Abstract
Ecological environment quality and resilience assessment is an important prerequisite for ensuring the coordination and stability of socio-economic development and eco-environment protection. Remote sensing technology has provided new approaches for quantitatively evaluating regional ecological environment quality and resilience rapidly, accurately, and objectively. Taking the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Economic Belt (YREBML) as an example, to assess ecological environment quality, this study calculated the remote sensing ecological index (RSEI) based on the Google Earth Engine using Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) data with a spatial resolution of 500 m during 2000–2020. An evaluation index to assess ecological resilience and its spatial pattern based on the RSEI of 2000–2020 was then constructed. The evaluation index was constructed from two dimensions, including the sensitivity and adaptability of the RSEI. Finally, this study identified key factors that affect ecological residence based on a structural equation model. The results showed that the overall RSEI was at moderate and good levels in the YREBML during 2000–2020, accounting for more than 85% of the total area. Its spatial characteristics showed that the RSEI was higher in the middle reaches than in the lower reaches of the YREB, and higher in the south than in the north. The overall RSEI in the YREBML showed a decreasing trend during 2000–2020, with 54.36% of the region improving and 45.64% declining. Areas with declining RSEI were concentrated in Anhui, while the increasing RSEI was observed in Zhejiang. In addition, the spatial pattern of ecological resilience was characterized by high resilience in the north and east, and low resilience in the south and west. High resilience areas accounted for 40.48% of the YREBML, mainly contributed by Jiangxi and Hunan provinces. The driving factors analysis results indicated that economic development, natural disaster risk, and environmental pollution would further affect ecological resilience of urban systems. This study provides more scientific and effective data support for ecological environment monitoring and governance.
1. Introduction
The ecological environment is a complex system composed of economic, natural, and social factors, and is closely related to the human living environment and social sustainable development. The obvious acceleration of industrialization and urbanization, population agglomeration, and urban expansion have intensified the disturbance and destruction of the ecological environment [1,2,3]. Environmental pollution, resource shortages, ecosystem degradation, and other ecological environmental problems have become an important bottleneck limiting social and economic development [4,5,6]. In addition, frequent extreme weather events affected by climate change, such as droughts, floods, heavy rains, and tropical typhoons, threaten the sustainable development of the ecological environment [7]. Ecological environment quality reflects the degree of good or bad ecological environment, which directly affects the human living environment and socio-economic development [8]. Therefore, it is important to establish a scientific evaluation system and quantitative model of ecological environment quality for objectively understanding and evaluating the ecological quality status and changes in the region, which has important guiding significance to achieve regional socio-economic green development.
Ecological environment quality assessment is an important tool to analyze the spatial and temporal changes of the eco-environment based on a specific evaluation criterion, reflecting the eco-environmental status and its suitability for economic and social development. Some research has used various indicators to evaluate the eco-environment, including the air quality index [9], water quality index [10], and vegetation cover [11]. Recently, some studies have combined various factors into one indicator to comprehensively assess the eco-environment instead of considering a single environmental indicator [12,13]. Therefore, eco-environment quality assessment has mostly used the pressure–state–response (PSR) model to construct an indicator system and applied hierarchical analysis, comprehensive index evaluation, the fuzzy judgment method, and cluster analysis [14,15,16] to quantify the ecological environment quality status. However, these methods are easily affected by human subjective factors and are limited by small-scale socioeconomic statistics. With the development of remote sensing technology, multi-source remote sensing data are widely applied in ecological environment research, providing information on land cover types, vegetation cover, surface temperature, and the water body index [17,18]. Remote sensing-derived environmental factors such as surface temperature, the NDVI, humidity, and land cover can reflect changes in the ecological environment and the impact of climate change on the environment [19]. Satellite remote sensing has provided global higher spatial and temporal resolution products, which are widely used for water resources management and ecological environment monitoring [20,21]. Xu et al. used the indicators of greenness, heat, humidity, and dryness extracted from Landsat satellite data to construct the remote sensing ecological index (RSEI) for ecological environment quality assessment, which is widely used in the evaluation of ecological quality on a small scale, such as municipalities and counties [22,23]. However, the temporal resolution of Landsat data is low, and it is difficult to obtain high-quality images of the same period in the region due to weather and terrain conditions. Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) data have high spatial resolution, complete time series, and a large spatial span. The use of MODIS data to construct the RSEI model is significant for achieving a comprehensive evaluation of ecological environment quality on a large scale.
