MFTSC: A Semantically Constrained Method for Urban Building Height Estimation Using Multiple Source Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. MDE
2.2. Semantic Segmentation
2.3. ViT
2.4. Multi-Modal Fusion and Joint Learning for Remote Sensing
2.5. Multi-Task Learning
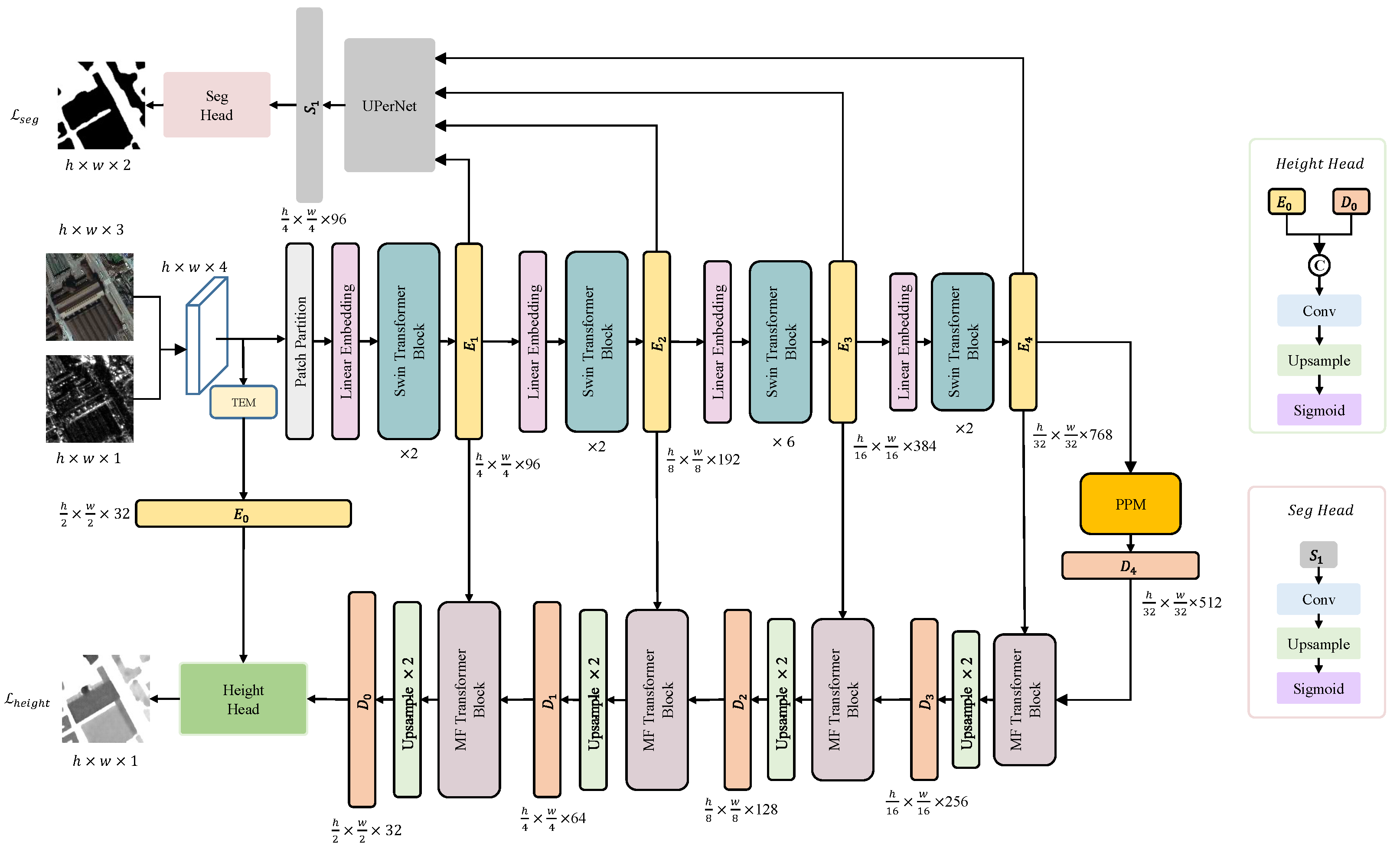
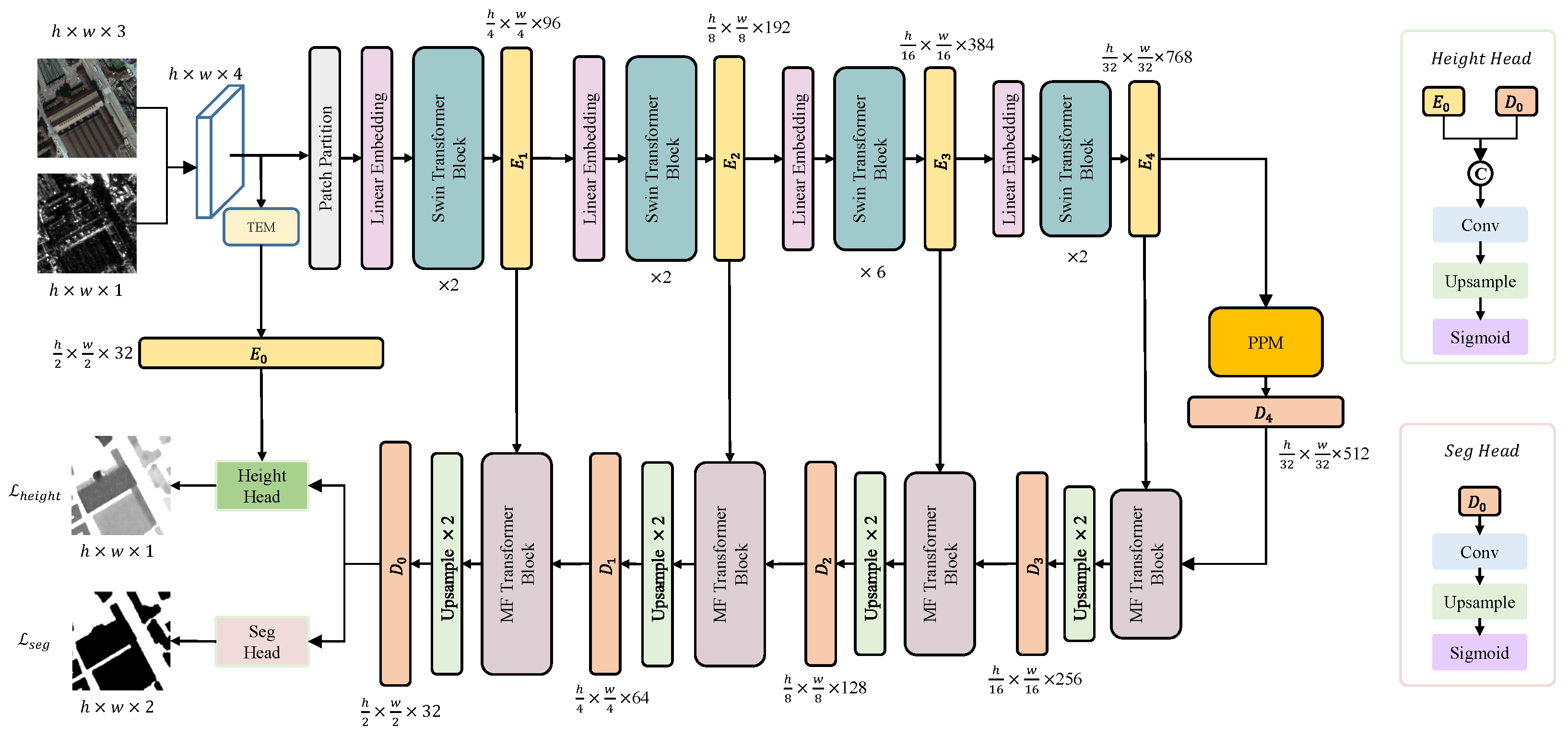
3. Method
3.1. TEM
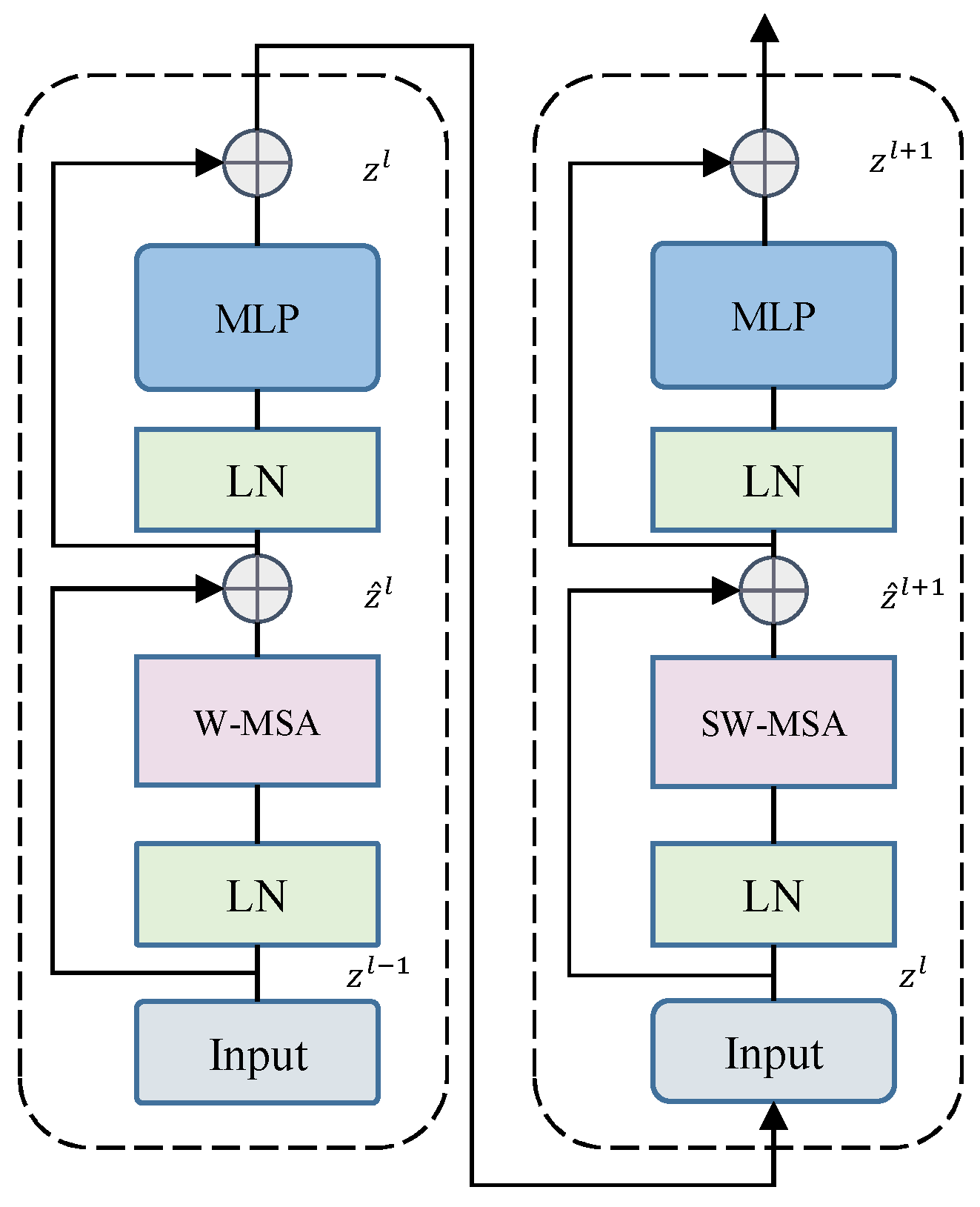
3.2. Swin Transformer
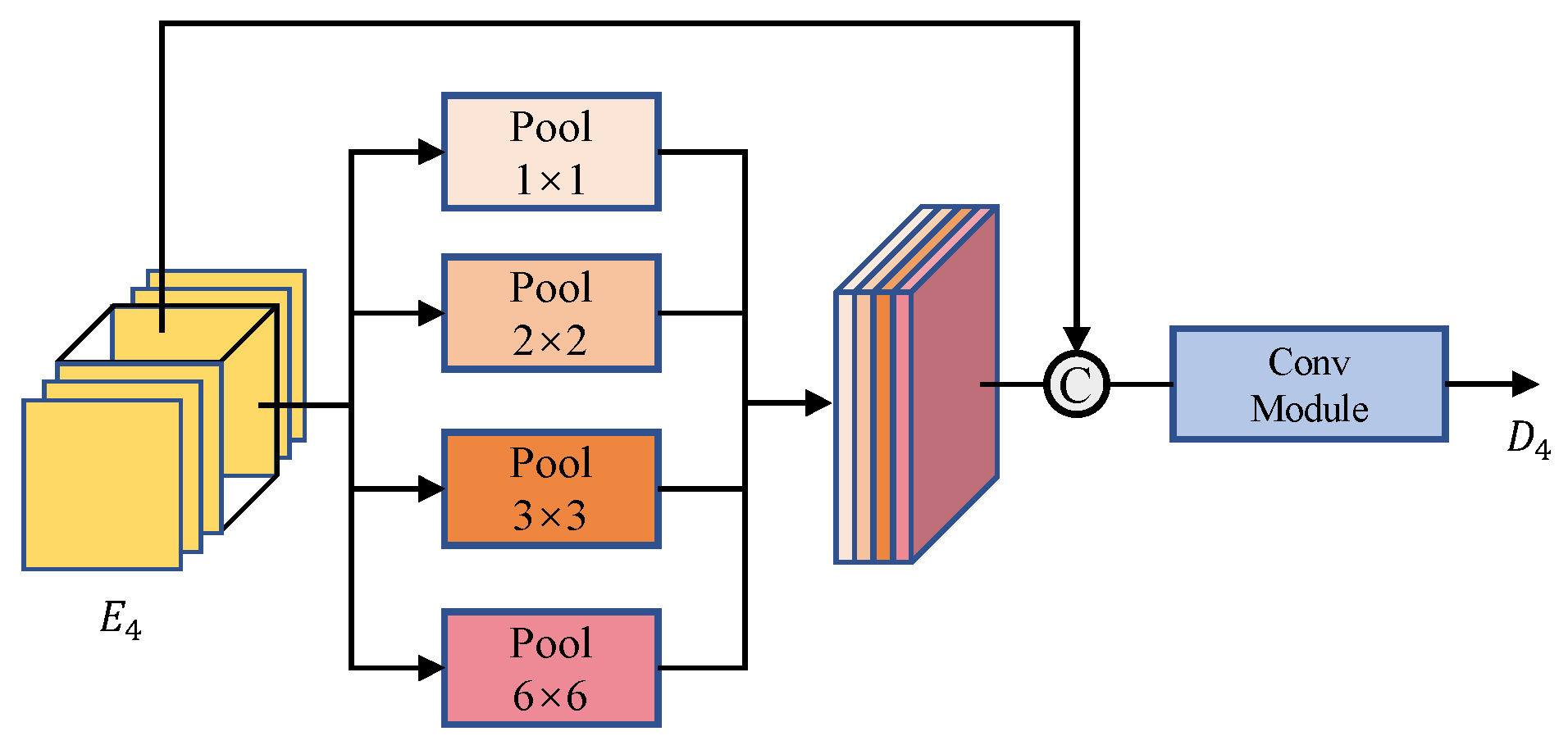
3.3. PPM
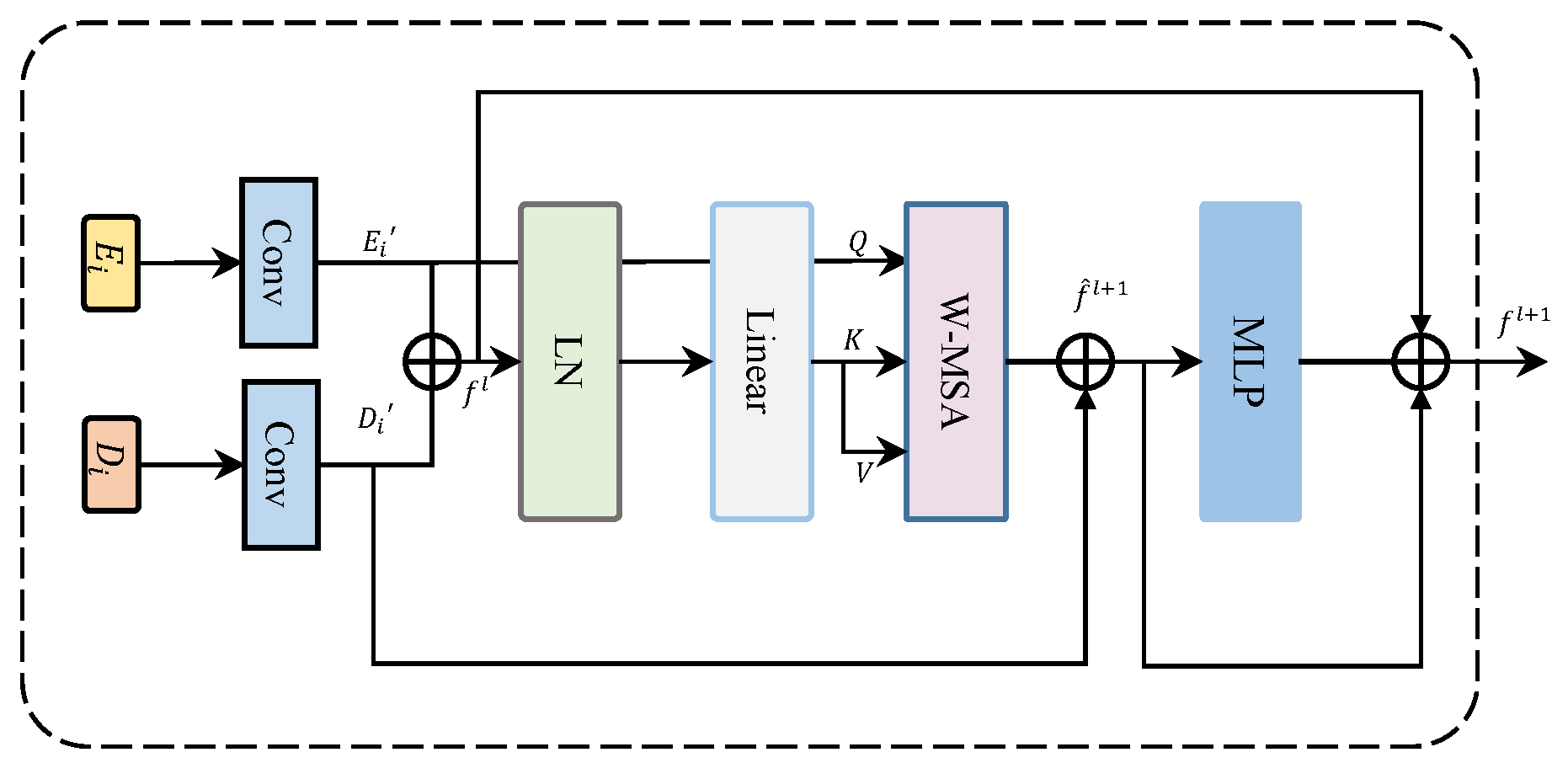
3.4. MFT
3.5. Decoder
3.6. Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Platform Parameter Settings
4.2. Datasets
4.3. Compare Experiment
4.4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| coefficient of determination | |
| RMSE | root mean square error |
| mIoU | mean intersection over union |
| MSE | mean square error |
| MAE | mean absolute error |
| SAR | synthetic aperture radar |
| MDE | monocular depth estimation |
| CNNs | convolutional neural networks |
| nDSM | normalized digital surface model |
| MFTSC | multi-level feature fusion Transformer with semantic constraint(s) |
| TEM | texture feature-extraction module |
| ViT | Vision Transformer |
| MFT | multi-dimensional feature-aggregation Transformer |
| PPM | pyramid pooling module |
| MSA | multi-head self-attention |
| LN | layer normalization |
| GELU | Gaussian error linear unit |
| W-MSA | window multi-head self-attention |
| SW-MSA | shifted window multi-head self-attention |
| PSP | pyramid spatial pooling |
| DFC2023 | Data Fusion Competition 2023 |
| FLOPs | floating point operations |
References
- Skalicky, V.; Čerpes, I. Comprehensive assessment methodology for liveable residential environment. Cities 2019, 94, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.L.; Mak, H.W.L. From comparative and statistical assessments of liveability and health conditions of districts in Hong Kong towards future city development. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabous, S.A.; Shanableh, A.; Al-Ruzouq, R.; Hosny, F.; Khalil, M.A. A spatio-temporal framework for sustainable planning of buildings based on carbon emissions at the city scale. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 82, 103890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shi, W.; Wang, Q.; Miao, Z. Extracting man-made objects from high spatial resolution remote sensing images via fast level set evolutions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 883–899. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Bao, S.; She, M.