Advancing Precise Orbit Determination and Precise Point Positioning of BDS-3 Satellites from B1IB3I to B1CB2a: Comparison and Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
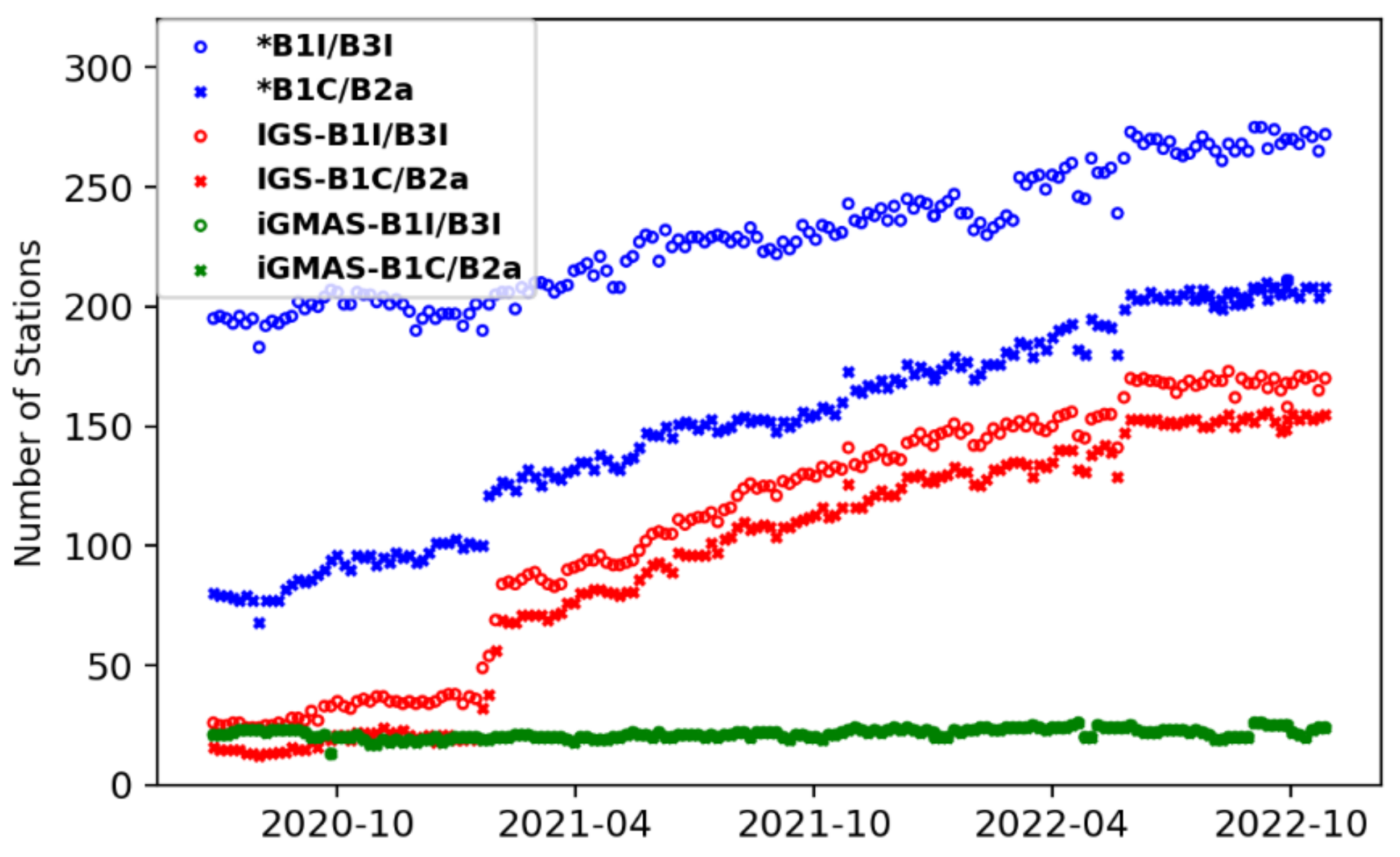
2. Data Collection and Availability
3. POD and PPP Strategies
3.1. POD Strategies
3.2. PPP Strategies
4. Analysis and Comparison of Results
