Linear and Nonlinear Land Use Regression Approach for Modelling PM2.5 Concentration in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia during Peak Hours
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
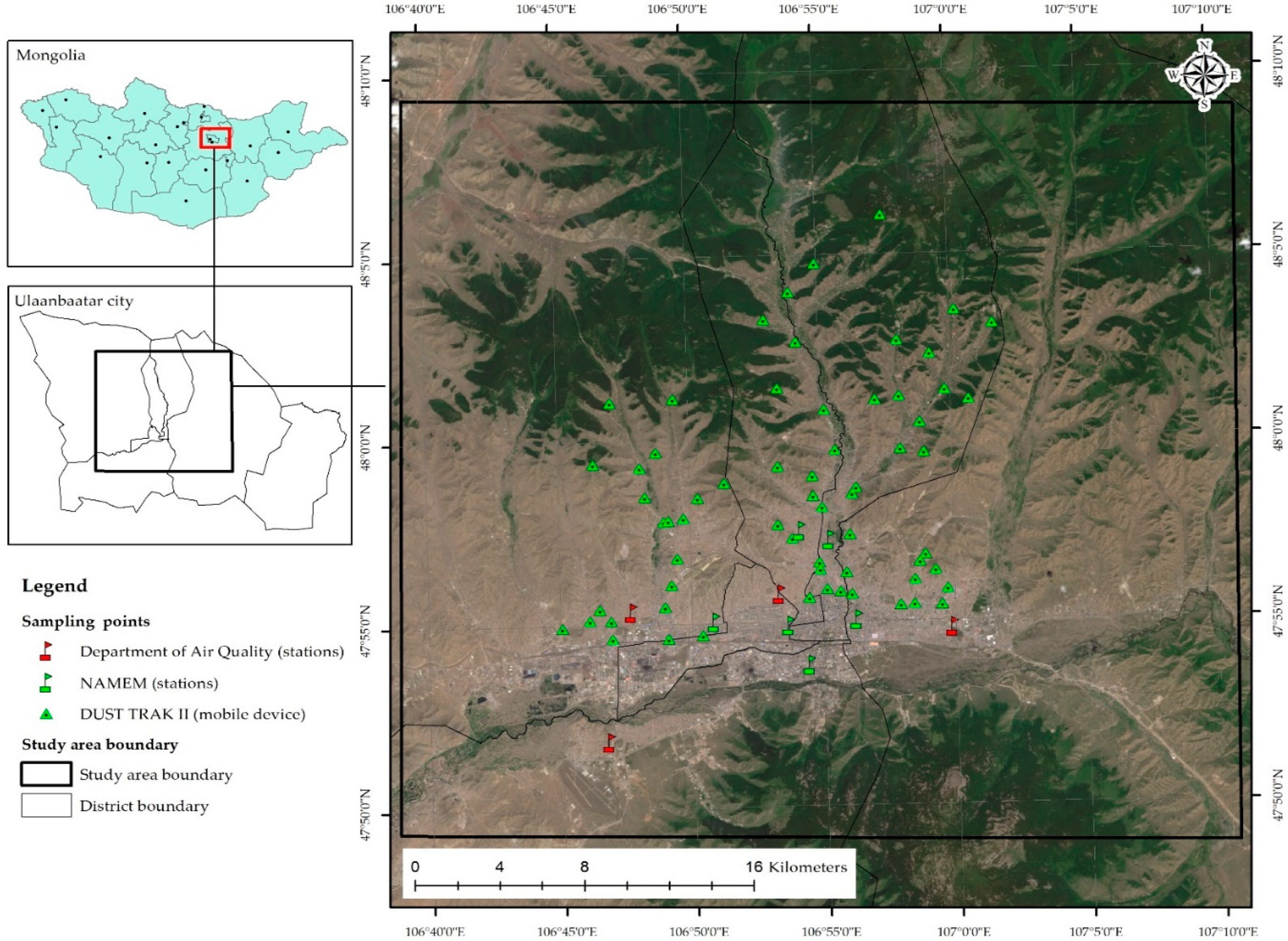
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Predictor Variables
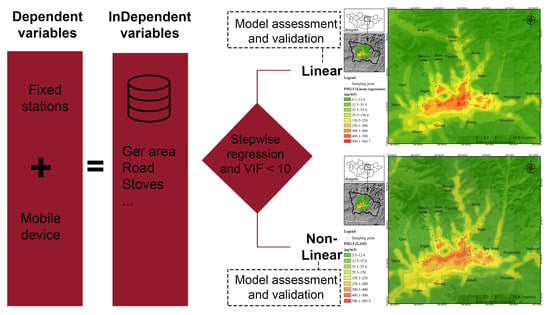
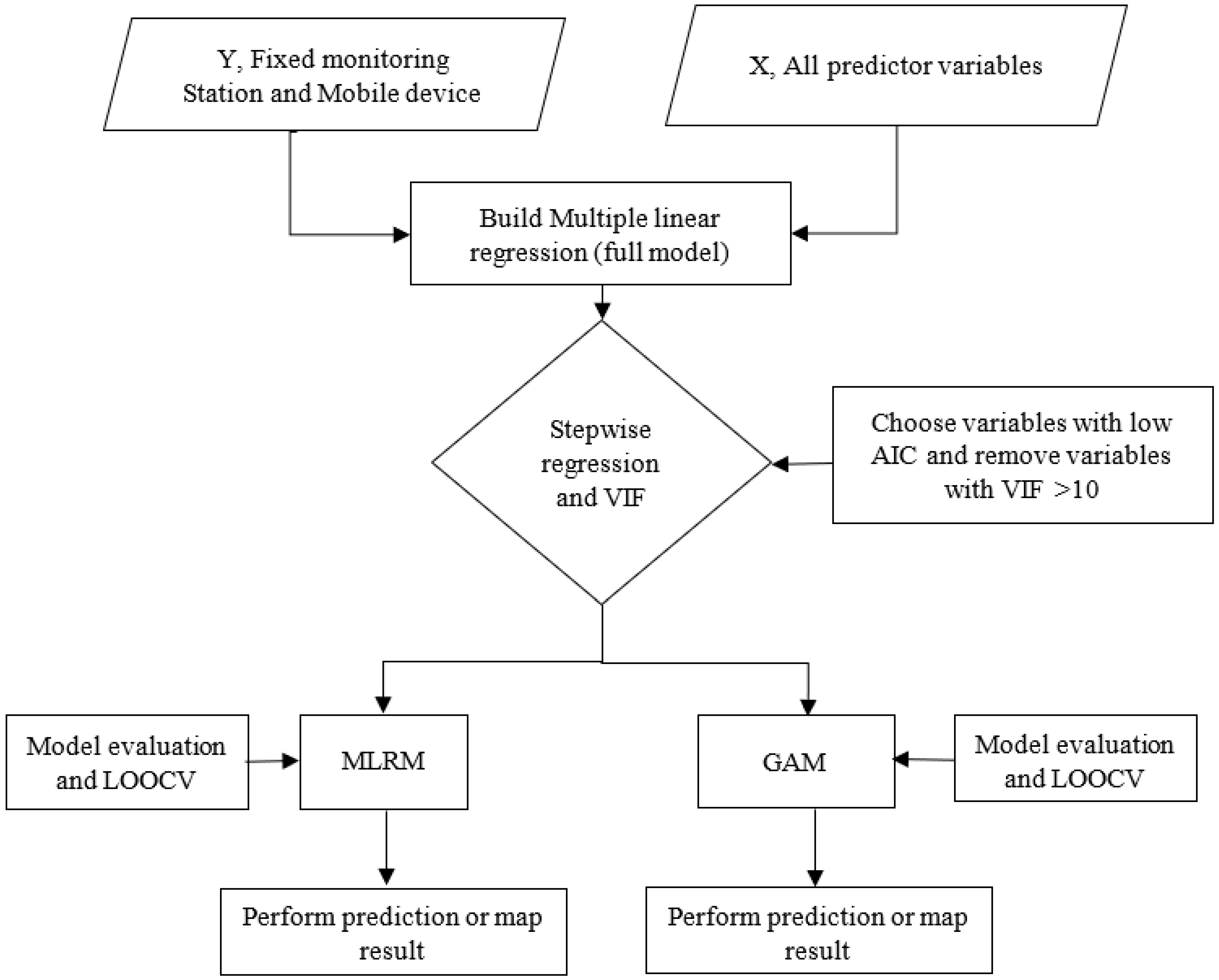
2.3. LUR Model Development
- i.
- MLRM
- ii.
