Abstract
The mapping of small-scale irrigation areas is essential for food security and water resource management studies. The identification of small-scale irrigation areas is a challenge, but it can be overcome using expert knowledge and satellite-derived high-spatial-resolution multispectral information in conjunction with monthly normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) time series, and additional terrain information. This paper presents a novel approach to characterize small-scale irrigation schemes that combine expert knowledge, multi-temporal NDVI time series, multispectral high-resolution satellite images, and the random forest classifier in the Zamra catchment, North Ethiopia. A fundamental element of the approach is mapping small-scale irrigation areas using expert decision rules to incorporate the available water resources. We apply expert decision rules to monthly NDVI composites from September 2020 to August 2021 along with the digital elevation model (DEM) data on the slope, drainage order, and distance maps to derive the sample set. The samples were based on the thresholds obtained by expert knowledge from field surveys. These data, along with the four spectral bands of a cloud-free Planet satellite image composite, 12 NDVI monthly composites, slope, drainage order, and distance map were used as input into a random forest classifier which was trained to classify pixels as either irrigated or non-irrigated. The results show that the analysis allows the mapping of small-scale irrigation areas with high accuracy. The classification accuracy for identifying irrigated areas showed a user accuracy ranging from 81% to 87%, along with a producer accuracy ranging from 64% to 79%. Furthermore, the classification accuracy and the kappa coefficient for the classified irrigation schemes were 80% and 0.70, respectively. As a result, these findings highlight a substantial level of agreement between the classification results and the reference data. The use of different expert knowledge-based decision rules, as a method, can be applied to extract small-scale and larger irrigation areas with similar agro-ecological characteristics.
1. Introduction
Similarly to approaches in other developing countries, Ethiopia has prioritized agricultural development through the expansion of an area under irrigation [1]. One of the strategies is to increase the total area of irrigated land from the current 2.3 million hectares to about 5.9 million hectares and improve existing irrigation schemes [1]. According to the Ministry of Water, Irrigation and Electricity (MoWIE), irrigation development is classified based on the size of the command area: small-scale (less than 200 hectares (ha)); medium-scale (200–3000 ha); and large-scale (greater than 3000 ha) [2,3]. This study focused on small-scale irrigation schemes. As part of the Growth and Transformation Plan (GTP) of Ethiopia [1], several small-scale irrigation projects have been implemented throughout the country, including in the regional state of Tigray, where this research was conducted [3,4,5]. To achieve the national targets, the regional government of Tigray, in Northern Ethiopia, has implemented water harvesting technologies such as dams, check dams, diversions, and wells to improve people’s livelihoods [6,7,8].
Irrigation schemes are classified based on the type of water storage and diversion structure [8]. Accordingly, first, traditional diversion irrigation schemes depend on river flows (intermittent), and the diversion was constructed through the pilling of brushwood, wood logs, and riverbed material [9] (Figure 1a). These schemes are typically built by the local community using unskilled labor and are prone to frequent headwork failure and siltation of the irrigation canal during the rainy season due to runoff [9,10]. The second diversion (modern) was constructed to avoid these challenges; development agencies and non-government organizations (NGOs) upgraded the headwork and the main canal to be constructed with concrete structures, as shown in Figure 1b [9,10]. Earth dam irrigation is the third type of irrigation scheme built from Earth materials on intermittent streams to store runoff during the rainy season [3,8].

Figure 1.
Examples of irrigation schemes found in the study area: (a) Traditional diversion; and (b) Modern diversion.
There are also small-scale irrigation schemes (grouped as others) in addition to the primary ones mentioned above, such as check dams, private and community wells, and springs. A check dam is constructed from stone bunds, filled with sediment, and has a 1–2 m height in the main channels [8,11]. Wells are used at the household and community levels to provide water for irrigation and are constructed using sand and cement [11,12] with a water level depth that varies from 5 to 20 m. Springs provide base flow for small-scale irrigation during the dry season [3,11,12].
It is vital for food security and water resource management studies to obtain accurate information about the location and extent of these small-scale irrigation areas [13]. Many studies have shown the usefulness of remote sensing (RS) for identifying irrigated areas [14,15,16]. A review of the literature generally shows three major approaches to mapping irrigated areas. (1) Numerous studies have been conducted to map irrigated areas using only the spectral reflectance characteristics of multispectral remote sensing images [13,14,15,17,18]. Satellite images with high spatial resolution, such as the Landsat-enhanced thematic mapper (ETM), were used to identify irrigated regions [17]. Additionally, a combination of Landsat ETM and moderate-resolution imaging spectrometer (MODIS) data were used to identify the fragmented and minor irrigation schemes [18]. However, it is recommended that using a very high spatial resolution (<5 m) is better to map fragmented and small irrigated areas; (2) Multispectral remote sensing images in combination with products derived from RS were also used to map irrigated areas. More recently, [19] developed a methodology that can map irrigated and rainfed agricultural areas of Ethiopia using Landsat 8, MODIS, and satellite-derived rainfall time series. Their study also highlighted the difficulty of identifying small-scale irrigation areas and the necessity of utilizing higher spatial resolution images [19]; (3) the identification of small-scale irrigated areas using RS-derived products only. An example is the seasonal water deficit index (WDI) approach by FAO-Water Productivity through the open access remotely sensed derived data (WaPOR) [20]. It was calculated using the ratio of satellite-derived seasonal precipitation (PCP) over seasonal evapotranspiration and interception (AETI). It compares the available water inputs from precipitation and the water output from transpiration, evaporation, and interception within a growing season [21]. According to the FAO WaPOR report, the seasonal water deficit index threshold value of less than 0.9 can be used to identify irrigated areas. When applying this approach, the irrigation area map’s distribution derived showed a large overestimation.
To overcome the challenges of the aforementioned approaches, multispectral time-series images with a very high spatial resolution made available by Norway’s International Climate and Forests Initiative (NICFI) in combination with digital elevation model (DEM) analysis and field knowledge are a new method to classify small-scale irrigation areas.
The application of expert knowledge has been successful in solving problems in the past [22,23,24,25], such as those relating to hydrology [26,27] and irrigation management [28,29]. Also, it can be used to develop a reliable model to manage the system of water resources [30,31]. As an alternative, complete environmental restoration priority areas were identified with the help of expert knowledge [32] and to improve spatially explicit ecosystem services [33]. Moreover, [34,35] explained that expert knowledge was more efficient in identifying crop types than knowledge based on statistical features only. An integral role in giving inputs for modeling and developing new algorithms relies on expert knowledge, which is developed through a combination of field experience and theoretical understanding [23,24]. But to our knowledge, no study has considered the integration of expert knowledge when mapping small-scale irrigation areas.
This paper proposes a new method that aims to classify small-scale irrigation schemes using expert knowledge, satellite-derived high-spatial-resolution multispectral information in conjunction with monthly NDVI time series, and additional terrain information obtained from a DEM analysis for Northern Ethiopia. The approach entails (1) Setting thresholds using expert knowledge to create samples using the NDVI-sum, slope, drainage order, and distance map. The sample set was split into two parts, as 2/3 were then used as input within the RF classifier and the remaining 1/3 was used for validation; (2) Applying the random forest classifier algorithm to produce the classification map for different years. The input for the random forest classifier contained the four spectral bands of a cloud-free composite Planet satellite image, 12 NDVI monthly composites, slope, and the drainage order and distance map. The spectral bands of the Planet satellite images are from March 2017, 2019, and 2021, representing the end of the irrigation season; (3) Characterizing the type of irrigation schemes and eventually the type of irrigation common in the area.
