Abstract
When synthetic aperture radar (SAR) is conducting remote sensing or terrain mapping, its radar beam is inevitably occluded by the variations in the under-test topography. Although back-projection algorithm (BPA) can theoretically directly solve the imaging problems of topography variations that most current SAR imaging algorithms cannot handle, these BPAs only solve the phase focusing of SAR echo signal, and do not consider the mismatch of SAR imaging results caused by topography occlusion. To solve the mis-imaging issue of the occluded area generated by BPA under the case of topography variation, a topography-based BPA (Topo-BPA) is proposed in this paper. Firstly, a new beam occlusion judgment algorithm based on spherical wave assumption is proposed, and its core is depression angle interpolation and depression angle updating. Then, the proposed Topo-BPA embeds the proposed beam occlusion judgment algorithm before the classical BPA, which not only did not reduce the focus depth of BPA, but improved the imaging accuracy of classical BPA. Finally, numerical experiments have demonstrated the superiority of the Topo-BPA’s performance in comparison with classical BPA.
1. Introduction
Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) has been turned into an important remote sensing device [1,2]. It not only generates high-resolution two-dimensional images all day and night and all-weather [3], but also collects quite different information than optical or infrared tools [4], such as the relief and morphological structure of the observed topography as well as changes in the ground conductivity [5]. As the demand for SAR in remote sensing applications continues to expand, e.g., from agricultural remote sensing to mountain surveying and mapping [6,7,8], the characteristics of SAR detection scenes have also changed from flat ground to fluctuant topography, which brings challenges to the design of SAR imaging algorithms.
As we all know, most existing imaging algorithms for SAR are based on the flat surface assumption, and according to the differences in imaging principles, they can be roughly divided into two types: time domain algorithms [9,10,11], and frequency domain algorithms [12,13,14]. The latter type aims to improve the imaging efficiency. However, this aim induces a lot of approximations in spectrum variation and de-coupling [15], in other words, the cost of improving the algorithms’ efficiencies is that these SAR imaging algorithms have many limitations in practical applications, particularly in conditions where the topography varies. By contrast, time domain methods, such as the well-known back-projection algorithms (BPAs), which is recognized as the theoretically optimal SAR data-processing algorithm [16,17], can directly solve the imaging issue of topography variations that most current SAR imaging algorithms cannot handle.
In principle, by gridding a two-dimensional radar map into pixels, BPA is a linear transformation to reconstruct the under-test scene from SAR echo data, so that superposition of imaged point pixels applies [18]. Although the matching calculation of BPA is performed pixel-by-pixel and pulse-by-pulse [19], the computational burden can be reduced by fast algorithms [16,19,20], especially with the rapid development of parallel processing technology and the widespread application of graphics processing units, the disadvantage of BPA with a large amount of calculation is no longer a difficulty. Hence, BPA has again received widespread attention and implemented in real SAR systems [21]. It is precisely because of the point-by-point matching feature, combined with a suitable digital elevation model (DEM), that BPA can achieve precise focus imaging of the fluctuant terrain. At the same time, several effective algorithms for SAR imaging with topography variations have also been proposed [11,22,23,24].
However, these BPAs can only obtain precise phase focusing of the SAR echoes, and do not consider the mismatch of SAR imaging results caused by topography occlusion. In fact, when SAR is working under the conditions of fluctuant terrain [25], its radar beam is inevitably blocked, causing some areas to be unable to scatter electromagnetic waves. Thus, these occluded areas should be presented as shadow on the focused SAR image [26]. However, topography variations make the azimuth coordinates and slant range coordinates of each grid pixel point no longer uniquely correspond. Then, during the point-to-point matching of BPA, imaging results appear in the shadow part that does not reflect SAR echo.
As a common phenomenon in the SAR image, shadow is caused by the occlusion of radar beams (e.g., Figure 1). Therefore, how to accurately calculate the shadow area through occlusion judgment has become a critical part of SAR imaging with topography variation. Although many shadow region judgment methods have been proposed in optical remote sensing image processing, most of them are based on certain conditions and designed for specific tasks [27,28,29,30,31]. Among these algorithms, the raytracing and the angle-based algorithms are mainly utilized for SAR. As an occlusion judgment method for fluctuant terrain, raytracing techniques in computer graphics can be utilized to generate the shadow areas in the target scene [32,33]. Unfortunately, this method needs to trace the path of a large number of rays, resulting in a huge amount of calculation. By contrast, the angle-based method [34,35], which judges whether a target or area is shadow or visible by comparing the depression angle [36,37], is easy to implement and can be used to quickly judge shadow regions. However, the traditional angle-based method assumes that the radar beam is a plane wave, and the effect of beam movement is not considered [38]. Thus, if the traditional angle-based method is directly applied to SAR imaging, it would produce inaccurate occlusion judgment results, which would lead to a mismatch of SAR imaging results caused by topography occlusion.
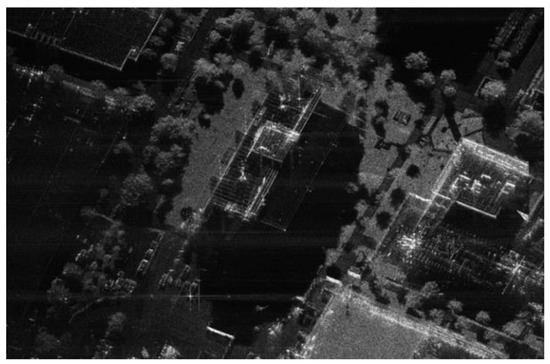
Figure 1.
Sandia National Laboratories SAR image of Kirtland AFB Building [39].