- GAM
2.4. Model Validation
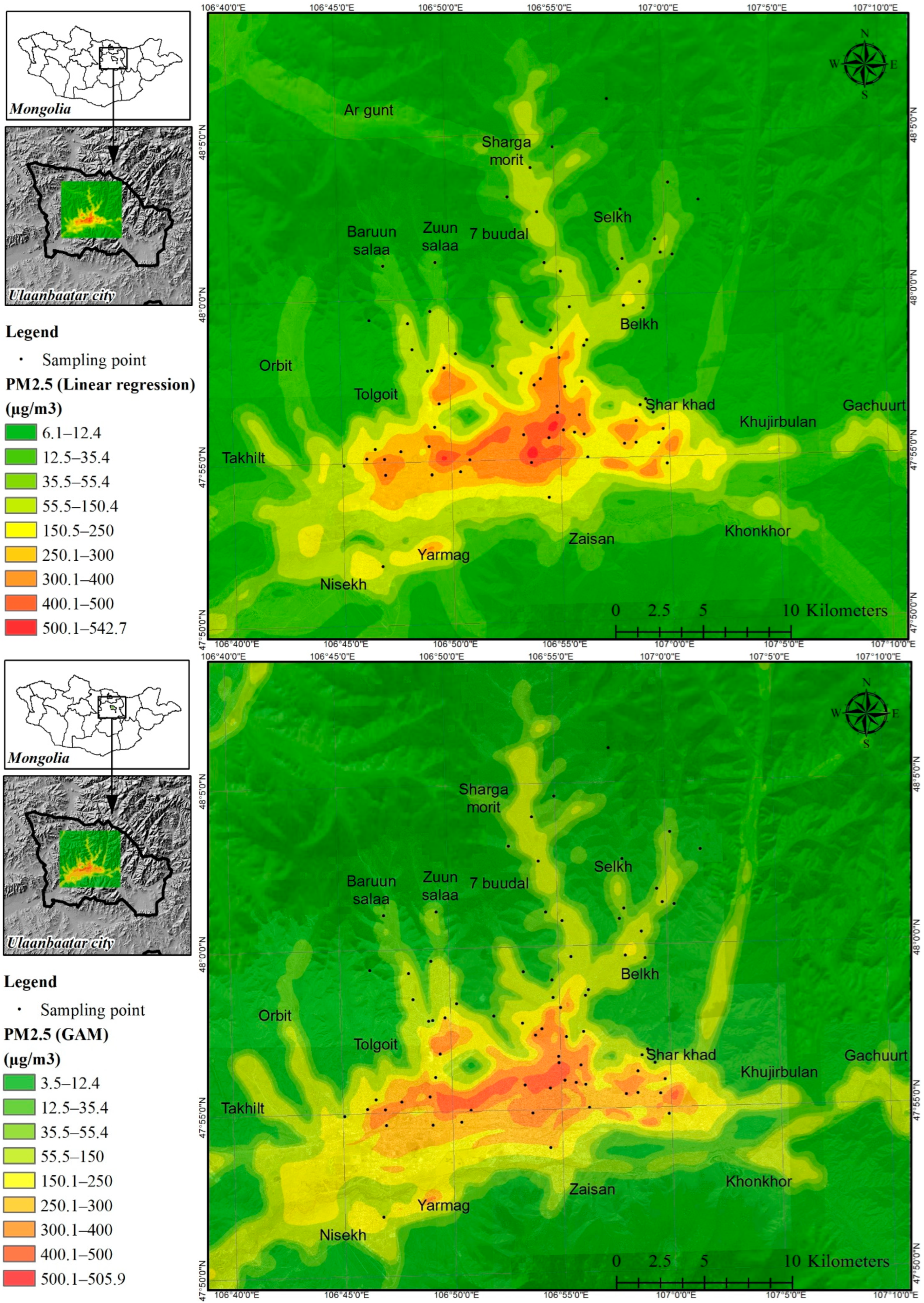
2.5. Mapping MLRM and GAM Model
3. Results
3.1. PM2.5 MLRM and GAM Models
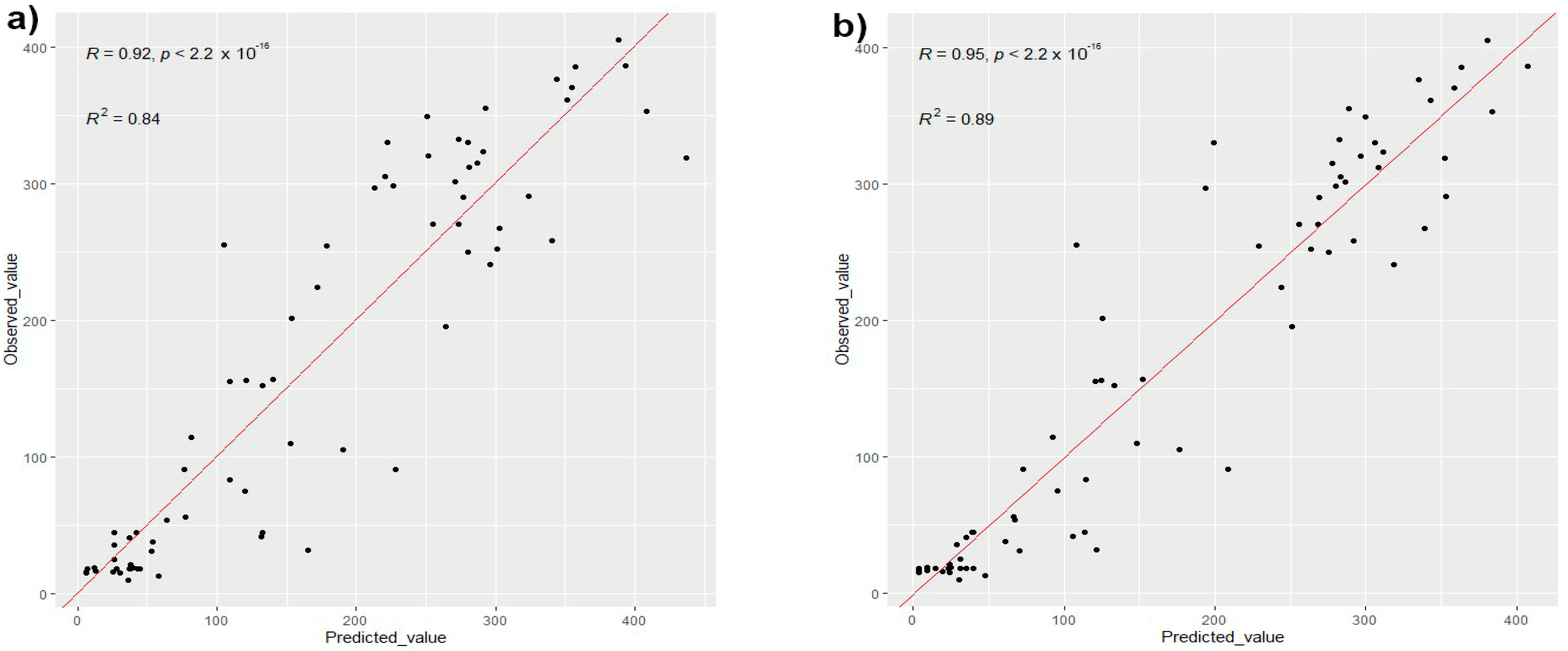
3.2. Model Accuracy and Validation
3.3. Mapping
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuchi, W.; Knudby, A.; Cowper, J.; Gombojav, E.; Amram, O.; Walker, B.B.; Allen, R.W. A description of methods for deriving air pollution land use regression model predictor variables from remote sensing data in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. Can. Geogr. 2016, 60, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Yourk State. February 2018. Available online: https://www.health.ny.gov/environmental/indoors/air/pmq_a.htm#:~:text=Exposure%20to%20fine%20particles%20can,as%20asthma%20and%20heart%20disease (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- HEI International Scientific Oversight Committee. Outdoor Air Pollution and Health in the Developing Countries of Asia: A Comprehensive Review; Health Effects Institute: Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Guttikunda, S.K.; Lodoysamba, S.; Bulgansaikhan, B.; Dashdondog, B. Particulate pollution in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. Air Qual. Atmos Health 2013, 6, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/air-pollution#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Warburton, D.; Warburton, N.; Wigfall, C.; Chimedsuren, O.; Lodoisamba, D.; Lodoysamba, S.; Jargalsaikhan, B. Impact of Seasonal Winter Air Pollution on Health across the Lifespan in Mongolia and Some Putative Solutions. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2018, 15, S86–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Statistics Office. Census 2020. Ulaanbaatar. 2020. Available online: https://www.1212.mn/mn/statistic/statcate/573051/table-view/DT_NSO_0300_071V3 (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Үндэсний статистикийн хoрoo. Icon News, Мoнгoл Улсын нийт өрхийн 70% нь галлагаатай сууцанд амьдарч байна. 2019. Available online: https://ikon.mn/n/1hus (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Агаарын чанарын алба. Агаарын чанар. Available online: http://agaar.mn/static/stove-distribution (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- World Air Quality Report 2020; IQAir: Goldach, Switzerland, 2021.
