Abstract
Climate change and human activities have caused a wide range of ecological risks in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau (QTP) over the past two decades, such as land degradation and biodiversity loss. Therefore, it is imperative to assess the ecological security and drivers for its sustainable development. However, there still lacks a spatial understanding of ecological security in the QTP, as well as the geographic driving forces. In this study, a pressure–state–response (PSR) framework and the coupled fuzzy and obstacle degree models were used to evaluate the spatial pattern and factors that modulate ecological security of the QTP. The southeast of the plateau exhibited high pressure and state levels, indicating that population and economic development activities were concentrated in these regions owing to the good natural conditions. The ecological security evaluation value of the QTP is moderately low, with a median value of 47.4 (the full mark is 100). Seven regions with low ecological security were identified where targeted planning and governance measures should be implemented based on the local natural and economic conditions. Population density, net primary productivity index (NPP) of vegetation, and GDP per unit area were the main factors that modulated ecological security in the QTP, with obstacles accounting for 17.52%, 13.20%, and 12.97%, respectively. These results improve our understanding of the major vulnerable areas and main driving forces of ecological security, providing key information for optimization of ecological security pattern in the QTP.
1. Introduction
Rapid development of the global economy and an increase in population exert a significant pressure on the national and regional ecological security, and the sustainable development in social–ecological systems [1]. Ecological security is widely explored globally as it provides a basis for sustainable development [2,3,4,5]. Ecological security refers to preservation of seminatural and natural ecosystems, including the health and integrity of ecosystems [6,7,8]. In 2006, the Chinese government announced the establishment of an international ecological security cooperation organization and began to evaluate ecological security to provide information for sustainable economic, environmental, and social development. In the most recent 20 years, different indicators and methods have explored for evaluation of regional ecological security. For example, Han et al. [9] established an evaluation system based on urban socioeconomic indicators and natural resources and environmental indicators, and evaluated the ecological security of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region. Ma et al. [7] evaluated the spatiotemporal changes in ecological security of the middle and lower reaches of the Shule River Basin based on the model of pressure–state–response (PSR). The PSR framework is widely utilized in the analysis of environmental issues such as evaluation of ecosystem services, land resource security [5], river basin health [10], and urban environmental capacity [11]. The PSR framework is used to evaluate the causal relationship between the factors related to human activities and the factors associated with natural resources and the environment. This approach has several advantage over single-factor evaluation, as it provides a systematic guide for construction of an index system to comprehensively evaluate ecological security [10]. Previous studies report integration of the PSR model to a fuzzy logic framework to evaluate the ecological security level and the main factors that affect urban agglomerations in the Pearl River Basin [12]. Fuzzy evaluation method provides a powerful measure by which to divide the values of continuous variables into several classes with clearly defined thresholds, due to its capacity to deal with fuzziness in threshold setting. However, it is still a challenge to map the ecological security based on limited spatial explicit indicators, and to determine the weights of the effects of each indicator on ecological security [13].
Ecological security is affected by geographical factors including environmental conditions, land use and cover changes, socioeconomic development, and level of local policy implementation [5,14,15,16]. Developed urban areas are characterized by high pressure caused by socioeconomic activities, leading to a low level of ecological security [5]. The top obstacles that affect the ecological security in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei area are landuse, economic density, transportation, warehousing, postal investment per unit land area, and per capita GDP [17]. However, the driving factors of ecological security are different in consideration of geographical heterogeneity. For example, the ecological security in Yunnan is mainly modulated by the natural environment, whereas poor economy and low level of urban development have less significant effects [18]. Fan et al. [19] used the obstacle degree model in Qinghai Province and found that the obstacle factors that affected ecological security between 2000 and 2017 shifted from the social response level to pressure from human activities. Therefore, it is imperative to explore the key factors that affect ecological security to lay a basis for formulating local policies and implementing measures based on the local conditions to promote sustainability. Obstacle degree model is widely used to measure the gap between the current state and the ideal security state. It has the advantage over traditional regression method, and shows good performance in analysing the internal factors of the system and their functions [11].
The Qinghai–Tibet Plateau (QTP) is in the southwest of China. The region is known as the “Asian water tower” [20]. The plateau plays an important role in providing several key ecosystem functions and services, including water and soil conservation, biodiversity protection, wind prevention and sand fixation, carbon sequestration, and climate regulation [21]. The region is an important ecological security barrier area in China and even in Asia, and plays an essential role in global biodiversity conservation [22]. However, the QTP is highly vulnerable. During the past decades, this region has suffered from multiple ecological risks and challenges caused by human activities and global warming, such as desertification, melting glaciers, and grassland degradation [23]. Global warming has significantly modulated the climate in the plateau [24]. Findings from the past 50 years of monitoring indicate a twofold increase in temperature in the region compared with the global average [25,26]. An increase in temperatures has causes several effects on the cryosphere of the QTP, including glacier retreat, snow cover reduction, lake expansion, permafrost degradation, and thickening of the active layer. In addition, increased temperatures have substantially impacted the water resources of the QTP [27], showing that the annual runoff has been increasing in the past 60 years [28]. Because global and regional climate changes currently exert high pressure on vulnerable ecosystems [29], it is important to explore the patterns and drivers of ecological security on the QTP. A spatial explicit evaluation of ecological security on the QTP is of great significance for decision-makers to identify key areas for ecological protection and restoration to enhance ecological security barrier.
Several studies have been conducted in the past to explore the ecological vulnerability in the QTP [30,31,32,33]. Analysis of the spatial–temporal distribution of the ecological vulnerability showed that areas with high ecological vulnerability were mainly distributed in the southwest border characterized by high altitude and low precipitation [34]. Evaluation showed a significant decrease in ecological vulnerability levels from the southeast to northwest of Tibet [35]. Lin et al. [36] evaluated the dynamic characteristics of ecosystem service flow and the findings showed that the Sanjiangyuan region has gradually become the shifting center of the ecological important belt of the QTP. Other studies have been conducted to explore the spatial and temporal pattern of ecological security in some sites, such as Lhaze County [37], Qinghai Lake Basin [31], and Qinghai Province [19]. However, a comprehensive evaluation of the ecological security of the whole area of the QTP has not been conducted. In addition, many previous studies focused on the administrative unit and failed to provide available information at finer scale, such as the grid scale of 1 km2. Evaluation of the ecological security and the obstacle factors at the grid scale has important theoretical and practical significance in formulating strategies for sustainable development of the QTP.