2. Study Areas and Dataset
2.1. Study Area
The study was conducted in the Zamra catchment, a tributary of the Tekeze sub-basin. The Tekeze sub-basin has a total area of 82,350 km2, and the Zamra catchment has an area of 1588 km2 (Figure 2). It is located between latitudes 12.966°N and 13.331°N and longitudes 39.003°E and 39.668°E. The altitude varies from 1248 m to 3542 m above sea level (m a.s.l). The topography of the study area is very complex, with mountains, plateau remnants, and steep escarpments with V-shaped and broad U-shaped valleys.
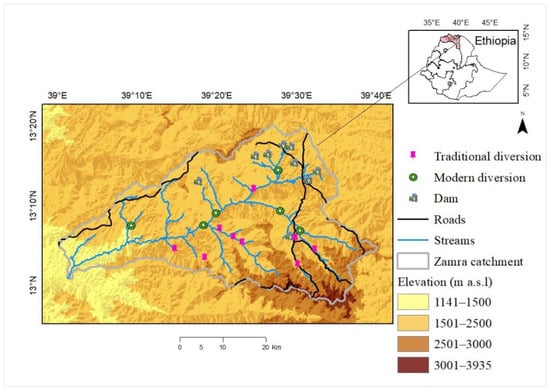
Figure 2.
Location of the Zamra catchment, including types of irrigation schemes.
The climatic condition of the Tigray region varies from arid to semi-arid [36]. The climate of the study area is mainly semi-arid; the primary rainfall season lasts from June to mid-September, with some areas also obtaining rainfall from February to May. Rainfall in the Tigray region is characterized as erratic and sometimes heavy rains cause flooding [3].
According to [37], a crop calendar is a summary chart showing a timetable of essential farming activities such as land preparation, planting, and harvesting. From May to June, the rainfed crop calendar begins with field preparation. From July through September, the crops are planted and start maturing, and the crops are harvested in October and November. The main crops grown in the rainfed season are maize, wheat, barley, and teff. The irrigation season, on the other hand, runs from November to April [37]. Farmers start planting their second crop as soon as the rainfed crops are harvested. From mid-December to March, different crops are planted, and in general, the crop is harvested in April. Crops like maize, onion, tomato, and pepper are grown during the irrigation season. Field visits and discussions with local farmers and extension workers provided additional information on the crop calendar during the irrigation season.
2.2. Dataset
2.2.1. Field Survey
A field survey was conducted during the irrigation season of 2020 to verify the accuracy of the remote sensing classification. Georeferenced data consisting of 163 represent homogenous areas were collected, encompassing various land cover types such as irrigated fields, rainfed fields, forests, and water bodies. Additionally, the detailed characteristics of the various irrigation schemes, such as dams and modern and traditional diversions, were also collected. The collected land cover data were used to interpret and analyze the various NDVI patterns observed over the year, and to verify the accuracy of the remote sensing classification results.
2.2.2. Remotely Sensed Data
Planet Scope Imagery
Planet operates a constellation of about 200 high-resolution satellites of Planet Scope, Rapid Eye, and Skysat that can image the whole land surface of the Earth every day in the visible and near-infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. Planet imagery is available in GeoTIFF file format, orthorectified and resampled to 3 m, and is projected into the UTM projection using the WGS84 Datum [38,39,40]. The Planet Scope Scenes are also radiometrically and atmospherically corrected [39,40]. For geometric correction, a digital elevation model with a post spacing between 30 and 90 m [39] is applied. In this study, the images taken at the end of the irrigation season in March were used (Figure A1a). The Planet images were collected for three years. To cover the whole area, separate dates were required, for example, (a) four dates in 2017 (2, 9, 16, and 17 March); (b) two dates in 2019 (19 and 21 March); and (c) one date in 2021 (March 8)—downloaded from: https://www.planet.com/explorer (accessed on 1 February 2022). The month of March, according to the crop calendar, reveals those areas having the highest likelihood of being irrigated as almost all the crops are at the maturity stage of their growth cycle [37]. However, no crops were grown outside the irrigated areas, such as within the rainfed areas in the Zamra catchment.
NICFI Base Maps
According to [41], the NICFI program (https://www.planet.com/nicfi/) (accessed on 6 October 2022) has provided free access to high-resolution satellite images. Currently, it covers historical biannual composites from December 2015 to present (one base map every six months) as well as a rolling archive for the last two years before present, consisting of one image mosaic for each month. NICFI has enabled the access and downloads of monthly mosaic data at a spatial resolution of 4.77 m [41]. Monthly composites (blue, green, red, and near-infrared (NIR)) from September 2020 to August 2021, available in Google Earth Engine (GEE) [42], have been processed and downloaded. NDVI monthly time series was calculated using bands 3 and 4, the red and NIR, respectively. Given the fact that, within the study area, according to the field survey conducted, no major changes have been observed within the overall cropping patterns, the NDVI time series are also used for the analysis of the other years, like 2017 and 2019, as the NDVI time series is regarded as a valid representation of these years as well.
DEM
A digital elevation model (DEM) of 30 m resolution was obtained from the Copernicus DEM GLO-30 (https://spacedata.copernicus.eu/, accessed on 10 February 2022). This elevation model describes the surface of the Earth, including buildings, infrastructure, and vegetation, identified water bodies are flattened, and a consistent flow of rivers is ensured [43]. A DEM is an essential information layer and is widely used to characterize the land surface used for topographic mapping and hydrological studies [44,45,46]. Furthermore, a DEM has been widely utilized to detect and characterize various topographical features that could be used for irrigation [18,46,47].
Precipitation
The mean monthly precipitation data from September 2020 to August 2021 for the Zamra catchment are shown in Figure 3. The precipitation was calculated from the Climate Hazards Group InfraRed Precipitation with the Station (CHIRPS) available within the WaPOR database [20]. The highest rainfall was obtained in July and August. However, the lowest was recorded in December and January. Additionally, the mean annual precipitation values of 2009–2021 for the Zamra catchment were analyzed using the WaPOR database [20], and the average annual precipitation was 600 mm. In the Zamra catchment, the minimum and maximum yearly precipitation over the analysis period was 514 mm and 715 mm, respectively.
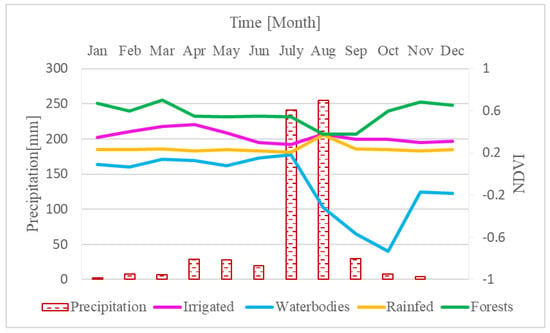
Figure 3.
Average monthly precipitation and NDVI for different classes from September 2020 to August 2021 in the Zamra catchment.
3. Methodology
Figure 4 provides an overview of the methodological approach developed for identifying and characterizing small-scale irrigation schemes in the Zamra catchment. Expert knowledge thresholds for the NDVI-sum, slope, drainage order, and distance maps were applied to identify suitable irrigation areas. The integration of multitemporal monthly NDVI analysis and topographic spatial expert decision rules, in conjunction with the utilization of the random forest classifier algorithm, facilitated the accurate delineation of small-scale irrigation areas.