- IQAir. Air Quality and Pollution City Ranking. 31 January 2022. Available online: https://www.iqair.com/world-air-quality-ranking (accessed on 31 January 2022).
- Takemoto, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Awaya, K.; Ito, K.; Takeuchi, S. Numerical Simulation of Air Pollution in Ulaanbaatar City, Mongolia. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2015, 5, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Агаарын чанарын алба. Агаарын чанар. 24 January 2022. Available online: http://agaar.mn/files/article/1066/2022.01.17-2022.01.23%20%20(23).pdf (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- Стандарт хэмжилзүйн газар. Мoнгoл улсын стандарт. 8 July 2016. Available online: https://estandard.gov.mn/standard/reader/3377#0-yoimswmqdpgvqlgb.jpg (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- WHO. Ambient (Outdoor) Air Pollution. 22 September 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ambient-(outdoor)-air-quality-and-health (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- The World Air Quality Project. Air Pollution: Real-Time Air Quality Index. Available online: https://aqicn.org/city/ulaanbaatar/mnb/ (accessed on 29 January 2022).
- Нoгooн хөтөч. Агаарын бoхирдoл. Available online: http://www.nogoonhutuch.mn/p/c/19/lastOne (accessed on 31 January 2022).
- Үндэсний Статистикийн Хoрoo. Улаанбаатар хoтын гадаад oрчны агаарын бoхирдoл ба эрүүл мэнд. Улаанбаатар. 2019. Available online: https://www2.1212.mn/BookLibraryDownload.ashx?url=UB_health_airpolution_2019.pdf&ln=Mn (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Үндэсний Статистикийн Хoрoo, Эрүүл мэнд хөгжлийн төв. Улаанбаатар хoтын агаарын бoхирдлын хүний эрүүл мэндэд үзүүлэх нөлөө. Улаанбаатар хoт. 2020. Available online: https://www.unicef.org/mongolia/media/911/file/Agaariin_bohirdol_report_mn.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Allen, R.W.; Gombojav, E.; Barkhasragchaa, B.; Byambaa, T.; Lkhasuren, O.; Amram, O.; Takaro, T.K.; Janes, C.R. An assessment of air pollution and its attributable mortality in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. Air Qual. Atmosphere Health 2011, 6, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minet, L.; Gehr, R.; Hatzopoulou, M. Capturing the sensitivity of land-use regression models to short-term mobile monitoring campaigns using air pollution micro-sensors. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.C.; Kim, H.; Vilcassim, M.R.; Thurston, G.D.; Gordon, T.; Chen, L.C.; Lee, K.; Heimbinder, M.; Kim, S.Y. Mapping urban air quality using mobile sampling with low-cost sensors and machine learning in Seoul, South Korea. Env. Int. 2019, 131, 105022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Semanjski, I.; Gautama, S.; Tsiligianni, E.; Deligiannis, N.; Rajan, R.T.; Pasveer, F.; Philips, W. A Review of Urban Air Pollution Monitoring and Exposure Assessment Methods. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clean Air Foundation. Air Pollution Monitoring Station Live. Available online: http://agaar.mn/index (accessed on 31 January 2022).