Accordingly, the aim of this study is to pursue an improved spatial understanding of the ecological security and its driving factors in the QTP. The objectives of this study were to (i) evaluate the spatial pattern of ecological security on the QTP by using the PSR and fuzzy mathematical models, and (ii) determine the factors that modulate the changes in ecological security. The results of this study will provide useful information to decision-makers to formulate strategies to improve the ecological security on the QTP, and to implement appropriate land-management measures to achieve sustainable development.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The QTP (26°00′N– 39°50′N, 73°27′E–104°40′E) (Figure 1) covers approximately 2.6 × 106 km2 and has an average altitude of more than 4000 m [38]. The QTP has multiple valuable ecosystem types and provides important ecosystem services (such as water conservation, carbon sequestration, biodiversity protection and climate regulation) for approximately 1.5 billion people [39,40]. In addition, it is an important ecological security barrier area in China [22]. The QTP is an early warning zone for the global environmental change, and the ecological system in the region is significantly affected by changes in climate and increase in human activities [41], which affect regional hydrological cycle characteristics, leading to glacial melting [42], changes in spatial patterns of water resources [43], and an increase in the risk of regional geological disasters [25]. Increases in human activities, such as grazing, have caused several ecological problems, including grassland degradation [44] and land desertification [45].

Figure 1.
A map of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.
2.2. Methods
An evaluation index system was constructed based on PSR model to evaluate the spatial pattern and the factors that affect the ecological security in the QTP (Figure 2). Data processing was conducted by using the fuzzy evaluation model to reduce the uncertainty of results caused by imprecision and fuzziness of concepts. Indicator weights were estimated by using entropy weighting approaches based on the intrinsic characteristics of data rather than subjective opinions from experts. The obstacle degree model was utilized to quantify factors that affect ecological security from the dimension level and index level, respectively. The spatial pattern of ecological security on the QTP and the driving forces were evaluated.
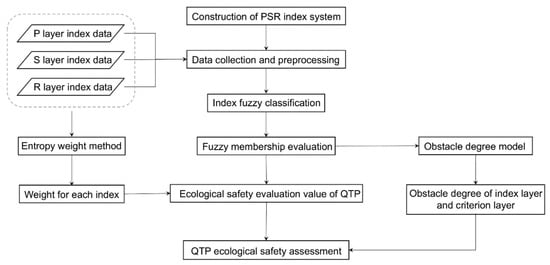
Figure 2.
A flowchart showing the PSR framework.
2.2.1. PSR Framework Construction
The PSR framework describes the relationship between man and nature by using a three-dimension evaluation. The pressure dimension represents the external pressure on the ecological environment caused by human activities and climate change [46]. The state dimension refers to the current conditions of the natural background state. The response dimension represents the human activities aimed at preventing and mitigating the negative effects of external pressure on the environment, including the intensity of relevant protection and governance measures implemented by people. In this study, a comprehensive evaluation index system for assessment of ecological security on the QTP was constructed based on the PSR framework.
A total of 17 indicators were selected for construction of the PSR framework based on previous literature, mainly spatial gridded dataset produced by remote sensed data (Table 1). Most of the indicators fall within the study period of 2015–2020, but two indicators (such as slope gradient and NPP) were not available due to the limitation of data availability and thus were replaced by nearby year data. The indicators comprised two levels as follows: (i) dimension, including pressure from nature, society and humans, the status of the ecosystem, and the responses of human society; and (ii) index, which refers to factors used to determine the justification criteria.

Table 1.
Evaluation index system and data sources for a comprehensive assessment of the ecological security in QTP.
The pressure dimension was used to evaluate the level of stress caused by socioeconomic development and environmental quality on ecosystems [5]. Annual precipitation and average temperature were selected due to their dominant role in modulating the regional production and lifestyle, water resources carrying capacity, and biological population community. Population density was selected to represent the pressure on ecosystems resulting from high demand of ecosystem products such as food, water, and fiber [5]. Chinese GDP (1480 dollars/km2) was selected to depict the pressure caused by economic development and commercial activities [47]. PM2.5 concentration was selected to indicate the pressure of environmental pollution on land ecosystems [5]. The original data of PM2.5 concentration comprised the monthly average with a one square kilometer resolution. The original data were then converted into the annual average value considering the effect of seasonal change on PM2.5 concentration. The safe threshold is PM2.5 < 10 μg/m3 as reported by the World Health Organization [48]. This threshold is stricter than the actual status in China. Therefore, a range of 0–10 μg/m3 was utilized as the lowest pressure interval in this study.
The state dimension refers to the current status of environment and resources (such as topography, vegetation, biology, soil, and land use), and environmental resilience to withstand the changes caused by the pressure [5]. A total of eight state indicators were evaluated. Topographic slope determines the suitability of land for cultivation and crop production as well as indicates the risk of soil erosion and water loss [34]. The level of topographic slope was classified based on the influence and limitation degree of land utilization according to the Soil and Water Conservation Law. Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) is an important index used to quantify vegetation coverage. NDVI is calculated from the infrared band (R) and near infrared band (IR) obtained from MODIS and other satellite remote sensing (NDVI = (IR − R)/(IR + R)). Net primary productivity of vegetation (NPP) represents the net carbon gain from the consumption of plants after respiration [49]. The NPP index is highly sensitive to ecosystem changes [50]. The content of soil organic matter is highly correlated with intensity of soil erosion and availability of regional land resources service function [5]. Data on soil organic matter were derived from the soil physical and chemical properties dataset reported by Shangguan et al. [51]. The SL190-96 industry standard of the People’s Republic of China, the Classification and Grading Standard of Soil Erosion report, indicates that soil erosion intensity is classified into three types and six levels of erosion intensities. Biodiversity data included spatial distribution data of mammalian richness and amphibian richness. Patch density is a landscape pattern index widely used to evaluate habitat fragmentation. Patch density is based on type of land use and is calculated by using Fragstats 4.2 software.
The response dimension indicates the degree of prevention, mitigation, and alleviation of stress through various human actions [5]. It mainly refers to the intensity of relevant protection and governance measures implemented by people [52]. Indicators with relatively complete statistical results were selected from the response layer to eliminate the effect of insufficient data samples. The type of natural reserves was used to indicate the response to environmental degradation which were grouped into different levels, namely national level, provincial level, municipal level, and county level. The tertiary industry (%) is an index used to determine the social health of industrial structure [19]. Tertiary industry activities have a lower demand for resources and exert less pressure on the environment compared with primary and secondary industries, and thus a high proportion of tertiary industry GDP indicates an increase in regional economic development quality. The rate of household garbage disposal (%) was determined by using data retrieved from the Statistical Survey System of Urban (county) and Village Construction formulated by the National Bureau of Statistics. The rate of household garbage disposal was presented as the proportion of treated domestic garbage relative to the total amount of domestic garbage. The green development index is a comprehensive evaluation index reported by the Ministry of Environmental Protection in China.
2.2.2. The Fuzzy Evaluation Model
The fuzzy evaluation model is a key approach of converting original data values to output evaluation scores (such as security level), by transforming the expert experience or practical cognition in natural language (linguistic variables) into a mathematical language expressed as fuzzy membership functions and fuzzy rules [5].
The fuzzy evaluation model was developed in four steps as presented below.
