AOD Derivation from SDGSAT-1/GLI Dataset in Mega-City Area
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Datasets
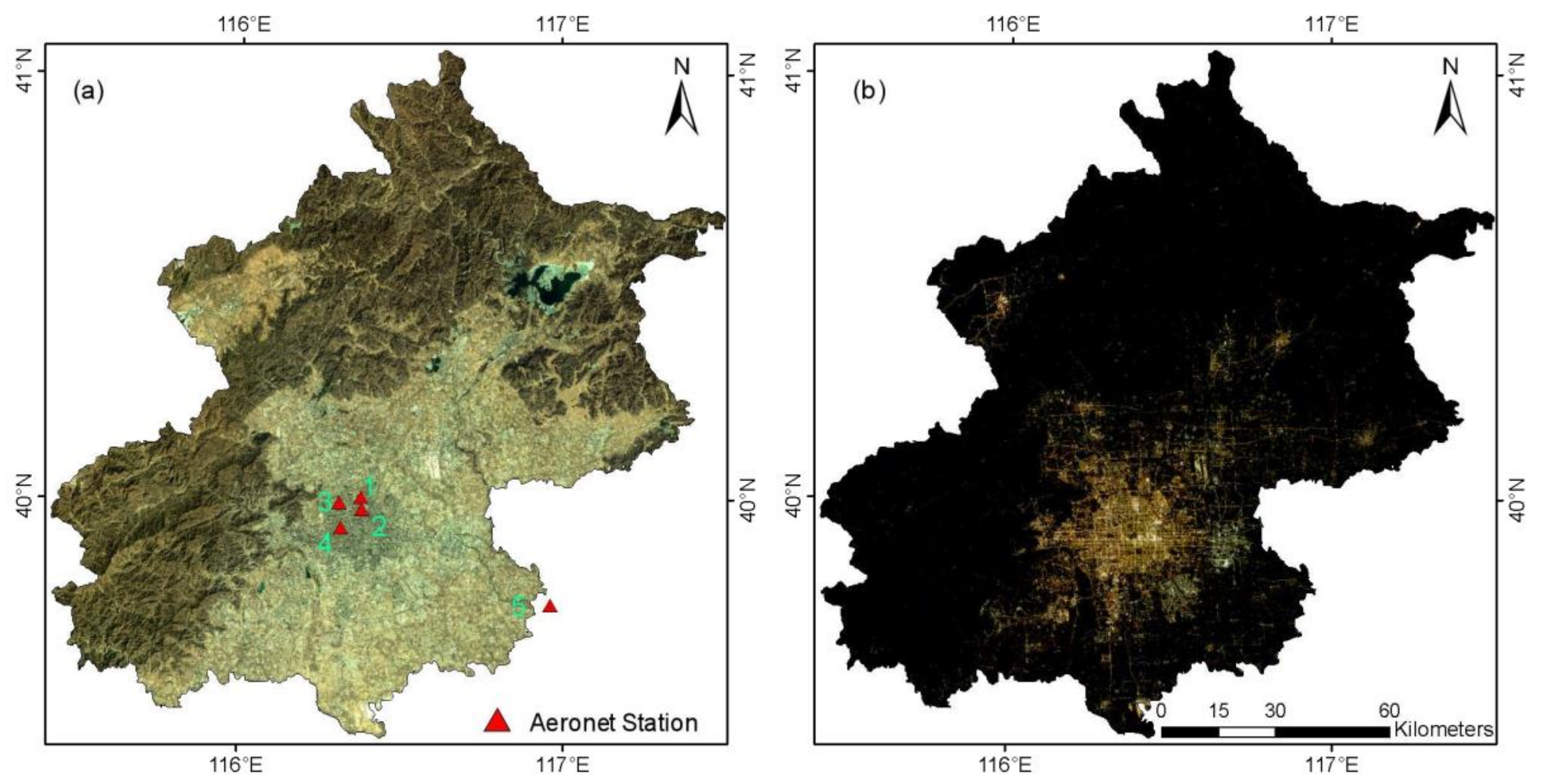
2.1. Study Area
2.2. SDGSAT-1 GLI Data
2.3. VIIRS/DNB Data
2.4. AERONET Data
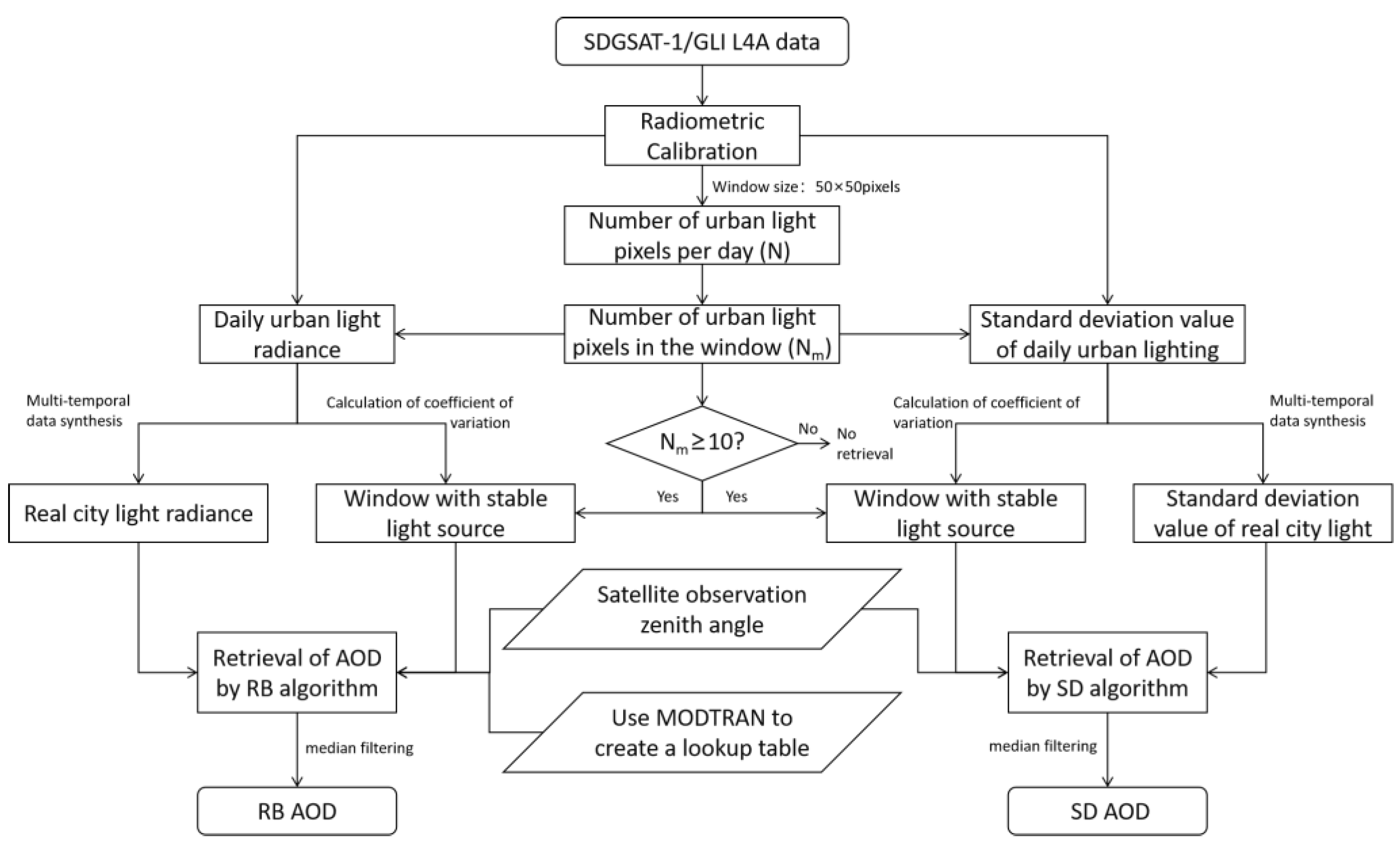
3. Aerosol Inversion Methods
3.1. Theoretical Basis
3.2. AOD Derivation Using Standard Deviation Method (SD Algorithm)
3.3. Radiance Background Method for AOD Inversion (RB Algorithm)
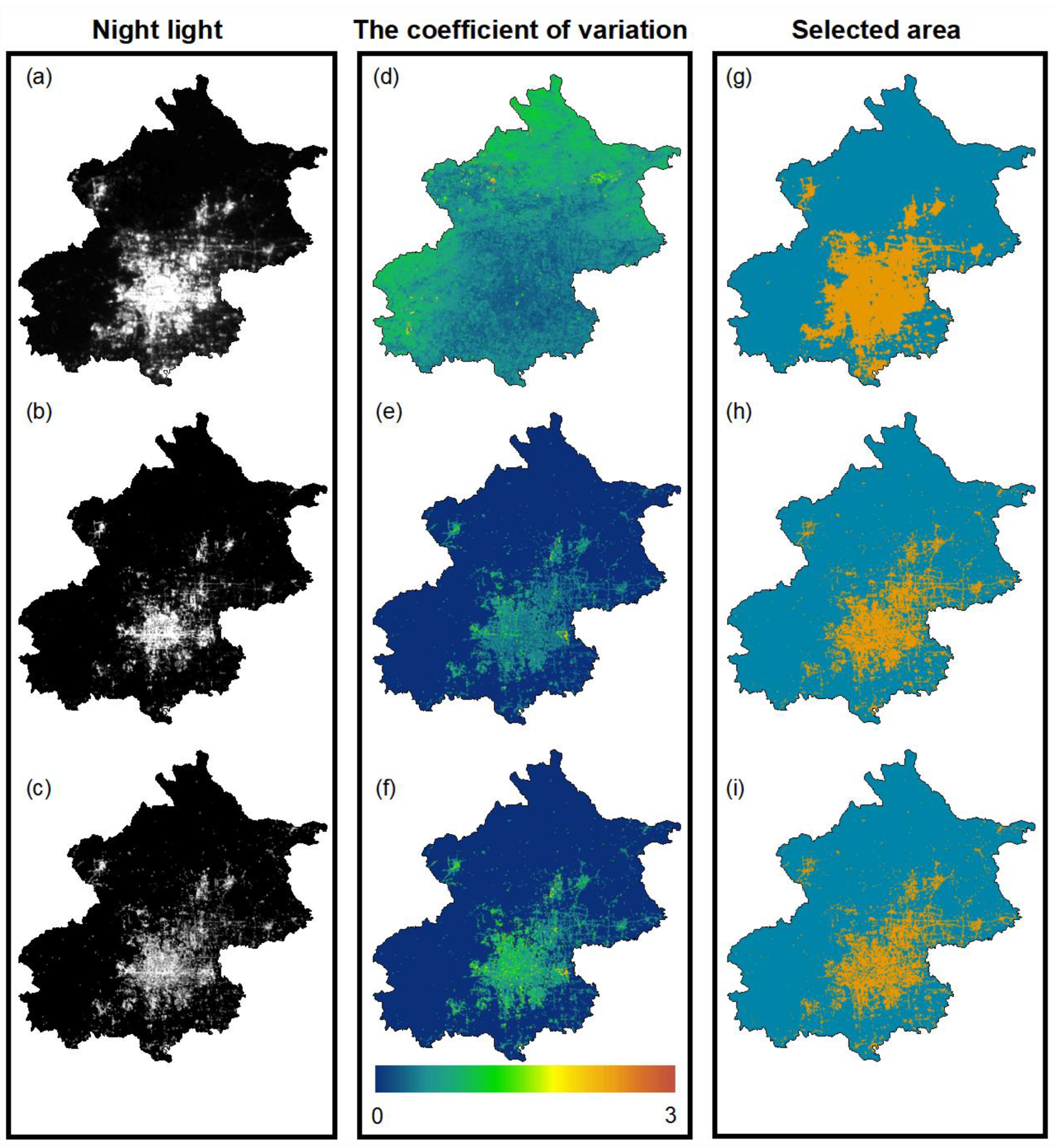
3.4. VIIRS/DNB Data Pre-Processing
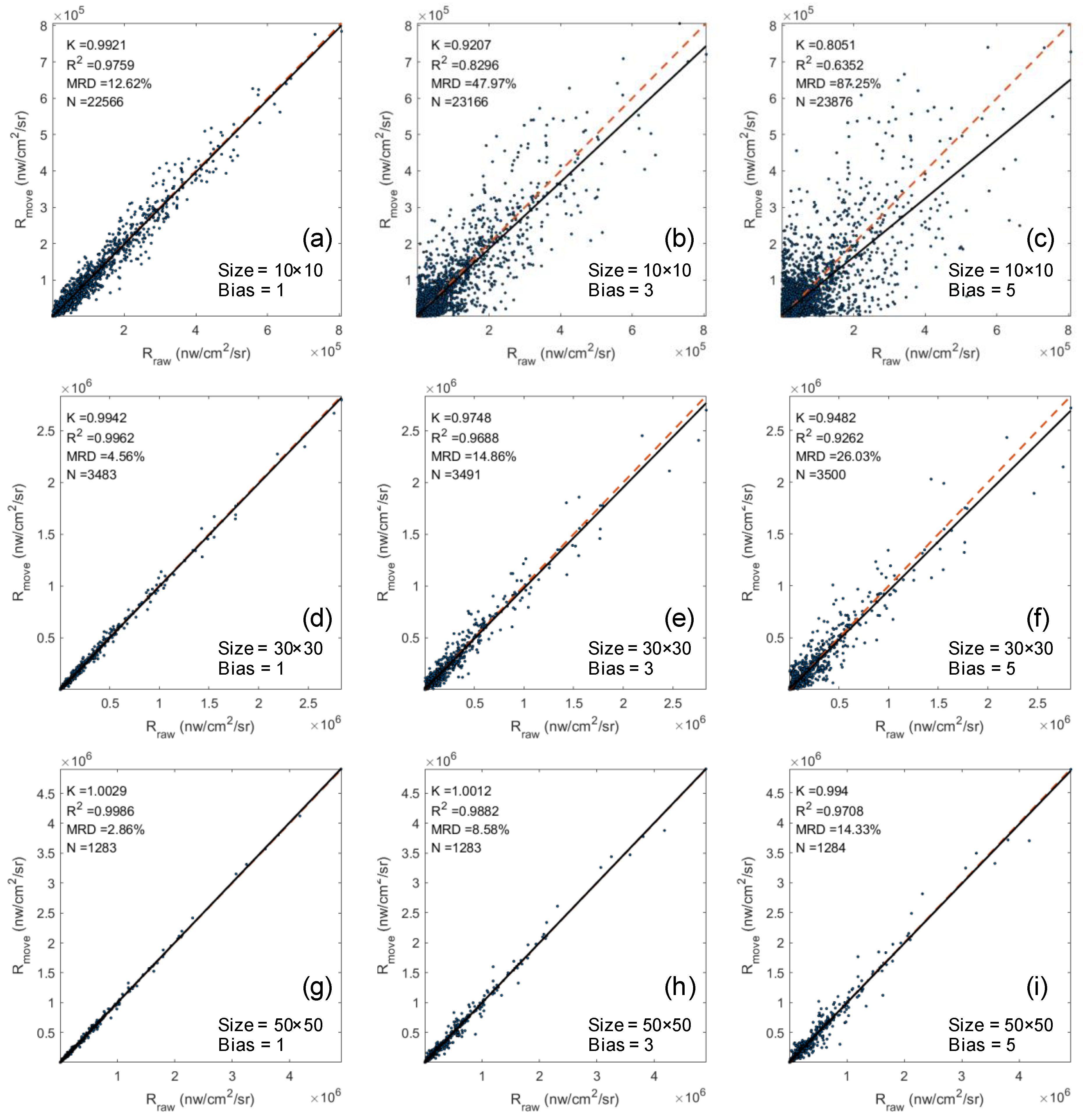
3.5. SDGSAT-1/GLI Data Preprocessing
3.6. Nighttime AOD Derivation
4. Results
4.1. The Nighttime AOD from SDGSAT-1/GLI
4.2. The Verification of Satellite-Based AOD Using Nighttime AERONET Observations
4.3. The Difference of AOD from SDGSAT/GLI and Daytime Stations
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; Cheng, B.; Zhang, X.; Long, T.; Chen, B.; Wang, G.; Zhang, D. A TIR-Visible Automatic Registration and Geometric Correction Method for SDGSAT-1 Thermal Infrared Image Based on Modified RIFT. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Dou, C.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.B.; Fu, B.H.; Li, X.M.; Zou, Z.; Liang, D. SDGSAT-1: The world’s first scientific satellite for Sustainable Development Goals. Sci. Bull. 2022, 22, S2095–S9273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huadong, G.; Dong, L.; Fang, C.; Zhongchang, S.; Jie, L. Big Earth Data Facilitates Sustainable Development Goals. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. (Chin. Version) 2021, 36, 874–884. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, N.; Kyba, C.C.M.; Zhang, Q.; Sánchez De Miguel, A.; Román, M.O.; Li, X.; Portnov, B.A.; Molthan, A.L.; Jechow, A.; Miller, S.D.; et al. Remote sensing of night lights: A review and an outlook for the future. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Chang, N.; Bai, K.; Gao, W. Satellite remote sensing of aerosol optical depth: Advances, challenges, and perspectives. Crit. Rev. Env. Sci. Tec. 2020, 50, 1640–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, J.; Fan, W.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, D. Review of aerosol optical depth retrieval using visibility data. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 200, 102986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambezidis, H.D.; Kaskaoutis, D.G. Aerosol climatology over four AERONET sites: An overview. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1892–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, A.K.; Patra, A.K.; Gorai, A.K. A Review on Estimation of Particulate Matter from Satellite-Based Aerosol Optical Depth: Data, Methods, and Challenges. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 57, 679–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, T.; Chen, J. A climatology of aerosol optical depth over China from recent 10 years of MODIS remote sensing data. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Li, R.; Wang, L.; Lan, F.; Wang, Z.; Tao, J.; Che, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, L. A critical view of long-term AVHRR aerosol data record in China: Retrieval frequency and heavy pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, R.A.; Gaitley, B.J. An analysis of global aerosol type as retrieved by MISR. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 4248–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Gautam, R.; Sayer, A.M.; Bettenhausen, C.; Li, C.; Jeong, M.J.; Tsay, S.C.; Holben, B.N. Global and regional trends of aerosol optical depth over land and ocean using SeaWiFS measurements