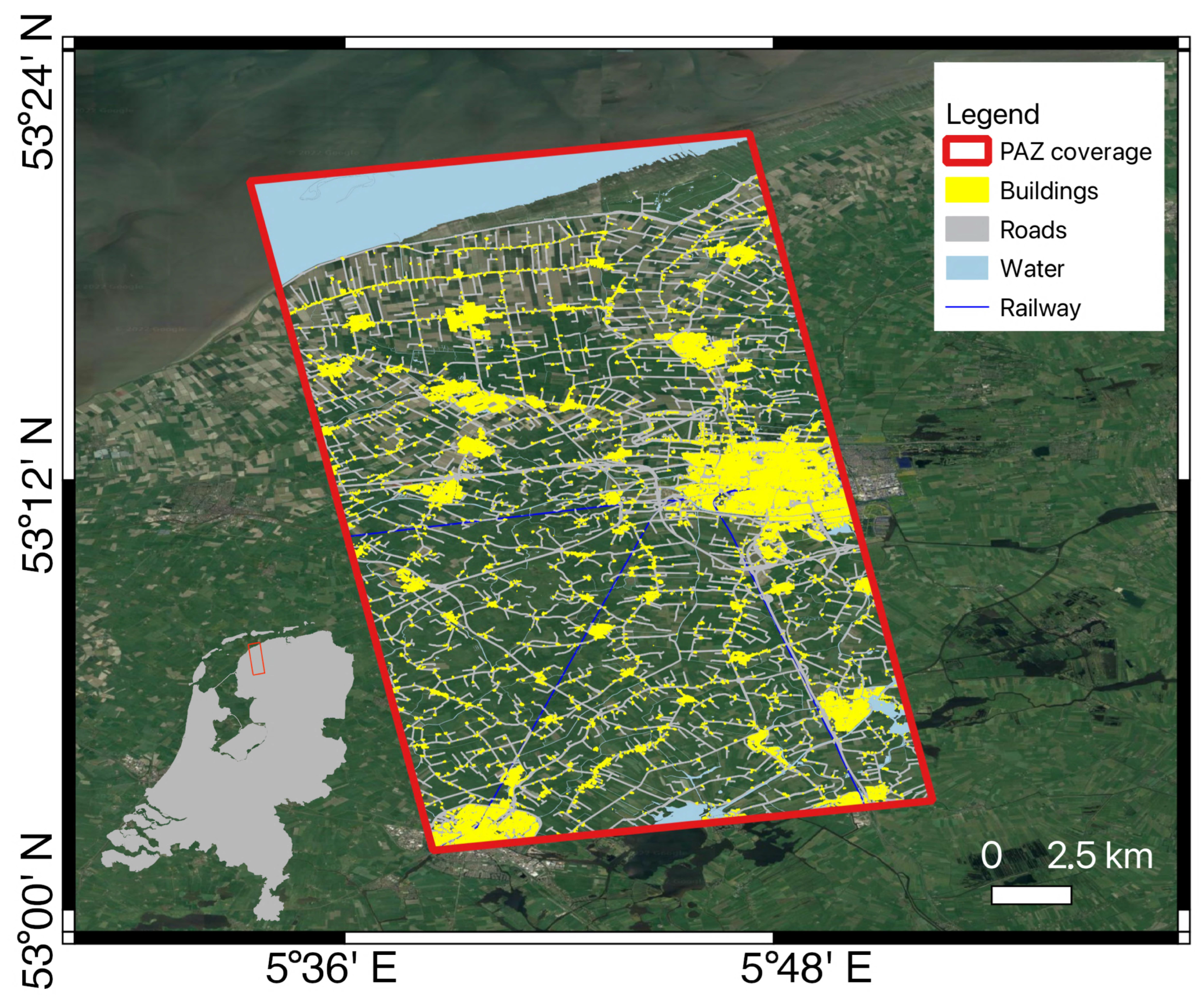
3. Data and Test Site Description
4. Results
4.1. IMP Geometric Attribute Extraction and Analysis
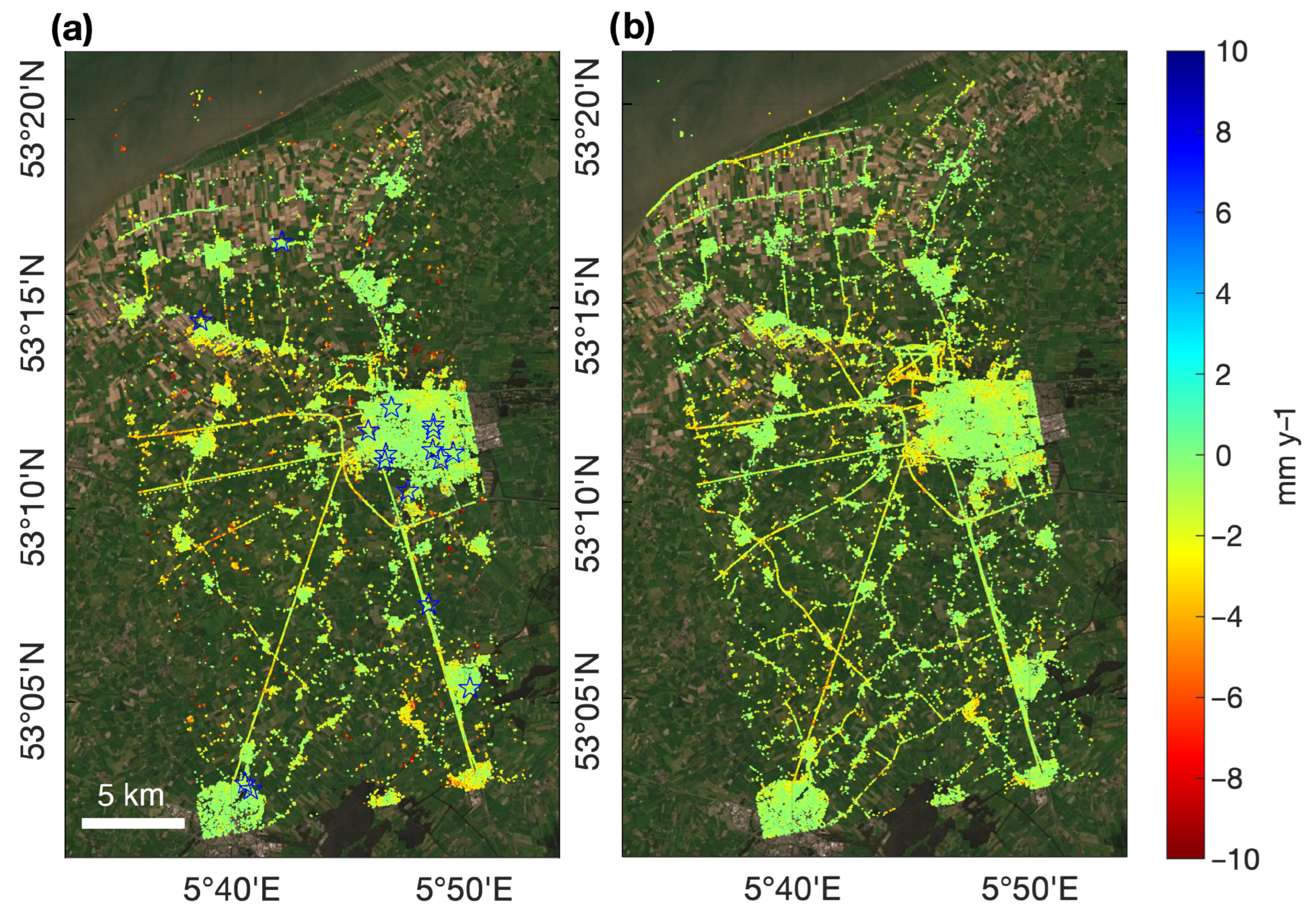
4.1.1. Coherence Scatterer Selection and Deformation Time Series Generation
4.1.2. Spatial Reference Selection and Alignment
4.2. IMP Physical Attribute Extraction and Analysis
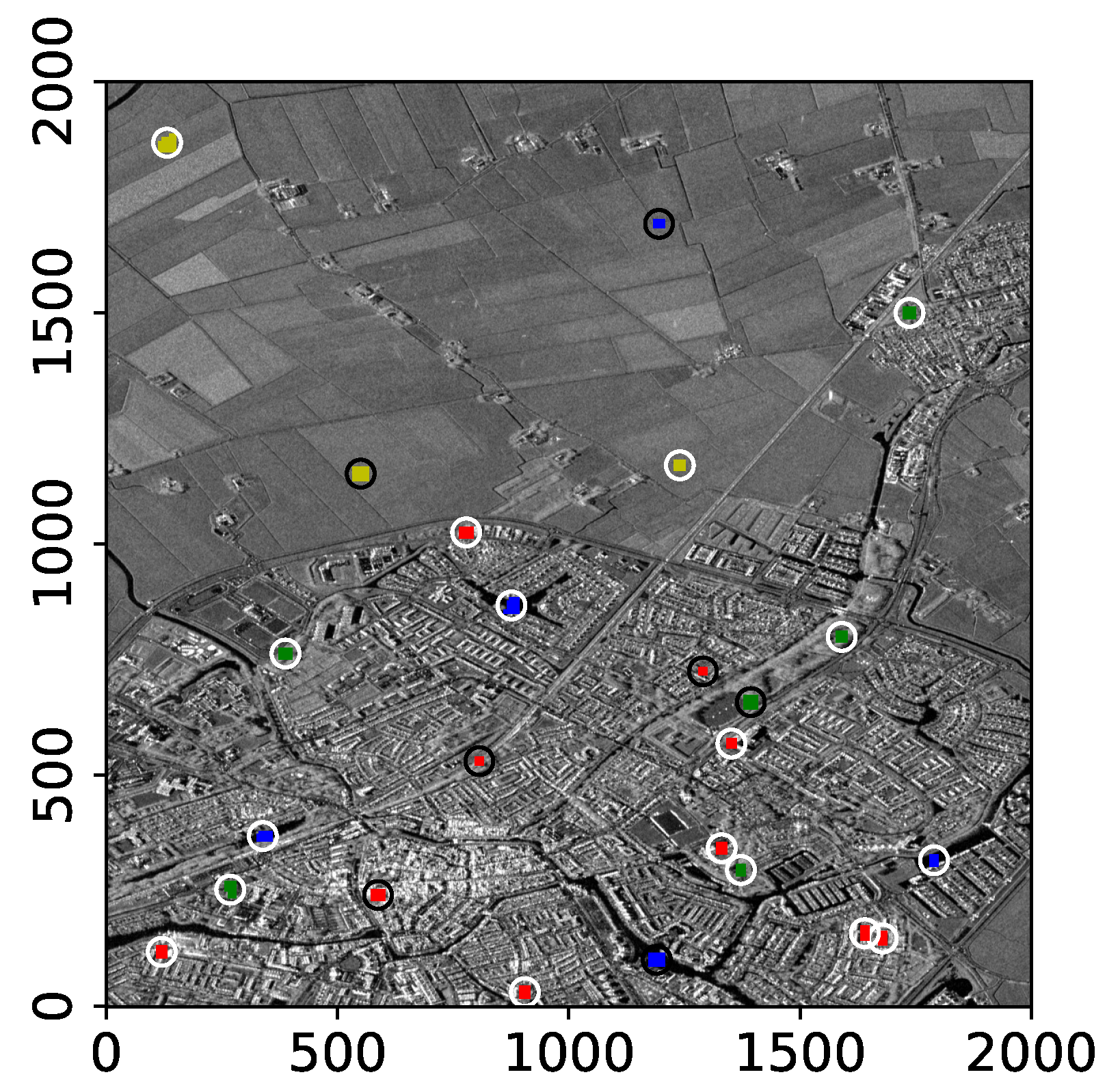
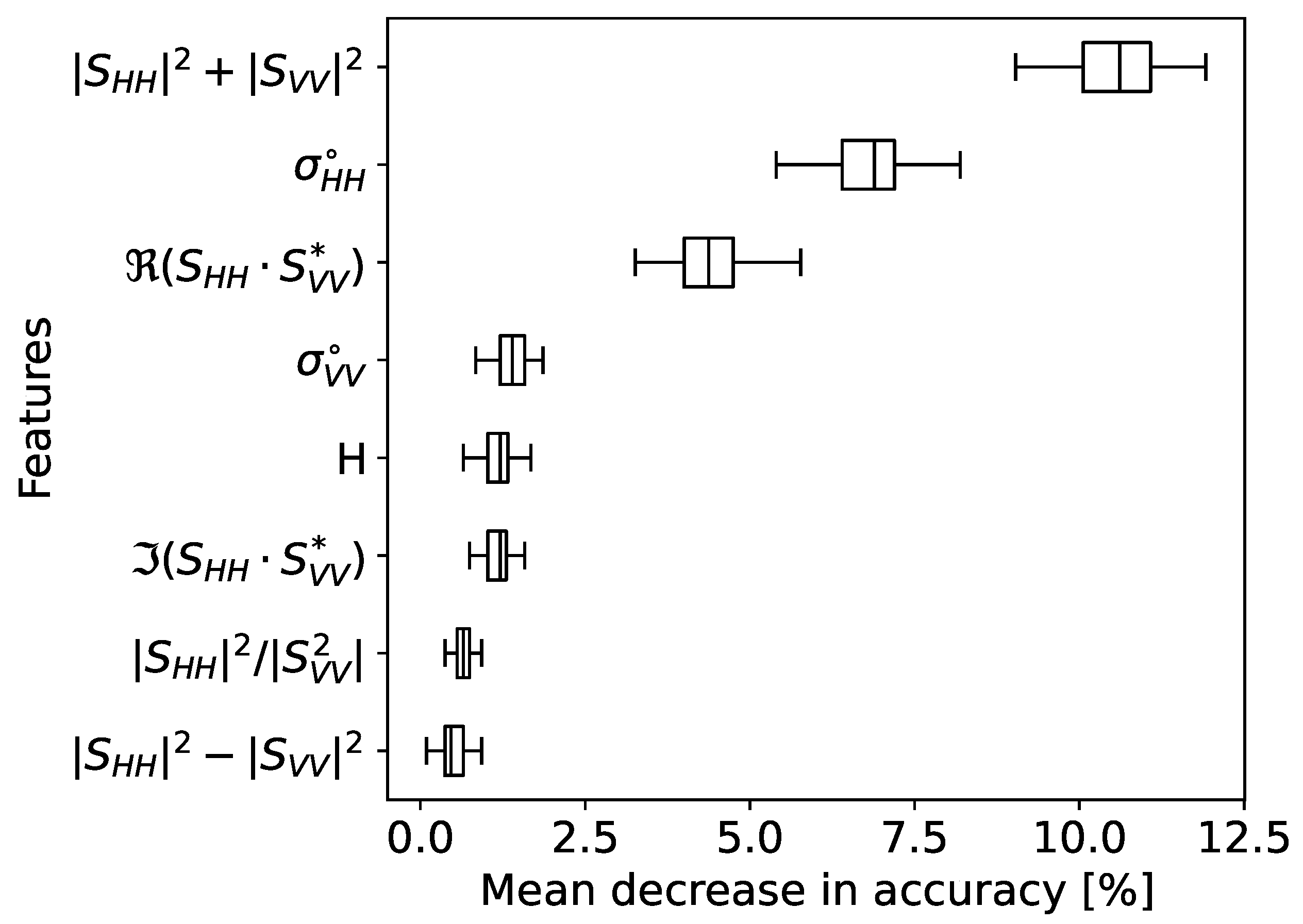
4.2.1. Scattering Mechanism Classification and Accuracy Analysis
4.2.2. IMP Land-Use Attribute Extraction and Association with Physical Attributes
4.2.3. Temporal Behavior of IMP Physical Attributes
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SAR | Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| InSAR | Interferometric SAR |
| TOP10NL | digital topographical base map of the Netherlands |
| PolSAR | Polarimetric SAR |
| TSInSAR | Time series InSAR |
| PSI | Persistent scatterer interferometry |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| LULC | Land use and land cover |
| GACOS | Generic Atmospheric Correction Online Service for InSAR |
| ERA5 | European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Reanalysis v5 |
| ERA-I | ERA-Interim |
| MERRA2 | Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications v2 |
| IMP | InSAR measurement point |
| CCS | Constantly coherent radar scatterer |
| TCS | Temporarily coherent radar scatterer |
| PS | Persistent scatterer |
| DS | Distributed scatterer |
| SLC | Single Look Complex |
| SBAS | Small baseline subset |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| NEBN | Noise Equivalent Beta Naught |
| RD | Rijksdriehoekscoordinaten |
| OOB | Out of the bag |
| MDA | Mean Decrease Accuracy |
| ECMWF | European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts |
| SRTM | Shuttle Radar Topography Mission |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| ASTER | Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer |
| GDEM | Global Digital Elevation Model |
| ITD | Iterative Tropospheric Decomposition |
| CPD | Co-polarimetric phase difference |
Appendix A. SAR Master Image Selection Criterion
Appendix B. Information on SAR Acquisitions for Interferogram Generation
| ID | Master, Slave Date | ID | Master, Slave Date | ID | Master, Slave Date | ID | Master, Slave Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20190928, 20191111 | 47 | 20200116, 20200618 | 92 | 20200618, 20210124 | 137 | 20210215, 20210422 |
| 2 | 20190928, 20191203 | 48 | 20200116, 20200801 | 93 | 20200618, 20210215 | 138 | 20210215, 20210514 |
| 3 | 20190928, 20191225 | 49 | 20200116, 20201028 | 94 | 20200618, 20210309 | 139 | 20210215, 20210605 |
| 4 | 20190928, 20200116 | 50 | 20200207, 20200229 | 95 | 20200618, 20210422 | 140 | 20210215, 20210719 |
| 5 | 20190928, 20200207 | 51 | 20200207, 20200413 | 96 | 20200801, 20201028 | 141 | 20210215, 20210810 |
| 6 | 20190928, 20200527 | 52 | 20200207, 20200505 | 97 | 20200801, 20201211 | 142 | 20210215, 20210923 |