- (i)
- A Mamdani FIS model (Figure 3) was constructed for each indicator through the fuzzy inference system toolbox in MATLAB software (version R2018b). The core part of fuzzification of the input index was establishment of fuzzy membership functions and fuzzy rules, which determines whether an index value belongs to a label of the fuzzy set (Equation (1)),where A represents the subfuzzy set, x indicates the actual value of a single index, X represents the domain of a certain index, μA (x) represents the membership degree of an index on the sub-fuzzy set and has a value between [0,1].
 Figure 3. A schematic diagram of fuzzy reasoning system framework. The fuzzy evaluation method maps uses original data as input and produces evaluation scores as output through fuzzy membership functions, inference rules, and the defuzzification method [5].
Figure 3. A schematic diagram of fuzzy reasoning system framework. The fuzzy evaluation method maps uses original data as input and produces evaluation scores as output through fuzzy membership functions, inference rules, and the defuzzification method [5].
The index domain was divided into five categories to distinguish the intervals of values for each index (Table 2). The intervals were grouped according to standards, government policies and regulations, and findings from previous studies [5]. The equivalent interval was used for intervals with no recognized classification standard reference. This method enables maximum similarity of elements in the same group but maximum differences among various groups.

Table 2.
Scale classification and weight of ecological safety assessment indicators.
- (ii)
- The fuzzy evaluation scores for each indicator were calculated by using a linear trigonometric function. The median value of the interval was the vertex of the triangle with a membership degree of 1.0, and the membership degree of the value at the intersection of the two intervals was set as 0.5. A defuzzification program was used to convert fuzzy membership degrees into fuzzy evaluation scores.
- (iii)
- With regard to the determination of weights, the dimensionality and magnitude of the original data were significantly different. Data were preprocessed and normalized to eliminate this influence. Different indicators have different positive and negative tendency toward the index layer, and thus they were treated separately. We havewhere represents the original value of the raster I on the index layer j, , and represent the maximum and minimum value in the grid of index layer j. The standardized values were used to calculate the information entropy of the index and determine the final weight wj,where represents the weight of the grid i under the index layer j. A new function rule was defined as follows: When = 0, it was specified = 0. Please refer to Table 2 for detailed calculation results.
The weighted sum model was used to aggregate the fuzzy scores of indicators to determine the comprehensive evaluation score for each dimension,
where, represent the comprehensive evaluation scores of the pressure, state, and response dimensions, respectively, represent the weights of each index layer j, which was calculated using Equation (6), and indicate the fuzzy evaluation score of grid i on the index layer j. This calculation was conducted by using the raster computing tool in ArcGIS.
- (iv)
- The comprehensive evaluation score of ecological security was determined based on the multiplication principle [5]:
The ecological safety score indicates the comprehensive evaluation score; S, R and P represent the evaluation score of state, response and pressure dimension, respectively.
2.2.3. Determinations of Obstacle Factors of Ecological Security
The obstacle degree model can be used to measure the gap between the current state and the ideal security state. This model is utilized to determine the influence degree of driving factors on an overall index, and to identify the main obstacles to ecological security [5]. In this study, the obstacle degree model was utilized to explore the obstacle factors affecting the criterion layer (pressure, state and response level, Equation (11)) and the target layer (ecological security, Equation (12)) of the ecological security on the QTP as shown below,
where, represents the fuzzy evaluation score after a minimum–maximum normalization of grid i and criterion layer j, indicates the deviation degree of index j in grid i, that is, the gap between the current state of index j and the ideal target 100%, denotes the factor contribution degree, which represents the degree of influence of factors on the overall evaluation objective (i.e., weight), represents the degree of obstacle of grid i, criterion j, which depicts the contribution rate of criterion j to the overall obstacle, and n represents the number of indicators under a criterion layer.
By using the criterion state layer as an example, the equation for calculating the obstacle value to ecological security is shown below,
where represents the obstacle degree of the indicator i in criterion state layer on ecological security. The obstacle values for the other two criterion pressure () and response () layers can be calculated similarly by using Equation (13). The obstacle degree of the region was expressed as the mean value of the raster data with the city as the unit. The obstacle types were grouped according to the obstacle ratio of the three criterion layers of PSR to determine the obstacle types of different urban areas and used for decision-making (Figure 4).
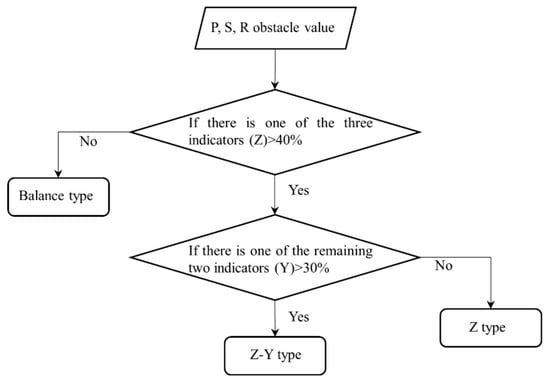
Figure 4.
Rules for determination of obstacle type.
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Spatial Pattern on PSR
The socioeconomic pressure on ecological security was highest in the east, southeast, and northwest regions of the QTP (Figure 5a). The pressure was lowest in Nyingchi Prefecture of the southern plateau and was moderate in the central and western hinterland of Tibet (Figure 5a). The pressure layer was largest in the southwest of Xinjiang that comprises the northern foot of Kunlun Mountain, where glacial meltwater flows into Tarim Basin to form a piedmont impact oasis. The glacial meltwater from the mountains forms an oasis of the piedmont water impingement. The piedmont plain has several crop production activities, and is favorable for social and economic development. The pressure from human activities in the central and southern region of QTP is high, mainly because Lhasa, the capital of Tibet Province, is in this region. In addition, the area is surrounded by relatively populated cities and towns; thus, the population pressure is relatively high.

Figure 5.
Spatial pattern of (a) pressure, (b) state, and (c) response scores in the QTP.
The spatial pattern of the status level was mainly modulated by the local geographic conditions, with the highest scores observed in Nyingchi Prefecture and the southern part of Shannan. The spatial pattern of the overall status scores gradually decreased from the southeast region to the northwest region (Figure 5b), which coincides with the change in elevation of the QTP. The eastern region has a typical mountain topography, and the region receives warm and moist water vapor from the Indian Ocean due to the longitudinal distribution of mountain ranges, resulting in hydrothermal conditions in the region. The terrain is flat with fertile soil and abundant water supply from the river, making it suitable for agricultural activities. The overall state scores were lower in the plateau hinterland and western area, which is mainly attributable to the poor native natural conditions. The region has an average altitude of 4500 m above sea level, resulting in low air oxygen content and high solar radiation.
The level of the response dimension was higher in the southern Xinjiang, Gansu, and northeastern Qinghai regions, and relatively low in Tibet (Figure 5c). The grassland ecosystem is the most important type of ecosystem in the QTP, and is mainly located in the central and western part of the plateau and carries the regional agriculture and animal husbandry production. In recent years, an increase in agricultural activities has caused a significant grass-livestock imbalance, resulting in a low level of response in these areas. A few areas in the counties of Xizang Province have high response values in terms of spatial distribution. Most of these regions are prefecture-level cities, such as Rikaze, Lhasa, Shannan, Nyingchi, and Changdu, which form population clusters in the region. Baiyu County, Litang County, and Rangtang County in Sichuan Province had the weakest response level compared with other regions on the QTP. The low response values were attributed to the unadvanced construction of urban environmental infrastructure. Development of basic ecological and livelihood activities has not reached the average level in these regions. Although these counties have a high level of ecosystem services [53], the favorable natural environment should be protected from factors that affect the ecological security.
