Green Space Compactness and Configuration to Reduce Carbon Emissions from Energy Use in Buildings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data
2.1. Remote Sensing Data
2.2. Socioeconomic Data
2.3. Regional Climate Data
2.4. Calculating Carbon Emissions
3. Methods
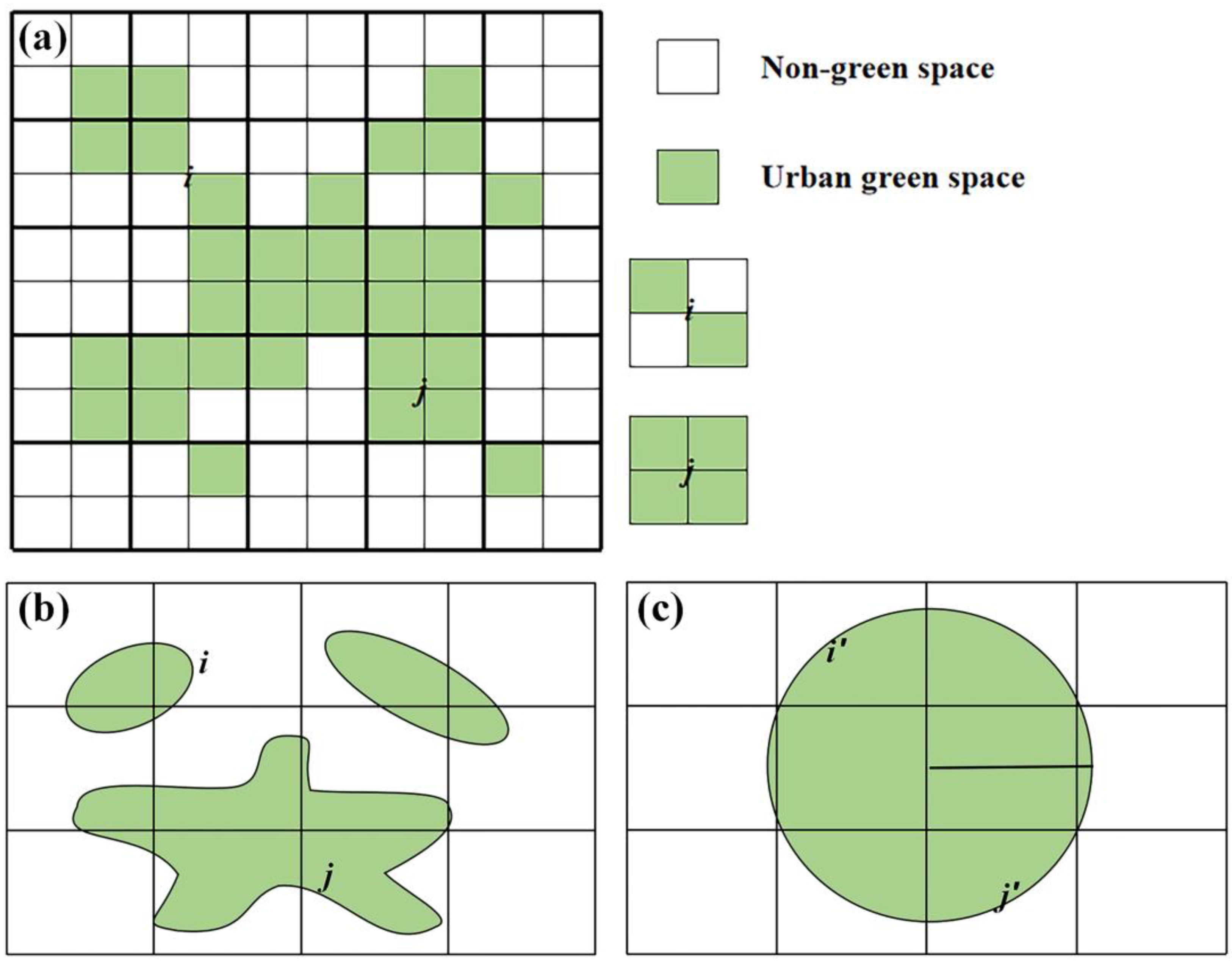
3.1. Two-Dimensional GSC Index
3.2. Three Models
3.2.1. Modeling Specification/Purpose of Using the Model
3.2.2. Partial Least Squares Regression (PLSR)
3.2.3. Random Forests (RF)
3.2.4. Geographical Detector Model (GDM)
3.3. Hot and Cold Spot Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Socioeconomic Conditions and Building Characteristics
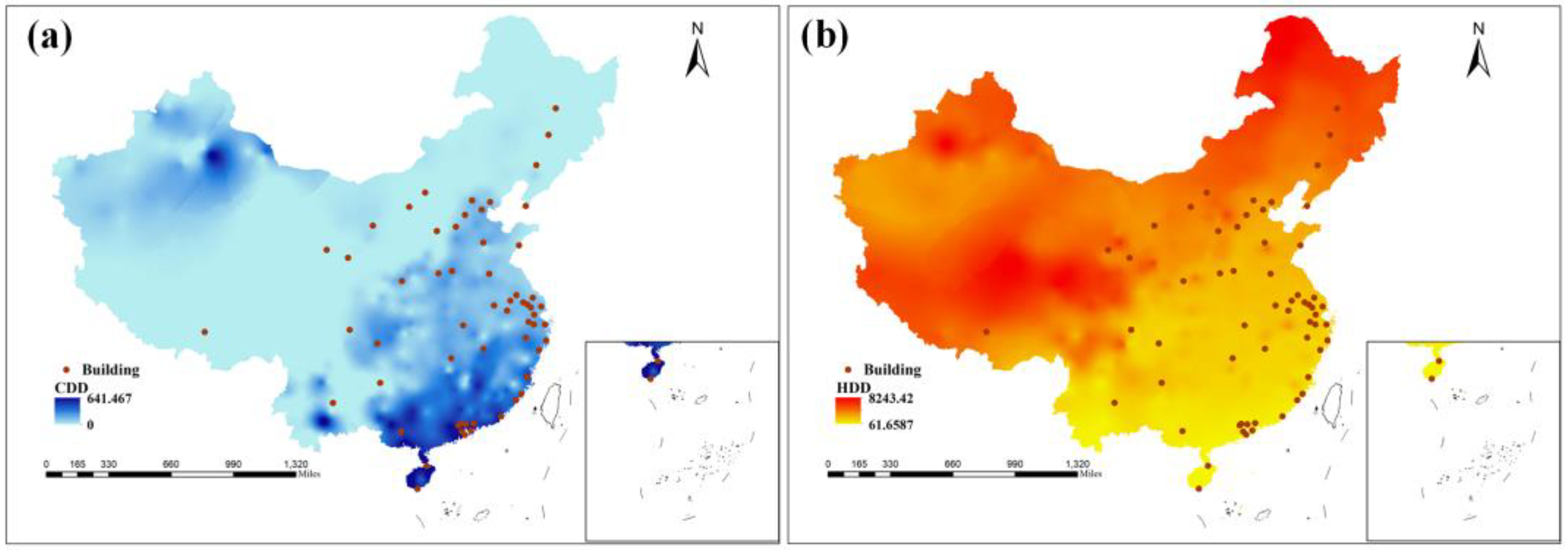
4.2. Regional Climate
4.3. BECCE
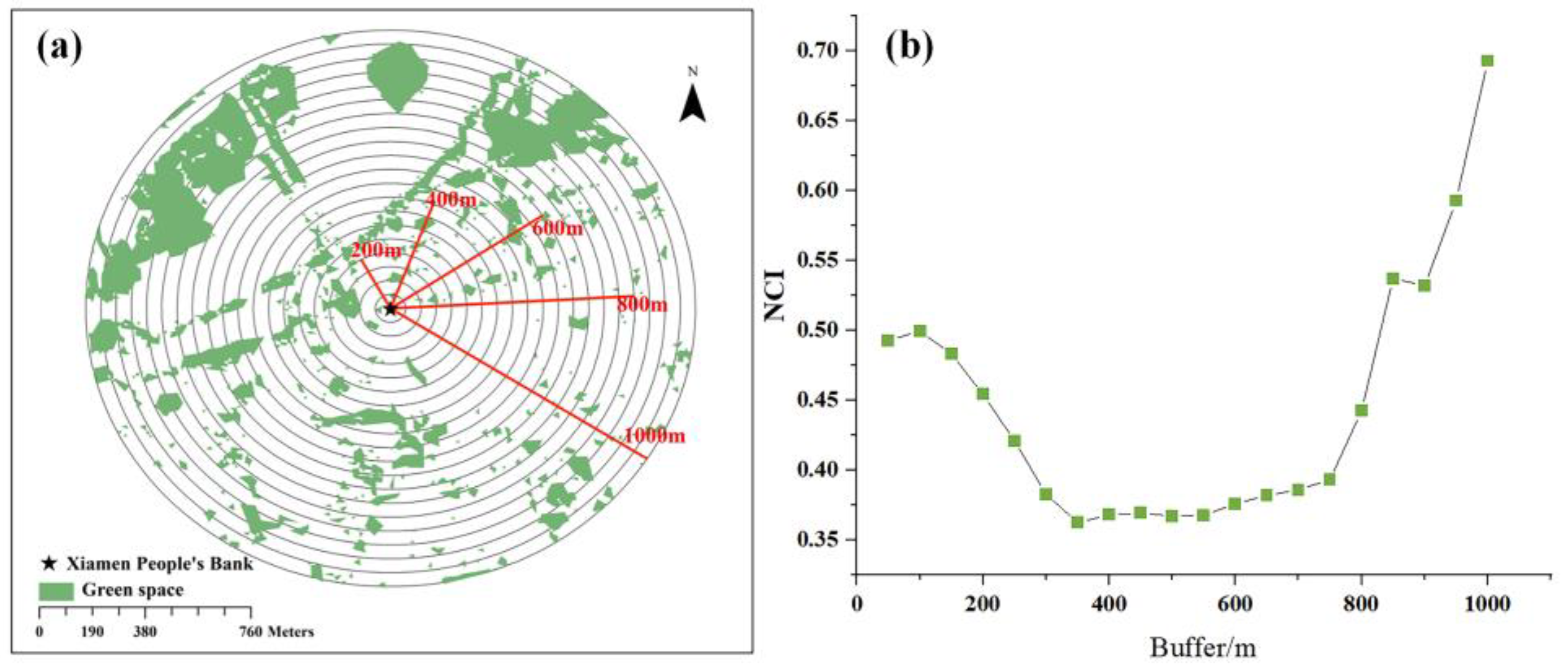
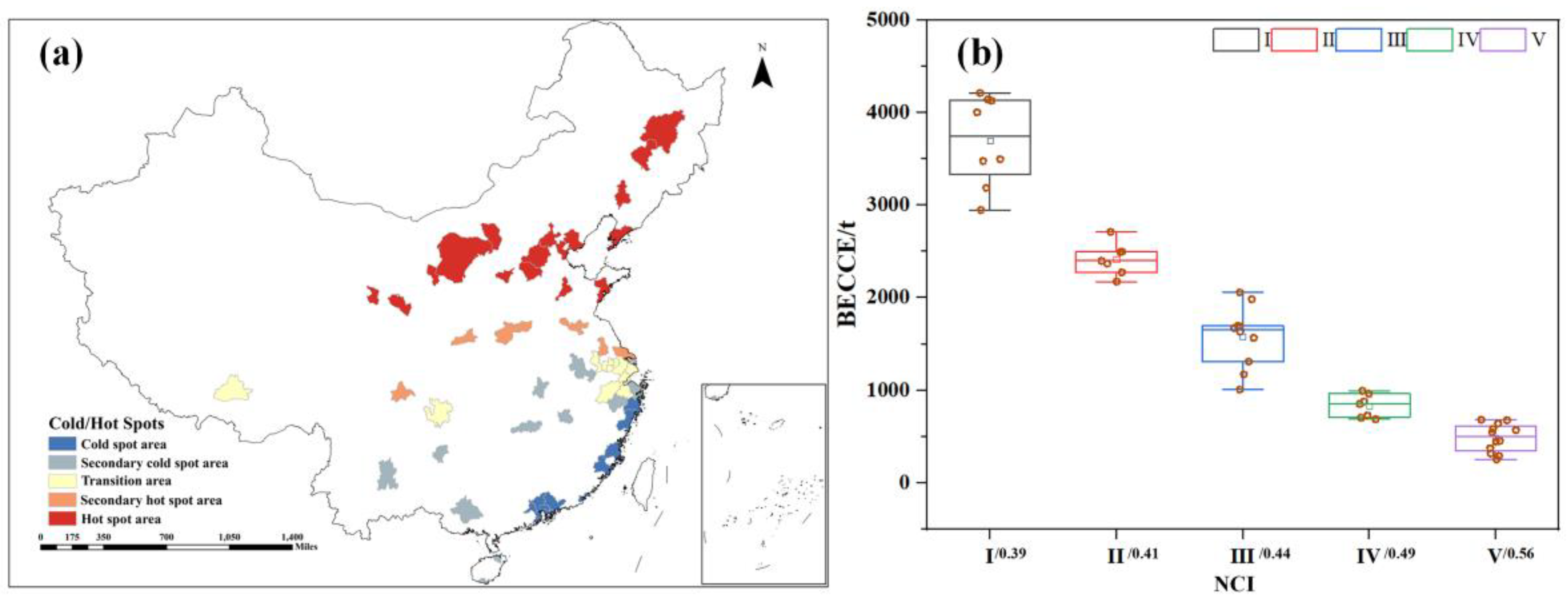
4.4. NCI
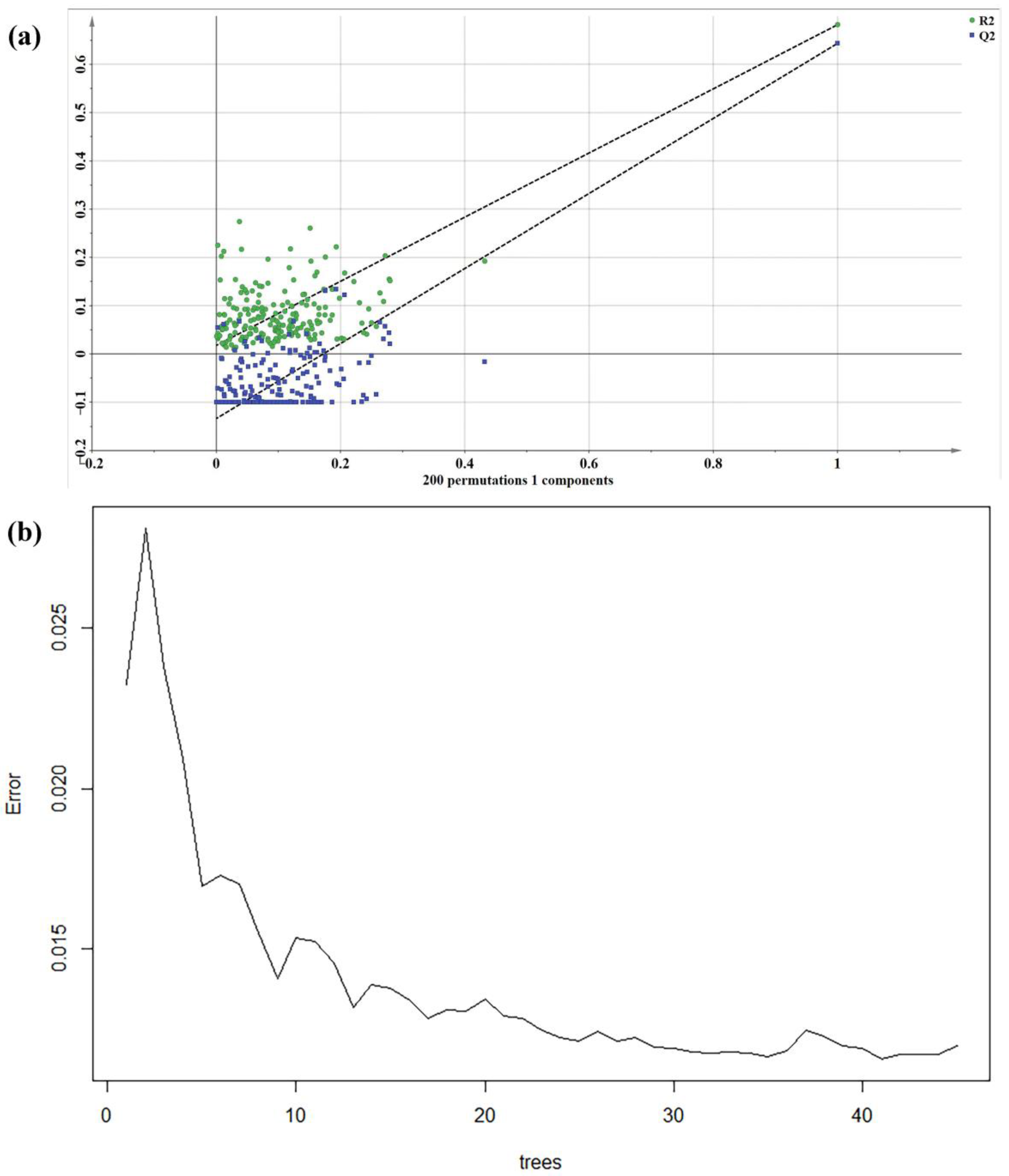
4.5. Validation of Three Model
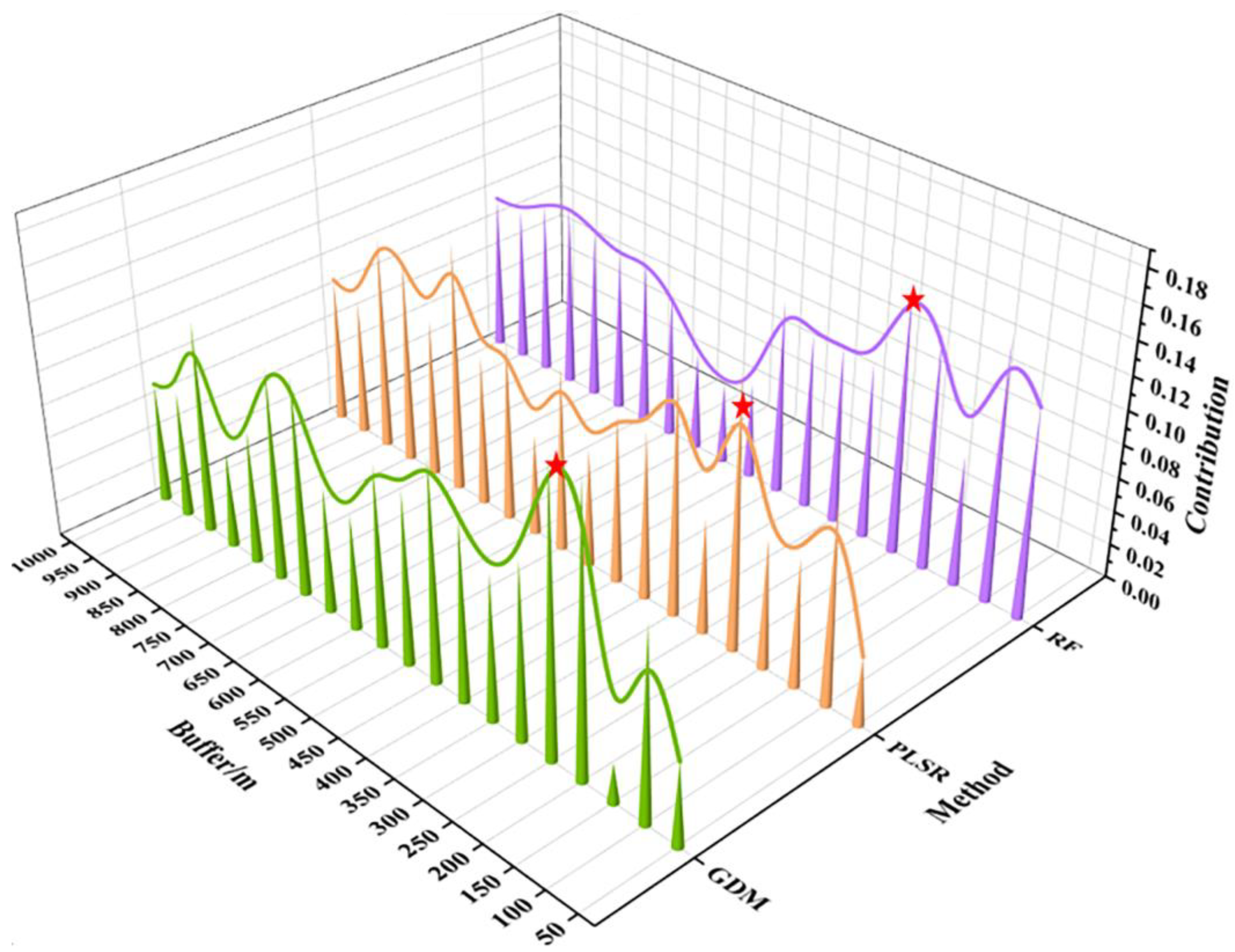
4.6. The Most Effective Influence Distance of GSC on BECCE
4.7. Optimization of Green Space Compactness in the 250 m Buffer Zone for Emission Reductions
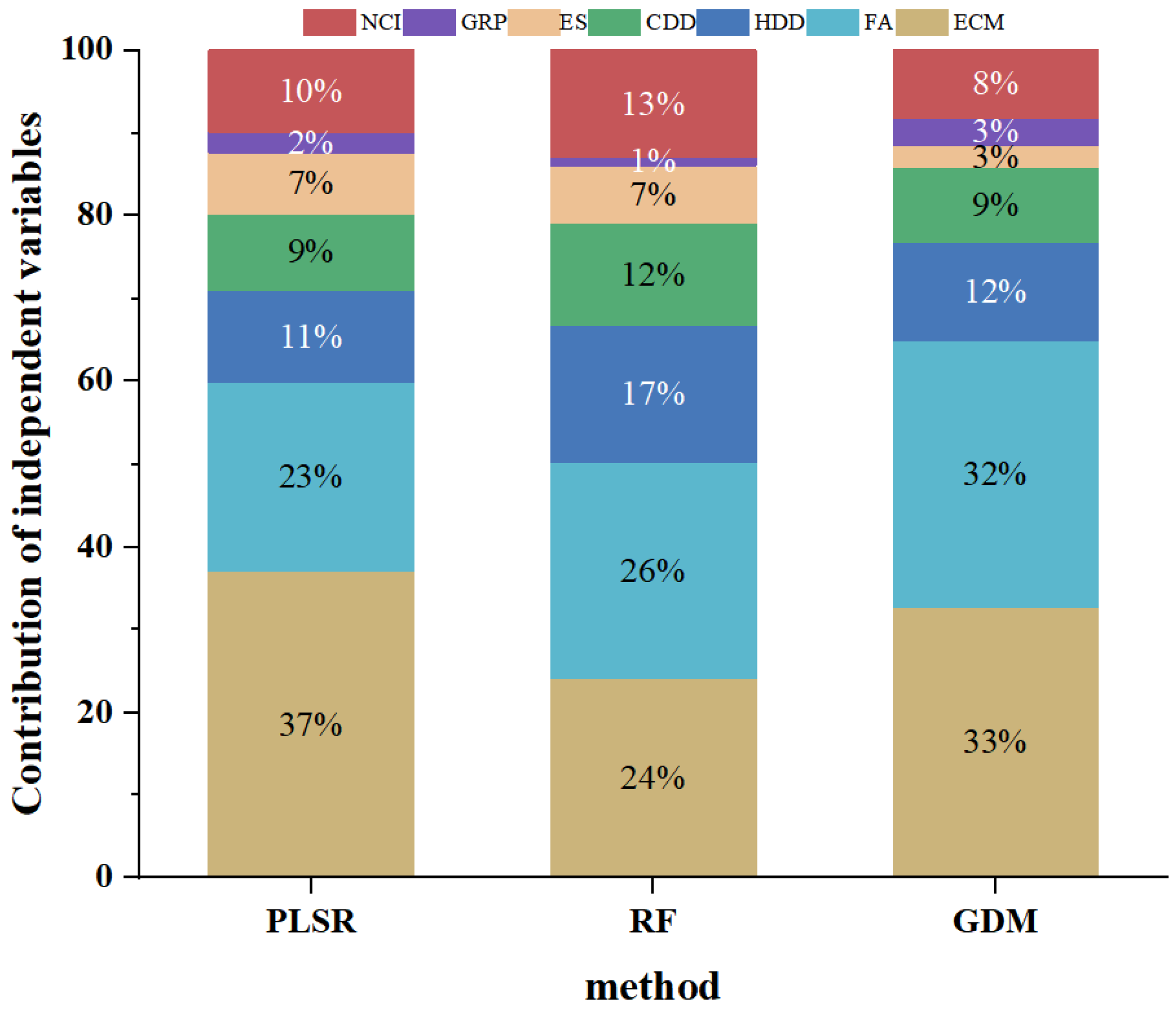
4.7.1. Contribution of Factors to BECCE
4.7.2. Impacts of Factors on BECCE
4.7.3. Optimization of GSC for BECCE Reduction
5. Discussion
5.1. The Significance of the Most Effective Distance
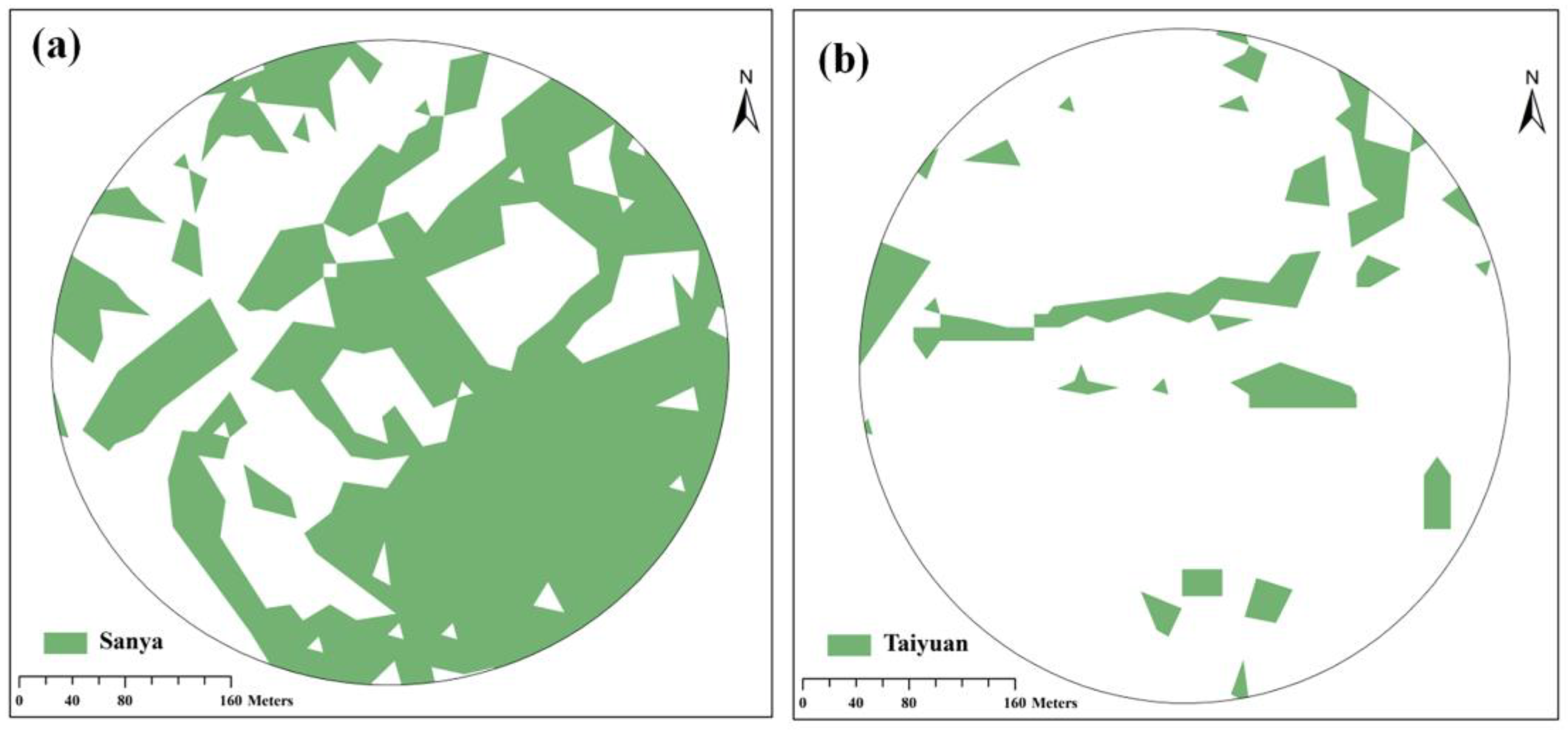
5.2. Optimization of Green Space Configuration Based on the Most Effective Distance
5.3. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BECCE | Building energy consumption carbon emission |
| GSC | Green space compactness |
| IPCC | Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change |
| UHI | Urban heat island |
| PLS | Partial least squares |
| RF | Random Forest |
| GDM | Geographical detector model |
| GRP | Gross Domestic Product per person |
| ES | Education spending |
| CDD | Cooling degree days |
| HDD | Heating degree days |
| PLSR | Partial Least Squares Regression |
| VIP | Variable importance of projection |
| RCs | Regression coefficients |
| ECM | Energy consumption membership |
| FA | Floor area of the buildings |
| VIF | Variance inflation factor |
| NTREE | Number of regression trees |
| PCI | Cooling effect intensity |
Appendix A
| BECCE | ECM | FA | GRP | ES | HDD | CDD | GSC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.318189 | 0.747646 | 0.772077 | 0.612256 | 0.197687 | 0.069528 | 0.816938 | 0.190194 |
| 0.134185 | 0.167608 | 0.091641 | 0.060579 | 0.006136 | 0.47575 | 0.167753 | 0.359675 |
| 0.449241 | 0.827997 | 0.392144 | 0.458169 | 1 | 0.465784 | 0.18445 | 0.47881 |
| 0.074628 | 0.127433 | 0.135465 | 0.482123 | 0.075007 | 0.275049 | 0.227713 | 0.231952 |
| 0.25124 | 0.458883 | 0.531519 | 0.296004 | 0.087959 | 0.242861 | 0.101426 | 0.342488 |
| 0.264145 | 0.330822 | 0.32189 | 0.511964 | 0.150569 | 0.489636 | 0.02643 | 0.532644 |
| 0.08447 | 0.103578 | 0.079041 | 1 | 0.00641 | 0.694908 | 0.00258 | 0.329226 |
| 0.180361 | 0.283114 | 0.19932 | 0.295874 | 0.031145 | 0.114525 | 0.648707 | 0.400756 |
