Subbasin Spatial Scale Effects on Hydrological Model Prediction Uncertainty of Extreme Stream Flows in the Omo Gibe River Basin, Ethiopia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
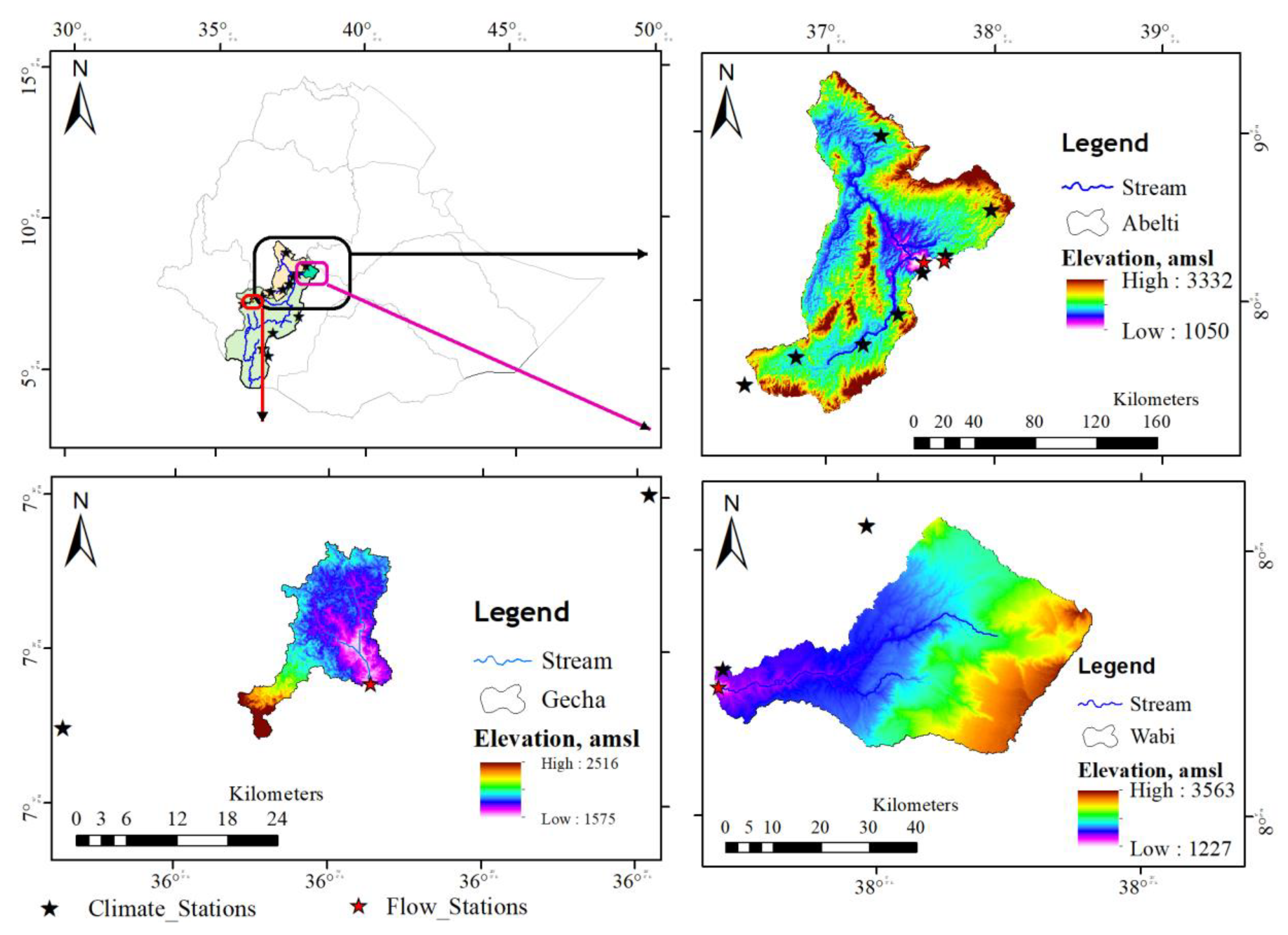
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Description
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. The SWAT Model
2.3.2. Parameter Sensitivity
2.3.3. Hydrologic Model Calibration and Validation
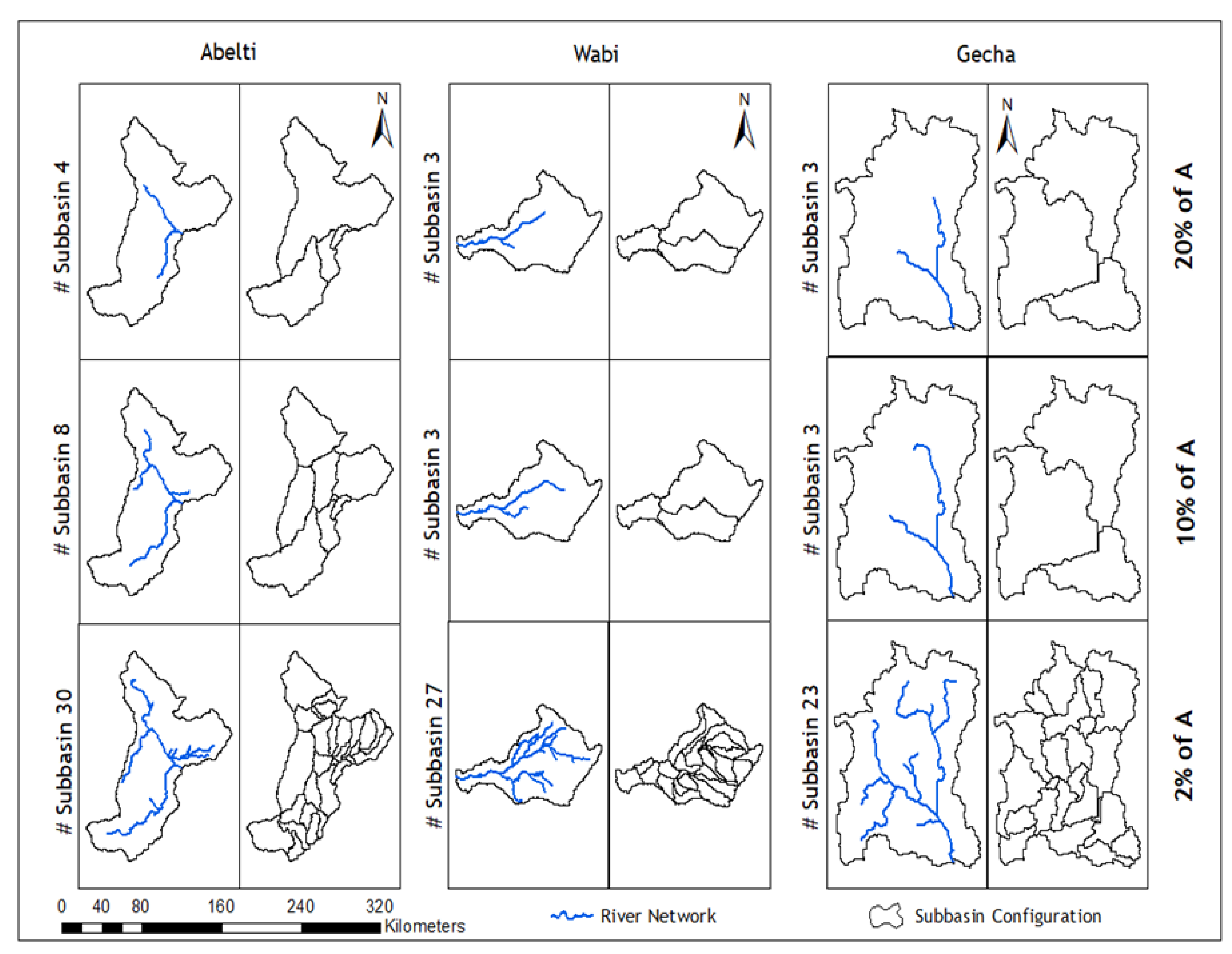
2.3.4. Spatial Scales of the Subbasin for Modeling High and Low Flows
3. Results
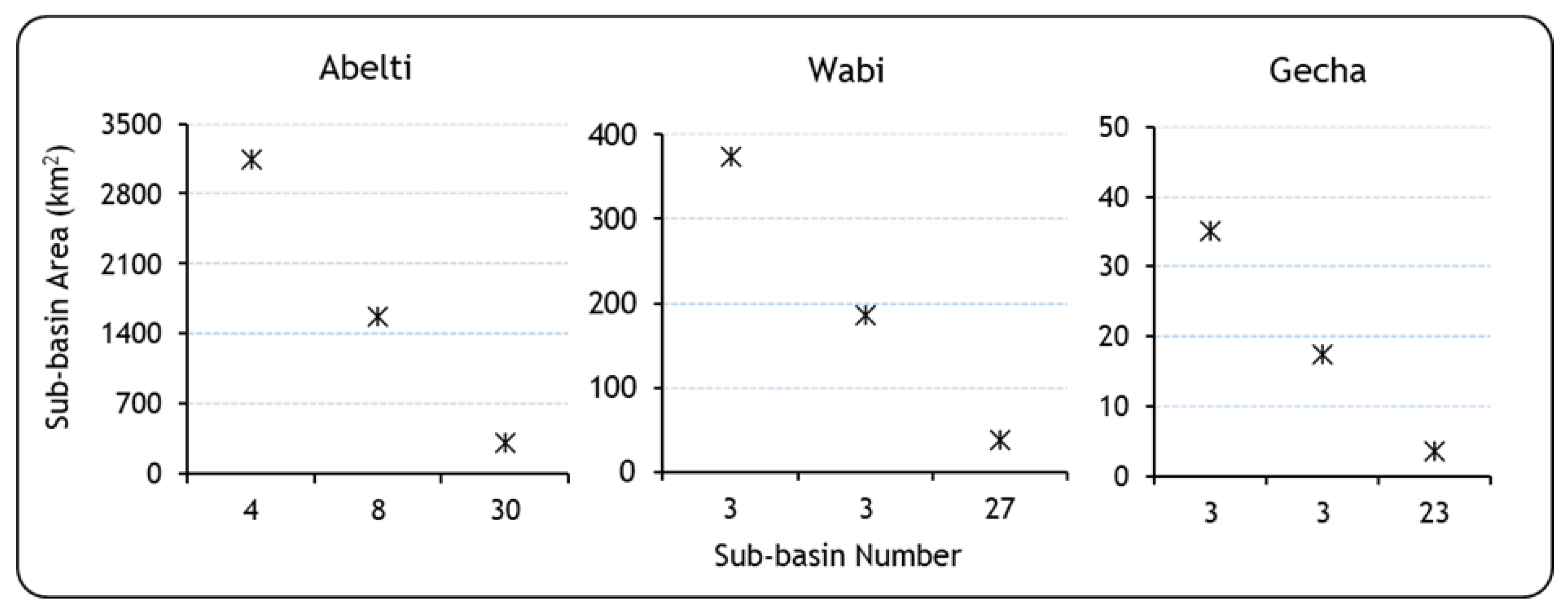
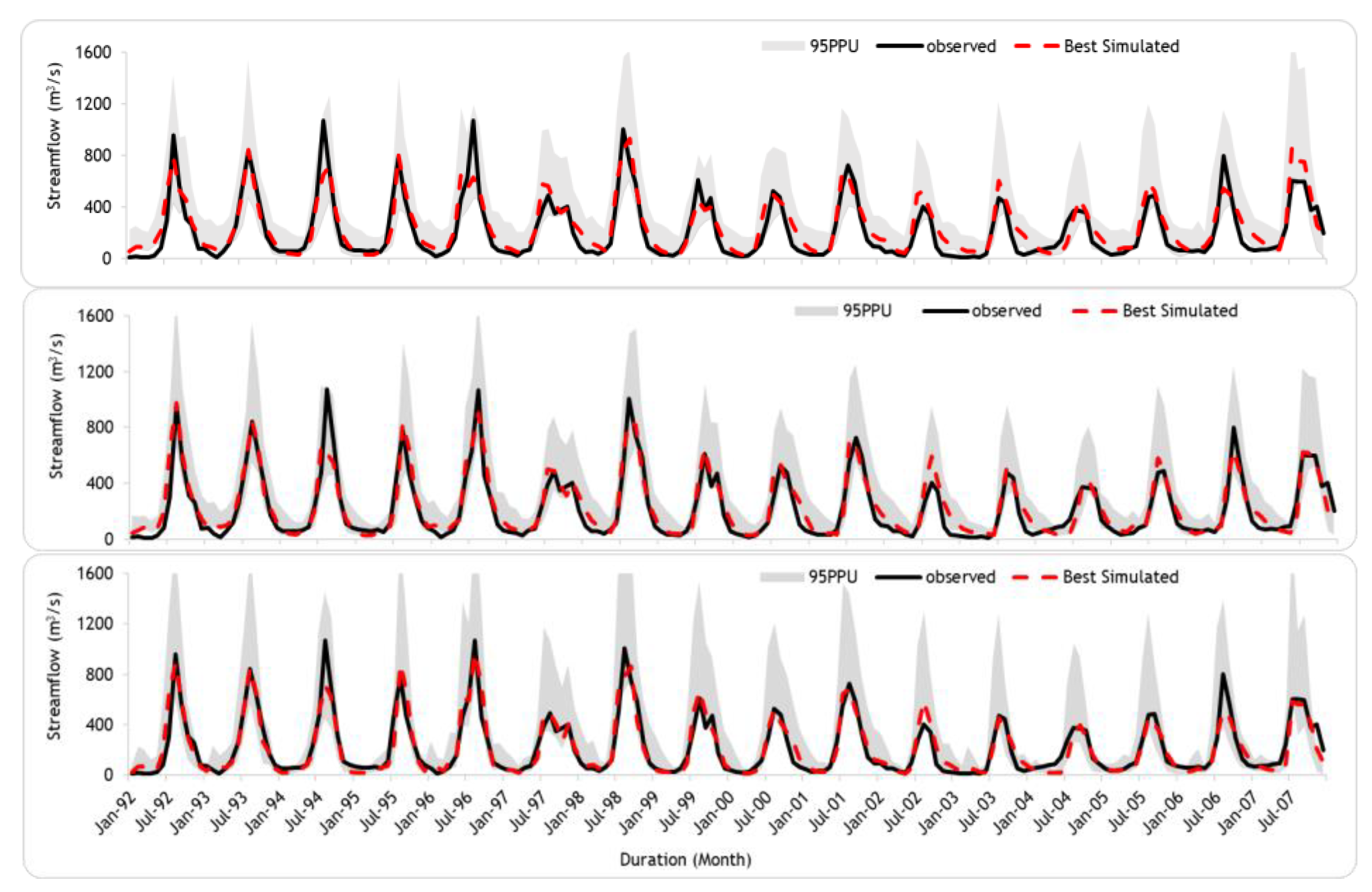
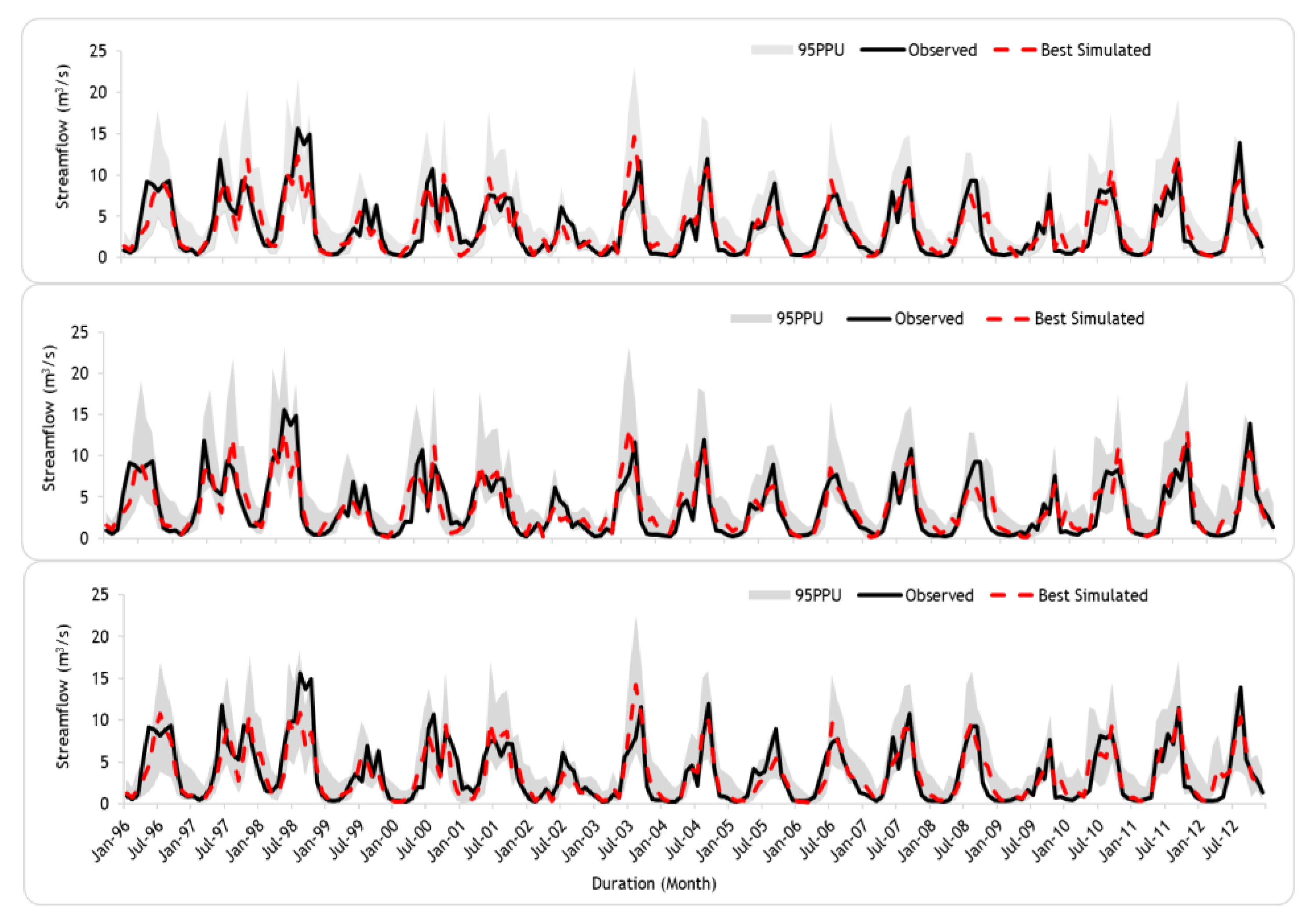
3.1. Hydrological Model Performance and Subbasin Discretization
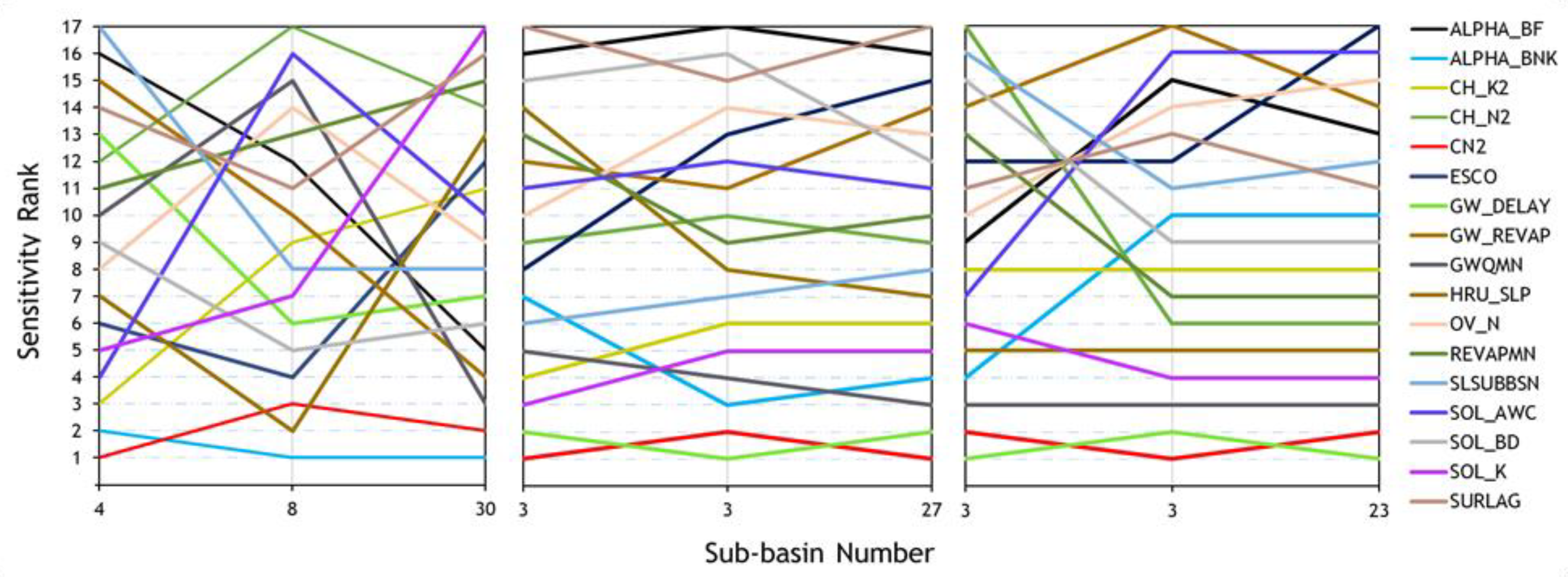
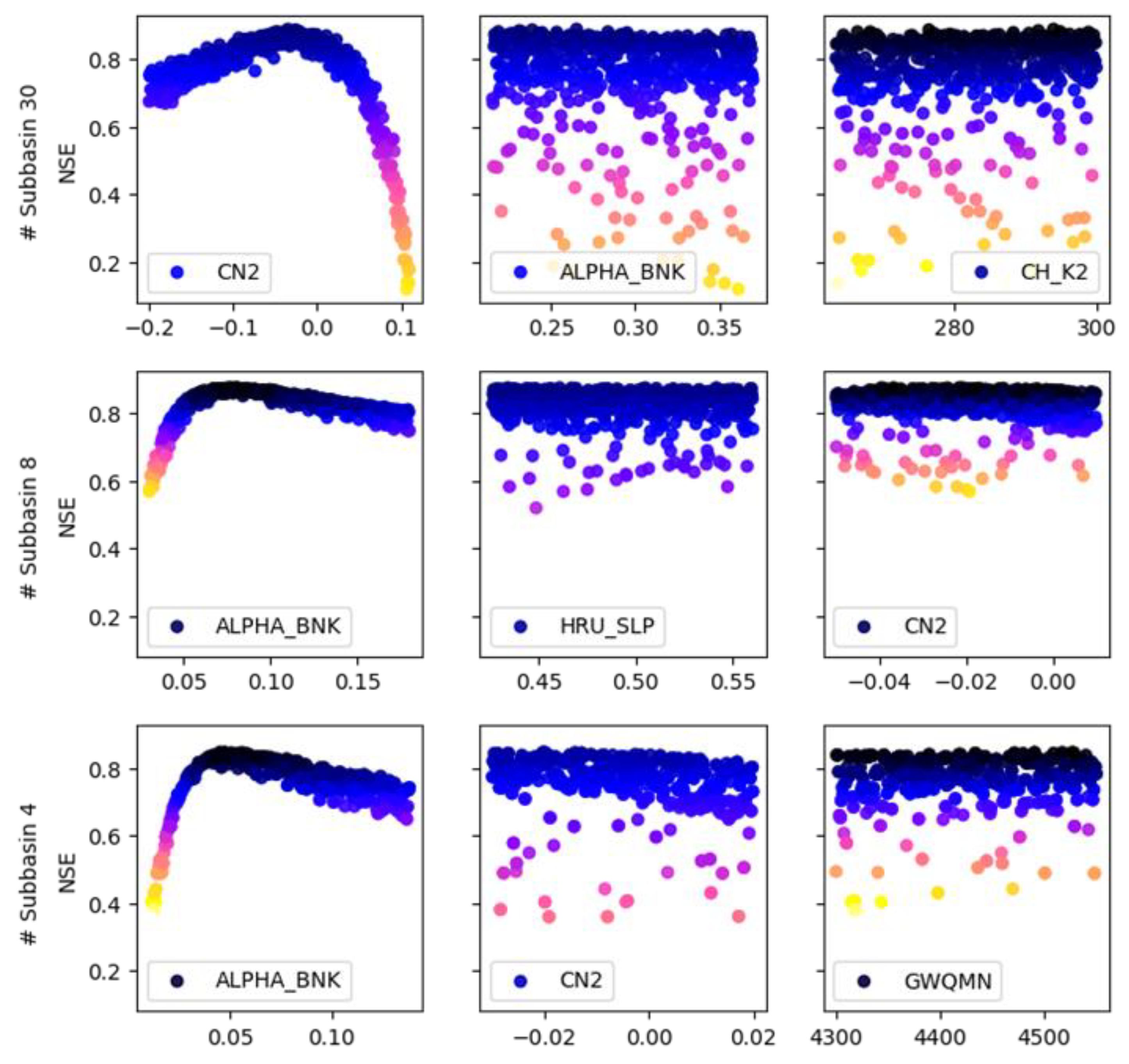
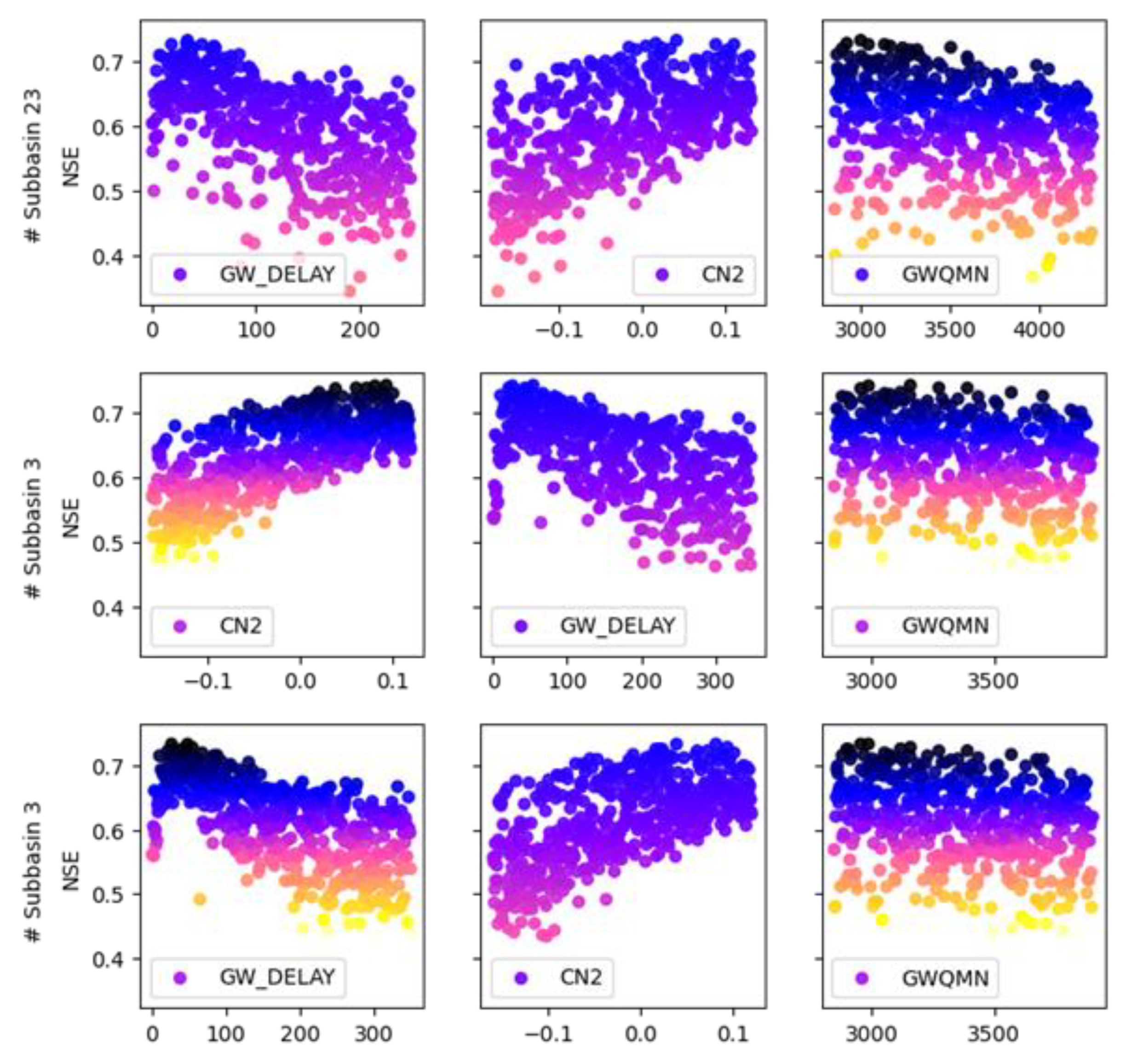
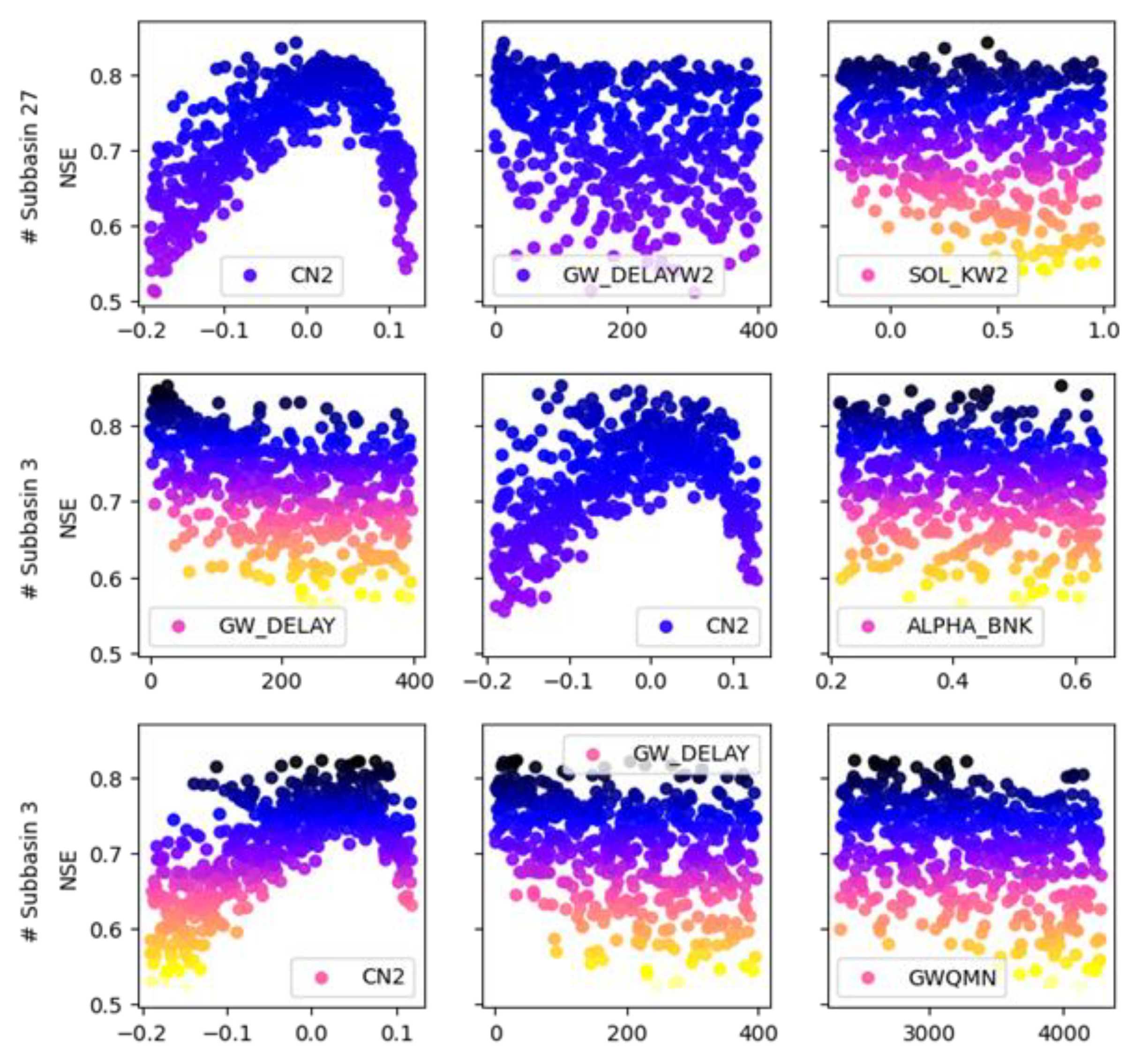
3.2. Impacts of Parameter Sampling Distribution on Subbasin Spatial Scale
3.3. Parameter Uncertainty in Hydrological Modeling across Various Subbasin Spatial Scales
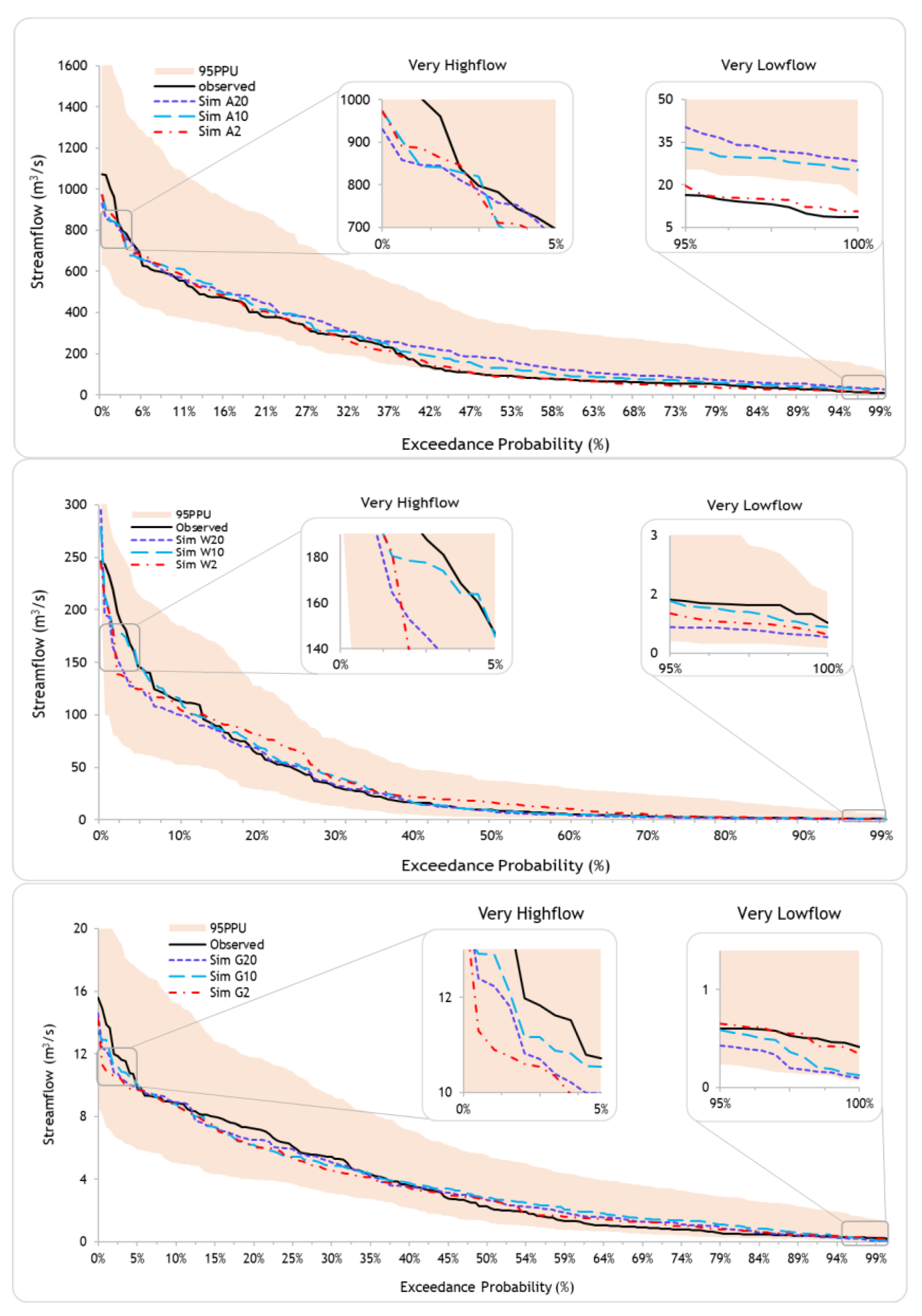
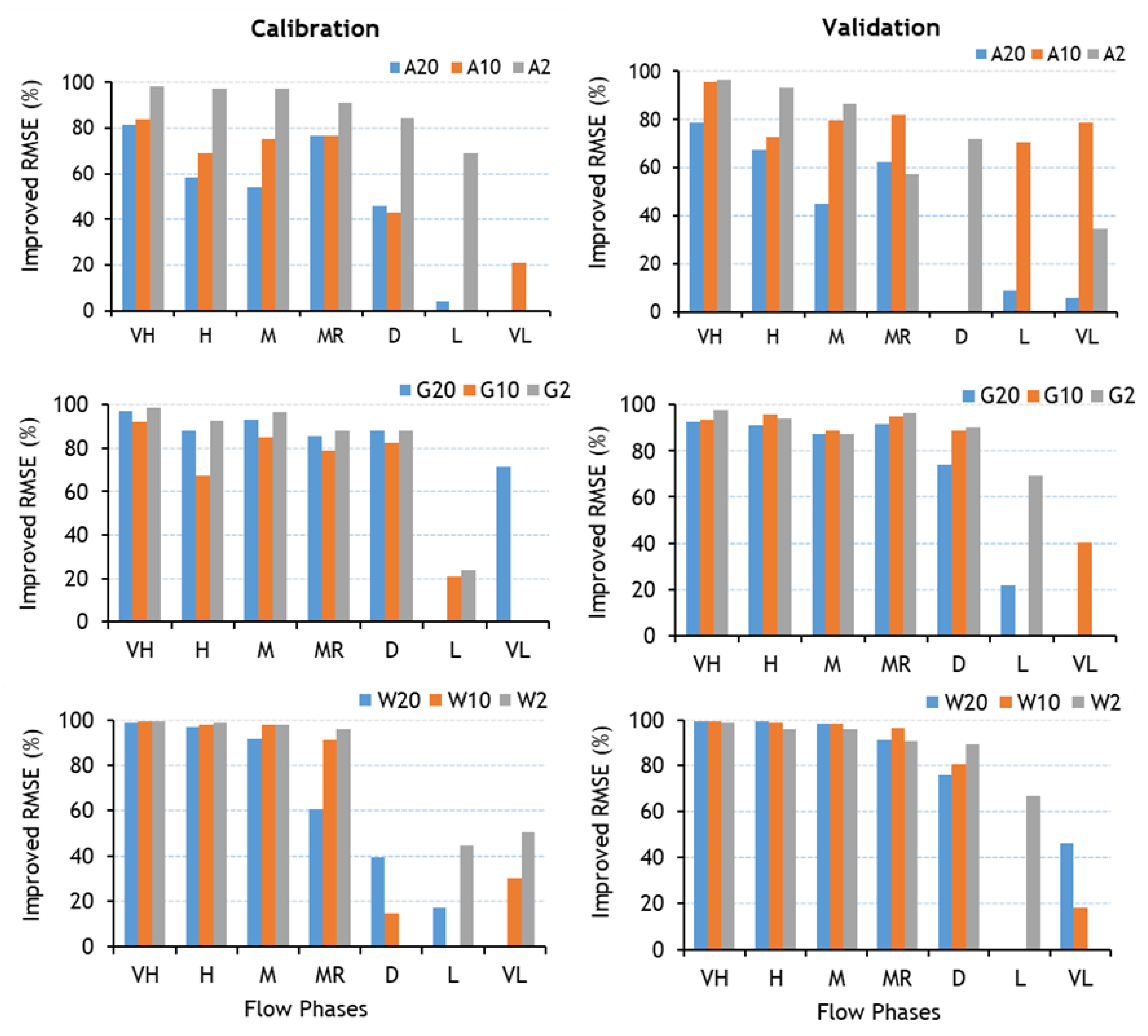
3.4. Impact of Subbasin Spatial Scales on the Reproduction of Various Flow Phases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kibuye, F.A.; Gall, H.E.; Veith, T.L.; Elkin, K.R.; Elliott, H.A.; Harper, J.P.; Watson, J.E. Influence of hydrologic and anthropogenic drivers on emerging organic contaminants in drinking water sources in the Susquehanna River Basin. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, J.G.; Moriasi, D.N.; Gassman, P.W.; Abbaspour, K.C.; White, M.J.; Srinivasan, R.; Santhi, C.; Harmel, R.; Van Griensven, A.; Van Liew, M.W. SWAT: Model use, calibration, and validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1491–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butts, M.B.; Payne, J.T.; Kristensen, M.; Madsen, H. An evaluation of the impact of model structure on hydrological modelling uncertainty for streamflow simulation. J. Hydrol. 2004, 298, 242–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devia, G.K.; Ganasri, B.P.; Dwarakish, G.S. A review on hydrological models. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 4, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Tang, Q.; Shi, X.; Zhu, C.; Bohn, T.; Su, F.; Pan, M.; Sheffield, J.; Lettenmaier, D.; Wood, E. Water budget record from Variable Infiltration Capacity (VIC) model. In Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document for Terrestrial Water Cycle Data Records; 2010; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/268367169_Water_Budget_Record_from_Variable_Infiltration_Capacity_VIC_Model (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Pandi, D.; Kothandaraman, S.; Kuppusamy, M. Hydrological models: A review. Int. J. Hydrol. Sci. Technol. 