3.2. Overall Spatial Pattern of Ecological Security
The overall ecological security of the QTP was highest in Nyingchi Prefecture in the southern part of the plateau and in the southern part of Shannan region (Figure 6a). The Qinghai Lake in the western part of Xining City, Zhangye City, and Jiuquan in the southern part of the northeastern edge of the Plateau, and areas bordering Xinjiang, Qinghai, and Xizang provinces exhibited relatively high levels of ecological security. The highest ecological security levels were mainly observed in areas with natural reserves and regions under strict supervision. The level of ecological security was lowest in the northern part of Kunlun Mountain followed by the Huangshui Valley. The Qaidam District located in the desert area was characterized by harsh conditions and exhibited a low level of ecological security. Other areas with a low ecological security level included areas with a more concentrated plateau population and clustered towns.
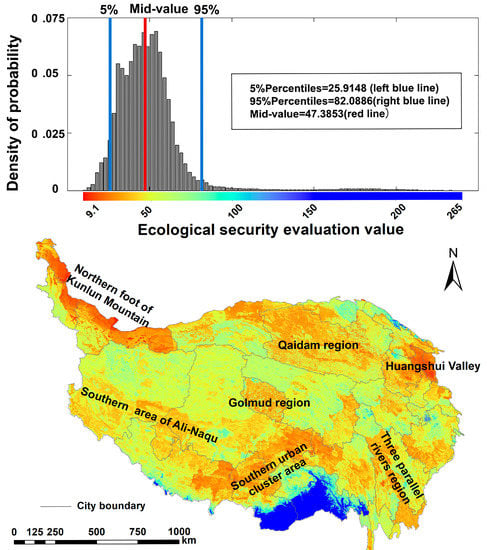
Figure 6.
Spatial pattern and values of the ecological security in the QTP.
The classification standard of fuzzy output membership function showed that median ecological security level of the QTP was 47.4 (Figure 6b). This was the value for the III level area, implying that the overall ecological security level was low. The ecological security level of the entire region ranged between 25.9 and 82.1 (Figure 6b), indicating a wide range of evaluation values. The results showed that seven regions had low ecological security, including the southern edge area of Ngari–Nagqu, Golmud City, Huangshui Valley, Qaidam District, the northern foot of Kunlun Mountain, and Sanjiang River Basin.
3.3. Spatial Pattern of Obstacle Factors
The transition zone of the eastern edge of the QTP (Figure 7a) and the central urban agglomeration of Tibet had a relatively large pressure dimension obstacle degree, owing to the relatively dense population activities and high intensity of crop production activities and habitation. The areas where the pressure dimension was the main obstacle included the area around the “three rivers” (Yarlung Zangbo River, Nianchu River, and Lhasa River) around Lhasa, the Huangshui Valley at Xining, and the confluence area of the “three rivers” (Jinsha River, Lantsang River, and Salween River) in Yunnan. This distribution is correlated with the population density distribution, indicating that approximately 95% of the population reside in the southeastern region. The overall pressure obstacle degree in the southwest part, especially in Ngari area, Nagqu prefecture area, and southern Xinjiang, was less than 40%. These results indicate that population and environmental pressure were not the main obstacles to regional ecological security in the northwest part of the QTP.
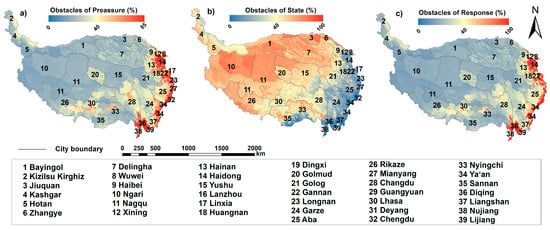
Figure 7.
Spatial pattern of the three different types of obstacle degree in the QTP, including (a) the pressure layer barrier degree; (b) the state layer barrier degree; and (c) the response layer barrier degree on QTP.
The obstacle degree of the state layer in causing low ecological security level decreased from west to east. The Ngari prefecture of Tibet, Nagqu prefecture of Tibet, Bayingol prefecture of Xinjiang, Jiuquan prefecture of Gansu Province, and western Yushu exhibited the highest obstacle degree of state layer (Figure 7b). The region has poor background natural conditions. It is found in the hinterland of the plateau and is characterized by high altitude. The region cannot receive warm and wet air from the ocean and is mainly an arid zone. Vegetation coverage in the region is relatively low, with 18.6% vegetation cover in Ngari area. High risk of soil erosion, water loss, and land degradation affect the level of regional state security. Areas with high state obstacle value are subjected to soil erosion by exogenic forces, resulting in a high risk of land stress. The northern Tibetan Plateau undergoes intense freeze–thawing erosion throughout the year. Surface soil and even rock layers are subjected to friction and movement through the dual action of gravity and freeze–thawing, which increases the risk of geological disasters at the local area. The northern part of the plateau is characterized by a high level of wind erosion. Qaidam Basin is mainly affected by erosion. The Qaidam Basin experiences soil erosion as well as high water loss and a high rate of transpiration. The region is characterized by sandy soil with high salinity. Most of the lakes in the region are saltwater lakes. The state layer is the main factor modulating ecological security due to these relatively harsh ecological conditions.
The response level obstacle reflects the effect of human activities on the ecological environment and whether the intensity level of targeted measures, such as active protection, restoration and construction, can alleviate an increase in ecological security. A high response obstacle degree indicates that the ecological measures implemented in the region had no significant effect, indicating an imbalanced state. The results showed that high response obstacle degrees were concentrated in Nyingchi prefecture and southern Shannan prefecture of the Tibet, and Golog prefecture, Garze prefecture, and Aba prefecture of Sichuan (Figure 7c). This finding indicates that these regions may not have effective ecological and environmental protection measures. Another possible explanation is that the pressure exerted by the pressure layer did not exert significant effects in the regions with a relatively good natural environment. As a result, policy makers did not implement extremely high standards of ecology protection in the region.