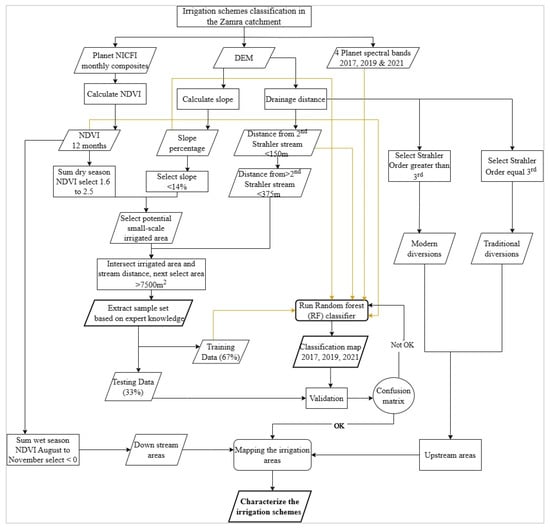
Figure 4.
Overview of the approach for mapping small-scale irrigation areas.
The procedure is as follows: initial sample set creation by classifying all pixels according to the decision rules based on expert knowledge obtained from field surveys. Second, using a median aggregation factor, a regular-spaced sample set—having a sample point density every five lines/columns for irrigated and non-irrigated areas for the whole study area was obtained. Third, the sample set was split into two parts, where 67% was used as input within the RF classifier and 33% was used for validation. Fourth, apply the random forest classifier algorithm to produce the different-year classification maps. The input for the random forest classifier contained the four spectral bands of a cloud-free composite Planet satellite image, 12 NDVI monthly composites, slope, and the drainage order and distance map. Lastly, a characterization to derive the type of irrigation schemes and the type of irrigation common in the area was applied. In addition, a sensitivity analysis was carried out using thresholds other than the expert decision rule to evaluate the thresholds selected.
The software used for this analysis was Python 3.8.5 and the Integrated Land and Water Information System (ILWIS 3.8.6). All the processing was performed using the ITC geospatial computing platform (http://crib.utwente.nl) (accessed on 30 November 2023).
3.1. Use of Expert Knowledge
Creating a distribution map of small-scale irrigation areas can be achieved by utilizing expert knowledge to create samples. The primary advantage of this approach is its ability to incorporate local knowledge and experience into the mapping process, which can lead to more accurate and reliable results. Additionally, such information can be combined with other relevant datasets to generate a comprehensive map of small-scale irrigation areas. Expert knowledge is particularly valuable when data are incomplete or insufficient, as it can provide a more comprehensive and formalized understanding of the topic at hand, as in [48]. Using expert knowledge, we derive samples that have proven successful in previous studies [34,35] for mapping and identifying crop types. They used expert knowledge inputs and image analysis. A more recent approach is the geoscience-aware deep learning (GADL) paradigm, developed by [49], which thoroughly integrates deep learning models with geoscience knowledge to extract information from remote sensing data. In their approach, incorporating geoscience knowledge with deep transfer learning, self-supervised or semi-supervised learning is a promising way to make models work well with insufficient labeled data. Therefore, expert knowledge identifies the factors that affect mapping irrigation areas and how these factors and relations affect the mapping of irrigation areas. The expert knowledge-based method of creating a sample set comprises three general processes: (1) calculate and sum NDVI to select the threshold significant to the study area; (2) calculate the slope and drainage distance that can be considered appropriate; and (3) derive the sample set based on the decision rules. The following sections describe each of these steps in more detail.
Step 1: Calculate NDVI
The NDVI was calculated by applying scripts in Google Earth Engine using band 4 (NIR) and band 3 (red) monthly NICFI composites from September 2020 to August 2021. The output NDVI values range from −1.0 to +1.0. For instance, values of less than 0 show water bodies [17]. In addition, the NDVI values ranging from 0 to 0.2 reflect sand, soil, or bare farmlands; 0.2–0.5 represent sparse vegetation such as bushes, grasses, or senescing crops; and larger than 0.5 represent crops at peak growth stages or forests [50,51]. As a result, one cover type can be distinguished from another based on NDVI values in relation to temporal changes over time in accordance with the crop calendar of the study area.
Figure 3 shows an average value of NDVI over a monthly temporal interval for some field-validated main cover types, such as forests, water bodies, and irrigated and rainfed fields. The NDVI time-series data reflect the cropping calendar [52] and allow for the identification of irrigated and non-irrigated areas [53]. Rainfed fields strongly correlate with rainfall, while the forests and irrigated fields had a weak relationship. For instance, irrigated fields depend on other sources of water during the dry season. Overall high NDVI values represent forests, and the rainfed areas show a remarkable increase in NDVI from the start of the rainy season. The irrigated areas show an increase in NDVI values from January until the end of April, which is considerably lower than for the forests but substantially higher than those of the rainfed areas, as no crops were grown.
Figure A2 shows the NDVI time series for the Zamra catchment from September 2020 to August 2021. During the wet season, the water bodies are clearly visible (August to November) and are represented within the NDVI time series by a sharp decrease in NDVI from July onwards until October and remain below 0 until the end of the year.
NDVI has proven to be a successful representation of identifying irrigated areas in other studies as well [17,18,54,55]. The NDVI-sum represents the summation of NDVI values during the irrigation season, which extends from January through May, with NDVI values falling within the range of −0.5–4.0. The derived NDVI thresholds are based on irrigated fields, water bodies, and forests validated by field surveys. The threshold selected that shows the best separation are non-irrigated (0–1.6), irrigated (1.6–2.5), forest (>2.5), and waterbodies (<0) (see Figure A1e).
Step 2: Calculate slope and drainage distance
The DEM was used to generate slope and drainage order and distance maps to identify areas suitable for irrigation in the Zamra catchment. In the study area, based on field observations, the maximum slope percentage for the various types of irrigation schemes was less than 14 percent (Figure A1f). A slope steepness of less than 20 percent was regarded as moderately suitable for water-harvesting structures in the region [3].
Furthermore, the DEM was used to derive the drainage distance map [18]. A drainage distance map is a spatial representation illustrating the distances water must traverse across a landscape to reach specific drainage points [56]. The following procedure was applied:
- First, the hydrological flow was determined; procedures followed included the calculation of a hydrologically consistent elevation model by the removal of sinks, flow direction, and flow accumulation.
- Second, the calculation of variable thresholds map to enable multiple flow accumulation thresholds was used in the drainage network extraction operation as the terrain consists of relatively flat plateau remnants (having larger flow accumulation thresholds) and steep escarpment with V-shaped valley floors (having lower flow accumulation thresholds) as well as broad U-shaped valleys (intermediate flow accumulation thresholds).
- Extract the drainage network (see Figure A1c) and conduct a drainage network ordering an operation to derive a full topological description of the network extracted.
The derived drainage network topological description, including the Strahler rank-ordering scheme [57,58], was subsequently used to derive another set of thresholds. The maximum distance from the drainage network for the 2nd Strahler stream order was set to less than 150 m and less than 375 m for higher-order stream thresholds to identify increased upstream areas. The stream order is the quantification of a stream’s position within the hierarchy of streams according to the Strahler ordering system [56]. Larger irrigation areas (based on the slope map and NDVI-sum map) were retained if they had a contiguous area of more than 7500 m2 based on the field survey conducted (see Figure A1d).
Step 3: Derive sample set based on the decision rules
To derive the sample set first, the NDVI and DEM were resampled for further processing to a 15 m resolution; this can improve the accuracy and reliability of the results. However, resampling from a higher resolution to a coarser resolution can result in a loss of spatial information, which may affect the accuracy of subsequent analyses. However, the NDVI data to a 15 m resolution are appropriate as long as the potential loss of spatial information is carefully considered and justified. The selected NDVI-sum threshold value from 1.6 to 2.5 and the slope gradient of less than 14 percent were used. Subsequently, this map intersected with the selected areas derived according to the drainage distance thresholds applied, including the larger irrigation areas. The sample set irrigation area was reduced to 2432 ha from the initial area based on the slope and NDVI-sum thresholds of 3421 ha by removing areas situated further away from the drainage network, which had a very low likelihood of being irrigated areas.