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B. Exploration of intelligent building planning for urban renewal. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Xu, C.; Aziz, N.M.; Kamaruzzaman, S.N. BIM–GIS integrated utilization in urban disaster management: The contributions, challenges, and future directions. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Shi, Q.; Du, B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Ding, H. Scene-driven multitask parallel attention network for building extraction in high-resolution remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 4287–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Kim, T. Automatic building height extraction by volumetric shadow analysis of monoscopic imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 5834–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licciardi, G.A.; Villa, A.; Dalla Mura, M.; Bruzzone, L.; Chanussot, J.; Benediktsson, J.A. Retrieval of the height of buildings from WorldView-2 multi-angular imagery using attribute filters and geometric invariant moments. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, D.; Lemoine, G.; Bruzzone, L.; Greidanus, H. Building height retrieval from VHR SAR imagery based on an iterative simulation and matching technique. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 48, 1487–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhrachy, I. Flash flood water depth estimation using SAR images, digital elevation models, and machine learning algorithms. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, L.; Mas, E.; Koshimura, S. Sparse representation-based inundation depth estimation using sAR data and digital elevation model. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 9062–9072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, B.R.; Tripathi, G.; Pandey, A.C.; Kumar, A. Estimating floodwater depth using SAR-derived flood inundation maps and geomorphic model in kosi river basin (India). Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 4336–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, P.; Seto, K.C.; Clinton, N. Developing a method to estimate building height from Sentinel-1 data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fieuzal, R.; Baup, F. Estimation of leaf area index and crop height of sunflowers using multi-temporal optical and SAR satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 2780–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sportouche, H.; Tupin, F.; Denise, L. Building detection by fusion of optical and SAR features in metric resolution data. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 12–17 July 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Liasis, G.; Stavrou, S. Satellite images analysis for shadow detection and building height estimation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 119, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Zhai, J.Z.; Dang, G. Building height estimation using Google Earth. Energy Build. 2016, 118, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.C.; Rege, P.P. Pixel level fusion techniques for SAR and optical images: A review. Inf. Fusion 2020, 59, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sportouche, H.; Tupin, F.; Denise, L. Extraction and three-dimensional reconstruction of isolated buildings in urban scenes from high-resolution optical and SAR spaceborne images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3932–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; O’Neill, B.C. Mapping global urban land for the 21st century with data-driven simulations and Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigen, D.; Fergus, R. Predicting depth, surface normals and semantic labels with a common multi-scale convolutional architecture. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 2650–2658. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Ricci, E.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, X.; Sebe, N. Multi-scale continuous crfs as sequential deep networks for monocular depth estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5354–5362. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, Y.; Meng, X.; Fan, C.; Yu, H. Deep learning for monocular depth estimation: A review. Neurocomputing 2021, 438, 14–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Arora, C. Depthformer: Multiscale vision transformer for monocular depth estimation with global local information fusion. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Bordeaux, France, 16–19 October 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 3873–3877. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, A.; Arora, C. Attention attention everywhere: Monocular depth prediction with skip attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–7 January 2023; pp. 5861–5870. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Fang, S.; Meng, X.; Li, R. Building extraction with vision transformer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhao, J.; Huang, K.; Yan, Q. Shallow-Guided Transformer for Semantic Segmentation of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Feng, D.; Xiong, S.