| 0.05566 | 0.19774 | 0.177555 | 0.466943 | 0.05258 | 0.065006 | 0.846282 | 0.461438 |
| 0.116549 | 0.351538 | 0.113591 | 0.214851 | 0.041946 | 0.306952 | 0.018555 | 0.590675 |
| 0.437372 | 0.392341 | 0.282942 | 0.208651 | 0.033625 | 0.935144 | 0.0127 | 0.438582 |
| 0.237357 | 0.328311 | 0.626597 | 0.187396 | 0.001776 | 0 | 0.997262 | 0.822529 |
| 0.294817 | 0.338355 | 0.390907 | 0.478823 | 0.183819 | 0.239519 | 0.290859 | 0.530976 |
| 0.372273 | 0.416196 | 0.53381 | 0.283399 | 0.10105 | 0.285853 | 0.225594 | 0.552416 |
| 0.272004 | 0.4457 | 0.297834 | 0.436345 | 0.010848 | 0.741209 | 0 | 0.535206 |
| 0.462519 | 0.500942 | 0.585977 | 0.3611 | 0.032104 | 0.360428 | 0.259573 | 0.404124 |
| 0.076188 | 0.110483 | 0.208484 | 0.314608 | 0.048011 | 0.254038 | 0.255843 | 0.39636 |
| 0.075348 | 0.096673 | 0.160372 | 0.236696 | 0.045519 | 0.206499 | 0.45477 | 0.588682 |
| 0.104947 | 0.284369 | 0.231394 | 0.22144 | 0.042641 | 0.177875 | 0.197884 | 0.319651 |
| 0.138092 | 0.28688 | 0.06644 | 0.223501 | 0.009517 | 0.780833 | 0.088589 | 0.625301 |
| 0.360755 | 0.326428 | 0.271029 | 0.213515 | 0.009293 | 0.703726 | 0.030689 | 0.182128 |
| 0.07246 | 0.152542 | 0.098514 | 0.184551 | 0.028113 | 0.342095 | 0.248606 | 0.393476 |
| 0.327729 | 0.575016 | 0.55672 | 0.297919 | 0.026101 | 0.208433 | 0.480869 | 0.562853 |
| 0.226869 | 0.34751 | 0.4961 | 0.499013 | 0.156556 | 0.282981 | 0.212251 | 0.538968 |
| 0.27207 | 0.413685 | 0.463933 | 0.151475 | 0.023768 | 0.084661 | 0.813339 | 0.445084 |
| 0.095192 | 0.094162 | 0.292496 | 0.336242 | 0.075303 | 0.292474 | 0.186674 | 0.482099 |
| 0.302671 | 0.392341 | 0.588795 | 0.449334 | 0.149844 | 0.229303 | 0.262033 | 0.678564 |
| 0.203962 | 0.24796 | 0.174118 | 0.439391 | 0.093821 | 0.396883 | 0.061395 | 0.286219 |
| 0.07171 | 0.116761 | 0.234831 | 0.286455 | 0.035563 | 0.121206 | 0.607363 | 0.44175 |
| 0.024945 | 0.037037 | 0.065294 | 0.212503 | 0.009539 | 0 | 0.997262 | 0.743105 |
| 0.196639 | 0.210295 | 0.306998 | 0.386959 | 0.059709 | 0.077895 | 0.640265 | 0.442587 |
| 0.052234 | 0.104834 | 0.087179 | 0.086005 | 0.005522 | 0.045787 | 0.821615 | 0.43792 |
| 0.415744 | 1 | 0.964523 | 0.443968 | 0.927631 | 0.247362 | 0.205764 | 0.694095 |
| 0.093119 | 0.158192 | 0.162663 | 0.383194 | 0.063493 | 0.244262 | 0.308466 | 0.332113 |
| 0.184264 | 0.322662 | 0.230226 | 0.725955 | 0.333344 | 0.035457 | 0.94567 | 0.408799 |
| 0.069572 | 0.093534 | 0.12257 | 0.299174 | 0.048069 | 0.058557 | 0.842451 | 0.848888 |
| 0.040386 | 0.138732 | 0.096223 | 0.261586 | 0.068132 | 0.060979 | 0.820498 | 0.424405 |
| 0.630392 | 0.375392 | 0.662222 | 0.381463 | 0.092232 | 0.686276 | 0.024143 | 0.218079 |
| 0.646749 | 0.610797 | 0.902666 | 0.182132 | 0.023926 | 0.528524 | 0.146169 | 0 |
| 0.125113 | 0.180163 | 0.261122 | 0.620085 | 0.266714 | 0.251512 | 0.241707 | 0.415426 |
| 0.051237 | 0.101695 | 0.138928 | 0.221289 | 0.032854 | 0.198716 | 0.314952 | 0.370312 |
| 1 | 0.514124 | 0.640343 | 0.236517 | 0.048224 | 0.555907 | 0.013811 | 0.328429 |
| 0.112443 | 0.213434 | 0.162663 | 0.352434 | 0.027001 | 0.514669 | 0.146036 | 0.496153 |
