Real-Time Synchronous Acquisition and Processing of Signal in Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar Using FPGA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar and Key Preprocessing Algorithm
2.1. Introduction to Windviewer100s Lidar
2.2. Key Preprocessing Algorithm
3. Experiment and Results
3.1. Detection Measurement
3.2. Detection Altitude
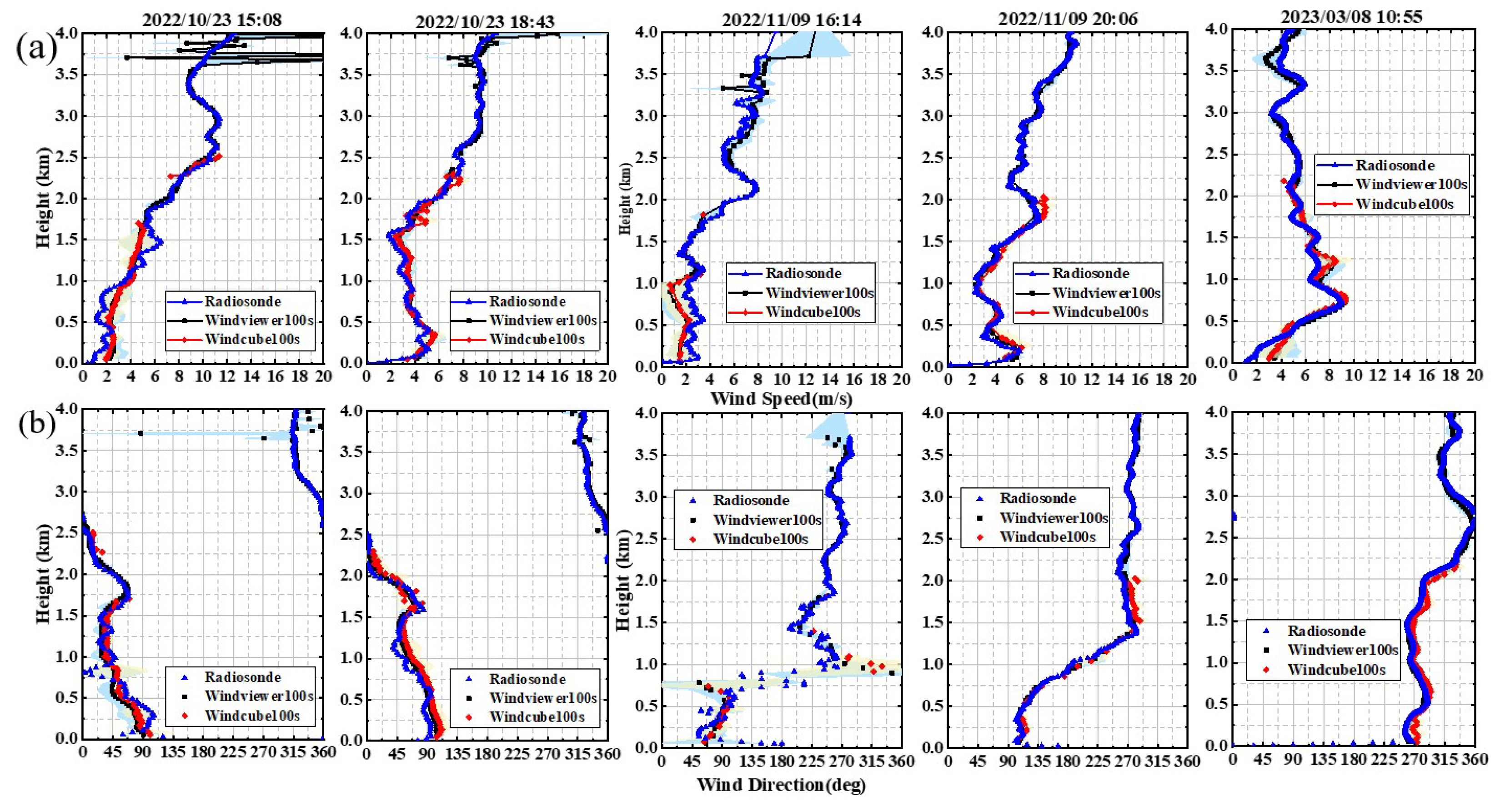
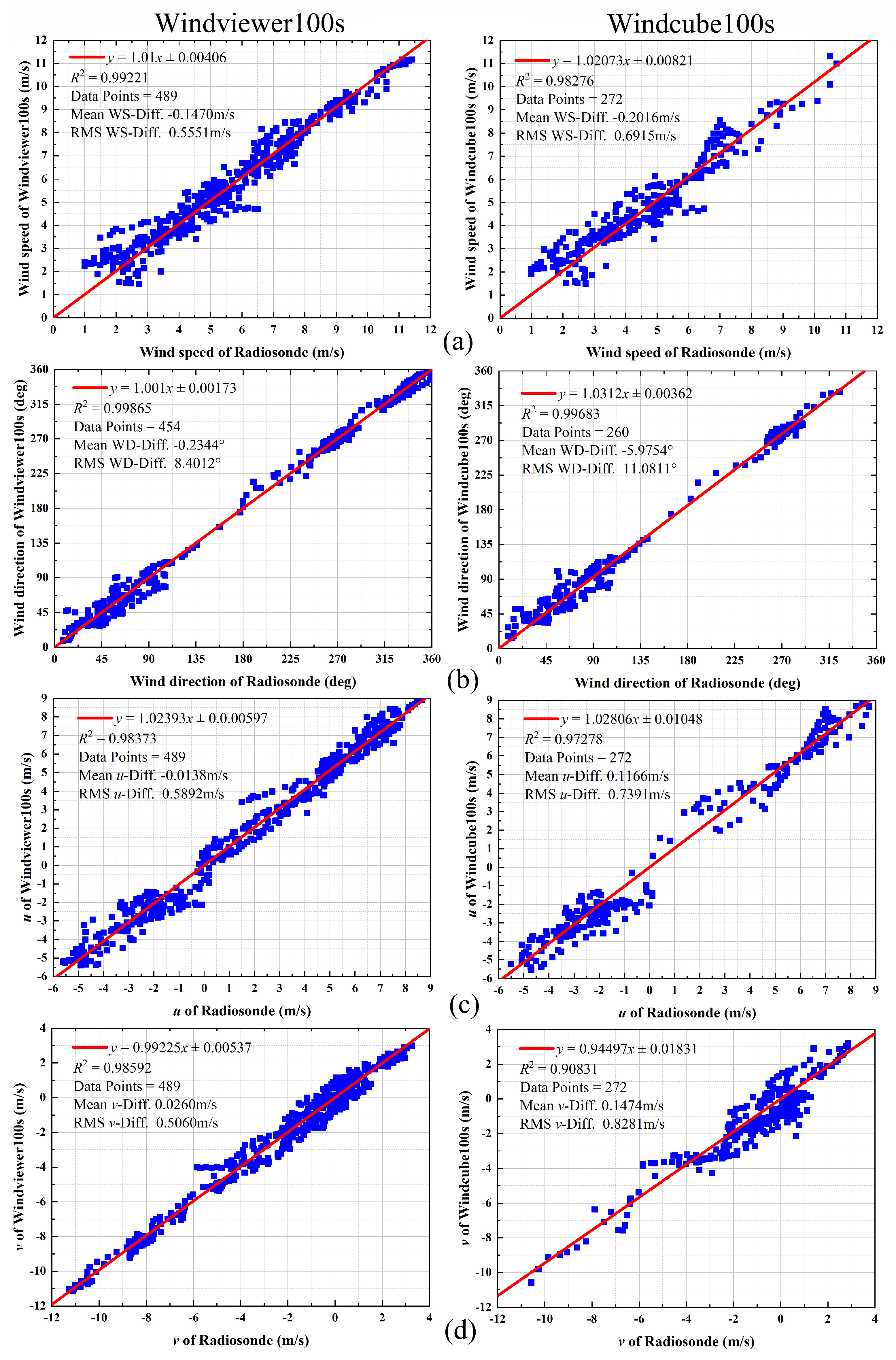
3.3. Comparison Experiments of Lidars and Radiosonde
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stanley, G.B.; Barry, E.S.; Eduard, J.S.; Koch, S.E. The value of wind profiler data in U.S. weather forecasting. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 1871–1886. [Google Scholar]
- Banakh, V.A.; Werner, C. Computer simulation of coherent Doppler lidar measurement of wind velocity and retrieval of turbulent wind statistics. Opt. Eng. 2005, 44, 071205. [Google Scholar]
- Cezard, N.; Mehaute, S.L.; Gout, J.L.; Valla, M.; Goular, D.; Fleury, D.; Planchat, C.; Dolfi-Bouteyre, A. Performance assessment of a coherent DIAL-Doppler fiber lidar at 1645 nm for remote sensing of methane and wind. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 22345–22357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.H.; Zhai, X.C.; Liu, B.Y. Aircraft wake vortex and turbulence measurement under near-ground effect using coherent Doppler lidar. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 1142–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitebuch, O. Wind Lidar for Atmospheric Research. In Atmospheric Physics; Schumann, U., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 487–507. [Google Scholar]
- Kliebisch, O.; Uittenbosch, H.; Thurn, J.; Mahnke, P. Coherent Doppler wind lidar with real-time wind processing and low signal-to-noise ratio reconstruction based on a convolutional neural network. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 5540–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yuan, L.C.; Fan, C.H.; Zhu, X.P.; Liu, J.Q.; Dai, B.; Xiao, W.G.; Zhu, X.L.; Chen, W.B. Wind retrieval for genetic algorithm-based coherent Doppler wind lidar employing airborne platform. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 2023, 129, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiljević, N.; Lea, G.; Courtney, M.; Cariou, J.P.; Mann, J.; Mikkelsen, T. Long-range windscanner system. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Fukuchi, T. Laser Remote Sensing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Huffaker, R.M. Laser Doppler detection systems for gas velocity measurement. Appl. Opt. 1970, 9, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banakh, V.A.; Smalikho, I.N. The impact of internal gravity waves on the spectra of turbulent fluctuations of vertical wind velocity in the stable atmospheric boundary layer. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariou, J.; Sauvage, L.; Thobois, L.; Gorju, G.; Machta, M.; Lea, G.; Duboué, M. Long range scanning pulsed Coherent Lidar for real time wind monitoring in the Planetary Boundary Layer. In Proceedings of the 16th Coherent Laser Radar Conference 2011 (CLRC XVI), Long Beach, CA, USA, 20–24 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Diao, W.F.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.Q.; Zhu, X.P.; Liu, Y.; Bi, D.C.; Chen, W.B. All fiber pulsed coherent lidar development for wind profiles measurements in boundary layers. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2014, 12, 072801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xia, H.Y.; Shangguan, M.J.; Wu, Y.B.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.J.; Qiu, J.W.; Zhang, R.J. 1.5 μm polarization coherent lidar incorporating time-division multiplexing. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 20663–20674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, X.F.; Fan, C.H.; Bi, D.C.; Liu, J.Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.L.; Chen, W.B. Field performance of all-fiber pulsed coherent Doppler lidar. In Proceedings of the 29th International Laser Radar Conference, Heifei, China, 24–28 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelazim, S.; Santoro, D.; Arend, M.; Moshary, F.; Ahmed, S. Signal to Noise Ratio Characterization of Coherent Doppler Lidar Backscattered Signals. In Proceedings of the 27th International Laser Radar Conference, New York, NY, USA, 5–10 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kameyama, S.; Ando, T.; Asaka, K.; Wadaka, S. Compact all-fiber pulsed coherent Doppler lidar system for wind sensing. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saklakova, V.; Han, Y.L.; Zhang, S.H.; Qin, Z.; Xue, X.H.; Chen, T.D.; Sun, D.S.; Zhao, Y.M.; Zheng, J. Field programmable gate array-based coherent lidar employing the ordinal statistics method for fast Doppler frequency determinatio. Opt. Eng. 2022, 61, 124102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.R.; Han, F.; Sun, D.S.; Han, Y.L.; Zheng, J.; Jiang, S. 1.55-μm pulse coherent LIDAR with 10-km detection range. Opt. Eng. 2019, 58, 096103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Wang, C.; Xue, X.H.; Dou, X.K.; Chen, T.D. Meter-scale and sub-second-resolution coherent Doppler wind LIDAR and hyperfine wind observation. Opt. Lett. 2022, 47, 3179–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, X.; Guo, P.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.C.; Zhao, M.; Wu, Y.W.; Zhao, P.T. Portable coherent Doppler light detection and ranging for boundary-layer wind sensing. Opt. Eng. 2019, 58, 034105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardesty, R.M. Performance of a discrete spectral peak frequency estimator for Doppler wind velocity measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1986, 24, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rye, B.J.; Hardesty, R.M. Discrete spectral peak estimation in incoherent backscatter heterodyne lidar. I. Spectral accumulation and the cramerrao lower bound. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1993, 31, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rye, B.J.; Hardesty, R.M. Discrete spectral peak estimation in incoherent backscatter heterodyne lidar. II. Correlogram accumulation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1993, 31, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelazim, S.; Santoro, D.; Arend, M.; Moshary, F.; Ahmed, S. Field programmable gate array processing of eye-safe all-fiber coherent wind Doppler lidar return signals. In Proceedings of the SPIE Remote Sensing, Prague, Czech Republic, 19–22 September 2011; SPIE, The International Society for Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelazim, S.; Santoro, D.; Arend, M.; Moshary, F.; Ahmed, S. A hardware implemented autocorrelation technique for estimating power spectral density for processing signals from a Doppler wind lidar system. Sensors 2018, 18, 4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliebisch, O.; Mahnke, P. Real-time laser Doppler anemometry for optical air data applications in low aerosol environments. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2020, 91, 095106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 28902-2:2017; Air Quality–Environmental Meteorology–Part 2: Ground–Based Remote Sensing of Wind by Heterodyne Pulsed Doppler Lidar. ISO: Vernier, Switzerland, 2017.
