Radar Reflectivity Assimilation Based on Hydrometeor Control Variables and Its Impact on Short-Term Precipitation Forecasting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. H-BEC in Variational Assimilation Framework
2.2. Hydrometeor Mixing Ratio Retrievals for Indirect Reflectivity Assimilation
3. Characteristics of H-BEC
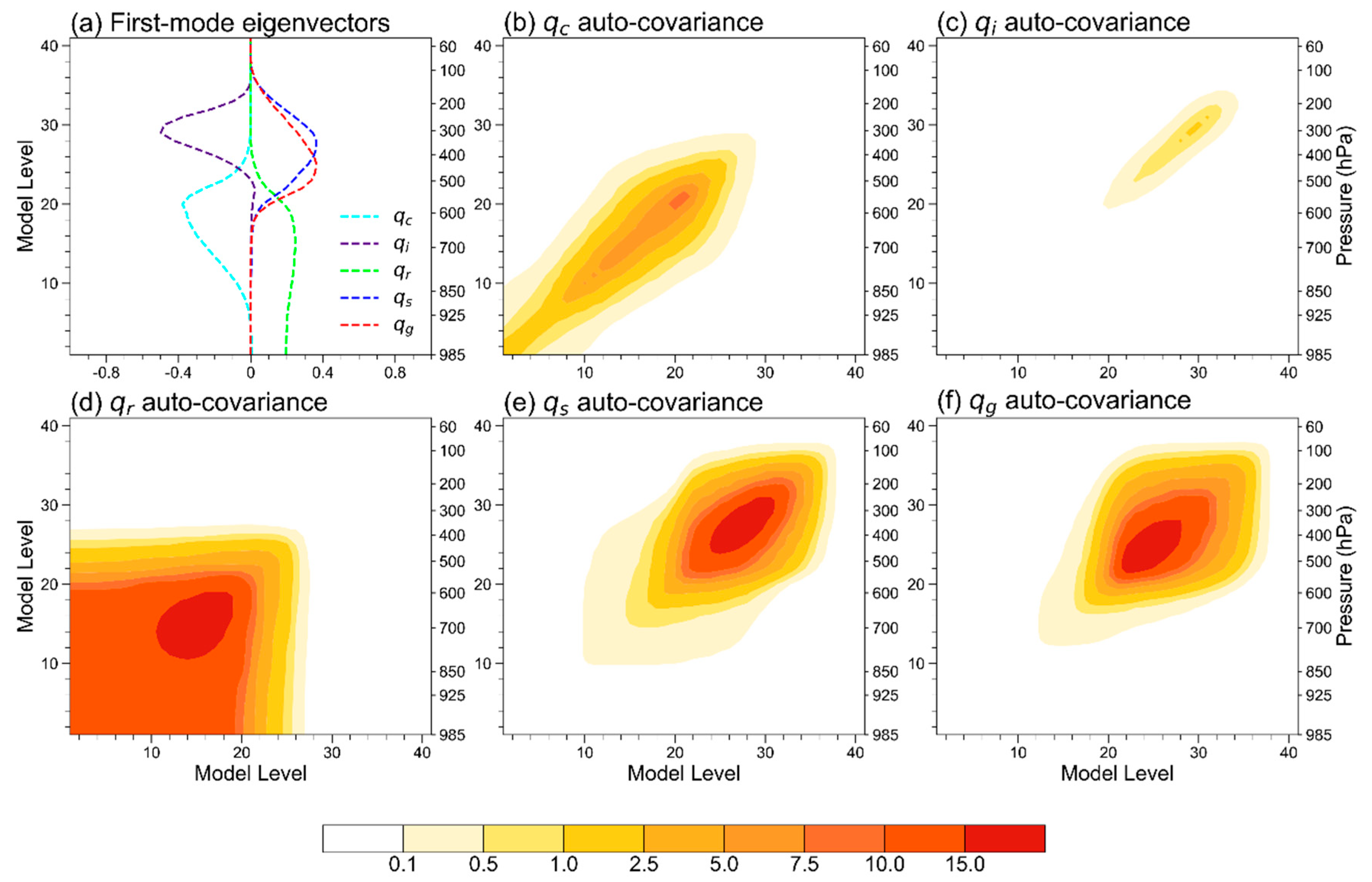
3.1. Vertical Correlations of the Hydrometeor Background Errors
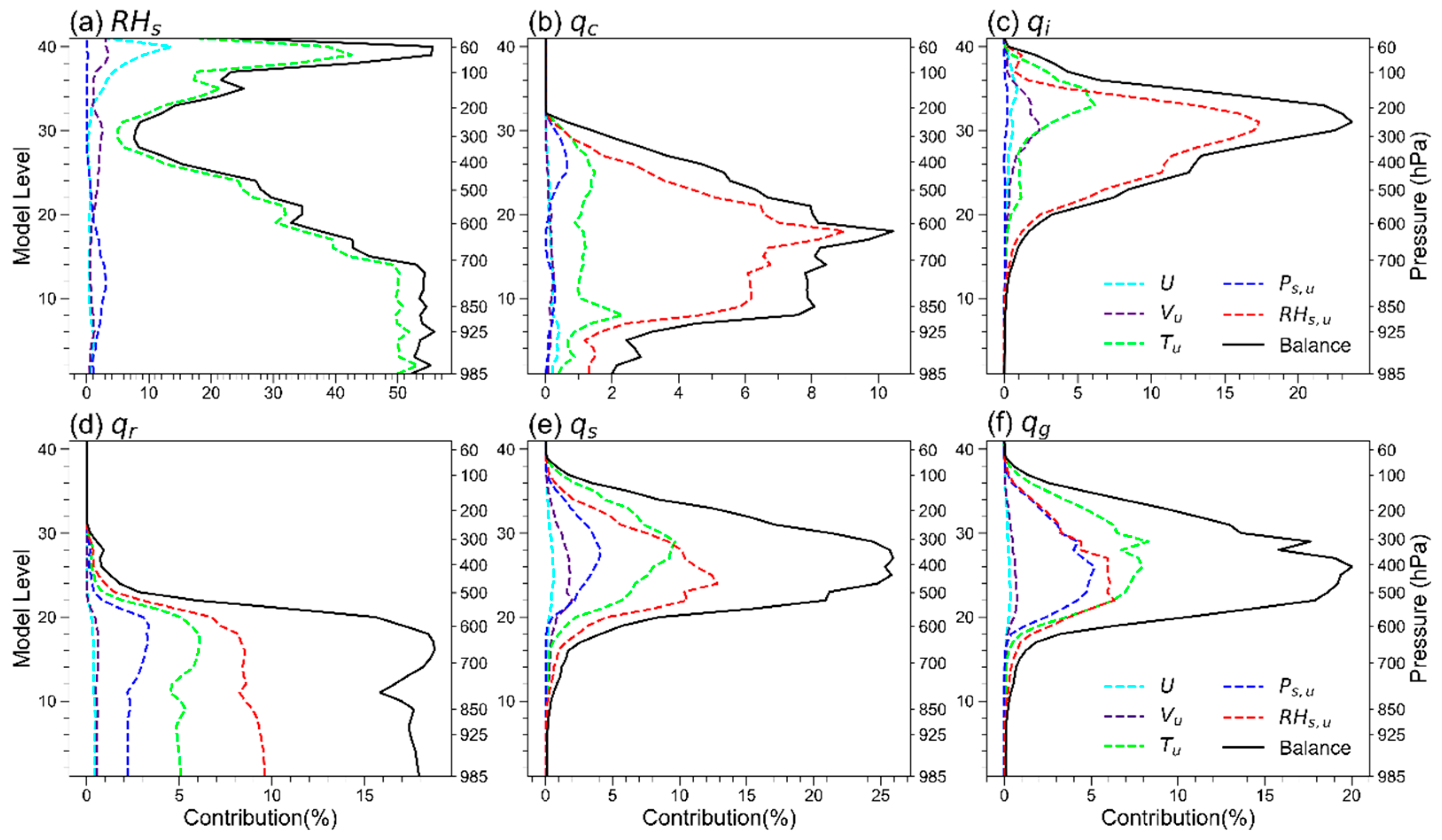
3.2. Multivariable Correlations in the H-BEC
3.3. Single Radar Reflectivity Observation Tests
4. Evaluation of Cycling Data Assimilation and Forecasting Experiments
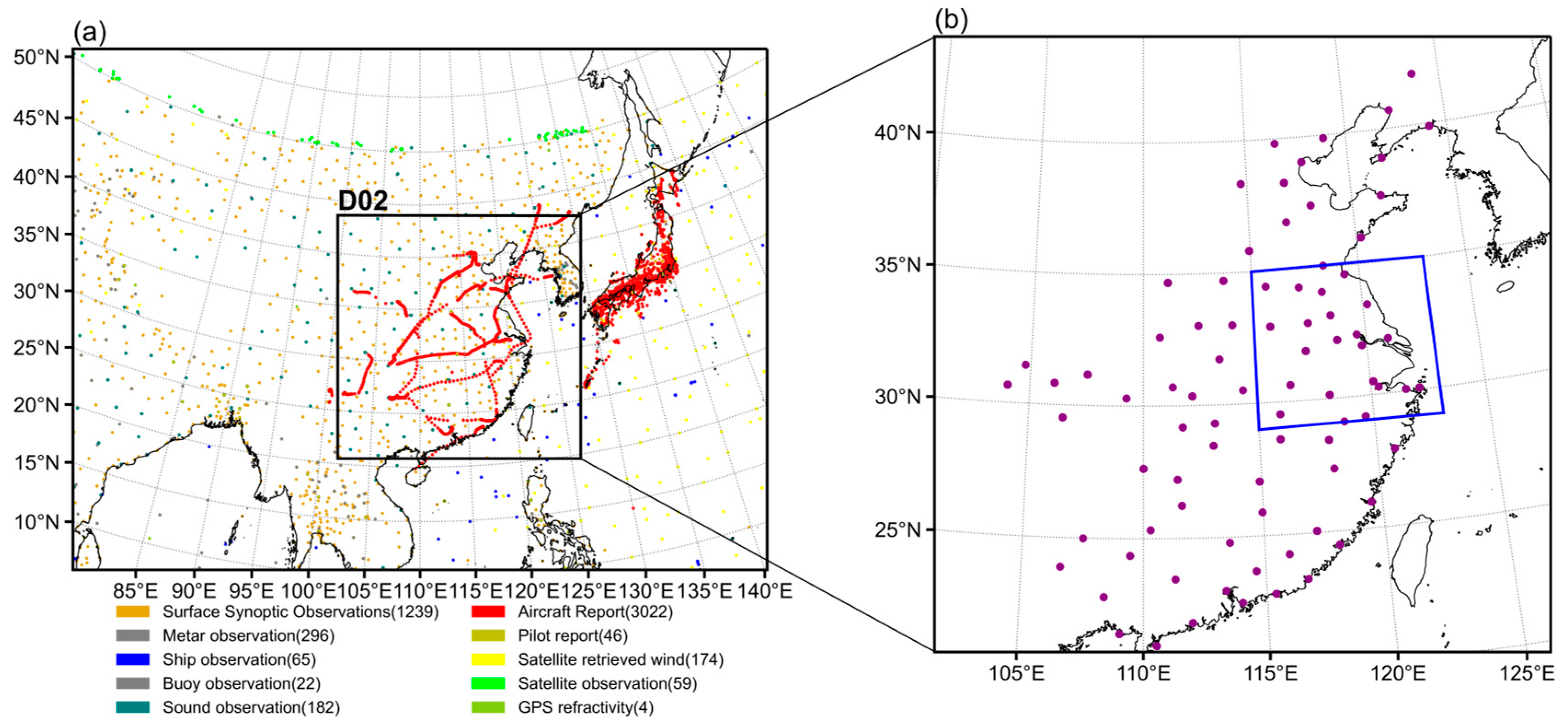
4.1. Model, Configurations, and Convective Rainfall Cases
4.2. Root Mean Square Error (RMSE)
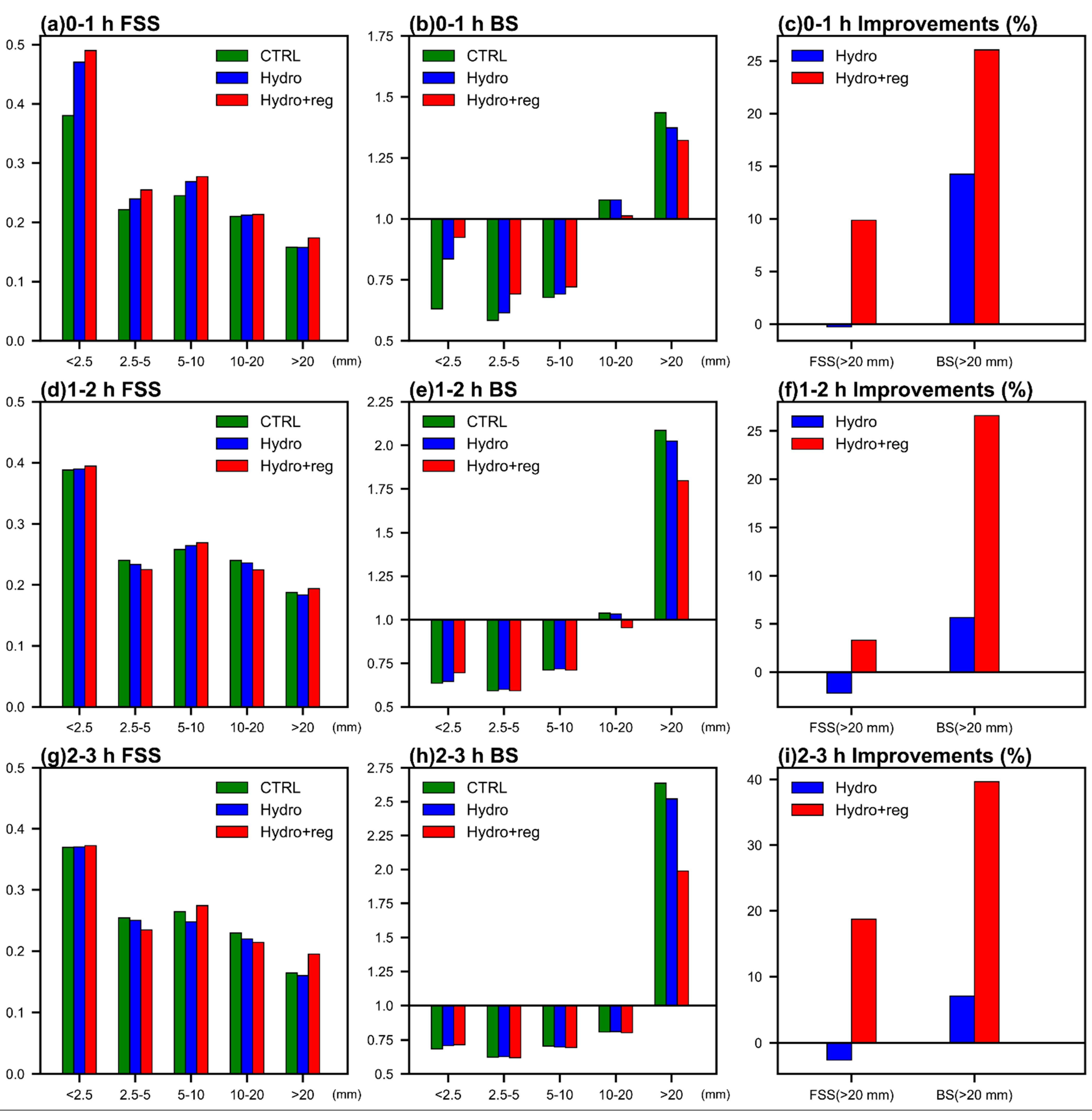
4.3. Precipitation Score
5. Diagnostics for a Fast-Moving Squall Line Case on 6 July 2019
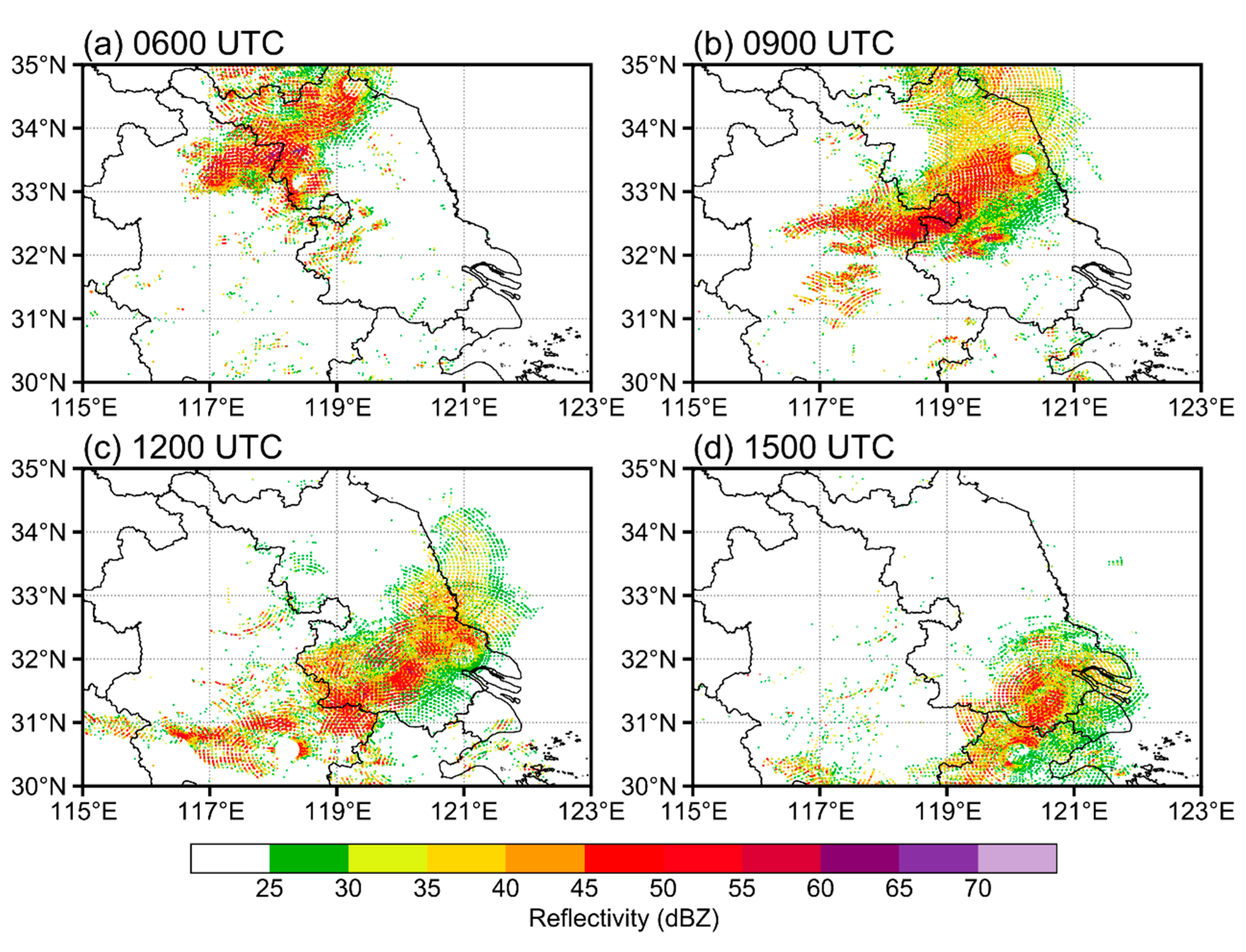
5.1. Overview of the Squall Line
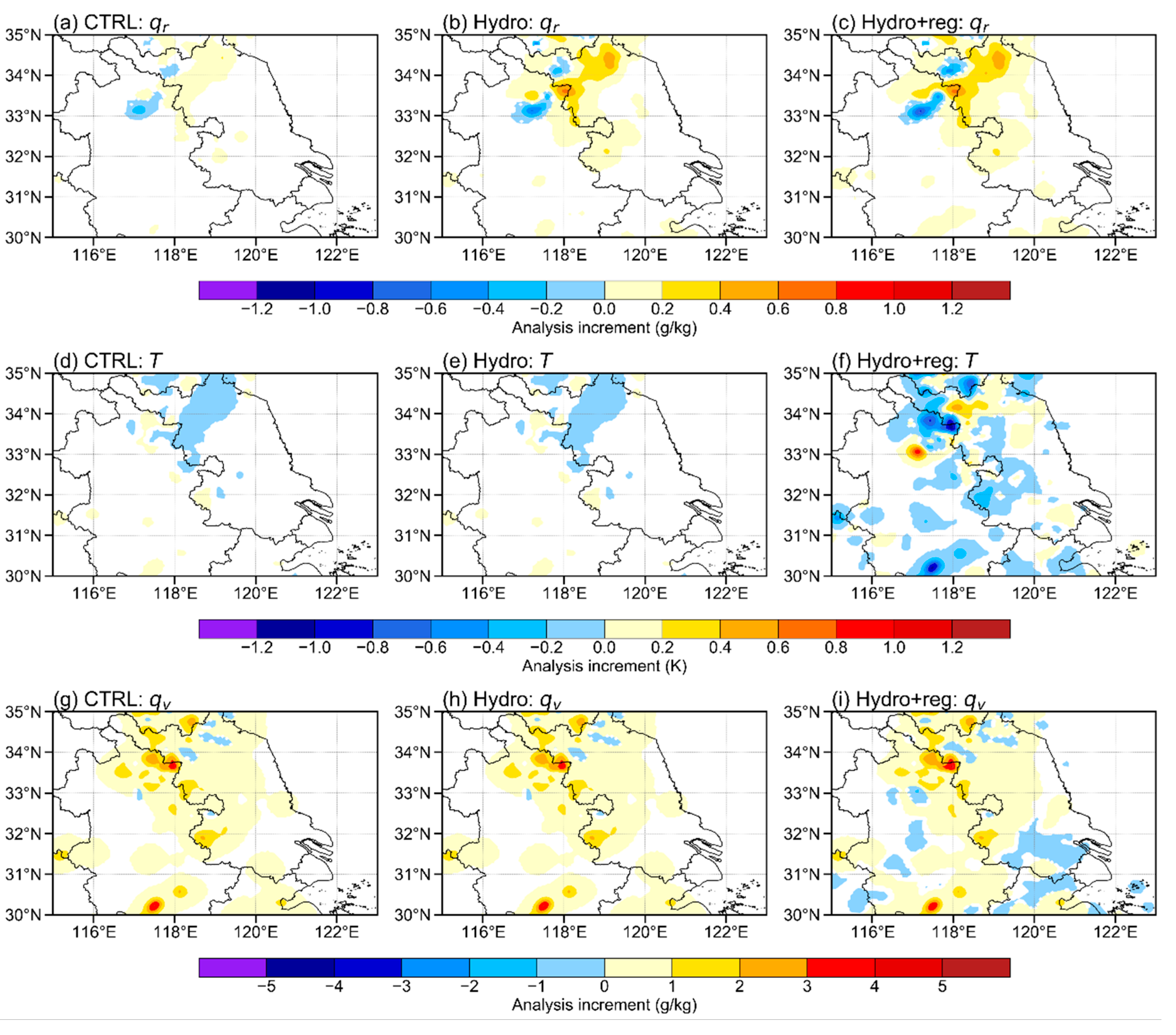
5.2. The Analysis Increment in the First Assimilation Cycle
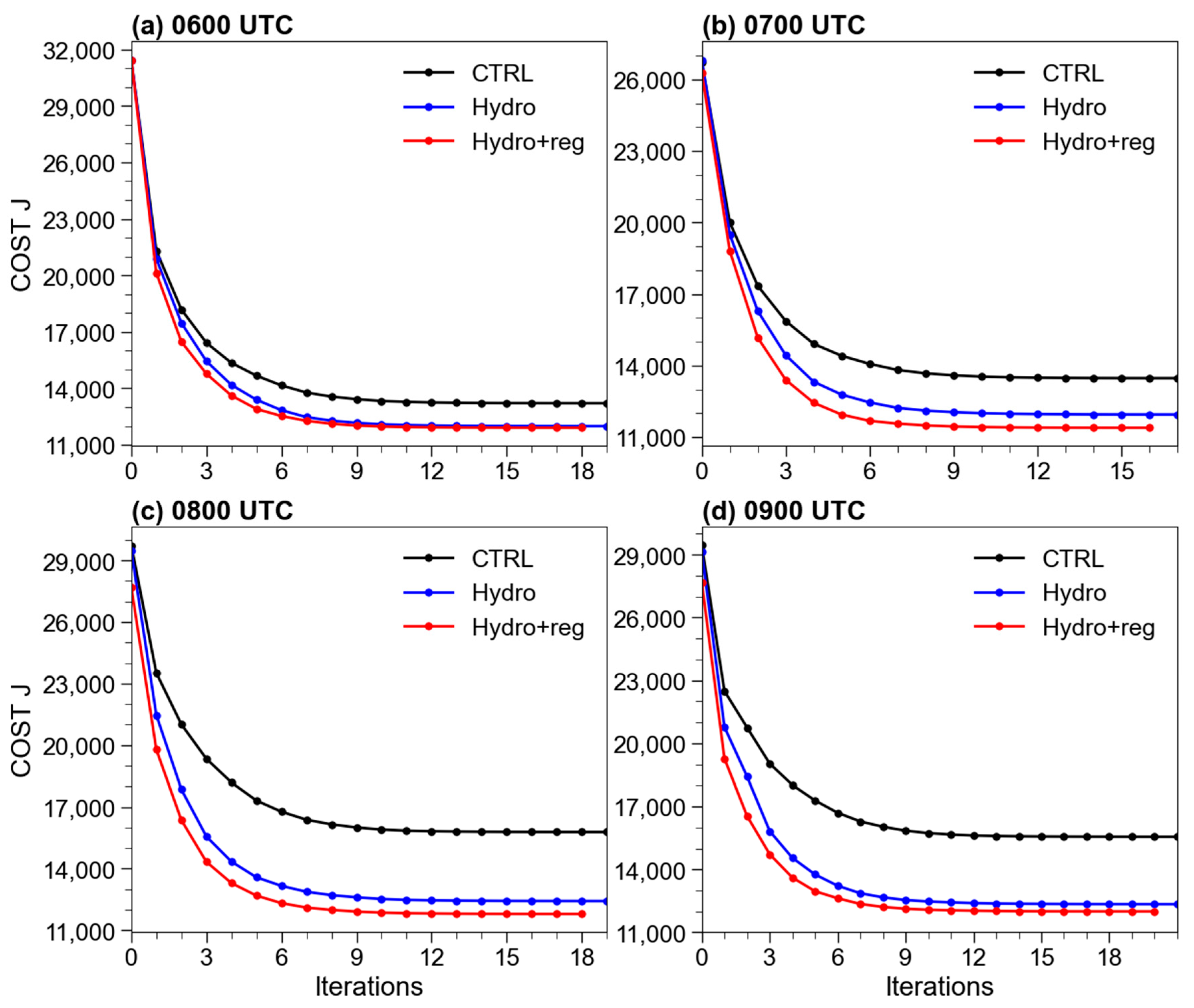
5.3. Cost Function
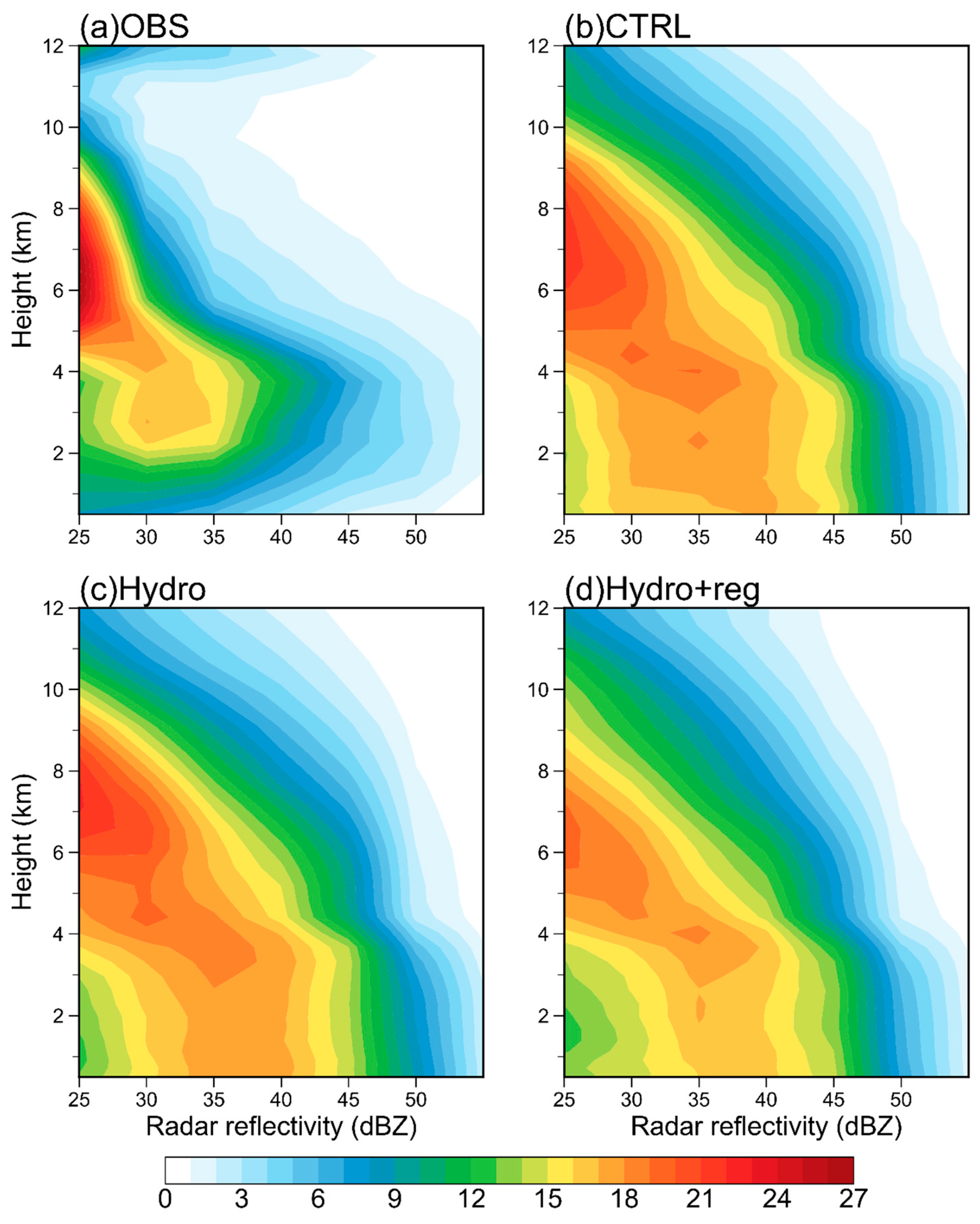
5.4. Precipitation Forecast
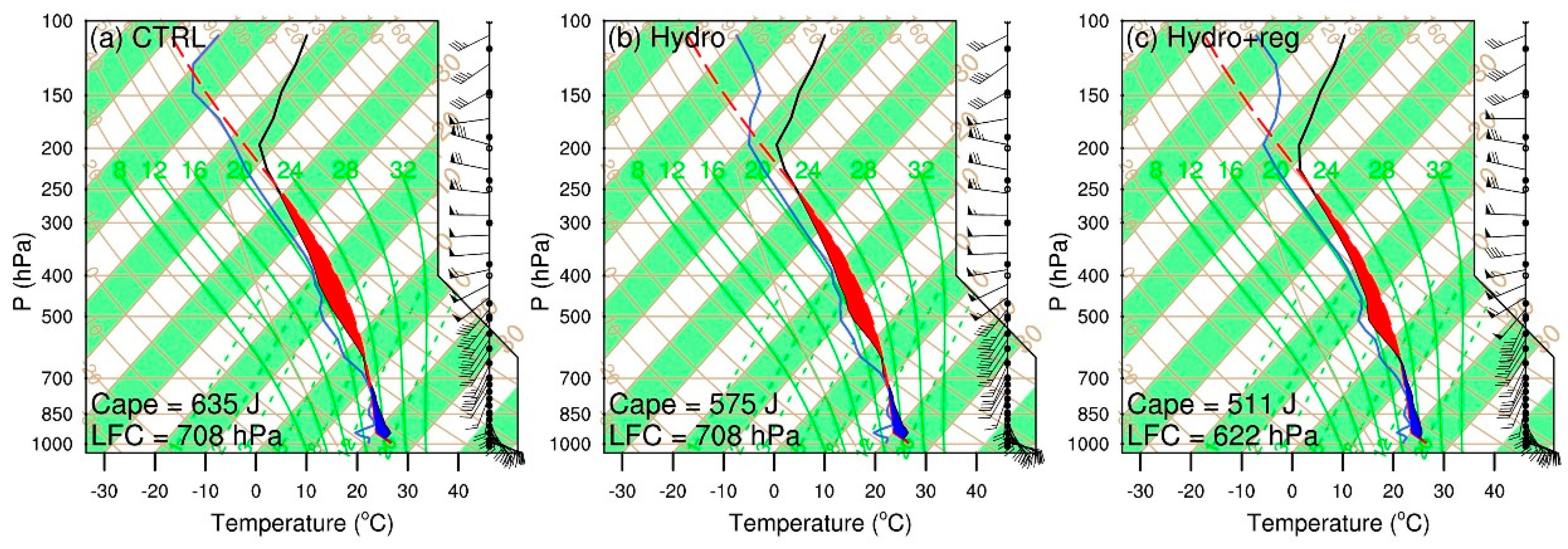
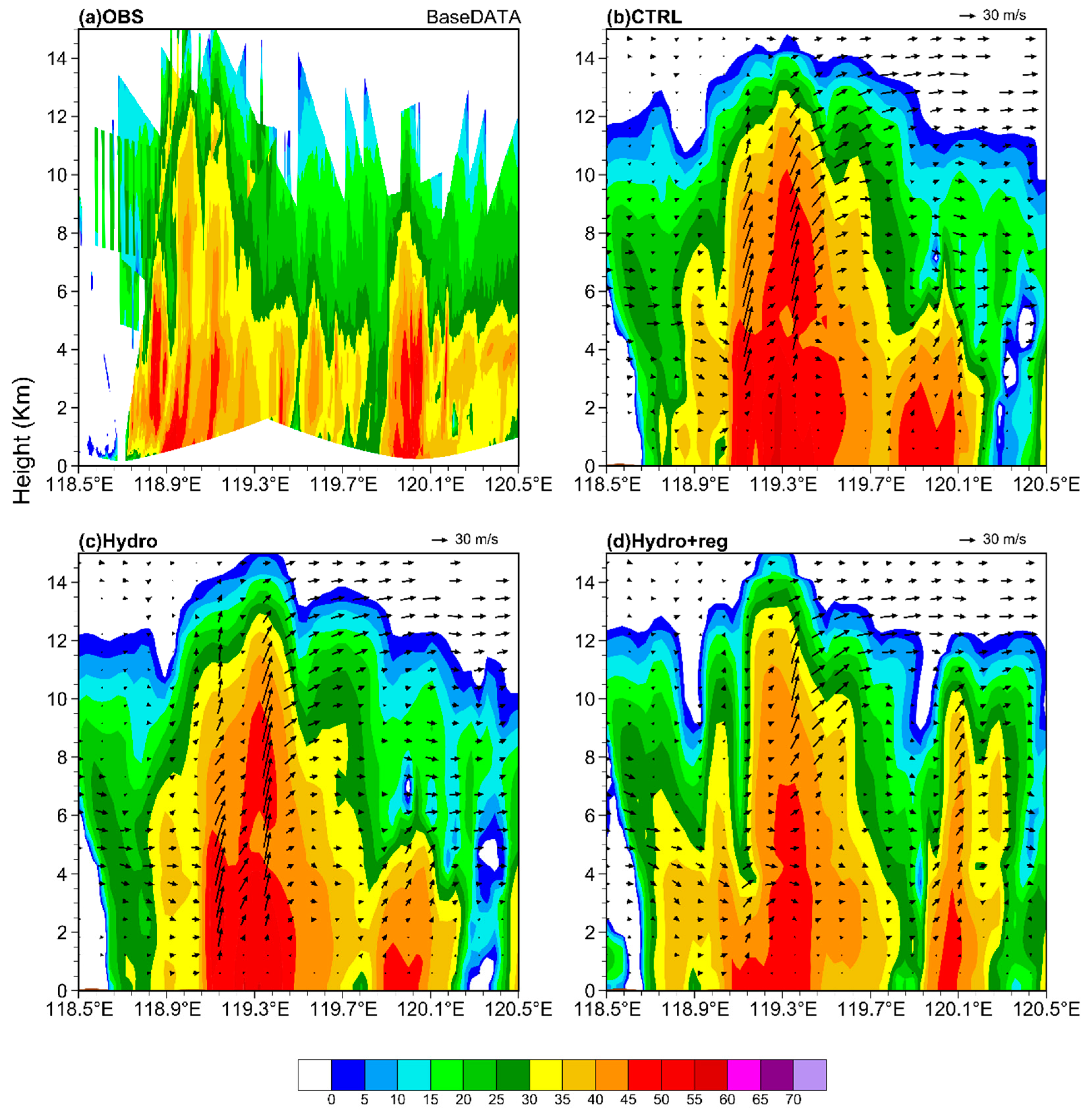
5.5. Thermodynamic and Dynamical Diagnostics
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bauer, P.; Thorpe, A.; Brunet, G. The Quiet Revolution of Numerical Weather Prediction. Nature 2015, 525, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Xiao, H.; Yang, H.; Chen, H.; Guo, J.; Sun, Y.; Feng, L. Raindrop Size Distribution and Microphysical Characteristics of a Great Rainstorm in 2016 in Beijing, China. Atmos. Res. 2020, 239, 104895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errico, R.M.; Bauer, P.; Mahfouf, J.F. Issues Regarding the Assimilation of Cloud and Precipitation Data. J. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 64, 3785–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, W.; Satoh, M. Evaluation of Precipitating Hydrometeor Parameterizations in a Single-Moment Bulk Microphysics Scheme for Deep Convective Systems over the Tropical Central Pacific. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 2654–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Min, J.; Huang, X.Y.; Minnis, P.; Zhang, R.; Haggerty, J.; Palikonda, R. Variational Assimilation of Cloud Liquid/Ice Water Path and Its Impact on NWP. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2015, 54, 1809–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, R.; Meng, D.; Min, J.; Zhang, L. Variational Assimilation of Satellite Cloud Water/Ice Path and Microphysics Scheme Sensitivity to the Assimilation of a Rainfall Case. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 33, 1158–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Potthast, R.W.E.; Wang, Y. The Evaluation of EnVar Method Including Hydrometeors Analysis Variables for Assimilating Cloud Liquid/Ice Water Path on Prediction of Rainfall Events. Atmos. Res. 2019, 219, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Development of Convective-Scale Static Background Error Covariance within GSI-Based Hybrid EnVar System for Direct Radar Reflectivity Data Assimilation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2021, 149, 2713–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckwerth, T.M.; Pettet, C.R.; Fabry, F.; Park, S.; Lemone, M.A.; Wilson, J.W. Radar Refractivity Retrieval: Validation and Application to Short-Term Forecasting. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2005, 44, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlin, J.T.; Ryzhkov, A.V.; Snyder, J.C.; Khain, A. Hydrometeor Mixing Ratio Retrievals for Storm-Scale Radar Data Assimilation: Utility of Current Relations and Potential Benefits of Polarimetry. Mon. Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 2981–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Qin, L.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Y. Improved Streamflow Forecast in a Small-Medium Sized River Basin with Coupled WRF and WRF-Hydro: Effects of Radar Data Assimilation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Xue, M.; Gao, J.; Brewster, K. 3DVAR and Cloud Analysis with WSR-88D Level-II Data for the Prediction of the Fort Worth, Texas, Tornadic Thunderstorms. Part II: Impact of Radial Velocity Analysis via 3DVAR. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 699–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xue, M.; Wilson, J.W.; Zawadzki, I.; Ballard, S.P.; Onvlee-Hooimeyer, J.; Joe, P.; Barker, D.M.; Li, P.W.; Golding, B.; et al. Use of NWP for Nowcasting Convective Precipitation: Recent Progress and Challenges. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 409–426. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Q.; Kuo, Y.H.; Sun, J.; Lee, W.C.; Barker, D.M.; Lim, E. An Approach of Radar Reflectivity Data Assimilation and Its Assessment with the Inland QPF of Typhoon Rusa (2002) at Landfall. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2007, 46, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montmerle, T.; Faccani, C. Mesoscale Assimilation of Radial Velocities from Doppler Radars in a Preoperational Framework. Mon. Weather Rev. 2009, 137, 1939–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, H. Radar Data Assimilation with WRF 4D-Var. Part II: Comparison with 3D-Var for a Squall Line over the U.S. Great Plains. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 2245–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Xue, M. Assimilation of Radar Radial Velocity Data with the WRF Hybrid Ensemble–3DVAR System for the Prediction of Hurricane Ike (2008). Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 3507–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, A.; Gao, J.; Koch, S.E.; Wang, Y.; Pan, S.; Fierro, A.O.; Cui, C.; Min, J. Assimilation of Radar Radial Velocity, Reflectivity, and Pseudo–Water Vapor for Convective-Scale NWP in a Variational Framework. Mon. Weather Rev. 2019, 147, 2877–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, K.; Klink, S.; Schraff, C. Assimilation of radar derived rain rates into the convective scale model COSMO-DE at DWD. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 134, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Stensrud, D.J. Assimilation of Reflectivity Data in a Convective-Scale, Cycled 3DVAR Framework with Hydrometeor Classification. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 69, 1054–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, J.; Fan, S.; Huang, X. Indirect Assimilation of Radar Reflectivity with WRF 3D-Var and Its Impact on Prediction of Four Summertime Convective Events. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Gao, J.; Sun, T.; Carlin, J.T. A Radar Reflectivity Data Assimilation Method Based on Background Dependent Hydrometeor Retrieval: An Observing System Simulation Experiment. Atmos. Res. 2020, 243, 105022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Chen, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Meng, D. A Multi-Time-Scale Four-Dimensional Variational Data Assimilation Scheme and Its Application to Simulated Radial Velocity and Reflectivity Data. Mon. Weather Rev. 2020, 148, 2063–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.-Y.; Auligné, T. Radar Data Assimilation with WRF 4D-Var. Part I: System Development and Preliminary Testing. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 2224–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auligné, T.; Lorenc, A.; Michel, Y.; Montmerle, T.; Jones, A.; Hu, M.; Dudhia, J. Toward a New Cloud Analysis and Prediction System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 92, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houtekamer, P.L.; Zhang, F. Review of the Ensemble Kalman Filter for Atmospheric Data Assimilation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 4489–4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Sun, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, Z.; Chen, H. Improving Short-Term Precipitation Forecasting with Radar Data Assimilation and a Multiscale Hybrid Ensemble–Variational Strategy. Mon. Weather Rev. 2022, 150, 2357–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, S.; Crook, N.A.; Sun, J.; Xiao, Q.; Barker, D.M. An Examination of WRF 3DVAR Radar Data Assimilation on Its Capability in Retrieving Unobserved Variables and Forecasting Precipitation through Observing System Simulation Experiments. Mon. Weather Rev. 2009, 137, 4011–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Tong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, C.Y.; Xu, D. Comparison of the Impacts of Momentum Control Variables on High-Resolution Variational Data Assimilation and Precipitation Forecasting. Mon. Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, N.; Janjić, T.; Schraff, C.; Leuenberger, D.; Weissmann, M.; Reich, H.; Brousseau, P.; Montmerle, T.; Wattrelot, É.; Bučánek, A.; et al. Survey of Data Assimilation Methods for Convective-scale Numerical Weather Prediction at Operational Centres. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 144, 1218–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y.; Pan, L.; Wang, H.; Cheng, W.Y.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Lan, H.; Yang, H.L.; et al. Forecasting Severe Convective Storms with WRF-Based RTFDDA Radar Data Assimilation in Guangdong, China. Atmos. Res. 2018, 209, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Yu, F.; Wei, W. Effect of the Assimilation Frequency of Radar Reflectivity on Rain Storm Prediction by Using WRF-3DVAR. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.H.; Min, K.H. Forecast Characteristics of Radar Data Assimilation Based on the Scales of Precipitation Systems. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannister, R.N. A Review of Forecast Error Covariance Statistics in Atmospheric Variational Data Assimilation. I: Characteristics and Measurements of Forecast Error Covariances. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 134, 1951–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Rizvi, S.R.H.; Huang, X.Y.; Min, J.; Zhang, X. Balance Characteristics of Multivariate Background Error Covariances and Their Impact on Analyses and Forecasts in Tropical and Arctic Regions. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2013, 121, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Cha, D.H.; Kim, J. Tuning of Length-Scale and Observation-Error for Radar Data Assimilation Using Four Dimensional Variational (4D-Var) Method. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2017, 18, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Hólm, E. Development of Cloud Condensate Background Errors. ECMWF Newsl. 2011, 128, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, Y.; Auligne, T.; Montmerle, T. Heterogeneous Convective-Scale Background Error Covariances with the Inclusion of Hydrometeor Variables. Mon. Weather Rev. 2011, 139, 2994–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descombes, G.; Auligne, T.; Vandenberghe, F.; Barker, D.M.; Barre, J. Generalized Background Error Covariance Matrix Model (GEN_BE v2.0). Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 669–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xue, M.; Kong, R. Direct Assimilation of Radar Reflectivity Data Using 3DVAR: Treatment of Hydrometeor Background Errors and OSSE Tests. Mon. Weather Rev. 2019, 147, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.M.; Huang, W.; Guo, Y.R.; Bourgeois, A.J.; Xiao, Q.N. A Three-Dimensional Variational Data Assimilation System for MM5: Implementation and Initial Results. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 897–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtier, P.; Thepaut, J.N.; Hollingsworth, A. A Strategy for Operational Implementation of 4D-Var, Using an Incremental Approach. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1994, 120, 1367–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derber, J.; Bouttier, F. A Reformulation of the Background Error Covariance in the ECMWF Global Data Assimilation System. Tellus A 1999, 51, 195–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Purser, R.J.; Parrish, D.F. Three-Dimensional Variational Analysis with Spatially Inhomogeneous Covariances. Mon. Weather Rev. 2002, 130, 2905–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-L.; Farley, R.D.; Orville, H.D. Bulk Parameterization of the Snow Field in a Cloud Model. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1983, 22, 1065–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, M.S.; Straka, J.M.; Rasmussen, E.N. Precipitation and Evolution Sensitivity in Simulated Deep Convective Storms: Comparisons between Liquid-Only and Simple Ice and Liquid Phase Microphysics. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 1897–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Xue, M. Ensemble Kalman Filter Assimilation of Doppler Radar Data with a Compressible Nonhydrostatic Model: OSS Experiments. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 1789–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowell, D.C.; Wicker, L.J.; Snyder, C. Ensemble Kalman Filter Assimilation of Radar Observations of the 8 May 2003 Oklahoma City Supercell: Influences of Reflectivity Observations on Storm-Scale Analyses. Mon. Weather Rev. 2011, 139, 272–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, D.F.; Derber, J.C. The National Meteorological Center’s Spectral Statistical-Interpolation Analysis System. Mon. Weather Rev. 1992, 120, 1747–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B. A Time-Split Nonhydrostatic Atmospheric Model for Weather Research and Forecasting Applications. J. Comput. Phys. 2008, 227, 3465–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.Y.; Lim, J.O.J. The WRF Single-Moment 6-Class Microphysics Scheme (WSM6). Asia Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 42, 129–151. [Google Scholar]
