The Plumb-Line Matching Algorithm for UAV Oblique Photographic Photos
Abstract
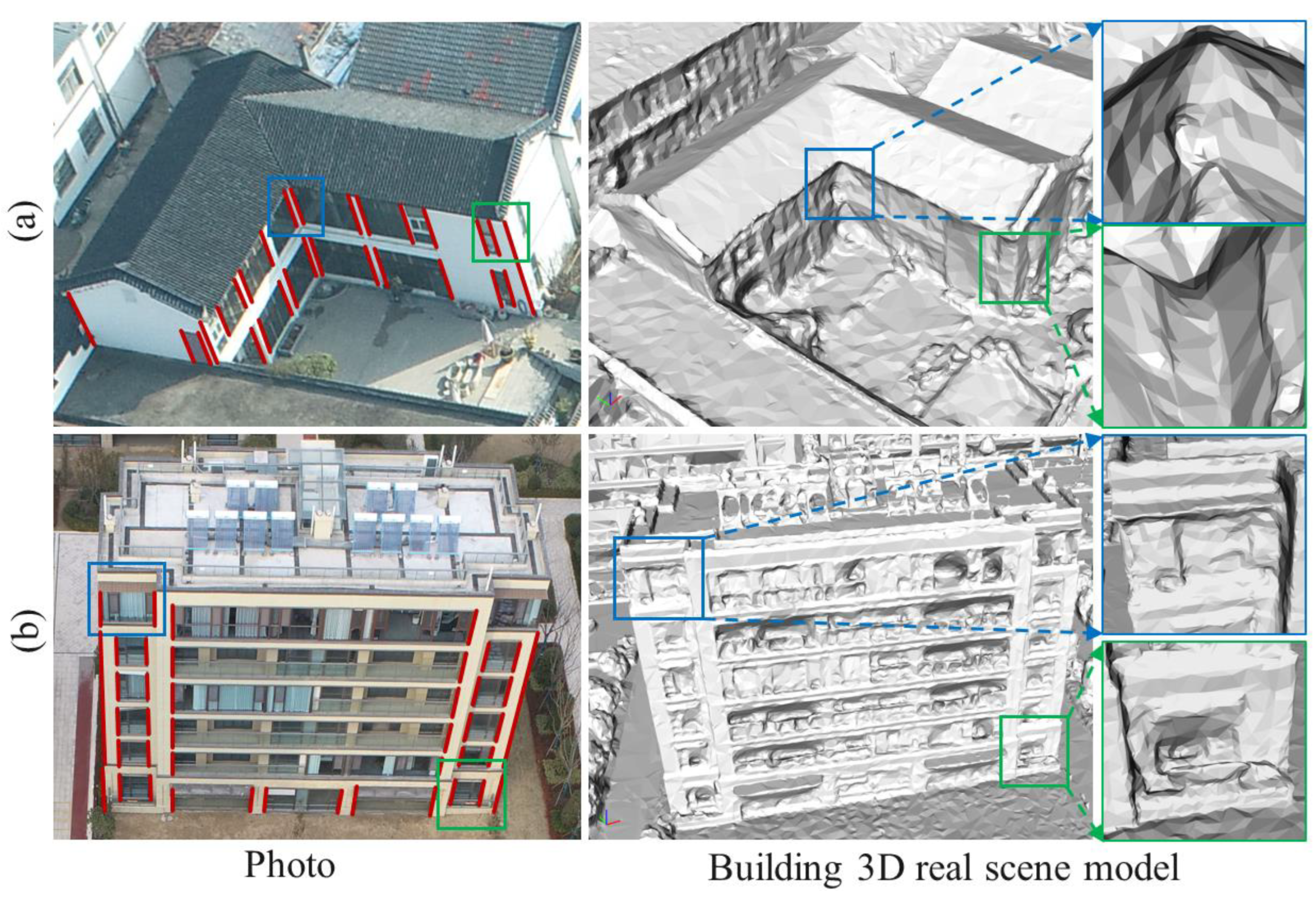
:1. Introduction
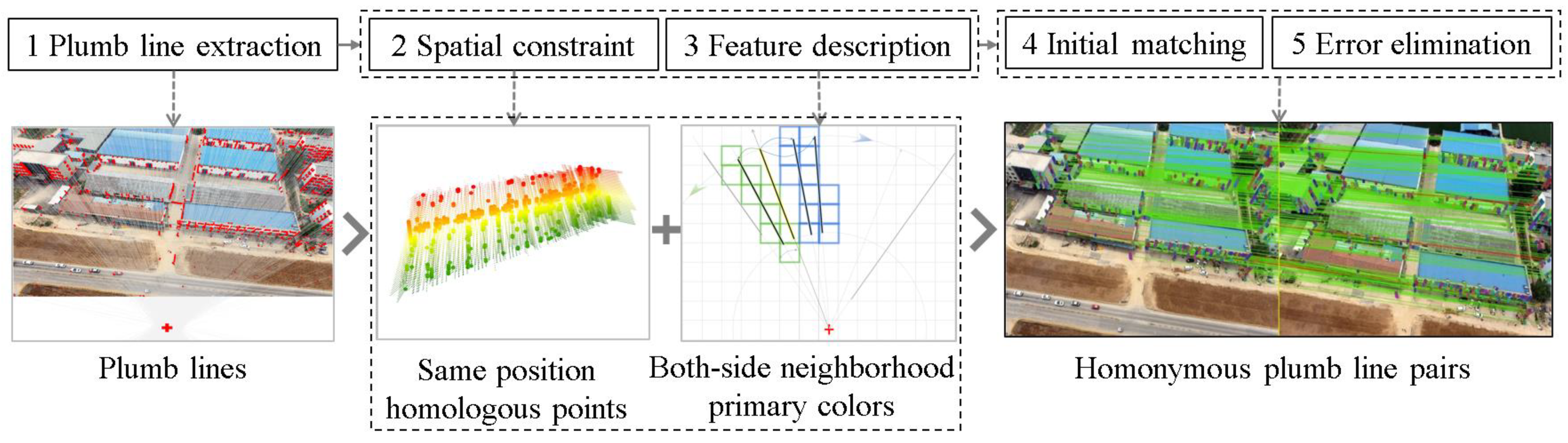
2. Methodology
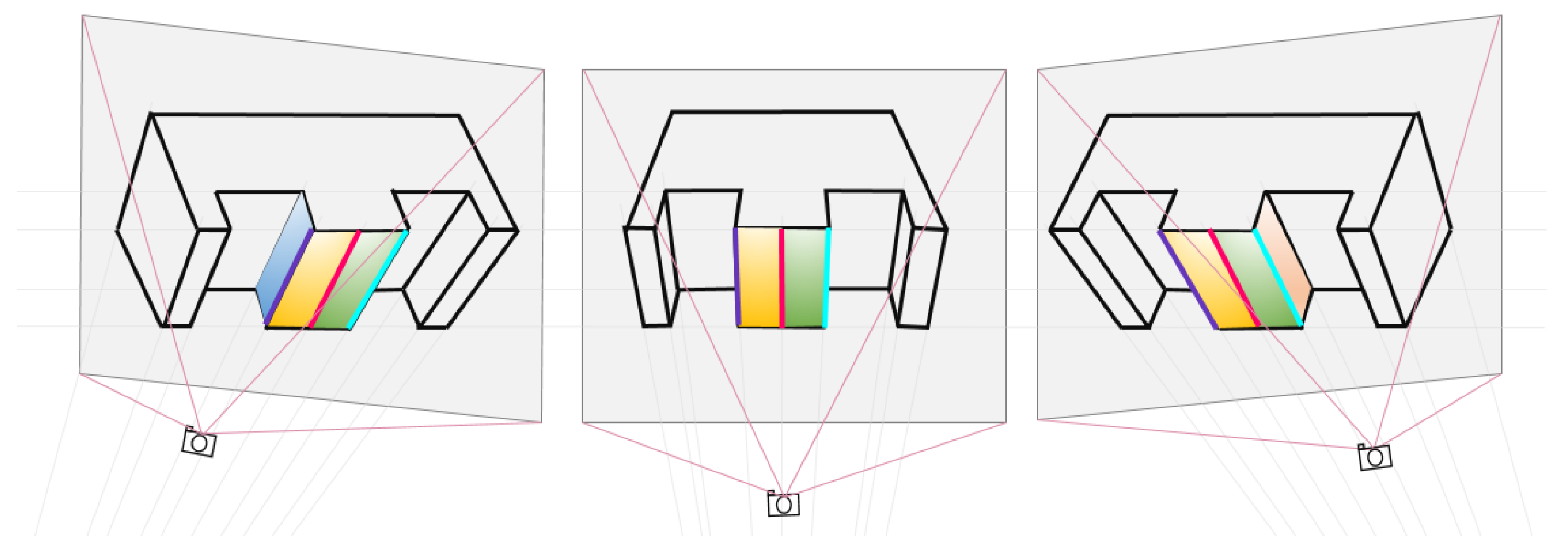
2.1. Plumb Line Extraction
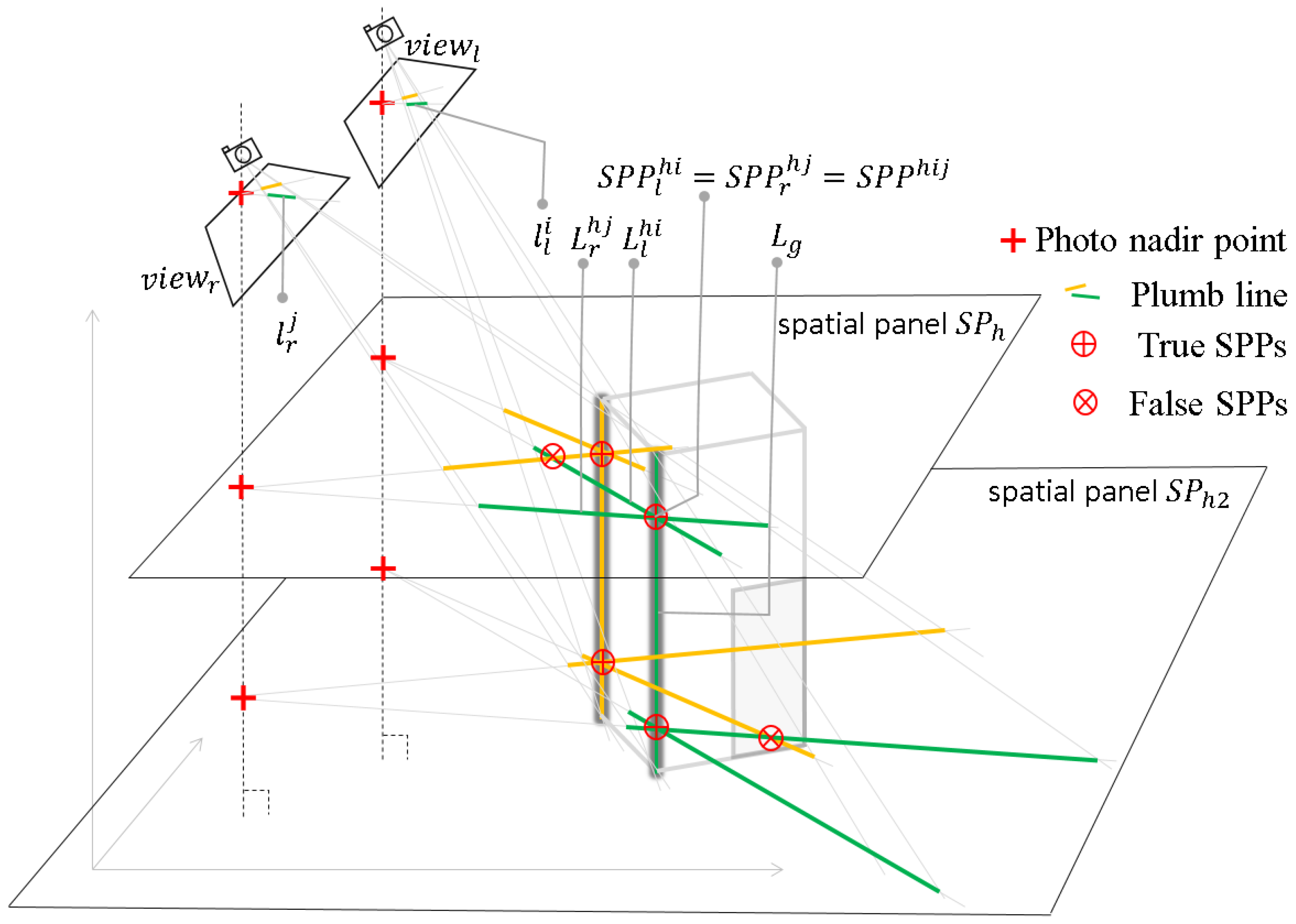
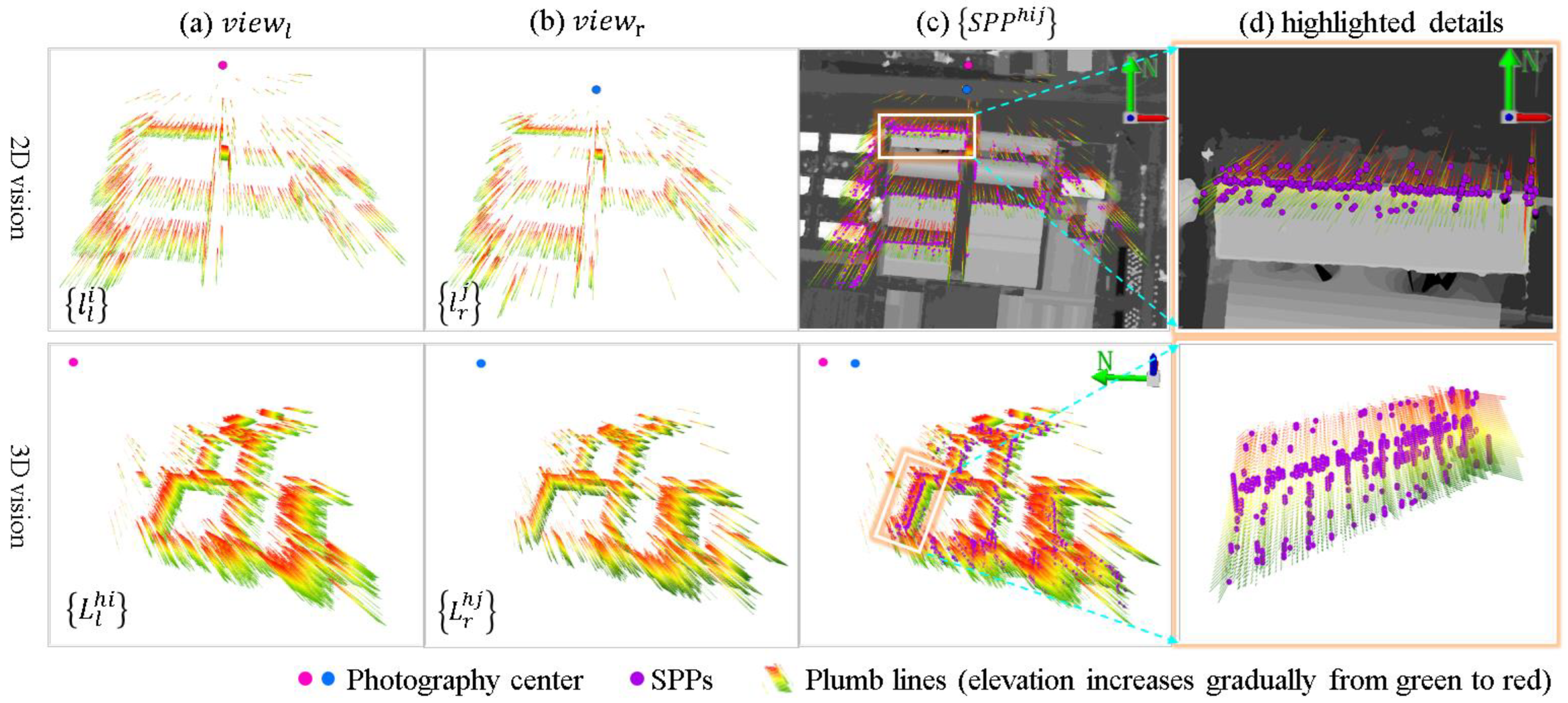
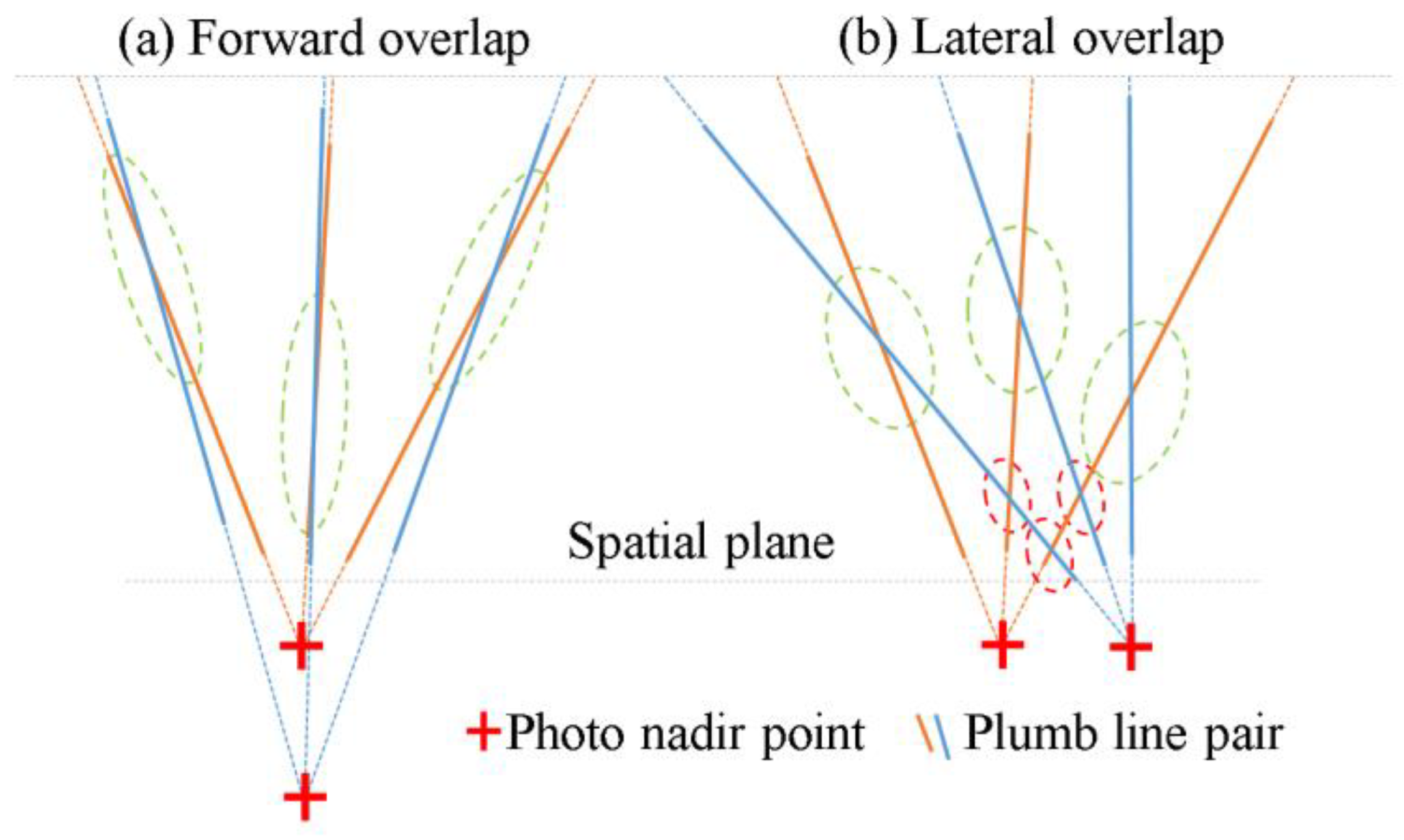
2.2. Spatial Constraint
2.3. Feature Description
2.3.1. Calculation of Chromatic Aberration
2.3.2. Partitioning and Extraction of Neighborhood Pixels
2.3.3. Description of Pixel Color Feature
2.3.4. Consistent Determination of the Primary Color
2.4. Initial Matching
2.5. Error Rejection
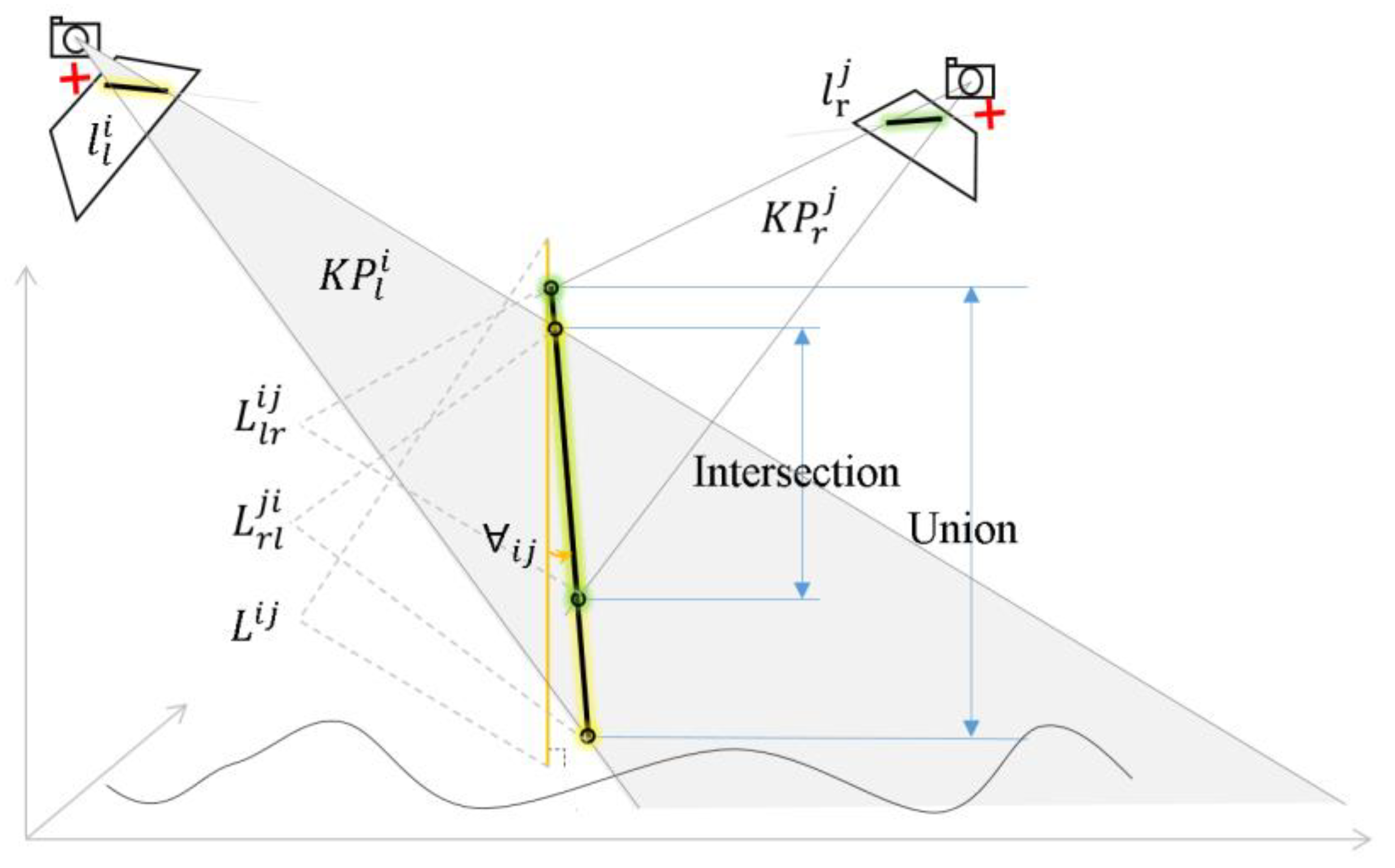
2.5.1. IoU Filtering
2.5.2. Verticalness Filtering
3. Experiment and Discussion
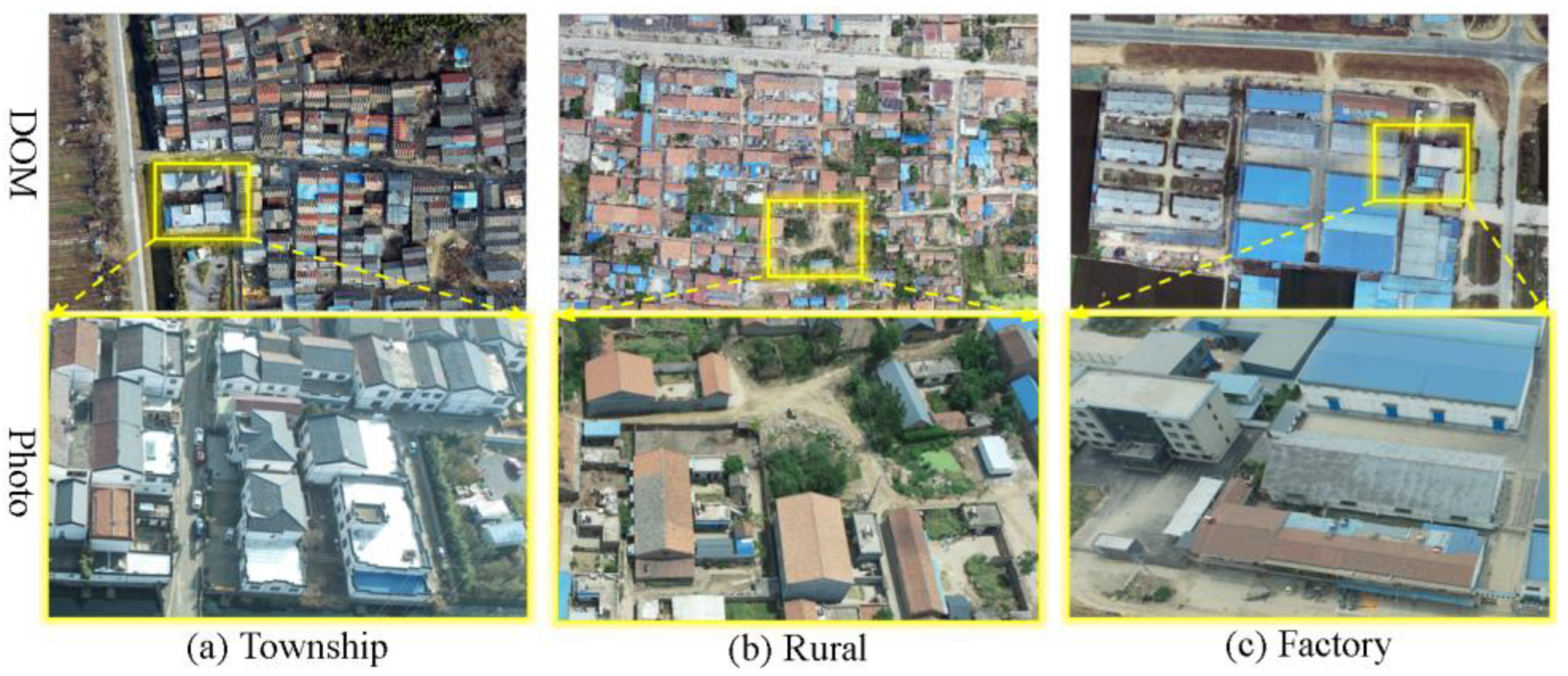
3.1. Data
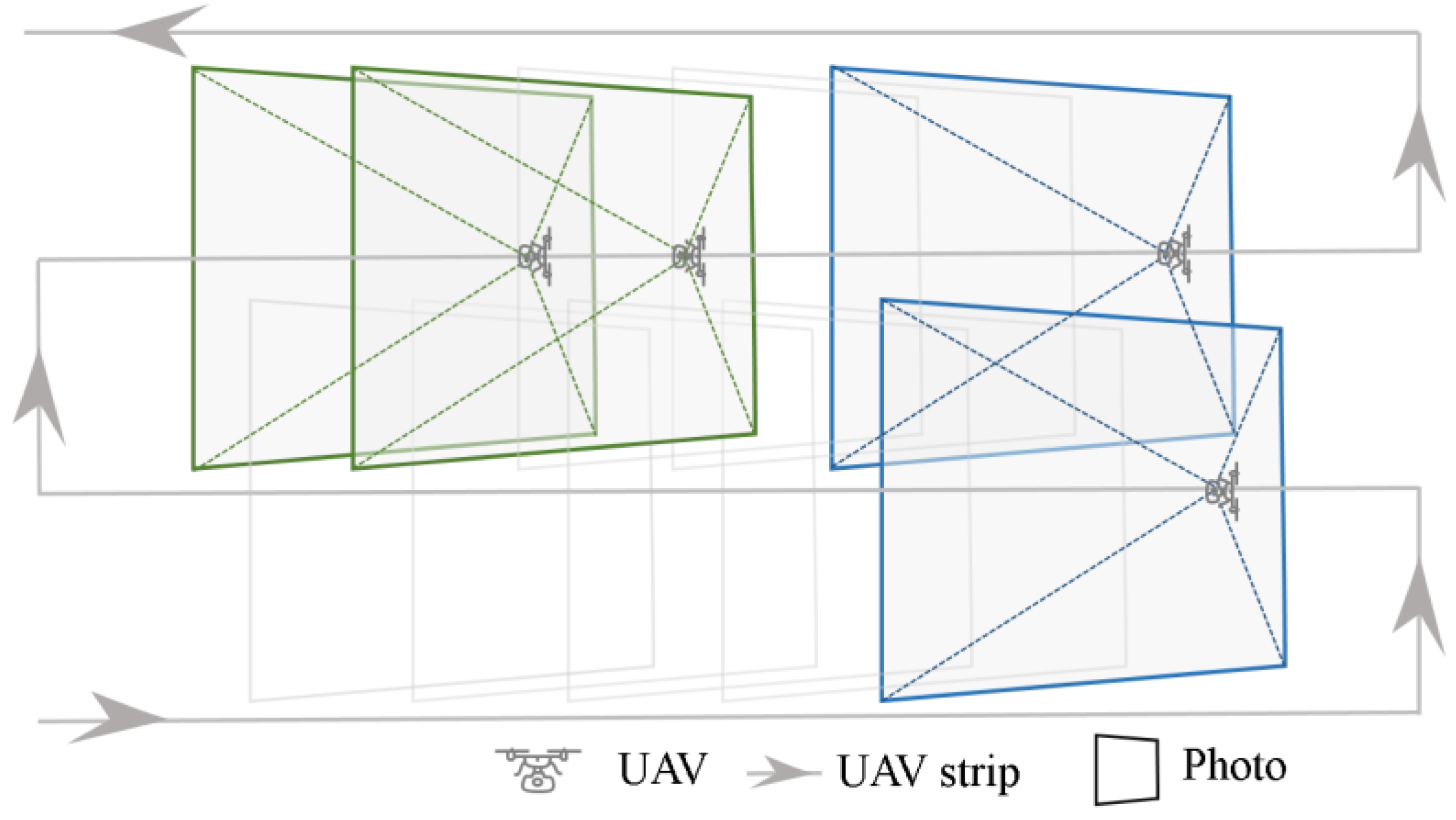
3.2. Matching Photo Pair Selection
3.3. Result
3.4. Discussion
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nex, F.; Remondino, F. UAV for 3D mapping applications: A review. Appl. Geomat. 2014, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Ali, F.; Zhou, B.; Li, S.; Yu, Y.; Yang, T.; Liu, X.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, K. A novel approach of efficient 3D reconstruction for real scene using unmanned aerial vehicle oblique photogrammetry with five cameras. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 99, 107804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Huang, H.; Yu, W.; Jiang, S. Optimized views photogrammetry: Precision analysis and a large-scale case study in qingdao. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 1144–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Jiang, C.; Jiang, W. Efficient structure from motion for large-scale UAV images: A review and a comparison of SfM tools. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 167, 230–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, D.; He, K.; Qiu, K.; Ma, B.; Liu, Q. Edge Restoration of a 3D Building Model Based on Oblique Photography. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remondino, F.; Gerke, M. Oblique aerial imagery—A review. Photogramm. Week 2015, 15, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Verykokou, S.; Ioannidis, C. Oblique aerial images: A review focusing on georeferencing procedures. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 3452–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Rottensteiner, F.; Heipke, C. Feature detection and description for image matching: From hand-crafted design to deep learning. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, 24, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Xie, L.; Hu, H.; Zhu, Q.; Yau, E. Integration of aerial oblique imagery and terrestrial imagery for optimized 3D modeling in urban areas. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 139, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Shu, H. Accuracy Analysis of Three-Dimensional Modeling of a Multi-Level UAV without Control Points. Buildings 2022, 12, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Shi, T.; Liao, G.; Xia, Q. Image registration using a point-line duality based line matching method. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2013, 24, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, M.; Wendel, A.; Bischof, H. Line-based 3D reconstruction of wiry objects. In Proceedings of the 18th Computer Vision Winter Workshop, Hernstein, Austria, 4–6 February 2013; pp. 78–85. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Li, Z. Robust line segment matching across views via ranking the line-point graph. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 171, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elqursh, A.; Elgammal, A. Line-based relative pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 3049–3056. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Zhang, G.; Lim, J.; Suh, I.H. Place recognition using straight lines for vision-based SLAM. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 3799–3806. [Google Scholar]
