A Reflection Symmetric Target Extraction Method Based on Hypothesis Testing for PolSAR Calibration
Abstract
1. Introduction
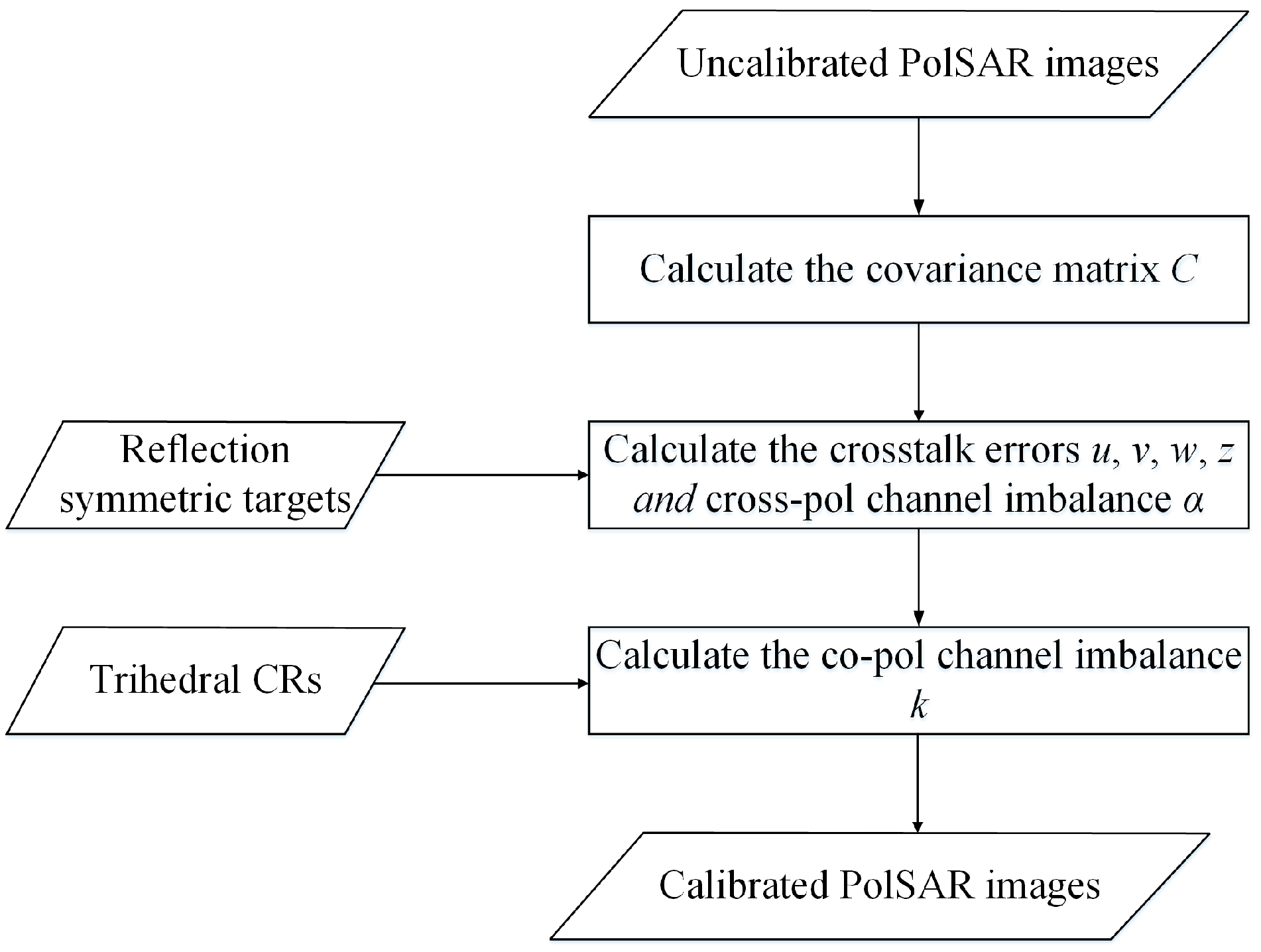
2. PolCal Error Model
3. Method
3.1. Calibration Methods
3.2. Optimized HTCI Approach
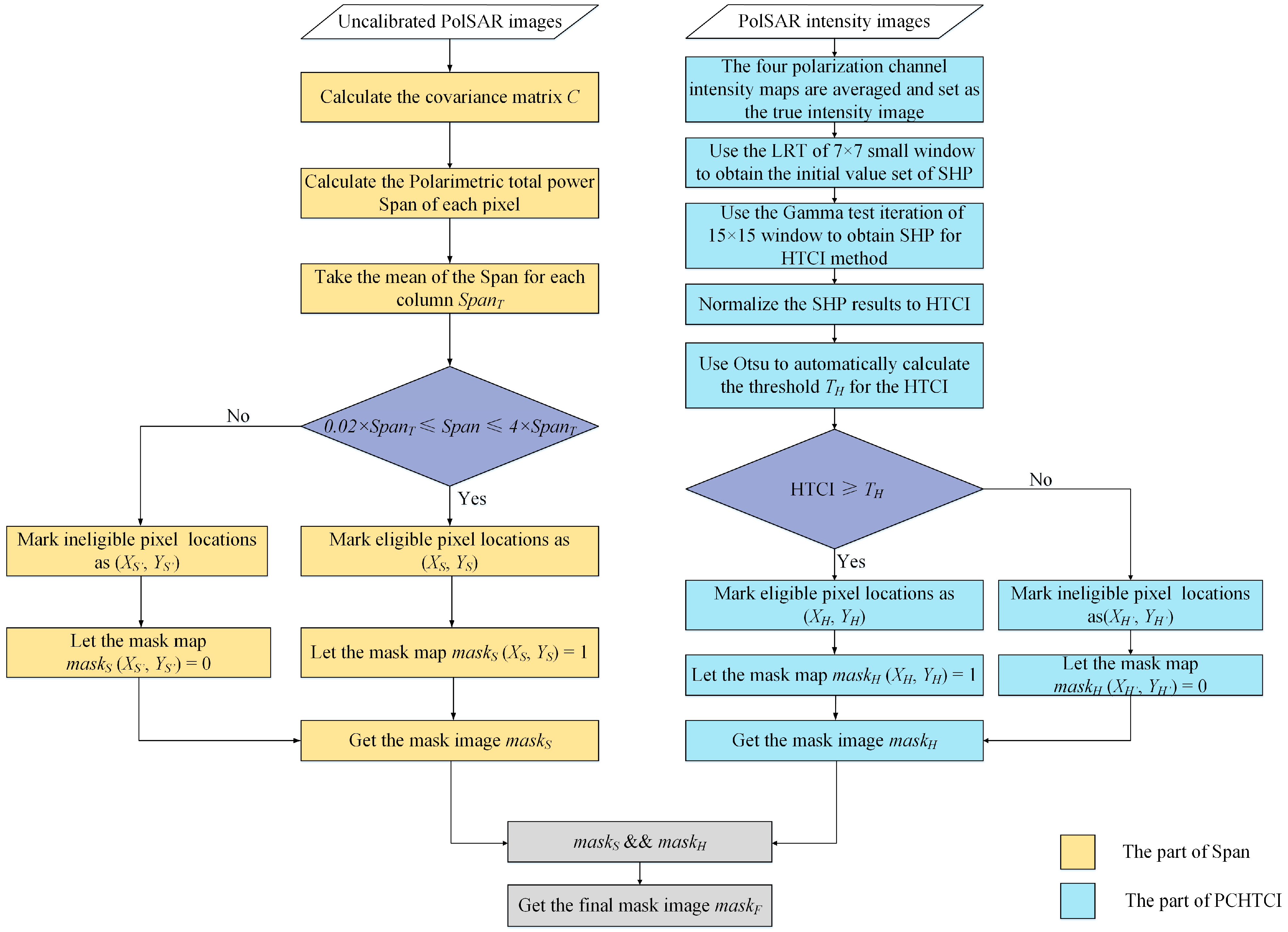
3.3. Improved Reflection Symmetric Target Extraction Method
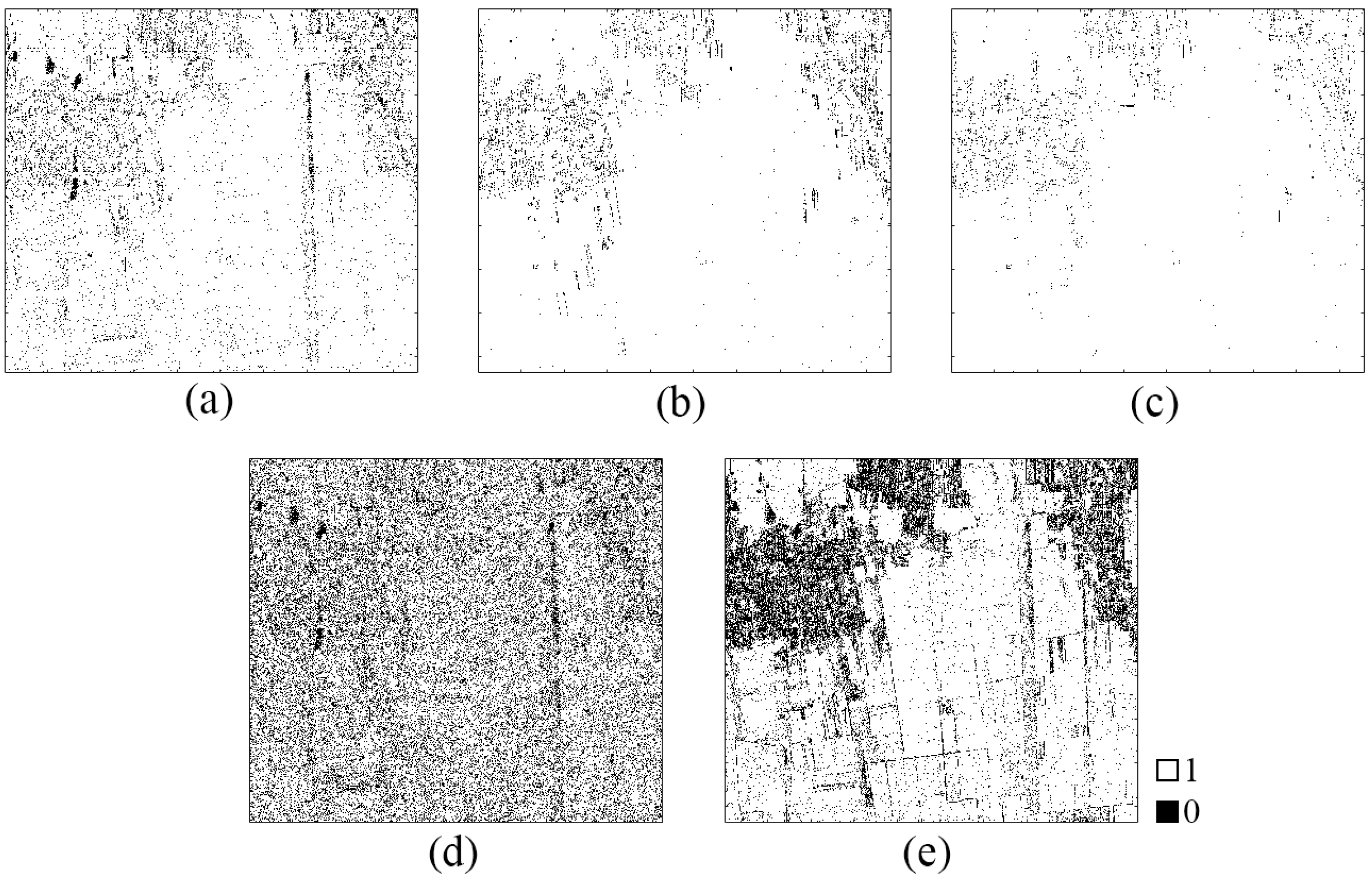
- Use the observed Sinclair matrix to obtain the Span of each pixel in the image and calculate the threshold SpanT corresponding to each column.
- Compare the Span of each pixel with 4 times and 0.02 times the SpanT corresponding to the column, save and record the position of the pixel that meets the conditions of expression (20) as (XS, YS), and the position of the pixel that does not meet the condition as (XS′, YS′).