- Mlawer, E.J.; Taubman, S.J.; Brown, P.D.; Iacono, M.; Clough, S.A. Radiative Transfer for Inhomogeneous Atmospheres: RRTM, a Validated Correlated-k Model for the Longwave. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 16663–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudhia, J. Numerical Study of Convection Observed during the Winter Monsoon Experiment Using a Mesoscale Two-Dimensional Model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46, 3077–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A New Vertical Diffusion Package with an Explicit Treatment of Entrainment Processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, J.S.; Kain, J. The Kain-Fritsch Convective Parameterization: An Update. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2004, 43, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, M.; Wang, W.; Dudhia, J.; LeMone, M.A.; Mitchell, K.; Ek, M.; Gayno, G.; Wegiel, J.; Cuenca, R. Implementation and Verification of the Unified NOAH Land Surface Mode in the WRF model. In Proceedings of the 20th Conference on Weather Analysis and Forecasting/16th Conference on Numerical Weather Prediction, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 January 2004; pp. 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, A.; Wang, X.; Carley, J.R.; Wicker, L.J.; Karstens, C.D. A Comparison of Multiscale GSI-Based EnKF and 3DVar Data Assimilation Using Radar and Conventional Observations for Midlatitude Convective-Scale Precipitation Forecasts. Mon. Weather Rev. 2015, 143, 3087–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhao, P.; Pan, Y.; Yu, J. A High Spatiotemporal Gauge-satellite Merged Precipitation Analysis over China. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2014, 119, 3063–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggian, N.; Roux, B.; Steinle, P.; Ebert, B. Fast Calculation of the Fractions Skill Score. MAUSAM 2021, 66, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuter, S.E.; Houze, R.A. Three-Dimensional Kinematic and Microphysical Evolution of