- Shipitko, O.; Kibalov, V.; Abramov, M. Linear features observation model for autonomous vehicle localization. In Proceedings of the 2020 16th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision (ICARCV), Shenzhen, China, 13–15 December 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1360–1365. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, B.; Wu, F.; Hu, Z. Line matching leveraged by point correspondences. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 390–397. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.; Kim, A. Line as a Visual Sentence: Context-Aware Line Descriptor for Visual Localization. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 8726–8733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Jiang, X.; Fan, A.; Jiang, J.; Yan, J. Image matching from handcrafted to deep features: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 23–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forero, M.G.; Mambuscay, C.L.; Monroy, M.F.; Miranda, S.L.; Méndez, D.; Valencia, M.O.; Gomez Selvaraj, M. Comparative analysis of detectors and feature descriptors for multispectral image matching in rice crops. Plants 2021, 10, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Jain, K.; Shukla, A.K. A Comparative Analysis of Feature Detectors and Descriptors for Image Stitching. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, C.; Zisserman, A. Automatic line matching across views. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Juan, PR, USA, 17–19 June 1997; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 666–671. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, C.; Zisserman, A. The geometry and matching of lines and curves over multiple views. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2000, 40, 199–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, L.; Huang, S.; Yan, L. Line matching based on planar homography for stereo aerial images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 104, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C. Robust line segment matching via reweighted random walks on the homography graph. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 111, 107693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, M.; Maurer, M.; Bischof, H. Efficient 3D scene abstraction using line segments. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2017, 157, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Yuan, Z.; Dong, Z.; Dong, M.; Gong, J.; Xiong, H. Smoothly varying projective transformation for line segment matching. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 183, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, F.; Hu, Z. MSLD: A robust descriptor for line matching. Pattern Recognit. 2009, 42, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Koch, R. An efficient and robust line segment matching approach based on LBD descriptor and pairwise geometric consistency. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2013, 24, 794–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakhitov, A.; Lempitsky, V. Learnable line segment descriptor for visual slam. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 39923–39934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, M.; Schweinfurth, F.; Schilling, A. Dld: A deep learning based line descriptor for line feature matching. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 5910–5915. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, M.; Raisch, C.; Schilling, A. Wld: A wavelet and learning based line descriptor for line feature matching. Proc. Intl. Symp. Vis. Mod. Vis. 2020, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.; Jiang, G.; Lai, D. Robust Line Segments Matching via Graph Convolution Networks. arXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pautrat, R.; Lin, J.T.; Larsson, V.; Oswald, M.R.; Pollefeys, M. SOLD2: Self-supervised occlusion-aware line description and detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 11368–11378. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J. Automatic building outlining from multi-view oblique images. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2012, 1, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wu, J.; Zhao, X.; Xu, G. Integrating TPS, cylindrical projection, and plumb-line constraint for natural stitching of multiple images. Vis. Comput. 2023, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Bai, Y.; Zheng, C. An attitude estimation method based on monocular vision and inertial sensor fusion for indoor navigation. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 27051–27061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Xie, W.; Hang, J. Automatic high-rise building extraction from aerial images. In Proceedings of the Fifth World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation (IEEE Cat. No. 04EX788), Hangzhou, China, 15–19 June 2004; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 4, pp. 3109–3113. [Google Scholar]
- Tardif, J.P. Non-iterative approach for fast and accurate vanishing point detection. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 29 September–2 October 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 1250–1257. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, T.; Gao, S. Auto Extracting Vertical Lines from Aerial Imagery over Urban Areas. Geospat. Inf. 2009, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habbecke, M.; Kobbelt, L. Automatic registration of oblique aerial images with cadastral maps. In Trends and Topics in Computer Vision: ECCV 2010 Workshops, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 10–11 September 2010, Revised Selected Papers, Part II 11; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 253–266. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Gerke, M.; Vosselman, G. Building extraction from oblique airborne imagery based on robust façade detection. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 68, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, F. Absolute Orientation of Aerial Imagery over Urban Areas Combined with Vertical Lines. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2007, 32, 197–200. [Google Scholar]
- Gioi, R.G.V.; Jakubowicz, J.; Morel, J.M.; Randall, G. LSD: A Fast Line Segment Detector with a False Detection Control. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 32, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasi, C.; Manduchi, R. Bilateral filtering for gray and color images. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Computer Vision, Bombay, India, 7 January 1998; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 839–846. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, A.; Carvalho, P.; Coelho, G.; Côrte-Real, L. Efficient ciede2000-based color similarity decision for computer vision. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2019, 30, 2141–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Kiya, H. Hue-correction scheme considering CIEDE2000 for color-image enhancement including deep-learning-based algorithms. APSIPA Trans. Signal Inf. Process. 2020, 9, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zou, T.; Huang, G.; Zhang, W. A high visual quality color image reversible data hiding scheme based on BRG embedding principle and CIEDE2000 assessment metric. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 32, 1860–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Qiu, S.; Li, W.; Zhong, G.; Chen, M.; Sarem, M. An improved NAMLab image segmentation algorithm based on the earth moving distance and the CIEDE2000 color difference formula. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Computing Theories and Application: 18th International Conference, ICIC 2022, Xi’an, China, 7–11 August 2022; Proceedings, Part I. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2022; pp. 535–548. [Google Scholar]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun. ACM 1981, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhao, J.; Tian, J.; Yuille, A.L.; Tu, Z. Robust point matching via vector field consensus. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 1706–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Aircraft | Camera | Platform | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Four-axis aircraft | Image sensor | 1-inch CMOS; 20 million effective pixels | Controlled rotation range | Pitch: −90° to +30° |
| Hovering accuracy | ±0.1 m | Camera Lens | FOV 84°; 8.8 mm/24 mm; Aperture f/2.8–f/11 | Stabilization system | Three-axis (pitch, roll, yaw) |
| Horizontal flight speed | Photo resolution | 5472 × 3648 (3:2) | Maximum control speed | Pitch: 90°/s | |
| Single flight time | Approx. 30 min | Photo format | JPEG | Angular jitter | ±0.02° |
| Parameter | Region a | Region b | Region c |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flight height | 120 m | 100 m | 110 m |
| Photography angle | −45 degrees | −45 degrees | −50 degrees |
| Lateral overlap rate | 70% | 70% | 70% |
| Forward overlap rate | 80% | 80% | 80% |
| Forward Overlap | Lateral Overlap | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scene | Our | BD | LT | Scene | Our | BD | LT |
| a1 | 884 (913) | 83 (1908) | 0 (345) | a2 | 374 (470) | 1 (4437) | 0 (191) |
| b1 | 309 (316) | 25 (1380) | 0 (133) | b2 | 131 (168) | 0 (1039) | 0 (75) |
| c1 | 530 (542) | 91 (1268) | 7 (168) | c2 | 203 (265) | 2 (1087) | 0 (59) |
| Total | 1723 (1771) | 198 (4556) | 7 (646) | Total | 708 (903) | 3 (6563) | 0 (325) |
| Forward Overlap | Lateral Overlap | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scene | Correct | Sum | Accuracy | Scene | Correct | Sum | Accuracy |
| a1 | 884 | 913 | 96.82% | a2 | 374 | 470 | 79.57% |
| b1 | 309 | 316 | 97.78% | b2 | 131 | 168 | 77.98% |
| c1 | 530 | 542 | 97.79% | c2 | 203 | 265 | 76.60% |