- In the mask image maskS, set the saved pixel position maskS (XS, YS) to 1, and set the removed pixel position maskS (XS′, YS′) to 0.
- Take the average value of the intensity images of the four polarization channels, and this is set as the true intensity image of the PolSAR image of the scene.
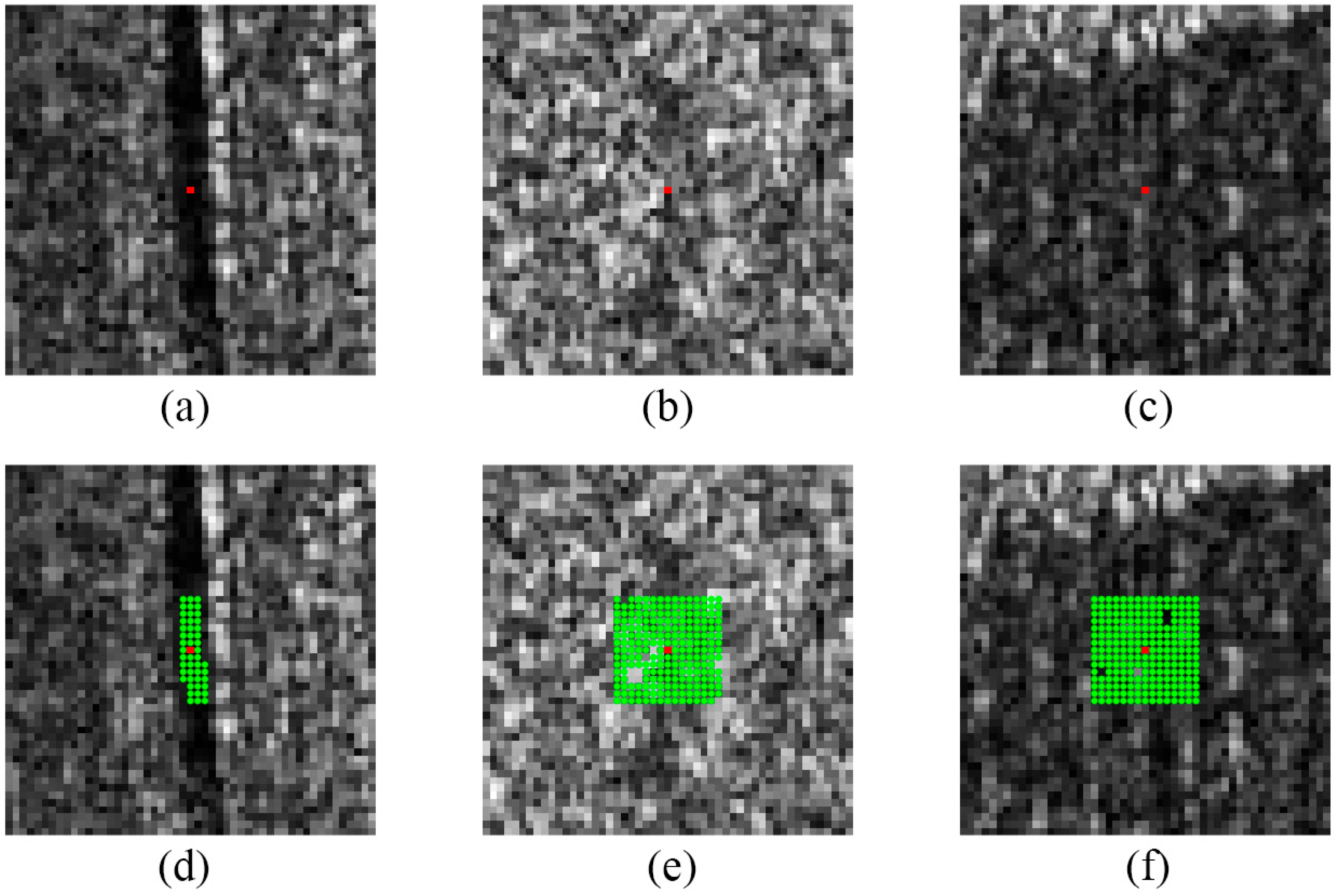
- For the true intensity image, use the 7 × 7 small window LRT to obtain the initial value of the homogeneous points for the HTCI test.
- For the initial value set, use the Gamma test iteratively to obtain the image for the results of the homogeneous points in the 15 × 15 window.
- Normalize the results and use Otsu to calculate automatically the threshold TH for the image of the SHPS result and judge the normalized result of each pixel with TH; save and record the pixel position greater than TH as (XH, YH), and the pixel position less than TH as (XH′, YH′).
- In the mask image maskH, set the recorded pixel position maskH (XH, YH) to 1, and set the removed pixel position maskH (XH′, YH′) to 0.
- Calculate the mask image maskS and maskH, by an operator to obtain the final mask image maskF; that is, for each pixel, if one of the two is 0, the result is 0, and if both are 1, the result is 1.
