Influence of Climate, Topography, and Hydrology on Vegetation Distribution Patterns—Oasis in the Taklamakan Desert Hinterland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
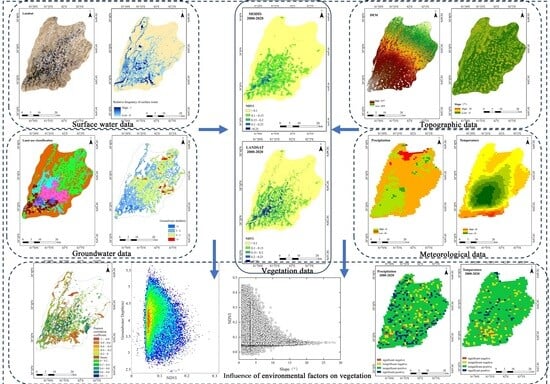
2. Materials and Methods
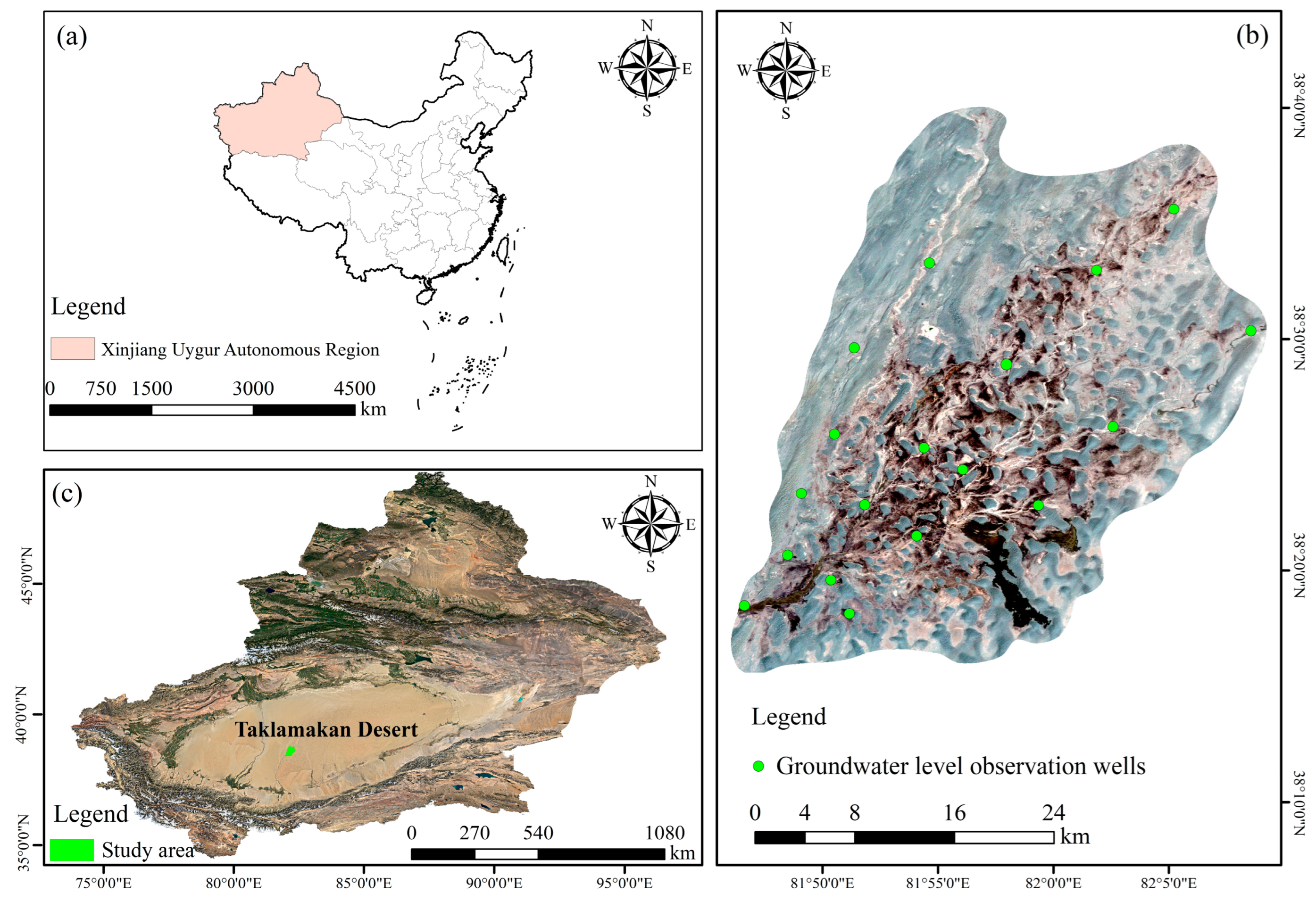
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methods
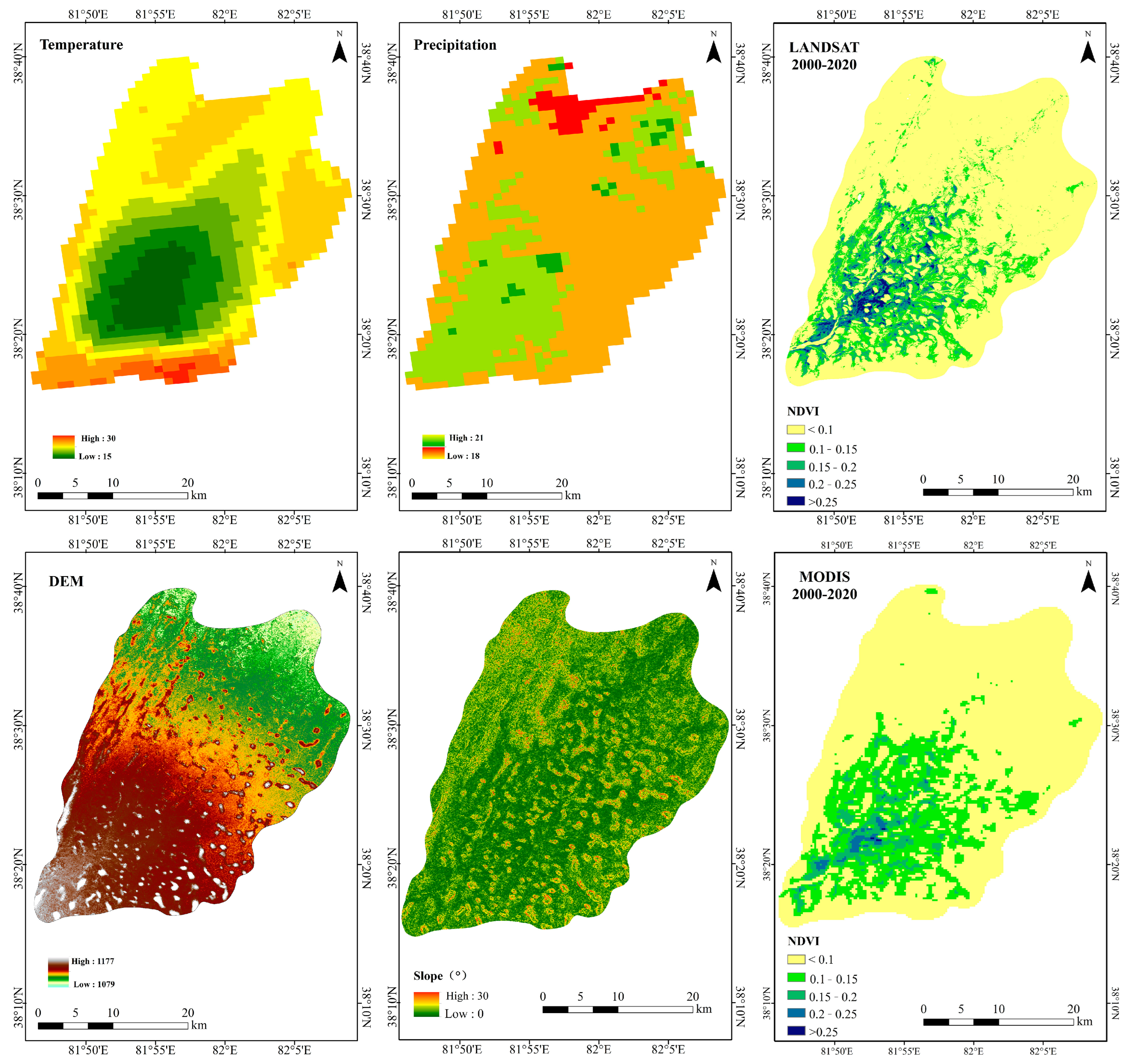
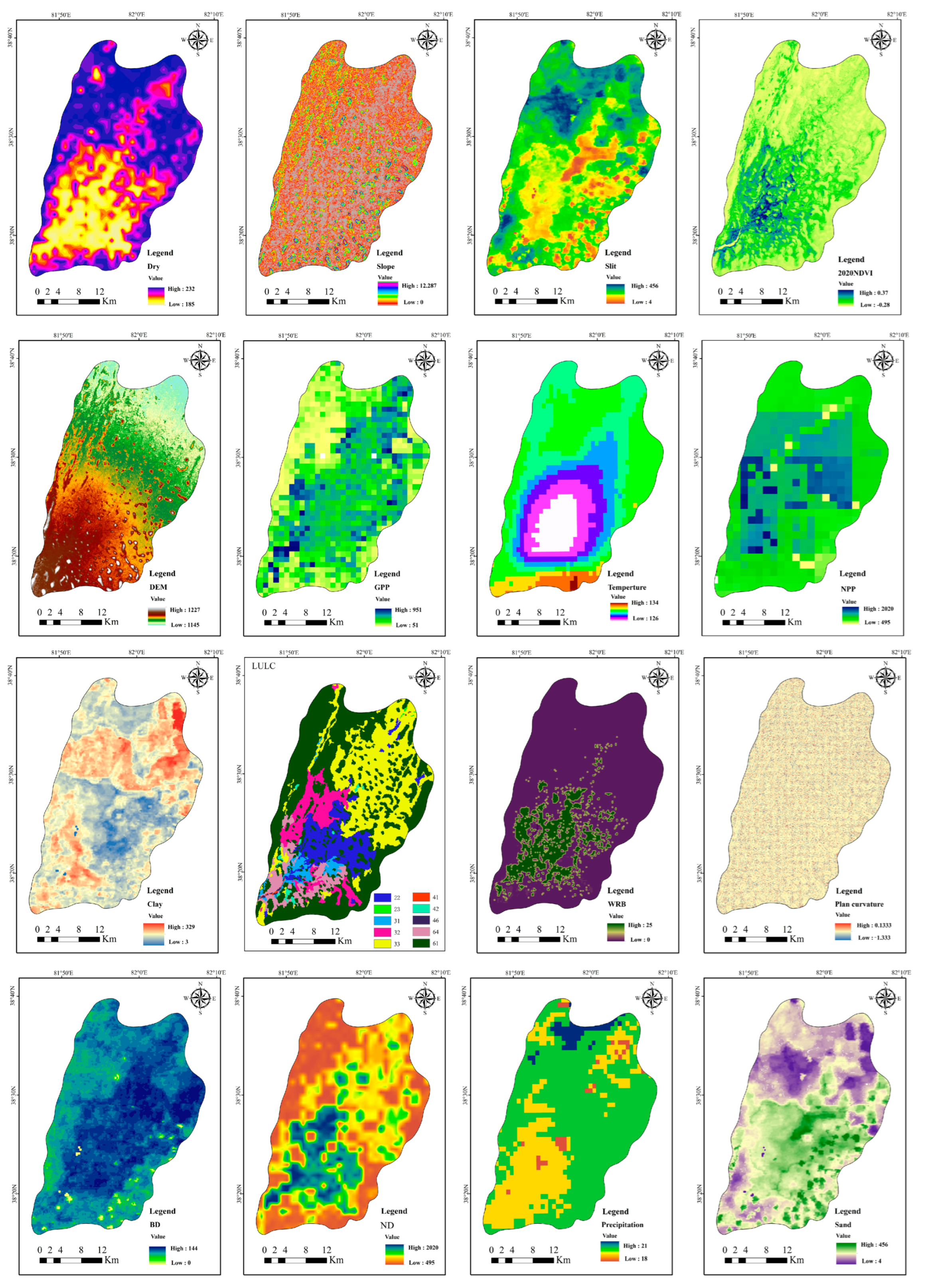
2.2.1. Meteorological and Topographic Data
2.2.2. Hydrological Data
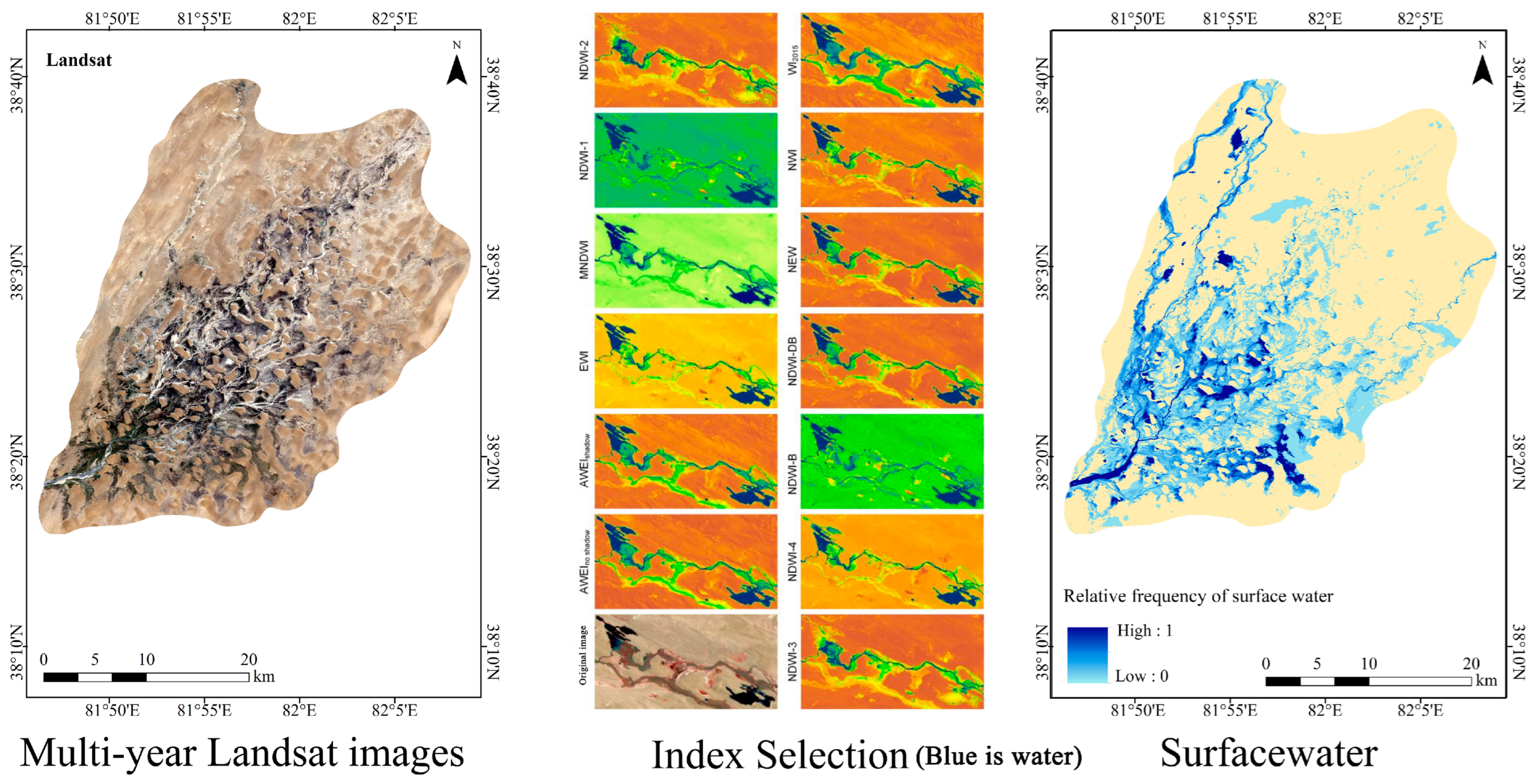
Surface Water Data
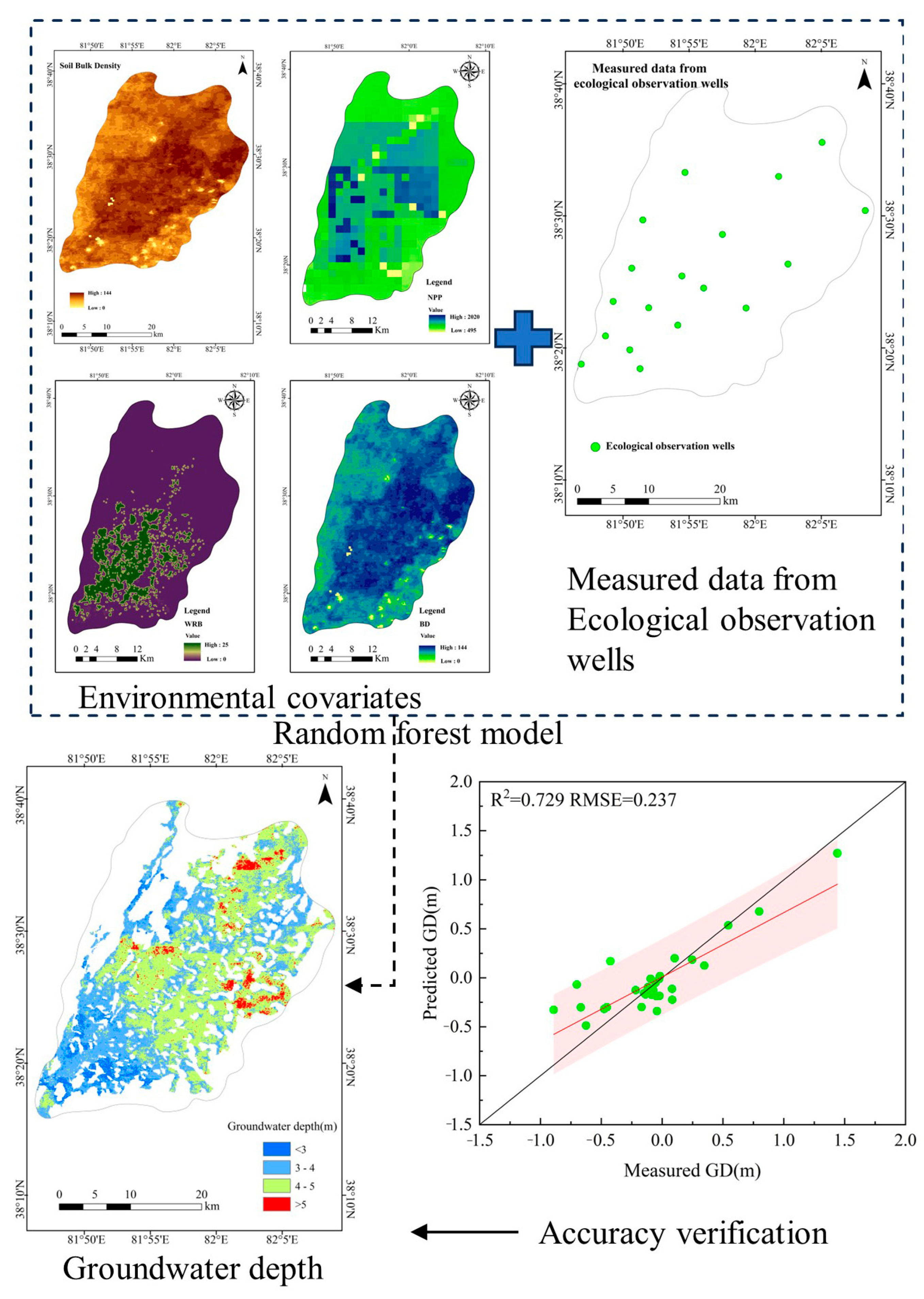
Groundwater Data
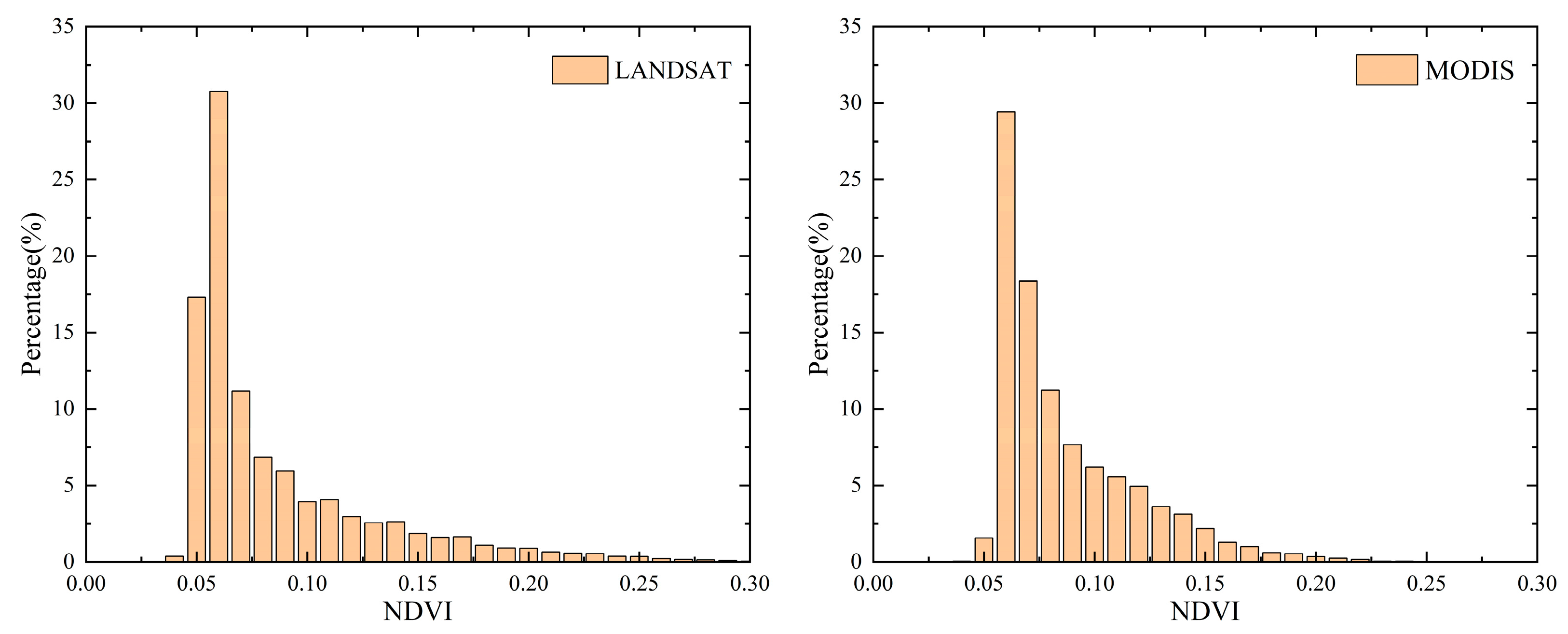
2.2.3. Vegetation Data
2.2.4. NDVI Calculation
2.2.5. Water Index Calculation
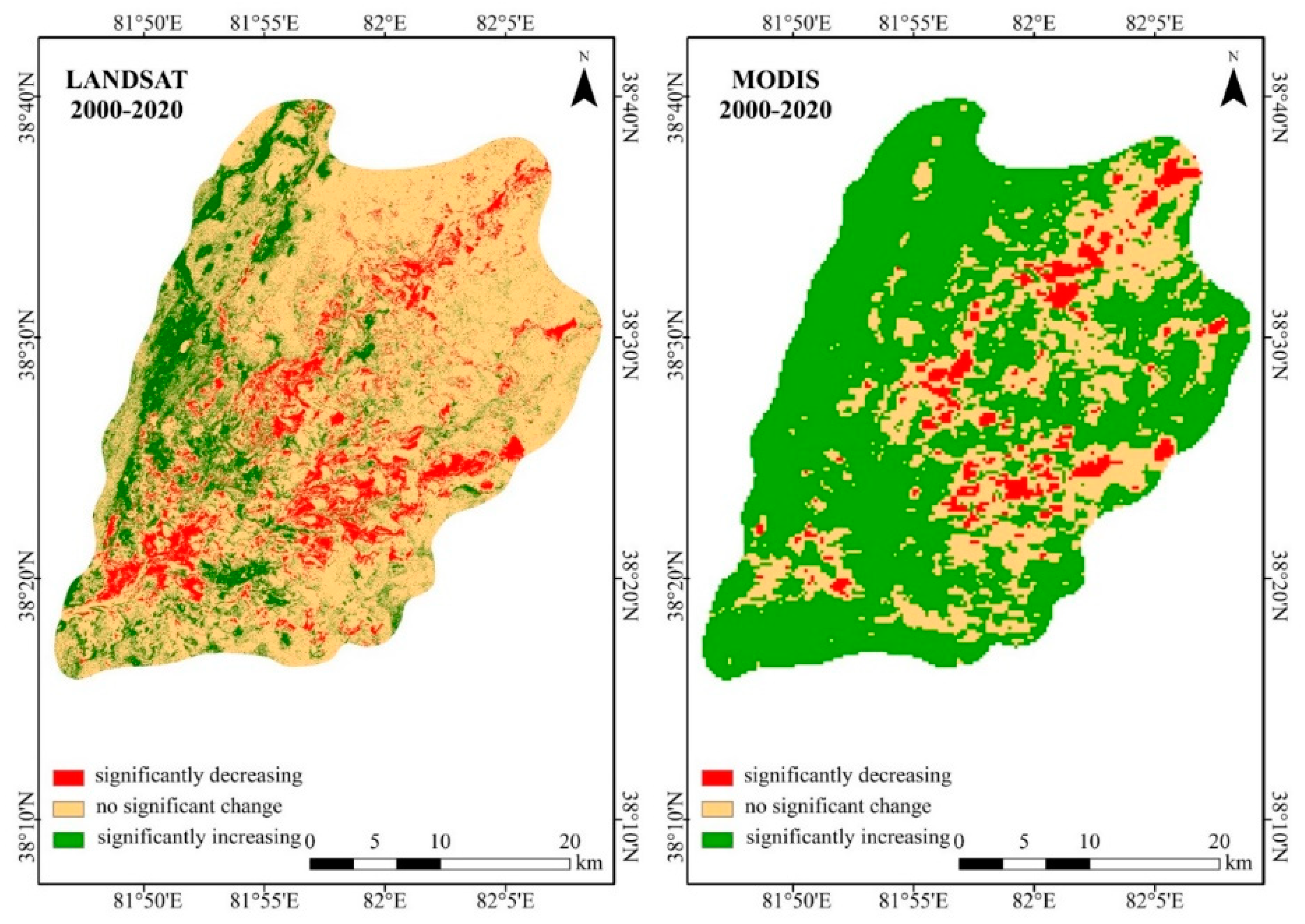
2.2.6. Mann–Kendall Test and Sen’s Slope Estimator—Trend Detection [36]
2.2.7. Calculation of Correlation Analysis
2.2.8. Random Forest (RF) Model
3. Results
3.1. Vegetation Distribution Pattern
3.2. Greening Trends in the Daliyabui Oasis
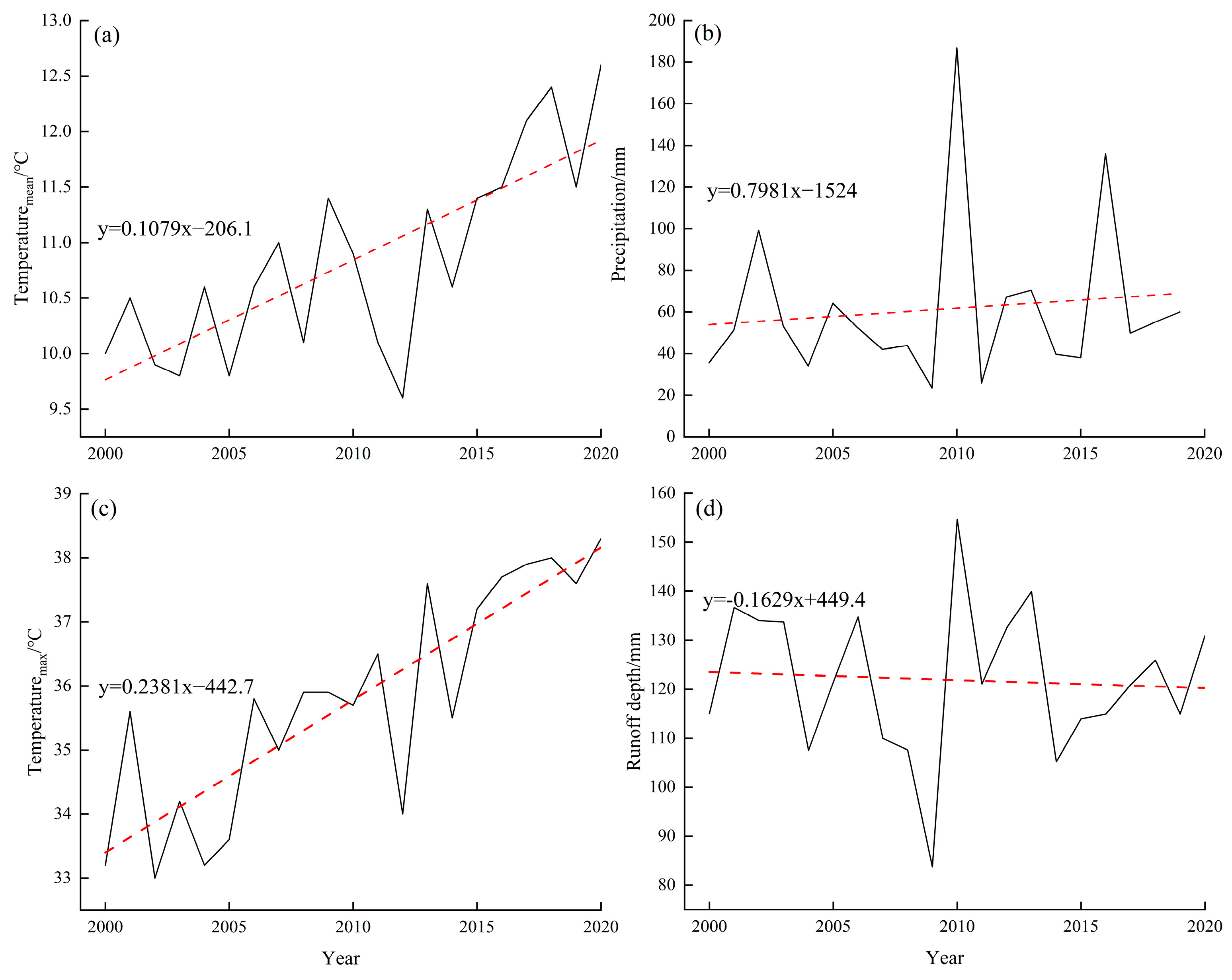
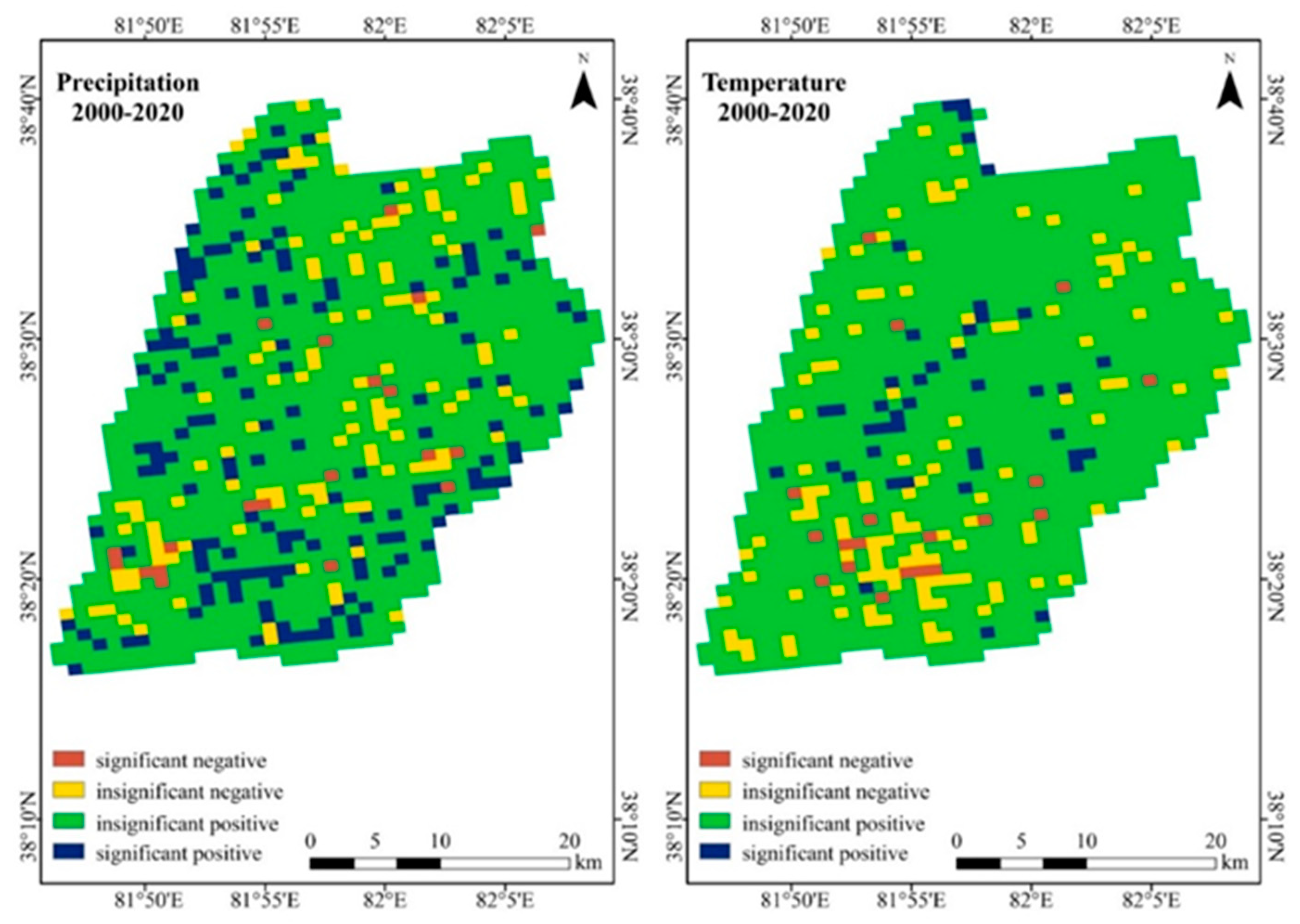
3.3. Climate Effects of Climate on Oasis Vegetation
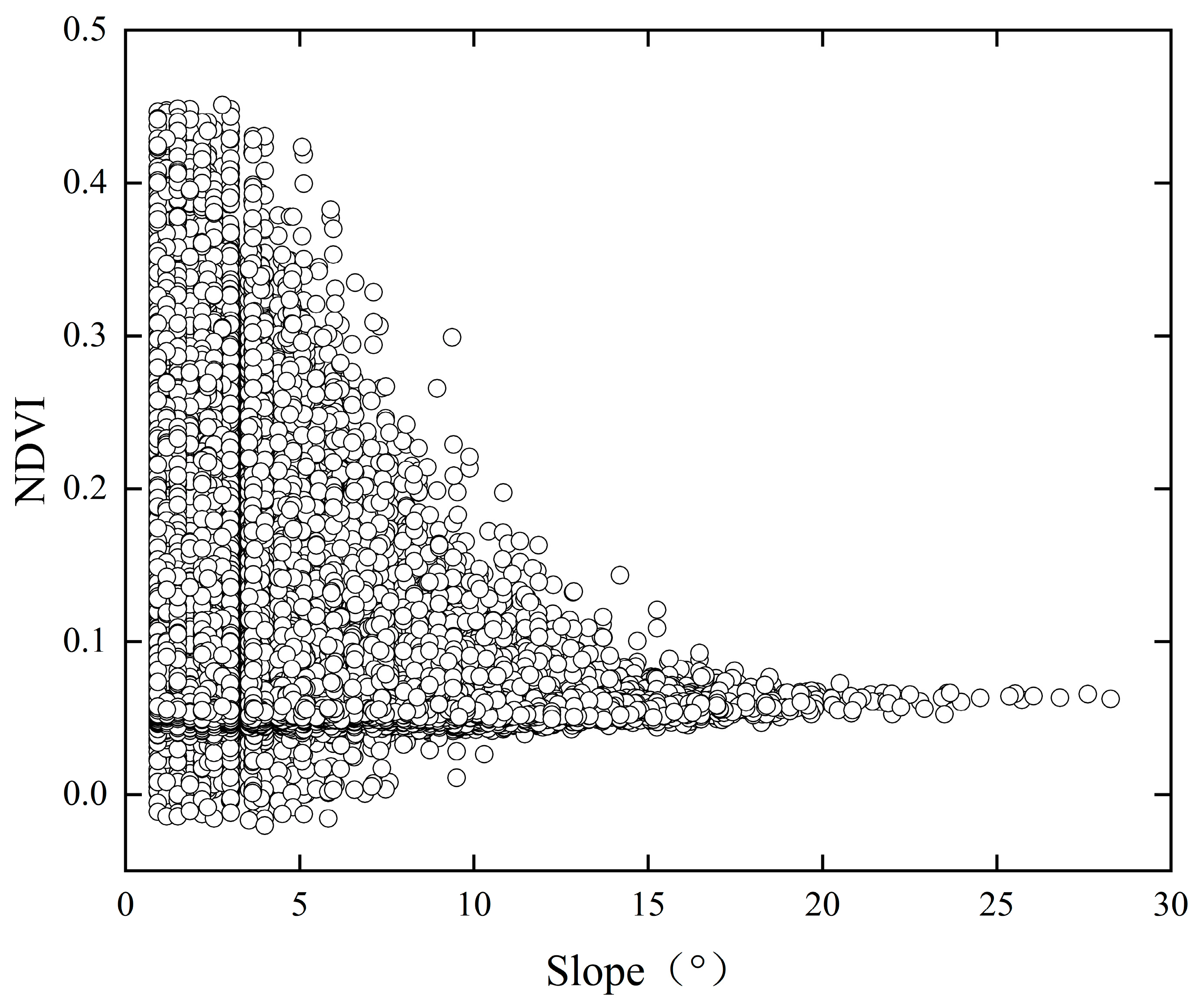
3.4. Effect of Topography on Oasis Vegetation
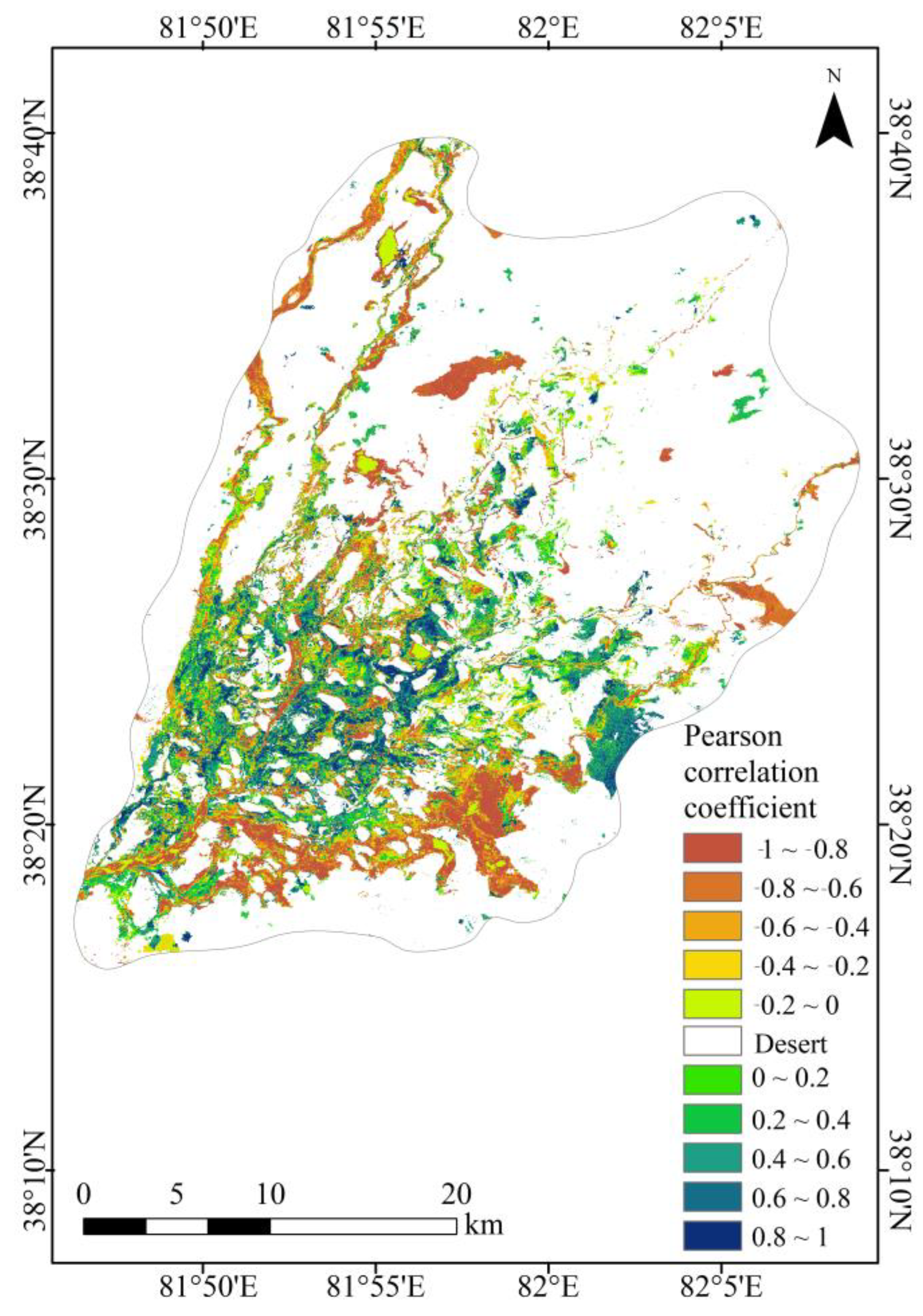
3.5. Effects of Spatial Distribution Frequency of Surface Water on Vegetation
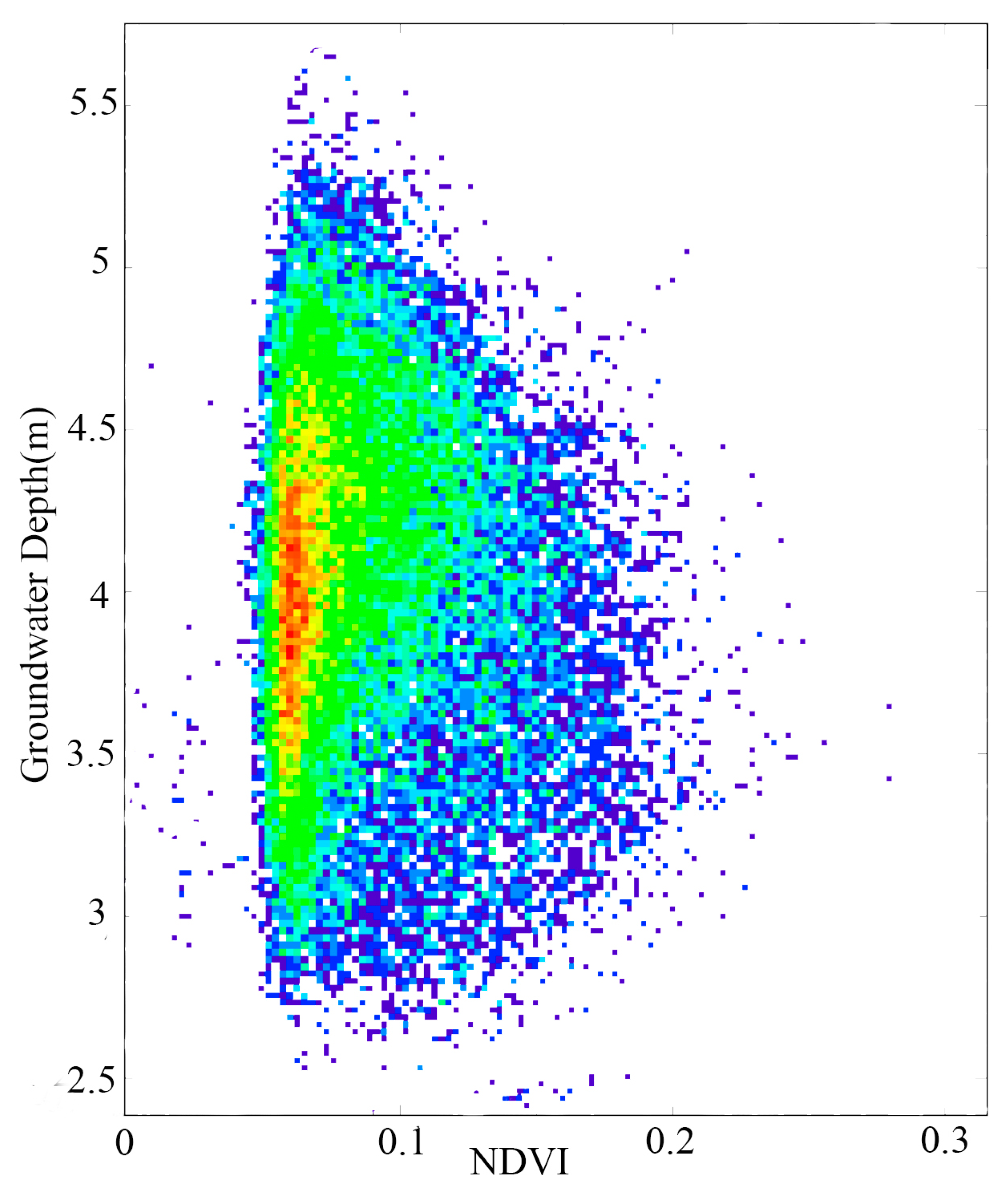
3.6. Effect of Groundwater Level on Oasis Vegetation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, L.; Cui, X.; Qian, J.; Zou, S.; Ma, X. Trend in Satellite-Observed Vegetation Cover and Its Drivers in the Gannan Plateau, Upper Reaches of the Yellow River, from 2000 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jin, X.; Liang, X.; Ren, J.; Han, B.; Liu, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, Y. Implications of land sparing and sharing for maintaining regional ecosystem services: An empirical study from a suitable area for agricultural production in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A.C.; Veras, C.E.; Rodriguez, D.A. Assessment of water policies contributions for sustainable water resources management under climate change scenarios. J. Hydrol. 