| 0.480345 | 0.561205 | 0.660962 | 0.486494 | 0.384365 | 0.438771 | 0.259779 | 0.417916 |
| 0.071573 | 0.121783 | 0.153029 | 0.172113 | 0.038146 | 0.178507 | 0.405418 | 0.760851 |
| 0.065014 | 0.150659 | 0.223261 | 0.600955 | 0.123807 | 0.259371 | 0.236065 | 0.203245 |
| 0.073543 | 0.123666 | 0.14548 | 0.263653 | 0.119599 | 0.257308 | 0.244642 | 0.269095 |
| 0.187177 | 0.349655 | 0.504162 | 0.447376 | 0.199722 | 0.262423 | 0.283815 | 0.462167 |
| 0.671526 | 0.448839 | 0.531519 | 0.262328 | 0.045884 | 0.369041 | 0.252873 | 0 |
| 0.367658 | 0.323289 | 0.601395 | 0.170188 | 0.004694 | 0.792069 | 0.021731 | 0.466047 |
| 0.056281 | 0.146265 | 0.174118 | 0.229117 | 0.060046 | 0.33095 | 0.241048 | 0.662404 |
| 0.060566 | 0.124294 | 0.187864 | 0.364357 | 0.038146 | 0.282922 | 0.205997 | 0.449239 |
| 0.183302 | 0.334589 | 0.317308 | 0.273948 | 0.011548 | 0.579842 | 0.066659 | 0.297938 |
| 0.690655 | 0.541745 | 0.624306 | 0.300721 | 0.022926 | 0.817749 | 0.011025 | 0.73958 |
| 0.483692 | 0.505336 | 1 | 0.499759 | 0.077674 | 0.21377 | 0.413991 | 0.415791 |
| 0.291484 | 0.837414 | 0.77895 | 0.312082 | 0.049455 | 0.312287 | 0.335889 | 0.274781 |
| 0.028009 | 0.080979 | 0.038948 | 0.396967 | 0.043696 | 0.046337 | 0.947621 | 0.482284 |
| 0.000722 | 0.007533 | 0.01031 | 0.176073 | 0.133341 | 0.181488 | 0.399687 | 0.561651 |
| 0.043754 | 0.098556 | 0.057276 | 0.547658 | 0.042453 | 0.037504 | 1 | 0.577845 |
Appendix B
| ECM | FA | GRP | ES | HDD | CDD | NCI | Cons | Sig | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 m | 0.305201 | 0.35986 | 0.166119 | 0.0817256 | 0.228903 | 0.0473396 | 0.0823886 | 0.0603391 | p < 0.05 |
| 950 m | 0.304216 | 0.360182 | 0.167533 | 0.0844465 | 0.229248 | 0.04668888 | 0.101299 | 0.0692255 | p < 0.05 |
| 900 m | 0.30183 | 0.3572 | 0.17182 | 0.0848071 | 0.229248 | 0.0459239 | 0.0459239 | 0.086017 | p < 0.05 |
| 850 m | 0.300175 | 0.353881 | 0.175214 | 0.0826662 | 0.227778 | 0.0466589 | 0.155681 | 0.0982501 | p < 0.05 |
| 800 m | 0.301175 | 0.354913 | 0.177489 | 0.0798333 | 0.225889 | 0.0475465 | 0.158625 | 0.100128 | p < 0.05 |
| 750 m | 0.30256 | 0.357197 | 0.179124 | 0.079243 | 0.224287 | 0.0472305 | 0.162457 | 0.101145 | p < 0.05 |
| 700 m | 0.303659 | 0.356833 | 0.185114 | 0.0764475 | 0.221304 | 0.0460905 | 0.17927 | 0.109838 | p < 0.05 |
| 650 m | 0.306978 | 0.362106 | 0.190085 | 0.0757981 | 0.219899 | 0.0453604 | 0.153132 | 0.0977835 | p < 0.05 |
| 600 m | 0.3109 | 0.370421 | 0.185572 | 0.0791872 | 0.218151 | 0.043282 | 0.102372 | 0.0706033 | p < 0.05 |
| 550 m | 0.311217 | 0.374508 | 0.18063 | 0.0849314 | 0.218977 | 0.0412042 | 0.0959552 | 0.0643862 | p < 0.05 |
| 500 m | 0.310596 | 0.373387 | 0.178106 | 0.0819165 | 0.217279 | 0.0399675 | 0.106434 | 0.0685193 | p < 0.05 |
| 450 m | 0.286967 | 0.262201 | 0.014691 | 0.0978542 | 0.181298 | 0.101819 | 0.0977435 | 0.0661807 | p < 0.05 |
| 400 m | 0.288109 | 0.263244 | 0.0147495 | 0.0982436 | 0.182019 | 0.102224 | 0.0877683 | 0.0617522 | p < 0.05 |