2021, 12, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refsgaard, J.C. Parameterisation, calibration and validation of distributed hydrological models. J. Hydrol. 1997, 198, 69–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, T.M.; Georgakakos, K.P. Intercomparison of lumped versus distributed hydrologic model ensemble simulations on operational forecast scales. J. Hydrol. 2006, 329, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Molin, M.; Schirmer, M.; Zappa, M.; Fenicia, F. Understanding dominant controls on streamflow spatial variability to set up a semi-distributed hydrological model: The case study of the Thur catchment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 1319–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veettil, A.V.; Green, T.R.; Kipka, H.; Arabi, M.; Lighthart, N.; Mankin, K.; Clary, J. Fully distributed versus semi-distributed process simulation of a highly managed watershed with mixed land use and irrigation return flow. Environ. Model. Softw. 2021, 140, 105000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegegne, G.; Kim, Y.-O.; Seo, S.B.; Kim, Y. Hydrological modelling uncertainty analysis for different flow quantiles: A case study in two hydro-geographically different watersheds. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2019, 64, 473–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C. SWAT-CUP: SWAT calibration and uncertainty programs—A user manual. Eawag. Dübendorf. Switz. 2015, 16–70. [Google Scholar]
- Beven, K. Prophecy, reality and uncertainty in distributed hydrological modelling. Adv. Water Resour. 1993, 16, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faramarzi, M.; Abbaspour, K.C.; Vaghefi, S.A.; Farzaneh, M.R.; Zehnder, A.J.; Srinivasan, R.; Yang, H. Modeling impacts of climate change on freshwater availability in Africa. J. Hydrol. 2013, 480, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozos, E.; Dimitriadis, P.; Bellos, V. Machine Learning in Assessing the Performance of Hydrological Models. Hydrology 2021, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdar, M.; Pourpanah, F.; Hussain, S.; Rezazadegan, D.; Liu, L.; Ghavamzadeh, M.; Fieguth, P.; Cao, X.; Khosravi, A.; Acharya, U.R. A review of uncertainty quantification in deep learning: Techniques, applications and challenges. Inf. Fusion 2021, 76, 243–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, H.K.; Westerberg, I.K.; Krueger, T. Hydrological data uncertainty and its implications. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2018, 5, e1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment part I: Model development. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöschl, G.; Sivapalan, M. Scale issues in hydrological modelling: A review. Hydrol. Process. 1995, 9, 251–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, J.R.; Brown, G.; Chlumsky, R.; Jenkinson, R.W.; Jost, G.; Lee, K.; Mai, J.; Serrer, M.; Sgro, N.; Shafii, M. Flexible watershed simulation with the Raven hydrological modelling framework. Environ. Model. Softw. 