Abstract
Continuous evapotranspiration (ET) data with high spatial resolution are crucial for water resources management in irrigated agricultural areas in arid regions. Many global ET products are available now but with a coarse spatial resolution. Spatial-temporal fusion methods, such as the spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model (STARFM), can help to downscale coarse spatial resolution ET products. In this paper, the STARFM model is improved by incorporating the temperature vegetation dryness index (TVDI) into the data fusion process, and we propose a spatial and temporal adaptive evapotranspiration downscaling method (STAEDM). The modified method STAEDM was applied to the 1 km SSEBOP ET product to derive a downscaled 30 m ET for irrigated agricultural fields of Northwest China. The STAEDM exhibits a significant improvement compared to the original STARFM method for downscaling SSEBOP ET on Landsat-unavailable dates, with an increase in the squared correlation coefficients (r2) from 0.68 to 0.77 and a decrease in the root mean square error (RMSE) from 10.28 mm/10 d to 8.48 mm/10 d. The ET based on the STAEDM additionally preserves more spatial details than STARFM for heterogeneous agricultural fields and can better capture the ET seasonal dynamics. The STAEDM ET can better capture the temporal variation of 10-day ET during the whole crop growing season than SSEBOP.
1. Introduction
Agricultural irrigation water accounts for more than 80% of total water use in arid regions, and most of the water used for agricultural irrigation returns to the atmosphere in the form of evapotranspiration (ET) [1,2,3]. Therefore, accurate continuous monitoring of crop ET is essential for water resource management and allocation. At present, many continuous remote sensing ET products with global spatial coverage have been released, such as MOD16 [4], SSEBOP [5], ETmonitor [6], and GLEAM [7]. However, their coarse spatial resolution of 500 m (or even coarser) makes it challenging to meet the requirement of water consumption monitoring in the fragmented land surface. Therefore, spatial downscaling has become an attractive way to obtain continuous ET with high temporal and spatial resolution.
Downscaling methods are mainly divided into two categories: statistical approaches and spatio-temporal fusion approaches. Statistical downscaling methods conduct the downscaling using geostatistical indices, such as albedo [8], land surface temperature (LST) [9,10], and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) [11,12,13,14]. Although statistical downscaling methods provide valuable means to improve the coarse resolution to finer spatial resolution, they cannot simultaneously enhance their temporal resolution.
Spatiotemporal fusion models use two or more images to obtain fine spatial resolution images; thus, they can simultaneously improve spatial resolution and temporal coverage [15,16,17,18,19]. Wang et al. [20] pointed out that the spatiotemporal fusion approach shows a better performance compared to the statistical downscaling method. However, the accuracy of algorithms is heavily dependent on the availability of low spatial resolution pixels, which causes bias in simulation results in the case of heterogeneous landscapes [21]. In addition, spatiotemporal fusion models are not suitable for direct application to ET, because ET changes drastically in a short period, and the spatiotemporal fusion model lacks the underlying factors [22]. For example, Cammalleri et al. [23] showed that the spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model (STARFM) algorithm cannot accurately capture the change process of ET when the time span between the existing day and the forecast day is long, because ET changes drastically during the fusion period. Based on moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) and Landsat images, Bai et al. [24] used the Enhance STARFM (ESTARFM) model to fuse the ET image in the Jiefangzha area of Hetao irrigation area in Inner Mongolia. He believed that the ESTARFM method makes it challenging to obtain continuous crop ET data during growing seasons due to the two high resolution images (Landsat satellite revisit period is 16 days without cloud and rain) demanding in ESTARFM. Yi et al. [25] used the STARFM model to fuse the image in the middle reaches of Heihe River Basin based on advanced space-borne thermal emission reflectance radiometer (ASTER) and MODIS satellite data. The results showed that the STARFM model cannot simulate the ET spatial texture of farmland with high spatial heterogeneity.
To solve the problem, efforts have been devoted to adding the underlying surface information into the spatiotemporal fusion models so as to improve the spatiotemporal downscaling of ET data. Wang et al. [22] proposed an improved ET fusion method (SADFAET, the spatiotemporal adaptive data fusion algorithm for ET mapping) by introducing soil moisture to the ESTARFM model. As it is more physically explainable, the SADFAET performs better than ESTARFM compared with ground-based ET measurements. Yi et al. [25] added the land cover component into the STARFM model, and the modified STARFM additionally preserved more spatial details than the original STARFM for heterogeneous agricultural fields. Wang et al. [20] incorporated the land classification data into STARFM and proposed a classification-based spatiotemporal adaptive fusion model (CSAFM) to evaluate remotely sensed ET in an irrigated agricultural area with a complex planting structure. They found that the proposed CSAFM model can significantly improve the ET fusion accuracy in irrigated agricultural regions. As soil moisture and land cover classification data have been successfully applied to the spatiotemporal fusion, a question is whether there are some other indices that could improve the accuracy of data fusion.
The objectives of this study are to: (1) present an improved STARFM fusion method, the spatial and temporal adaptive evapotranspiration downscaling method (STAEDM), by combining the temperature vegetation dryness index (TVDI) statistical downscaling method with STARFM, for downscaling the SSEBOP ET product from 1 km to 30 m in the agricultural area in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin; (2) compare STAEDM with original STARFM method using in situ observations and reference Landsat images; and (3) assess the STAEDM ET in terms of temporal variation with SSEBOP and in situ observations. Section 2 describes the study area and data used in this paper. Section 3 presents detailed descriptions of STAEDM. The validation of ET based on STAEDM across various land cover types is presented in Section 4. Discussion and conclusions are presented in Section 5 and Section 6.
2. Materials
2.1. Study Area
The study area is located in an oasis–desert heterogeneity region in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin (HRB) (Figure 1). HRB is located in the interior of the continent and is characterized by a temperate continental dry climate with an annual mean air temperature of 6.53 °C, an annual precipitation 139.7 mm, an annual mean relative humidity 58.1%, and a wind speed 1.5 m/s during the period of 2013–2018. The altitude in HRB ranges between 1450 and 2000 m, and the potential yearly evaporation ranges from 1200 mm to 1800 mm [26]. The case study area is a 30 km × 30 km square area (between longitude 100.3° to 100.7°E and latitude 38.7° to 39.0°N) centered by irrigated croplands (60%). There were five meteorological and flux observation sites (i.e., Daman, Zhangye, Huazhaizi, Shenshawo, and Bajitan) in the area. The land surfaces of these five sites are corn, wetland, desert steppe, desert, and Gobi, respectively (Figure 1). The farmland irrigation area in the study area consumes considerable agricultural water, and the irrigation water comes from the Heihe River and groundwater. During the period of crop growth, there are 4–5 periods of irrigation every year.