Facing multiple crises and challenges caused by global changes and intensified human activities, how to cope with various risks and maintain ecological resilience has become one of the most important issues for regional sustainable development. The concept of ecological resilience was originally introduced by Holling (1973) as a concept for understanding the ability of an ecosystem with alternative attractors to persist within a state when subjected to disturbances [24,25,26,27,28]. Ecological resilience is mainly influenced by factors such as environmental change, social progress, economic growth, or political change, and is widely used in various ecological and socio-economic research. Resilience research mainly focuses on natural ecosystems and socio-economic–ecological complex systems. Some studies have constructed resilience assessment models and resilience evaluation indicator systems to assess ecological resilience or analyzed the relationship between ecological resilience and urbanization [29,30,31,32]. Among which, building a comprehensive evaluation index with indicators representing the resilience of system elements or resilience process and further assigning weights for each indicator is most widely used [31]. For example, Zhang et al. used a multi-criteria comprehensive evaluation system with a GIS-based method to assess wetland restoration potential [33]. The weights of the evaluation index can be identified by hierarchical analysis, the entropy weighting method, and factor analysis. However, resilience is a process concept that encompasses two processes, namely resistance and recovery [34], though few studies have conducted ecological resilience assessment studies based on the concept of resilience. The RSEI reflects the level of ecological ecosystem quality, while resilience further reflects the degree of disturbance withstanding environmental, political, economic, and social shocks and stresses. Therefore, taking the RSEI as the ecological resilience surrogate, this study quantitatively analyzed the spatial pattern of regional ecological resilience based on the above concept of resilience and identified high or low-resilience areas of cities, which can provide data support for targeted adaptive management.
The middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Economic Belt (YREBML) is a typical region with rapid economic development while facing multiple environmental problems. Therefore, taking the YREBML as the research object, this study aimed to comprehensively detect the spatiotemporal changes of the RSEI from 2000 to 2020 and further analyze the spatial pattern of ecological resilience. Firstly, this study employed four ecological environment indicators, including the NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), SWCI (Surface Water Content Index), NDSIM (MODIS Normalized Difference Built-up and Soil Index), and LST (Land Surface Temperature Index), to construct the RSEI model based on MODIS data from 2000 to 2020. This study then assessed spatiotemporal changes of the RSEI. Further, based on the concept of resilience, this study analyzed the spatial pattern of ecological resilience of urban systems in the YREBML. Finally, the key driving factors that affect ecological resilience were identified based on a structural equation model (SEM). This study aims to provide a new method to achieve a comprehensive evaluation of ecological environment quality and ecological resilience on a regional scale, which can support monitoring, restoration, and adaptation studies of fragile ecosystems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
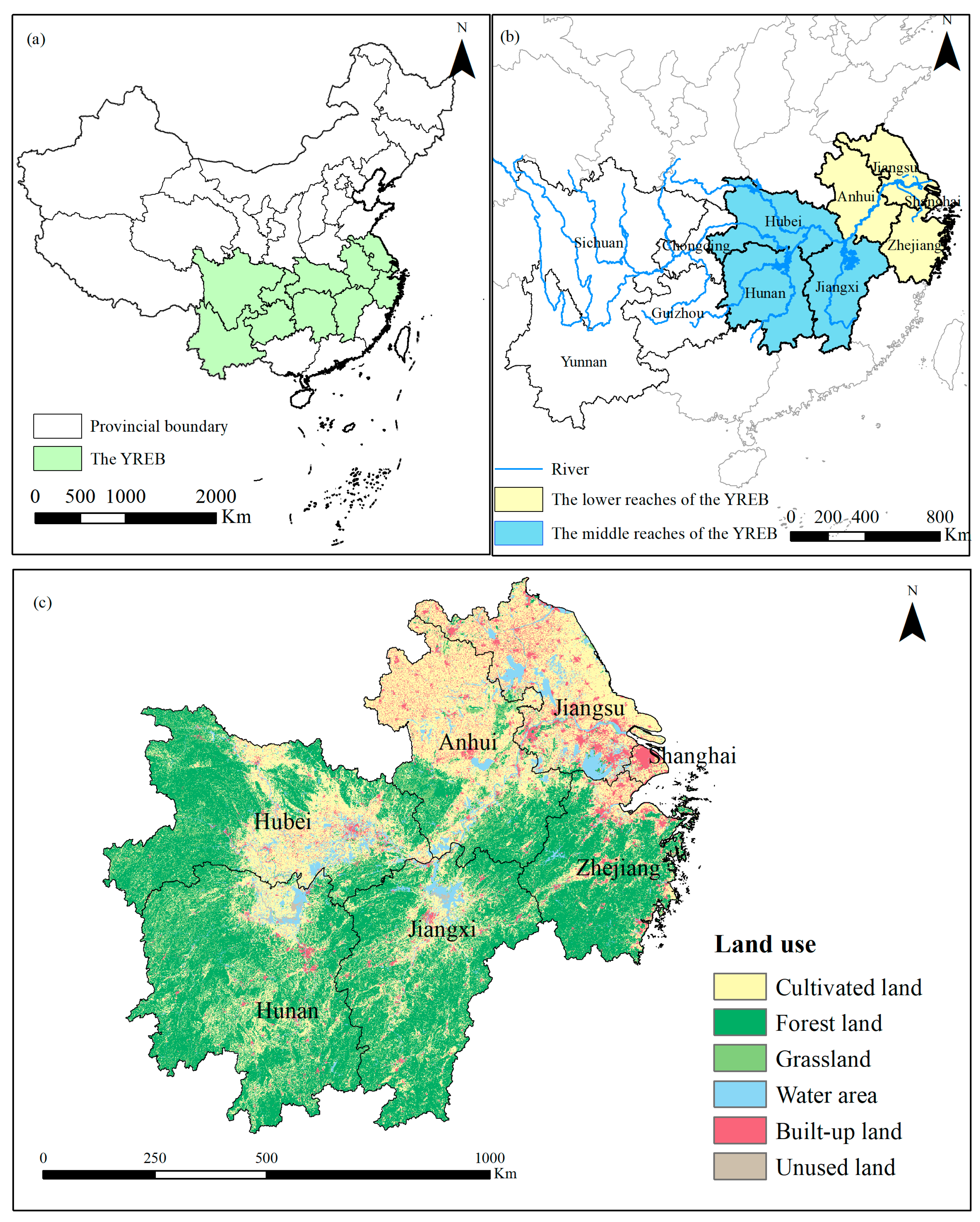
The YREB plays an important supporting role in the strategy for large-scale development of western China, strategy for the rise of central China, and strategy for the trailblazing development of eastern China, and is an important link in the coordinated development of the regional economy. The YREBML is an important economic development area and agricultural production area in China. The YREBML covers seven provinces and municipalities, including Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui, Jiangxi, Hubei, and Hunan, with an area of 0.92 million km2, accounting for 9.41% of China’s total area (Figure 1). Its GDP accounted for 35.08% of China’s total in 2020. However, the increasing intensity of regional development such as urbanization, industrialization, and rapid land use changes, as well as unreasonable human activities, threatens the sustainable development of the ecological environment in the YREBML. In addition, the multiple effects of natural disasters, climate change, and uncoordinated land development have a negative effect on the green development of natural resources and the ecological environment in this region. The sloppy and wasteful use of resources, increasingly serious environmental pollution, and degradation of the ecosystem have become major bottlenecks that limit high-quality economic development. Hence, assessing spatial and temporal changes of ecological environment quality and ecological resilience has a significant importance for sustainable development in the YREBML.
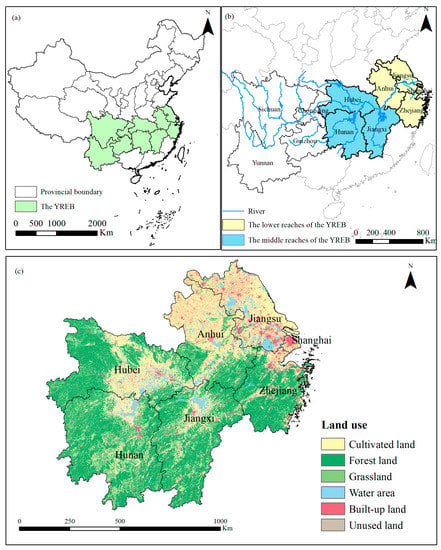
Figure 1.