The classification of the obstacle degree of the three dimensions resulted in six types of obstacles (Figure 8 and Table 3). (1) The balanced type was mainly distributed around the three rivers (Jinsha River, Lantsang River, and Salween River) on the eastern margin, which accounted for 18.24% of the total area and comprised approximately 20.08% of the total population on the plateau. (2) The pressure-dominated obstacle type indicated that the regional ecological security was mainly affected by excessive external interference factors, such as climate change and human activities. The pressure-dominated obstacle type was mainly distributed in developed areas and the eastern edge of the plateau. The area with the pressure dominated obstacle type only accounted for 3.15% of the plateau, but it comprised approximately 34.95% of the entire population in the plateau. (3) The state-dominated obstacle type was mainly distributed in the western parts of the plateau, which accounted 59.94% of the entire area, and comprised 17.04% of the plateau population. The region comprised large areas of no man’s land or sparse population and natural reserves. The northwest part of the plateau is a high-altitude area with low temperatures and large area of alpine meadows and frozen soil, which are favored by agriculture and animal husbandry development. The unfavorable natural conditions lower the ecological security of the region making the area an ecologically sensitive region. The effect of grazing and livestock production on ecological security has been widely explored in the recent past. (4) The joint pressure–state-dominated obstacle type was distributed in the natural condition and the economic development level was the second gradient level in the plateau. This obstacle type was mainly observed in the Lhasa region in Tibet, Golmud City in Qinghai Province, and Lanzhou in Gansu Province. The fragility and imbalance of the region’s natural ecosystem should be evaluated more strictly compared with the pressure dominated type cities. (5) The pressure–response-dominated obstacle type was mainly observed in Sichuan and Yunnan areas, accounting for 4.38% of the regional area and the region comprised 12.18% of the total population. The obstacles in these areas were mainly caused by the pressure of social and economic development and the lack of social response measures. (6) The joint response–state-dominated obstacle type was mainly observed in the Hotan (Xinjiang) and Nyingchi (Tibet) regions. The socioeconomic development in these regions was negatively affected by unfavorable natural conditions. The areas have the lowest population in plateau, about 4.55%.
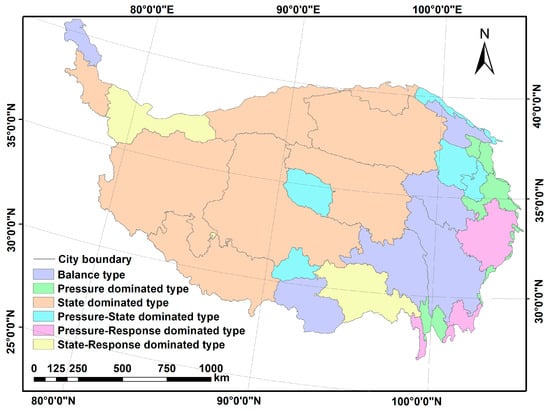
Figure 8.
Spatial pattern of the six major types of obstacles to ecological security in the QTP.

Table 3.
Criterion layer obstacle degree of prefecture-level city in the QTP.
3.4. Relative Importance of Obstacle Indicators
The percentage of the obstacle degree of 17 indicators was calculated by using the obstacle calculation method of the indicator layer. The top five major obstacle factors for each province and city were selected to determine the main contradictions (Figure 9). The population density (P3) index had the highest average obstacle degree in the whole region, contributing 17.52%. The population density (P3) was used as the highest obstacle index in 20 out of the 39 cities. This indicates that human activities significantly affect ecological security under the current level of social development. The NPP (S3) of vegetation net primary productivity, with an average obstacle degree of 13.20%, was among the top five factors. NPP represents regional metabolic activity and carbon sequestration level, and is used to indicate the level of vegetation cover. NPP is a major obstacle factor, which indicates the role of the ecosystem type of the region in modulating ecological security. The GDP per unit area (P4) exhibited a high obstacle degree, with an average obstacle degree of 12.97%. Per capita GDP and population density indicators complement each other. The most important obstacle degree in the most developed areas in the eastern part of the plateau were correlated with population and economic factors.
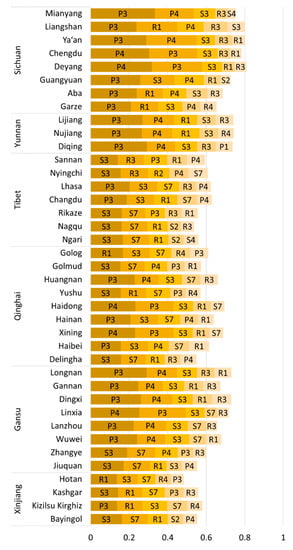
Figure 9.
Top five obstacle factors of prefecture-level cities.
Natural reserves were among the top five obstacle indicators in 30 out of the 39 regions. The global average obstacle degree value was 10.04%, which was the fourth-highest obstacle index. Notably, natural reserves can effectively limit the effect of the human activities on the natural ecosystem, maintain good environment of a region, and provide a good habitat for organisms. The construction of ecological security barrier in the QTP has promoted establishment of a complete nature reserve system [54]. Currently, natural reserves in the region accounts for 31.63% of the whole plateau. The effect of this index on the ecological security is significant on areas without natural reserves, such as the Kashgar region in Xinjiang, Ngari and Nagqu regions in Tibet, the Golog and Yushu regions in Qinghai, and the Aba and Garze regions in Sichuan.
4. Discussion
4.1. The PSR on the QTP
The pattern of pressure distribution reflects the living characteristics of residents. This implies that population density has a strong spatial coupling relationship with river basins and main traffic systems [55]. For instance, river valley zones of Yarlung Zangbo River Basin exhibited a relatively low altitude and warm climate suitable for human habitation. Therefore, these regions are conducive to economic development, resulting in a relatively dense population and urban distribution, and ultimately high external pressure level. The area surrounding Lancang River in the southeast of the plateau exhibits similar characteristics. The pressure level was high in the Golmud region, a city in the central of Tibet region that is the economic center of Haixi Prefecture and is the hub for the passage of the railway into Tibet. These findings indicate overlapping of high-pressure area and prefecture-level cities. The results indicate a decrease in divergence from the urban center outward.
The state level was higher in the southeast and lower in the northwest regions of the QTP. Xia et al. [34] conducted an integrated analysis of the characteristics of natural elements (land resources, hydrological conditions, topography, etc.) to evaluate the ecosystem vulnerability of the QTP. The findings showed that the level of ecosystem vulnerability was consistent with the state level reported in the current study, which reflects the natural environmental conditions. Findings from spatial pattern of the ecological vulnerability reported by Xia et al. [34] showed low ecosystem vulnerability in the southeast region whereas high-value areas were located in the northwest. The northern part of the QTP, mainly the Qaidam Basin, had the lowest safety assessment value of the state dimension. Jia et al. [56] conducted a study using an improved remote sensing ecological index (MRSEI) and observed that the Qaidam Basin had a low ecological environment quality of only 0.191, which is consistent with the current findings. The Qaidam Basin has an arid and semiarid climate and closed terrain in which the ocean water cannot flow freely, leading to low precipitation and soil moisture, long periods of sunshine, and high annual evaporation, which indicates low ecological security [57].