To solve the above mis-imaging issue of the occluded area generated by BPA under the case of topography variation, in this paper a topography-based BPA (Topo-BPA) is proposed by embedding a new beam occlusion judgment method before the classical BPA. The keys of the proposed beam occlusion judgment method are depression angle interpolation and depression angle updating. The reminder of this paper is organized as follows. Firstly, the basic signal model of SAR and preliminary knowledge about BPA and traditional angle-based method are described in Section 2. Then, Section 3 builds a new echo signal model of SAR with topography variations and Topo-BPA is proposed. In Section 4, discussions on the detailed implementation of the proposed Topo-BPA are presented. Finally, the numerical experiments are presented to verify the performance and effectiveness of the proposed Topo-BPA in Section 5, and the conclusions of this paper are summarized in Section 6.
2. Fundamentals
In this section, the basic echo signal model of SAR, the kernel of the classical BPA, and the idea of the traditional angel-based occlusion judgment method is briefly reviewed, which serves as preliminary knowledge for the subsequent modeling and design of the method in Section 3.
2.1. Basic Echo Signal Model of SAR
As a microwave remote sensing tool, SAR collects echo signals backscattered from the detection area by sequentially transmitting and receiving electromagnetic waves [40,41]. Assume that SAR transmits the linear frequency modulation (LFM) signal [42], which can be formulated as:
where is a rectangle window function and equals to 1 for 0.5 [43], denotes the fast-time variable, and , , and represent the duration of the transmit pulse, the carrier frequency of the transmit signal, and the chirp rate of the transmit LFM signal [44], respectively.
The echo signal of the SAR for an ideal point target is as follows [45]:
where and represent the fast-time and slow-time variable, respectively. is the reflection amplitude of the point target, which is mainly composed of target scattering coefficient, transceiver antenna gains, and propagation loss. denotes the instantaneous round-trip slant range between the SAR and the point target. represents the speed of light.
Then, the received baseband echo signal of SAR after performing down-conversion can be written as [46]:
Referring to the Wald clutter model [47], the echo signal of the entire detection scene can be regarded as the superposition of the echo signals of countless scattering points at different positions [48,49], yielding:
where denotes the echo signal from the -th scattering point, which has the same form as (3).
2.2. Principles of BPA
The kernel of the BPA is to make the coherent data enhanced but the incoherent diminished [50,51]. Thus, BPA generates a radar image of two coordinates, i.e., an image where each target is located at its range and azimuth position, as shown in Figure 2. The image can be recognized as signal reconstruction, i.e., a linear transformation from SAR echo so that superposition of the imaged target applies [52]. Therefore, BPA consists of two steps:
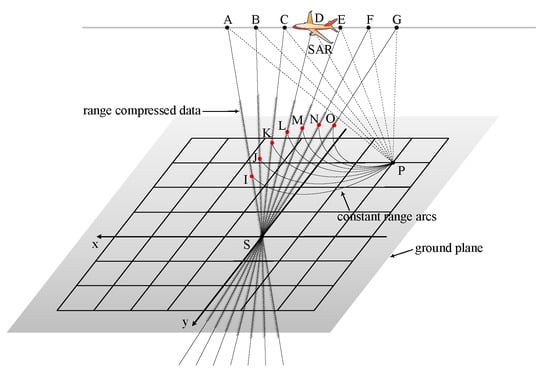
Figure 2.
The schematic diagram of BPA.
Firstly, pulse compression [16] is performed on (4), yielding:
where represents the pulse-compressed signal of the -th scattering point, and it can be expressed by:
where [53,54] and is the sinc function.
Secondly, by the integral along on (5), the output SAR image of BPA can be represented as [11,16,19,20,22,23,24,26]:
where is the transceiving delay time of the pixel located at the coordinate of .
2.3. Principles of the Traditional Angle-Based Occlusion Judgment Method
The basic echo signal model of SAR in Section 2.1 is based on the flat terrain assumption. However, the working environment of SAR is usually complex and may have rich elevation information [40], and these topography variations cause the SAR beam to be blocked during propagation, resulting in shadows on the back of the irradiated area. The point targets located in the shadow region cannot generate echo signal because they are not illuminated by SAR. Therefore, the occlusion judgment for fluctuant terrain should be completed before SAR imaging processing.
The idea of the traditional angle-based occlusion judgment method is to determine whether the point target is occluded by comparing the depression angle in the same line of sight [34,35], as sketched in Figure 3. In the range direction, the red area is visible to SAR platforms and can backscatter echo signals only if the depression angles decrease monotonically. On the contrary, the points on the blue line are obscured and cannot generate echoes because their depression angles are greater than . Thus, the SAR shadow area is closely related to the size of the depression angle, and it can be obtained by comparing the depression angle of different points in the same line of sight.
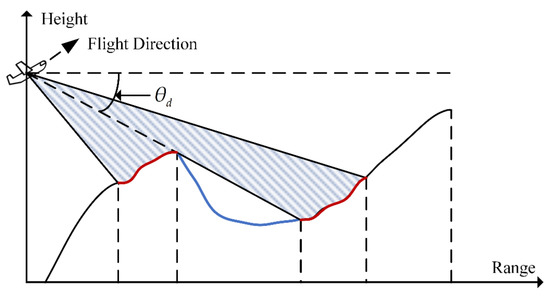
Figure 3.
Illustration of the traditional angle-based occlusion judgment method.
However, two main problems exist in the traditional angle-based occlusion judgment method: first, it is based on the plane wave assumption and only has the ability to make occlusion judgment in range direction. Second, it ignores the fact that the judgment results vary with the motion of the SAR platform. Thus, under the condition of the actual spherical beam and the motion of SAR, the tradition angle-based method is impossible to guarantee the accuracy of the occlusion judgment, and it may make the SAR imaging result be inconsistent with the actual scene.