Geographic location and land use pattern of the YREBML ((a) The location of the YREBML in China; (b) The provincial administrative division of the YREBML; (c) Land user pattern of YREBML). Note: Datum: D_WGS_1984; Projection: WGS_1984_UTM_Zone_50N; Representation scale: 1: 17,000,000; Nominal scale: 1:250.
2.2. Data Source
The MODIS data provide an effective data support to regularly observe and monitor the ecological environment on a large scale. Therefore, in order to distinguish vegetation from non-vegetation, the products of MOD091A and MOD11A2 covering the YREBML from May to October of 2000–2020 were obtained to calculate the RSEI. The remote sensing data were obtained from the MODIS data product website (https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 9 November 2022)). The products of MOD09A1 and MOD11A2 were pre-treated with radiation calibration and atmospheric calibration for reliable accuracy and quality. The MOD09A1 product consists of seven wavelength bands (620 to 2155 nm) from visible to short-wave infrared, with a spatial resolution of 500 m and a temporal resolution of 8 day. The MOD11A2 product is a 1 km resolution surface temperature product that includes both daytime and nighttime surface temperatures and has a temporal resolution of 8 day. In terms of data processing, this study processed MODIS images based on the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform for removing clouds and anomalous values, and took the average value to obtain image data for each year in the YREBML. The study further obtained the NDVI, SWCI, NDSIM, and LST, based on which the RSEI was calculated by principal component analysis. In addition, this study used SEM to identify the driving factors of ecological resilience on a city scale based on natural environment and socioeconomic data in 2020. The natural environment data mainly included precipitation, the DEM, land use data, and the NDVI. The daily precipitation was collected from the National Meteorological Information Center (http://data.cma.cn (accessed on 9 November 2022)). Land use data and digital elevation model (DEM) data were derived from the Chinese Academy of Sciences Resource and Environment Data Center (http://www.resdc.cn/ (accessed on 9 November 2022)). The NDVI, land use, and precipitation data were at a spatial resolution of 1 km. Volumes of industrial particulate emission, sulfur dioxide emission, and nitrogen dioxide emission were used to indicated environmental pollution. The social development factors included population density, urban population, and ratio of the building area, while the economic development factors included per capita GDP, total gas supply, and liquefied petroleum gas supply. Road density, density of urban sewage pipes, technology input, and ratio of green area were obtained to represent infrastructure construction. The socioeconomic data and environmental data were collected from the China City Statistical Yearbook.