3.2. Create a Sample Set
The sample set, based on sample ground truth data, was obtained through expert terrain knowledge in combination with a decision rule concept. To generate regularly spaced sample points, the original sample set was aggregated by a factor of five. This ground truth dataset was then randomized to avoid sampling bias. Figure A1b concisely describes the sample point used to distinguish between irrigated and non-irrigated areas during the 2021 irrigation season. Also, the samples were used as input to generate classification maps for different years such as 2017 and 2019. Two-thirds of the sample points were used as input for the RF classifier and the remaining 1/3 was used for validation.
3.3. Random Forest Classifier
A random forest classifier creates several decision trees from a subset of training samples and variables that are chosen at random [59,60]. RF was selected because it has been used to classify particular target classes [53,61]. In addition, RF was considered a robust classifier with high-resolution satellite images [59,60,61,62] and had a high degree of accuracy in identifying classes [59,60,62,63]. The random forest method can use various datasets and process data quickly [53,60]. The diversity of the input datasets may be used to enhance the classification, and it was determined that the input datasets were crucial for the classification [60,63]. RF has been proven to be a successful classifier for identifying classes when using multi-sources of remote sensing data in other studies [61,63,64,65]. The map stack, which included the four Planet spectral channels, the drainage order, the distance map, the slope map, and the 12 NDVI monthly composites, totaled 18 layers as inputs to the random forest algorithm.
3.4. Validation
The accuracy of the mapped irrigation schemes was evaluated by comparing the ground truth obtained from field surveys and high-resolution satellite images to the irrigation scheme types identified through the expert decision rules. Visual interpretation with prior knowledge of the study area also contributed to the accuracy assessment. Furthermore, overlaying the irrigation scheme types onto classified images allows for the validation of the detailed characteristics of the irrigation schemes. The accuracy assessment was essential in determining the quality of the classified irrigation areas. The classification error matrix, overall accuracy (OA), user accuracy (UA), produce accuracy (PA), and the kappa coefficient were used to evaluate the result of the classification process [66,67]. The accuracy assessment was based on the output of the RF classified maps and the validation dataset.
3.5. Classify Types of Irrigation Schemes
From August through November, the NDVI value of the water bodies remained negative (Figure 3). As a result, the sum of the NDVI during the wet seasons (from August to November) was chosen to be smaller than 0 to identify the water bodies. A previous study [17] selected water bodies based on an NDVI value of 0.1 or less. In addition, modern and traditional diversions are based on upstream contributing areas considering flow velocities in the stream network at a higher Strahler order. For instance, it was observed that modern diversions are located in areas having Strahler stream orders greater than the third order. Traditional diversions are observed in areas having smaller contributing upstream areas and are therefore situated in areas having a third Strahler stream order.
3.6. Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis was conducted to quantify the sensitivity of variables using different thresholds [68]. Table 1 indicates the input with different thresholds. Set 1 uses actual field data and expert knowledge, while Sets 2 and 3 use modified values to anticipate large and small areas. The purpose of using different sets of inputs with different thresholds is to see how sensitive the analysis is to different input values and assess the robustness of the result. The sample area for the first set was 2324 ha, while for the second and third sets, it was 4911 ha and 1924 ha, respectively. Accordingly, the modified thresholds are sensitive to the expert knowledge utilized in this study. Based on the analysis, it was found that NDVI is the most sensitive input variable in the classification process, meaning it had the greatest impact on accurately distinguishing between irrigated and non-irrigated areas. The slope was found to be the second most sensitive input variable. However, it was observed that the drainage distance was not as sensitive as the other two variables in distinguishing between irrigated and non-irrigated areas. Hence, the three samples were input into the random forest classifier, and the accuracy assessment result was compared.

Table 1.
Inputs for the three sets with various thresholds.
4. Results
4.1. Expert and Other Decision Rules
The irrigated areas obtained from the three sets are presented in Table 2. These values represent the specific areas of land that were classified as irrigated using the RF classifier based on the sample set. The results show that Set 2 had the largest irrigated area, followed by Set 1 and then Set 3. The modified values used in Set 2 may have resulted in more areas being classified as irrigated but potentially not irrigated. On the other hand, Set 3 may have smaller candidate irrigation areas, leading to lower accuracy. Set 1 had the highest overall accuracy and kappa coefficient, indicating that it provided the most accurate classification results compared to Set 2 and Set 3. Therefore, the threshold determined by expert knowledge shows a satisfactory result, showing no overestimation or underestimation. Sample Set 1 was utilized as a valid input to generate classification maps for different years, such as 2017 and 2019.

Table 2.
Area coverage, overall accuracy, and kappa coefficient for the three sets.
4.2. Feature Importance Scores
The RF algorithm produces an accuracy assessment called “Out-of-Bag” (OOB) and measures feature importance scores [59,65]. The accuracy assessment for three years produced by the RF classifier is presented in Table 3. The OOB is calculated using out-of-bag samples and measures the model’s performance on unseen data. The OOB samples in each tree can be used to validate each tree [59]. Generally, the default 500 decision trees were popularly implemented and used in RF modeling [60]. As a result, the chance that an object is left out of the bootstrap dataset is low. The final classification decision is taken using the arithmetic mean of the class assignment probabilities calculated by all produced trees. New unlabeled data input is thus evaluated against all decision trees created in the collective, and each tree votes for class membership. The membership class with the maximum votes will be the one that is finally selected [59,60]. According to [60], the RF feature importance measurement is used to identify the most relevant multi-source remote sensing data and to select the most suitable season to classify particular target classes. As a result, bands 4 and 3, representing NIR and red, slope, and drainage distance were identified as the most important input features. In addition, the monthly NDVI had the highest importance from March to May during all years (Table 3).

Table 3.
OOB prediction accuracy and feature importance scores for the years 2017, 2019, and 2021.
4.3. Irrigated Area Classification
The classified images of the three study periods (2017, 2019, and 2021) are presented in Figure 5a–c. The map distinguishes the spatial and temporal distribution of the irrigated and non-irrigated areas. In 2017, 2019, and 2021, the irrigated areas covered 2078, 2093, and 2186 hectares (ha), respectively, as shown in Table 4. It also shows that the irrigation area is expanding over time.
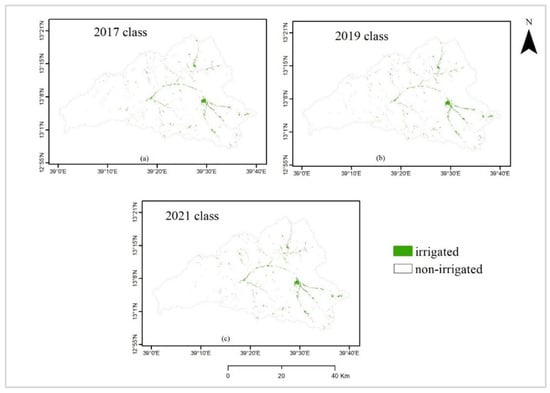
Figure 5.
(a) Classified maps from the random forest classification of the three periods: (a) 2017, (b) 2019, and (c) 2021.

Table 4.
Irrigated and non-irrigated area distribution in 2017, 2019, and 2021.
Table 5 presents the results of the overall accuracy, kappa coefficient, PA, and UA of the irrigated and non-irrigated areas. The results showed that OA ranged from 99.6% to 99.7% over the three years and the Kappa coefficient ranged from 0.71 to 0.83. The classified image in 2021 achieved the highest kappa coefficient of 0.83 and an OA of 99.7%. The classified image in 2017 produced the lowest kappa coefficient of 0.71 and an OA of 99.6%. The classification accuracy of the irrigated areas was, with the PA and UA, above 64% in all periods (Table 5). This finding shows that high-resolution satellite images obtained a high PA and UA.