- Kumer, V.-M.; Joachim, R.; Birgitte, R.; Furevik, A. Comparison of LiDAR and radiosonde wind measurements. Energy Procedia 2014, 53, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschke, E.; Leinweber, R.; Lehmann, V. A one year comparison of 482 MHz radar wind profiler, RS92-SGP radiosonde and 1.5 μm Doppler lidar wind measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2014, 7, 11439–11479. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, L.B.; Qiu, Z.J.; Gao, H.Y.; Zhu, X.P.; Liu, J.Q. All-fiber pulse coherent Doppler LIDAR and its validations. Opt. Eng. 2015, 54, 123103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, I.S.; Anandan, V.K.; Reddy, P.N. Evaluation of DBS wind measurement technique in different beam configurations for a VHF wind profiler. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 2304–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.H.; Yoon, H.; Kim, J. New efficient FFT algorithm and pipeline implementation results for OFDM/DMT application. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2003, 49, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolfi-Bouteyre, A.; Canat, G.; Lombard, L.; Matthieu, V.; Durécu, A.; Besson, C. Long-range wind monitoring in real time with optimized coherent lidar. Opt. Eng. 2019, 56, 031217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Sun, D.S.; Han, Y.L.; Han, F.; Zhou, A.R.; Zheng, J. Performance of continuous wave coherent Doppler lidar for wind measurement. Curr. Opt. Photonics 2019, 3, 466–472. [Google Scholar]
- Feist, T. Vivado design suite. White Pap. 2012, 5, 30. [Google Scholar]
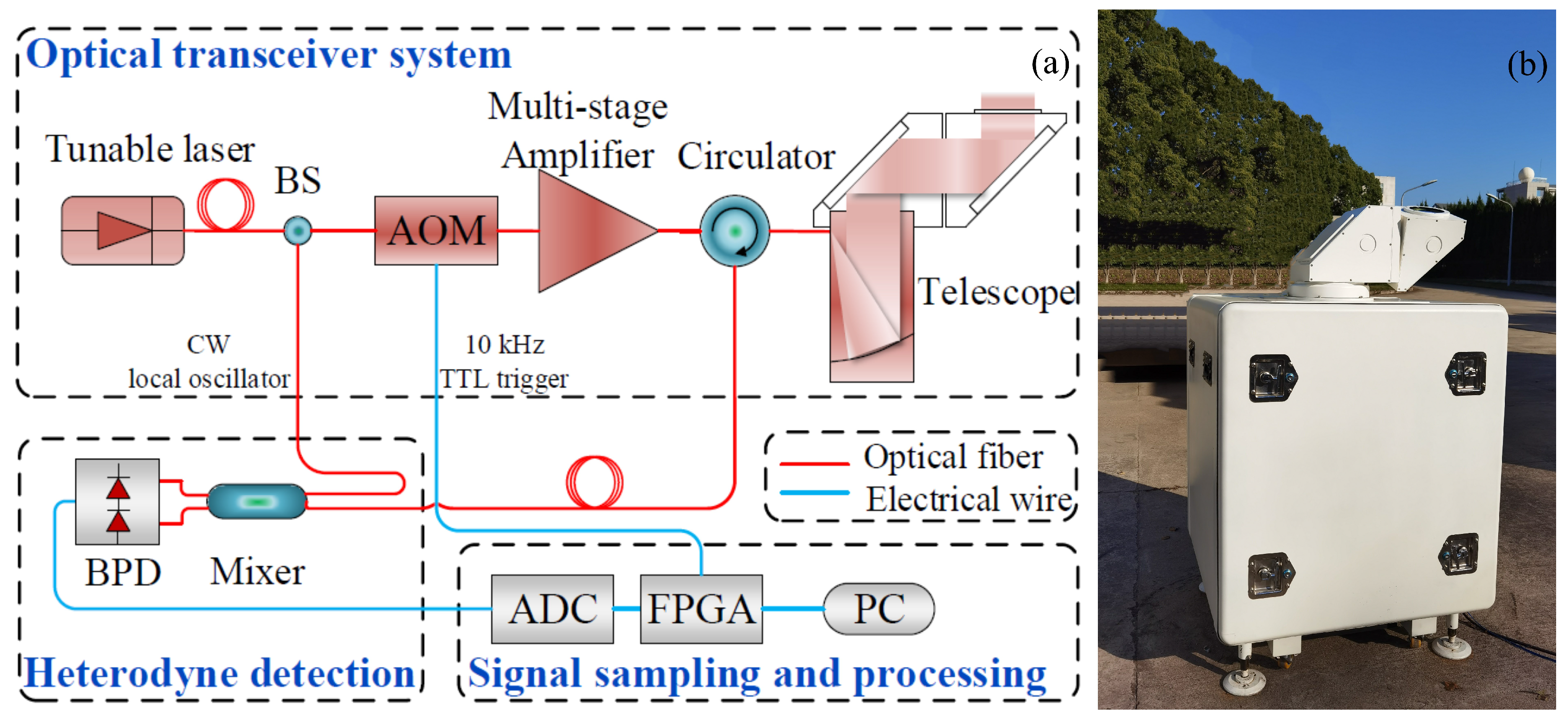



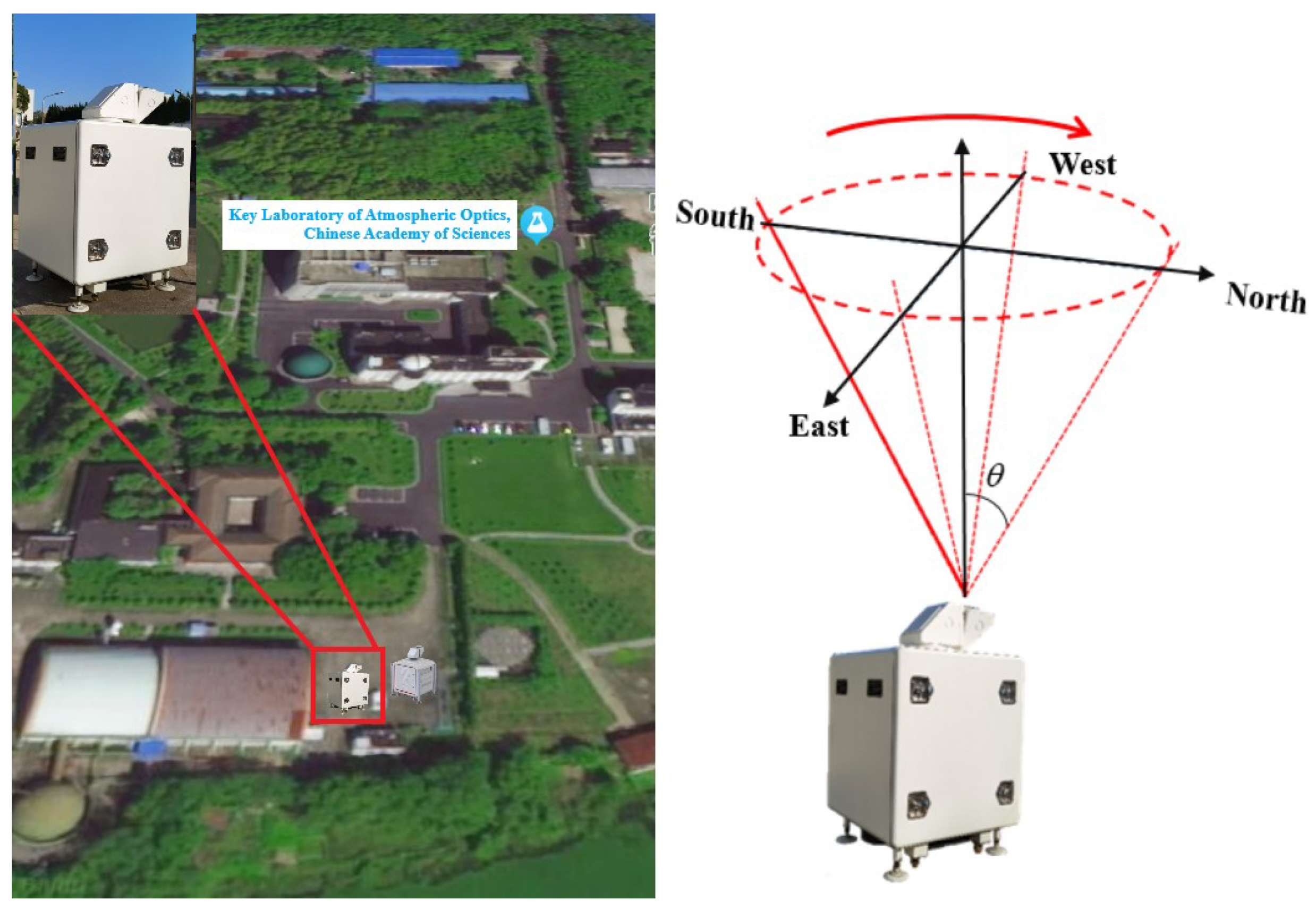


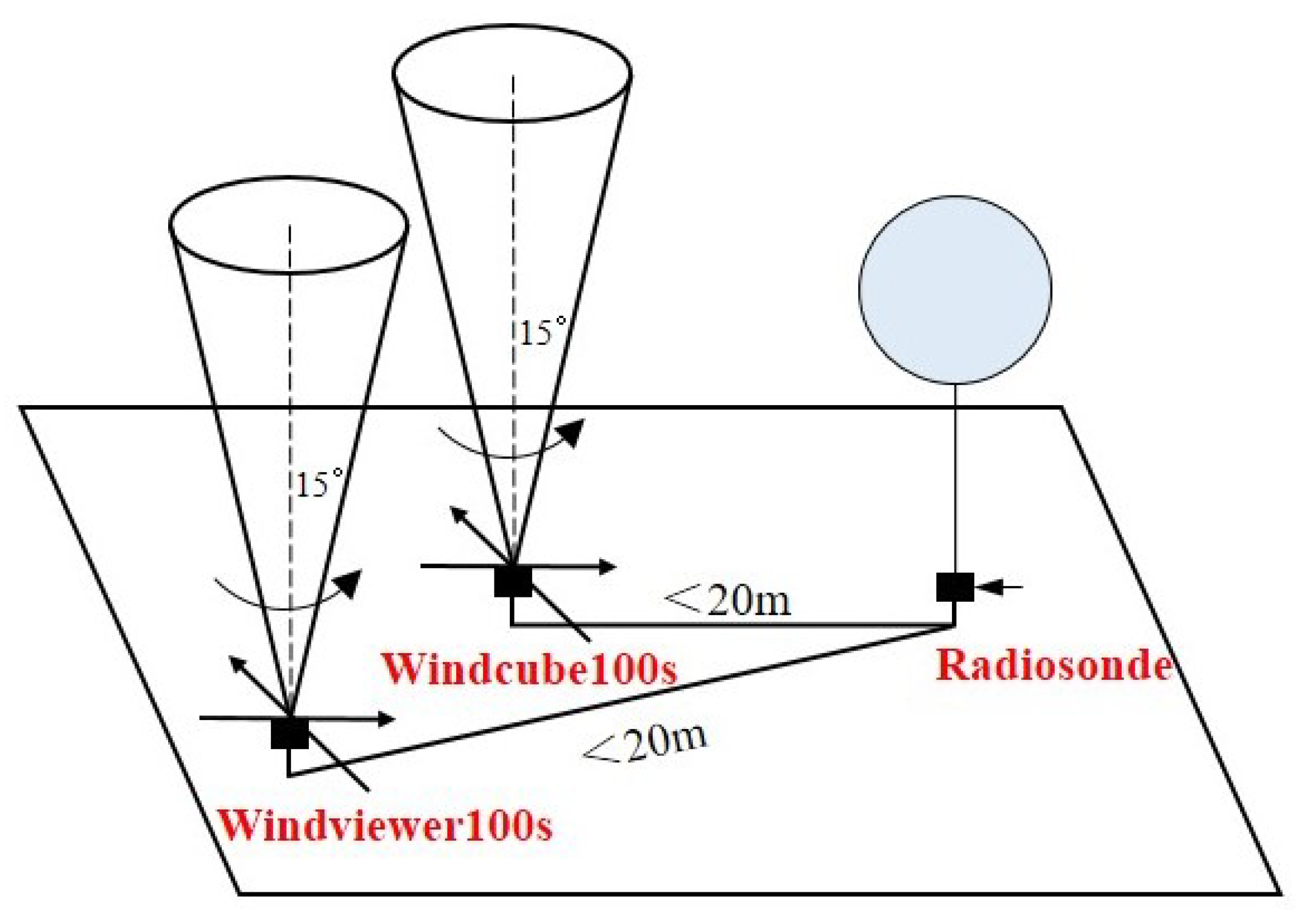
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Wavelength | 1550 nm |
| Pulse energy | 110 J |
| Pulse width | 300 ns |
| Pulse repetition rate | 10 kHz |
| Laser linewidth | 5 kHz |
| AOM frequency shift | 80 MHz |
| Detector bandwidth | 350 MHz |
| Telescope diameter | 100 mm |
| Beam diameter | 80 mm |
| Sampling frequency | 400 MHz |
| Temporal resolution | 1 s |
| Range resolution | 30 m |
| Pointing accuracy | 0.1 |
| Maximum speed | 50/s |
| Azimuth coverage | 0–360 |
| Elevation coverage | −90–90 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Wavelength | 1.54 m |
| Accumulation time | 1 s |
| Pulse repetition rate | 40 kHz |
| Range resolution | 25 m |
| Display resolution | 30 m |