3. Method Descriptions
Here, a new echo signal model of SAR with topography variations is first built and the problem of BPA applied to SAR with topography variations is analyzed, then the Topo-BPA is described in detail, and finally, the implementations of the Topo-BPA are discussed.
3.1. Echo Signal Model of SAR with Topography Variations
Without loss of generality, the geometry between SAR and the under-detected fluctuant scene is sketched in Figure 4, where the point is the reference position of the SAR platform at the aperture center moment, and the point is an arbitrary target on the ground scene. Since BPA has no special restrictions on the trajectory of the SAR platform, and the terrain of the area to be detected is undulating, vector analysis is more suitable for us to establish the geometric configuration between the SAR and the under-detected scene to achieve the universality of the model [55,56,57].
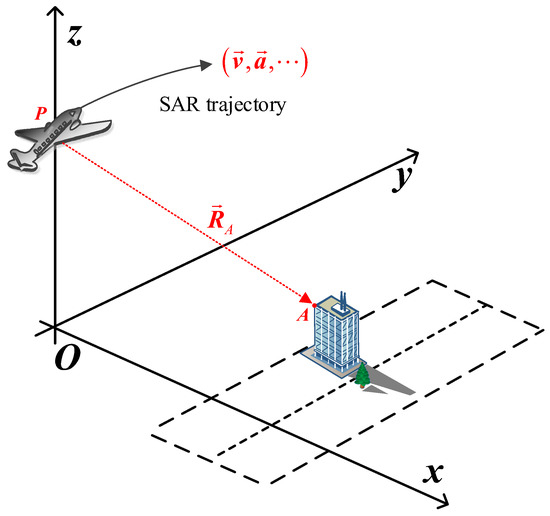
Figure 4.
General geometry between SAR and the under-detected fluctuant scene.
Then, the instantaneous round-trip slant range between the radar and the target can be written as:
where represents the slant range vector from to , is the vector modulus operator, and is the motion vector of the SAR platform, which can be modeled by the Newtonian motion equation combined with the velocity vector , acceleration vector , and other kinetic parameters of the SAR platform. under a typical uniform linear motion case can be expressed as .
Due to the topography variations in the detection terrain, the SAR beam may not illuminate because of terrain occlusion. Therefore, combined with the actual working scene of SAR, a new echo signal model of SAR with topography variations is proposed to truly reflect the elevation information of undulating terrain. Then, the received baseband echo signal of the point after performing down-conversion can be written as:
where is the amplitude of the reflected echo signal of the point , is the transceiving delay time of the point , denotes the Hardmard product, and is the occlusion identifier of the point with following expression:
From (9) and (10), it can be seen that the proposed echo signal model of SAR with topography variations not only considers the effect of occlusion on the echo signal, but also is a function of slow time and beamwidth , that is it has the ability to accurately determine the irradiation range of the SAR beam. Thus, according to (4) and (9), the echo signal of an undulating terrain can be written as follows:
where and denote the echo signal and occlusion identifier of the -th scattering point, which has the same form as (9) and (10), respectively.
3.2. Problem Formation
From Section 2.2, the BPA image is the superposition of imaged point target pixel, then (7) can be rewritten as:
where denotes the focused BPA image of the -th pixel located at the coordinate of , and specific description of is:
Substituting (5), (6) and occlusion identifier into (13), we have:
For a target that is occluded due to topography variations such as target T1 at the coordinate of because it does not have scattered echo signals, that is , the theoretical value of the modulus of (14) should be:
However, the fluctuant terrain makes it possible for each target to have elevation information, which causes the range history of the target and that of the pixel to no longer uniquely correspond. In other words, in the case of fluctuant terrain, there inevitably exists at least one target T2 with the coordinate of that makes hold, where denotes a certain slow time. Then, the imaging result of T1 contains the reconstructed component of the echo signal of T2. Extremely, if the round-trip slant ranges of T1 and T2 are equal at every slow time, the modulus of (14) turns into:
where is the number of pulses during the synthetic aperture.
Evidently from (16), during the point-to-point matching of BPA, mis-imaging results appear in the occluded part that does not reflect SAR echo, which is not only inconsistent with the theoretical result of (14), but also inconsistent with reality. To solve the mis-imaging issue of BPA with topography occlusion, a Topo-BPA is proposed in the next sub-section.
3.3. Proposed Topo-BPA Description
According to the analyses in Section 3.2, the main reason for the failure of BPA in the case of topography occlusion can be summarized as the over-match of the range history between the pixel coordinates and the real target coordinates. This over-matching means that the signal reconstruction of the occluded pixel does not need to be performed, but the classical BPA processed it. Obviously, the most straightforward solution of the over-matching is to make BPA remove the occluded pixels when performing signal reconstruction. To this end, the kernel of the proposed Topo-BPA can be expressed as:
where is the occlusion identifier of the pixel located at coordinate of in Figure 4, and it has the same form as (10).
It can be found in (17) that the key to the proposed Topo-BPA is how to accurately calculate the occlusion identifier. According to the description in Section 2.3, the traditional angle-based method can calculate the occlusion identifier by comparing the depression angle information of different point targets in the range direction. However, under the condition of the actual spherical beam, it is impossible to guarantee that the result of occlusion judgment is consistent with the actual scene. In theory, by dividing the SAR beam into many sub-beams, the occlusion judgment result of any pixel can be determined by comparing the depression angle relative to SAR of the pixel and its neighboring pixel on the same line of sight to calculate an accurate occlusion identifier. However, this way only has theoretical significance since we need to divide the beam interval small enough and clever enough to ensure that each neighboring pixel can fall on the line of the sight of the SAR sub-beams, as sketched in Figure 5. It is difficult to achieve sufficiently fine beam division in practical applications. To address this issue, the practical implementations of the proposed Topo-BPA are discussed in the next sub-section.