2.3. Methodology
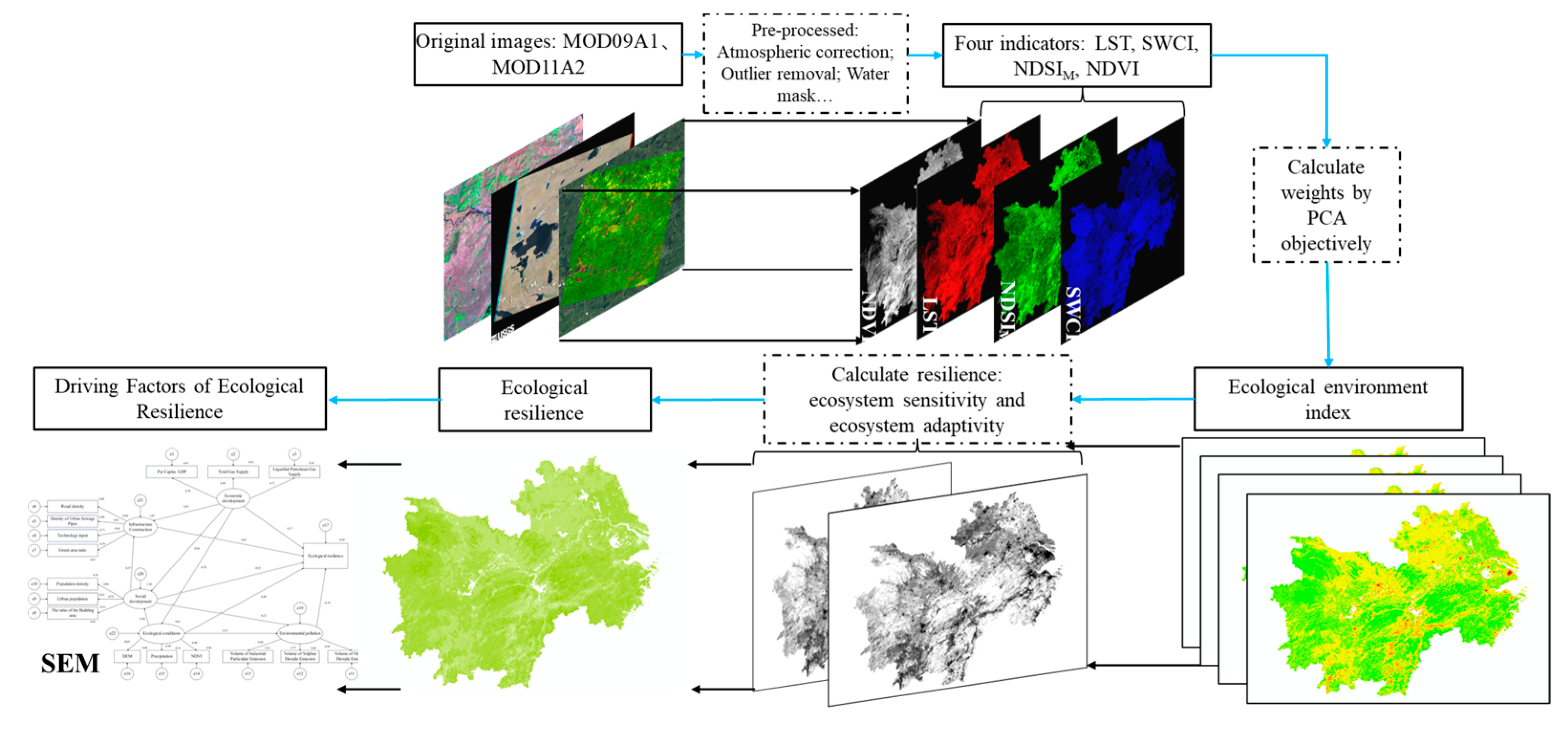
The methodology framework to assess the RSEI and ecological resilience in the YREBML is shown in Figure 2. First, four indicators, including the NDVI, SWCI, NDSIM, and LST, were calculated based on long time series MOD09A1 and MOD11A2 products. Based on principal component analysis (PCA), this study then calculated the RSEI to quantitatively assess the characteristics of ecological environment quality changes during 2000–2020 in the YREBML. Finally, this study introduced the concept of resilience and adopted a bottom-up approach to calculate the ecological sensitivity and adaptability based on the RSEI of 2000–2020, then the ecological resilience was derived by the combination of the ecological sensitivity and adaptability. Based on SEM, this study identified the driving factors of ecological resilience and further proposed suggestions for ecological resilience improvement.
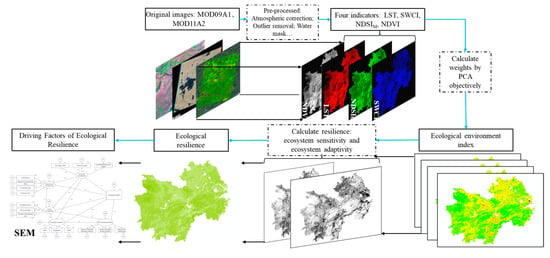
Figure 2.
The methodology framework of RSEI and ecological resilience calculation.
2.3.1. Remote Sensing Ecological Index
The RSEI was proposed to monitor and assess regional ecological changes, and combines four indicators that are strongly correlated to ecological status [22,23]. These four indicators represented greenness, wetness, dryness, and heat, and were widely used in ecological environment assessment. The RSEI can be expressed as a function of these four indicators:
The NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) is used to represent the greenness index. The biomass, leaf area index, and vegetation cover of green vegetation are further quantified by obtaining the difference between Near Infrared (NIR) and red band (R) of remote sensing data. Thus, the NDVI can be expressed by the following equations:
where represent the reflectance of Near Infrared and red band, and and are the 2nd and 1st bands of MOD09A1, respectively.
The wetness index is denoted with the SWCI. The SWCI can effectively extract the moisture content of the vegetation canopy and ground surface, and is widely used in surface drought research. The SWCI can be calculated through the following equations:
where are reflectance of the short-wave infrared, and and are the 6th and 7th bands of MOD09A1, respectively.