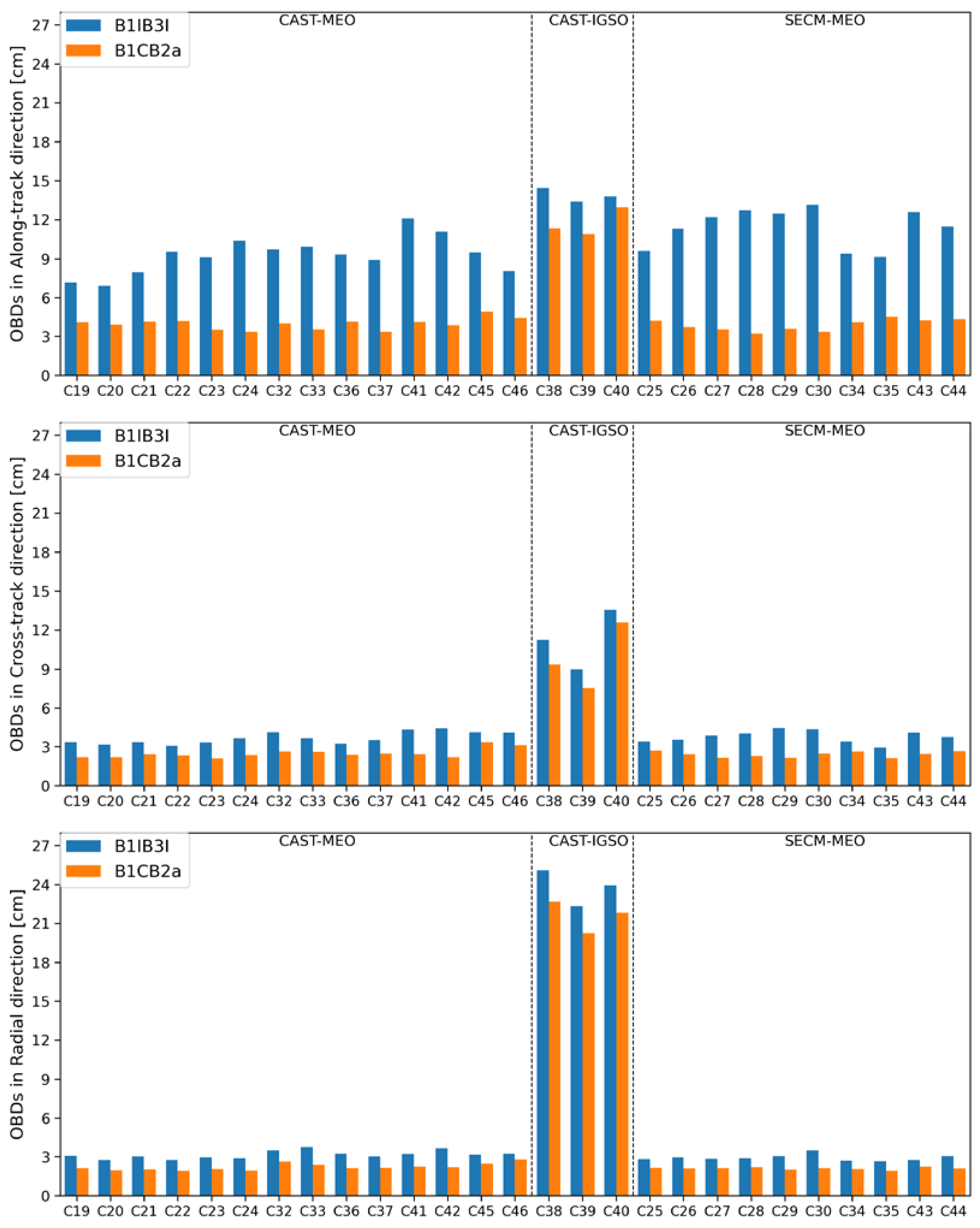
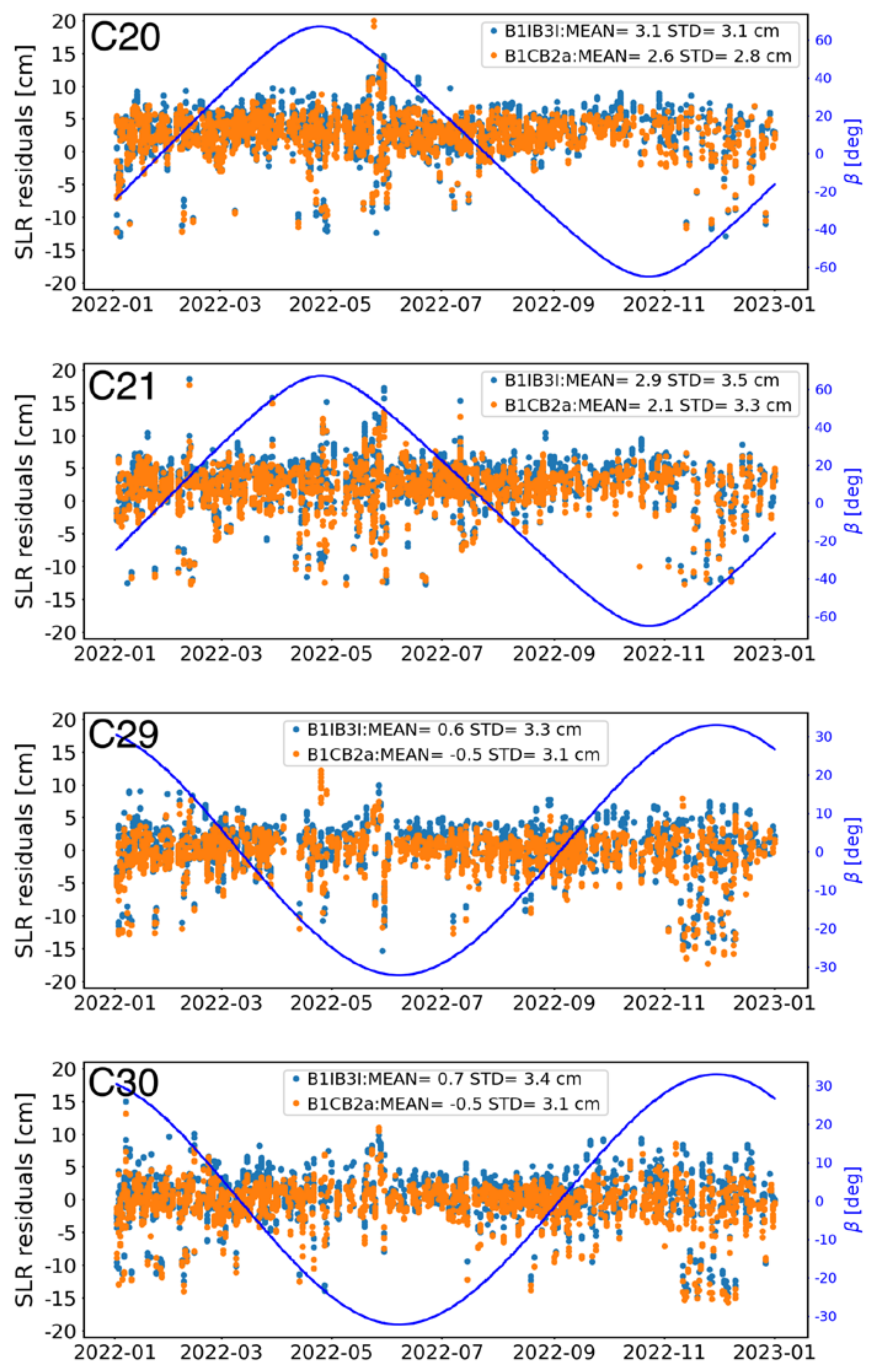
4.1. Orbit Performance
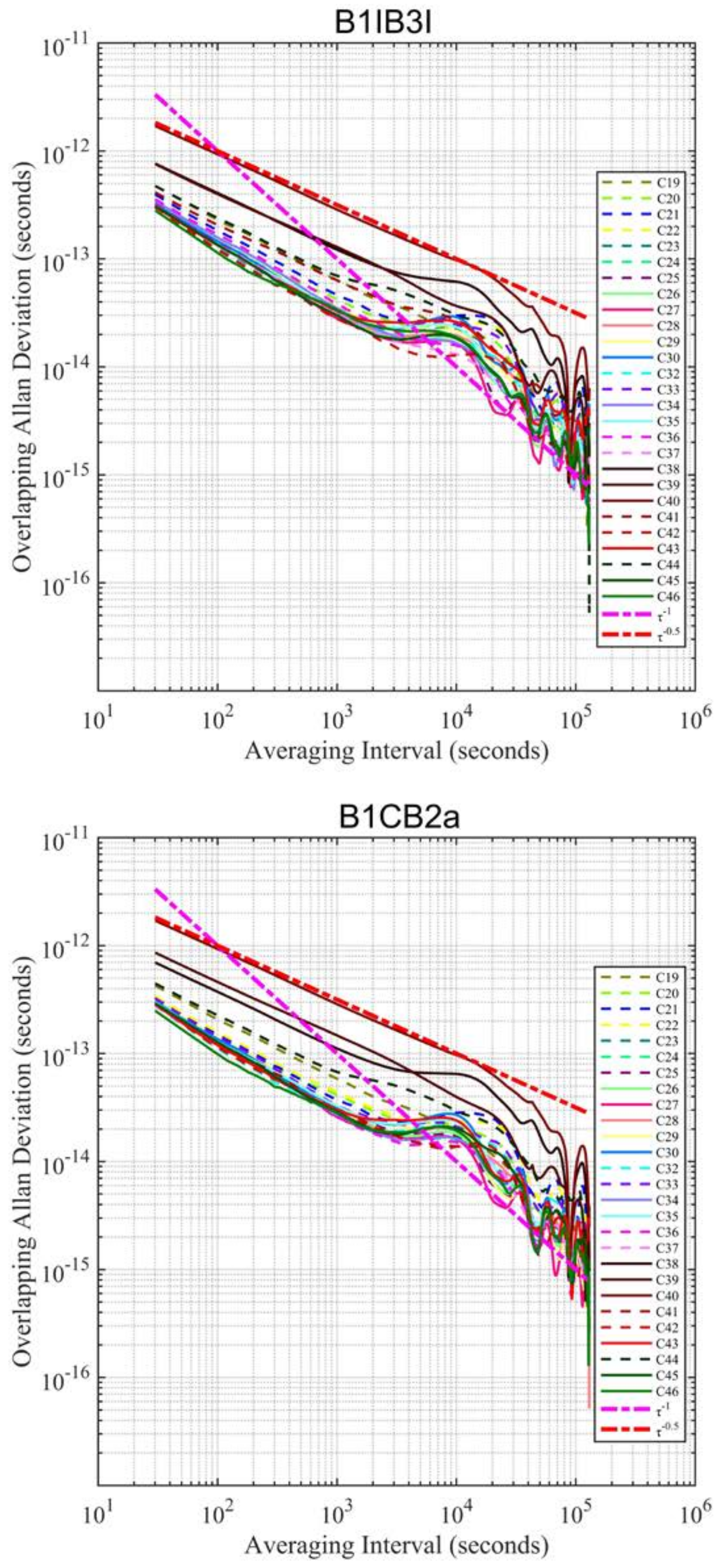
4.2. Clock Performance
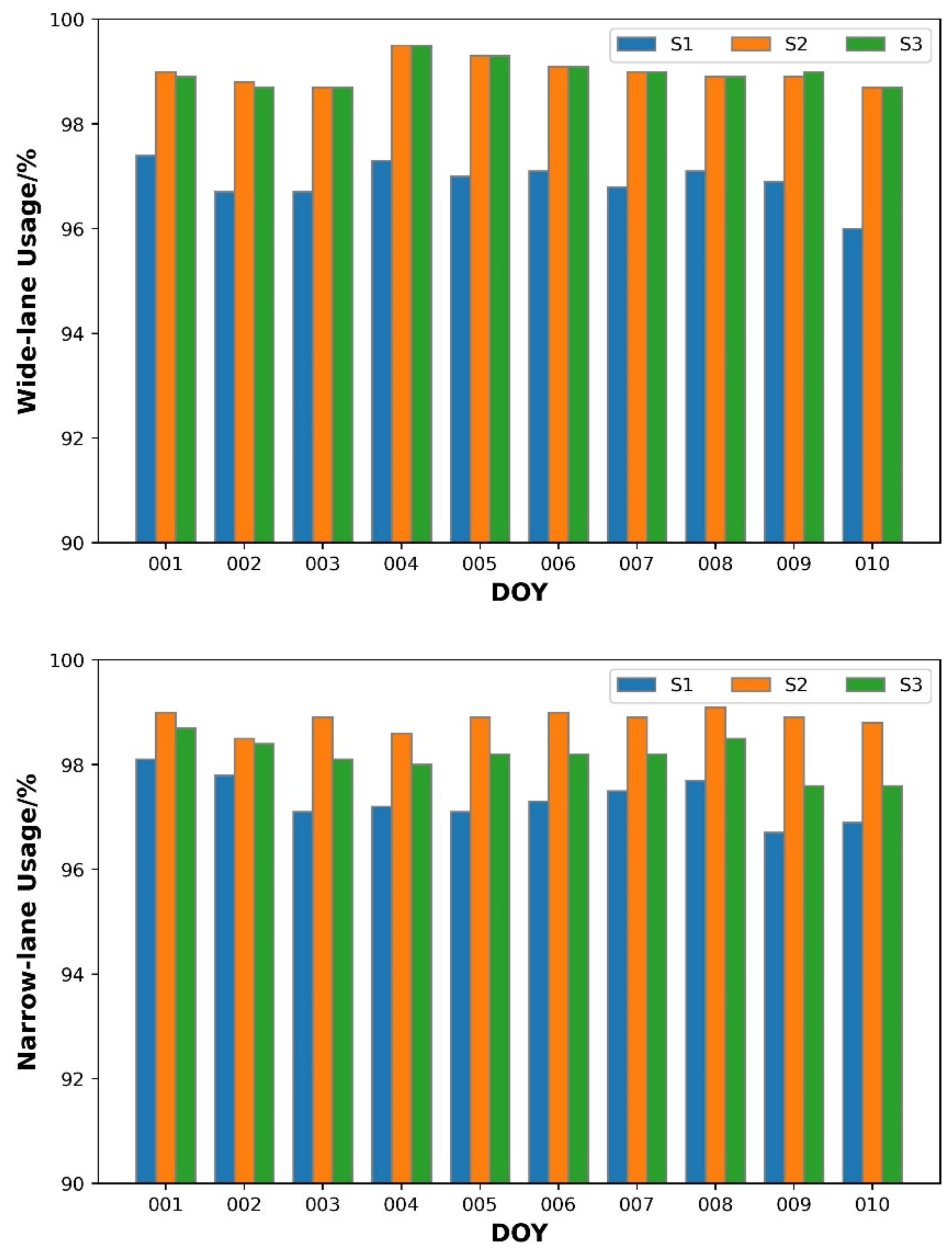