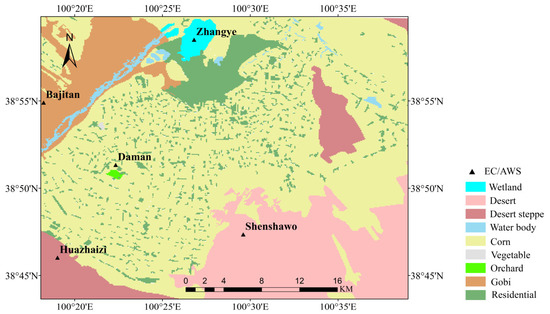
Figure 1.
Land cover of the study area and observation sites.
2.2. Satellite Data
2.2.1. Landsat
Landsat 7 (Enhanced Thematic Mapper, ETM+) and Landsat 8 (Operational Land Imager, OLI, and Thermal Infrared Sensor, TIRS) Collection 2 Level 2 products were downloaded from USGS (http://glovis.usgs.gov/) (accessed on 10 October 2022). The products were already atmospherically corrected and geometrically corrected by USGS. To make full use of Landsat 7 images, gaps caused by the malfunction of the Scan Line Corrector were filled using a triangulation algorithm based on the ENVI 5.3 software [27]. According to the quality of images over the study area during 2013–2018, 89 Landsat 7/8 images with clear sky were selected. The numbers of images with less than 5% cloud cover in every month during the study period are summarized below (Table 1). The Collection 2 Level 2 LST products of Landsat 7 and 8 retrieved with a single-channel algorithm [28] were used in this paper.

Table 1.
The number of Landsat images.
2.2.2. SSEBOP ET Product
The SSEBOP ET product is generated utilizing the Simplified Surface Energy Balance approach, which requires a combination of meteorological and satellite data as inputs [5]. The meteorological data were obtained from the parameter-elevation regressions on independent slopes model, while the satellite data were acquired from MODIS [5]. Previous studies show that the SSEBOP ET product has a better performance than other ET products in arid areas [29,30,31]. Yin et al. [30] compared SSEBOP with eight coarse resolution ET products in the Yellow River Basin, and showed that SSEBOP had a better performance than other products (such as MOD16A2). Ayyad et al. [31] evaluated SSEBOP and MOD16A2 in Egypt and demonstrated the higher precision of SSEBOP. The SSEBOP parameterization is special due to the predefined seasonally dynamic boundary conditions, which is unique for each pixel of the “hot/dry” and “cold/wet” reference points. The 1 km SSEBOP ET dataset has a 10-day temporal resolution, covering the period from 2000 to the present. For this study, data from March to November from 2013 to 2018 were utilized. The data were downloaded from USGS (https://earlywarning.usgs.gov/ssebop) (accessed on 10 October 2022).
2.3. Observations
The study area contains five long-term continuous observations, i.e., Daman, Zhangye, Huazhaizi, Shenshawo, and Bajitan. The underlying surfaces of these five sites are corn, wetland, desert steppe, desert, and Gobi, respectively. The field observation system of the HiWATER (Heihe Watershed Allied Telemetry Experimental Research) mainly includes an automatic weather station (AWS), and an eddy covariance (EC) (https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/en) (accessed on 11 October 2022) [26].
The meteorological data measured by each AWS for calculating ET included air temperature (°C), humidity (%), and air pressure (hPa). These variables were measured at 10-min intervals and interpolated with a resolution of 30 m by 30 m using the inverse distance weighted method. This process was carried out by the R 4.3.0 software to generate gridded spatial data.
The height of the EC tower at each site was 4.5 m, the sampling frequency was 10 Hz, and the observation interval was 30 min. The latent heat flux observations were processed with outlier value elimination, delay time correction, coordinate rotation, frequency response correction, ultrasonic virtual temperature correction, and density correction. In order to match the temporal scale of SSEBOP ET product, the latent heat flux was processed from 30 min to 10-day composite ET observations (mm/10 d). The missing data were interpolated using a linear interpolation method.
3. Methods
A schematic overview of the STAEDM (spatial and temporal adaptive evapotranspiration downscaling method) framework for retrieving high spatial-temporal resolution ET is illustrated in Figure 2. The process consists of three stages. The first stage involves generating 30-m instantaneous ET data using Landsat satellite images and subsequently upscaling the instantaneous ET into 10-day upscaled results on Landsat over-pass dates (, a 10-day period including the Landsat instantaneous over-pass time). The second stage is downscaling 10-day SSEBOP ET from 1 km to 30 m based on the TVDI computed with Landsat images. The third stage is generating 10-day 30 m ET by combining the 10-day upscaling Landsat ET on and 30-m STARFM ET based on TVDI downscaling results (TVDI-based STARFM) on Landsat-unavailable dates (, a 10-day period when no Landsat data are available).
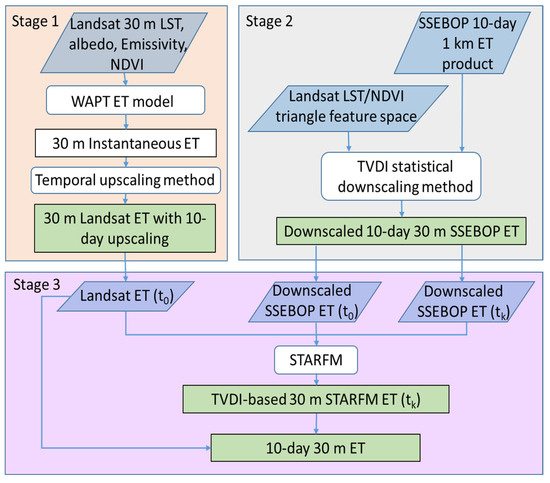
Figure 2.
Schematic overview of the inputs and processing in the STAEDM framework. (Note: is a 10-day period including the Landsat instantaneous over-pass time, is a 10-day period excluding the Landsat instantaneous over-pass time).
3.1. Generating 30-m Resolution Remote Sensing Evapotranspiration Data
At stage 1, we needed to choose a one-source ET model to calculate instantaneous Landsat ET to match the SSEBOP ET product (the combination of vegetation transpiration and soil evaporation). The WAPT model [32] was chosen for utilization because it demonstrated superior performance compared to other models in the study area. WAPT is a robust physical satellite-based wind speed avoiding Priestley–Taylor algorithm based on a wind-independent theoretical trapezoidal space. It has a good performance in the study area, with the squared correlation coefficients (r2) between Landsat instant latent flux and observed instant flux data being 0.95 [32]. The input of WAPT comprises Landsat albedo, emissivity, and NDVI, which are derived using the method of Liang et al. [33], Sobrino et al. [34], and Tucker [35], respectively. Then, we upscaled the instantaneous ET images to daily ET using the constant solar radiation ratio method [36,37]. Tang et al. [38] showed that in Northern China, the constant solar radiation ratio method performs better in upscaling ET from the instantaneous to diurnal scale than other three temporal upscaling methods. The daily ET was further upscaled into a 10-day upscaling Landsat ET using the reference evapotranspiration method from Delogu et al. [39]. This method has been tested in our study area and displays better performance than other temporal upscaling methods in terms of reconstructing ET on days when satellite data are unavailable [40].