NDSIM represents the dryness index, compositing of the bare soil index (BSI) and the normalized difference building index (NDBI). NDSIM has a negative effect on the ecological environment, which is expressed as follows:
where and are the reflectance of the blue and green bands, respectively, and is the 3rd band of MOD09A1. The meanings of the other parameters are the same as those in the previous equations.
The heat index is denoted by LST. The LST reflects the degree of heat radiated from the ground and is a non-negligible variable in the ecological environment. The LST can be calculated via the following equation:
where is the grayscale value of the surface temperature product image of MOD11A2.
Thus, the RSEI can be expressed as a function of four indicators, including the NDVI, SWCI, NDSIM, and LST. PCA is a multivariate statistical method which is widely used to determine the weight of indicators. In addition, the number of variables is reduced by linear orthogonal transformation of multiple variables, while keeping the information of the original variables as much as possible in the PCA. PCA can effectively integrate the four components, and determine the weight of the component indicators according to the nature of the data itself and the contribution to each principal component, so as to avoid deviations caused by human subjective factors. In order to eliminate the influence of the dimension, the dispersion standardization method was used to unify the four index components between 0 and 1 before PCA in this study. Thus, the RSEI can be expressed by the following equations:
where is the first principal component of the four indicators; is the initial ecological index; and are the minimum and maximum values of the initial ecological index, respectively; and RSEI is the normalized remote sensing ecological index.
2.3.2. Ecological Resilience
The IPCC’s fifth report proposed that vulnerability is the tendency or habit of a system to be susceptible to adverse effects, including sensitivity and adaptability. Vulnerability is positively correlated with sensitivity and negatively correlated with adaptability. Thus, vulnerability is the sensitivity index minus the adaptability index. In terms of resilience, ecological resilience is the opposite of ecological vulnerability [35,36,37,38]. Therefore, based on a bottom-up approach, this study calculated ecosystem sensitivity with the degree of deviation of the RSEI from the multi-year average condition, and ecosystem adaptation with the trend of the RSEI deviation from the multi-year average condition. Finally, it assessed ecological resilience to climate change and other external disturbances at the ecosystem scale, where ecological resilience was the value of ecological adaptation minus ecological sensitivity.
- (1)
- Ecological sensitivity
Sensitivity is the degree to which a system responds to climate change or other perturbations. Therefore, the ecological sensitivity is expressed by the interannual fluctuations of the RSEI from 2000 to 2020 to reflect the dispersion of the RSEI from the mean value. The calculation equation is as follows:
where i represents the th year (n = 21); represents the RSEI value of the th year; represents the average value of the RSEI; and S represents the variability of the RSEI, namely the ecological sensitivity index, which reflects the degree of dispersion of the RSEI relative to the average value in a specific time period.
- (2)
- Ecological adaptability
Adaptability is the ability of a system to maintain and restore its structure facing climate change or other disturbances. Ecological adaptability refers to the variability trend of a system over a certain period of time, which is used to measure its deviation from homeostasis. Thus, the ecological adaptability in this study is represented by the slope of the linearly fitted trend line of the interannual variability of the RSEI from 2000 to 2020.
where x is the time series, corresponding to the years from 2000 to 2020; y is the interannual variability of the RSEI, that is, the absolute change of the RSEI per year, which is the value of the annual RSEI minus the average value of the RSEI from 2000 to 2020; A is the change trend of the RSEI variability, namely the fitness index, which is the regression slope of the datasets y and x; and B is the intercept.
Resilience is a combination of the sensitivity and adaptability of the system to external disturbances, which is negatively correlated with sensitivity and positively correlated with adaptability. Before the calculation of resilience, the results of sensitivity and adaptability should be standardized, respectively [39]. Ecological resilience can then be expressed by the following equation:
where is ecological resilience, is the standardized ecological sensitivity, and is the standardized ecological adaptability.
2.3.3. Structural Equation Model
The structural equation model (SEM) can not only simulate the intrinsic logical relationships between multiple independent variables and multiple dependent variables simultaneously, but also estimate the factor structure and inter-factor relationships simultaneously [40]. The variables in SEM can be divided into observed and latent variables, where the latent variables cannot be measured directly and need to be reflected indirectly by the observed variables. Based on the correlation between variables, variables can be classified into exogenous and endogenous variables [41]. Exogenous variables only play an explanatory role in SEM, that is, they can only affect other variables, while endogenous variables can be affected by both exogenous and endogenous variables in the model.