Florida Cumulonimbus. Part I: Spatial Distribution of Updrafts, Downdrafts, and Precipitation. Mon. Weather Rev. 1995, 123, 1921–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posselt, D.J.; Li, X.; Tushaus, S.A.; Mecikalski, J.R. Assimilation of Dual-Polarization Radar Observations in Mixed- and Ice-Phase Regions of Convective Storms: Information Content and Forward Model Errors. Mon. Weather Rev. 2015, 143, 2611–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
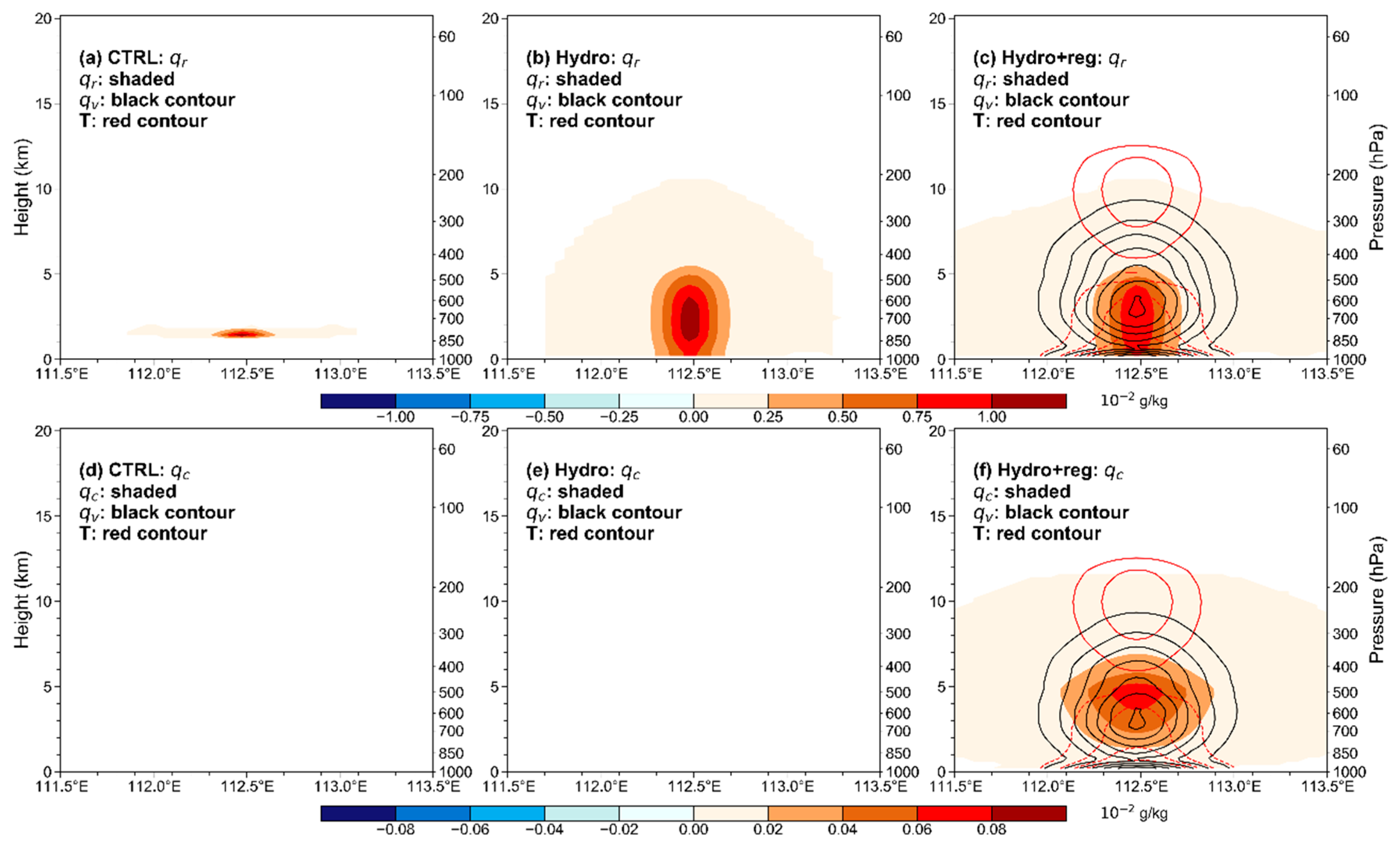



| Name | Vertical Correlations | Multivariable Correlations |
|---|---|---|
| CTRL | No | No |
| Hydro | Yes | No |
| Hydro+reg | Yes | Yes |
| Case (Period in the Whole Process Except Spin-Up) | Type and Characteristics of the Case |
|---|---|
| 17 July 2018, 0600–1200 UTC | Squall line, slow-moving |
| 6 July 2019, 0600–1200 UTC | Squall line, fast-moving |
| 17 July 2019, 0900–1500 UTC | Multicellular storm, stable |
| 26 July 2019, 1800 UTC–27 July, 0000 UTC | Multicellular storm, local |
| 27 July 2019, 1200–1800 UTC | Multicellular storm, fast-moving |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, H.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, S.; Meng, D.; Sun, T. Radar Reflectivity Assimilation Based on Hydrometeor Control Variables and Its Impact on Short-Term Precipitation Forecasting. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030672
Zheng H, Chen Y, Zheng S, Meng D, Sun T. Radar Reflectivity Assimilation Based on Hydrometeor Control Variables and Its Impact on Short-Term Precipitation Forecasting. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(3):672. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030672
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Hong, Yaodeng Chen, Shiwei Zheng, Deming Meng, and Tao Sun. 2023. "Radar Reflectivity Assimilation Based on Hydrometeor Control Variables and Its Impact on Short-Term Precipitation Forecasting" Remote Sensing 15, no. 3: 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030672
APA StyleZheng, H., Chen, Y., Zheng, S., Meng, D., & Sun, T. (2023). Radar Reflectivity Assimilation Based on Hydrometeor Control Variables and Its Impact on Short-Term Precipitation Forecasting. Remote Sensing, 15(3), 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030672