2020, 129, 104728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kling, H.; Gupta, H. On the development of regionalization relationships for lumped watershed models: The impact of ignoring sub-basin scale variability. J. Hydrol. 2009, 373, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.L.; Gassman, P.W.; Yang, X.; Haywood, J. A review of SWAT applications, performance and future needs for simulation of hydro-climatic extremes. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 143, 103662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, E.F.; Sivapalan, M.; Beven, K.; Band, L. Effects of spatial variability and scale with implications to hydrologic modeling. J. Hydrol. 1988, 102, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamillapalli, S.; Srinivasan, R.; Arnold, J.; Engel, B.A. Effect of spatial variability on basin scale modeling. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference/Workshop on Integrating GIS and Environmental Modeling, Santa Fe, NM, USA, 21–25 January 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bingner, R.; Garbrecht, J.; Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R. Effect of Watershed Subdivision on Simulation Runoff and Fine Sediment Yield. Trans. ASAE 1997, 40, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Merwade, V. Impact of watershed subdivision and soil data resolution on SWAT model calibration and parameter uncertainty. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2009, 45, 1179–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tianqi, A.; Yoshitani, J.; Takeuchi, K.; Fukami, K. Effects of sub-basin scale on runoff simulation in distributed hydrological model: BTOPMC. In Weather Radar Information and Distributed Hydrological Modelling, Proceedings of the International Symposium (Symposium HS03) Held During IUGG 2003, the XXIII General Assembly of the International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics, Sapporo, Japan, 30 June–11 July 2003; International Association of Hydrological Sciences: Wallingford, UK, 2003; p. 227. [Google Scholar]
- Hamby, D.M. A review of techniques for parameter sensitivity analysis of environmental models. Environ. Monit. Assess. 1994, 32, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegegne, G.; Kim, Y.-O. Modelling ungauged catchments using the catchment runoff response similarity. J. Hydrol. 2018, 564, 452–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Yang, J.; Maximov, I.; Siber, R.; Bogner, K.; Mieleitner, J.; Zobrist, J.; Srinivasan, R. Modelling hydrology and water quality in the pre-alpine/alpine Thur watershed using SWAT. J. Hydrol. 2007, 333, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coxon, G.; Freer, J.; Westerberg, I.K.; Wagener, T.; Woods, R.; Smith, P. A novel framework for discharge uncertainty quantification applied to 500 UK gauging stations. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 5531–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwelle, M.C.; Kim, J.; Sargsyan, K.; Ivanov, V.Y. Streamflow, stomata, and soil pits: Sources of inference for complex models with fast, robust uncertainty quantification. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 125, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y. Uncertainty quantification in hydrologic predictions: A brief review. J. Environ. Inform. Lett. 2019, 2, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, G.; Viviani, G. An urban drainage stormwater quality model: Model development and uncertainty quantification. J. Hydrol. 2010, 381, 248–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.C. Uncertainty Quantification: Theory, Implementation, and Applications; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Uniyal, B.; Jha, M.K.; Verma, A.K. Parameter identification and uncertainty analysis for simulating streamflow in a river basin of Eastern India. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 3744–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez, E.S.; Anctil, F.; Ramos, M.-H. Choosing between post-processing precipitation forecasts or chaining several uncertainty quantification tools in hydrological forecasting systems. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 197–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Duan, Q.; Tong, C.H.; Di, Z.; Gong, W. A GUI platform for uncertainty quantification of complex dynamical models. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 76, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Yu, C. Bayesian forecasting and uncertainty quantifying of stream flows using Metropolis–Hastings Markov Chain Monte Carlo algorithm. J. Hydrol. 2017, 549, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Johnson, C.; Van Genuchten, M.T. Estimating uncertain flow and transport parameters using a sequential uncertainty fitting procedure. Vadose Zone J. 2004, 3, 1340–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K.; Binley, A. The future of distributed models: Model calibration and uncertainty prediction. Hydrol. Process. 1992, 6, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorenson, H.W.; Alspach, D.L. Recursive Bayesian estimation using Gaussian sums. Automatica 1971, 7, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, D.; Karniadakis, G.E. Modeling uncertainty in flow simulations via generalized polynomial chaos. J. Comput. Phys. 2003, 187, 137–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrugt, J.A.; Gupta, H.V.; Bouten, W.; Sorooshian, S. A Shuffled Complex Evolution Metropolis algorithm for optimization and uncertainty assessment of hydrologic model parameters. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrugt, J.A.; Diks, C.G.; Gupta, H.V.; Bouten, W.; Verstraten, J.M. Improved treatment of uncertainty in hydrologic modeling: Combining the strengths of global optimization and data assimilation. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, W01017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moges, E.; Demissie, Y.; Larsen, L.; Yassin, F. Review: Sources of Hydrological Model Uncertainties and Advances in Their Analysis. Water 2021, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awulachew, S.B.; Yilma, A.D.; Loulseged, M.; Loiskandl, W.; Ayana, M.; Alamirew, T. Water Resources and Irrigation Development in Ethiopia; IWMI: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2007; Volume 123. [Google Scholar]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R. Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation Version 2009; Texas Water Resources Institute: College Station, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chaemiso, S.E.; Abebe, A.; Pingale, S.M. Assessment of the impact of climate change on surface hydrological processes using SWAT: A case study of Omo-Gibe river basin, Ethiopia. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussainzada, W.; Lee, H.S. Hydrological modelling for water resource management in a semi-arid mountainous region using the soil and water assessment tool: A case study in northern Afghanistan. Hydrology 2021, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhu, J.; Chen, W.; Hu, Y.; Yao, J.; Yu, S.; Jia, G.; He, X.; Wang, A. Identification of Suitable Hydrologic Response Unit Thresholds for Soil and Water Assessment Tool Streamflow Modelling. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 696–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.V.; Dietrich, J.; Dang, T.D.; Tran, D.A.; Van Doan, B.; Sarrazin, F.J.; Abbaspour, K.; Srinivasan, R. An interactive graphical interface tool for parameter calibration, sensitivity analysis, uncertainty analysis, and visualization for the Soil and Water Assessment Tool. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 156, 105497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullrich, A.; Volk, M. Application of the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) to predict the impact of alternative management practices on water quality and quantity. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesru, M.; Shetty, A.; Nagaraj, M. Multi-variable calibration of hydrological model in the upper Omo-Gibe basin, Ethiopia. Acta Geophys. 2020, 68, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K. Changing ideas in hydrology—The case of physically-based models. J. Hydrol. 1989, 105, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, P.; Gupta, H.; Wagener, T. A spatial regularization approach to parameter estimation for a distributed watershed model. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W12419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, J.; Staudinger, M.; Meerveld, H. Validation and over-parameterization—Experiences from hydrological modeling. In Computer Simulation Validation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 811–834. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, M.A.; Dar, A.Q.; Jain, M.K. Modelling streamflow using the SWAT model and multi-site calibration utilizing SUFI-2 of SWAT-CUP model for high altitude catchments, NW Himalaya’s. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhan, C.; Xuan, Y.; Ye, M.; Xu, C. Global sensitivity analysis in hydrological modeling: Review of concepts, methods, theoretical framework, and applications. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 739–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Jomaa, S.; Rode, M. Spatiotemporally distributed sensitivity analysis for catchment water quality models. Geophys. Res. Abstr. 2019, 21, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Vaghefi, S.A.; Srinivasan, R. A guideline for successful calibration and uncertainty analysis for soil and water assessment: A review of papers from the 2016 international SWAT conference. Water 2017, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibin, R.; Sudheer, K.; Chaubey, I. Sensitivity and identifiability of stream flow generation parameters of the SWAT model. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2010, 24, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakhlalla, A.O.; Parajuli, P.B. Assessing model parameters sensitivity and uncertainty of streamflow, sediment, and nutrient transport using SWAT. Inf. Process. Agric. 2019, 6, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narsimlu, B.; Gosain, A.K.; Chahar, B.R.; Singh, S.K.; Srivastava, P.K. SWAT model calibration and uncertainty analysis for streamflow prediction in the Kunwari River Basin, India, using sequential uncertainty fitting. Environ. Process. 2015, 2, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spruill, C.A.; Workman, S.R.; Taraba, J.L. Simulation of daily and monthly stream discharge from small watersheds using the SWAT model. Trans. ASAE 2000, 43, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.V.; Kling, H.; Yilmaz, K.K.; Martinez, G.F. Decomposition of the mean squared error and NSE performance criteria: Implications for improving hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.H.; Khaleghi, M.R. Application of SWAT model and SWAT-CUP software in simulation and analysis of sediment uncertainty in arid and semi-arid watersheds (case study: The Zoshk–Abardeh watershed). Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 6, 2003–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, K.; Ali, M.F.; Abd Rahman, N.F.; Mispan, M.R.; Haron, S.H.; Othman, Z.; Bachok, M.F. Sensitivity analysis in watershed model using SUFI-2 algorithm. Procedia Eng. 2016, 162, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Rouholahnejad, E.; Vaghefi, S.; Srinivasan, R.; Yang, H.; Kløve, B. A continental-scale hydrology and water quality model for Europe: Calibration and uncertainty of a high-resolution large-scale SWAT model. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 733–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, N.; Jeong, J. An approach for estimating stream health using flow duration curves and indices of hydrologic alteration. EPA Reg. 2011, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Pfannerstill, M.; Guse, B.; Fohrer, N. Smart low flow signature metrics for an improved overall performance evaluation of hydrological models. J. Hydrol. 2014, 510, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, K.K.; Gupta, H.V.; Wagener, T. A process-based diagnostic approach to model evaluation: Application to the NWS distributed hydrologic model. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W09417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Yu, Y.; Ma, X. Overcoming equifinality: Time-varying analysis of sensitivity and identifiability of SWAT runoff and sediment parameters in an arid and semiarid watershed. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 31631–31645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira, T.L.; Mello, C.R.; Beskow, S.; Timm, L.C.; Viola, M.R. LASH hydrological model: An analysis focused on spatial discretization. Catena 2019, 173, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Jha, S.K. Identification of sensitive parameters in daily and monthly hydrological simulations in small to large catchments in Central India. J. Hydrol. 2021, 601, 126632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassman, P.W.; Reyes, M.R.; Green, C.H.; Arnold, J.G. The soil and water assessment tool: Historical development, applications, and future research directions. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 1211–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckhardt, K.; Arnold, J. Automatic calibration of a distributed catchment model. J. Hydrol. 2001, 251, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Su, X. Parameter sensitivity analysis of SWAT model for streamflow simulation with multisource precipitation datasets. Hydrol. Res. 2019, 50, 861–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverkamp, S.; Srinivasan, R.; Frede, H.; Santhi, C. Subwatershed spatial analysis tool: Discretization of a distributed hydrologic model by statistical criteria. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2002, 38, 1723–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter Name with Their Extension | Parameter Descriptions | Unit | Valid Ranges |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALPHA_BF.gw | Baseflow alpha factor | (days) | 0–1 |
| ALPHA_BNK.rte | Baseflow alpha factor for bank storage | (-) | 0–1 |
| CH_K2.rte | Effective hydraulic conductivity in main channel | (mm/h) | −0.01–500 |
| CH_N2.rte | Manning’s “n” value for the main channel | (-) | −0.01–0.3 |