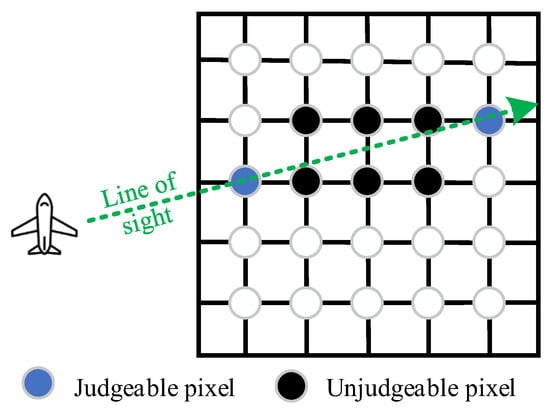
Figure 5.
Schematic of the influence of the pixel division on occlusion judgment.
4. Implementation Discussions
As shown in Figure 4, it is difficult to ensure that adjacent pixels are always in the same line of sight of the SAR sub-beams. Fortunately, combined with the idea of interpolation, it is easy to obtain arbitrary pixels on the same line of sight of the SAR beam artificially. Hence, a new beam occlusion judgment method based on depression angle interpolation and depression angle updating is proposed for the construction of the occlusion identifier of the proposed Topo-BPA (c.f. Step 2 and Figure 6).
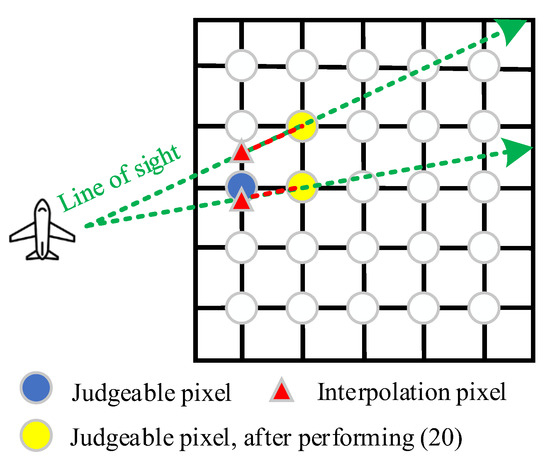
Figure 6.
Schematic of the proposed interpolation algorithm.
Specifically, the idea of the new beam occlusion judgment algorithm is depression angle interpolation and update: firstly, in order to solve the problem that each pixel is on the same beam line of sight, so that the occlusion of some pixels cannot be judged, the pixel located in the azimuth cell and range cell is interpolated to the range cell by following the line of sight of the SAR sub-beam in which is located, and the size of range cell and azimuth cell is related to the beamwidth, detection range and resolution of SAR. Then, the depression angle interpolation can only ensure that the occlusion judgment results of two adjacent pixels are correct, thus after each depression angle comparison, the smaller one is selected as the reference for the next comparison to guarantee the accuracy of subsequent occlusion judgment.
According to the proposed beam occlusion judgment algorithm, the specific implementation steps of the proposed Topo-BPA are presented as follows:
Step 1: Grid processing of the area to be imaged to obtain the three-dimensional coordinate of each pixel, where the height coordinate of each pixel can be calculated in combination with the existing DEM data of the area to be imaged [22,23]. Note that the pixel’s range and azimuth interval should be finer than the value defined in (18) and (19) to avoid aliasing of the final BPA image or the signal frequency support. A detail derivation of (18) and (19) can be referred to [34]:
where and are the range and azimuth interval of the pixels, respectively, is the transmit bandwidth, and is the total azimuth angle traversed during the synthetic aperture.
Step 2: Depression angle interpolation (i.e., point target pixel interpolation) by (20):
where ,, and represent the range, azimuth, and height coordinate of the pixel located at the -th range cell and -th azimuth cell, respectively; is the azimuth position of the pixel located at the -th range cell and -th azimuth cell relative to SAR; denotes the interpolated height coordinate of the pixel located at the -th range cell and -th azimuth cell; and denotes the interpolation operator. The function of (20) is to interpolate all pixels on a certain range cell that need to be judged to the previous range cell according to their relative azimuth positions, thus ensuring that neighboring pixels can always be in the same line of sight of the SAR beam, that is the depression angle of the pixel located at can always be compared. Figure 6 sketched this interpolation process.
Step 3: Calculate the depression angle of the pixel by (21):
where is the depression angle of the pixel located at the -th range cell and -th azimuth cell, denotes the arc sine function, and represent the height coordinate of the SAR platform and the pixel located at the -th range cell and -th azimuth cell, respectively, and is the slant range between the pixel and the SAR platform. The specific expression of is as follows:
where and represent the range, azimuth, and height coordinate of the SAR platform and the pixel located at the -th range cell and -th azimuth cell, respectively.
Step 4: Determine the topography occlusion of each pixel by comparing the depression angle relative to SAR of the pixel and its neighboring pixels. If , then turn to the next steps, and we have:
Otherwise, we have:
After calculating the occlusion identifier , the next step is to update depression angle for subsequent depression angle comparison, which can be written as follows:
This is because for the beam occlusion judgment, it is not enough to compare the depression angle of adjacent pixels, and the wrong occlusion identifier may be calculated if the depression angle updating is not performed. Figure 7 shows a case as an example, which also describes the process of depression angle updating.