The northern parts of the QTP (including southern Xinjiang) had a higher response level, which is consistent with findings reported by Cheng et al. [5]. The high response level is attributed to the high-quality agricultural areas characterized by advanced facilities for irrigation, and the central government is involved in construction of infrastructure and education. Evaluation of temporal and spatial changes of ecological vulnerability in Tibet by Jiang et al. [35] showed that the enhanced response ability of government and improved societal awareness of increased urbanization induced a gradual change of the Lhasa, Nyingchi, and Changdu regions from a moderate ecological fragile zone to a nonecological fragile zone [35]. Land use significantly modulates the spatial pattern of ecological security [5]. The urban response level was higher compared with the level of mountainous areas and pastoral areas mainly because environmental protection infrastructure and construction measures are implemented in cities and towns. The high level of education and scientific research in cities and towns has resulted in a development of environmental protection strategies through continuous improvement of residents’ education quality and awareness of ecological and environmental protection. The northern Tibet area had a lower response level due to the relatively poor economic conditions, resulting in fewer investment initiatives for agricultural infrastructure, science, and education [5].
4.2. Ecological Security on the QTP
The results showed that the QTP had low security scores, with a median value of 47.4 (Figure 6), indicating a relatively low ecological security. This is consistent with the findings reported by Cheng et al. [5]. However, the present results were different from findings by Zhang and Xu [14], who reported that the region can be classified as safe and basically safe regions. This difference was observed mainly because poor social response was included in analysis in addition to the natural environmental conditions. The spatial pattern of the ecological security in the QTP was evaluated in the present study. The regions with high risk potential and low ecological security scores in the current study were consistent with those reported in a previous study conducted to evaluate the spatial patterns of ecological risks in Tibet and Qinghai provinces [58]. Haixi, Haidong, and Lhasa were reported as high-risk areas across the plateau [58]. The level of ecological security in the QTP was correlated with the environmental and socioeconomic conditions [14]. The observed low ecological security in the Qaidam basin was mainly attributed to the harsh environmental conditions. The Qiji Line (Qilian County in Qinghai Province and Jilong County in Tibet Province) divides the plateau into two parts based on population density [59]. The ecological security for the two sides of the Qiji Line was significantly different. The east of Qiji Line exhibited better natural environmental conditions, infrastructure and economic development than the west, corresponding to a higher state level and response level. The pressure in areas with high population density and intense human activities (such as farming) was markedly higher than the rural areas.
A significant spatial heterogeneity in the ecological security was observed across the plateau. Therefore, the relevant department involved in ecological conservation should consider the local conditions and regional differences when formulating and implementing planning and governance measures. In this study, seven regions with low ecological security were identified as follows. (1) The northern foot of Kunlun Mountain, has several oases formed by the alpine meltwater rivers. The pressure exerted by the population and socioeconomic activities in the region significantly reduces water resources. The oasis water resources can be used as the core of ecological protection and reconstruct the regional water conservation function through afforestation convert farmland to grassland, and maintain the marginal zone to prevent land degradation and desertification. The relevant authorities should advocate for activities that save available water and practice water-saving agriculture to maximize efficiency utilization of resources. (2) The southern edge of Ngari–Nagqu has a low population density and relatively harsh natural environmental conditions. People’s living habits in these areas are more primitive with low management level compared with developed cities, and the regions are characterized by poor environmental protection measures. Golmud is a pressure–state–barrier area, with significant external pressure and high natural state level. Mining is a major industrial activity in the region. Measures such as timely treatment of wastes, land reclamation, and ecological restoration should be conducted on the abandoned mines. (3) Qaidam Basin is a large mountainous basin in the northern part of QTP [60]. The region is characterized by scarce water resources, and ecological problems, such as land desertification and soil erosion. Authorities should implement desertification control initiatives and conduct vegetation restoration projects in Qaidam Basin. The production by industries and agricultural activities in the region can only meet local demand due to the low GDP of the region. The high population pressure and high pressure on agriculture and animal husbandry in this region [57] negatively affects the environment the environment [56]. Moreover, agricultural industry can be improved by planting more cash crops [61], such as medlar, bitter rose, and quinoa. The geological features adjacent to the desert and the unique inland salt lakes and oases should be utilized to promote tourism industry in the region. (4) Huangshui Valley is a region bordering the QTP and the Loess Plateau. Xining, the capital of Qinghai Province, is located in this region. The region is characterized by rapid urbanization. The urbanization rate increased from 56.6% to 72.9% between 2000 and 2019. Ecological destruction and water pollution have significantly affected the region. Xining is a tourist city and the tertiary industry GDP accounts for about 66% of the GDP of the city. The city is characterized by urban development, ecological civilization and ecotourism. (5) The Sanjiang River Basin in eastern Tibet comprises three major rivers including Jinsha River, Lancang River, and Nujiang River. The eco-environment of the river source is related to results in high the eco-environmental quality of the cities downstream of the river cities. The results showed the state dimension did not markedly affect the ecological security in this region. Pressure and response dimensions had significant effects on the regional ecological security. Soil erosion was a major factor that affected the ecological system in this region. Soil erosion was mainly caused by overexploitation of land for agriculture and destruction of forests, resulting in a reduction of regional forest area and increased geological disasters. (6) The southern urban agglomeration of Tibet, with Lhasa as the center and the surrounding cities as the auxiliary, is a region with poor ecological security compared with other regions in the QTP. The areas with low ecological security are mainly distributed along the main stream of the Yarlung Zangbo River, the valley plain of Lhasa River and Nianchu River and the upper reaches of Nujiang River and Lancang River. The trend of the ecological security is consistent with the population density pattern in Tibet [55].
4.3. Major Obstacle Factors of Ecological Security on the QTP
The potential obstacles to ecological security play important roles during formulation of targeted land use management policies to enhance ecological security while maintaining sustainable social and economic development [11]. Six types of ecological security obstacles were identified in this study (Figure 8). It is imperative to effectively control the population in pressure-dominated areas and transfer industries to the surrounding low-pressure areas [5]. The high pressure can be alleviated through these initiatives and the response level in the surrounding areas can be improved through increased social and economic development. Financial and policy support should be increased in the response-dominated area to improve infrastructure and increase funding on science and education. Ecological conservation and restoration projects should be implemented the state-dominated area to protect vulnerable ecosystems, conserve soil and water, and alleviate desertification [45]. A key strategy for the joint pressure–state-dominated area should be protection of farmland by land leveling and consolidation of scattered and fragmented land [5]. Measures for improving infrastructure (such as transportation) and water conservation should be implemented in the joint state–response-dominated area and more funding provided to enhance science and education in the region.
The obstacle degree of state layer covered the largest area, and NPP index was the most important obstacle factor in this study area. Xia et al. [34] reported that low vegetation coverage in the northwest region of the QTP was correlated with low state values and high ecological vulnerability consistent with the present findings. The poor natural conditions affect survival of animals and plant; thus, they are important factors that affect the regional ecological security. Population density and GDP were the major obstacles in the eastern region, with population density modulating ecological security in 20 regions. High population density and relatively high economic development in these regions exerted high pressure on ecological security.