4. Experiment
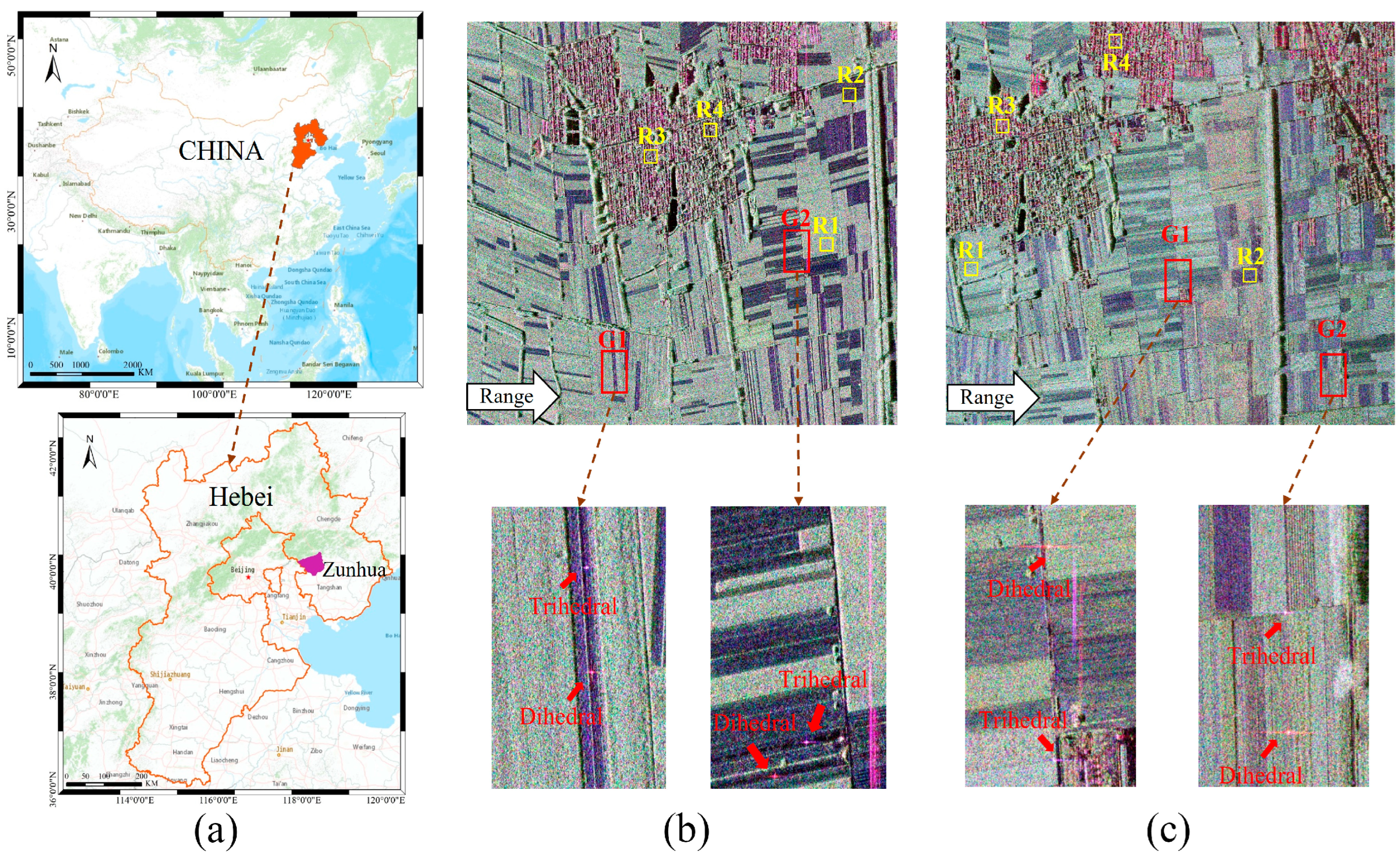
4.1. Overview of Experimental Area
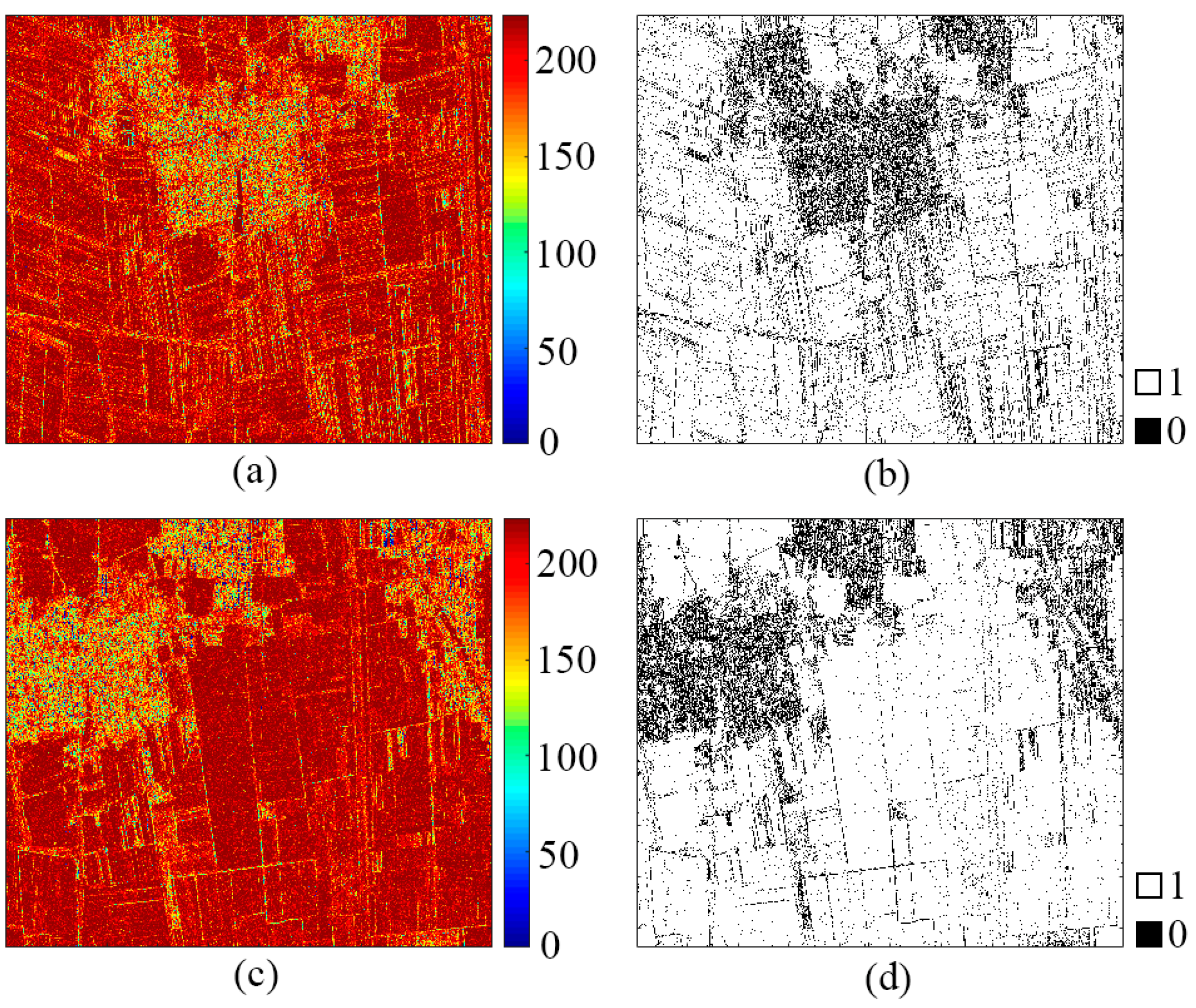
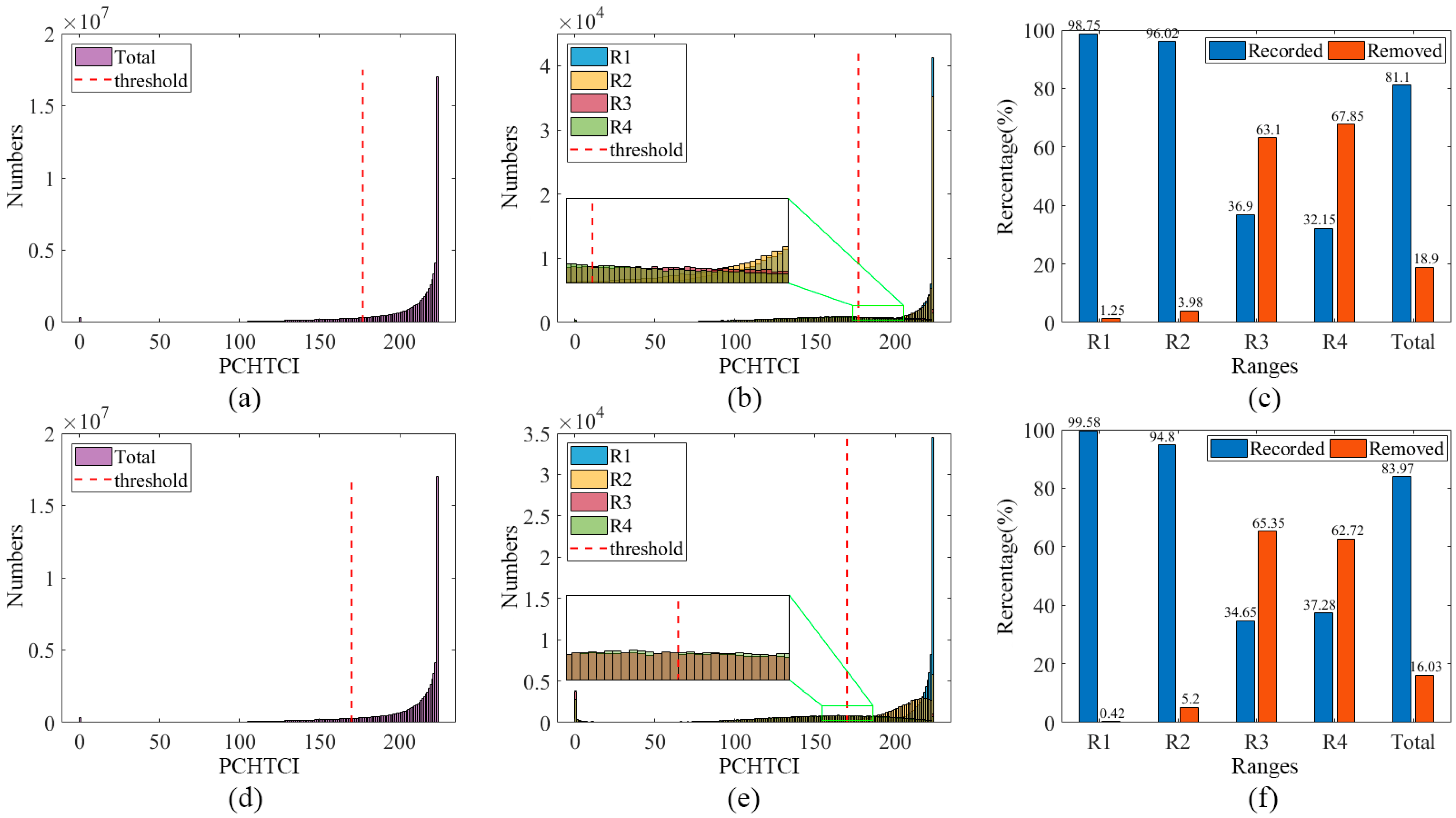
4.2. Extraction of Reflection Symmetric by PCHTCI
4.3. Extraction of Reflection Symmetric Targets
4.4. Verification of PolCal Effect
5. Discussion
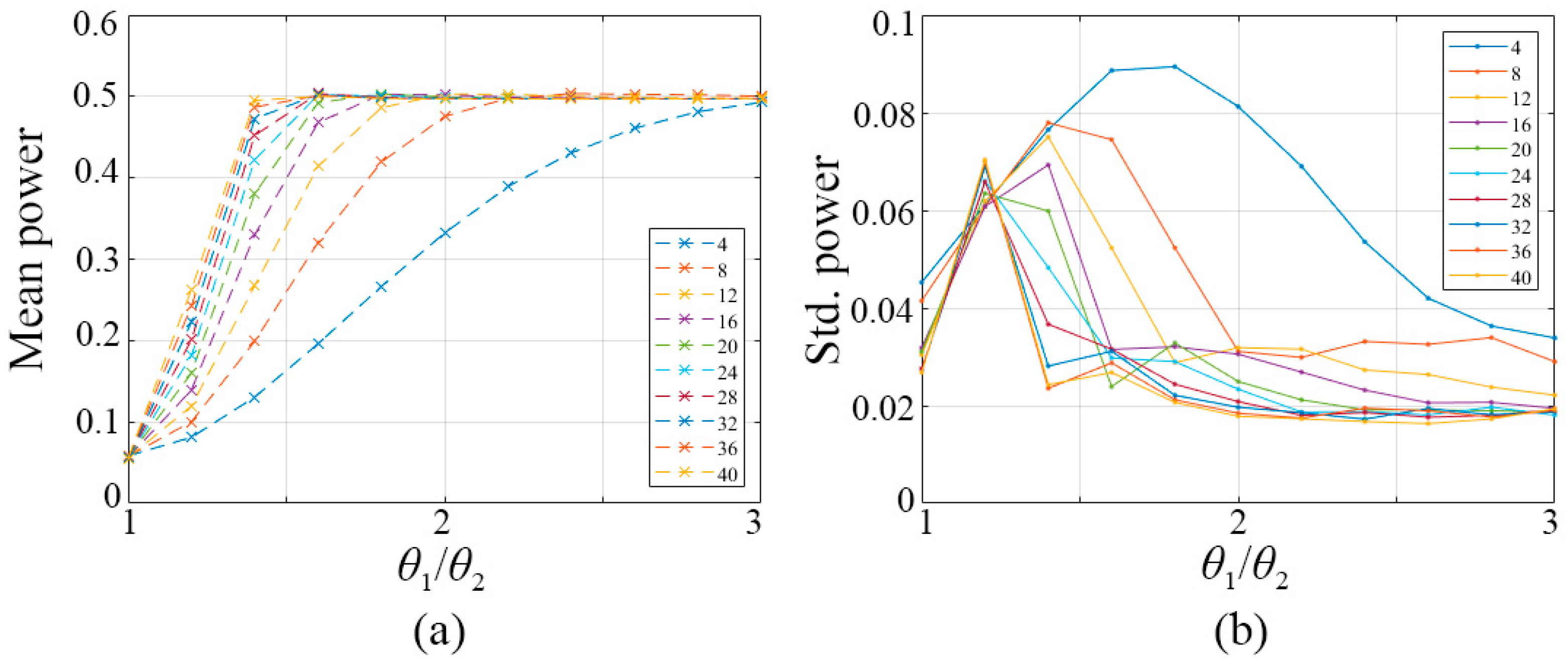
5.1. Selection of Parameter N
5.2. Examples with Different Reference Points in PCHTCI
5.3. Statistical Analysis of PCHTCI
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, B.; Ding, C.; Zhong, L.; Liu, J.; Qiu, X.; Hu, Y.; Lei, B. The GF-3 SAR Data Processor. Sensors 2018, 18, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Li, R.; Hu, T. Using a fully polarimetric SAR to detect landslide in complex surroundings: Case study of 2015 Shenzhen landslide. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 174, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.E.; Lee, S.G. On the Use of Single-, Dual-, and Quad-Polarimetric SAR Observation for Landslide Detection. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imani, M. A random patches based edge preserving network for land cover classification using Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 4942–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Zhang, F.; Yin, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.-C.; Hong, W. Random Neighbor Pixel-Block-Based Deep Recurrent Learning for Polarimetric SAR Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 7557–7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, E.Z.; Yasser, M.; Seyed Ali, S. Assessing the performance of indicators resulting from three-component Freeman–Durden polarimetric SAR interferometry decomposition at P-and L-band in estimating tropical forest aboveground biomass. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 41, 433–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, G. The Transmission and Reception of Elliptically Polarized Waves. Proc. IRE 1950, 38, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Shi, L.; Nie, Y.; Hui, Z.; Xiong, Q.; Li, P. Polarimetric calibration of SAR images using reflection symmetric targets with low helix scattering. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 104, 102559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A. SAR calibration: An overview. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 1107–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitt, M.W.; Ulaby, F.T.; Polatin, P.; Liepa, V.V. A general polarimetric radar calibration technique. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1991, 39, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.; van Zyl, J.J.; Klein, J.D.; Zebker, H.A.; Shen, Y. Calibration of Stokes and scattering matrix format polarimetric SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zyl, J.J. Calibration of polarimetric radar images using only image parameters and trihedral corner reflector responses. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1990, 28, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.D. Calibration of complex polarimetric SAR imagery using backscatter correlations. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1992, 28, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, A.; Iannini, L.; Giudici, D.; Monti-Guarnieri, A.; Tebaldini, S. Calibration of SAR Polarimetric Images by Means of a Covariance Matching Approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, T.L.; Ferro-Famil, L.; Lee, J.-S. Orientation angle preserving a posteriori polarimetric SAR calibration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chang, Y.; Li, P.; Zhao, L.; Shi, L. Distributed Targets Extraction for SAR Polarimetric Calibration Using Helix Scattering. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2018, 43, 2023–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Moriyama, T.; Ishido, M.; Yamada, H. Four-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR image decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quegan, S. A unified algorithm for phase and cross-talk calibration of polarimetric data-theory and observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Mizuno, T.; Papathanassiou, K.P.; Hajnsek, I. Improvement of polarimetric SAR calibration based on the Quegan algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience & Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Fei, W.; Wang, R.; Song, H.; Wang, J.; Li, N. Modified Statistically Homogeneous Pixels’ Selection with Multitemporal SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1930–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, W.; Schindlerl, H. A Nonparametric Test for the General Two-Sample Problem. Int. Biom. Soc. 1998, 54, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. A New Algorithm for Processing Interferometric Data-Stacks: SqueeSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Ding, X.; Li, Z. Homogeneous pixel selection algorithm for multitemporal InSAR. Chin. J. Geophys. 2018, 61, 4767–4776. [Google Scholar]
- Otsu, N. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 2007, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzi, R.; Shimada, M. Polarimetric PALSAR Calibration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 3951–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Li, P.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L.; Ding, X.; Zhao, L. Polarimetric SAR Calibration and Residual Error Estimation When Corner Reflectors Are Unavailable. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 4454–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quegan, S.; Lomas, M.; Papatha Na Ssiou, K.P.; Kim, J.S.; Paillou, P. Calibration Challenges for the Biomass P-Band SAR Instrument. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018—2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, B.; Fan, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhuang, H. A distributed scatterers InSAR method based on adaptive window with statistically homogeneous pixel selection for mining subsidence monitoring. Geocarto Int. 2021, 37, 7819–7842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Guarnieri, A.M. Distributed Scatterer Interferometry with the Refinement of Spatiotemporal Coherence. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 3977–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