| 350 m | 0.287101 | 0.262323 | 0.0146978 | 0.0978997 | 0.181382 | 0.101866 | 0.0891686 | 0.06379 | p < 0.05 |
| 300 m | 0.286347 | 0.261634 | 0.0146593 | 0.0976427 | 0.180906 | 0.101599 | 0.0875556 | 0.0647297 | p < 0.05 |
| 250 m | 0.284522 | 0.259967 | 0.0145658 | 0.0970203 | 0.179753 | 0.100951 | 0.105011 | 0.0715619 | p < 0.05 |
| 200 m | 0.301157 | 0.354913 | 0.177489 | 0.0798333 | 0.225889 | 0.0475465 | 0.158625 | 0.100128 | p < 0.05 |
| 150 m | 0.293589 | 0.268251 | 0.01503 | 0.100112 | 0.185481 | 0.104168 | 0.03757 | 0.0377408 | p < 0.05 |
| 100 m | 0.274614 | 0.250914 | 0.0140586 | 0.0936417 | 0.173493 | 0.0974355 | 0.0522553 | 0.0614491 | p < 0.05 |
| 50 m | 0.319747 | 0.38092 | 0.162974 | 0.0754476 | 0.218005 | 0.0411308 | 0.0126272 | 0.0114444 | p < 0.05 |
References
- Wei, Y.-M.; Han, R.; Liang, Q.-M.; Yu, B.-Y.; Yao, Y.-F.; Xue, M.-M.; Zhang, K.; Liu, L.-J.; Peng, J.; Yang, P.; et al. An integrated assessment of INDCs under Shared Socioeconomic Pathways: An implementation of C(3)IAM. Nat. Hazards 2018, 92, 585–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhao, C.; Yan, W.; Zhao, X. Influences of 1.5 degrees C and 2.0 degrees C global warming scenarios on water use efficiency dynamics in the sandy areas of northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.-M.; Chen, K.; Kang, J.-N.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.-Y. Policy and Management of Carbon Peaking and Carbon Neutrality: A Literature Review. Engineering 2022, 14, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbon, C. The road from Paris: China’s progress toward its climate pledge. Nat. Resour. Déf. CouGSCl (NRDC) 2017, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Climate, C.-F.; Solutions, E. China’s Contribution to the Paris Climate Agreement; C2ES: Arlington, VA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, D.; Zhou, D.; Zhou, P. Driving forces of residential CO2 emissions in urban and rural China: An index decomposition analysis. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 3377–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, M.; Laiola, E.; Tricase, C.; Rana, R. Assessing the urban carbon footprint: An overview. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2017, 66, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhuang, Q.; Meng, X.; Zhu, P.; Han, J.; Huang, L. A fine spatial resolution modeling of urban carbon emissions: A case study of Shanghai, China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robati, M.; Oldfield, P.; Nezhad, A.A.; Carmichael, D.G.; Kuru, A. Carbon value engineering: A framework for integrating embodied carbon and cost reduction strategies in building design. Build. Environ. 2021, 192, 107620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Khanna, N.; Feng, W.; Ke, J.; Levine, M. Scenarios of energy efficiency and CO2 emissions reduction potential in the buildings sector in China to year 2050. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, S.; Li, S. Case analysis of GHG emission and reduction from food consumption of Beijing relish restaurant based on life cycle. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2021, 17, 140–150. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Zuo, B.; Qu, C.; Ge, L.; Shen, Q. A reasonable distribution of natural landscape: Utilizing green space and water bodies to reduce residential building carbon emissions. Energy Build. 2022, 267, 112150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.L.H.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; He, Y.; Chen, S.S. Energy savings of block-scale facade greening for different urban forms. Appl. Energy 2020, 279, 115844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Yang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Causone, F.; Jin, X.; Zhou, X.; Shi, X. An evidence-based framework for designing urban green infrastructure morphology to reduce urban building energy use in a hot-humid climate. Build. Environ. 2022, 219, 109181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Li, Y.; Wei, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Jin, X.; Shi, X. The impact of urban vegetation morphology on urban building energy consumption during summer and winter seasons in Nanjing, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 228, 104576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleghani, M.; Kleerekoper, L.; Tenpierik, M.; van den Dobbelsteen, A. Outdoor thermal comfort within five different urban forms in the Netherlands. Build. Environ. 2015, 83, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.L.; Ding, F.; Yang, L.; Hou, H.R.; Ye, J.Y. Spatial relations between city parks and urban heat/cold islands in summer and winter seasons. J. Fujian Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2020, 36, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Gioia, A.; Paolini, L.; Malizia, A.; Oltra-Carrió, R.; Sobrino, J.A. Size matters: Vegetation patch size and surface temperature relationship in foothills cities of northwestern Argentina. Urban Ecosyst. 2014, 17, 1161–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganmohan, M.; Knapp, S.; Buchmann, C.M.; Schwarz, N. The bigger, the better? The influence of urban green space design on cooling effects for residential areas. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Hu, X.; Ren, Q.; Lin, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Shi, L. Effect of urban micro-climatic regulation ability on public building energy usage carbon emission. Energy Build. 2017, 154, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athamena, K. Microclimatic coupling to assess the impact of crossing urban form on outdoor thermal comfort in temperate oceanic climate. Urban Clim. 2022, 42, 101093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Hien, W.N. Thermal benefits of city parks. Energy Build. 2006, 38, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Cui, S.; Li, Y.; Zhai, X. Crucial factors of the built environment for mitigating carbon emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 806, 150864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, F.; Gaughan, A.; Linard, C.; Tatem, A. Disaggregating census data for population mapping using Random Forests with remotely-sensed and ancillary data. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0107042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Du, H.; Zhang, X. Driving Forces of Carbon Dioxide Emissions in China’s Cities: An Empirical Analysis Based on the Geodetector Method. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 125169, 0959–6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Clinton, N.; Ji, L.; Li, W.; Bai, Y.; et al. Stable classification with limited sample: Transferring a 30-m resolution sample set collected in 2015 to mapping 10-m resolution global land cover in 2017. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yan, H.; Lam, J.C. Thermal comfort and building energy consumption implications—A review. Appl. Energy 2014, 115, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis.Summary for Policymakers. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Song, Y.; Shi, L.; Tang, L. Study on the compactness assessment model of urban spatial form. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 6338–6343. [Google Scholar]
- Skelhorn, C. A Fine Scale Assessment of Urban Greenspace Impacts on Microclimate and Building Energy in Manchester. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Brain Sciences. Partial least squares regression and projection on latent structure regression (PLS Regression). Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, S.; Sjostrom, M.; Eriksson, L. PLS-regression: A basic tool of chemometrics. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2001, 58, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geladi, P.; Kowalski, B.R. Partial least-squares regression: A tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 1986, 185, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhu, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, K. Sediment yield is closely related to lithology and landscape properties in heterogeneous karst watersheds. J. Hydrol. 2018, 568, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogun, A.-L.; Tella, A. Modelling and investigating the impacts of climatic variables on ozone concentration in Malaysia using correlation analysis with random forest, decision tree regression, linear regression, and support vector regression. Chemosphere 2022, 299, 134250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, O.; Tahmasebipour, N.; Haghizadeh, A.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Feizizadeh, B. Evaluation of different machine learning models for predicting and mapping the susceptibility of gully erosion. Geomorphology 2017, 298, 118–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Mei, L.; Wei, Y.; Zheng, R.; Guo, Y. The influence of the neighbourhood environment on peer-to-peer accommodations: A random forest regression analysis. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2022, 51, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-F.; Li, X.