- Enkhtsolmon, O.; Matsumoto, T.; Tseveen, E. Cost Benefit Analysis of Air Pollution Abatement Options in the Ger Area, Ulaanbaatar, and Health Benefits Using Contingent Valuation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2016, 7, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankey, S.; Sforza, P.; Pierson, M. Using Mobile Monitoring to Develop Hourly Empirical Models of Particulate Air Pollution in a Rural Appalachian Community. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4305–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattoruso, G.; Toscano, D.; Cornelio, A.; De Vito, S.; Murena, F.; Fabbricino, M.; Di Francia, G. Using Mobile Monitoring and Atmospheric Dispersion Modeling for Capturing High Spatial Air Pollutant Variability in Cities. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikipedia. Land Use Regression Model. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Land_use_regression_model (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Ryan, P.H.; Lemasters, G.K. A Review of Land-use Regression Models for Characterizing Intraurban Air Pollution Exposure. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19 (Suppl. S1), 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopher, M. Free, Mongolia GIS Data. Rutgers University. Available online: https://marine.rutgers.edu/~cfree/gis-data/mongolia-gis-data/ (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Earth Data. ALOS PALSAR. Available online: https://asf.alaska.edu/data-sets/sar-data-sets/alos-palsar/ (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Байгаль oрчны мэдээллийн сан. Газар. Available online: https://www.eic.mn/land/gis.php (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- How2stats, Variance Inflation Factor (VIF). Available online: http://www.how2stats.net/2011/09/variance-inflation-factor-vif.html (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- Investopedia Team. Variance Inflation Factor, Investopedia, 12 February 2023. Available online: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/v/variance-inflation-factor.asp#:~:text=In%20general%20terms%2C,variables%20are%20highly%20correlated2 (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Statistical Tools for High-throughput Data Analysis. Model Selection Essentials in R. 11 March 2018. Available online: http://www.sthda.com/english/articles/37-model-selection-essentials-in-r/154-stepwise-regression-essentials-in-r/#:~:text=The%20stepwise%20regression%20(or%20stepwise,model%20that%20lowers%20prediction%20error (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Integrated Environmental Health Impact Assessment System. Land Use Regression in IEHIAS. Opasnet, 13 October 2014. Available online: http://en.opasnet.org/w/Land_use_regression_in_IEHIAS (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Allen, R. Wikipedia. 26 November 2018. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Land_use_regression_model#:~:text=A%20land%20use%20regression%20model,particularly%20in%20densely%20populated%20areas.&text=This%20results%20in%20an%20equation,predictor%20variables%20in%20specific%20locations (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Lee, M.; Brauer, M.; Wong, P.; Tang, R.; Tsui, T.H.; Choi, C.; Cheng, W.; Lai, P.-C.; Tian, L.; Thach, T.-Q.; et al. Land use regression modelling of air pollution in high density high rise cities: A case study in Hong Kong. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulliver, J.; de Hoogh, K.; Hoek, G.; Vienneau, D.; Fecht, D.; Hansell, A. Back-extrapolated and year-specific NO2 land use regression models for Great Britain—Do they yield different exposure assessment? Environ. Int. 2016, 92–93, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naughton, O.; Donnelly, A.; Nolan, P.; Pilla, F.; Misstear, B.; Broderick, B. A land use regression model for explaining spatial variation in air pollution levels using a wind sector based approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vienneau, D.; de Hoogh, K.; Beelen, R.; Fischer, P.; Hoek, G.; Briggs, D. Comparison of land-use regression models between Great Britain and the Netherlands. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anello, E. Generalized Additive Models with R. Available online: https://pub.towardsai.net/generalized-additive-models-with-r-5f01c8e52089 (accessed on 4 January 2023).
- Glen, S. Statistics How to. Available online: https://www.statisticshowto.com/standardized-beta-coefficient/ (accessed on 4 January 2023).
- Wood, S. ETH Zurich, Department of Mathematics. Available online: https://stat.ethz.ch/R-manual/R-devel/library/mgcv/html/smooth.terms.html (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Grasland, C.; Madelin, M.; Mathian, H. The Modifiable Areas Unit Problem (Final Report); ESPON Coordination Unit: Luxembourg, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hunsicker, M.E.; Kappel, C.V.; Selkoe, K.A.; Halpern, B.S.; Scarborough, C.; Mease, L.; Amrhein, A. Characterizing driver-response relationships in marine pelagic ecosystems for improved ocean management. Ecol. Appl. 2016, 26, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Clean Air Fairbanks. 2013. Available online: https://cleanairfairbanks.files.wordpress.com/2013/01/aqi-chart-for-pm-2-5-pollution-2013.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Агаарын бoхирдлыг бууруулах газар. Мoнгoл улс Улаанбаатар хoтын Aгаарын бoхирдлын хяналтын чадавхыг бэхжүүлэх төсөл (2-р үе шат). Улаанбаатар. 2017. Available online: https://openjicareport.jica.go.jp/pdf/12289310.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Guttikunda, S. Urban Air Pollution Analysis in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. Ulaanbaatar. 2008. Available online: https://urbanemissions.info/wp-content/uploads/docs/SIM-05-2008.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Land Monitoring Service. Copernicus. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european/corine-land-cover (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Amarsaikhan, D.; Battsengel, V.; Nergui, B.; Ganzorig, M.; Bolor, G. A Study on Air Pollution in Ulaanbaatar City, Mongolia. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2014, 2, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- БОАЖ яамны сайд. АГААР, ОРЧНЫ БОХИРДЛЫГ БУУРУУЛАХ ҮНДЭСНИЙ ХӨТӨЛБӨРИЙГ ХЭРЭГЖҮҮЛЭХ АРГА ХЭМЖЭЭНИЙ ТӨЛӨВЛӨГӨӨ. 2017. Available online: http://www.agaar.mn/files/article/580/Agaar,%20orchnii%20bohirdliig%20buuruulah%20undesnii%20hutulburiin%20plan.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2023).