from 1997 to 2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 8037–8053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Spurr, R.J.D.; Reid, J.S.; Xian, P.; Colarco, P.R.; Campbell, J.R.; Hyer, E.J.; Baker, N.L. Development of an Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) aerosol index (AI) data assimilation scheme for aerosol modeling over bright surfaces—A step toward direct radiance assimilation in the UV spectrum. Geosci. Model Dev. 2021, 14, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Campbell, J.R.; Reid, J.S.; Westphal, D.L.; Baker, N.L.; Campbell, W.F.; Hyer, E.J. Evaluating the impact of assimilating CALIOP-derived aerosol extinction profiles on a global mass transport model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Campbell, J.R.; Hyer, E.J.; Reid, J.S.; Westphal, D.L.; Johnson, R.S. Evaluating the impact of multisensor data assimilation on a global aerosol particle transport model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 4674–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Kahn, R.; Mishchenko, M.; Remer, L.; Lee, K.H.; Wang, M.; Laszlo, I.; Nakajima, T.; Maring, H. Uncertainties in satellite remote sensing of aerosols and impact on monitoring its long-term trend: A review and perspective. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 2755–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, M.; Xu, X.; Roudini, S.; Sander, S.P.; Pongetti, T.J.; Miller, S.D.; Reid, J.S.; Hyer, E.; Spurr, R. Development of a nighttime shortwave radiative transfer model for remote sensing of nocturnal aerosols and fires from VIIRS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 241, 111727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutgens, N.; Sayer, A.M.; Heckel, A.; Hsu, C.; Jethva, H.; de Leeuw, G.; Leonard, P.J.T.; Levy, R.C.; Lipponen, A.; Lyapustin, A.; et