4.3. FCB Performance
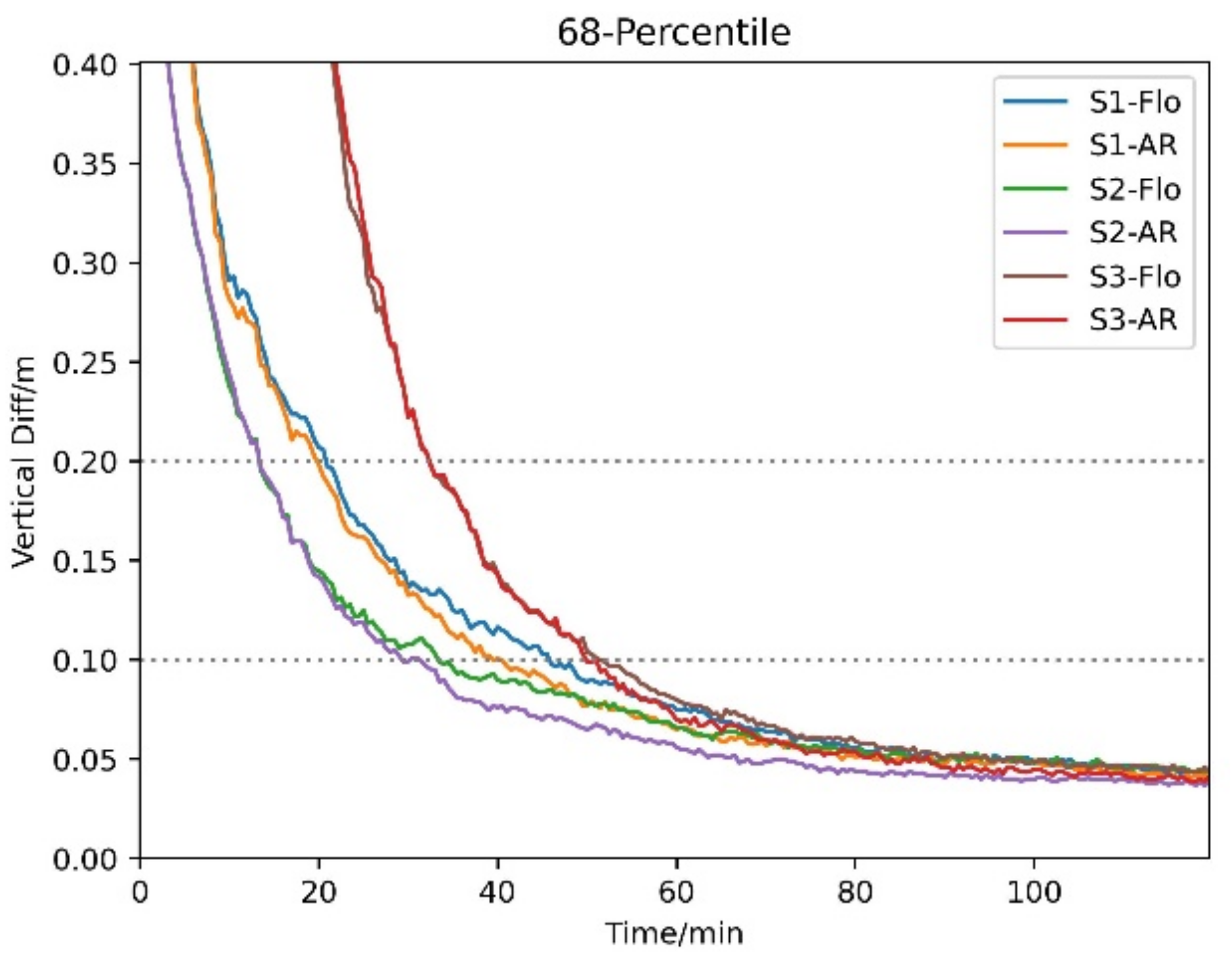
4.4. PPP Performance
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- Regarding orbit quality, when compared with the orbits determined using B1IB3I observations, clear improvement in quality is achieved with the B1CB2a solution. The orbit consistency indicated by OBDs is improved by around 25% on average.
