Time Ring Data: Definition and Application in Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Urban Expansion and Forest Loss
Abstract
1. Introduction
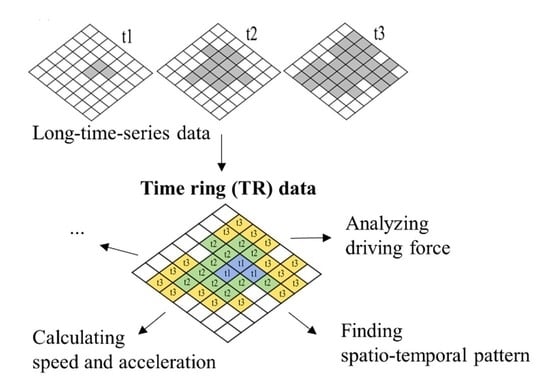
2. Details of Time Ring (TR) Data
2.1. Definition of TR Data
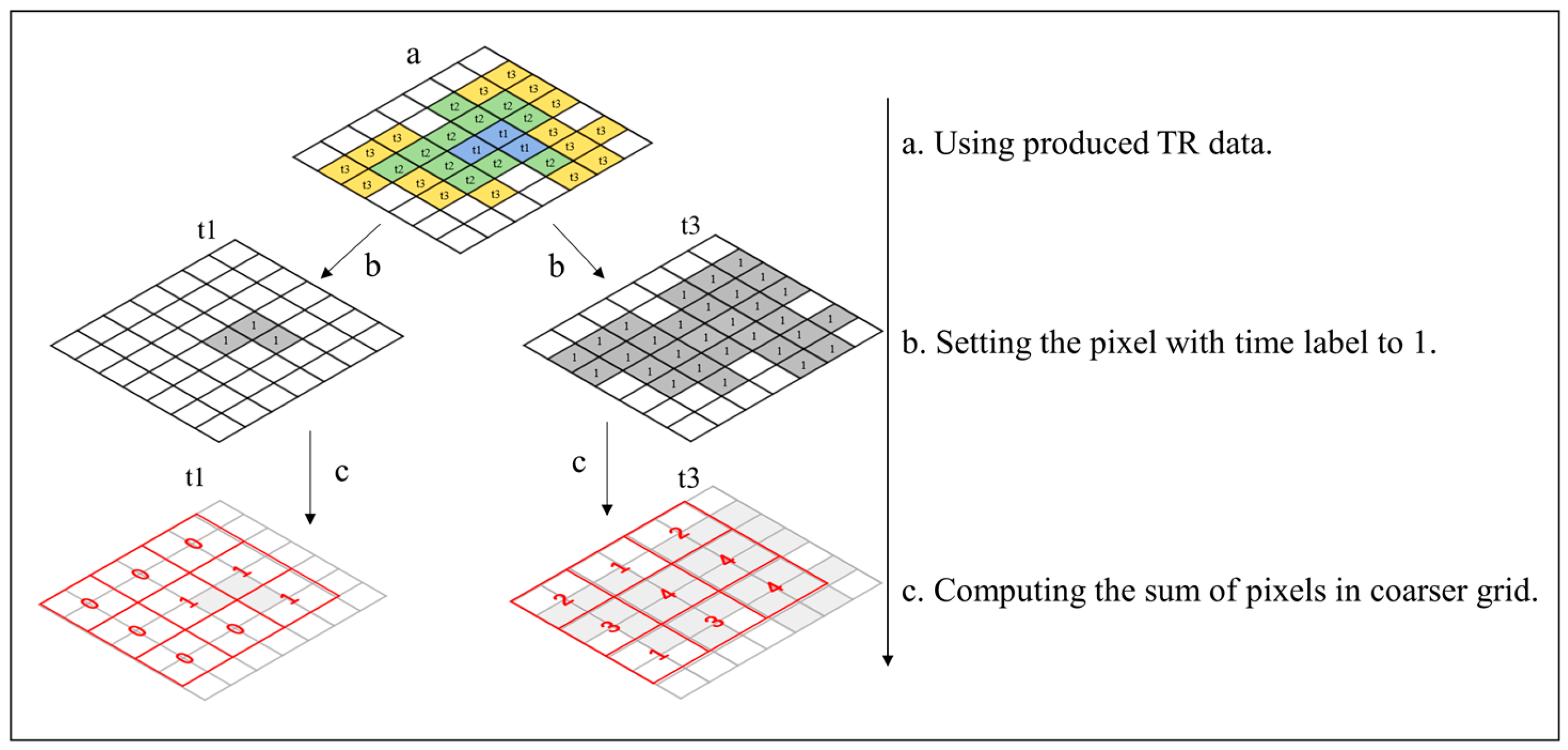
2.2. Generation of TR Data
2.3. Calculation of TR Data
3. Application to Urban Expansion
3.1. Nighttime Light Data
3.2. Results of Urban Expansion
3.2.1. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of NTL TR Data
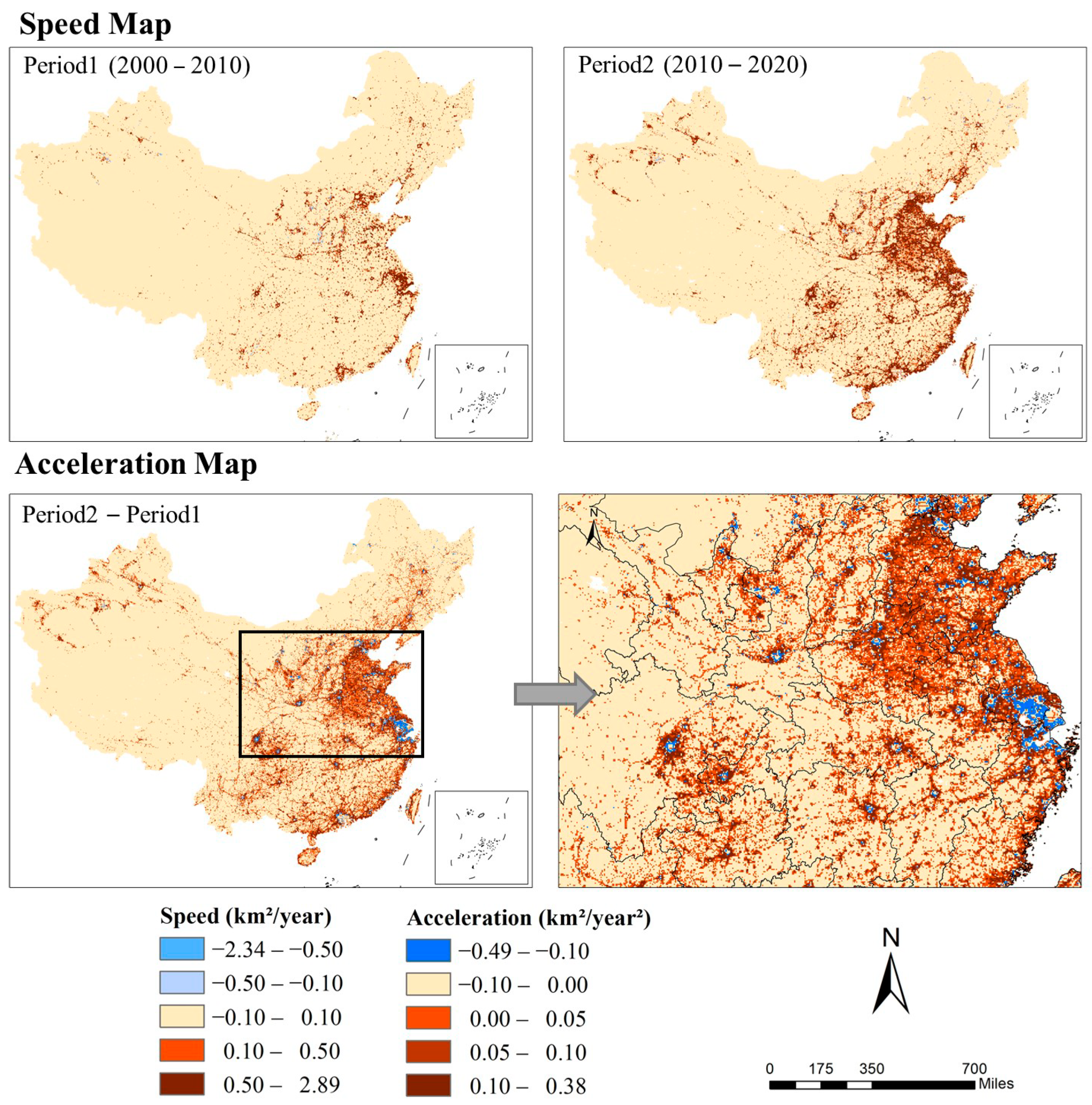
3.2.2. Analysis of Speed and Acceleration of NTL in China
4. Application to Forest Cover Change
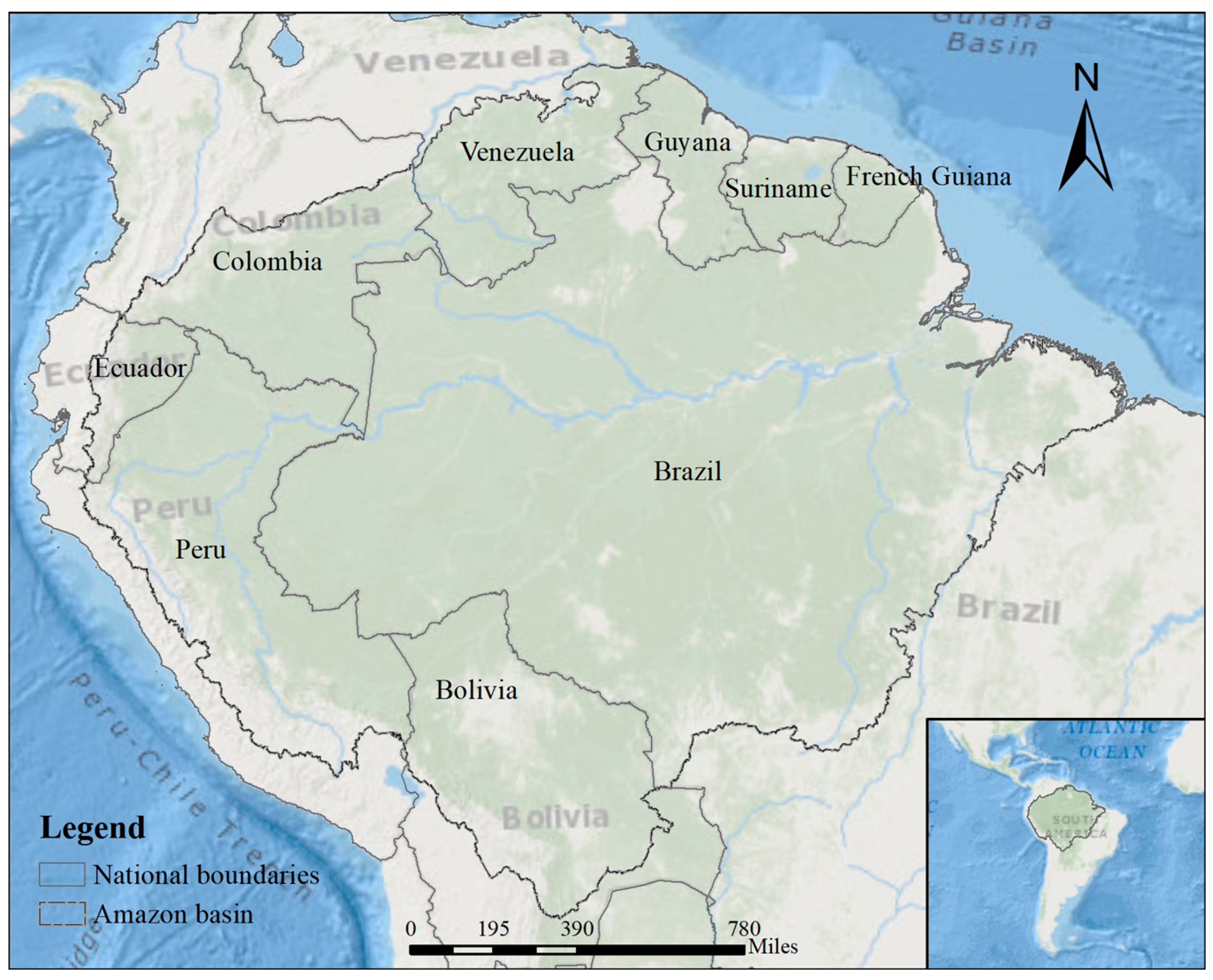
4.1. Study Area and Data
4.2. Results of Forest Cover Change
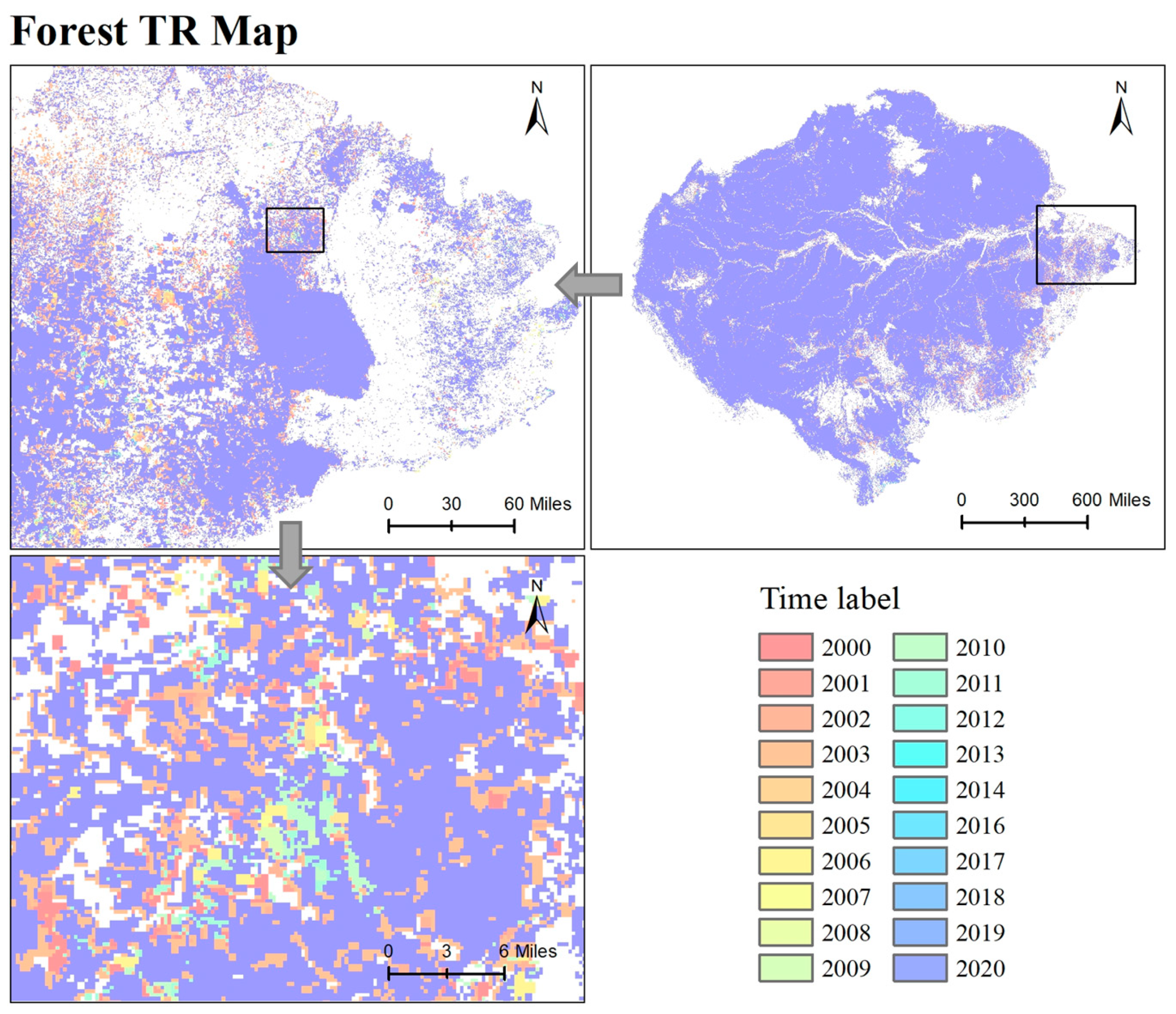
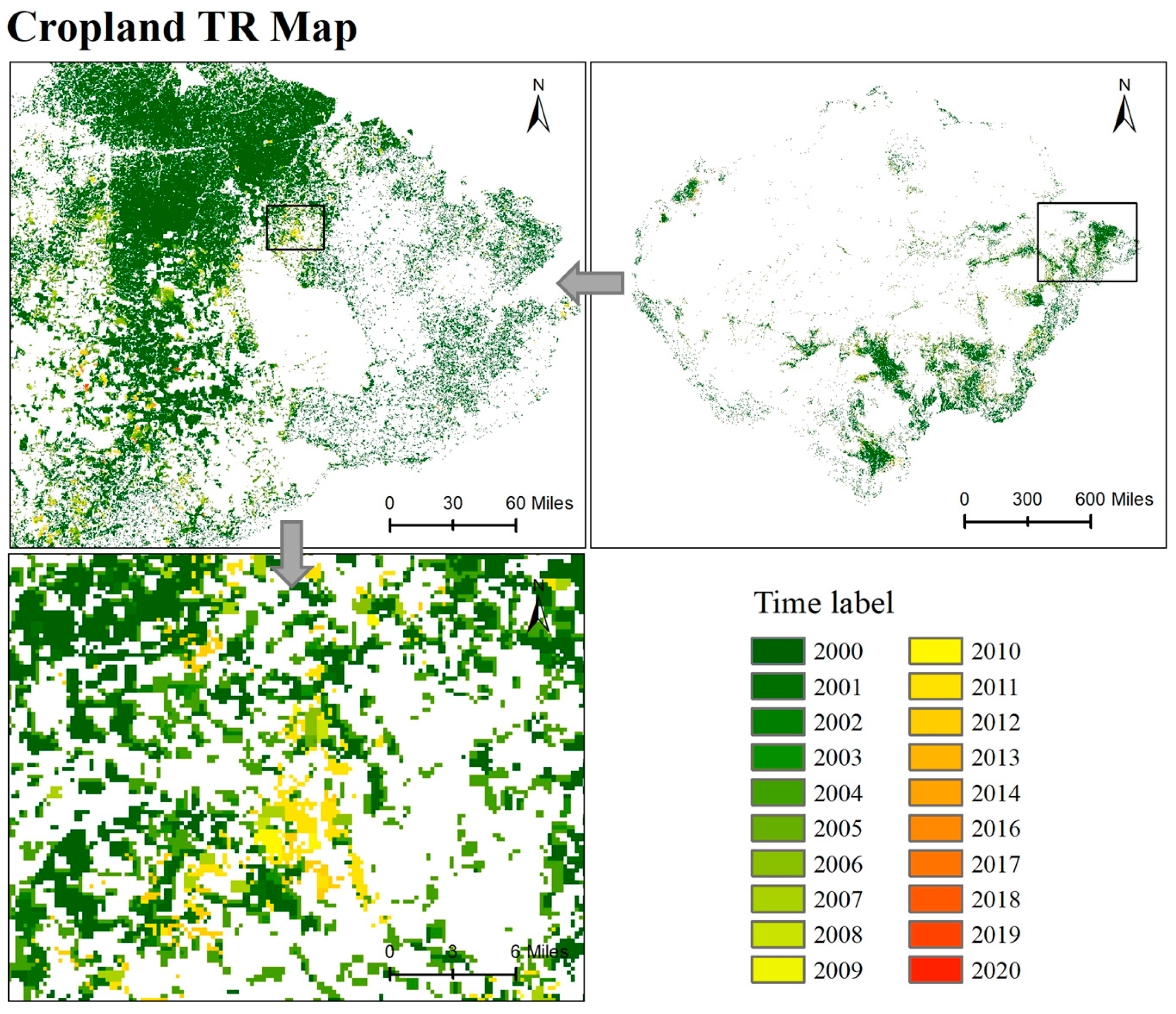
4.2.1. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Forest TR Data
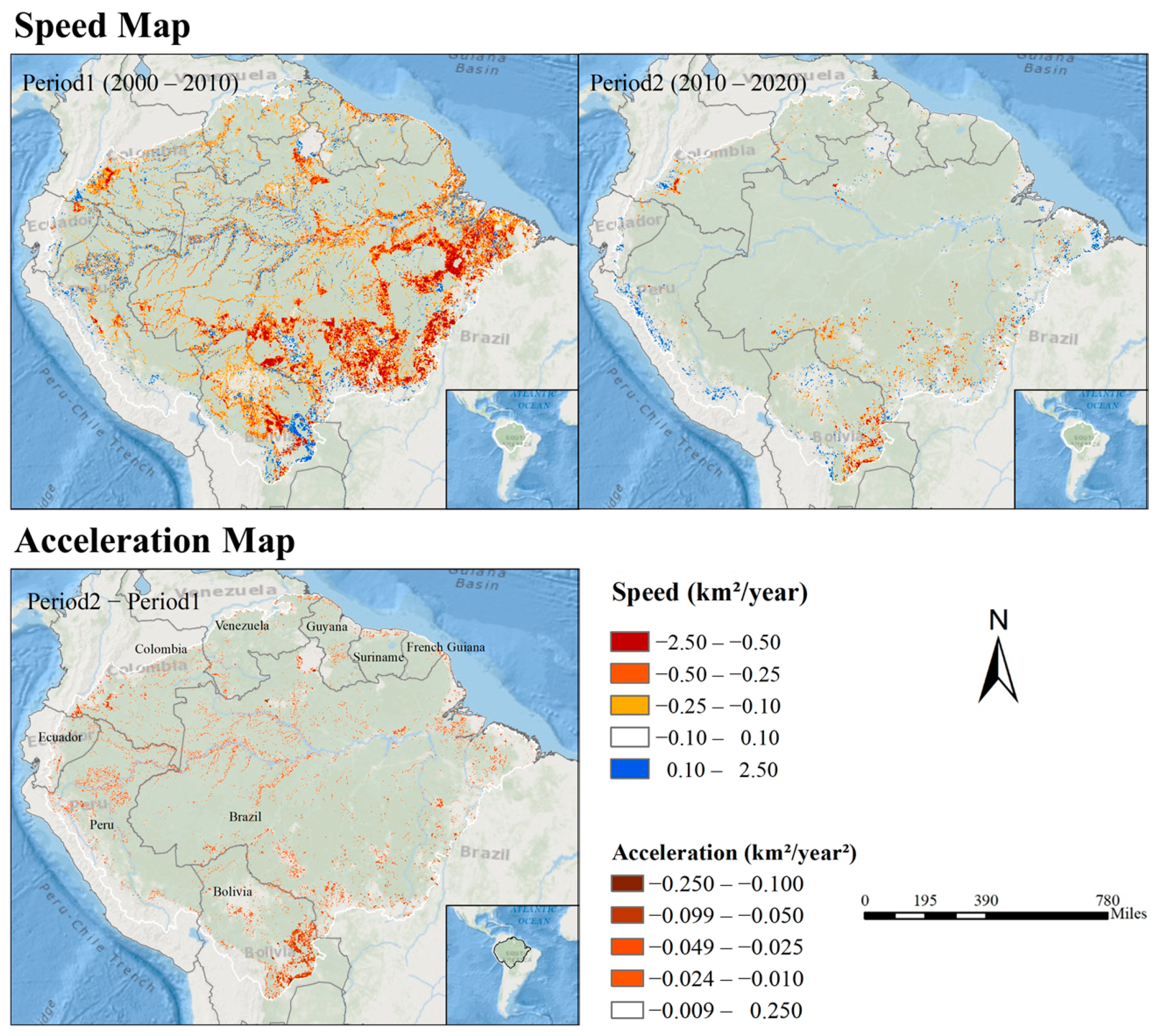
4.2.2. Analysis of Speed and Acceleration
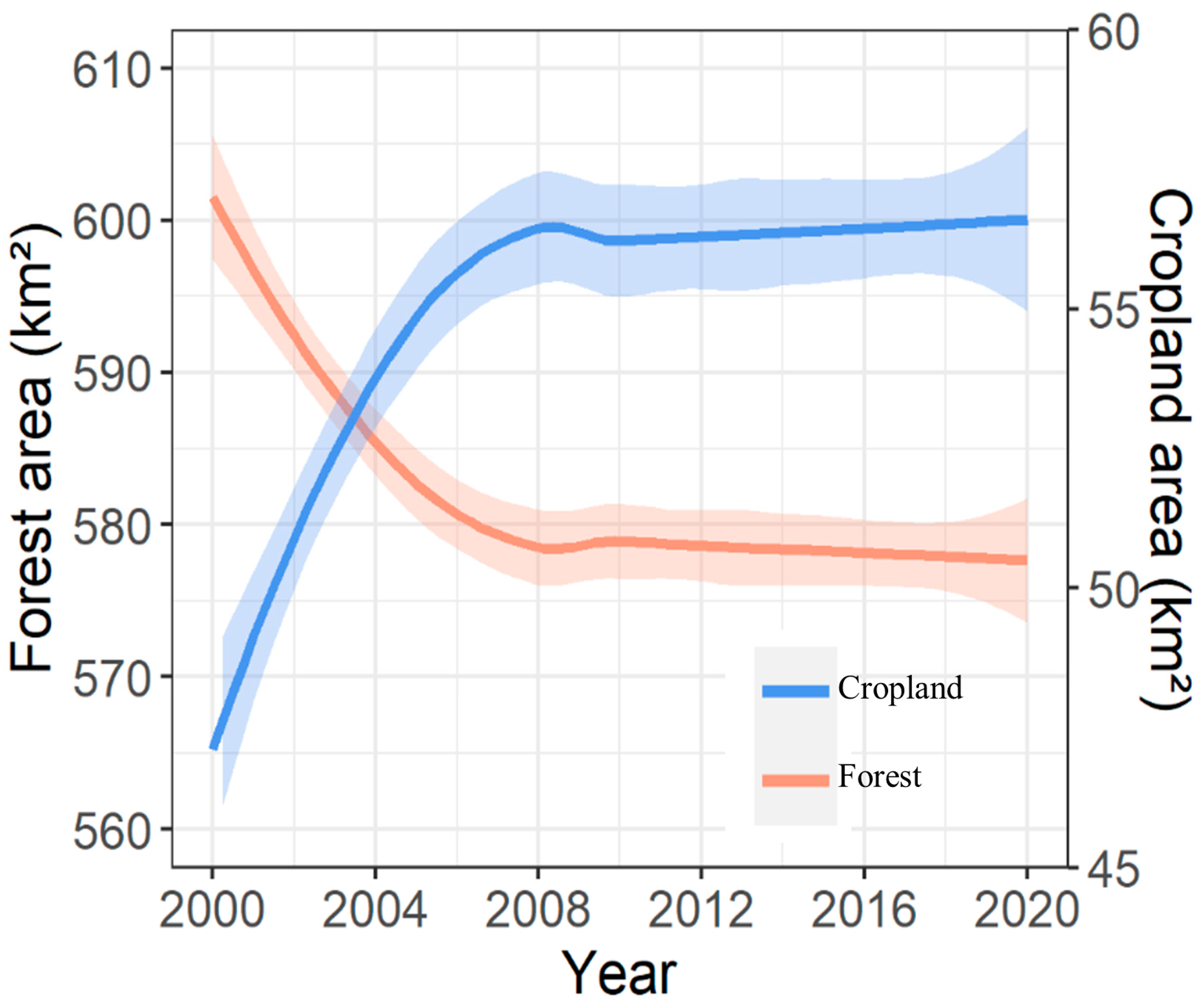
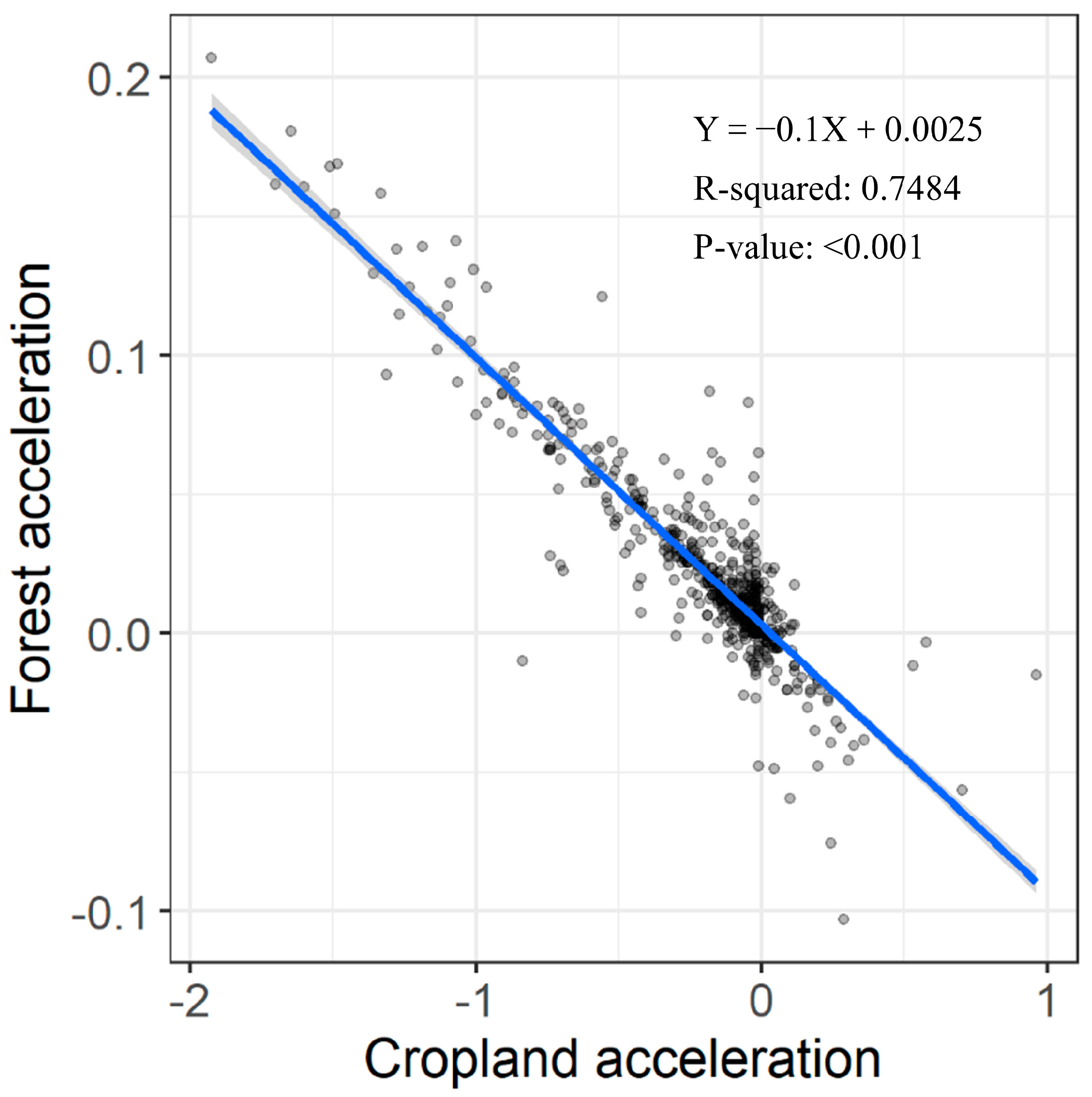
4.2.3. Driving Force of Forest Cover Change
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Han, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, L.; Shen, X.; Yang, Z.; Xu, S.; Li, G.; Chen, F. Analysis on Ecological Status and Spatial–Temporal Variation of Tamarix Chinensis Forest Based on Spectral Characteristics and Remote Sensing Vegetation Indices. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 37315–37326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Despini, F.; Ferrari, C.; Bigi, A.; Libbra, A.; Teggi, S.; Muscio, A.; Ghermandi, G. Correlation between Remote Sensing Data and Ground Based Measurements for Solar Reflectance Retrieving. Energy Build. 2016, 114, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militino, A.F.; Ugarte, M.D.; Pérez-Goya, U. An Introduction to the Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Satellite Remote Sensing Data for Geostatisticians. In Handbook of Mathematical Geosciences: Fifty Years of IAMG; Daya Sagar, B.S., Cheng, Q., Agterberg, F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 239–253. ISBN 9783319789996. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Huang, R.; Cheng, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Shao, Q.; Duan, D.; Wei, P.; Chen, Y.; Huang, J. Monitoring Meteorological Drought in Southern China Using Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Skutsch, M.; Paneque-Gálvez, J.; Ghilardi, A. Remote Sensing of Forest Degradation: A Review. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Di, L.; Zhang, C.; Guo, L.; Di, Y. Remote Sensing of Urban Poverty and Gentrification. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, J.; Santos, J.V.; Neiva, R.M.; Souza, J.; Duarte, L.; Teodoro, A.C.; Freitas, A. Remote Sensing in Human Health: A 10-Year Bibliometric Analysis. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Kong, J.; Hu, H.; Du, Y.; Gao, M.; Chen, F. A Review of Remote Sensing for Water Quality Retrieval: Progress and Challenges. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Xu, Y.; Li, N. Population Spatialization in Beijing City Based on Machine Learning and Multisource Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Ma, Y.; Yan, J.; Liu, P.; Chen, L. Spatial-Feature Data Cube for Spatiotemporal Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis. Computing 2020, 102, 1447–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Du, X.; Fan, X.; Yan, Z.; Kang, X.; Zhu, J.; Hu, Z. A Modular Remote Sensing Big Data Framework. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, C.N.; Watanabe, M.; Hayashi, M.; Ogawa, T.; Shimada, M. Mapping the Spatial-Temporal Variability of Tropical Forests by ALOS-2 L-Band SAR Big Data Analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hitchcock, D.B.; Samadi, S.Z. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Flood Data from South Carolina. J. Stat. Distrib. Appl. 2020, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jia, Y.; Li, X.; Gong, P. Analysing the Driving Forces and Environmental Effects of Urban Expansion by Mapping the Speed and Acceleration of Built-up Areas in China between 1978 and 2017. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, M.S.; Wasonga, O.V.; Mbau, J.S.; Elhadi, Y.A. Spatial and Temporal Analysis of Forest Cover Change in Falgore Game Reserve in Kano, Nigeria. Ecol. Process. 2017, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, P.; Ranjan, R. Towards Building a Data-Intensive Index for Big Data Computing—A Case Study of Remote Sensing Data Processing. Inf. Sci. 2015, 319, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M.; Plaza, A.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Sun, Z.; Shen, J.; Zhu, Y. Big Data for Remote Sensing: Challenges and Opportunities. Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 2207–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Urban Heat Island Using Multisource Remote Sensing Data: A Case Study in Hangzhou, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 3317–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Jin, S.; Li, J.; He, Y.; Shang, W. Spatio-Temporal Variations and Driving Forces of Harmful Algal Blooms in Chaohu Lake: A Multi-Source Remote Sensing Approach. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.; Galvanin, E.A.S.; Menezes, R. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Land Use/Land Cover Change Dynamics in Paraguai/Jauquara Basin, Brazil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.; He, Q.; Ma, G. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Ecological Vulnerability and Driving Factor Analysis in the Dongjiang River Basin, China, in the Recent 20 Years. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B.; Hu, T.; Liu, X.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Annual Maps of Global Artificial Impervious Area (GAIA) between 1985 and 2018. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, W. 40-Year (1978–2017) Human Settlement Changes in China Reflected by Impervious Surfaces from Satellite Remote Sensing. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Lin, A.; He, L.; Zhou, Z.; Yuan, M. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Driving Forces of Urban Land-Use Expansion: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Li, X.; Tong, F.; Li, Z.; Jendryke, M. Mapping Urban Expansion Using Night-Time Light Images from Luojia1-01 and International Space Station. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 2603–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, A.K.; Yadav, N.K.; Kandel, P.N.; Mondol, S.; Pandav, B.; Natarajan, L.; Subedi, N.; Naha, D.; Reddy, C.S.; Lamichhane, B.R. Tracking Forest Loss and Fragmentation between 1930 and 2020 in Asian Elephant (Elephas Maximus) Range in Nepal. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugonnet, R.; McNabb, R.; Berthier, E.; Menounos, B.; Nuth, C.; Girod, L.; Farinotti, D.; Huss, M.; Dussaillant, I.; Brun, F.; et al. Accelerated Global Glacier Mass Loss in the Early Twenty-First Century. Nature 2021, 592, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, S.; Qian, X.; Wang, C.; Wu, B.; Wu, J. An Extended Time Series (2000-2018) of Global NPP-VIIRS-like Nighttime Light Data from a Cross-Sensor Calibration. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 889–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, K.; Wu, J. Urban Land Use Change and Its Socio-Economic Driving Forces in China: A Case Study in Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei Region. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2018, 20, 1405–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Yin, K.; Lu, D.; Hua, L.; Zhao, Q.; Wen, M. Examining Land Use and Land Cover Spatiotemporal Change and Driving Forces in Beijing from 1978 to 2010. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10593–10611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Xiao, X.; Dong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Shimabukuro, Y.; Arai, E.; Biradar, C.; Wang, J.; Zou, Z.; et al. Improved Estimates of Forest Cover and Loss in the Brazilian Amazon in 2000–2017. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defourny, P.; Schouten, L.; Bartalev, S.; Bontemps, S.; Caccetta, P.; De Wit, A.J.W.; Di Bella, C.; Gérard, B.; Giri, C.; Gond, V.; et al. Accuracy Assessment of a 300 m Global Land Cover Map: The GlobCover Experience. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Symposium on Remote Sensing of Environment (ISRSE), Stresa, Italy, 4–8 May 2009; pp. 400–403. [Google Scholar]
- Bontemps, S.; Defourny, P.; Radoux, J.; Van Bogaert, E.; Lamarche, C.; Achard, F.; Mayaux, P.; Boettcher, M.; Brockmann, C.; Kirches, G.; et al. Consistent Global Land Cover Maps for Climate Modeling Communities: Current Achievements of the ESA’s Land Cover CCI. In Proceedings of the ESA Living Planet Symposium, Edimburgh, UK, 9–13 September 2013; Volume 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Xia, J.; Xiao, R.; He, T. Urban Expansion Patterns of 291 Chinese Cities, 1990–2015. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2019, 12, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Gao, X.; Shen, Z.; Li, R. Expansion of Urban Impervious Surfaces in Xining City Based on GEE and Landsat Time Series Data. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 147097–147111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, H. Monitoring Long-Term Annual Urban Expansion (1986–2017) in the Largest Archipelago of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 146015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.-L.; DU, P.-J.; Guo, D.-Z. Analysis of Urban Expansion and Driving Forces in Xuzhou City Based on Remote Sensing. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2007, 17, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Zhang, K.; Ba, M.; Wen, D. Spatial Characteristics Analysis of Urban Expansion in Luoyang, China. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2022, 14, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Shen, L.; Wong, S.W.; Meng, C.; Yang, Z. Night-Time Light Data Based Decoupling Relationship Analysis between Economic Growth and Carbon Emission in 289 Chinese Cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 73, 103119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Gao, J. The Night Light Development and Public Health in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 35, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PRODES 2019 Amazon Deforestation Database. Available online: www.obt.inpe.br/prodes (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Kröger, M. Inter-Sectoral Determinants of Forest Policy: The Power of Deforesting Actors in Post-2012 Brazil. For. Policy Econ. 2017, 77, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearnside, P.M. The Roles and Movements of Actors in the Deforestation of Brazilian Amazonia. Ecol. Soc. 2008, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, A.S.; Bhattarai, N.; Campolo, J.; Crompton, O.; Dralle, D.; Duncan, J.; Thompson, S. Forest Loss in Brazil Increases Maximum Temperatures within 50 Km. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 84047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemp, D.C.; Schleussner, C.F.; Barbosa, H.M.J.; Rammig, A. Deforestation Effects on Amazon Forest Resilience. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 6182–6190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.P.; Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.; Adusei, B.; Pickering, J.; Adami, M.; Lima, A.; Zalles, V.; Stehman, S.V.; Di Bella, C.M.; et al. Massive Soybean Expansion in South America since 2000 and Implications for Conservation. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalles, V.; Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.V.; Stehman, S.V.; Tyukavina, A.; Pickens, A.; Song, X.P.; Adusei, B.; Okpa, C.; Aguilar, R.; et al. Near Doubling of Brazil’s Intensive Row Crop Area since 2000. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosetto, M.D.; Paez, R.A.; Ballesteros, S.I.; Jobbágy, E.G. Higher Water-Table Levels and Flooding Risk under Grain vs. Livestock Production Systems in the Subhumid Plains of the Pampas. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 206, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, L.; Jing, Y.; Yin, H.; Li, X.; Guan, X. High-Quality Vegetation Index Product Generation: A Review of NDVI Time Series Reconstruction Techniques. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 105, 102640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.; Shen, H.; Guan, X.; Chen, J.M.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, L. Long Time-Series NDVI Reconstruction in Cloud-Prone Regions via Spatio-Temporal Tensor Completion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Li, X.; Cheng, Q.; Zeng, C.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; Zhang, L. Missing Information Reconstruction of Remote Sensing Data: A Technical Review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2015, 3, 61–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Yi, L.; Zuo, L.; Xu, J.; Hu, S.; Sun, F.; et al. Urban Expansion of China from the 1970s to 2020 Based on Remote Sensing Technology. Chinese Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 765–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şevik, M.; Doğan, M. Epidemiological and Molecular Studies on Lumpy Skin Disease Outbreaks in Turkey during 2014–2015. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1268–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, G.; Korennoy, F.; Alvarez, J.; Picasso-Risso, C.; Perez, A.; VanderWaal, K. Mapping Changes in the Spatiotemporal Distribution of Lumpy Skin Disease Virus. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 2045–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Song, C.; Ren, Z.; Wang, S. Predicting the Geographical Distribution of Malaria-Associated Anopheles Dirus in the South-East Asia and Western Pacific Regions Under Climate Change Scenarios. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 841966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gething, P.W.; Smith, D.L.; Patil, A.P.; Tatem, A.J.; Snow, R.W.; Hay, S.I. Climate Change and the Global Malaria Recession. Nature 2010, 465, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Wang, D.; Ma, A.; Hwang, J.; Bennett, A.; Sturrock, H.J.W.; Fan, J.; Zhang, W.; Yang, D.; Feng, X.; et al. Predicting Malaria Vector Distribution under Climate Change Scenarios in China: Challenges for Malaria Elimination. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, J.P.; Brady, O.J.; Golding, N.; Kraemer, M.U.G.; Wint, G.R.W.; Ray, S.E.; Pigott, D.M.; Shearer, F.M.; Johnson, K.; Earl, L.; et al. The Current and Future Global Distribution and Population at Risk of Dengue. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1508–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocklöv, J.; Dubrow, R. Climate Change: An Enduring Challenge for Vector-Borne Disease Prevention and Control. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Li, X.; Bao, H. Time Ring Data: Definition and Application in Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Urban Expansion and Forest Loss. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15040972
Liu X, Li X, Bao H. Time Ring Data: Definition and Application in Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Urban Expansion and Forest Loss. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(4):972. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15040972
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xin, Xinhu Li, and Haijun Bao. 2023. "Time Ring Data: Definition and Application in Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Urban Expansion and Forest Loss" Remote Sensing 15, no. 4: 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15040972
APA StyleLiu, X., Li, X., & Bao, H. (2023). Time Ring Data: Definition and Application in Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Urban Expansion and Forest Loss. Remote Sensing, 15(4), 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15040972