2022, 608, 127690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, L.V. Global observed long-term changes in temperature and precipitation extremes: A review of progress and limitations in IPCC assessments and beyond. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2016, 11, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Wei, J.; Luo, S.; Ma, M.; Tang, X. Potential and environmental control of carbon sequestration in major ecosystems across arid and semi-arid regions in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleland, E.E.; Chiariello, N.R.; Loarie, S.R.; Mooney, H.A.; Field, C.B. Diverse responses of phenology to global changes in a grassland ecosystem. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13740–13744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Peylin, P.; Reichstein, M.; Luyssaert, S.; Margolis, H.; Fang, J.; Barr, A.; Chen, A. Net carbon dioxide losses of northern ecosystems in response to autumn warming. Nature 2008, 451, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemani, R.R.; Keeling, C.D.; Hashimoto, H.; Jolly, W.M.; Piper, S.C.; Tucker, C.J.; Myneni, R.B.; Running, S.W. Climate-driven increases in global terrestrial net primary production from 1982 to 1999. Science 2003, 300, 1560–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, D.; Lin, H.; Montenegro, A.; Zhu, X. NDVI and vegetation phenology dynamics under the influence of sunshine duration on the Tibetan plateau. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wei, W.; Chen, L.; Chen, W.; Wang, J. Response of temporal variation of soil moisture to vegetation restoration in semi-arid Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2014, 115, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auslander, M.; Nevo, E.; Inbar, M. The effects of slope orientation on plant growth, developmental instability and susceptibility to herbivores. J. Arid. Environ. 2003, 55, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Lin, S.-L.; He, J.-K.; Kong, F.-M.; Yu, J.-H.; Jiang, H.-S. Climatic water availability is the main limiting factor of biotic attributes across large-scale elevational gradients in tropical forests. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jucker, T.; Bongalov, B.; Burslem, D.F.; Nilus, R.; Dalponte, M.; Lewis, S.L.; Phillips, O.L.; Qie, L.; Coomes, D.A. Topography shapes the structure, composition and function of tropical forest landscapes. Ecol. Lett. 2018, 21, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeslund, J.E.; Arge, L.; Bøcher, P.K.; Dalgaard, T.; Svenning, J.C. Topography as a driver of local terrestrial vascular plant diversity patterns. Nord. J. Bot. 2013, 31, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.; Gerstner, K.; Kreft, H. Environmental heterogeneity as a universal driver of species richness across taxa, biomes and spatial scales. Ecol. Lett. 2014, 17, 866–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundholm, J.T. Plant species diversity and environmental heterogeneity: Spatial scale and competing hypotheses. J. Veg. Sci. 2009, 20, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.P.; Bhatia, S.; Shenoy, K. Vegetation-environment relationships in a South Asian tropical montane grassland ecosystem: Restoration implications. Trop. Ecol. 2015, 56, 201–217. [Google Scholar]
- Gow, L.; Barrett, D.J.; Renzullo, L.J.; Phinn, S.R.; O’Grady, A. A detection problem: Sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of a land surface temperature approach to detecting dynamics of water use by groundwater-dependent vegetation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 85, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanafield, M.; Cook, P.G.; Gutiérrez-Jurado, H.; Faux, R.; Eamus, D. Field comparison of methods for estimating groundwater discharge by evaporation and evapotranspiration in an arid-zone playa. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, M.; Mokhtar, M.; Bakheit, A.; Elfeky, A.M.; Gameh, M.; Mostafa, A.; Sefelnasr, A.; Kantoush, S.A.; Sumi, T.; Hori, T. An integrated assessment approach for fossil groundwater quality and crop water requirements in the El-Kharga Oasis, Western Desert, Egypt. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 40, 101016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, Q.; Wan, Y.; Shi, H.; Imin, B.; Li, M.S. Influence of Surface Water on Desert Vegetation Expansion at the Landscape Scale: A Case Study of the Daliyabuyi Oasis, Taklamakan Desert. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Li, H.; Miguez-Macho, G. Global patterns of groundwater table depth. Science 2013, 339, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Niu, J.; Phanikumar, M.S. Evaluating controls on coupled hydrologic and vegetation dynamics in a humid continental climate watershed using a subsurface-land surface processes model. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 2552–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imin, B.; Dai, Y.; Shi, Q.; Guo, Y.; Li, H.; Nijat, M. Responses of two dominant desert plant species to the changes in groundwater depth in hinterland natural oasis, Tarim Basin. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 9460–9471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcdonald, A.K.; Wilcox, B.P.; Moore, G.W.; Hart, C.R.; Sheng, Z.; Owens, M.K. Tamarix transpiration along a semiarid river has negligible impact on water resources. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 5117–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Shi, Q.; Zhou, X.; Imin, B.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Kahaer, Y. Effect of the competition mechanism of between co-dominant species on the ecological characteristics of Populus euphratica under a water gradient in a desert oasis. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 27, e01611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slayback, D.A.; Pinzon, J.E.; Los, S.O.; Tucker, C.J. Northern hemisphere photosynthetic trends 1982–1999. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2003, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braswell, B.; Schimel, D.S.; Linder, E.; Moore Iii, B. The response of global terrestrial ecosystems to interannual temperature variability. Science 1997, 278, 870–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, L.-J.; Jiang, J.; Chu, L.; Zhang, J.-C. Threshold effect of ecosystem services in response to climate change and vegetation coverage change in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau ecological shelter. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 318, 128592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ma, X.; Dou, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, C. Impacts of climate change on vegetation phenology and net primary productivity in arid Central Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 149055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Gong, P.; Fu, R.