-H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.-L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.-Y. Geographical Detectors-Based Health Risk Assessment and its Application in the Neural Tube Defects Study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inform. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; He, S.; Liu, L. Growing-season vegetation coverage patterns and driving factors in the China-Myanmar Economic Corridor based on Google Earth Engine and geographic detector. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getis, A.; Ord, J.K. The Analysis of Spatial Association by Use of Distance Statistics. Geogr. Anal. 2010, 24, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornmann, L.; Angeon, F.d.M. Hot and cold spots in the US research: A spatial analysis of bibliometric data on the institutional level. J. Inform. Sci. 2019, 45, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yao, L.; Ren, Y. Characterizing the spatial heterogeneity and controlling factors of land surface temperature clusters: A case study in Beijing. Build. Environ. 2020, 169, 106598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, Z.; Tian, Y.; Zhong, J.; Yang, W. Impact of Land Use/Cover Change on Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration Ecosystem Services Value: Temporal-Spatial Patterns and Cold/Hot Spots Ecosystem Services Value Change Brought by Urbanization. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Yan, C.; Yu, L.; Jiang, X.; Ding, J.; Qin, L.; Wang, B.; Qiu, G. Impacts of land use/land cover types on interactions between urban heat island effects and heat waves. Build. Environ. 2021, 204, 108138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibuike, E.M.; Ibukun, A.O.; Abbas, A.; Kunda, J.J. Assessment of green parks cooling effect on Abuja urban microclimate using geospatial techniques. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2018, 11, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Sun, Z.; Tao, Y.; Shang, J.; Miao, S.; Xiao, C.; Zheng, C. Projections of future temperature-related cardiovascular mortality under climate change, urbanization and population aging in Beijing, China. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Guo, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhong, J.; Fei, F.; Chen, F.; Qi, J. Temperature variability and mortality in rural and urban areas in Zhejiang province, China: An application of a spatiotemporal index. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhou, M. A review of urban green space wind environment simulation and multi-scale application research. China Urban For. 2021, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Fang, Y.; Lin, Y. Analysis of the effect of street greenbelt on microclimate in a hottumid area of China using a numerical simulation method. J. Meteorol. Environ. 2016, 32, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Zhou, X.; Cheng, W. Water effects on urban heat islands in summer using WRF-UCM with gridded urban canopy parameters-A case study of Wuhan. Build. Environ. 