Ecological resilience requires the ecological system to be responsive to impacts caused by natural disasters or human activities [42]. Economic growth, social development, environmental pollution, land use changes, infrastructure construction, and climate change have contributed to ecological resilience [43,44,45]. Therefore, this study identified the factors affecting ecological resilience as social development, economic development, infrastructure construction, environmental pollution, and natural disaster risk. Social development included population growth and urbanization, which were represented by population density, urban population, and ratio of the building area. Economic development included economic growth and energy consumption, which were denoted with per capita GDP, total gas supply, and liquefied petroleum gas supply. Climate change has increased the frequency of extreme events and increased natural disaster risk such as floods, droughts, and storm surges. Studies have mostly used the NDVI, topographic relief, and maximum continuous three-day precipitation to monitor and assess natural disaster risk, such as the occurrence of floods and droughts [46,47]. The NDVI is an indicator to characterize the hazard-inducing environment. Topographic relief and maximum continuous three-day precipitation were used to characterize the topography and intensity of precipitation. Therefore, the study calculated topographic relief and maximum continuous three-day precipitation indicators based on the DEM and daily precipitation data, and used three indicators to represent natural disaster risk. Infrastructure construction mainly included the construction of roads, drainage pipes, and urban green areas. Thus, road density, density of urban sewage pipes, technology input, and ratio of green area were used to characterize infrastructure construction. Environmental pollution was mainly characterized by the emissions of different pollutants (Table 1).

Table 1.
Selected variable for identifying key driving factors of ecological resilience.
This study used covariance-based SEM (CB-SEM) in our analysis. CB-SEM is a statistical technique that is used to test a proposed structural model by estimating the relationships between observed variables and latent constructs based on the covariances among the observed variables. It is a widely used approach that allows for testing complex, multi-factor models and has the advantage of being based on the observed data rather than relying on subjective judgment or preconceived notions about the relationships in the model. The CB-SEM construction includes five parts, namely, model setting, identification, estimation, evaluation, and correction. Model setting represents the relationship among variables in SEM with the measurement model and structural model. According to the relevant literature, the following hypotheses are proposed: H1: Natural disaster risk has a significant negative effect on ecological resilience; H2: Social development has a significant positive impact on ecological resilience; H3: Infrastructure development has a significant positive impact on ecological resilience; H4: Economic development has a significant positive impact on ecological resilience; H5: Environmental pollution has a significant negative impact on ecological resilience; H6: Economic development has a significant positive impact on social development; H7: Economic development has a significant positive impact on infrastructure development; H8: Economic development has a significant positive impact on natural disaster risk; H9: Social development has a significant positive impact on infrastructure construction; H10: Social development has a significant positive effect on environmental pollution. Due to the large sample size, the maximum likelihood method was used for model parameter estimation and correction to obtain the path coefficients among the variables in this study.
3. Results
3.1. PCA Results of RSEI Indicators
Table 2 displays the PCA results of the four indicators, including the NDVI, SWCI, NDSIM, and LST. The results showed that the contribution of the four indicators to the first principal component (PC1) was relatively stable. The contribution of the eigenvalues of PC1 was 83.27%, 79.88%, 77.23%, 87.24%, and 72.40% during 2000 and 2020, respectively, which were greater than 70%. It indicated that PC1 already contained most of the information of these four indicators. In addition, the LST and NDSIM had a negative effect on ecological environment quality; however, the SWCI and NDVI had a positive effect on ecological environment quality. The ecological benefits of these four indicators were similar to the actual situation. Therefore, this study used PC1 to construct a comprehensive ecological environment quality index.

Table 2.
Results of PCA for four indicators of RSEI in the YREBML during 2000–2020.
The mean values of the four normalized indicators in the middle and lower reaches of the YREB during 2000–2020 are shown in Table 3. The NDVI and SWCI of the middle reaches of the YREB were higher than those of the lower reaches, while the LST and NDSIM were lower than those of the lower reaches during 2000–2020. The NDVI of the middle reaches of the YREB decreased from 0.76 in 2000 to 0.71 in 2020, while in the lower reaches of the YREB, it decreased from 0.74 to 0.72. The decreased NDVI led to the reduction of ecological environment quality. In addition, the increased LST and NDSIM had a negative effect on ecological environment quality during 2000 and 2015. Compared with 2000, the positive effect of decreased NDVI was greater than the negative effect of the other three indexes on ecological environment quality.