| 7 | 20191020, 20191111 | 53 | 20200207, 20200527 | 98 | 20200801, 20210102 | 143 | 20210309, 20210331 |
| 8 | 20191020, 20191203 | 54 | 20200207, 20200618 | 99 | 20200801, 20210124 | 144 | 20210309, 20210422 |
| 9 | 20191020, 20200116 | 55 | 20200207, 20200801 | 100 | 20200801, 20210215 | 145 | 20210309, 20210514 |
| 10 | 20191020, 20200229 | 56 | 20200207, 20201211 | 101 | 20200801, 20210309 | 146 | 20210309, 20210605 |
| 11 | 20191020, 20200322 | 57 | 20200229, 20200322 | 102 | 20200801, 20210422 | 147 | 20210309, 20210719 |
| 12 | 20191020, 20200413 | 58 | 20200229, 20200413 | 103 | 20201006, 20201028 | 148 | 20210309, 20210810 |
| 13 | 20191111, 20191203 | 59 | 20200229, 20200505 | 104 | 20201006, 20210124 | 149 | 20210309, 20210901 |
| 14 | 20191111, 20191225 | 60 | 20200229, 20200527 | 105 | 20201006, 20210331 | 150 | 20210309, 20210923 |
| 15 | 20191111, 20200116 | 61 | 20200229, 20200618 | 106 | 20201028, 20201211 | 151 | 20210309, 20211015 |
| 16 | 20191111, 20200207 | 62 | 20200229, 20200801 | 107 | 20201028, 20210124 | 152 | 20210331, 20210422 |
| 17 | 20191111, 20200229 | 63 | 20200229, 20201028 | 108 | 20201028, 20210215 | 153 | 20210331, 20210605 |
| 18 | 20191111, 20200322 | 64 | 20200322, 20200413 | 109 | 20201028, 20210309 | 154 | 20210331, 20210901 |
| 19 | 20191111, 20200413 | 65 | 20200322, 20200505 | 110 | 20201028, 20210331 | 155 | 20210331, 20211015 |
| 20 | 20191111, 20200505 | 66 | 20200322, 20200618 | 111 | 20201028, 20210422 | 156 | 20210422, 20210514 |
| 21 | 20191111, 20200527 | 67 | 20200322, 20201006 | 112 | 20201028, 20210605 | 157 | 20210422, 20210605 |
| 22 | 20191111, 20200618 | 68 | 20200322, 20201028 | 113 | 20201211, 20210102 | 158 | 20210422, 20210719 |
| 23 | 20191111, 20200801 | 69 | 20200413, 20200505 | 114 | 20201211, 20210124 | 159 | 20210422, 20210810 |
| 24 | 20191203, 20191225 | 70 | 20200413, 20200527 | 115 | 20201211, 20210215 | 160 | 20210422, 20210901 |
| 25 | 20191203, 20200116 | 71 | 20200413, 20200618 | 116 | 20201211, 20210309 | 161 | 20210422, 20210923 |
| 26 | 20191203, 20200207 | 72 | 20200413, 20200801 | 117 | 20201211, 20210422 | 162 | 20210422, 20211015 |
| 27 | 20191203, 20200229 | 73 | 20200413, 20201028 | 118 | 20201211, 20210514 | 163 | 20210514, 20210605 |
| 28 | 20191203, 20200322 | 74 | 20200413, 20210124 | 119 | 20201211, 20210605 | 164 | 20210514, 20210719 |
| 29 | 20191203, 20200413 | 75 | 20200505, 20200527 | 120 | 20201211, 20210719 | 165 | 20210514, 20210810 |
| 30 | 20191203, 20200505 | 76 | 20200505, 20200618 | 121 | 20201211, 20210810 | 166 | 20210514, 20210923 |
| 31 | 20191203, 20200527 | 77 | 20200505, 20200801 | 122 | 20210102, 20210215 | 167 | 20210605, 20210719 |
| 32 | 20191203, 20200618 | 78 | 20200505, 20201028 | 123 | 20210102, 20210309 | 168 | 20210605, 20210810 |
| 33 | 20191203, 20200801 | 79 | 20200505, 20201211 | 124 | 20210102, 20210422 | 169 | 20210605, 20210901 |