3.2. Downscaling SSEBOP Coarse ET Statistically Based on TVDI
At stage 2, the statistical downscaling method based on TVDI was applied to SSEBOP to convert 1 km ET into 30 m. TVDI was calculated based on the LST/NDVI triangular feature space [41] using Landsat images. In the triangle feature space, the dry edge represents the driest soil humid condition and smallest ET, and the wet edge represents the wettest soil condition and biggest ET (potential ET).
The formula for computing TVDI is as follows:
where LST is the land surface temperature; and are the LST/NDVI triangular feature space’s dry and wet edges, respectively. and are the fitting coefficients of the dry edge equation, whereas and are the fitting coefficients of the wet edge equation. Assuming that there is a linear relationship between ET and TVDI, a simple linear model of TVDI and ET is established:
where the parameters and are obtained by the least square method.
The statistical downscaling method based on TVDI is performed in the following procedure: (1) resample Landsat LST and NDVI from 30 m to 1 km, and calculate the TVDI index at the 1 km resolution; (2) construct the linear model between SSEBOP ET and TVDI at 1 km resolution by sliding window (after applying several trials, we found the sliding window size 7 × 7 was the best) on ; (3) construct the linear model between SSEBOP ET on and Landsat TVDI on using SSEBOP/Landsat pairs based on the nearest date selection method [42]; (4) calculate TVDI based on Landsat NDVI and LST at 30 m resolution; and (5) apply the linear fitting equation to Landsat 30 m TVDI for obtaining 30 m downscaled ET data.
3.3. Generating ET with STARFM
At stage 3, The Landsat ET from stage 1 and downscaled SSEBOP ET from stage 2 were input into the STARFM model to predict ET. Note that STARFM is widely used and requires only one high-resolution image, thereby reducing the duration of image data acquisition. This characteristic makes it highly suitable for ET fusion, as ET changes drastically within a short period of time. The following steps were performed:
(1) Select the Landsat/SSEBOP pairs for inputs
A pair of Landsat/downscaled SSEBOP 30 m ET for and a 30 m downscaled SSEBOP ET for were selected as the inputs of the STARFM model. The Landsat/downscaled SSEBOP pairs were from the step 3 of stage 2.
(2) Use moving window to search for similar pixels
The pixels in the moving window were classified according to land cover types. The size of the moving window w was defined as 13 by comparing the fusion ET accuracy of different window sizes. Based on the STARFM [15], the classification result was used to select similar pixels (i.e., the same land cover type with the central pixel).
(3) Construct the weight function for similar pixels
Based on the STARFM [15], the weight function was composed of ET difference , temporal difference , and spatial distance . The expression of the weight function is:
B is a scale factor (equal to 10,000 based on STARFM [15]).
where L represents Landsat-based ET data with 30 m spatial resolution, M represents downscaled 30 m SSEBOP ET data, where is a given pixel location for both Landsat and SSEBOP images. The smaller ET difference indicates the closer ET values between Landsat and SSEBOP pixels.
The smaller temporal difference represents the smaller difference of SSEBOP ET values from to .
where A equals to w/2. The size of the relative distance varies with the w, from 1 to [1 + (1/√2) × (w/A)], and the expression of is as follows:
where is the position of the central pixel in moving window at date . The smaller indicates the closer distance between and .
(4) Calculate ET at the predicted central pixels
Expression of the ET value of the central pixel is as follows:
where represents the central pixel of the moving window for the Landsat ET prediction, is the value of the SSEBOP pixel on the prediction date, and and are the ET values of the Landsat and SSEBOP pixels of the base pair images. is the weight of similar pixels in the moving window, which is calculated by step (3). determines the contribution of each similar pixel to the predicted ET value of the central pixel.
(5) Produce 10-day 30 m ET
The TVDI-based STARFM 30 m ET on was generated through above steps (1) (2) (3) (4), and the 10-day upscaling Landsat ET on was obtained by stage 1. The 10-day 30 m ET was composed of the aforementioned two sets of data.
4. Results
4.1. The Performance of Landsat ET and SSEBOP Evapotranspiration Data
The Landsat ET data at 89 dates were produced with the WAPT algorithm using cloud-free Landsat images from 2013 to 2018, and daily ET were upscaled to 10-day data using the temporal upscale method. The 10-day upscaling Landsat ET and SSEBOP ET were evaluated using the observed ET data at five sites (corn, wetland, desert steppe, desert, and Gobi). The scatterplots comparing the satellite-based ET data (SSEBOP ET and Landsat ET) with observations from flux tower measurements were presented in Figure 3. Performance metrics of SSEBOP ET and Landsat ET data were listed in Table 2. The statistical metrics included r2, Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency coefficient (NASH), mean bias error (MBE), and root mean square error (RMSE).
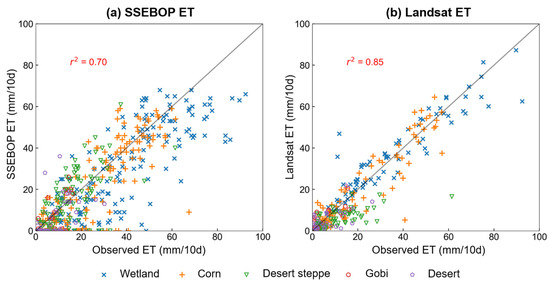
Figure 3.
Comparison of remote sensing estimated ET data and observed ET at the five sites with difference land covers during 2013 to 2018. (a) SSEBOP ET and (b) Landsat ET.

Table 2.
Performance measures of Landsat ET and SSEBOP ET data.
The Landsat ET and SSEBOP ET were in good agreement with the observations. The Landsat ET data had a higher accuracy (r2 = 0.85) than SSEBOP ET (r2 = 0.70) due to the finer spatial resolution of remote sensing images and refined evapotranspiration estimation algorithm WAPT.
We can see from Table 2 that SSEBOP ET has a better accuracy at vegetable sites (wetland and corn) than non-vegetable sites (desert steppe, Gobi, and desert). For example, the r2 values of SSEBOP ET in wetland and corn were 0.65 and 0.68, respectively. The r2 values of SSEBOP ET in desert steppe, Gobi, and desert sites were lower than the vegetable sites. Some researchers also found that SSEBOP ET shows a stronger correlation at vegetable sites (such as agriculture and grass) than at non-vegetable sites (such as barren) [43,44]. It is related to the worse performance of the input data (MOD11A2 LST product) of SSEBOP at non-vegetable sites than vegetable sites [5,45]; the lower LST precision decreases the accuracy of SSEBOP ET at non-vegetable sites.