al. An AeroCom–AeroSat study: Intercomparison of satellite AOD datasets for aerosol model evaluation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 12431–12457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.S.; Zhang, J.; Hyer, E.J.; Miller, S.D.; Reid, J.S. Preliminary investigations toward nighttime aerosol optical depth retrievals from the VIIRS Day/Night Band. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHardy, T.M.; Zhang, J.; Reid, J.S.; Miller, S.D.; Hyer, E.J.; Kuehn, R.E. An improved method for retrieving nighttime aerosol optical thickness from the VIIRS Day/Night Band. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 4773–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Aegerter, C.; Xu, X.; Szykman, J.J. Potential application of VIIRS Day/Night Band for monitoring nighttime surface PM 2.5 air quality from space. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jaker, S.L.; Reid, J.S.; Miller, S.D.; Solbrig, J.; Toth, T.D. Characterization and application of artificial light sources for nighttime aerosol optical depth retrievals using the Visible Infrared Imager Radiometer Suite Day/Night Band. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 3209–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Xu, X.; Colarco, P.R.; Miller, S.D.; Reid, J.S.; Kondragunta, S.; Giles, D.M.; Holben, B. Nighttime smoke aerosol optical depth over U.S. rural areas: First retrieval from VIIRS moonlight observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 267, 112717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hu, S.; Ma, S.; Tan, Z.; Ai, W.; Yan, W. Retrieving nighttime aerosol optical depth using combined measurements of satellite low light channels and ground-based integrating spheres. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2022, ahead-of-print. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.D.; Chen, L.; He, Y.Q.; Hu, X.Q.; Liu, M.Q.; Zhang, P. Nighttime aerosol optical depth retrievals from VIIRS day/night band data. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2022, 3, 493–504. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Reid, J.S.; Miller, S.D.; Turk, F.J. Strategy for studying nocturnal aerosol optical depth using artificial lights. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4599–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, Á.; Cuevas, E.; Granados-Muñoz, M.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Romero, P.M.; Gröbner, J.; Kouremeti, N.; Almansa, A.F.; Stone, T.; Toledano, C.; et al. The new sun-sky-lunar Cimel CE318-T multiband photometer—A comprehensive performance evaluation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 631–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Xu, W.; Hu, Y.; Tao, J.; Kuang, Y.; Zhao, C. Method to retrieve aerosol extinction profiles and aerosol scattering phase functions with a modified CCD laser atmospheric detection system. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Omar, A.; Hu, Y.; Powell, K.A.; Liu, Z.; Hunt, W.H.; Young, S.A. Overview of the CALIPSO Mission and CALIOP Data Processing Algorithms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 2009, 26, 2310–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Reid, J.S.; Miller, S.D.; Román, M.; Wang, Z.; Spurr, R.J.; Jaker, S. Sensitivity studies of nighttime TOA radiances from artificial light sources using a 3-D radiative transfer model for nighttime aerosol retrievals. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2022, 2022, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X. Modeling the climatic effects of urbanization in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei metropolitan area. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2013, 113, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ban, J.; Chen, N.X.; Li, T. High-resolution daily AOD estimated to full coverage using the random forest model approach in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 203, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Román, M.O.; Kalb, V.L.; Zhao, Y. Continuous monitoring of nighttime light changes based on daily NASA’s Black Marble product suite. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 282, 113269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, M.O.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Kalb, V.; Miller, S.D.; Molthan, A.; Schultz, L.; Bell, J.; Stokes, E.C.; Pandey, B.; et al. NASA’s Black Marble nighttime lights product suite. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 113–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.M.; Sinyuk, A.; Sorokin, M.G.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Lewis, J.R.; Campbell, J.R.; et al. Advancements in the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Version 3 database—Automated near-real-time quality control algorithm with improved cloud screening for Sun photometer aerosol optical depth (AOD) measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A Tlreshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. 1979, 9, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.Q.; Li, Z.Q.; Hou, W.Z. Aerosol optical depth retrieval over land using data from AGRI onboard FY-4A. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2022, 5, 913–922. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.; Zhang, B.; Xia, F.; Bai, Y. Exploring VIIRS Night Light Long-Term Time Series with CNN/SI for Urban Change Detection and Aerosol Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veefkind, J.P.; Boersma, K.F.; Wang, J.; Kurosu, T.P.; Krotkov, N.; Chance, K.; Levelt, P.F. Global satellite analysis of the relation between aerosols and short-lived trace gases. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 1255–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Vermote, E.F.; Kaufman, Y.J. Second-generation operational algorithm: Retrieval of aerosol properties over land from inversion of Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer spectral reflectance. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Tao, M.H.; Guo, L.; Chen, L.F.; Tao, J.H.; Gui, L. Progress of near-surface PM2.5 concentration retrieve based on satellite remote sensing. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2022, 9, 1757–1776. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Q.; Li, D.; Liu, S.; He, T.; Zhao, L. Anisotropic characteristic of artificial light at night—Systematic investigation with VIIRS DNB multi-temporal observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, R. Modeling the direction and magnitude of angular effects in nighttime light remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
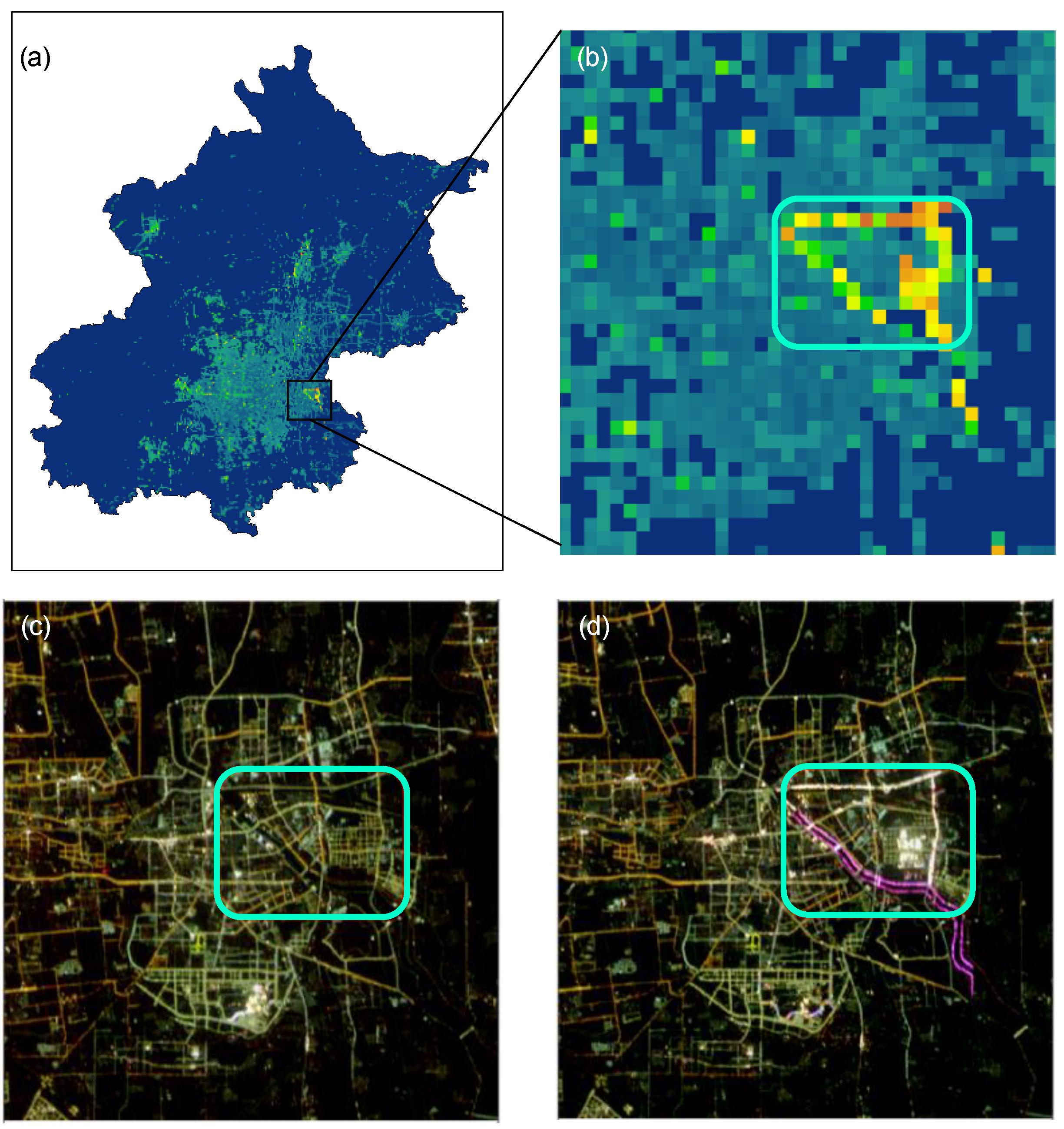
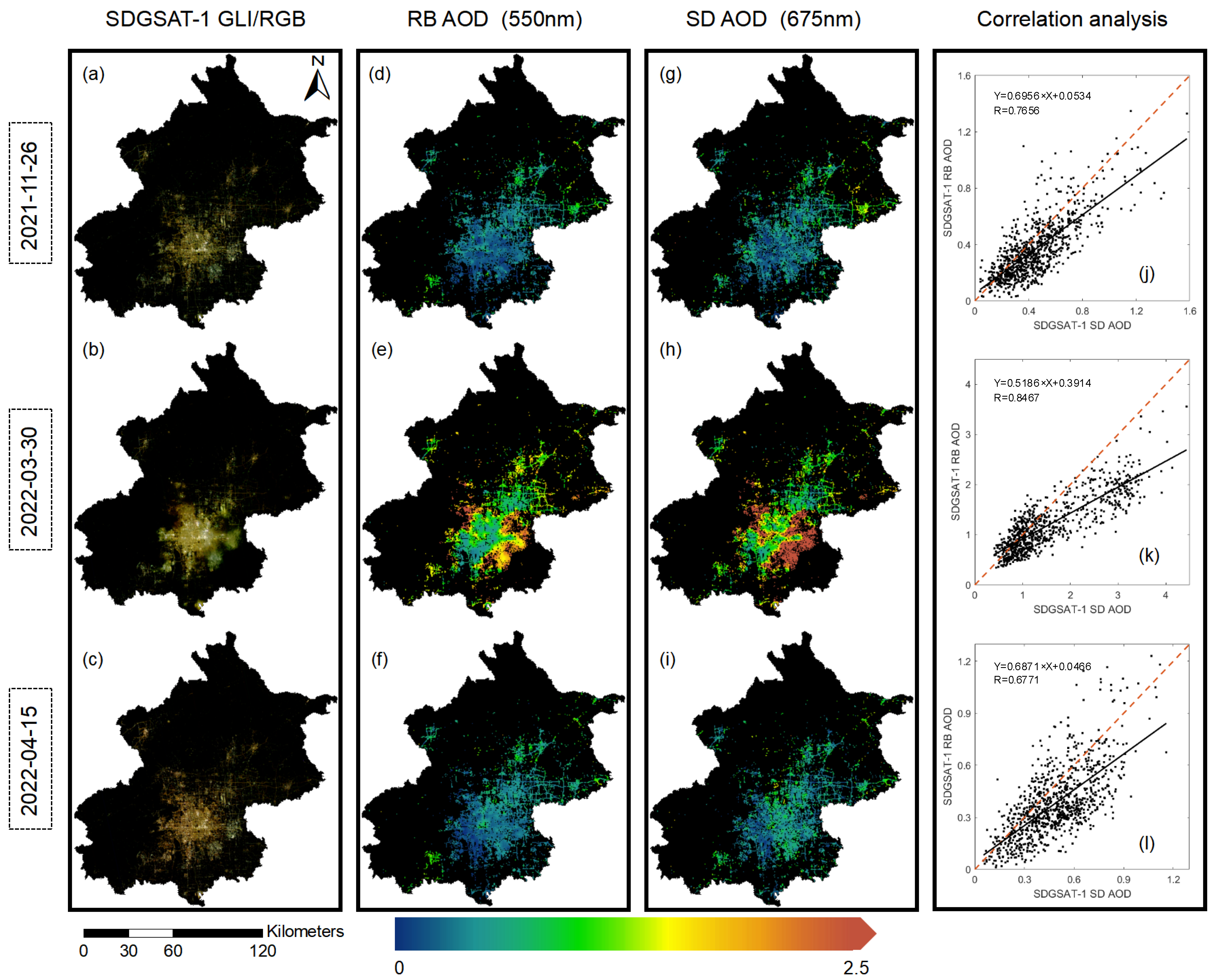
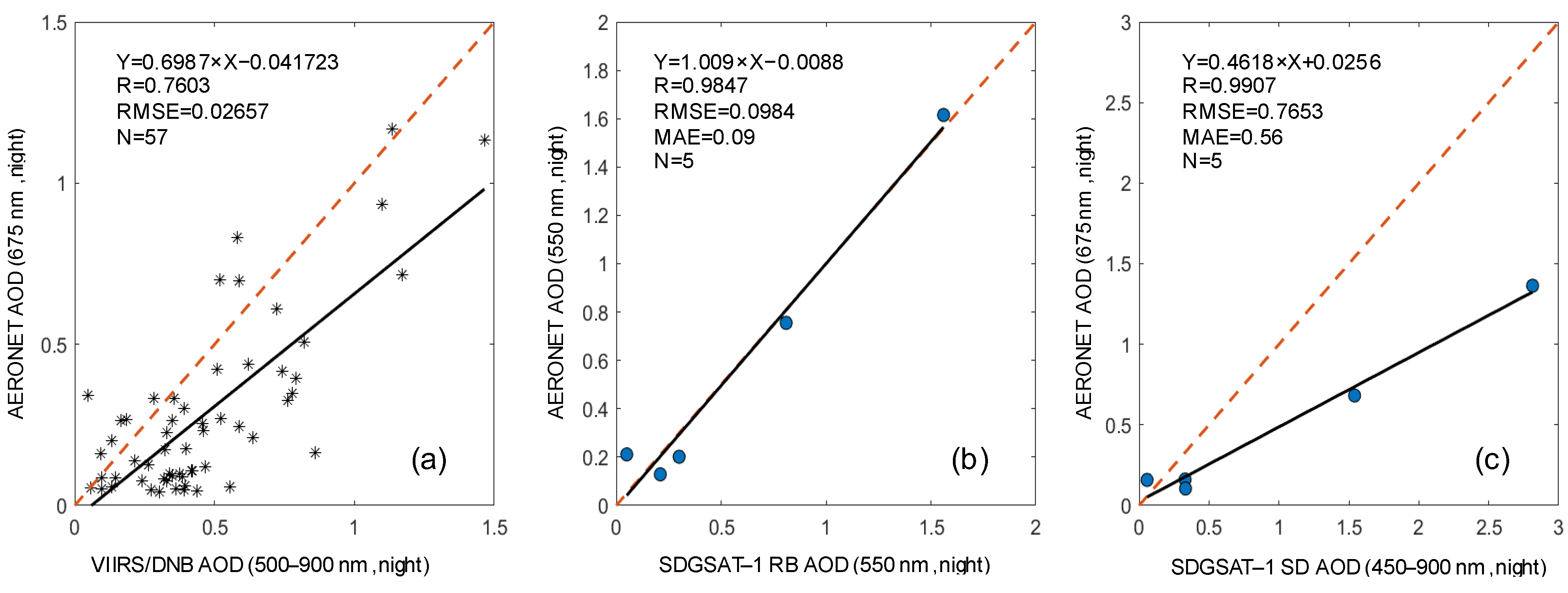
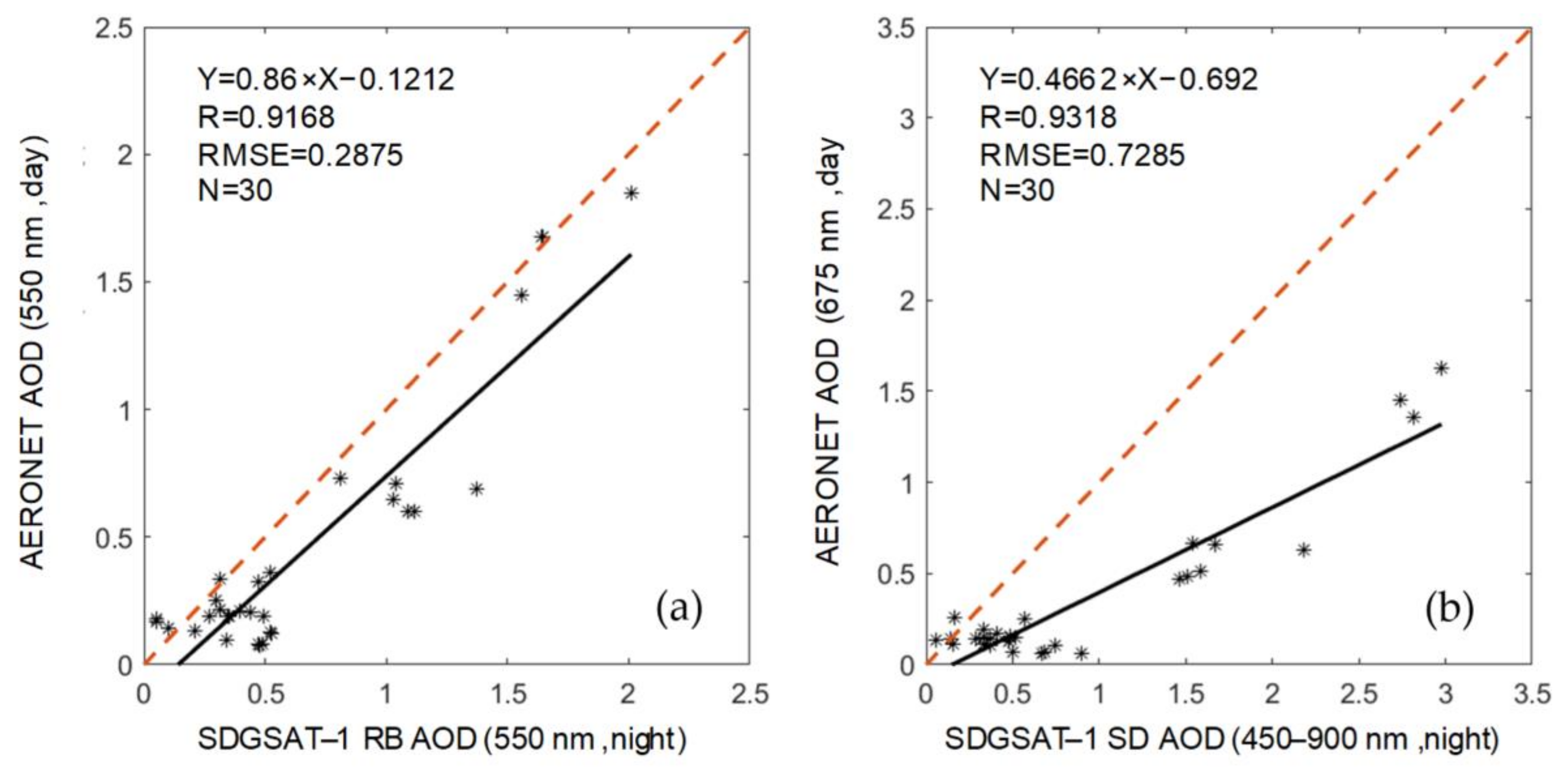
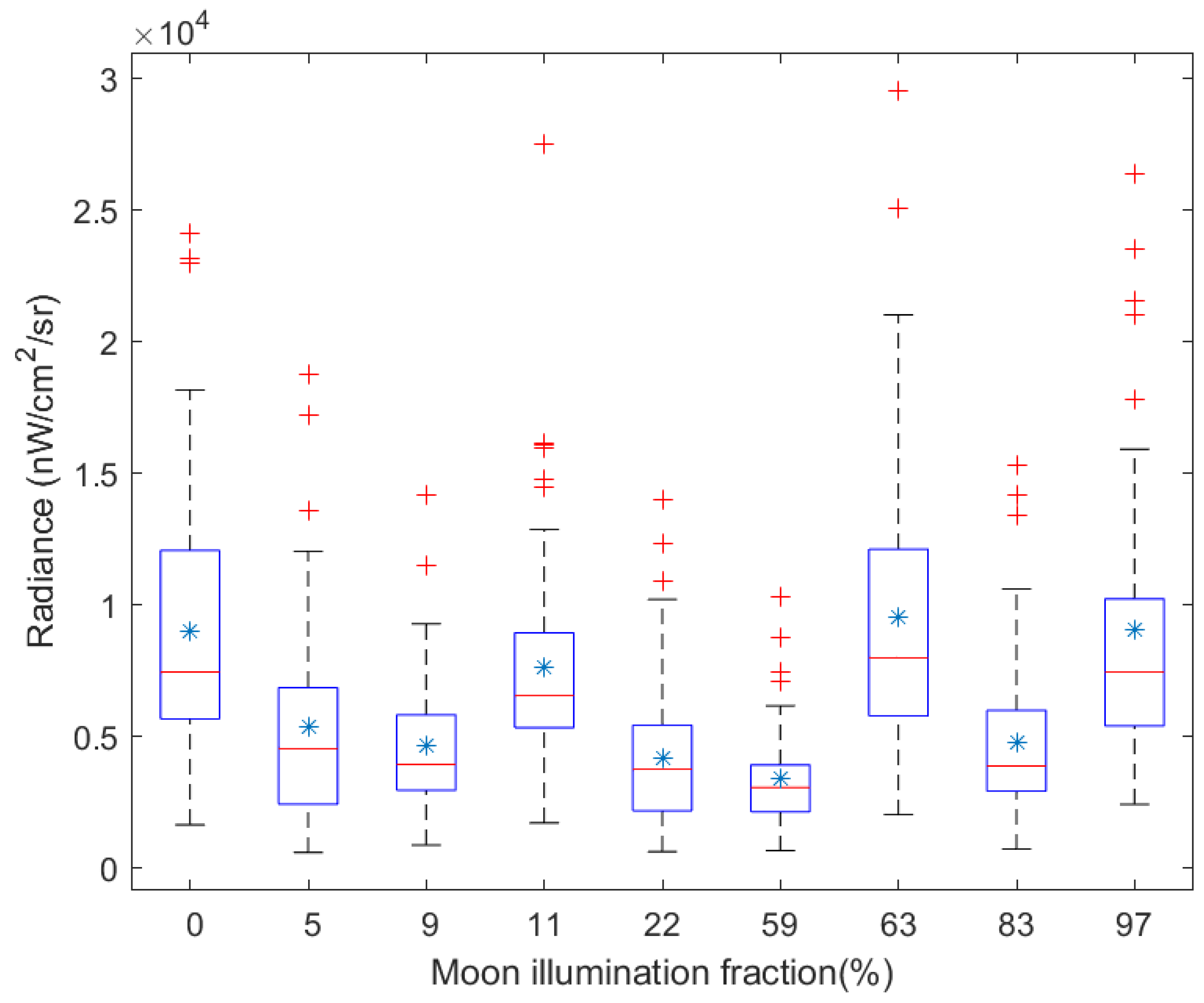
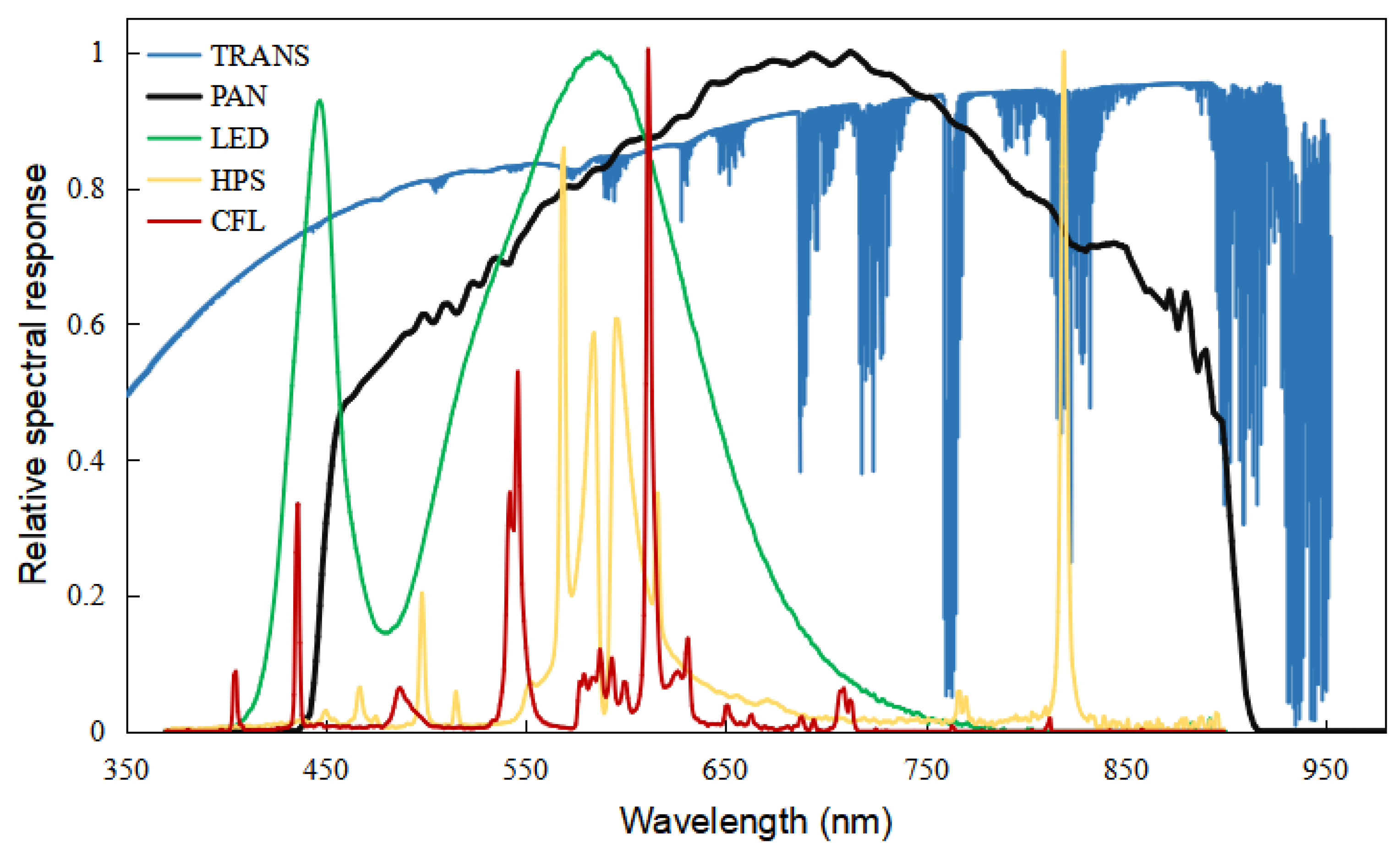
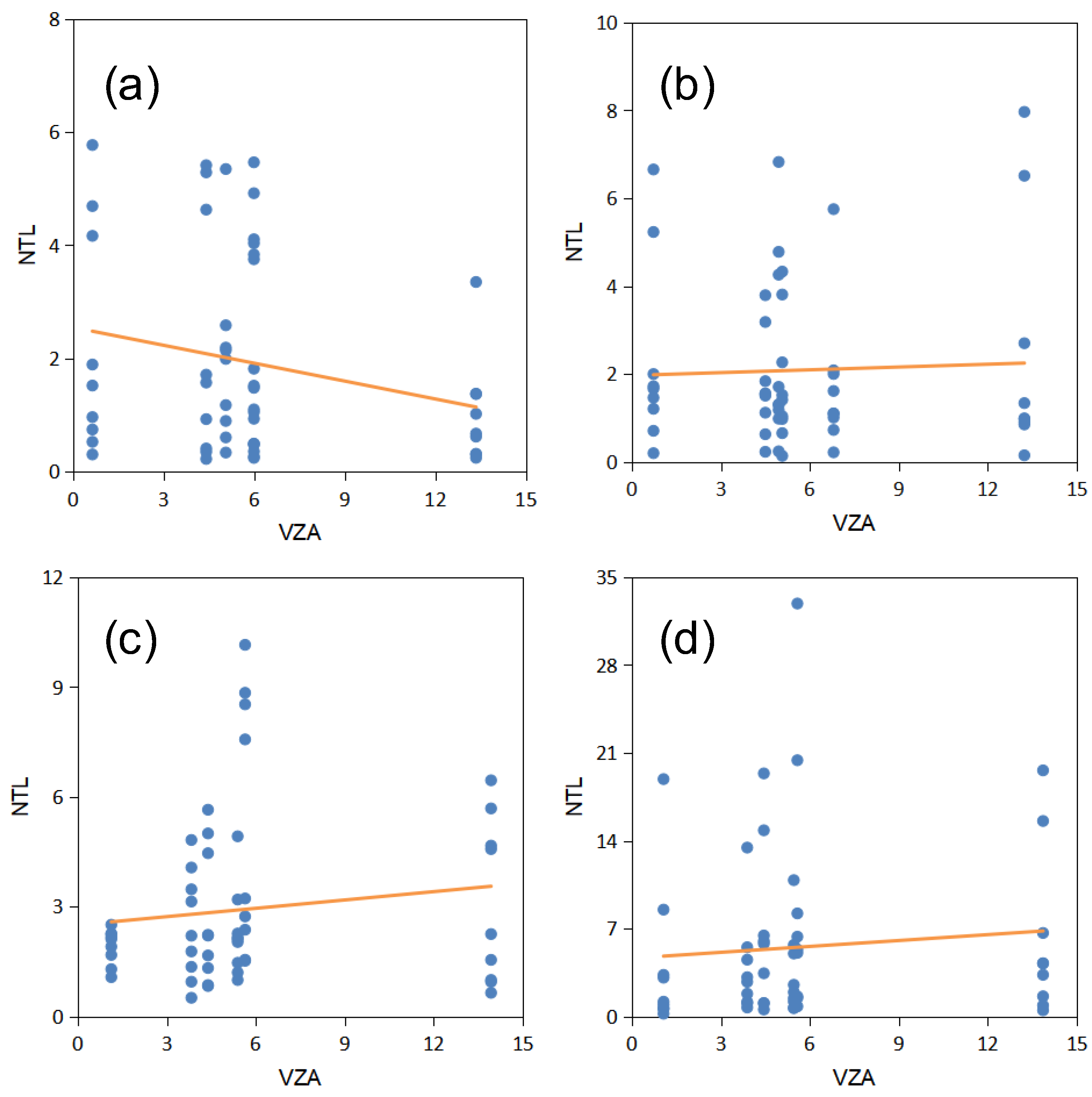
| Number | Date | Overpass Time (UTC) | Number | Date | Overpass Time (UTC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 November 2021 | 13:10:52 | 10 | 14 March 2022 | 13:22:30 |
| 2 | 26 November 2021 | 13:17:02 | 11 | 30 March 2022 | 13:23:26 |
| 3 | 3 January 2022 | 13:18:49 | 12 | 4 April 2022 | 13:29:17 |