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y. Multi-scene building height estimation method based on shadow in high resolution imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shahzad, M.; Zhu, X.X. Building height estimation in single SAR image using OSM building footprints. In Proceedings of the 2017 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 6–8 March 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Pei, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J.; Yang, H.; Yang, J. When deep learning meets multi-task learning in SAR atr: Simultaneous target recognition and segmentation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Ji, K.; Zhang, L.; Feng, S.; Xiong, B.; Kuang, G. An open set recognition method for SAR targets based on multitask learning. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiselberg, P.; Sørensen, K.; Heiselberg, H. Ship velocity estimation in SAR images using multitask deep learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 288, 113492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Mou, L.; Zhu, X.X. GAMUS: A geometry-aware multi-modal semantic segmentation benchmark for remote sensing data. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.14914. [Google Scholar]
- Hambarde, P.; Dudhane, A.; Patil, P.W.; Murala, S.; Dhall, A. Depth estimation from single image and semantic prior. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 25–28 October 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1441–1445. [Google Scholar]
- Hambarde, P.; Murala, S.; Dhall, A. UW-GAN: Single-image depth estimation and image enhancement for underwater images. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Atteia, G.; Collins, M.J.; Algarni, A.D.; Samee, N.A. Deep-Learning-Based Feature Extraction Approach for Significant Wave Height Prediction in SAR Mode Altimeter Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hua, Y.; Mou, L.; Zhu, X.X. Large-scale building height estimation from single VHR SAR image using fully convolutional network and GIS building footprints. In Proceedings of the 2019 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), Vannes, France, 22–24 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Lin, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, D. Digging into the multi-scale structure for a more refined depth map and 3D reconstruction. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 11217–11228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Garratt, M.A.; Anavatti, S.G.; Abbass, H.A. Towards real-time monocular depth estimation for robotics: A survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 16940–16961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Gu, X.; Dai, Z.; Zhu, S.; Tan, P. New crfs: Neural window fully-connected crfs for monocular depth estimation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.01502. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Ka, W.; Ahn, P.; Joo, D.; Chun, S.; Kim, J. Global-local path networks for monocular depth estimation with vertical cutdepth. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.07436. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.Y.; Liu, A.H.; Liu, Y.C.; Wang, Y.C.F. Towards scene understanding: Unsupervised monocular depth estimation with semantic-aware representation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2624–2632. [Google Scholar]
- Petrovai, A.; Nedevschi, S. Exploiting pseudo labels in a self-supervised learning framework for improved monocular depth estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1578–1588. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Yan, Q. Vision Transformer is required for hyperspectral semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2022 5th International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence (PRAI), Chengdu, China, 19–21 August 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Chaurasia, A.; Culurciello, E. Linknet: Exploiting encoder representations for efficient semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 10–13 December 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Q.; Chen, Y.; Jin, S.; Liu, S.; Jia, Y.; Zhen, Y.; Chen, T.; Huang, W. Inland water mapping based on GA-LinkNet from CyGNSS data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z.; Tang, P.; Wang, Z.; Saleem, N.; Yam, S.; Sommai, C. BRRNet: A fully convolutional neural network for automatic building extraction from high-resolution remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Shi, Q.; Li, J. Attention-gate-based encoder–decoder network for automatical building extraction. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, J. Pop-Net: Encoder-dual decoder for semantic segmentation and single-view height estimation. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019-2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 4963–4966. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, S.; Dong, Q.; Hu, Z. SCE-Net: Self-and cross-enhancement network for single-view height estimation and semantic segmentation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. JSH-Net: Joint semantic segmentation and height estimation using deep convolutional networks from single high-resolution remote sensing imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 43, 6307–6332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Yan, Q.; Huang, B.; Jia, T.; Xue, B. Hyperspectral Remote-Sensing Classification Combining Transformer and Multiscale Residual Mechanisms. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2023, 60, 1228002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, D.; Zhang, T.; Süsstrunk, S.; Salzmann, M. Mult: An end-to-end multitask learning transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 12031–12041. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, S.; Volpi, M.; Tuia, D. Joint height estimation and semantic labeling of monocular aerial images with CNNs. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 5173–5176. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, M.; Le Saux, B.; Trouvé-Peloux, P.; Champagnat, F.; Almansa, A. Multitask learning of height and semantics from aerial images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 1391–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Sun, W.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Song, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, R. Joint learning of semantic segmentation and height estimation for remote sensing image leveraging contrastive learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5614015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, F.; Xiang, Y. Multi-Task learning of relative height estimation and semantic segmentation from single airborne rgb images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Persello, C.; Stein, A. Semantic-aware unsupervised domain adaptation for height estimation from single-view aerial images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 196, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q.; Wang, M. Swin-unet: Unet-like pure transformer for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 205–218. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Q.; Huang, W. Sea Ice Sensing From GNSS-R Data Using Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 18160835. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, J. Unified perceptual parsing for scene understanding. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 418–434. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, S.F.; Alhashim, I.; Wonka, P. Adabins: Depth estimation using adaptive bins. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 4009–4018. [Google Scholar]