Landsat ET also had better accuracy at vegetable sites than non-vegetable sites. The RMSE values of Landsat ET at vegetable sites (8.04 and 7.38 for wetland and corn, respectively) exhibited lower magnitudes than non-vegetable sites. It is related to the WAPT model, which has a better performance in vegetable sites [32]. The primary reason for the WAPT accuracy difference is the precision of net radiation estimations varied between vegetation and non-vegetation surfaces. Compared with SSEBOP ET, the accuracy of Landsat ET was higher at vegetable sites (e.g., for the r2 value in wetland, 0.87 compared with 0.65, respectively) but was as good as SSEBOP at non-vegetable sites.
4.2. Assessing the Performance of Statistical Downscaling Method Using TVDI
To compare the TVDI-based statistical downscaling ET, we employed LST and NDVI to explore the impact of different indices on downscaling results. Different downscaling results in the third dekad of June and the second dekad of September in 2016 are shown in the Figure 4 and Figure 5.
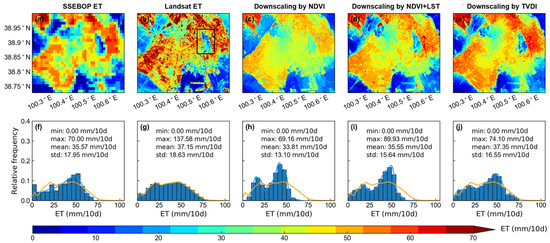
Figure 4.
Spatial pattern of maps in the 3rd dekad of June 2016 from (a) SSEBOP ET, (b) Landsat ET, (c) downscaling ET by NDVI, (d) downscaling ET by NDVI and LST, and (e) downscaling ET by TVDI. The frequency distribution curves of maps from (f) SSEBOP ET, (h) downscaling ET by NDVI, (i) downscaling ET by NDVI and LST, and (j) downscaling ET by TVDI are colored by blue. The frequency distribution curve of map from (g) Landsat ET are colored by orange. The orange curves shown by (f), (h), (i) and (j), respectively are the same as those shown by (g). The black rectangle in (b) is magnified in Figure 8a.
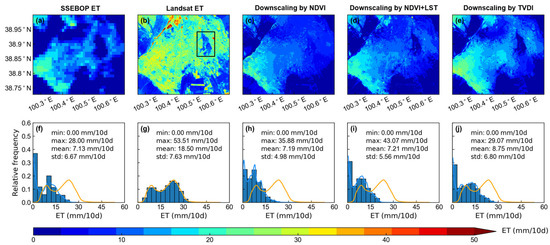
Figure 5.
Spatial pattern of maps in the 2nd dekad of September, 2016 from (a) SSEBOP ET, (b) Landsat ET, (c) downscaling ET by NDVI, (d) downscaling ET by NDVI and LST, and (e) downscaling ET by TVDI. The frequency distribution curves of maps from (f) SSEBOP ET, (h) downscaling ET by NDVI, (i) downscaling ET by NDVI and LST, and (j) downscaling ET by TVDI are colored by blue. The frequency distribution curve of map from (g) Landsat ET are colored by orange. The orange curves shown by (f), (h), (i) and (j), respectively are the same as those shown by (g). The black rectangle in (b) is magnified in Figure 8d.
The downscaled results of various indices exhibited significant discrepancies when compared to the reference Landsat ET data (Figure 4b and Figure 5b), with the TVDI-based statistical downscaled ET proving to be the optimal choice. The downscaled ET based on NDVI was underestimated in wetland and waters (Figure 4c and Figure 5c), which is related to the inappropriate fitting equations in these land covers due to the NDVI values less than 0. Compared to Landsat ET, downscaled ET based on NDVI + LST had a closer spatial pattern than that based on NDVI, possibly because NDVI can only reveal the general land cover distribution pattern but cannot explain the temporal variations of ET in complex underlying surfaces, whereas LST can compensate such a deficiency. However, downscaled ET data based on NDVI + LST also had underestimation in wetland and waters. Downscaling ET based on TVDI had better similarity in spatial pattern to Landsat ET than NDVI and NDVI + LST, as shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5. For example, in the third dekad of June 2016, the mean value of downscaling ET based on TVDI (37.35 mm/10 d) was closer to that of the Landsat ET reference image (37.15 mm/10 d) than that based on NDVI and NDVI + LST (33.81 mm/10 d, 35.55 mm/10 d, respectively). In mid-September, all downscaling methods underestimated the ET. TVDI downscaling had a slightly closer mean value than other downscaling methods. This can be attributed to the unreasonably low ET values of SSEBOP in September.
In summary, the choice of downscaling indices is crucial to the accuracy of downscaling ET, and the combined indices of NDVI and LST are more suitable for downscaling ET than a single factor. Downscaled ET based on the TVDI performs the best in terms of the spatial pattern and the mean values compared to the reference Landsat ET, possibly because TVDI is a better representation of the non-linear relationship based on the triangular feature space between the ET and LST/NDVI than establishing a linear relationship between ET and NDVI alone, or between ET and LST + NDVI jointly.
4.3. Spatial Characteristics of TVDI-Based STARFM ET
In this section, to analyze the spatial quality of TVDI-based STARFM results, the original STARFM ET based on the nearest neighbor resampling downscaling results (resampled STARFM) were calculated for comparison (Figure 6 and Figure 7).
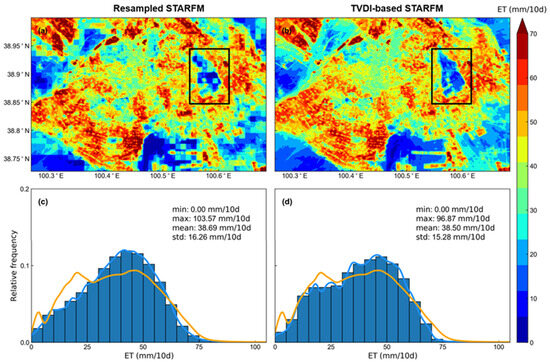
Figure 6.
Spatial pattern of ET maps in the 3rd dekad of June, 2016 from (a) resampled STARFM, and (b) TVDI-based STARFM models. And frequency distribution curves of ET maps from (c) resampled STARFM, and (d) TVDI-based STARFM models are colored by blue. The frequency distribution curves of ET maps from Landsat are colored by orange. The ET is predicted by the Landsat/SSEBOP ET pairs in the 1st dekad of July 2016. The black rectangle in (a) is magnified in Figure 8b, and the black rectangle in (b) is magnified in Figure 8c.
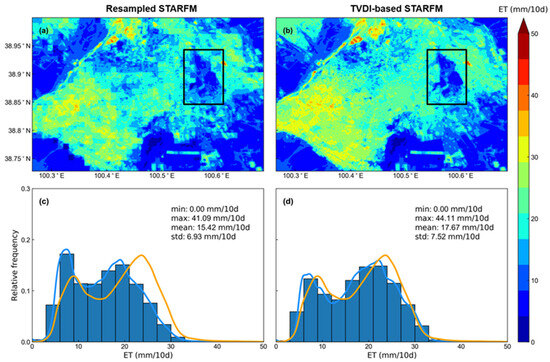
Figure 7.