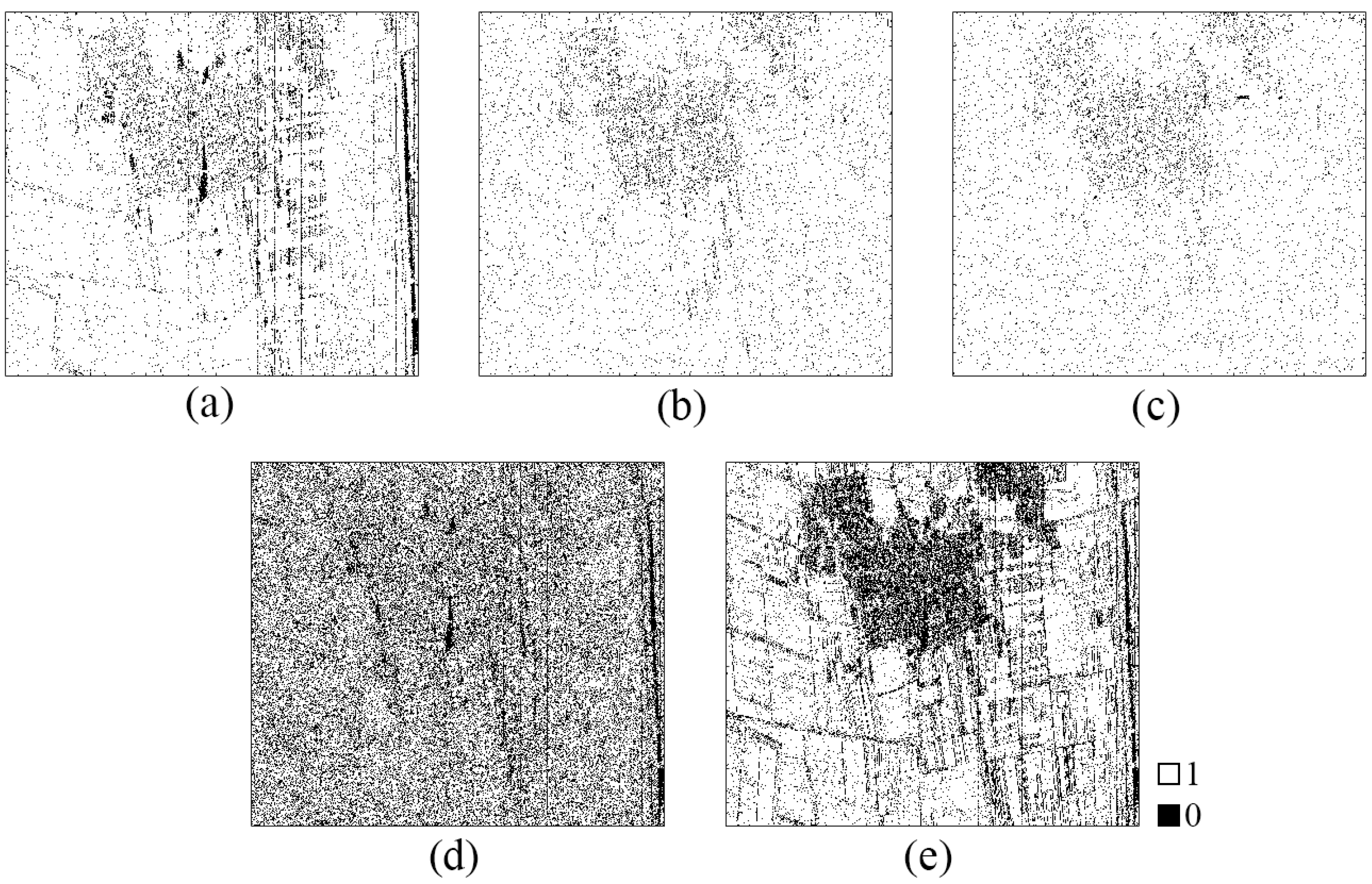


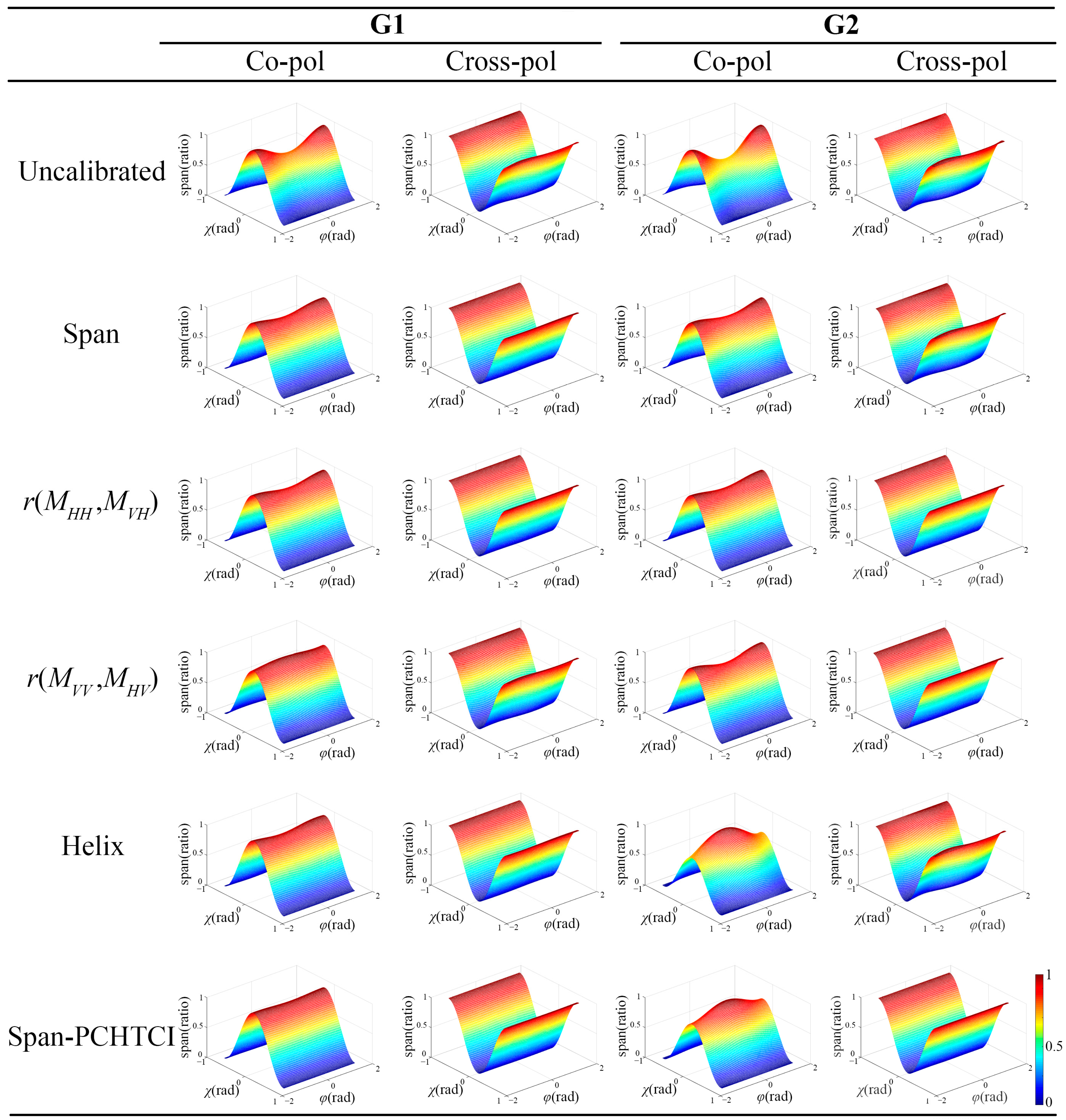
| Methods | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Span | 97.04% | 96.95% | 82.86% | 81.75% | 91.05% |
| r(MHH, MVH) | 97.74% | 96.54% | 83.93% | 79.32% | 94.53% |
| r(MVV, MHV) | 98.68% | 98.14% | 86.64% | 83.36% | 95.46% |
| Helix | 66.40% | 77.24% | 60.42% | 57.97% | 65.13% |
| Span-PCHTCI | 95.83% | 93.18% | 29.96% | 26.56% | 74.90% |
| Methods | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Span | 95.80% | 98.53% | 84.61% | 81.65% | 93.62% |
| r(MHH, MVH) | 99.98% | 99.52% | 85.63% | 93.36% | 96.79% |
| r(MVV, MHV) | 99.99% | 99.94% | 86.79% | 92.78% | 98.29% |
| Helix | 71.98% | 83.49% | 70.68% | 68.28% | 72.32% |
| Span-PCHTCI | 95.41% | 93.56% | 31.57% | 31.69% | 79.90% |
| Original | Span | r(MHH, MVH) | r(MVV, MHV) | Helix | Span-PCHTCI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | Trihedral CR | CIA (dB) | −0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CIP (°) | 1.07 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Crosstalk (dB) | −53.48 | −55.79 | −54.90 | −53.84 | −55.08 | −57.61 | ||
| Dihedral CR | CIA (dB) | 0.71 | 0.48 | 0.51 | 0.20 | 0.46 | 0.43 | |
| CIP (°) | −178.94 | 179.84 | −179.78 | −178.49 | −178.04 | −179.83 | ||
| Crosstalk (dB) | −47.64 | −56.24 | −46.75 | −56.14 | −51.19 | −54.27 | ||
| G2 | Trihedral CR | CIA (dB) | 0.65 | 0.31 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.26 | 0.28 |
| CIP (°) | −7.86 | −1.47 | −0.24 | −1.84 | −1.98 | −0.19 | ||
| Crosstalk (dB) | −39.52 | −58.21 | −59.02 | −55.14 | −63.98 | −58.59 | ||
| Dihedral CR | CIA (dB) | 0.34 | −0.29 | −0.33 | −0.57 | −0.29 | −0.28 | |
| CIP (°) | 171.55 | 177.28 | 174.92 | 178.36 | 174.45 | 174.38 | ||
| Crosstalk (dB) | −33.51 | −40.86 | −40.31 | −40.98 | −41.11 | −41.09 |