- Persello, C.; Hänsch, R.; Vivone, G.; Chen, K.; Yan, Z.; Tang, D.; Huang, H.; Schmitt, M.; Sun, X. 2023 IEEE GRSS Data Fusion Contest: Large-scale fine-grained building classification for semantic urban reconstruction [Technical Committees]. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2023, 11, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Lian, S.; Luo, Z.; Li, S. Weighted res-unet for high-quality retina vessel segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 9th International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education (ITME), Hangzhou, China, 19–21 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 327–331. [Google Scholar]
- Iglovikov, V.; Shvets, A. Ternausnet: U-net with vgg11 encoder pre-trained on imagenet for image segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.05746. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Rahman Siddiquee, M.M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: A nested U-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support: 4th International Workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018, Granada, Spain, 20 September 2018; Proceedings 4. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Xiong, P.; An, J.; Wang, L. Pyramid attention network for semantic segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.10180. [Google Scholar]
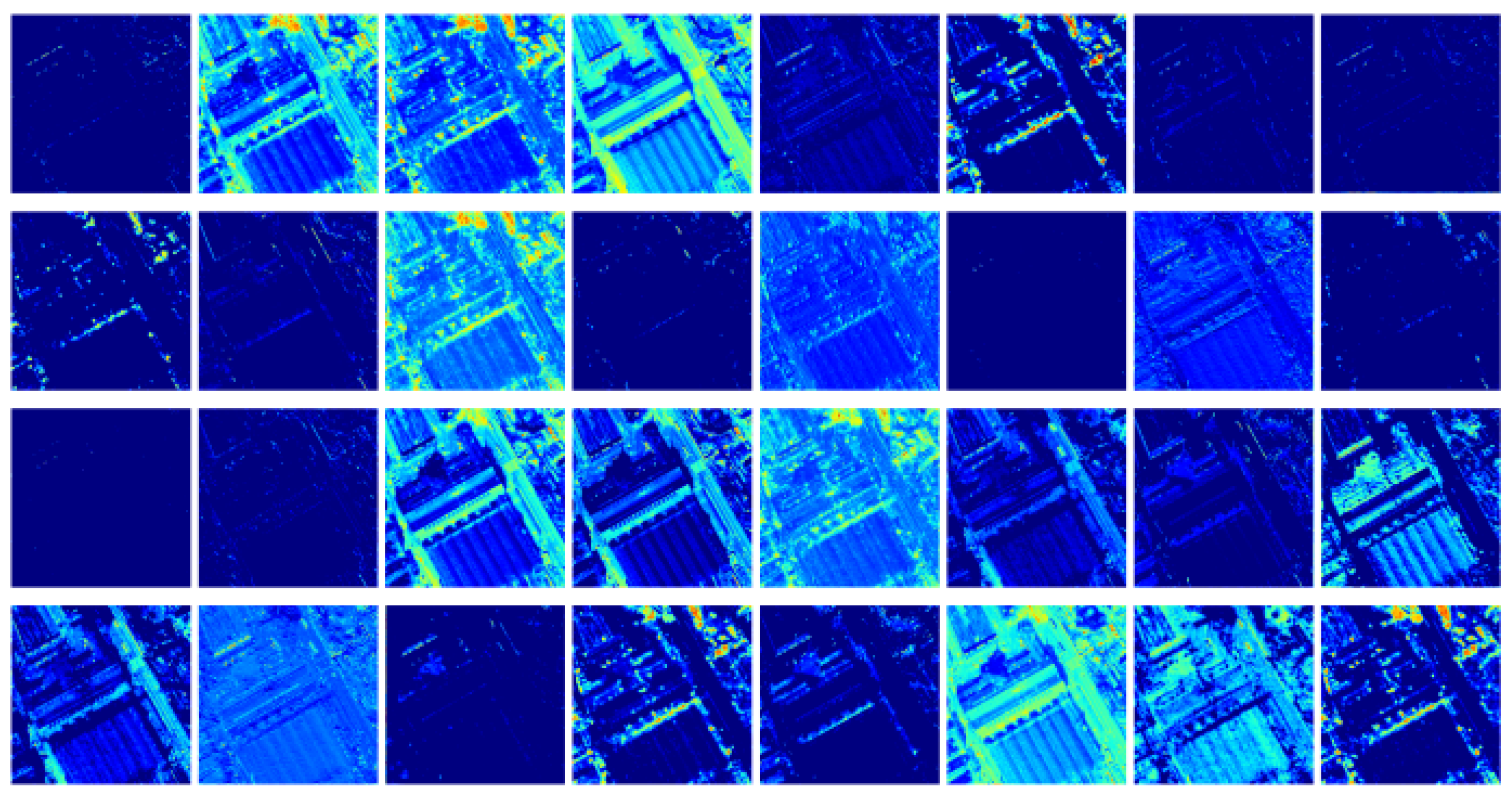
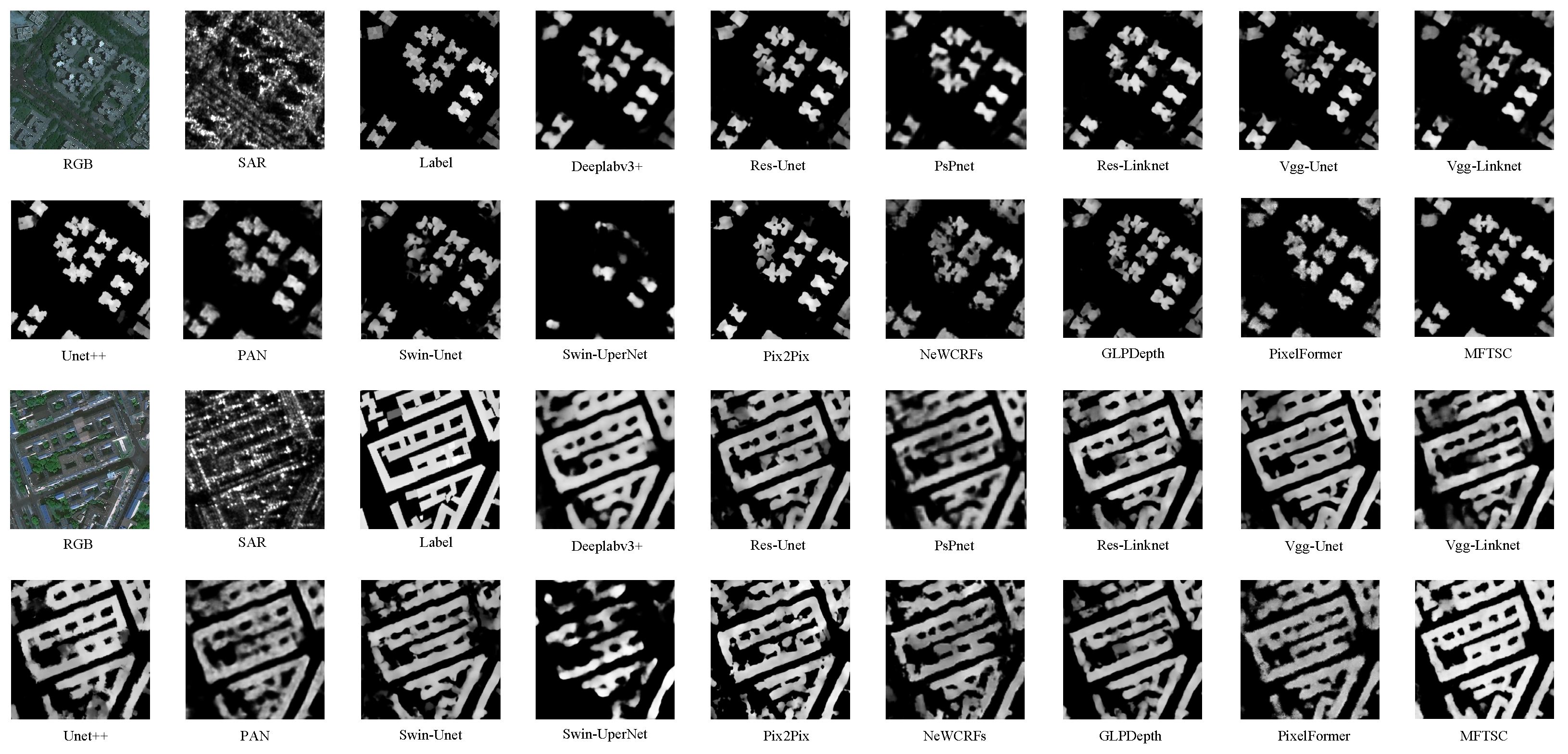
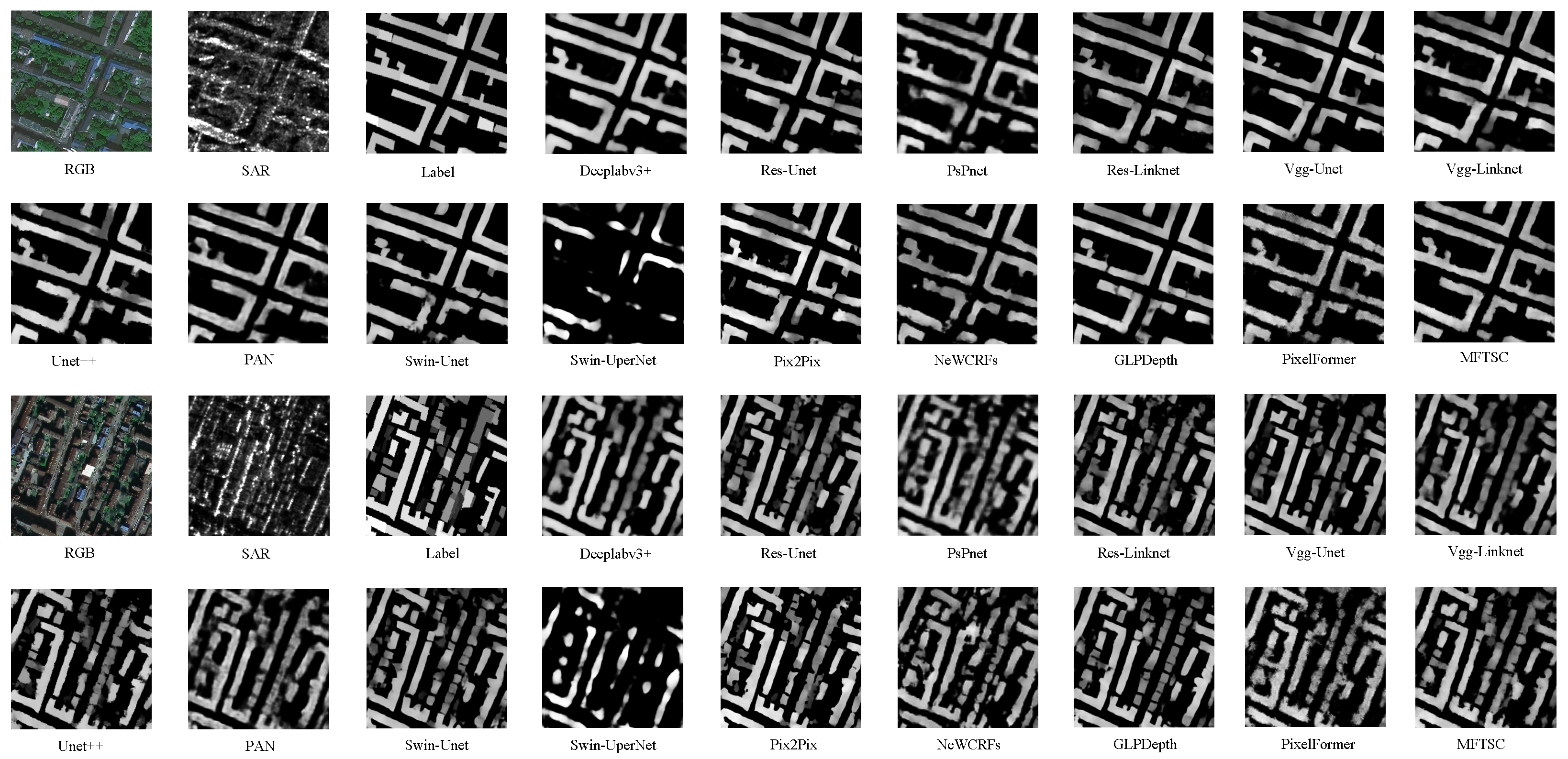
| Method | Backbone | mIoU ↑ | MAE (m) ↓ | MSE (m2) ↓ | RMSE (m) ↓ | R2 ↑ | Params ↓ | FLOPs ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepLabv3+ | ResNet50 | 0.628 | 0.7488 | 2.4398 | 1.4834 | 0.9064 | 106.72 M | 1.369 G |
| Res-Unet | ResNet50 | 0.718 | 0.7289 | 2.4882 | 1.4895 | 0.9129 | 130.10 M | 1.325 G |
| PSPNET | ResNet50 | 0.648 | 0.7785 | 2.5575 | 1.5089 | 0.9127 | 8.96 M | 0.743 G |
| Res-LinkNet | ResNet50 | 0.745 | 0.7763 | 2.7441 | 1.5660 | 0.9047 | 124.72 M | 1.620 G |
| VGG-Unet | VGG13 | 0.713 | 0.7193 | 2.4169 | 1.4644 | 0.9187 | 73.76 M | 0.856 G |
| VGG-LinkNet | VGG13 | 0.631 | 0.8039 | 2.6927 | 1.5545 | 0.8952 | 42.68 M | 1.245 G |
| Unet++ | ResNet50 | 0.782 | 0.6809 | 2.4893 | 1.4652 | 0.9218 | 195.96 M | 2.130 G |
| PAN | ResNet50 | 0.666 | 0.8102 | 2.7240 | 1.5700 | 0.8778 | 97.05 M | 1.174 G |
| Swin-Unet | Swin-T | 0.671 | 0.8608 | 3.5535 | 1.7884 | 0.9177 | 168.89 M | 1.087 G |
| Swin-UPerNet | Swin-T | 0.521 | 1.2082 | 6.4657 | 2.3984 | 0.8616 | 80.79 M | 0.565 G |
| Pix2Pix | ResNet50 | 0.749 | 0.7676 | 2.9890 | 1.6394 | 0.9398 | 141.17 M | 1.434 G |