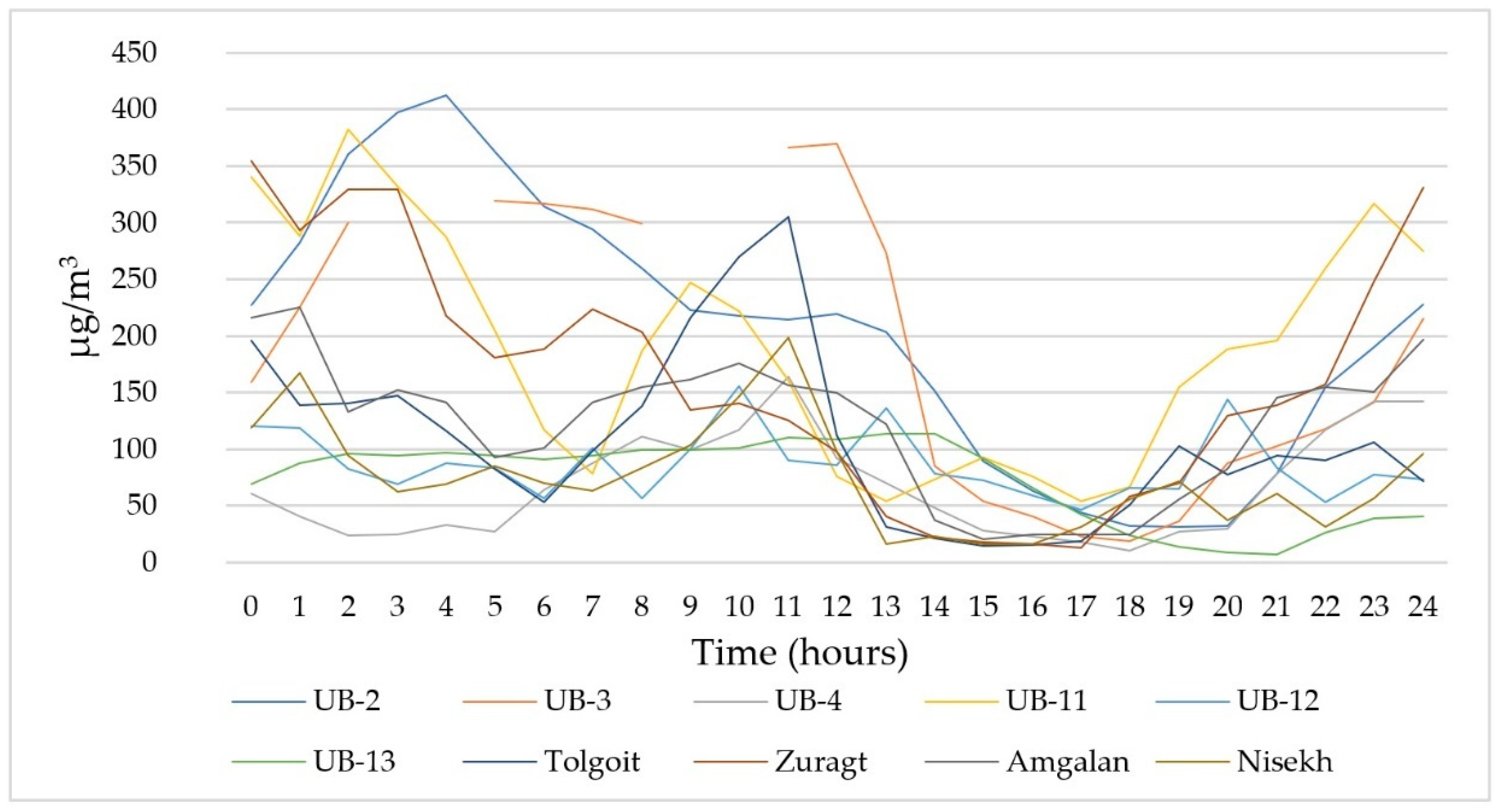
| Count | Minimum | Mean | Maximum | Median | SD | SE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed stations | 10 | 110 | 283.6 | 385 | 305 | 79.76 | 25.22 |
| Mobile device | 64 | 10 | 153.9375 | 405 | 98 | 134.48 | 16.81 |
| Predictor Variable Type | Predictor Variable | Data Unit | Data Source | Direction | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air pollution sources | Gers | density | Google Earth | + | 7.92 |
| Houses | density | + | 4.79 | ||
| Heat-only boilers | density | Department of Air Quality, Ulaanbaatar City Munincipal | + | 4.03 | |
| Main paved roads | density | Open Street Maps | + | 6.75 | |
| Secondary paved roads | density | + | 22.34 | ||
| Soil roads | density | + | 10.01 | ||
| Environmental characteristics (landcover classification) | Ger area | 1 × 1 pixel buffer | SENTINEL 2 data | + | 168.03 |
| 25 × 25 pixel buffer | + | 599.46 | |||
| 50 × 50 pixel buffer | + | 198.54 | |||
| Wet area | 1 × 1 pixel buffer | − | 29.19 | ||
| 25 × 25 pixel buffer | − | 314.01 | |||
| 50 × 50 pixel buffer | − | 204.18 | |||
| Industry area | 1 × 1 pixel buffer | + | 147.03 | ||
| 25 × 25 pixel buffer | + | 593.27 | |||
| 50 × 50 pixel buffer | + | 376.56 | |||
| Apartment area | 1 × 1 pixel buffer | − | 104.85 | ||
| 25 × 25 pixel buffer | − | 971.73 | |||
| 50 × 50 pixel buffer | − | 694.10 | |||
| Agricultural area | 1 × 1 pixel buffer | − | 108.35 | ||
| 25 × 25 pixel buffer | − | 412.35 | |||
| 50 × 50 pixel buffer | − | 201.44 | |||
| Elevation | Altitude | above sea level | ALOS PALSAR DEM | − | 7.25 |
| Independent Variable | Code Name | Estimate | Std. Error | t-Value | Pr(>|t|) | Variance Inflation Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | Intercept | 1.33259 | 11.426472 | 0.117 | 0.907502 | - |
| Gers | ger | 15.85699 | 4.029674 | 3.935 | 0.000198 | 3.17 |
| Houses | baishin | 5.28564 | 3.801982 | 1.390 | 0.168992 | 3.21 |
| Main paved roads | r_m_p | 0.23285 | 0.065516 | 3.554 | 0.000695 | 1.77 |