| 34 | 20191225, 20200116 | 80 | 20200505, 20210124 | 125 | 20210102, 20210514 | 170 | 20210605, 20210923 |
| 35 | 20191225, 20200207 | 81 | 20200505, 20210309 | 126 | 20210102, 20210719 | 171 | 20210605, 20211015 |
| 36 | 20191225, 20200229 | 82 | 20200527, 20200618 | 127 | 20210102, 20210810 | 172 | 20210719, 20210810 |
| 37 | 20191225, 20200505 | 83 | 20200527, 20200801 | 128 | 20210124, 20210215 | 173 | 20210719, 20210901 |
| 38 | 20191225, 20200527 | 84 | 20200527, 20201028 | 129 | 20210124, 20210309 | 174 | 20210719, 20210923 |
| 39 | 20191225, 20200618 | 85 | 20200527, 20201211 | 130 | 20210124, 20210331 | 175 | 20210719, 20211015 |
| 40 | 20191225, 20200801 | 86 | 20200527, 20210102 | 131 | 20210124, 20210422 | 176 | 20210810, 20210901 |
| 41 | 20200116, 20200207 | 87 | 20200527, 20210215 | 132 | 20210124, 20210605 | 177 | 20210810, 20210923 |
| 42 | 20200116, 20200229 | 88 | 20200618, 20200801 | 133 | 20210124, 20210901 | 178 | 20210810, 20211015 |
| 43 | 20200116, 20200322 | 89 | 20200618, 20201028 | 134 | 20210124, 20210923 | 179 | 20210901, 20210923 |
| 44 | 20200116, 20200413 | 90 | 20200618, 20201211 | 135 | 20210124, 20211015 | 180 | 20210901, 20211015 |
| 45 | 20200116, 20200505 | 91 | 20200618, 20210102 | 136 | 20210215, 20210309 | 181 | 20210923, 20211015 |
| 46 | 20200116, 20200527 |
Appendix C. Random Forest Classifier Performance Assessment
| Reference Data | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Double Bounce | Low-Volume | High-Volume | Surface | ||
| Classified data | Double bounce | 651 | 8 | 10 | 4 |
| Low-volume | 0 | 641 | 15 | 19 | |
| High-volume | 4 | 19 | 652 | 0 | |
| Surface | 0 | 0 | 0 | 649 | |
Appendix D. Parametrization for the Temperature-Related Deformation
References
- Curlander, J.C.; McDonough, R.N. Synthetic Aperture Radar; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1991; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Bamler, R.; Hartl, P. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Inverse Probl. 1998, 14, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent Scatterers in SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelung, F.; Galloway, D.L.; Bell, J.W.; Zebker, H.A.; Laczniak, R.J. Sensing the ups and downs of Las Vegas: InSAR reveals structural control of land subsidence and aquifer-system deformation. Geology 1999, 27, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motagh, M.; Djamour, Y.; Walter, T.R.; Wetzel, H.U.; Zschau, J.; Arabi, S. Land subsidence in Mashhad Valley, northeast Iran: Results from InSAR, levelling and GPS. Geophys. J. Int. 2007, 168, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Lin, H.; Yeung, K.; Cheng, S. Detection of slope instability in Hong Kong based on multi-baseline differential SAR interferometry using ALOS PALSAR data. GISci. Remote Sens. 2010, 47, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Amelung, F. Land subsidence in central Mexico detected by ALOS InSAR time-series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowska, A.A.; Witkowski, W.T.; Hejmanowski, R.; Chang, L.; van