| 4 | 25 January 2022 | 13:13:45 | 13 | 5 April 2022 | 13:11:52 |
| 5 | 4 February 2022 | 13:27:33 | 14 | 10 April 2022 | 13:17:27 |
| 6 | 5 February 2022 | 13:10:33 | 15 | 15 April 2022 | 13:23:28 |
| 7 | 15 February 2022 | 13:24:13 | 16 | 26 April 2022 | 13:16:18 |
| 8 | 20 February 2022 | 13:30:45 | 17 | 1 May 2022 | 13:21:17 |
| 9 | 21 February 2022 | 13:13:30 |
| Satellite | NPP-VIIRS/DNB | SDGSAT-1/GLI |
|---|---|---|
| Orbit height | 750 km | 505 km |
| Spatial resolution | 740 m | Panchromatic: 10 m RGB: 40 m |
| Bands | Panchromatic: 500–900 nm | Panchromatic: 444–910 nm Blue: 424~526 nm Green: 506~612 nm Red: 600~894 nm |
| Swath width | 3060 km | 300 km |
| Revisit cycle | 1 d | 11 d |
| Overpass time (Local time) | About 1:30 | About 21:20 |
| Available Period | 2021-present | 2012-present |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, N.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.M.; Kang, C.; Yan, L. AOD Derivation from SDGSAT-1/GLI Dataset in Mega-City Area. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1343. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051343
Wang N, Hu Y, Li XM, Kang C, Yan L. AOD Derivation from SDGSAT-1/GLI Dataset in Mega-City Area. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(5):1343. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051343
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ning, Yonghong Hu, Xiao Ming Li, Chuanli Kang, and Lin Yan. 2023. "AOD Derivation from SDGSAT-1/GLI Dataset in Mega-City Area" Remote Sensing 15, no. 5: 1343. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051343
APA StyleWang, N., Hu, Y., Li, X. M., Kang, C., & Yan, L. (2023). AOD Derivation from SDGSAT-1/GLI Dataset in Mega-City Area. Remote Sensing, 15(5), 1343. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051343