Table 5.
The overall accuracy, producer accuracy, and user accuracy of the classified image.
The irrigated areas were crossed to check all-time irrigated, non-irrigated at all, and each year irrigated (Figure 6). Almost every year, the irrigated areas were extracted for the same locations.
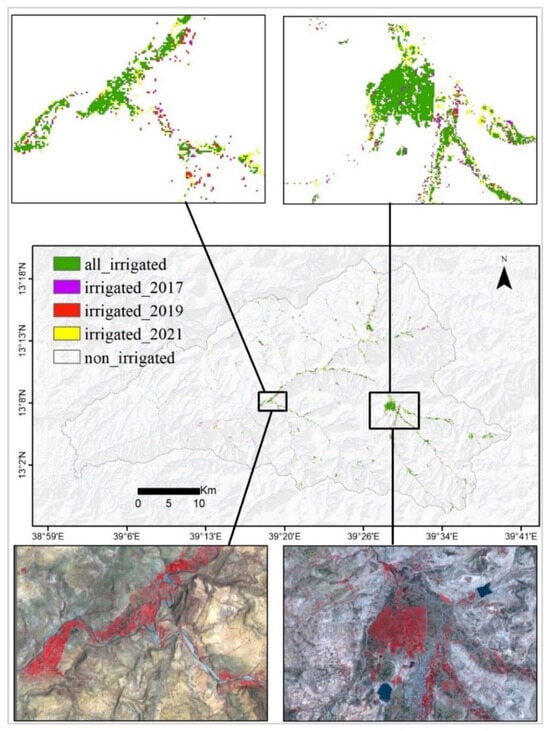
Figure 6.
Three years of irrigated areas within the Zamra catchment combined.
4.4. Characterize Irrigation Scheme Types
Using the developed approach, it is also possible to characterize the small-scale irrigation schemes, as shown in Figure 7, such as dams, modern, and traditional diversions, and other irrigation schemes (check dams, private and community wells, and springs). The results are in agreement with field observations. Also, other irrigation schemes like private and community wells are commonly used in places of the study area. The dam is located downstream of the water bodies and upstream of an irrigation area. They are mainly located in the upper part of the catchment. Modern and traditional diversions are based on upstream contributing areas. Traditional diversions are found in upstream areas and nearby streams, whereas modern diversions are situated further downstream. Dams, modern diversions, traditional diversions, and other schemes covered 309 ha, 470 ha, 598 ha, and 809 ha, respectively in 2021.
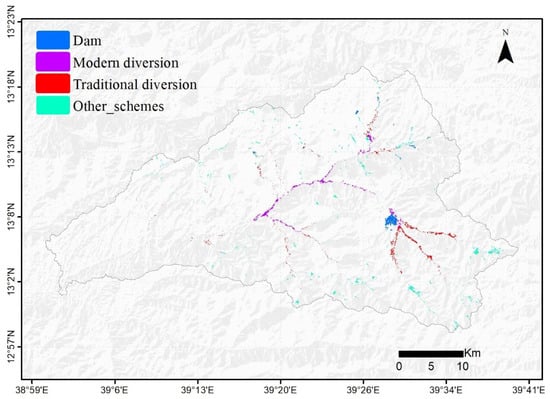
Figure 7.
Type of irrigation schemes within the Zamra catchment.
4.5. Evaluation of Irrigation Schemes
The results of the small-scale irrigation scheme characterization demonstrate the potential of remote sensing data and random forest algorithms to accurately identify and map different types of irrigation schemes. Additional information, such as field data, is needed to accurately differentiate between these different types of irrigation schemes. Table 6 presents the results of the small-scale irrigation scheme characterization. The results show that OA and kappa coefficients were 80% and 0.70, respectively, indicating a substantial agreement between the classification results and the reference data. The accuracy of other irrigation schemes was also relatively high, with a PA and UA above 80%. However, there were confusions with the dam, traditional, and modern diversions.

Table 6.
Contingency matrix for the classified irrigation schemes of the Zamra catchment.
5. Discussion
5.1. Using Expert Knowledge
This study was the first to apply expert knowledge together with the random forest classifier algorithm to extract and characterize small-scale irrigation schemes in the Northern Ethiopian highlands. The advantage of expert knowledge is the ability to incorporate the threshold values of the NDVI-sum, slope, stream threshold map distance, and Strahler stream order. The approach in this paper is applicable for immediate execution without additional data; it only requires the different thresholds. In addition, there is no need to collect training data every year, making it very time- and labor-efficient for a large area. When transferred to a new region, the threshold needs to be adapted. However, the existing approach may still be helpful, and the threshold may only need slight adjustments, especially when the areas have similar agro-ecological characteristics. Therefore, the better the expert knowledge representing the actual field situation, the better the outcome will be [27].
Extracting irrigation areas using different more traditional classification routines was inappropriate as it resulted in misclassification, especially with respect to forest areas. In addition, the irrigation areas were not correctly estimated using the WaPOR data products. To improve the accuracy of mapping the small-scale irrigation areas, an approach was developed using multitemporal monthly NDVI analysis and topographic spatial expert decision rules as input for a random forest classifier algorithm. The 5 m resolution monthly NDVI time series permits the characterization of land cover types and agricultural smallholder cropping patterns in the area.
The expert decision rule can be constructed from the NDVI time series and a DEM. The NDVI time series used in 2021 is considered valid even for other years, like 2017 and 2019. The NDVI-sum threshold was chosen because it distinguished irrigated areas from non-irrigated and forest areas. Also, previous research shows that NDVI makes it possible to identify irrigated areas [17,18,53,54]. In addition, the DEM has been used to identify drainage networks and slope processes [46,69,70]. As the study area topography is very complex and mountainous, an appropriate slope threshold was considered. In addition, the drainage network distance and Strahler stream order thresholds were applied. Because of the steep escarpments with V-shaped and broad U-shaped valleys, identified irrigation areas are affected by terrain complexity. According to [24], expert knowledge improves the quality of produced data.
Based on the analysis of different thresholds from expert knowledge, this study characterizes small-scale irrigation scheme types. The result showed that the modern and traditional diversions are based on upstream contributing areas considering the flow amount and velocities in the stream as, at a higher Strahler order, the stream would destroy the traditional intake. For instance, it is observed that modern diversions are situated further downstream (Figure 7). Modern diversion structures directly utilize available water from perennial and ephemeral streams [71]. On the other hand, traditional diversions are linked to smaller contributing upstream areas (Figure 7). Moreover, the dam is located downstream of the water bodies and upstream of an irrigation area [3,8,71]. Identifying other irrigation scheme types remains difficult.
Traditional diversion identification accuracies, like the producer and user accuracies, were lower than the other irrigation scheme types, which could be confused with modern diversion and other schemes (Table 6). According to [3], traditional diversions of the perennial stream use temporary structures during the dry season. So, traditional diversions may be confused with modern diversions. Overall, when comparing and discussing the accuracies of various irrigation scheme types, it can be observed that the classification achieved a good kappa value [72]. Generally, expert knowledge achieves the objective of the study as, in previous studies [23,25,33], it has been used for mapping ecosystem services, landslide, and flood-based farming systems.
5.2. Random Forest Classifier
In the image classification to improve the classification accuracy, the NDVI monthly composite, slope, drainage order and distance map, and spectral bands of the Planet satellite images were used as input layers. The inputs were also used for other years, for example, in 2017 and 2019. The result of feature importance is presented in Table 3. The general trend observed was that the four most important features are composed of two spectral bands (NIR and red), slope, and drainage distance; the slope was the most important input feature for all the analyzed periods. The next important input was the NIR spectral band. The importance of NIR can be explained by the presence of vegetation and its coverage [73]. In addition, the most important NDVI layers were from March through May. High NDVI values on cultivated land during the dry season indicated irrigation, given the presence of denser vegetation [53,73].