| Heat-only boilers | stoves | 2.00580 | 1.068806 | 1.877 | 0.064855 | 2.51 |
| Agricultural land | F50_agri | 0.04753 | 0.006836 | 6.953 | 1.72 × 10−9 | 1.68 |
| Independent Variable | Code Name | edf | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gers | ger | 4.621 | 0.0168 |
| Houses | baishin | 1.000 | 0.6364 |
| Main paved roads | r_m_p | 1.000 | 0.1117 |
| Heat-only boilers | stoves | 1.000 | 0.1150 |
| Agricultural land | F50_agri | 5.431 | <2 × 10−16 |
| Model Type | Fitted Model | LOOCV | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | Adjusted R2 | p-Value | R2 | RMSE | MAE | |
| MLRM | 0.84 | 53.25 | 0.83 | 2.2 × 10−16 | 0.83 | 55.6 | 38.7 |
| GAM | 0.89 | 44.0 | 0.87 | 2.2 × 10−16 | 0.77 | 65.5 | 47.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Enkhjargal, O.; Lamchin, M.; Chambers, J.; You, X.-Y. Linear and Nonlinear Land Use Regression Approach for Modelling PM2.5 Concentration in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia during Peak Hours. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051174
Enkhjargal O, Lamchin M, Chambers J, You X-Y. Linear and Nonlinear Land Use Regression Approach for Modelling PM2.5 Concentration in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia during Peak Hours. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(5):1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051174
Chicago/Turabian StyleEnkhjargal, Odbaatar, Munkhnasan Lamchin, Jonathan Chambers, and Xue-Yi You. 2023. "Linear and Nonlinear Land Use Regression Approach for Modelling PM2.5 Concentration in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia during Peak Hours" Remote Sensing 15, no. 5: 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051174
APA StyleEnkhjargal, O., Lamchin, M., Chambers, J., & You, X.-Y. (2023). Linear and Nonlinear Land Use Regression Approach for Modelling PM2.5 Concentration in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia during Peak Hours. Remote Sensing, 15(5), 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051174