- The SLR validations of the four BDS-3 MEOs indicate that the B1CB2a-based solution demonstrates a shift in the mean SLR residuals of around 1 cm, in addition to a slightly improved accuracy compared to that of the B1IB3I, by about 0.3 cm.
- The B1CB2a solution obtains slightly smaller ADEVs in comparison with the B1IB3I solution, by 6~12%.
- Regarding the PPP-AR performance, the advantage of the B1CB2a-based solution can be also observed with respect to the estimates of wide-lane/narrow-lane FCBs, convergence time, and positioning accuracy.
- A significant reduction beyond 10 min in PPP convergence time was noted when the new BDS-3 signals were used. However, the worst PPP performance in convergence time and positioning accuracy was achieved if the observations and orbit/clock products were used inconsistently.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Mao, Y.; Sun, B. Basic performance and future developments of BeiDou global navigation satellite system. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Hauschild, A. Comparing the ‘Big 4’—A User’s View on GNSS Performance. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Portland, OR, USA, 20–23 April 2020; pp. 407–418. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, M.; Li, W.; Yao, Z.; Cui, X. Overview of BDS III new signals. Navigation 2019, 66, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Mu, R.; Jiang, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chang, C.; Zhao, Q. Precise orbit determination for the Haiyang-2D satellite using new onboard BDS-3 B1C/B2a signal measurements. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zha, J. Stochastic modeling of BDS2/3 observations with application to RTD/RTK positioning. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2019, 30, 095002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.P.; Hu, X.G.; Tang, C.P.; Zhou, S.S.; Yang, Y.F.; Pan, J.Y.; Ren, H.; Ma, Y.X.; Tian, Q.N.; Wu, B.; et al. SIS accuracy and service performance of the BDS-3 basic system. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2020, 63, 269511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, M.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Yu, S.; Lu, C.; Wickert, J. Initial assessment of the COMPASS/BeiDou-3: New-generation navigation signals. J. Geod. 2017, 91, 1225–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Li, P.; Wang, W.; He, C.; Cai, C.; Pan, Z. Elevation-dependent pseudorange variation characteristics analysis for the new-generation BeiDou satellite navigation system. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Lyu, Y.; Xu, X.; Yang, C.; Li, J. Precise orbit determination for BDS satellites. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Q. Characteristics of BD3 global service satellites: POD, open service signal and atomic clock performance. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Ai, Q.; Yuan, Y. Analysis of Precise Orbit Determination of BDS-3 MEO and IGSO Satellites Based on Several Dual-Frequency Measurement Combinations. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.; Sheng, C.; EI-Mowafy, A.; Zhang, B. Characteristics of receiver-related biases between BDS-3 and BDS-2 for five frequencies including inter–system biases, differential code biases, and differential phase biases. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, N.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ma, H. Precise orbit determination of BDS-3 satellites using B1C and B2a dual-frequency measurements. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; He, X.; Huang, Y. Enhanced precise orbit determination of bds-3 meo satellites based on ambiguity resolution with b1c/b2a dual-frequency combination. Measurement 2022, 205, 112197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Ding, Q.; Li, J.; Lu, X.; Feng, L.; Ma, J.; Chen, G. Monitoring and assessment of GNSS open services. J. Navig. 2011, 64, S19–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, Z. Validation and evaluation on B1IB3I-based and B1CB2a-based BDS-3 precise orbits from iGMAS. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 70, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zeng, P.; Wen, Y.; He, L.; He, X. Comprehensive Assessment of BDS-2 and BDS-3 Precise Orbits Based on B1I/B3I and B1C/B2a Frequencies from iGMAS. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kubo, N.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, H. Initial Positioning Assessment of BDS New Satellites and New Signals. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Yang, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Shu, W.; Qu, P. Performance evaluation of precise point positioning for BeiDou-3 B1c/B2a signals in the global range. Sensors 2021, 21, 5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Yuan, Y.; Freeshah, M.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, F. BDS multi-frequency PPP ambiguity resolution with new B2a/B2b/B2a+b signals and legacy B1I/B3I signals. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tu, R.; Wu, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R. Initial accuracy and reliability of current BDS-3 precise positioning, velocity estimation, and time transfer (PVT). Adv. Space Res. 2019, 65, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Bisnath, S.; Pan, L. Precise Point Positioning with BDS-2 and BDS-3 constellations: Ambiguity resolution and positioning comparison. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 70, 1830–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Hu, C.; Yu, Z.; Wu, W. Modeling and assessment of five-frequency BDS precise point positioning. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Cao, X.; Wang, J.; Ge, Y.; Shen, F. The benefit of B1C/B2a signals for BDS-3 wide-area decimeter-level and centimeter-level point positioning with observable-specific signal bias. Measurement 2023, 214, 112815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Prange, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Perosanz, F.; Romero, I.; Noll, C.; Stürze, A.; Weber, G.; et al. The Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) of the International GNSS Service (IGS): Achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 59,1671–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Qi, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zou, X.; Tang, W.; Guo, C. A comparative analysis of navigation signals in BDS-2 and BDS-3 using zero-baseline experiments. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prange, L.; Villiger, A.; Sidorov, D.; Schaer, S.; Beutler, G.; Dach, R.; Jäggi, A. Overview of CODE’s MGEX solutionwith the focus on Galileo. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 66, 2786–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J. Precise orbit determination for quad-constellation satellites at Wuhan University: Strategy, result validation, and comparison. J. Geod. 2015, 90, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigenberger, P.; Deng, Z.; Guo, J.; Prange, L.; Song, S.; Montenbruck, O. BeiDou-3 orbit and clock quality of the IGS Multi-GNSS Pilot Project. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 71, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, G.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Q. BDS-3 precise orbit and clock solution at Wuhan University: Status and improvement. J. Geod. 2023, 97, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Tu, R.; Zhang, P.; Fan, L.; Han, J.; Wang, S.; Hong, J.; Lu, X. Optimization of Ground Tracking Stations for BDS-3 Satellite Orbit Determination. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 4069–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ge, M. PANDA software and its preliminary result of positioning and orbit determination. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 2003, 8, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Hugentobler, U.; Selmke, I.; Marz, S.; Killian, M.; Rott, M. BeiDou satellite radiation force models for precise orbit determination and geodetic applications. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 58, 2823–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Solano, C.J. Impact of the albedo modeling on GPS orbits. Master’s Thesis, Technische Universität München (TUM), München, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- CSNO. Available online: http://www.beidou.gov.cn/yw/gfgg/201912/t20191209_19613.html (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Boehm, J.; Niell, A.; Tregoning, P.; Schuh, H. Global mapping function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Guo, J.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J. Yaw attitude modeling for BeiDou I06 and BeiDou-3 satellites. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilssner, F.; Laufer, G.; Springer, T.; Schonemann, E.; Enderle, W. The BeiDou attitude model for continuous yawing MEO and IGSO spacecraft. EGU. 2018. Available online: http://navigation-office.esa.int/attachments/32834482/1/EGU2018_Dilssner_Final.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Petit, G.; Luzum, B. IERS Conventions 2010, Technical Report; IERS Convention Center: Frankfurt, Germany, 2010; Available online: https://iers-conventions.obspm.fr/content/tn36.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Steigenberger, P.; Thoelert, S. Initial BDS-3 transmit power analysis (with BDS-2 gain pattern). 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, M.; Gendt, G.; Dick, G.; Zhang, F.P. Improving carrier-phase ambiguity resolution in global GPS network solutions. J. Geod. 2005, 79, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Gendt, G.; Rothacher, M.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Resolution of GPS carrier-phase ambiguities in Precise Point Positioning (PPP) with daily observations. J. Geod. 2008, 82, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. A new method for fast carrier phase ambiguity estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Position, Location and Navigation Symposium, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 11–15 April 1994; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 562–573. [Google Scholar]