| Radial wind speed range | −30–30 m/s |
| Telescope diameter | 100 mm |
| Radial velocity measurement accuracy | ≤0.5 m/s |
| Pointing accuracy | 0.1 |
| Maximum speed | 30/s |
| Azimuth coverage | 0–360 |
| Elevation coverage | −19–199 |
| Scanning method | DBS |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Altitude range | ≥30 km |
| Wind speed accuracy | <0.3 m/s |
| Wind direction accuracy | <3 (at wind speed > 3 m/s) |
| Lidar | Time | Valid Samples | ME of Wind Speed (m/s) | ME of Wind Direction () | RMSE of Wind Speed (m/s) | RMSE of Wind Direction () |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A lidar | 2022/10/23 15:08 | 119 | 0.041 | −2.472 | 0.645 | 12.335 |
| 2022/10/23 18:43 | 113 | 0.249 | 2.550 | 0.434 | 7.204 | |
| 2022/11/09 16:14 | 62 | 0.042 | 1.534 | 0.628 | 8.793 | |
| 2022/11/09 20:06 | 76 | 0.072 | 2.225 | 0.332 | 5.522 | |
| 2023/03/08 10:55 | 119 | 0.259 | −0.227 | 0.630 | 5.633 | |
| B lidar | 2022/10/23 15:08 | 65 | 0.124 | 1.400 | 0.836 | 15.314 |
| 2022/10/23 18:43 | 76 | 0.308 | 8.792 | 0.548 | 12.965 | |
| 2022/11/09 16:14 | 16 | −0.723 | 9.688 | 0.868 | 16.248 | |
| 2022/11/09 20:06 | 43 | 0.340 | 7.110 | 0.611 | 9.795 | |
| 2023/03/08 10:55 | 72 | 0.280 | 7.658 | 0.680 | 8.981 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Zhu, W.; Jin, X.; Qing, C. Real-Time Synchronous Acquisition and Processing of Signal in Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar Using FPGA. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5673. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245673
Liu Q, Zhu W, Jin X, Qing C. Real-Time Synchronous Acquisition and Processing of Signal in Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar Using FPGA. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(24):5673. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245673
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qing, Wenyue Zhu, Xiaomei Jin, and Chun Qing. 2023. "Real-Time Synchronous Acquisition and Processing of Signal in Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar Using FPGA" Remote Sensing 15, no. 24: 5673. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245673
APA StyleLiu, Q., Zhu, W., Jin, X., & Qing, C. (2023). Real-Time Synchronous Acquisition and Processing of Signal in Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar Using FPGA. Remote Sensing, 15(24), 5673. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245673