The classified maps of the Zamra catchment are shown in Figure 5a–c. Overall, the results of the irrigated areas in the classified maps are good. Over different years, the random forest classifier algorithm has been shown to be an excellent approach for classifying irrigated and non-irrigated areas. Previous studies also confirmed that the RF classifier was a robust and effective method [53,54,66,67,74]. High-resolution satellite images gave a substantially higher overall accuracy for mapping irrigated areas [17]. The kappa coefficient was significantly better in 2021 compared to 2019 and 2017 (Table 5). This outcome occurred because the NDVI time-series data from 2021 was utilized as input for the other years. However, according to [72], a kappa coefficient of 0.4–0.75 was considered a good value, which was also the case for the other years analyzed. Figure 6 and Table 4 present a gradual increase in irrigation areas from 2017 to 2021. Therefore, the results showed an increase in irrigation areas over time, regardless of the rainfall variability in the given years.
5.3. High-Resolution Multispectral Satellite Images
Generally, the analysis conducted followed the recommendation of previous studies, stating that using high-resolution satellite images to map small-scale irrigation areas is a requirement [18,19,74]. Now, NICFI base maps at a spatial resolution of 4.77 m and monthly cloud-free composite images are a unique opportunity to identify irrigation areas. The advantage of the NICFI base maps can be summarized as follows: First, NICFI has provided free access to high-resolution satellite images [41]. Currently, it covers historical biannual composites from December 2015 to the present day (one base map every six months) as well as a rolling archive for the last two years before the present day, consisting of one image mosaic for each month; Second, for the NDVI analysis, NICFI composite images were used. As a result, the monthly NDVI data are utilized to observe the cropping patterns for the dry and wet seasons and to provide details on the temporal changes in crop calendars between irrigated and non-irrigated areas. Third, the NICFI, in conjunction with expert knowledge, could classify small-scale irrigation areas such as dams and diversions (traditional and modern).
6. Conclusions
This research aimed to develop a new methodology for mapping and characterizing small-scale irrigation schemes by combining expert knowledge and applying a random forest classifier algorithm. Expert knowledge was used to create the sample set, which was partially used as training input for the random forest classifier. The remaining was used for the classification error matrix validation. The random forest classifier inputs included satellite-derived high-spatial-resolution multispectral information in conjunction with monthly NDVI time series and additional terrain information. Overall, the approach has shown the ability to accurately map small-scale irrigation schemes and allows the characterization of the type of irrigation common within the study area.
NDVI monthly data are used to characterize the cropping season over the years investigated. The cropping patterns have not changed (e.g., for rainfed and irrigated agriculture); therefore, the NDVI time series used is a valid representation even for other years, like 2017 and 2019. The RF produces feature importance measures that indicate each variable’s influence on the classification. As a result, the slope was the most important input feature that provided the most valuable information to the classification. Moreover, the Planet satellite spectral bands 4 and 3, representing NIR and red, were identified as the most relevant variable for mapping irrigation areas. The NDVI time series feature importance scores followed a similar pattern for all three years, with the highest importance from March to May; this shows the most suitable season to classify the irrigated areas. Therefore, using the NDVI time series as additional input to classify small-scale irrigation areas is an important asset to distinguish rainfed from small-scale irrigation. In addition, the DEM analysis is used to generate slope for irrigation terrain suitability and to derive hydrological characteristics like upstream areas identified as potential water availability. Hence, the random forest classifier with expert knowledge could classify small-scale irrigation areas, including various types of diversions, such as traditional and modern diversions and dams. Furthermore, a sensitivity analysis was executed to assess the impact of variables by applying modified thresholds to generate the sample sets. As a result, biased sample sets were created, which led to both overestimation and underestimation. However, when using the sample set derived from the initial expert knowledge incorporating the field survey information, good results could be obtained.
Therefore, it is suggested that this approach can be generally applied to extract small-scale and larger irrigation areas with similar agro-ecological characteristics and likely elsewhere in Ethiopia, using conceptually different expert knowledge-based thresholds for NDVI-sum, slope, drainage order, and distance. However, identifying the class of “other irrigation schemes” remains challenging, so further research is recommended.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.M. and B.H.P.M.; methodology, A.A.M. and B.H.P.M.; formal analysis, A.A.M.; writing original draft preparation, A.A.M., writing, review and editing, A.A.M., B.H.P.M. and C.M.M.; visualization, A.A.M.; supervision, C.M.M., B.H.P.M. and D.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Dutch Organization for Internationalization in Education (Nuffic), the University of Twente, the Faculty of Geo-information Science and Earth Observation (ITC), and the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of Ethiopia (MoSHE) under the Ethiopian Educational Network to Support Agricultural Transformation (EENSAT) project (CF13198, 2016).
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on the Data Archiving and Networking Service (DANS) of the University of Twente, Enschede, the Netherlands.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
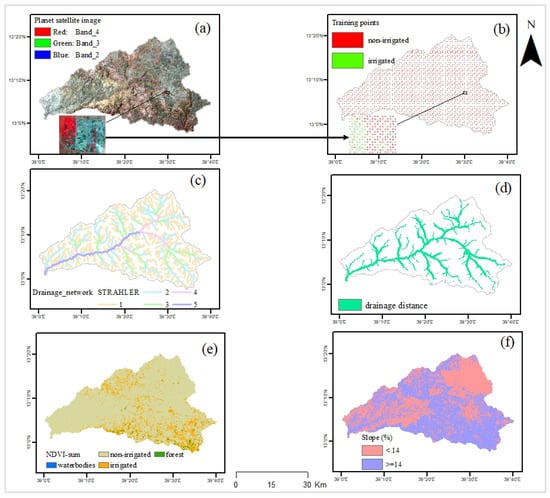
Figure A1.
(a) Planet Scope imagery Bands 4, 3, and 2 (NIR, red, and green, respectively); (b) sample training points; (c) drainage network Strahler; (d) drainage distance with a selected large area; (e) NDVI-sum of the irrigation season; and (f) slope.
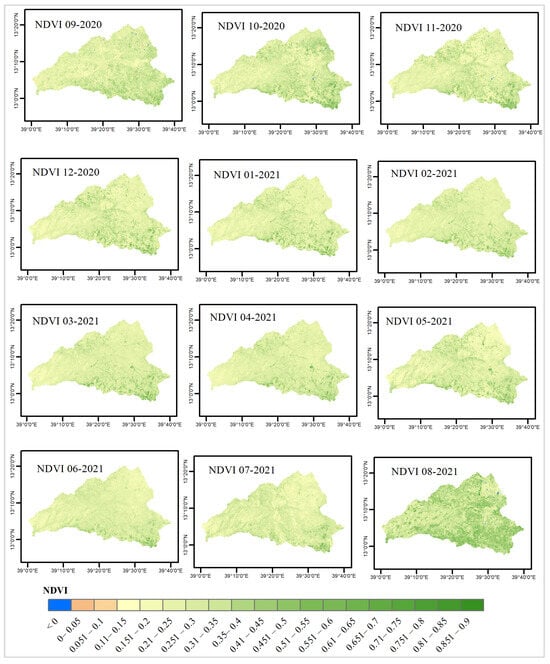
Figure A2.
NDVI time-series map from September 2020 to August 2021.