| Original | Span | r(MHH, MVH) | r(MVV, MHV) | Helix | Span-PCHTCI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | Trihedral CR | CIA (dB) | −0.89 | −0.22 | −0.18 | 0.1 | 0.72 | 0.44 |
| CIP (°) | 13.17 | 10.01 | 1.05 | 6.79 | 12.3 | 0.73 | ||
| Crosstalk (dB) | −27.59 | −45.07 | −48.28 | −41.31 | −44.18 | −51.63 | ||
| Dihedral CR | CIA (dB) | −1.16 | −1.08 | −1.10 | −0.39 | −1.04 | −0.17 | |
| CIP (°) | −163.38 | −168.46 | −169.4 | −177.40 | −167.59 | −176.69 | ||
| Crosstalk (dB) | −29.43 | −32.67 | −32.85 | −34.42 | −32.48 | −33.67 | ||
| G2 | Trihedral CR | CIA (dB) | −0.60 | −0.18 | −0.18 | −0.26 | −0.12 | −0.05 |
| CIP (°) | 9.52 | −1.53 | 1.49 | −0.31 | −1.97 | 0.84 | ||
| Crosstalk (dB) | −31.02 | −43.31 | −41.93 | −41.95 | −43.97 | −42.36 | ||
| Dihedral CR | CIA (dB) | −1.28 | −0.59 | −0.68 | −0.63 | −0.60 | −0.30 | |
| CIP (°) | −168.31 | −176.44 | 179.19 | 179.51 | −176.09 | −179.57 | ||
| Crosstalk (dB) | −33.99 | −37.78 | −35.22 | −35.44 | −34.36 | −34.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chi, B.; Zhang, J.; Lu, L.; Yang, S.; Huang, G.; Gao, X. A Reflection Symmetric Target Extraction Method Based on Hypothesis Testing for PolSAR Calibration. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051252
Chi B, Zhang J, Lu L, Yang S, Huang G, Gao X. A Reflection Symmetric Target Extraction Method Based on Hypothesis Testing for PolSAR Calibration. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(5):1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051252
Chicago/Turabian StyleChi, Bowen, Jixian Zhang, Lijun Lu, Shucheng Yang, Guoman Huang, and Xu Gao. 2023. "A Reflection Symmetric Target Extraction Method Based on Hypothesis Testing for PolSAR Calibration" Remote Sensing 15, no. 5: 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051252
APA StyleChi, B., Zhang, J., Lu, L., Yang, S., Huang, G., & Gao, X. (2023). A Reflection Symmetric Target Extraction Method Based on Hypothesis Testing for PolSAR Calibration. Remote Sensing, 15(5), 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051252