Leijen, F.J.; Hanssen, R.F. Sinkhole occurrence monitoring over shallow abandoned coal mines with satellite-based persistent scatterer interferometry. Eng. Geol. 2019, 262, 105336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chang, L.; Stein, A. A model-backfeed deformation estimation method for revealing 20-year surface dynamics of the Groningen gas field using multi-platform SAR imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 111, 102847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, J.S.; Gonzalez, A.S.; Hervas, I.M.; Sanz, F.M.; Labriola, M.; Cengotitabengoa, J.M.; Molleda, F.G.; Aguado, S.M.; Perez, P.S.; Soteras, J.C.; et al. SAR panel design and performance for the PAZ mission. In Proceedings of the 8th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 7–10 June 2010; VDE Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Eoportal. PAZ SAR Satellite Mission of Spain. 2019. Available online: https://directory.eoportal.org/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/p/paz (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- Torres, R.; Snoeij, P.; Geudtner, D.; Bibby, D.; Davidson, M.; Attema, E.; Potin, P.; Rommen, B.; Floury, N.; Brown, M.; et al. GMES Sentinel-1 mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.A. Overview of the RADARSAT constellation mission. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 41, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenqvist, A.; Shimada, M.; Ito, N.; Watanabe, M. ALOS PALSAR: A pathfinder mission for global-scale monitoring of the environment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3307–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Pottier, E. Polarimetric Radar Imaging: From Basics to Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shamshiri, R.; Nahavandchi, H.; Motagh, M. Persistent scatterer analysis using dual-polarization Sentinel-1 data: Contribution from VH channel. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 3105–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antropov, O.; Rauste, Y.; Hame, T. Volume scattering modeling in PolSAR decompositions: Study of ALOS PALSAR data over boreal forest. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3838–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Yeh, A.G.O.; Li, X.; Lin, Z. A novel algorithm for land use and land cover classification using RADARSAT-2 polarimetric SAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, A.W.; Vicente-Guijalba, F.; Lopez-Martinez, C.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Litzinger, M.; Kristen, H.; Mestre-Quereda, A.; Ziółkowski, D.; Lavalle, M.; Notarnicola, C.; et al. Sentinel-1 InSAR coherence for land cover mapping: A comparison of multiple feature-based classifiers. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H.; Segall, P.; Kampes, B. A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other non-urban areas using InSAR persistent scatterers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L23611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, R.; Mora, O.; Manunta, M.; Mallorquí, J.J.; Berardino, P.; Sansosti, E. A small-baseline approach for investigating deformations on full-resolution differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, X.; Lu, Z. Ground settlement monitoring based on temporarily coherent points between two SAR acquisitions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Leijen, F.J.v.; Chang, L.; Wu, J.; Hanssen, R.F. Monitoring deformation along railway systems combining multi-temporal InSAR and LiDAR data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Stein, A. Exploring PAZ co-polarimetric SAR data for surface movement mapping and scattering characterization. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 96, 102280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Hanssen, R.F. Detection of cavity migration and sinkhole risk using radar interferometric time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Grunes, M.R.; Ainsworth, T.L.; Du, L.J.; Schuler, D.L.; Cloude, S.R. Unsupervised classification using polarimetric decomposition and the complex Wishart classifier. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 2249–2258. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, H.; Sun, J.; Xu, Z. A graph-based semisupervised deep learning model for PolSAR image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 2116–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, H.; Patel, S.; Patel, V. Classification of SAR and PolSAR images using deep learning: A review. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2020, 11, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millard, K.; Richardson, M. On the importance of training data sample selection in random forest image classification: A case study in peatland ecosystem mapping. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8489–8515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A New Algorithm for Surface Deformation Monitoring Based on Small Baseline Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizzani, P.; Berardino, P.; Casu, F.; Euillades, P.; Manzo, M.; Ricciardi, G.; Zeni, G.; Lanari, R. Surface deformation of Long Valley caldera and Mono Basin, California, investigated with the SBAS-InSAR approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, R.; Berardino, P.; Bonano, M.; Casu, F.; Manconi, A.; Manunta, M.; Manzo, M.; Pepe, A.; Pepe, S.; Sansosti, E.; et al. Surface displacements associated with the L’Aquila 2009 Mw 6.3 earthquake (central Italy): New evidence from SBAS-DInSAR time series analysis. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampes, B.M. Radar Interferometry; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Simonetto, E.; Follin, J.M. An overview on interferometric SAR software and a comparison between DORIS and SARSCAPE packages. In Geospatial Free and Open Source Software in the 21st Century; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 107–122. [Google Scholar]