References
- National Planning Commission, Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia. Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia Growth and Transformation Plan II (GTP II); National Planning Commission, Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Awulachew, S.; Erkossa, T.; Namara, R.E. Irrigation Potential in Ethiopia: Constraints and Opportunities for Enhancing the System; F1000Research; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hagos, E. Development and Management of Irrigation Lands in Tigray, Ethiopia. Ph.D Thesis, Wageningen University, Delft, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Teka, D.; van Wesemael, B.; Vanacker, V.; Poesen, J.; Hallet, V.; Taye, G.; Deckers, J.; Haregeweyn, N. Evaluating the Performance of Reservoirs in Semi-Arid Catchments of Tigray: Tradeoff between Water Harvesting and Soil and Water Conservation. Catena 2013, 110, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yohannes, D.F.; Ritsema, C.J.; Solomon, H.; Froebrich, J.; van Dam, J.C. Irrigation Water Management: Farmers’ Practices, Perceptions and Adaptations at Gumselassa Irrigation Scheme, North Ethiopia. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 191, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behailu, M.; Haile, M. Water Harvesting in Northern Ethiopia: Environmental, Health and Socio-Economic Impacts | Mendeley. Available online: https://www.mendeley.com/search/?page=1&query=Water%20harvesting%20in%20northern%20Ethiopia%3A%20environmental%2C%20health%20and%20socio-economic%20impacts&sortBy=relevance (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Haregeweyn, N.; Poesen, J.; Nyssen, J.; de Wit, J.; Haile, M.; Govers, G.; Deckers, S. Reservoirs in Tigray (Northern Ethiopia): Characteristics and Sediment Deposition Problems. Land Degrad. Dev. 2006, 17, 211–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teka, D. Multi-Scale Analysis of Surface Runoff and Water-Harvesting Dams in a Semi-Arid Region: A Case Study in Tigray (Ethiopia). Ph.D. Thesis, UCL—Université Catholique de Louvain, Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yami, M. Sustaining Participation in Irrigation Systems of Ethiopia: What Have We Learned about Water User Associations? Water Policy 2013, 15, 961–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrehiwot Yihdego, A. The Impact of Small—Scale Irrigation on Income of Rural Farm Households: Evidence from Ahferom Woreda in Tigray, Ethiopia. Int. J. Bus. Econ. Res. 2015, 4, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segers, K.; Dessein, J.; Nyssen, J.; Haile, M.; Deckers, J. Developers and Farmers Intertwining Interventions: The Case of Rainwater Harvesting and Food-for-Work in Degua Temben, Tigray, Ethiopia. J. Agric. Sustain. 2011, 6, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meaza, H.; Demissie, B.; Hermans, L.; Haftu, B.; Biruk, B.; Poesen, J.; Gebreyohannes Asfaha, T.; Zenebe, A.; Nyssen, J. Spatial and Seasonal Water Level Dynamics in Dryland Grabens along the Rift Valley of Northern Ethiopia. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2022, 67, 1418–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, K.; Ma, M.; Liu, W.; Dong, J.; Zhu, X.; Yuan, W. Mapping Irrigated Areas of Northeast China in Comparison to Natural Vegetation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guermazi, E.; Bouaziz, M.; Zairi, M. Water Irrigation Management Using Remote Sensing Techniques: A Case Study in Central Tunisia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbahria, Z.; Sebari, İ.; Hajji, H.; Smiej, M.F. Intelligent mapping of irrigated areas from landsat 8 images using transfer learning. Int. J. Eng. Geosci. 2021, 6, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abera, A.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; Tilahun, S.; Inyang, H.; Nyssen, J. Assessment of Irrigation Expansion and Implications for Water Resources by Using RS and GIS Techniques in the Lake Tana Basin of Ethiopia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 193, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velpuri, N.; Thenkabail, P.; Gumma, M.; Biradar, C.; Dheeravath, V.; Noojipady, P.; Yuanjie, L. Influence of Resolution in Irrigated Area Mapping and Area Estimation. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2009, 75, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumma, M.K.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Hideto, F.; Nelson, A.; Dheeravath, V.; Busia, D.; Rala, A. Mapping Irrigated Areas of Ghana Using Fusion of 30 m and 250 m Resolution Remote-Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 816–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekharan, K.M.; Subasinghe, C.; Haileslassie, A. Mapping Irrigated and Rainfed Agriculture in Ethiopia (2015–2016) Using Remote Sensing Methods; International Water Management Institute (IWMI): Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- WaPOR. FAO’s Portal to Monitor Water Productivity through Open Access of Remotely Sensed Derived Data. Available online: https://wapor.apps.fao.org/home/WAPOR_2/1 (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- FAOP Water Productivity. Available online: https://data.apps.fao.org/catalog/organization/wapor (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Huang, Z.; Jia, X. Integrating Remotely Sensed Data, GIS and Expert Knowledge to Update Object-Based Land Use/Land Cover Information. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 905–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Wang, R.; Qiao, J.; Qin, C.Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Du, F.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, T. An Expert Knowledge-Based Approach to Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using GIS and Fuzzy Logic. Geomorphology 2014, 214, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yathish, H.; Athira, K.V.; Preethi, K.; Pruthviraj, U.; Shetty, A. A Comparative Analysis of Forest Fire Risk Zone Mapping Methods with Expert Knowledge. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2019, 47, 2047–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harou, I.L.; Whitney, C.; Kung’u, J.; Luedeling, E. Mapping Flood-Based Farming Systems with Bayesian Networks. Land 2020, 9, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Her, Y.; Kang, M.S. Estimating Reservoir Inflow and Outflow From Water Level Observations Using Expert Knowledge: Dealing With an Ill-Posed Water Balance Equation in Reservoir Management. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2020WR028183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonetti, M.; Zappa, M. How Can Expert Knowledge Increase the Realism of Conceptual Hydrological Models? A Case Study in the Swiss Pre-Alps. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 4425–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigussie, E.; Olwal, T.; Musumba, G.; Tegegne, T.; Lemma, A.; Mekuria, F. IoT-Based Irrigation Management for Smallholder Farmers in Rural Sub-Saharan Africa. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 177, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merot, A.; Bergez, J.E. IRRIGATE: A Dynamic Integrated Model Combining a Knowledge-Based Model and Mechanistic Biophysical Models for Border Irrigation Management. Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi, H.R.; Golmohammadi, M.H.; Sandoval-Solis, S. Expert Knowledge Based Modeling for Integrated Water Resources Planning and Management in the Zayandehrud River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2015, 528, 773–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrachowitz, M.; Fovet, O.; Ruiz, L.; Euser, T.; Gharari, S.; Nijzink, R.; Freer, J.; Savenije, H.H.G.; Gascuel-Odoux, C. Process Consistency in Models: The Importance of System Signatures, Expert Knowledge, and Process Complexity. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 7445–7469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.R.; Shi, Z.H.; Chongfa, C. Assessing Regional Environmental Quality by Integrated Use of Remote Sensing, GIS, and Spatial Multi-Criteria Evaluation for Prioritization of Environmental Restoration. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 6993–7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grêt-Regamey, A.; Brunner, S.H.; Altwegg, J.; Christen, M.; Bebi, P. Integrating Expert Knowledge into Mapping Ecosystem Services Tradeoffs for Sustainable Forest Management. Ecol. Soc. 2013, 18, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Hu, L.; Yu, L.; Gong, P.; Biging, G.S. Automated Mapping of Soybean and Corn Using Phenology. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 119, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Zhu, W.; Zhan, P.; Ding, S. An Identification Method for Spring Maize in Northeast China Based on Spectral and Phenological Features. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataklti, Y.T. Assessing the Potential of Geonetcast Earth Observation and In Situ Data for Drought Early Warning and Monitoring in Tigray, Ethiopia. Master’s Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Behailu, M.; Nata, T. Monitoring Productivity of Water in Agriculture and Interacting Systems: The Case of Tekeze/Atbara River Basin in Ethiopia. In Proceedings of the East Africa Integrated River Basin Management, Morogoro, Tanzania, 7–9 March 2005. International Water Management Institute Conference Papers (No. h037543). [Google Scholar]