4.4. Implications
Based on the PSR framework, we considered the comprehensive relationship between society and nature to evaluate the ecological security [5]. The potential obstacles to ecological security on the QTP were determined. Our research avoided the shortcomings of traditional hard classification and grading [5], but adopted the fuzzy mathematics methods. The fuzziness of threshold setting for continuous variables, the fuzziness of people’s subjective judgment and uncertainty caused by the subjective selection of index were considered in the analysis [13]. The fuzzy membership function was used to calculate the attribution ratio of the status quo in different ecological security grades, and avoids single qualitative delineation [12]. The weighed sum method was used to avoid the uncertainty resulting from simultaneous use of multiple fuzzy rules [12]. The multiplication principle with more synergistic effect was adopted to determine the evaluation score for the ecological security across the QTP [5,62]. Although the PSR framework and the coupled fuzzy evaluation and obstacle degree models were found to be a useful tool for assessing the spatial pattern and driving forces of ecological security on the QTP, further improvement is needed to conduct model validation and uncertainty analysis. A range of landscape pressure and state indicators, such as land use change and net primary productivity, could be used for validation of ecological security modelling. In addition, temporal analysis could be conducted in the future to capture how ecological security varies with time, which could provide additional evidence and guidance for land management.
5. Conclusions
In this study, the ecological security on the QTP was assessed based on the PSR framework and the fuzzy evaluation method by using remote sensing-oriented spatial datasets. Areas with high-pressure values were primarily located on the main river valleys and the alluvial oases adjacent to the glacier–meltwater mountains. These areas were characterized by high population density and intense crop production activities. The state scores decreased from the southeast to the northwest region of the plateau, showing a similar spatial pattern to topographic features. The response levels were high in Xinjiang and northern Qinghai, whereas the low response levels were observed in Tibet, Yunnan, and Sichuan. The urban areas had relatively higher response levels than the surrounding regions. The differences in the response level among different regions were mainly attributed to the intensity of regional ecological and environmental protection measures. The northern parts of the study area exhibited low pressure and state levels but high response level, caused by the high-quality agricultural development owing to advanced irrigation facilities, and funding from the local government to improve infrastructure and education.
The QTP exhibited low ecological security scores. The region had a median value of 47.4, indicating a relatively low ecological security. Seven regions with low ecological security were identified in this study. Targeted planning and governance measures should be implemented in these regions according to the local natural conditions. The areas with high obstacle degree of pressure dimension and response dimension were mainly concentrated in the eastern edge of the QTP. The population in these areas accounted for approximately 35% of the population of the QTP. Effective strategies should be formulated to balance the relationship between population distribution, social and economic development, and ecological security in this region. The obstacle degree of state layer was associated with low ecological security level and the findings showed that it decreased from the western part to the eastern part of the plateau. Six types of obstacles, including the balanced type, the pressure dominated type, the state dominated type, the joint pressure–state-dominated type, the pressure–response-dominated type, and the joint response–state-dominated type, were identified based on the classification of the obstacle degree of the three dimensions. Population density, GDP per unit area, and NPP of vegetation, were the main factors that reduced ecological security in the QTP, with the contribution of 17.52%, 12.97%, and 13.20%, respectively. The findings from this study provide information on the spatial understanding of ecological security and its driving forces in the QTP and has methodological generalizability for the spatial evaluations in other regions in the world.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.L. and C.L.; methodology, T.L. and W.Z.; software, T.L. and C.L.; validation, T.L. and C.L.; formal analysis, T.L.; writing—original draft preparation, T.L. and C.L.; writing—review and editing, C.L., W.Z. and Y.L.; visualization, T.L.; supervision, C.L.; funding acquisition, C.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was jointly funded by the China’s Second Scientific Research Project on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau (grant 2019QZKK0405) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China Project (grant 42007052), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Steffen, W.; Richardson, K.; Rockström, J.; Cornell, S.E.; Fetzer, I.; Bennett, E.M.; Biggs, R.; Carpenter, S.R.; De Vries, W.; De Wit, C.A. Planetary boundaries: Guiding human development on a changing planet. Science 2015, 347, 1259855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Li, W.; Xu, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, C.; Wang, W. Global trends and characteristics of ecological security research in the early 21st century: A literature review and bibliometric analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirgaliev, N.A.; Askarova, M.; Opp, C.; Medeu, A.; Kulbekova, R.; Medeu, A.R. Water quality problems analysis and assessment of the ecological security level of the Transboundary Ural-Caspian Basin of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkhipova, N.; Kozhukhova, V. Environmental performance index as an assessment method of the country’s ecological security. In Economic Systems in the New Era: Stable Systems in an Unstable World; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Zhu, L.; Meng, J. Fuzzy evaluation of the ecological security of land resources in mainland China based on the Pressure-State-Response framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Hou, K. Research on the progress of regional ecological security evaluation and optimization of its common limitations. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Bo, J.; Li, X.; Fang, F.; Cheng, W. Identifying key landscape pattern indices influencing the ecological security of inland river basin: The middle and lower reaches of Shule River Basin as an example. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Li, Z.; Yuan, M.; Fan, C.; Xia, B. Spatial differentiation of ecological security and differentiated management of ecological conservation in the Pearl River Delta, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Liu, H.; Wang, R. Urban ecological security assessment for cities in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei metropolitan region based on fuzzy and entropy methods. Ecol. Model. 2015, 318, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazbavi, Z.; Sadeghi, S.H.; Gholamalifard, M.; Davudirad, A.A. Watershed health assessment using the pressure–state–response (PSR) framework. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhu, L. Evaluation of resources and environmental carrying capacity of 36 large cities in China based on a support-pressure coupling mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 838–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Gao, P.; Xia, B. A Mamdani fuzzy inference approach for assessing ecological security in the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, M.; Hu, Z.; Brinkman, R.; Sun, S.; Sun, X.; Schaffelke, B. Ecosystem health report cards: An overview of frameworks and analytical methodologies. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 105834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, E. An evaluation of the ecological and environmental security on China’s terrestrial ecosystems. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global change and the ecology of cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-T.; Yuan, M.-J.; Hu, M.-M.; Wang, Y.-F.; Xia, B.-C. Evaluation of ecological security and influencing factors analysis based on robustness analysis and the BP-DEMALTE model: A case study of the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Wang, D.; Zhong, X.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, L. Spatiotemporal changes of land ecological security and its obstacle indicators diagnosis in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region. Land 2021, 10, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Z.-r.; Zhu, Q.-k.; Sun, Y.-y. Regional ecological security and diagnosis of obstacle factors in underdeveloped regions: A case study in Yunnan Province, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2017, 14, 870–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Fang, C. Evolution process and obstacle factors of ecological security in western China, a case study of Qinghai province. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Wu, F.; Ding, L.; Sun, J.; Zhu, L.; Piao, S.; Deng, T.; Ni, X.; Zheng, H.; Ouyang, H. Multispherical interactions and their effects on the Tibetan Plateau’s earth system: A review of the recent researches. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2015, 2, 468–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zou, C.; Xu, D.; Lin, N.; Wang, L.; Zhang, K. China’s ecological conservation redline: A solution for future nature conservation. Ambio 2020, 49, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FU, B.; OUYANG, Z.; SHI, P.; FAN, J.; WANG, X.; ZHENG, H.; ZHAO, W.; WU, F. Current Condition and Protection Strategies of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Ecological Security Barrier. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 36, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.; Shang, Z.; Gao, J.; Boone, R.B. Enhancing sustainability of grassland ecosystems through ecological restoration and grazing management in an era of climate change on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 287, 106684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasunari, T.; Niles, D.; Taniguchi, M.; Chen, D. Asia: Proving ground for global sustainability. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T. Tackling on environmental changes in Tibetan Plateau with focus on water, ecosystem and adaptation. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Cai, Z.; Pepin, N.; Chen, D.; Ahrens, B.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, F.; Kang, S.; Zhang, R.; Wu, T. Warming amplification over the Arctic Pole and Third Pole: Trends, mechanisms and consequences. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 217, 103625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Xue, Y.; Chen, D.; Chen, F.; Thompson, L.; Cui, P.; Koike, T.; Lau, W.K.-M.; Lettenmaier, D.; Mosbrugger, V. Recent third pole’s rapid warming accompanies cryospheric melt and water cycle intensification and interactions between monsoon and environment: Multidisciplinary approach with observations, modeling, and analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Jin, J.; Ma, T.; Wang, G.; Liu, H.; Min, X.; Wang, H.; Lin, J.; Bao, Z.; et al. Evolution and Trend Analysis of Water Resources in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2019, 34, 1264–1273. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. The effect of urbanization on environmental pollution in rapidly developing urban agglomerations. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-h.; Zheng, J.-w.; Wang, Z.-r.; Li, R.; Wu, T.-h. A bibliometric review of ecological research on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, 1990–2019. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 64, 101337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Long, H.; Li, X.; Yu, F. Evaluation of changes in ecological security in China’s Qinghai Lake Basin from 2000 to 2013 and the relationship to land use and climate change. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Shen, J.; Zhang, Y. Ecological vulnerability assessment for ecological conservation and environmental management. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Dong, J. Scenario-based ecological security patterns to indicate landscape sustainability: A case study on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2175–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Jia, K.; Zhao, W.; Liu, S.; Wei, X.; Wang, B. Spatio-temporal changes of ecological vulnerability across the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 123, 107274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Shi, B.; Su, G.; Lu, Y.; Li, Q.; Meng, J.; Ding, Y.; Song, S.; Dai, L. Spatiotemporal analysis of ecological vulnerability in the Tibet Autonomous Region based on a pressure-state-response-management framework. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.-y.; Xiao, Y.; Ouyang, Z.-y. Assessment of ecological importance of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau based on ecosystem service flows. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 1725–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-Z.; Zou, X.-Y.; Cheng, H.; Jia, H.-K.; Wu, Y.-Q.; Wang, G.-Y.; Zhang, C.-L.; Gao, S.-Y. Assessing the ecological security of the Tibetan plateau: Methodology and a case study for Lhaze County. J. Environ. Manag. 2006, 80, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, S.; Li, S. Spatial pattern of non-stationarity and scale-dependent relationships between NDVI and climatic factors—A case study in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 20, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Milne, R.I.; Cadotte, M.W.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Provan, J.; Zhu, G.-F.; Gao, L.-M.; Li, D.-Z. Protect Third Pole’s fragile ecosystem. Science 2018, 362, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Lutz, A.; Andrade, M.; Bahl, A.; Biemans, H.; Bolch, T.; Hyde, S.; Brumby, S.; Davies, B.; Elmore, A. Importance and vulnerability of the world’s water towers. Nature 2020, 577, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; You, Q.; Wu, F.; Pepin, N.; Kang, S. Surface mean temperature from the observational stations and multiple reanalyses over the Tibetan Plateau. Climate Dynamics 2020, 55, 2405–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Thompson, L.; Yang, W.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Duan, K.; Zhao, H.; Xu, B. Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Bolch, T.; Chen, D.; Gao, J.; Immerzeel, W.; Piao, S.; Su, F.; Thompson, L.; Wada, Y.; Wang, L. The imbalance of the Asian water tower. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lv, W.; Xue, K.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Hu, R.; Zeng, H.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L. Grassland changes and adaptive management on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 668–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Stringer, L.C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, W. Drivers and impacts of changes in China’s drylands. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 858–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Hu, F. Analysis of ecological carrying capacity using a fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, Q.; Tong, X.; Chen, L. Evaluating land ecological security and examining its relationships with driving factors using GIS and generalized additive model. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pai, S.J.; Carter, T.S.; Heald, C.L.; Kroll, J.H. Updated World Health Organization Air Quality Guidelines Highlight the Importance of Non-anthropogenic PM2. 5. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, D.A.; Brown, S.; Kicklighter, D.W.; Chambers, J.Q.; Thomlinson, J.R.; Ni, J. Measuring net primary production in forests: Concepts and field methods. Ecol. Appl. 2001, 11, 356–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, A.K.; Carroll, C.J.; Fahey, T.J. Patterns and controls of terrestrial primary production in a changing world. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 8, 205–246. [Google Scholar]
- Shangguan, W.; Dai, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhu, A.; Duan, Q.; Wu, L.; Ji, D.; Ye, A.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, Q. A China data set of soil properties for land surface modeling. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2013, 5, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyar-Naimi, H.; Vaez-Zadeh, S. Sustainable development based energy policy making frameworks, a critical review. Energy Policy 2012, 43, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Gao, B.; Zheng, K.; Wu, Y.; Li, C. Multi-scenario simulation of ecosystem service value for optimization of land use in the Sichuan-Yunnan ecological barrier, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honglie, S.; Du, Z.; Tandong, Y.; Lithium, Y. Protection and Construction of National Ecological Security Barrier in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 67, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, W.; Ke, K.; Yelong, Z.; Li, G.; Min, W.; Tsering. Population distribution pattern and influencing factors in Tibet based on random forest model. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 74, 664–680. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, H.; Yan, C.; Xing, X. Evaluation of Eco-Environmental Quality in Qaidam Basin Based on the Ecological Index (MRSEI) and GEE. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Yang, T.-B. Impacts of climate warming on vegetation in Qaidam Area from 1990 to 2003. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 144, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Liang, L. Ecological risk in the Tibetan Plateau and influencing urbanization factors. Environ. Chall. 2022, 6, 100445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Liu, S.; Zhou, L. The Law of Population Regional Differentiation in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the Application of “Hu Huanyong Line”. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 75, 255–267. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Ni, W.; Li, T.; Zhou, B.; Qu, Y.; Yuan, K. Influences of anthropogenic factors on lakes area in the Golmud Basin, China, from 1980 to 2015. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, L.; Yao, X.; Chen, M.; Yan, C. Effect of ecological construction engineering on vegetation restoration: A case study of the loess plateau. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, U.; Welsch, H. Meaningful environmental indices: A social choice approach. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2004, 47, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).