Spatial pattern of ET maps in the 2nd dekad of September 2016 from (a) resampled STARFM, and (b) TVDI-based STARFM models. And frequency distribution curves of ET maps from (c) resampled STARFM, and (d) TVDI-based STARFM models are colored by blue. The frequency distribution curves of ET maps from Landsat are colored by orange. The ET is predicted by the Landsat/SSEBOP ET pairs in the 1st dekad of October 2016. The black rectangle in (a) is magnified in Figure 8e, and the black rectangle in (b) is magnified in Figure 8f.
Compared with the reference Landsat ET (Figure 4b and Figure 5b), TVDI-based STARFM had a closer ET spatial distribution than the resampled STARFM in summer and autumn. Resampled STARFM had mosaics in the prediction ET result, whereas TVDI-based STARFM can eliminate the mosaic effect of ET results. Compared with the ET image predicted by resampled STARFM, the result produced by the TVDI-based STARFM had a more precise description of the fragmentation region because the resampled data used in STARFM cannot reflect the heterogeneity of ET within the SSEBOP pixel. TVDI-based STARFM results can better predict the spatial texture of Landsat ET than resampled STARFM. The TVDI-based STARFM prediction exhibited a higher similarity in the relative frequency of ET values to the Landsat ET image (Figure 4g) than that of resampled STARFM. Compared with the image predicted by resampled STARFM, the standard deviations of TVDI-based STARFM results were lower (e.g., 16.26 mm/10 d of resampled STARFM compared with 15.28 mm/10 d of TVDI-based STARFM in the third dekad of June).
A surface with strong heterogeneity (including woodland, farmland, and human construction land) was selected to further compare the spatial distribution of ET results produced by resampled STARFM and TVDI-based STARFM models. Figure 8 showed the magnified view of ET maps in the rectangle of Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7. For the spatial distribution of reference Landsat ET (Figure 8a,d), the woodland is in the middle, surrounded by farmland, resulted in the higher ET in the surrounding areas and the lower ET in the central region during the growth period of crops (late-June and mid-September). This spatial distribution can be clearly seen from the TVDI-based STARFM prediction results (Figure 8c,f), and ET from TVDI-based STARFM has a closer spatial texture to the reference Landsat ET than resampled STARFM. It is difficult to distinguish built-up land (road) and woodland in the middle of the picture from the resampled STARFM predictions (Figure 8). We attribute these differences to the TVDI adding to the downscaling ET results of TVDI-based STARFM.
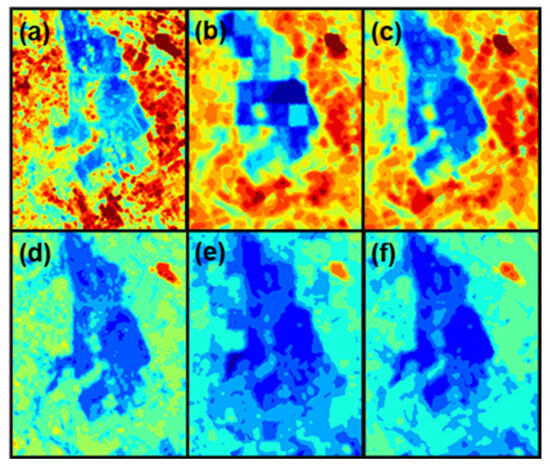
Figure 8.
Magnified view of ET in different dates. (a,d) from Landsat ET, (b,e) from the resampled STARFM model, and (c,f) from the TVDI-based STARFM model. (a–c) in the 3rd dekad of June and (d–f) on the 2nd dekad of September 2016.
4.4. Assessing the Performance of TVDI-Based STARFM ET on Sites
In order to further investigate the accuracy of TVDI-based STARFM ET, observations from five sites (wetland, corn, Gobi, desert, and desert steppe) were used for comparison, as shown in Figure 9 and Table 3. The 89 Landsat/downscaled SSEBOP ET pairs on Landsat over-pass dates and 73 downscaled SSEBOP ET images on Landsat-unavailable dates were utilized as inputs for the STARFM, resulting in 73 downscaled TVDI-based STARFM ET on Landsat-unavailable dates. Similarly, an additional set of 73 downscaling ET was produced from the resampled STARFM model.
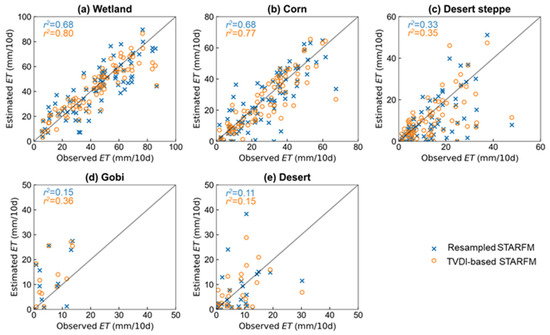
Figure 9.
Scatterplot of the observed ET and downscaled ET by TVDI-based STARFM (in orange) and resampled STARFM (in blue) on Landsat-unavailable dates for the wetland (a), corn (b), desert steppe (c), Gobi (d), and desert (e). r2 values of resampled and TVDI-based STARFM ET in the plot are colored by blue and orange, respectively.

Table 3.
Performance measures of the downscaled ET by TVDI-based STARFM and resampled STARFM on Landsat-unavailable dates.
Overall, the performance of TVDI-based STARFM ET was better than resampled STARFM ET for all underlying surfaces. The ET estimated by TVDI-based STARFM was more closely matched to the observations (1:1 line) than that of resampled STARFM (Figure 9). For example, the r2 value in the wetland for TVDI-based STARFM ET was higher than resampled STARFM (0.80 compared with 0.68, Figure 9a). This is because of the consideration of underlying surface parameters (TVDI) for the TVDI-based STARFM model. Resampled STARFM directly uses resampled SSEBOP data as the input, which makes it difficult to reflect the ET characteristics of wet and arid underlying surfaces. Compared to resampled STARFM, the TVDI-based STARFM model could better capture the ET differences among various underlying surfaces.
The TVDI-based STARFM ET demonstrated significant variations across different underlying surfaces, exhibiting higher accuracy at vegetable surfaces (NASH of 0.72 on corn) than non-vegetable surfaces (NASH of 0.09 on desert steppe). This can be attributed to the higher accuracy of the input data (downscaled SSEBOP and Landsat ET) at vegetable sites than non-vegetable sites. In addition, the accuracy of TVDI-based STARFM ET was higher than that of resampled STARFM ET in all sites, particularly in the vegetable sites. For example, the RMSE differences between TVDI-based STARFM and resampled STARFM ET were 2.75 and 0.62 mm/10 d in the wetland and Gobi sites, respectively (Table 3). This shows that the accuracy of TVDI-based STARFM is significantly improved compared with resampled STARFM in high vegetation coverage areas. Incorporating TVDI into the STARFM algorithm can significantly enhance the accuracy of ET fusion for vegetation-covered surfaces.