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Liang, S.; Xu, B.; Shi, J.; Dickinson, R. The role of satellite remote sensing in climate change studies. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniya, B.; Tang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Sun, S.; Techato, K.-a. Spatial and temporal variation of NDVI in response to climate change and the implication for carbon dynamics in Nepal. Forests 2018, 9, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, P.S.; Atzberger, C.; Høgda, K.A.; Johansen, B.; Skidmore, A.K. Improved monitoring of vegetation dynamics at very high latitudes: A new method using MODIS NDVI. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Huete, A.R.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, G.; Zhang, X. Analysis of NDVI and scaled difference vegetation index retrievals of vegetation fraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 101, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.; Flood, N.; Danaher, T. Comparing Landsat water index methods for automated water classification in eastern Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ding, J.; Zhu, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Han, L.; Ma, X.; Xu, D. Bivariate empirical mode decomposition of the spatial variation in the soil organic matter content: A case study from NW China. Catena 2021, 206, 105572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.A.; Bachelet, D.M.; Symstad, A.J.; Ferschweiler, K.; Hobbins, M. Estimation of potential evapotranspiration from extraterrestrial radiation, air temperature and humidity to assess future climate change effects on the vegetation of the Northern Great Plains, USA. Ecol. Model. 2015, 297, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenihan, J.M. Climate Cahnge Effects on Vegetation Distribution, Carbon Stocks, and Fire Regimes in California. AGU Fall Meet. Abstr. 2002, 2002, B21A-0719. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.Y. The influence of temperature and precipitation climate regimes on vegetation dynamics in the US Great Plains: A satellite bioclimatology case study. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 4947–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Price, K.; Rich, P. Spatial patterns of NDVI in response to precipitation and temperature in the central Great Plains. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 3827–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Huo, Z.; Dai, X.; Ma, S.; Xu, X.; Huang, G. Impact of agricultural water-saving practices on regional evapotranspiration: The role of groundwater in sustainable agriculture in arid and semi-arid areas. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 263, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qiu, Y.; Han, Z.; Xu, C.; Wu, S.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Holmgren, M.; Xu, Z. Climate, topography and anthropogenic effects on desert greening: A 40-year satellite monitoring in the Tengger desert, northern China. Catena 2022, 209, 105851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, D.; Körner, C. Topographically controlled thermal-habitat differentiation buffers alpine plant diversity against climate warming. J. Biogeogr. 2011, 38, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bärlocher, F.; Corkum, M. Nutrient enrichment overwhelms diversity effects in leaf decomposition by stream fungi. Oikos 2010, 101, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.C.; Bradley, B.A.; Brown, C.S.; D’Antonio, C.; Germino, M.J.; Grace, J.B.; Hardegree, S.P.; Miller, R.F.; Pyke, D.A. Resilience to stress and disturbance, and resistance to Bromus tectorum L. invasion in cold desert shrublands of western North America. Ecosystems 2014, 17, 360–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkouche, S.; Guerrache, N.; Bouderbala, R.; Kadik, L. Choice of fixing species dunes and their effect on vegetation. Int. J. 2014, 2, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Lai, Q.; Yin, S.; Bao, Y.; Qing, S.; Mei, L.; Bu, L. Exploring sandy vegetation sensitivities to water storage in China’s arid and semi-arid regions. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestrini, R.; Delconte, C.; Sacchi, E.; Buffagni, A. Groundwater-dependent ecosystems as transfer vectors of nitrogen from the aquifer to surface waters in agricultural basins: The fontanili of the Po Plain (Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 141995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y. Effects of different groundwater depths on the distribution characteristics of soil-Tamarix water contents and salinity under saline mineralization conditions. Catena 2016, 142, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eamus, D.; Hatton, T.; Cook, P.; Colvin, C. Ecohydrology: Vegetation Function, Water and Resource Management; Csiro Publishing: Clayton, Australia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes, C.; Diaz Barradas, M.C.; Zunzunegui, M.; Vieira, S.; Pereira, Â.; Anjos, A.; Correia, O.; Pereira, M.J.; Máguas, C. Contrasting plant water-use responses to groundwater depth in coastal dune ecosystems. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 1931–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Zhang, F.; Wei, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, T. An improved IBIS model for simulating NPP dynamics in alpine mountain ecosystems: A case study in the eastern Qilian Mountains, northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Catena 2021, 206, 105479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Jia, L.; Menenti, M. Reconstruction of global MODIS NDVI time series: Performance of Harmonic Analysis of Time Series (HANTS). Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 163, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; McVicar, T.R.; van Dijk, A.I.; Schellekens, J.; de Jeu, R.A.; Bruijnzeel, L.A. Global evaluation of four AVHRR–NDVI data sets: Intercomparison and assessment against Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2547–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. SPAD monitoring of saline vegetation based on Gaussian mixture model and UAV hyperspectral image feature classification. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 200, 107236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, R.; Ye, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, D.; Hua, K. Winter wheat SPAD estimation from UAV hyperspectral data using cluster-regression methods. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 105, 102618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Satellites Sensors | Year | Resolution (m) | Period (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat-5 MSS, TM | 2000–2013 | 90 | 16 |