| NeWCRFs | Swin-T | 0.678 | 0.9701 | 3.8080 | 1.8679 | 0.8896 | 353.65 M | 1.897 G |
| GLPDepth | MiT-b4 | 0.723 | 0.7679 | 2.8529 | 1.5950 | 0.9058 | 244.90 M | 2.282 G |
| PixelFormer | Swin-T | 0.682 | 0.8396 | 3.0784 | 1.6694 | 0.9044 | 305.35 M | 1.620 G |
| MFTSC | Swin-T | 0.785 | 0.5390 | 1.5167 | 1.1733 | 0.9671 | 302.38 M | 1.686 G |
| Backbone | mIoU ↑ | MAE (m) ↓ | MSE (m2) ↓ | RMSE (m) ↓ | R2 ↑ | Params ↓ | FLOPs ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet | 0.7462 | 0.8119 | 3.0569 | 1.6610 | 0.9646 | 257.28 M | 1.172 G |
| VGG | 0.7633 | 0.7633 | 2.8127 | 1.5867 | 0.9610 | 202.93 M | 2.541 G |
| Swin-T | 0.7855 | 0.5390 | 1.5167 | 1.1733 | 0.9671 | 302.38 M | 1.686 G |
| Method | mIoU ↑ | MAE (m) ↓ | MSE (m2) ↓ | RMSE (m) ↓ | R2 ↑ | Params ↓ | FLOPs ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.7789 | 0.6085 | 1.6432 | 1.2449 | 0.9627 | 302.24 M | 1.619 G |
| B | 0.7387 | 0.7633 | 2.8127 | 1.5867 | 0.9481 | 298.03 M | 1.651 G |
| C | 0.6919 | 0.8608 | 3.5535 | 1.7884 | 0.9425 | 169.00 M | 1.357 G |
| D | 0.7419 | 0.7207 | 2.4858 | 1.5005 | 0.9625 | 258.32 M | 1.640 G |
| E | 0.7752 | 0.5689 | 1.6732 | 1.2304 | 0.9595 | 258.19 M | 1.573 G |
| Method | mIoU ↑ | MAE (m) ↓ | MSE (m2) ↓ | RMSE (m) ↓ | R2 ↑ | Params ↓ | FLOPs ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soft | 0.7855 | 0.5390 | 1.5167 | 1.1733 | 0.9671 | 302.38 M | 1.686 G |
| Hard | 0.7339 | 0.7386 | 2.4585 | 1.4963 | 0.9544 | 254.12 M | 1.611 G |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Yan, Q.; Huang, W. MFTSC: A Semantically Constrained Method for Urban Building Height Estimation Using Multiple Source Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5552. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235552
Chen Y, Yan Q, Huang W. MFTSC: A Semantically Constrained Method for Urban Building Height Estimation Using Multiple Source Images. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(23):5552. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235552
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yuhan, Qingyun Yan, and Weimin Huang. 2023. "MFTSC: A Semantically Constrained Method for Urban Building Height Estimation Using Multiple Source Images" Remote Sensing 15, no. 23: 5552. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235552
APA StyleChen, Y., Yan, Q., & Huang, W. (2023). MFTSC: A Semantically Constrained Method for Urban Building Height Estimation Using Multiple Source Images. Remote Sensing, 15(23), 5552. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235552