- Quegan, S.; Yu, J.J. Filtering of multichannel SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 2373–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Wen, J.H.; Ainsworth, T.L.; Chen, K.S.; Chen, A.J. Improved sigma filter for speckle filtering of SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 47, 202–213. [Google Scholar]
- Vasile, G.; Trouvé, E.; Lee, J.S.; Buzuloiu, V. Intensity-driven adaptive-neighborhood technique for polarimetric and interferometric SAR parameters estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1609–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulshrestha, A.; Chang, L.; Stein, A. Use of LSTM for Sinkhole-Related Anomaly Detection and Classification of InSAR Deformation Time Series. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 4559–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, D. Flattening gamma: Radiometric terrain correction for SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3081–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. A review of target decomposition theorems in radar polarimetry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 498–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafai, S.S.; Kumar, S. PolInSAR coherence and entropy-based hybrid decomposition model. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2020EA001279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M. Random forest classifier for remote sensing classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gislason, P.O.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Sveinsson, J.R. Random forests for land cover classification. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biau, G.; Scornet, E. A random forest guided tour. Test 2016, 25, 197–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, C.D. Classification and regression trees, bagging, and boosting. Handb. Stat. 2005, 24, 303–329. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, D.M. Evaluation: From precision, recall and F-measure to ROC, informedness, markedness and correlation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.16061. [Google Scholar]
- Archer, K.J.; Kimes, R.V. Empirical characterization of random forest variable importance measures. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2008, 52, 2249–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louppe, G.; Wehenkel, L.; Sutera, A.; Geurts, P. Understanding variable importances in forests of randomized trees. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2013, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Hisdesat. PAZ Image Product Guide, PAZ-HDS-GUI-001. 2019. Available online: https://www.hisdesat.es/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/PAZ-HDS-GUI-001-PAZ-Image-Product-Guide-issue-1.1-.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2019).