2022, 225, 109528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Ren, Q.; Shi, L.; Song, J.; Hu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Lin, T.; Xue, X. The role of climate, construction quality, microclimate, and socio-economic conditions on carbon emissions from office buildings in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Qiu, Q.; Zhang, G.; Lin, T.; Li, X. Effects of natural environment on urban household energy usage carbon emissions. Energy Build. 2013, 65, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Wang, K.; Zhao, X.; Chen, F.; Li, X.; Pan, L. Relationship between construction characteristics and carbon emissions from urban household operational energy usage. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Yan, W.; Zheng, G.; Yin, H.; Cavan, G.; Zhan, W.; Zhang, N.; Cheng, L. Retrieval of three-dimensional tree canopy and shade using terrestrial laser scanning (TLS) data to analyze the cooling effect of vegetation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 217, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooke, T.R.; Coops, N.C.; Voogt, J.A.; Meitner, M.J. Tree structure influences on rooftop-received solar radiation. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 102, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Max | Min | Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ECM/person | 1648 | 114 | 550 |
| FA/hm2 | 9 | 0.62 | 3.28 |
| GRP/yuan | 153,110 | 31,284 | 89,700 |
| ES/yuan | 2,827,117 | 10,406 | 293,778 |
| Independent Variable | Tolerance | VIF |
|---|---|---|
| ECM | 0.177 | 5.651 |
| FA | 0.262 | 3.812 |
| GRP | 0.815 | 1.228 |
| ES | 0.442 | 2.263 |
| HDD | 0.305 | 3.276 |
| CDD | 0.322 | 3.106 |
| NCI | 0.845 | 1.183 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, R.; Wang, K.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Wu, X.; Yan, H.; Zhao, Z.; Ye, H. Green Space Compactness and Configuration to Reduce Carbon Emissions from Energy Use in Buildings. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15061502
Ji R, Wang K, Zhou M, Zhang Y, Bai Y, Wu X, Yan H, Zhao Z, Ye H. Green Space Compactness and Configuration to Reduce Carbon Emissions from Energy Use in Buildings. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(6):1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15061502
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Ranran, Kai Wang, Mengran Zhou, Yun Zhang, Yujia Bai, Xian Wu, Han Yan, Zhuoqun Zhao, and Hong Ye. 2023. "Green Space Compactness and Configuration to Reduce Carbon Emissions from Energy Use in Buildings" Remote Sensing 15, no. 6: 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15061502
APA StyleJi, R., Wang, K., Zhou, M., Zhang, Y., Bai, Y., Wu, X., Yan, H., Zhao, Z., & Ye, H. (2023). Green Space Compactness and Configuration to Reduce Carbon Emissions from Energy Use in Buildings. Remote Sensing, 15(6), 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15061502