| Models | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Observations | Ionosphere-free observations of B1IB3I and B1CB2a |
| Time period | DOY 1 to 365 in 2022 |
| Arc length and interval | 24 h and 30 s |
| Elevation angle cutoff | 10 degrees |
| Observation weight | Elevation > 30°: 1; Elevation ≤ 30°: 2 × sin(e) |
| BDS-3 PCO values | Values from CSNO [35] |
| Tropospheric delay | Saastamoinen model for a priori dry and wet zenith delay model with estimation of wet delay global mapping function for dry and wet zenith delays [36] |
| Gravity model | EGM2008 with 12 degrees and orders |
| Third body effect | Applied |
| Satellite attitude model | Continuous yaw steering models [37,38] |
| Solar radiation pressure | 5-parameter ECOM with a priori box-wing model [33] |
| Relativistic effects | IERS conventions 2010 [39] |
| Solid earth pole tides | IERS conventions 2010 [39] |
| Ocean tides | None |
| Earth radiation model | Applied [34] |
| Antenna thrust | Applied [40] |
| Ambiguity fixing | Fixed to integer [41] |
| Inter system bias (ISB) | Estimated as arc-dependent constant for each receiver |
| Parameters estimated | Orbit dynamic parameters, initial satellite positions and velocities, ISB, ambiguity, etc. |
| Observations for POD | Observations for PPP | |
|---|---|---|
| Scheme 1 | B1IB3I | B1IB3I |
| Scheme 2 | B1CB2a | B1CB2a |
| Scheme 3 | B1IB3I | B1CB2a |
| Solution | Along-Track | Cross-Track | Radial | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAST-MEO | CAST-IGSO | SECM-MEO | CAST-MEO | CAST-IGSO | SECM-MEO | CAST-MEO | CAST-IGSO | SECM-MEO | |
| B1IB3I | 9.2 | 13.9 | 11.4 | 3.7 | 11.2 | 3.8 | 3.2 | 23.1 | 2.9 |
| B1CB2a | 4.0 | 11.7 | 3.9 | 2.5 | 9.8 | 2.4 | 2.2 | 20.6 | 2.1 |
| PRN | Primary Clock Type | 1000 s (× 10−14) | 10,000 s (× 10−14) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1I/B3I | B1c/B2a | B1I/B3I | B1c/B2a | |||
| MEO-CAST | C19 | Rb | 6.06 | 5.66 | 2.20 | 1.93 |
| C20 | Rb | 4.23 | 4.10 | 2.20 | 2.13 | |
| C21 | Rb | 4.35 | 3.45 | 2.98 | 2.84 | |
| C22 | Rb | 3.54 | 4.32 | 2.40 | 2.33 | |
| C23 | Rb | 3.41 | 3.12 | 2.18 | 1.71 | |
| C24 | Rb | 3.21 | 2.71 | 1.86 | 1.58 | |
| C32 | Rb | 2.92 | 2.84 | 1.93 | 2.03 | |
| C33 | Rb | 3.05 | 3.04 | 2.55 | 2.11 | |
| C36 | Rb | 3.60 | 2.56 | 1.53 | 1.45 | |
| C37 | Rb | 2.96 | 2.99 | 1.30 | 1.39 | |
| C41 | Rb | 6.39 | 2.83 | 2.65 | 1.36 | |
| C42 | Rb | 2.71 | 3.06 | 1.28 | 1.38 | |
| C45 | PHM | 2.70 | 2.59 | 1.84 | 2.01 | |
| C46 | PHM | 3.59 | 2.85 | 1.92 | 1.92 | |
| MEO-SECM | C25 | PHM | 3.18 | 2.89 | 1.95 | 1.67 |
| C26 | PHM | 3.12 | 3.06 | 1.81 | 1.83 | |
| C27 | PHM | 2.65 | 2.43 | 1.66 | 1.61 | |
| C28 | PHM | 2.86 | 2.58 | 1.88 | 1.87 | |
| C29 | PHM | 3.26 | 3.12 | 2.14 | 2.01 | |
| C30 | PHM | 3.23 | 2.99 | 2.89 | 2.70 | |
| C34 | PHM | 3.33 | 2.56 | 1.73 | 1.63 | |
| C35 | PHM | 3.27 | 3.15 | 2.37 | 2.33 | |
| C43 | PHM | 3.24 | 2.92 | 2.60 | 2.40 | |
| C44 | PHM | 7.47 | 6.76 | 3.04 | 2.93 | |
| IGSO-CAST | C38 | PHM | 11.80 | 10.80 | 6.16 | 6.19 |
| C39 | PHM | 13.10 | 12.00 | 3.68 | 3.58 | |
| C40 | PHM | 28.90 | 28.90 | 9.80 | 9.77 | |
| PPP Result | East (min) | North (min) | Up (min) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | float | 37.5 | 15.5 | 46.0 |
| AR | 36.5 | 15.0 | 41.0 | |
| S2 | float | 25.0 | 9.5 | 33.5 |
| AR | 24.0 | 9.5 | 30.5 | |
| S3 | float | 45.0 | 33.0 | 52.0 |
| AR | 45.0 | 32.5 | 50.0 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Luo, T.; Chen, S.; Li, P. Advancing Precise Orbit Determination and Precise Point Positioning of BDS-3 Satellites from B1IB3I to B1CB2a: Comparison and Analysis. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4926. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15204926
Wang C, Luo T, Chen S, Li P. Advancing Precise Orbit Determination and Precise Point Positioning of BDS-3 Satellites from B1IB3I to B1CB2a: Comparison and Analysis. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(20):4926. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15204926
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chen, Tengjie Luo, Shitong Chen, and Pan Li. 2023. "Advancing Precise Orbit Determination and Precise Point Positioning of BDS-3 Satellites from B1IB3I to B1CB2a: Comparison and Analysis" Remote Sensing 15, no. 20: 4926. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15204926
APA StyleWang, C., Luo, T., Chen, S., & Li, P. (2023). Advancing Precise Orbit Determination and Precise Point Positioning of BDS-3 Satellites from B1IB3I to B1CB2a: Comparison and Analysis. Remote Sensing, 15(20), 4926. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15204926