- Planet Team. Planet Application Program Interface: In space for life on Earth; Planet Team: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Marta, S. Planet Imagery Product Specifications; Planet Labs: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, D.P.; Huang, H.; Houborg, R.; Martins, V.S. A Global Analysis of the Temporal Availability of PlanetScope High Spatial Resolution Multi-Spectral Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norway’s International Climate and Forests Initiative (NICFI). Planet NICFI DATA Program User Guide Third-Party Participants (Level 1 Users); Norway’s International Climate and Forests Initiative (NICFI): Oslo, Norway, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- O’Shea, T. NICFI Tropical Forest Basemaps now Available in Google Earth Engine. Available online: https://www.planet.com/pulse/nicfi-tropical-forest-basemaps-now-available-in-google-earth-engine/ (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Airbus Defence and Space GmbH. Copernicus DEM Copernicus Digital Elevation Model Product Handbook; GEO.2018-1988-2; Airbus Defence and Space GmbH: Taufkirchen, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.P.; Gallant, J.C. Digital Terrain Analysis. In Terrain Analysis: Principles and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lohani, S.; Baffaut, C.; Thompson, A.L.; Aryal, N.; Bingner, R.L.; Bjorneberg, D.L.; Bosch, D.D.; Bryant, R.B.; Buda, A.; Dabney, S.M.; et al. Performance of the Soil Vulnerability Index with Respect to Slope, Digital Elevation Model Resolution, and Hydrologic Soil Group. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 75, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzurul Hassan, M.; Ashraf Ali, M.; Hassan, M.M.; Ali, M.A. Digital Elevation Model and Irrigation Management Planning in Bangladesh. In Livelihood Enhancement through Agriculture, Tourism and Health; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 111–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, N.; Saeed, R.; Afzaal, M.; Ahmad, A.; Muhammad, N.; Iqbal, J.; Khan, A.; Maqbool, Y.; Hameed, S. Water Quality Assessment of Lower Jhelum Canal in Pakistan by Using Geographic Information System (GIS). Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavel, L.; Soudais, J.; Baudet, D.; Leenhardt, D. Integrating Expert Knowledge and Quantitative Information for Mapping Cropping Systems. Land Use Policy 2011, 28, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zhang, X.; Atkinson, P.M.; Stein, A.; Li, L. Geoscience-Aware Deep Learning: A New Paradigm for Remote Sensing. Sci. Remote Sens. 2022, 5, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, A.; Mossivand, A.M.; Ouri, A.E. Utility of the NDVI for Land/Canopy Cover Mapping in Khalkhal County (Iran). Ann. Biol. Res. 2012, 3, 5494–5503. [Google Scholar]
- Demissie, B.; Nyssen, J.; Annys, S.; Negash, E.; Gebrehiwet, T.; Abay, F.; Wolff, E. Geospatial Solutions for Evaluating the Impact of the Tigray Conflict on Farming. Acta Geophys. 2022, 70, 1285–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldoni, L.V.; Cattani, C.E.V.; Mercante, E.; Johann, J.A.; Antunes, J.F.G.; Almeida, L. Annual Cropland Mapping Using Data Mining and OLI Landsat-8. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agríc. Ambient. 2019, 23, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magidi, J.; Nhamo, L.; Mpandeli, S.; Mabhaudhi, T. Application of the Random Forest Classifier to Map Irrigated Areas Using Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogels, M.F.A.; de Jong, S.M.; Sterk, G.; Addink, E.A. Mapping Irrigated Agriculture in Complex Landscapes Using SPOT6 Imagery and Object-Based Image Analysis—A Case Study in the Central Rift Valley, Ethiopia. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 75, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirasi, A.; Mahmoudi, A.; Navid, H.; Valizadeh Kamran, K.; Asoodar, M.A. Evaluation of Sum-NDVI Values to Estimate Wheat Grain Yields Using Multi-Temporal Landsat OLI Data. Geocarto Int. 2021, 36, 1309–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherler, D.; Schwanghart, W. Drainage Divide Networks—Part 1: Identification and Ordering in Digital Elevation Models. Earth Surf. Dyn. 2020, 8, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, M.P.; Ghose, M.K.; Kharka, Y.R. Automatic Association of Strahler’s Order and Attributes with the Drainage System. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, J.B.; Yang, W.; Hornby, D.D. Drainage Network Analysis and Structuring of Topologically Noisy Vector Stream Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăgu, L. Random Forest in Remote Sensing: A Review of Applications and Future Directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliphant, A.J.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Teluguntla, P.; Xiong, J.; Gumma, M.K.; Congalton, R.G.; Yadav, K. Mapping Cropland Extent of Southeast and Northeast Asia Using Multi-Year Time-Series Landsat 30-m Data Using a Random Forest Classifier on the Google Earth Engine Cloud. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 81, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gislason, P.O.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Sveinsson, J.R. Random Forests for Land Cover Classification. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, J.M.; Knight, J.F.; Gallant, A.L. Influence of Multi-Source and Multi-Temporal Remotely Sensed and Ancillary Data on the Accuracy of Random Forest Classification of Wetlands in Northern Minnesota. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3212–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, J.; Tang, Q.; Qi, J.; Zhou, X. Classifying the Nunivak Island Coastline Using the Random Forest Integration of the Sentinel-2 and ICESat-2 Data. Land 2022, 11, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Sharma, R.; Joshi, P.K. Random Forest Classification of Urban Landscape Using Landsat Archive and Ancillary Data: Combining Seasonal Maps with Decision Level Fusion. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 48, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, K.; Abdel-Rahman, E.M.; Subramanian, S.; Nyasani, J.O.; Thiel, M.; Jozani, H.; Borgemeister, C.; Landmann, T. Maize Cropping Systems Mapping Using RapidEye Observations in Agro-Ecological Landscapes in Kenya. Sensors 2017, 17, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellington, M.J.; Renzullo, L.J. High-Dimensional Satellite Image Compositing and Statistics for Enhanced Irrigated Crop Mapping. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangecroft, S.; Van Loon, A.F.; Maureira, H.; Verbist, K.; Hannah, D.M. An Observation-Based Method to Quantify the Human Influence on Hydrological Drought: Upstream–Downstream Comparison. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2019, 64, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, S.J.; Stokes, M. Which DEM Is Best for Analyzing Fluvial Landscape Development in Mountainous Terrains? Geomorphology 2018, 310, 168–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.J.; Kadavi, P.R.; Lee, C.W.; Lee, S. Evaluation of Landslide Susceptibility Mapping by Evidential Belief Function, Logistic Regression and Support Vector Machine Models. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2018, 9, 1053–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embaye, T.A.G.; Kahsay, G.H.; Abadi, N.; Kebede, M.M.; Dessie, D.T. Evaluation of Water Harvesting Structures on Agricultural Productivity: The Case of Tigray Region, Ethiopia. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharatkar, P.S.; Patel, R. Approach to Accuracy Assessment Tor RS Image Classification Techniques. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2013, 4, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Zhao, K.; Zheng, X.; Jiang, T. Temporal Dynamics of Spatial Heterogeneity over Cropland Quantified by Time-Series NDVI, near Infrared and Red Reflectance of Landsat 8 OLI Imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 30, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurqani, H.A.; Allen, J.S.; Post, C.J.; Pellett, C.A.; Walker, T.C. Mapping and Quantifying Agricultural Irrigation in Heterogeneous Landscapes Using Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Appl. 2021, 23, 100590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).