4.5. Temporal Variation of 10-day 30 m ET
The 10-day 30 m STAEDM ET was compared with SSEBOP ET in spatial distribution variation to evaluate the performance in capturing temporal dynamics (Figure 10). In addition, STAEDM ET was further compared with observations from 2013 to 2018 under five different land covers (Figure 11). Overall, the STAEDM ET could better capture the dynamics of the actual ET than SSEBOP.
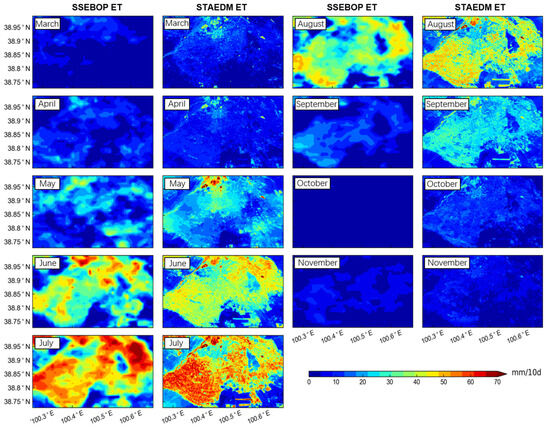
Figure 10.
The spatial pattern of SSEBOP ET and STAEDM ET in the 2nd dekad from March to November 2016. The STAEDM ET includes 4 TVDI-based STARFM ET images on May, June, July, and October on Landsat-unavailable dates and 5 Landsat ET images on Landsat over-pass dates.
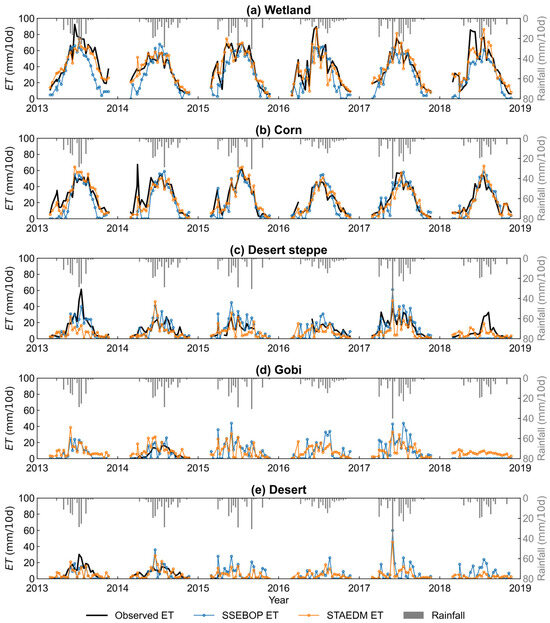
Figure 11.
Time series of observed ET (black line), SSEBOP ET (blue line with dots), STAEDM ET (orange line with dots), and rainfall (grey bars) from 2013 to 2018.
During the growing season in 2016 (May, June, July, August, and September), STAEDM ET can display the complete crop growth process in heterogeneous agricultural areas compared with SSEBOP ET (Figure 10). The ET values for cropland were clearly larger than surrounding deserts during the whole growing season. In May, only wetland and areas where crops start to grow have the highest ET, and the values can reach 50 mm/10 d. In June, with the accelerated growth of crops, the water consumption from crop ET increased, so the area with ET values exceeding 50 mm/10 d expanded. In July, the ET value of the study area reached the maximum over the year, showing a typical spatial distribution pattern with higher values on the farmland and lower values over the desert. In mid-August, the spatial distribution was similar to that in mid-July, but the ET value began to decline. For example, the ET value from farmland dropped from about 60 mm/10 d in mid-July to 40–50 mm/10 d in mid-August. In September, from the STAEDM ET spatial distribution map, we can still see the clear outline of the farmland. As the temperature dropped and the crops were harvested in September, the ET value of farmland decreased rapidly to about 20 mm/10 d. These results demonstrate that the STAEDM downscaling model has the potential to produce long-term high spatial resolution ET results.
As shown in Figure 11, STAEDM can well capture the seasonal variation of ET in wetland. In spring, STAEDM ET has a close value with observations, while SSEBOP generally underestimates the ET values. In summer, when observed ET exceeds 60 mm/10 d, STAEDM ET is in closer agreement with observations than SSEBOP ET.
In corn land, STAEDM ET has a closer variation to the observations in spring and autumn than SSEBOP. The ET observation sharply rises under the low precipitation due to spring irrigation. STAEDM ET can better reflect spring irrigation than SSEBOP and is similar to the variation of observations. For example, in April 2014, there was little rainfall, but evapotranspiration increased sharply, which was caused by spring irrigation in early April. In summer, due to the frequent irrigation events, the observed ET has a much more complex variation than spring. Both STAEDM and SSEBOP fail to capture the irrigation events of summer accurately. Lei et al. [46] also revealed the limitations of remote sensing ET in detecting frequent irrigation. Due to the decrease of irrigation in autumn, STAEDM can follow the observed ET variation well.
In non-vegetable surfaces, the seasonal variation of ET is mainly influenced by precipitation. When there is no rainfall, the ET value is very low, usually less than 10 mm/10 d (Figure 11). With rainfall, both SSEBOP and STAEDM ET values increase sharply. The increase of STAEDM ET is similar to the variation of observations. Note that the rainfall data from the corn station was applied to the five sites due to the limited size of the study area and the discontinuity of rainfall data from other stations.
5. Discussion
5.1. Novelty of STAEDM
Remote sensing ET data with a spatial resolution of 30 m or even finer is demanded for agricultural water resource management; however, the spatial resolution of available remote sensing ET products is too rough [4,5,6,7]. STAEDM has the potential to produce long-term ET results with 30 m resolution, which might be valuable for precise management of agricultural water consumption.
The STAEDM is a spatial-temporal fusion model combined with the TVDI land surface factor. TVDI can reflect moisture conditions, and it has a strong correlation with ET. Adding the TVDI into the STARFM model can enhance the spatial resolution of coarse ET images, thereby significantly improving the spatial texture and accuracy of STARFM downscaling results.
The STAEDM results have a closer agreement with the observations and exhibit a clear spatial texture. This shows that the proposed downscaling framework is feasible in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin. In the future, the method can be applied over large areas or basins for ET estimation. This study used the SSEBOP product as the input of STAEDM, generating the downscaled ET of 30 m resolution. Incorporating other coarse resolution ET products into the proposed downscaling framework deserves to be explored in the future.
5.2. Challenges of STAEDM
The TVDI plays an essential role in the downscaling framework. In this study, TVDI was empirically calculated based on dry and wet edges of triangle feature space. The triangle feature space was established by the scatterplot between LST and NDVI. The precision of TVDI is constrained by the calculation method of the dry and wet edges. The empirical method used in this paper depends on the satellite image size. The image should provide a wide range of soil wetness and fractional vegetation cover conditions, which is often difficult to ensure. In addition, NDVI has a saturation phenomenon in high vegetation coverage, which limits the accuracy of TVDI. The application of TVDI in areas of dense vegetation needs further investigation.