| Total | 1723 | 1771 | 97.29% | Total | 708 | 903 | 78.41% |
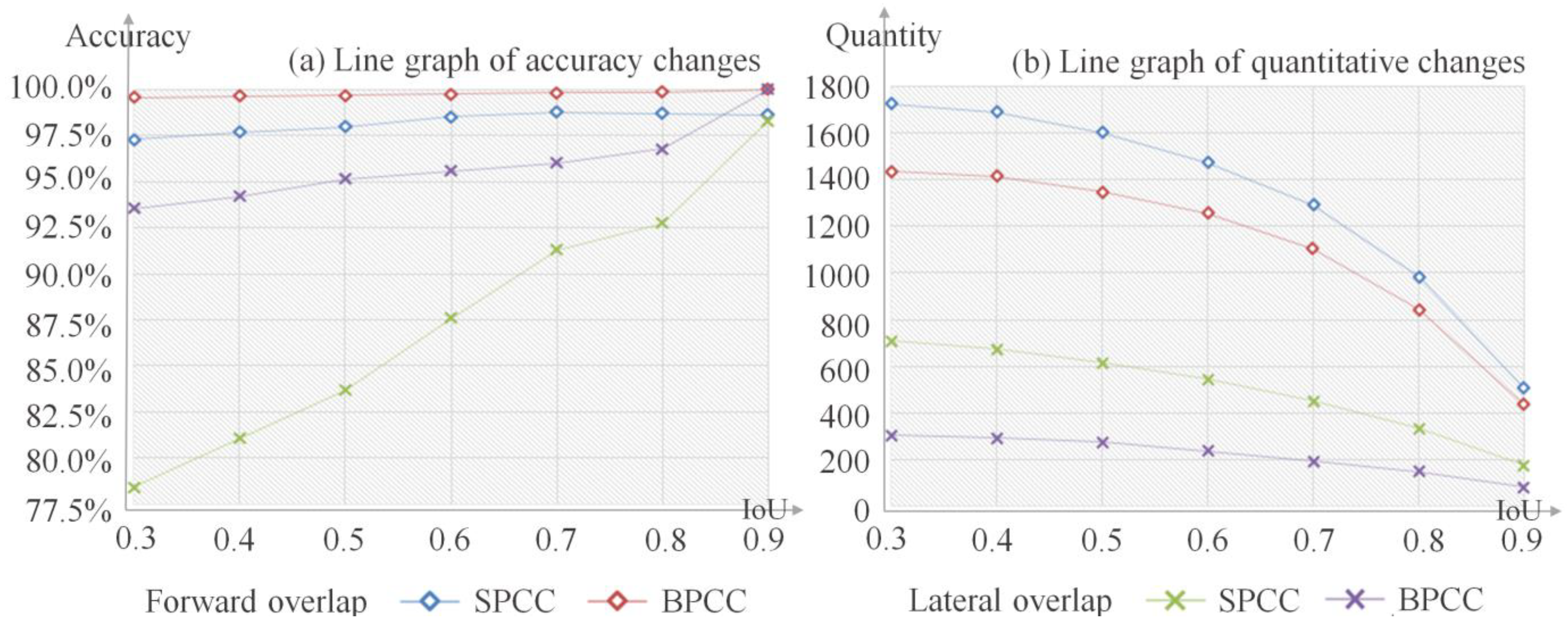
| IoU | Forward Overlap | Lateral Overlap | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPCC | BPCC | SPCC | BPCC | |||||||||
| Correct Sum Accuracy | Correct Sum Accuracy | Correct Sum Accuracy | Correct Sum Accuracy | |||||||||
| 0.3 | 1723 | 1771 | 97.29% | 1435 | 1441 | 99.58% | 708 | 903 | 78.41% | 305 | 326 | 93.56% |
| 0.4 | 1688 | 1728 | 97.69% | 1414 | 1419 | 99.65% | 672 | 829 | 81.06% | 293 | 311 | 94.21% |
| 0.5 | 1600 | 1633 | 97.98% | 1347 | 1351 | 99.70% | 614 | 734 | 83.65% | 274 | 288 | 95.14% |
| 0.6 | 1473 | 1495 | 98.53% | 1256 | 1259 | 99.76% | 543 | 620 | 87.58% | 237 | 248 | 95.56% |
| 0.7 | 1289 | 1305 | 98.77% | 1103 | 1105 | 99.82% | 450 | 493 | 91.28% | 193 | 201 | 96.02% |
| 0.8 | 983 | 996 | 98.69% | 843 | 844 | 99.88% | 332 | 358 | 92.74% | 150 | 155 | 96.77% |
| 0.9 | 506 | 513 | 98.64% | 437 | 437 | 100.00% | 175 | 178 | 98.31% | 81 | 81 | 100.00% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Gao, J.; Yu, K.; Zhang, S. The Plumb-Line Matching Algorithm for UAV Oblique Photographic Photos. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5290. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15225290
Zhang X, Sun J, Gao J, Yu K, Zhang S. The Plumb-Line Matching Algorithm for UAV Oblique Photographic Photos. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(22):5290. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15225290
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xinnai, Jiuyun Sun, Jingxiang Gao, Kaijie Yu, and Sheng Zhang. 2023. "The Plumb-Line Matching Algorithm for UAV Oblique Photographic Photos" Remote Sensing 15, no. 22: 5290. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15225290
APA StyleZhang, X., Sun, J., Gao, J., Yu, K., & Zhang, S. (2023). The Plumb-Line Matching Algorithm for UAV Oblique Photographic Photos. Remote Sensing, 15(22), 5290. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15225290