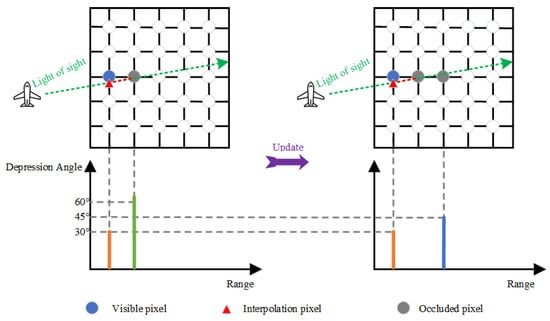
Figure 7.
Schematic of the proposed depression angle updating algorithm.
Step 5: Topo-BPA imaging by (17). Generally, the scenario containing topography variations are often large, but the BPA induces image aliasing when directly handling large scenes. To avoid aliasing of the final image result, the maximum scope in range and azimuth of performing Topo-BPA cannot exceed (26) and (27), respectively:
where is the range sample number per pulse, is the pulse number, and . A detailed derivation of (26) and (27) can be found in [58]. Based on (26) and (27), we can divide the entire detection scene into multiple sub-scenes for parallel Topo-BPA processing according to the computing efficiency of the imaging device, and finally obtain the final imaging result through image stitching.
In order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed beam occlusion judgment algorithm, a simulated scene with topography occlusion is depicted in Figure 8, and according to the SAR system parameters listed in Table 1, Figure 9 shows the occlusion judgment results of the proposed beam occlusion judgment algorithm.
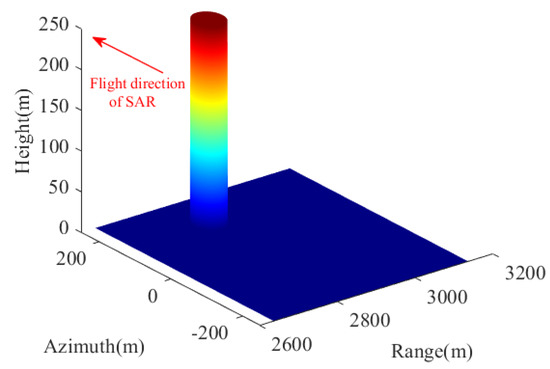
Figure 8.
Simulated scene with topography occlusion to verify the effectiveness of the proposed beam occlusion judgment algorithm.

Table 1.
Basic SAR system parameters for experiments in Figure 9.
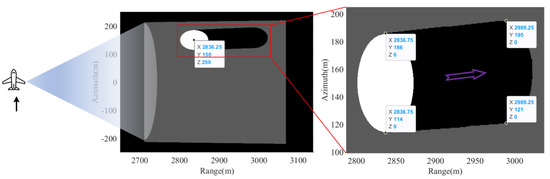
Figure 9.
Occlusion judgment results of the proposed beam occlusion judgment.
Theoretically, according to the spatial geometric relationship between the SAR platform and the cylinder as shown in Figure 8, the feature of light propagation in a straight line and the spherical wave characteristics of the SAR beam, it can be calculated that the direction of the shadow caused by cylinder occlusion at slow time should diverge outward. As can be seen from Figure 9, the shadow direction of the cylinder is offset within the range of SAR beam irradiation, which is consistent with the above analysis. Moreover, the direction of purple arrows and the information of the data cursor (i.e., coordinate) in Figure 9, also proves that the occlusion judgment results of the proposed beam occlusion judgment algorithm are more in line with the radiation trajectory of electromagnetic waves.
Repeat the above steps for each slow time, then the imaging result of the entire scene can be obtained. Figure 10 shows the flowchart of proposed Topo-BPA method for undulating terrain.
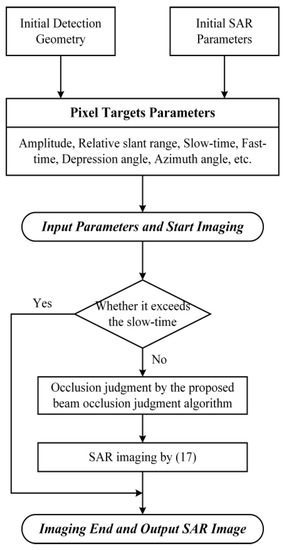
Figure 10.
Flowchart of the proposed Topo-BPA for undulating terrain.
5. Numerical Experiments
Here, two sets of numerical experiments, i.e., the simulated point target experiment and the scenario experiment, are carried out to verify the performance of the proposed Topo-BPA.
5.1. Point Target Experiment
In fact, the purpose of the point target experiment is to validate the correctness of the Topo-BPA and related analysis proposed in Section 3. For this reason, we set two-point targets, named T1 and T2, with the same range history in the detection scene. One should note that the point target T1 located at the pixel coordinate of (130, 200) is always occluded during SAR irradiation, but the point target T2 located at the pixel coordinate of (203, 301) is always visible.
Based on the above scene settings, the received echo signal of SAR can be simulated by SAR raw data simulation method in time-domain. It is worth noting that the phase history of the simulated echo signal is calculated pulse-by-pulse and target-by-target to ensure its accuracy, and Figure 11 shows the amplitude of the echo signal. According to the above analysis, the echo signal of SAR only contains the components of T2, and T1 does not generate echo because it is in the occluded state. Thus, the SAR imaging result of T1 should not exist theoretically, and the signal amplitude of the BPA imaging result at the position of T1 should be 0. However, because the range histories of T1 and T2 are the same, directly using the classical BPA leads to the imaging result of T1 contains the reconstructed component of the echo signal of T2, which leads to mis-imaging results appearing in the position of T1, as shown in Figure 12a. Comparatively, the proposed Topo-BPA can obtain imaging results consistent with theoretical values, as shown in Figure 12b. This is because the proposed Topo-BPA considers that T1 was occluded and constructed an occlusion identifier shown in (17) to ensure that the signal of T2 is not reconstructed at the position of T1.