The possible solution to the first limitation is using theoretical trapezoidal feature space to replace empirical triangle feature space to calculate TVDI in the area without a wide range of vegetation coverage. The dry and wet edges in theoretical trapezoidal feature space can be determined on a pixel basis, and it is not affected by the vegetation coverage of the image [47,48,49]. The second limitation can be addressed using improved vegetation parameters instead of NDVI to establish feature space in dense vegetation areas, such as enhanced vegetation index (EVI) [50]. Using an enhanced TVDI factor may further improve the performance of downscaling results.
This study used the SSEBOP ET product that combines evaporation and transpiration. Other ET products that provide separate estimations for soil evaporation, transpiration, and interception, such as GLEAM, can also be incorporated into the STAEDM framework. Accordingly, multi-source ET models should be employed to match the ET products [51,52,53,54].
Although the proposed schemes were evaluated over the arid area, they should be further evaluated over different regions to examine how they work. Our future research will incorporate an extensive examination of the sensitivity of this approach by applying it to other areas considering climate and environmental variabilities.
6. Conclusions
The spatial resolution of most available remote sensing ET products is too coarse to be applied to fragmented farmland. A feasible way to obtain ET data of higher spatial resolution is downscaling. In this paper, we propose a spatial and temporal adaptive evapotranspiration downscaling method (STAEDM) to downscale the SSEBOP product from 1 km to 30 m ET. The STAEDM involves three stages: (1) generating Landsat ET on Landsat-available dates; (2) statistically downscaling SSEBOP ET based on the temperature vegetation dryness index (TVDI); and (3) generating TVDI-based spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model (STARFM) ET on Landsat-unavailable dates. Our method incorporates the TVDI into the STARFM, thereby enhancing the accuracy of downscaled ET compared to the original STARFM.
Based on the results, the following conclusions can be drawn. (1) The Landsat ET data have a higher precision (r2 = 0.85) than SSEBOP ET (r2 = 0.70) due to the finer spatial resolution of remote sensing images and refined evapotranspiration estimation algorithm WAPT. (2) The choice of downscaling indices is crucial to the accuracy of ET, and downscaled ET based on the TVDI performs better than NDVI and NDVI + LST. (3) TVDI-based STARFM exhibits a higher level of spatial accuracy than resampled STARFM when compared with the reference Landsat ET. Additionally, TVDI-based STARFM has a higher accuracy than resampled STARFM when compared with observation data from in situ stations (e.g., r2 of 0.77 vs. 0.68 on the corn site). (4) The STAEDM ET could better capture the dynamics of the of 10-day ET than SSEBOP compared with observations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.W. and J.S.; methodology, J.S., W.W. and X.W.; software, J.S.; validation, J.S., X.W. and L.B.; formal analysis, J.S., W.W. and X.W.; investigation, J.S., W.W. and L.B.; resources, J.S., W.W. and L.B.; data curation, X.W.; writing—original draft preparation, J.S.; writing—review and editing, all authors; visualization, J.S.; supervision, W.W. and L.B.; project administration, W.W.; funding acquisition, W.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 41971042; 41961134003).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and suggestions that have significantly improved this article. The Landsat and SSEBOP products were acquired from United States Geological Survey (https://glovis.usgs.gov/app) (accessed on 10 October 2022). The in situ data used in this paper were provided by the National Qinghai Tibet Plateau Scientific Data Center (https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/en) (accessed on 11 October 2022).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, K.; Dickinson, R.E. A review of global terrestrial evapotranspiration: Observation, modeling, climatology, and climatic variability. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Kimball, J.S.; Running, S.W. A review of remote sensing based actual evapotranspiration estimation. WIREs Water 2016, 3, 834–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Huang, J.J.; Dash, S.S.; Wei, Y.; Li, H. A hybrid deep learning framework with physical process description for simulation of evapotranspiration. J. Hydrol. 2022, 606, 127422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senay, G.B.; Bohms, S.; Singh, R.K.; Gowda, P.H.; Velpuri, N.M.; Alemu, H.; Verdin, J.P. Operational Evapotranspiration Mapping Using Remote Sensing and Weather Datasets: A New Parameterization for the SSEB Approach. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2013, 49, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Jia, L.; Hu, G. Global land surface evapotranspiration monitoring by ETMonitor model driven by multi-source satellite earth observations. J. Hydrol. 2022, 613, 128444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, D.G.; Holmes, T.R.H.; De Jeu, R.A.M.; Gash, J.H.; Meesters, A.G.C.A.; Dolman, A.J. Global land-surface evaporation estimated from satellite-based observations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Im, J.; Park, S.; Gong, H. Spatiotemporal Downscaling Approaches for Monitoring 8-Day 30 m Actual Evapotranspiration. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 126, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, X.; Zhang, H.K.; Sun, Q.; Ouyang, Z.; Liu, J. MODIS Evapotranspiration Downscaling Using a Deep Neural Network Trained Using Landsat 8 Reflectance and Temperature Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaloiya, A.; Duhan, D.; Denis, D.; Singh, D.; Kumar, M.; Singh, M. Modeling Medium Resolution Evapotranspiration Using Downscaling Techniques in North-Western Part of India. MAUSAM 2023, 74, 561–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wong, M.S.; Shi, W.Z.; Wu, L.X.; Qin, K. Advancing of land surface temperature retrieval using extreme learning machine and spatio-temporal adaptive data fusion algorithm. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 4424–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisquert, M.; Sánchez, J.M.; López-Urrea, R.; Caselles, V. Estimating High Resolution Evapotranspiration from Disaggregated Thermal Images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahour, M.; Tolpekin, V.; Stein, A.; Sharifi, A. A comparison of two downscaling procedures to increase the spatial resolution of mapping actual evapotranspiration. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 126, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Wu, B.; Yan, N.; Zhu, W. An NDVI-based statistical ET downscaling method. Water 2017, 9, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Masek, J.; Schwaller, M.; Hall, F. On the blending of the landsat and MODIS surface reflectance: Predicting daily landsat surface reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Gao, F.; Chen, X.; Masek, J.G. An enhanced spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model for complex heterogeneous regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2610–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, D.P.; Sahoo, B.; Tiwari, M.K. MODIS-Landsat fusion-based single-band algorithms for TSS and turbidity estimation in an urban-waste-dominated river reach. Water Res. 2022, 224, 119082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, D.P.; Sahoo, B.; Tiwari, M.K.; Behera, G.K. Integrated remote sensing and machine learning tools for estimating ecological flow regimes in tropical river reaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 322, 116121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, D.P.; Sahoo, B.; Tiwari, M.K. Copula-based probabilistic spectral algorithms for high-frequent streamflow estimation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 251, 112092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; Xue, J.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Huang, G.; et al. A classification-based spatiotemporal adaptive fusion model for the evaluation of remotely sensed evapotranspiration in heterogeneous irrigated agricultural area. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 273, 112962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilker, T.; Wulder, M.A.; Coops, N.C.; Linke, J.; McDermid, G.; Masek, J.G.; Gao, F.; White, J.C. A new data fusion model for high spatial-and temporal-resolution mapping of forest disturbance based on Landsat and MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1613–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Tang, R.; Li, Z.L.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, M.; Niu, L. An improved spatio-temporal adaptive Data fusion algorithm for evapotranspiration mapping. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammalleri, C.; Anderson, M.C.; Gao, F.; Hain, C.R.; Kustas, W.P. A data fusion approach for mapping daily evapotranspiration at field scale. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 4672–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Cai, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, B.; Huang, L. Responses of field evapotranspiration to the changes of cropping pattern and groundwater depth in large irrigation district of Yellow River basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 188, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, Y. Continuous Daily Evapotranspiration Estimation at the Field-Scale over Heterogeneous Agricultural Areas by Fusing ASTER and MODIS Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.; Liu, S.; Xiao, Q.; Ma, M.; Jin, R.; Che, T.; Liu, Q.; Wang, W.; Qi, Y.; et al. Heihe watershed allied telemetry experimental research (HiWater) scientific objectives and experimental design. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaramuzza, P.; Micijevic, E.; Chander, G. SLC gap-filled products phase one methodology. Landsat Tech. Notes 2004, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sayler, K.; Zanter, K. Landsat 8 Level 2 Science Product (L2SP) Guide. Nasa. 2020. Available online: https://d9-wret.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/assets/palladium/production/s3fs-public/media/files/LSDS-1619_Landsat8-9-Collection2-Level2-Science-Product-Guide-v5.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- Lian, J.; Huang, M. Comparison of three remote sensing based models to estimate evapotranspiration in an oasis-desert region. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 165, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Wang, X.; Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Chen, Y. A Comparison of SSEBop-Model-Based Evapotranspiration with Eight Evapotranspiration Products in the Yellow River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyad, S.; Al Zayed, I.S.; Ha, V.T.T.; Ribbe, L. The Performance of Satellite-Based Actual Evapotranspiration Products and the Assessment of Irrigation Efficiency in Egypt. Water 2019, 11, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Huang, D. Estimating Regional Evapotranspiration Using a Satellite-Based Wind Speed Avoiding Priestley–Taylor Approach. Water 2021, 13, 3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Shuey, C.J.; Russ, A.L.; Fang, H.; Chen, M.; Walthall, C.L.; Daughtry, C.S.T.; Hunt, R. Narrowband to broadband conversions of land surface albedo: II. Validation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Sòria, G.; Romaguera, M.; Guanter, L.; Moreno, J.; Plaza, A.; Martínez, P. Land surface emissivity retrieval from different VNIR and TIR sensors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.D.; Hatfield, J.L.; Reginato, R.J.; Idso, S.B.; Pinter, P.J. Estimation of daily evapotranspiration from one time-of-day measurements. Agric. Water Manag. 1983, 7, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Black, T.A.; Detto, M.; Law, B.E.; Leuning, R.; Miyata, A.; Reichstein, M.; Vargas, R.; Ammann, C.; et al. On the Temporal Upscaling of Evapotranspiration from Instantaneous Remote Sensing Measurements to 8-Day Mean Daily-Sums. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 152, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Li, Z.-L.; Sun, X. Temporal upscaling of instantaneous evapotranspiration: An intercomparison of four methods using eddy covariance measurements and MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 138, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delogu, E.; Boulet, G.; Olioso, A.; Coudert, B.; Chirouze, J.; Ceschia, E.; Le Dantec, V.; Marloie, O.; Chehbouni, G.; Lagouarde, J.-P. Reconstruction of temporal variations of evapotranspiration using instantaneous estimates at the time of satellite overpass. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 2995–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Liu, S.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Jia, Z.; Xu, Z.; Nielson, J. Temporal upscaling and reconstruction of thermal remotely sensed instantaneous evapotranspiration. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 3400–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandholt, I.; Rasmussen, K.; Andersen, J. A simple interpretation of the surface temperature/vegetation index space for assessment of surface moisture status. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 79, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Gao, F.; Sun, L.; Anderson, M. Improving Spatial-Temporal Data Fusion by Choosing Optimal Input Image Pairs. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitz, M.; Senay, G.; Sanford, W. Combining Remote Sensing and Water-Balance Evapotranspiration Estimates for the Conterminous United States. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velpuri, N.M.; Senay, G.B.; Singh, R.K.; Bohms, S.; Verdin, J.P. A comprehensive evaluation of two MODIS evapotranspiration products over the conterminous United States: Using point and gridded FLUXNET and water balance ET. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 139, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, T.; Wang, T.; Zhou, X. Evaluation of Collection-6 MODIS Land Surface Temperature Product Using Multi-Year Ground Measurements in an Arid Area of Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Yang, D.; Yang, H.; Yuan, Z.; Lv, H. Simulated impacts of irrigation on evapotranspiration in a strongly exploited region: A case study of the Haihe River basin, China. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 2704–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Singh, V.P. A Two-source Trapezoid Model for Evapotranspiration (TTME) from satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 370–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kang, Q.; Chen, X.; Fu, Q.; Wang, P. A Temperature-Domain SEBAL Model Based on a Wind Speed-Independent Theoretical Trapezoidal Space Between Fractional Vegetation Coverage and Land Surface Temperature. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H. Two-Stage Trapezoid: A New Interpretation of the Land Surface Temperature and Fractional Vegetation Coverage Space. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lei, Y.; Zheng, L.; Mao, R. Calculating regional drought indices using evapotranspiration (ET) distribution derived from Landsat7 ETM+ data. In Remote Sensing and Modeling of Ecosystems for Sustainability II; Gao, W., Shaw, D.R., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; Volume 5884, p. 58841E. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Huang, J.J.; McBean, E.; Singh, V.P. Evaluation of alternative two-source remote sensing models in partitioning of land evapotranspiration. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Huang, J.J.; Dash, S.S.; McBean, E.; Wei, Y.; Li, H. Assessing the impact of urbanization on urban evapotranspiration and its components using a novel four-source energy balance model. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 316, 108853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaizzi, P.D.; Kustas, W.P.; Anderson, M.C.; Agam, N.; Tolk, J.A.; Evett, S.R.; Howell, T.A.; Gowda, P.H.; O’Shaughnessy, S.A. Two-source energy balance model estimates of evapotranspiration using component and composite surface temperatures. Adv. Water Resour. 2012, 50, 134–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Yu, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Lin, Y.; Fisher, J.B.; McVicar, T.R.; Cheng, J.; Jia, K.; et al. A simple temperature domain two-source model for estimating agricultural field surface energy fluxes from Landsat images. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 5211–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).