| CN2.mgt (r) | SCS runoff curve number | (-) | −0.2–0.2 |
| ESCO.hru | Soil evaporation compensation factor | (-) | 0–1 |
| GW_DELAY.gw | Groundwater delay time | (days) | 0–500 |
| GW_REVAP.gw | Groundwater “revap” coefficient | (-) | 0.02–0.2 |
| GWQMN.gw | Threshold depth of water in the shallow aquifer | (mmH2O) | 0–500 |
| HRU_SLP.hru | Average slope steepness | (-) | 0–1 |
| OV_N.hru | Manning’s “n” value for overland flow | (-) | 0.01–30 |
| REVAPMN.gw | Threshold depth of water | (mm) | 0–500 |
| SLSUBBSN.hru | Average slope length | (-) | 10–150 |
| SOL_AWC (..).sol (r) | Available water capacity of the soil layer | (mmH2O/mm soil) | 0–1 |
| SOL_BD (..).sol (r) | Moist bulk density | (g/cm3) | 0.9–2.5 |
| SOL_K (..).sol (r) | Saturated hydraulic conductivity | (mm/h) | 0–2000 |
| SURLAG.bsn | Surface runoff lag time | (days) | 0.05–24 |
| Watershed | No. of Subbasins | No. of HRUs | P-Factor | R-Factor | NSE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | Validation | Calibration | Validation | Calibration | Validation | |||
| Abelti | 4 | 36 | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.85 | 1.14 | 0.85 | 0.74 |
| 8 | 62 | 0.71 | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.84 | 0.88 | 0.88 | |
| 30 | 172 | 0.82 | 0.77 | 0.92 | 1.16 | 0.89 | 0.86 | |
| Wabi | 3 | 26 | 0.79 | 0.76 | 0.67 | 0.90 | 0.82 | 0.77 |
| 3 | 26 | 0.84 | 0.81 | 0.73 | 1.06 | 0.85 | 0.82 | |
| 27 | 170 | 0.81 | 0.79 | 0.81 | 0.76 | 0.84 | 0.80 | |
| Gecha | 3 | 12 | 0.74 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.89 | 0.73 | 0.83 |
| 3 | 12 | 0.76 | 0.72 | 0.84 | 0.90 | 0.74 | 0.81 | |
| 23 | 80 | 0.74 | 0.75 | 0.88 | 0.99 | 0.73 | 0.82 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gebeyehu, B.M.; Jabir, A.K.; Tegegne, G.; Melesse, A.M. Subbasin Spatial Scale Effects on Hydrological Model Prediction Uncertainty of Extreme Stream Flows in the Omo Gibe River Basin, Ethiopia. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030611
Gebeyehu BM, Jabir AK, Tegegne G, Melesse AM. Subbasin Spatial Scale Effects on Hydrological Model Prediction Uncertainty of Extreme Stream Flows in the Omo Gibe River Basin, Ethiopia. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(3):611. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030611
Chicago/Turabian StyleGebeyehu, Bahru M., Asie K. Jabir, Getachew Tegegne, and Assefa M. Melesse. 2023. "Subbasin Spatial Scale Effects on Hydrological Model Prediction Uncertainty of Extreme Stream Flows in the Omo Gibe River Basin, Ethiopia" Remote Sensing 15, no. 3: 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030611
APA StyleGebeyehu, B. M., Jabir, A. K., Tegegne, G., & Melesse, A. M. (2023). Subbasin Spatial Scale Effects on Hydrological Model Prediction Uncertainty of Extreme Stream Flows in the Omo Gibe River Basin, Ethiopia. Remote Sensing, 15(3), 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030611