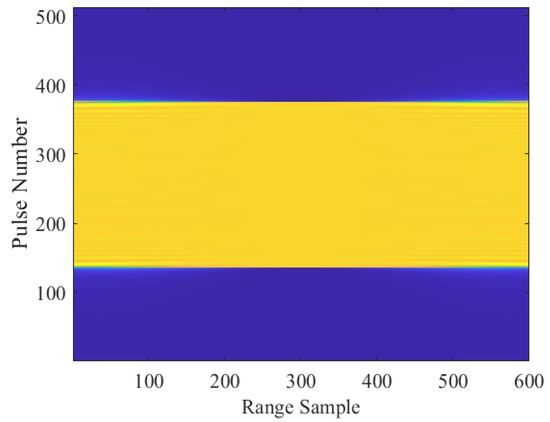
Figure 11.
SAR echo signal simulation result of point target experiment.
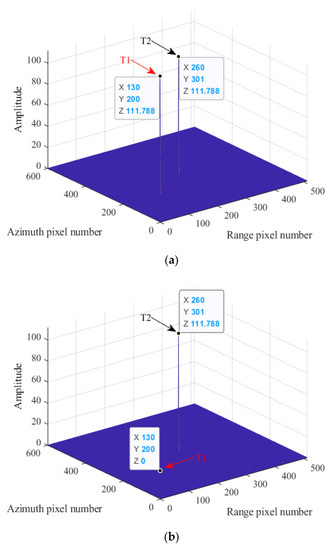
Figure 12.
Point target experiment results. (a) SAR imaging result of the classical BPA. (b) SAR imaging result of the proposed Topo-BPA.
5.2. Scenario Experiment
The point target experiment in Section 5.1 can only verify the theoretical correctness of the proposed Topo-BPA. However, to verify the effectiveness of Topo-BPA in application, imaging experiments for the scenario are essential. Due to the lack of SAR real data with occlusion phenomena, we combined the real SAR imaging result in Figure 13a with the measured DEM data in Figure 13b, and according to the SAR system parameters listed in Table 2, simulated a set of SAR echo signal with the characteristics of topography variation and occlusion as shown in Figure 13c. Moreover, in order to be able to visually verify the effectiveness of the proposed Topo-BPA, the theoretical occlusion result of Figure 13a, which can be calculated by combining the parameters in Table 2 and the DEM in Figure 12b [34], is depicted in Figure 13d.
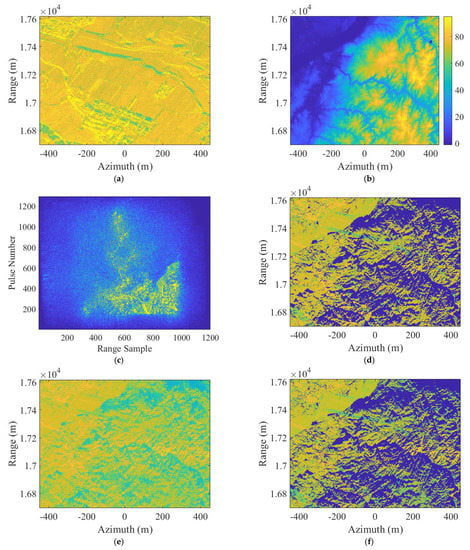
Figure 13.
Scenario experiment results. (a) Real SAR imaging. (b) Measured DEM data. (c) Simulated SAR echo signal. (d) Theoretical occlusion result. (e) SAR imaging result of the classical BPA. (f) SAR imaging result of the proposed Topo-BPA.

Table 2.
Basic SAR system parameters for experiments in Figure 12.
The SAR imaging result of the simulated scenario by the classical BPA and the proposed Topo-BPA are shown in Figure 13e,f, respectively. Because the classical BPA does not avoid the over-matching of the range history between the pixel coordinates and the real target coordinates, its imaging result in Figure 13e is clearly different from Figure 13d, i.e., imaging result appear in the shadow part that does not reflect SAR echo. In contrast, the proposed Topo-BPA ensures that the signal is not correctly reconstructed to the position of the occluded target by constructing an occlusion identifier, so its imaging result in Figure 13f is consistent to Figure 13d, i.e., the amplitude of the imaging results of the occluded area are all 0. To intuitively illustrate the above analyses, as displayed in Table 3, we counted the amplitude values of the imaging results in Figure 13e,f for three randomly selected occluded points in Figure 13a. Evidently, the effectiveness of the proposed Topo-BPA can be further confirmed by the results in Table 3.

Table 3.
Amplitude value of occluded pixel’s imaging result.
In addition to verifying the correctness of the imaging results of the proposed Topo-BPA, the focusing depth of the proposed Topo-BPA was verified through the interpolation refinement contour map in Figure 14. The peak side lobe ratio [59] (−16.2 dB), the integrated side lobe ratio [60] (−10.8 dB), and the resolution [61,62] (1.1 m) calculated from Figure 12 are all close to the theoretical values.
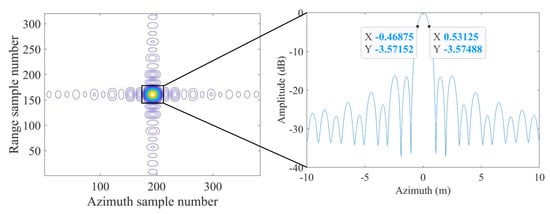
Figure 14.