| Landsat-8 OLI | 2013–2020 | 90 | 16 |
| MODIS | 2000–2020 | 250 | 16 |
| Classification | Relevance | Percentage | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive correlation | 0.8–1 | Very strong positive correlation | 8.27% | 45.54% |
| 0.6–0.8 | Strong positive correlation | 9.41% | ||
| 0.4–0.6 | Moderate positive correlation | 9.84% | ||
| 0.2–0.4 | Weak positive correlation | 9.32% | ||
| 0–0.2 | Very weak positive correlation | 8.70% | ||
| Negative correlation | −0.2–0 | Very weak negative correlation | 10.20% | 54.46% |
| −0.4–0.2 | Weak negative correlation | 8.08% | ||
| −0.6–0.4 | Moderate negative correlation | 7.60% | ||
| −0.8–0.6 | Strong negative correlation | 11.02% | ||
| −1–0.8 | Very strong negative correlation | 17.56% | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, L.; Wan, Y.; Shi, H.; Anwaier, A.; Shi, Q. Influence of Climate, Topography, and Hydrology on Vegetation Distribution Patterns—Oasis in the Taklamakan Desert Hinterland. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5299. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15225299
Peng L, Wan Y, Shi H, Anwaier A, Shi Q. Influence of Climate, Topography, and Hydrology on Vegetation Distribution Patterns—Oasis in the Taklamakan Desert Hinterland. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(22):5299. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15225299
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Lei, Yanbo Wan, Haobo Shi, Abudureyimu Anwaier, and Qingdong Shi. 2023. "Influence of Climate, Topography, and Hydrology on Vegetation Distribution Patterns—Oasis in the Taklamakan Desert Hinterland" Remote Sensing 15, no. 22: 5299. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15225299
APA StylePeng, L., Wan, Y., Shi, H., Anwaier, A., & Shi, Q. (2023). Influence of Climate, Topography, and Hydrology on Vegetation Distribution Patterns—Oasis in the Taklamakan Desert Hinterland. Remote Sensing, 15(22), 5299. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15225299