- Mulder, G.; Van Leijen, F.J.; Barkmeijer, J.; De Haan, S.; Hanssen, R.F. Estimating Single-Epoch Integrated Atmospheric Refractivity From InSAR for Assimilation in Numerical Weather Models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molteni, F.; Buizza, R.; Palmer, T.N.; Petroliagis, T. The ECMWF ensemble prediction system: Methodology and validation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 122, 73–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zyl, J.J. The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM): A breakthrough in remote sensing of topography. Acta Astronaut. 2001, 48, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachikawa, T.; Hato, M.; Kaku, M.; Iwasaki, A. Characteristics of ASTER GDEM version 2. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011; pp. 3657–3660. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Penna, N.T.; Li, Z. Generation of real-time mode high-resolution water vapor fields from GPS observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 2008–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicks, C.W., Jr.; Dzurisin, D.; Ingebritsen, S.; Thatcher, W.; Lu, Z.; Iverson, J. Magmatic activity beneath the quiescent Three Sisters volcanic center, central Oregon Cascade Range, USA. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 26-1–26-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartemink, A.E.; Sonneveld, M.P. Soil maps of the Netherlands. Geoderma 2013, 204, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DEOS. Delft Object-Oriented Radar Interferometric Software: Unser’s Manual and Technical Documentation. 2012. Available online: http://doris.tudelft.nl (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Hooper, A.; Bekaert, D.; Hussain, E.; Spaans, K. StaMPS/MTI Manual, Version 4.1b. 2018. Available online: https://homepages.see.leeds.ac.uk/~earahoo/stamps/ (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Chang, L.; Hanssen, R.F. A probabilistic approach for InSAR time-series postprocessing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 54, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, P.; Torgo, L.; Ribeiro, R.P. A survey of predictive modeling on imbalanced domains. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2016, 49, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pultz, T.; Leconte, R.; Brown, R.; Brisco, B. Quantitative soil moisture extraction from airborne SAR data. Can. J. Remote Sens. 1990, 16, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, P.; der Marel, H.v.; van Leijen, F.; Samiei-Esfahany, S.; Klees, R.; Hanssen, R. InSAR datum connection using GNSS-augmented radar transponders. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinss, S.; Parrella, G.; Hajnsek, I. Snow height determination by polarimetric phase differences in X-band SAR data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 3794–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehman, S.V. Selecting and interpreting measures of thematic classification accuracy. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




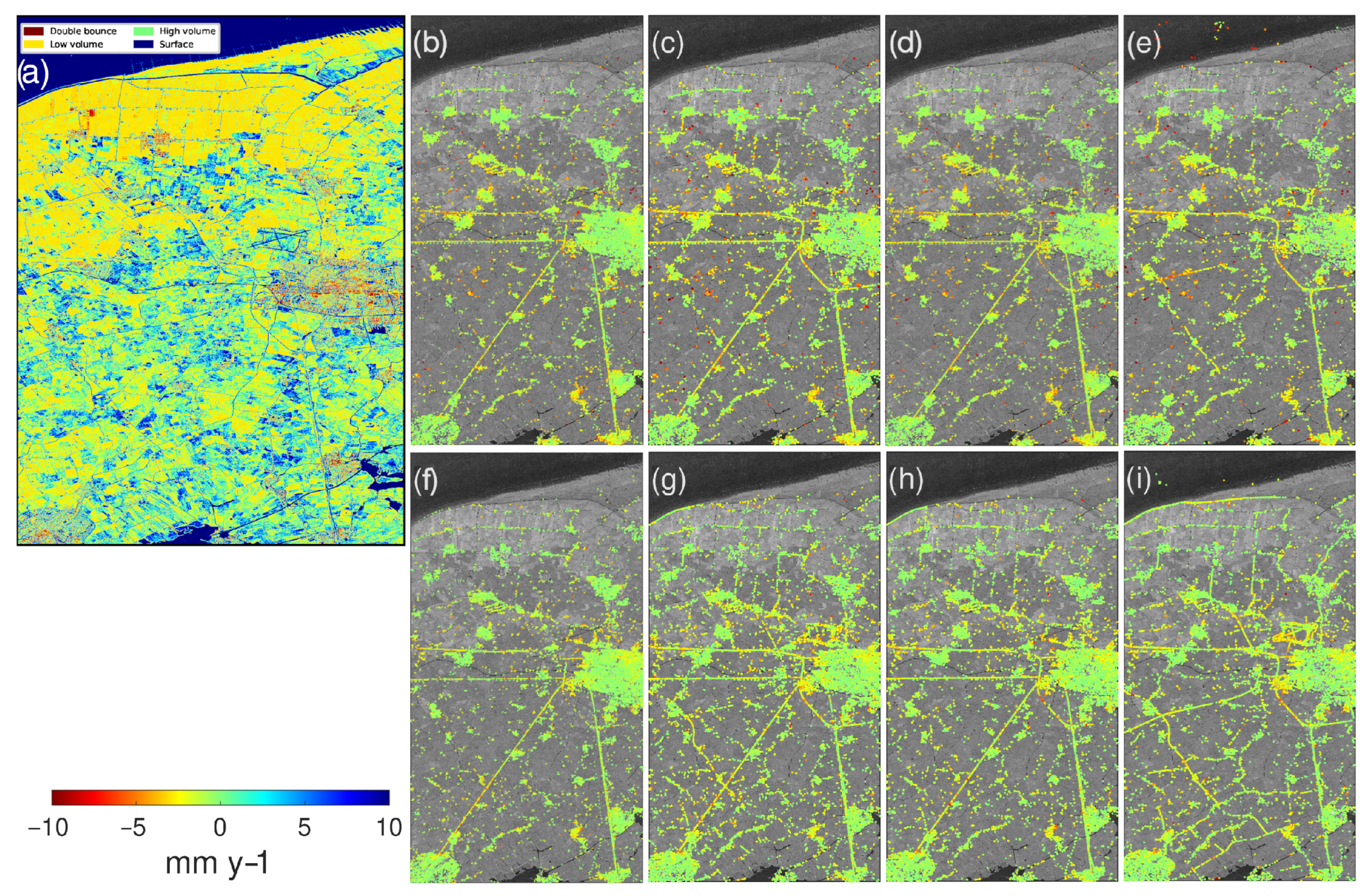
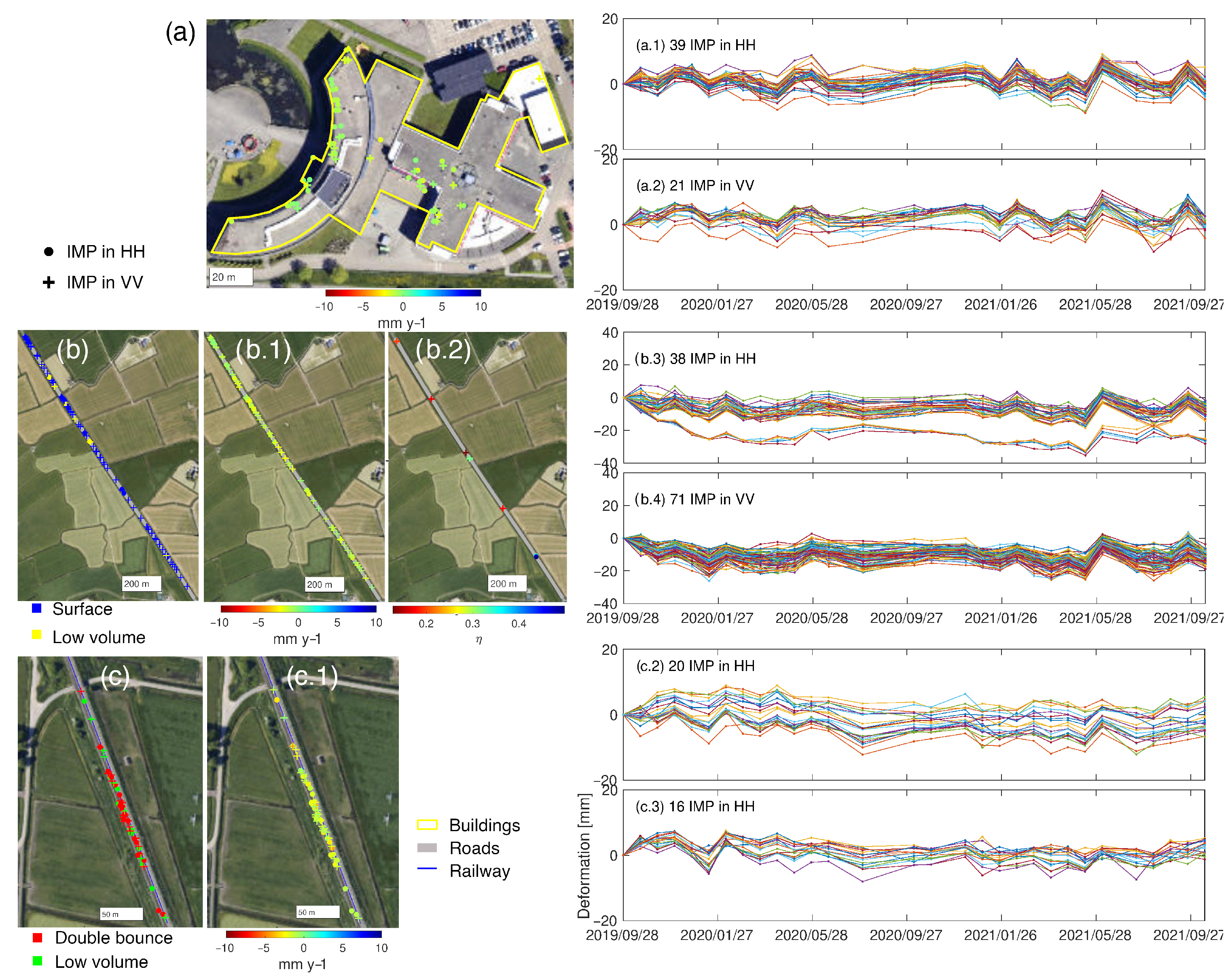

| SM | Double Bounce | Low-Volume | High-Volume | Surface |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HH | 302,586 | 64,482 | 120,112 | 50,806 |
| VV | 245,056 | 71,504 | 91,102 | 78,012 |
| Buildings | Roads | Water | Railways | Uncharted | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HH | 343,967 | 81,701 | 1133 | 32,975 | 78,210 |
| VV | 273,612 | 109,944 | 1093 | 32,291 | 68,734 |
| Double Bounce | Low-Volume | High-Volume | Surface | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buildings | HH | 64% | 9% | 21% | 6% |
| VV | 64% | 11% | 19% | 6% | |
| Roads | HH | 37% | 20% | 18% | 25% |
| VV | 23% | 22% | 11% | 44% | |
| Railways | HH | 55% | 9% | 35% | 1% |
| VV | 52% | 13% | 34% | 1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, L.; Kulshrestha, A.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X. Extraction and Analysis of Radar Scatterer Attributes for PAZ SAR by Combining Time Series InSAR, PolSAR, and Land Use Measurements. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15061571
Chang L, Kulshrestha A, Zhang B, Zhang X. Extraction and Analysis of Radar Scatterer Attributes for PAZ SAR by Combining Time Series InSAR, PolSAR, and Land Use Measurements. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(6):1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15061571
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Ling, Anurag Kulshrestha, Bin Zhang, and Xu Zhang. 2023. "Extraction and Analysis of Radar Scatterer Attributes for PAZ SAR by Combining Time Series InSAR, PolSAR, and Land Use Measurements" Remote Sensing 15, no. 6: 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15061571
APA StyleChang, L., Kulshrestha, A., Zhang, B., & Zhang, X. (2023). Extraction and Analysis of Radar Scatterer Attributes for PAZ SAR by Combining Time Series InSAR, PolSAR, and Land Use Measurements. Remote Sensing, 15(6), 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15061571