Interpolation refinement result of the proposed Topo-BPA.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we proposed a Topo-BPA for SAR imaging in the condition of topography variations. The proposed Topo-BPA embeds a newly proposed beam occlusion judgment method before the classical BPA, which not only did not reduce the focus depth of BPA, but improved the imaging accuracy of classical BPA. Numerical experiments show that the proposed Topo-BPA can obtain more precise imaging results compared with the classical BPA. However, we only analyzed the theoretical principles of the Topo-BPA in this paper; whether there is a more efficient implementation in practical applications requires further research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.C.; methodology, Z.C. and J.W.; software, Z.C. and Z.Z.; validation, Z.C., Z.Z. and D.F.; formal analysis, Z.C.; investigation, Z.C. and D.F.; resources, Z.C., Y.H., Q.L. and J.W.; data curation, Z.C. and X.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.C.; writing—review and editing, Z.Z., Q.L. and X.Z.; visualization, Z.C. and Z.Z.; supervision, J.W.; project administration, Z.C., Y.H. and J.W.; funding acquisition, Z.C., Y.H. and J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant numbers 62001062, 62201099, 62271142, and 61901112; by the Engineering Research Center of Mobile Communications, Ministry of Education, grant number cqupt-mct-202103; by the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, China, grant number cstc2021jcyj-bshX0085; by the Opening Project of Guangxi Wireless Broadband Communication and Signal Processing Key Laboratory, grant number GXKL06200214; and the APC was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 62001062.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this paper. Data sharing is not applicable to this paper.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Sandia National Laboratories for providing SAR images.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sun, H.; Shimada, M.; Xu, F. Recent advances in synthetic aperture radar remote sensing—Systems, data processing, and applications. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 2013–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reigber, A.; Scheiber, R.; Jager, M.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Hajnsek, I.; Jagdhuber, T.; Papathanassiou, K.P.; Nannini, M.; Aguilera, E.; Baumgartner, S.; et al. Very-high-resolution airborne synthetic aperture radar imaging: Signal processing and applications. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 759–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, I.G.; Wong, F.H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Savelonas, M.A.; Veinidis, C.N.; Bartsokas, T.K. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition for the Analysis of 2D/3D Remote Sensing Data in Geoscience: A Survey. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Mao, X.; Yu, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Multirotors video synthetic aperture radar: System development and signal processing. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2020, 35, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzter, H.; Cole, B.; Thiel, C.; Schmullius, C. Mapping CORINE Land Cover from Sentinel-1A SAR and SRTM Digital Elevation Model Data using Random Forests. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14876–14898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Feng, L.; Li, S.; Yang, W.; Guo, D. A Refined Pyramid Scene Parsing Network for Polarimetric SAR Image Semantic Segmentation in Agricultural Areas. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Shum, C.K.; Bao, J.; Mao, W. Investigating the Intra-Annual Dynamics of Kunlun Glacier in the West Kunlun Mountains, China, From Ascending and Descending Sentinel-1 SAR Observations. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 1272–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.D.; Jenkins, W.K. Convolution backprojection image reconstruction for spotlight mode synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Trans Image Process. 1992, 1, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulander, L.M.H.; Hellsten, H.; Stenstrom, G. Synthetic-aperture radar processing using fast factorized back-projection. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2003, 39, 760–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Cassola, M.; Prats, P.; Krieger, G.; Moreira, A. Efficient Time-Domain Image Formation with Precise Topography Accommodation for General Bistatic SAR Configurations. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2011, 47, 2949–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.L. Range-Doppler Imaging of Rotating Objects. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1980, AES-16, 23–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M. A New Approach to Range-Doppler SAR Processing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1991, 12, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raney, R.K.; Runge, H.; Bamler, R.; Cumming, I.G.; Wong, F.H. Precision SAR processing using chirp scaling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 786–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sun, G.; Xing, M.; Liang, B.; Gao, Y. Focusing improvement of curved trajectory spaceborne SAR based on optimal LRWC preprocessing and 2-D singular value decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 4246–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Qiao, Z.; Xu, Z. A fast BP algorithm with wavenumber spectrum fusion for high-resolution spotlight SAR imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1460–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhao, F.; Li, N.; Zhang, H. A Modified Cartesian Factorized Back-Projection Algorithm for Highly Squint Spotlight Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 902–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radecki, K.; Samczyński, P.; Gromek, D. Fast Barycentric-Based Back Projection Algorithm for SAR Imaging. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 10635–10643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Liu, Z.; Li, T.; Xie, R.; Zhang, L. An adaptive fast factorized back-projection algorithm with integrated target detection technique for high-resolution and high-squint spotlight SAR imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, W.; Wu, J.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, H. Fast factorized backprojection imaging algorithm integrated with motion trajectory estimation for bistatic forward-looking SAR. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 3949–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulgar, O.; Arif Ergin, A. Improved Pencil Back-Projection Method with Image Segmentation for Far-Field/Near-Field SAR Imaging and RCS Extraction. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 2572–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, O.; Magnard, C.; Ruegg, M.; Meier, E. Focusing of airborne synthetic aperture radar data from highly nonlinear flight tracks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 1844–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Tang, S.; Zhang, L.; Guo, P. Focusing high-resolution airborne SAR with topography variations using and extended BPA based on a time/frequency rotation principle. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Yang, L. A new fast factorized back-projection algorithm with reduced topography sensibility for missile-borne SAR focusing with diving movement. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Xing, M. InSAR phase denoising: A review of current technologies and future directions. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2020, 8, 64–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yang, Z.; Tian, M.; Sun, Y.; Liao, G. An extended moving target detection approach for high-resolution multichannel SAR-GMTI systems based on enhanced shadow-aided decision. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 715–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, H.C.; Poz, A.P.D.; Galo, M.; Habib, A.F. Surface gradient approach for occlusion detection based on triangulated irregular network for true orthophoto generation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Chen, W.; Kelmelis, J.A.; Zhang, D. A comprehensive study on urban true orthorectification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 2138–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Teo, T.; Wen, J.; Rau, J. Occlusion-compensated true orthorectification for high-resolution satellite images. Photogramm. Rec. 2007, 22, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, E.; Habib, A. Automatic representation and reconstruction of DBM from LiDAR data using recursive minimum bounding rectangle. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 93, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H.C.; Galo, M.; Dal Poz, A.P. Height-gradient-based method for occlusion detection in true orthophoto generation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 2222–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschetti, G.; Migliaccio, M.; Riccio, D.; Schirinzi, G. SARAS: A synthetic aperture radar (SAR) raw signal simulator. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, S.; Hinz, S.; Bamler, R. Ray-Tracing Simulation Techniques for Understanding High-Resolution SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 1445–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.F.; Kim, E.M.; Kim, C.J. New methodologies for true orthophoto generation. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2007, 73, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasath, V.B.S.; Haddad, O. Radar shadow detection in synthetic aperture radar images using digital elevation model and projections. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 083628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Wu, R.; Su, Z.; Lu, X. Ground clutter suppression in airborne weather radar via terrain visibility analysis. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2012, 34, 351–355. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, M.V.A.; Magalhães, S.V.G.; Magalhães, M.A.; Franklin, W.R.; Cutler, B.M. Efficient viewshed computation on terrain in external memory. GeoInformatica 2011, 15, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, G.B.; Zhang, Y.J.; Sun, G.C.; Xing, M.D.; Bao, Z. Fast method for SAR echo simulation of a three-dimensional ground scene. J. Xidian Univ. 2017, 44, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Sandia National Laboratories SAR image of Kirtland AFB Building. Available online: https://www.sandia.gov/app/uploads/sites/124/2021/06/Ku-band-image-of-a-building-on-Kirtland-AFB.png (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Moreira, A.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Younis, M.; Krieger, G.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhang, L.; Guo, P.; Zhao, Y. An Omega-K Algorithm for Highly Squinted Missile-Borne SAR with Constant Acceleration. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1569–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tao, M.; Chen, S.; Xi, F.; Liu, Z. On the Mutual Interference Between Spaceborne SARs: Modeling, Characterization, and Mitigation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 8470–8485. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.; Xia, X.G.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X.; Liao, G.; Jiang, X. Ground moving target refocusing in SAR imagery based on RFRT-FrFT. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 5476–5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y.; Cao, Y. High-resolution forward-looking multichannel SAR imagery with array deviation angle calibration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 6914–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wei, H.; Lin, C.; Liu, N.; Wan, J. General range model for multi-channel SAR/GMTI with curvilinear flight trajectory. Electron. Lett. 2019, 55, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, X. Reweighted Tensor Factorization Method for SAR Narrowband and Wideband Interference Mitigation Using Smoothing Multiview Tensor Model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 3298–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Jiang, W. On clutter sparsity analysis in space-time adaptive processing airborne radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1214–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qiao, Z.; Xing, M.D.; Yang, L.; Bao, Z. A robust motion compensation approach for UAV SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3202–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, F.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Hong, W. An improved map-drift algorithm for unmanned aerial vehicle SAR imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tang, J.; Wang, R.; Deng, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, N. An Accelerated Backprojection Algorithm for Monostatic and Bistatic SAR Processing. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Suo, Z.; Jiang, P.; Li, H. A Fast Back-Projection SAR Imaging Algorithm Based on Wavenumber Spectrum Fusion for High Maneuvering Platforms. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Bao, M.; Sun, G.; Han, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, M. Refocusing of Moving Ships in Squint SAR Images Based on Spectrum Orthogonalization. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ash, J.N. An Autofocus Method for Backprojection Imagery in Synthetic Aperture Radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Pu, W.; Li, Z.; Yang, J. An Effective Autofocus Method for Fast Factorized Back-Projection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6145–6154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Wan, J.; Li, D.; Tan, X. Efficient Ground Moving Target Imaging Method for Synthetic Aperture Radar With Target Azimuth Ambiguity. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 23297–23307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Hong, W. An Efficient Graph-Based Algorithm for Time-Varying Narrowband Interference Suppression on SAR System. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 8418–8432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lin, C.; Huang, Y.; Tang, S. Ground Moving Target Imaging and Analysis for Near-Space Hypersonic Vehicle-Borne Synthetic Aperture Radar System with Squint Angle. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorham, L.A.; Moore, L.J. SAR image formation toolbox for MATLAB. In Proceedings of the SPIE Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XVII, Orlando, FL, USA, 8–9 April 2010; Volume 7699, p. 769906. [Google Scholar]
- Khwaja, A.S.; Ferro-Famil, L.; Pottier, E. Efficient stripmap SAR raw data generation taking into account sensor trajectory deviations. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, O.; Kartal, M. Efficient stripmap-mode SAR raw data simulation including platform angular deviations. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yao, X.; Tang, H.; Yin, Q.; Hu, Y.; Lei, B. Multiple mode SAR raw data simulation and parallel acceleration for Gaofen-3 mission. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liang, X.-D.; Chen, L.-Y.; Wang, L.-N.; Li, K. First Demonstration of Joint Wireless Communication and High-Resolution SAR Imaging Using Airborne MIMO Radar System. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6619–6632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).