Table 3.
Mean values of four normalized indicators of RSEI in the middle and lower reaches of the YREB during 2000–2020.
3.2. Spatial and Temporal Changes of RSEI
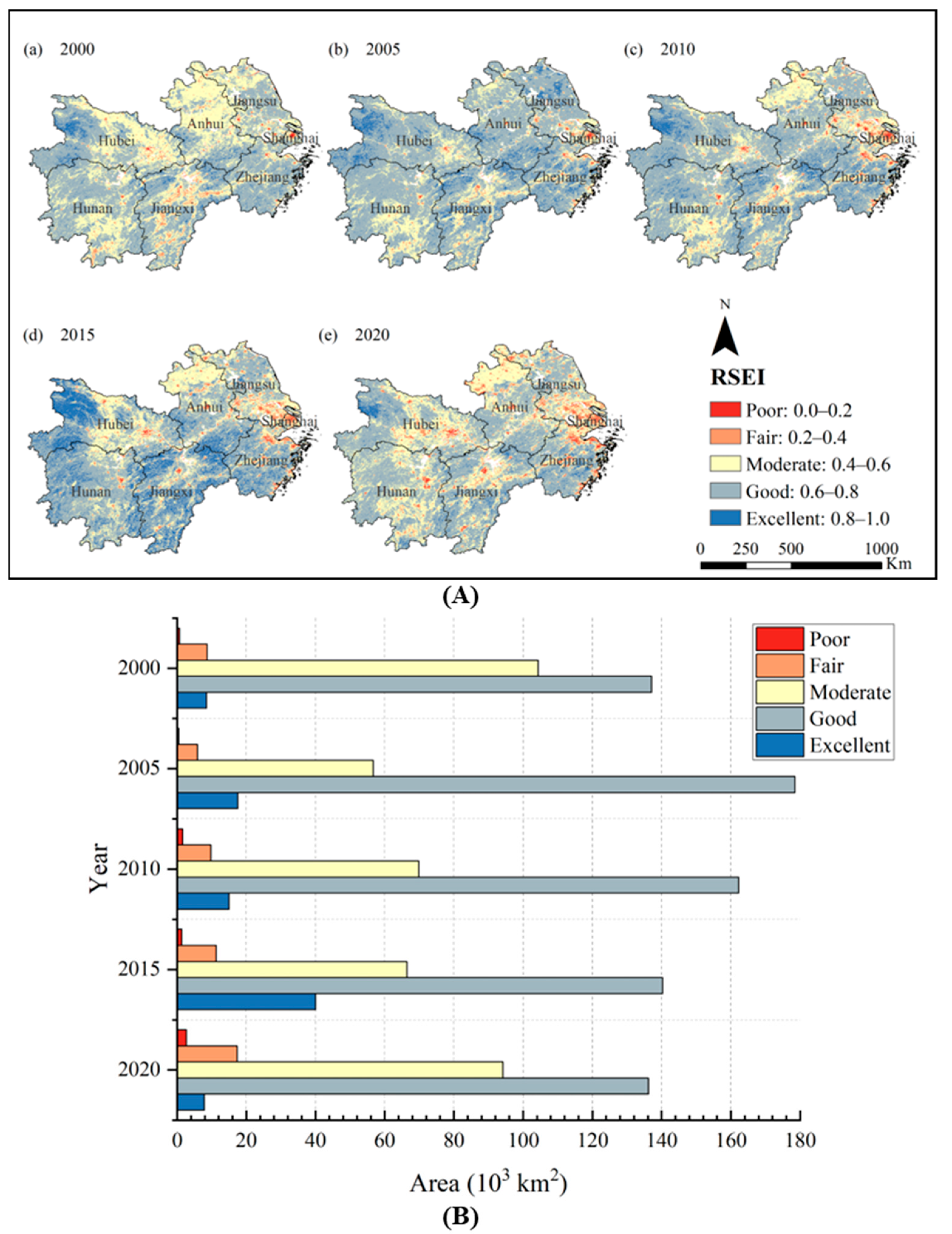
The results revealed that the RSEI showed a trend of increasing and then decreasing in the YREBML during 2000–2020. The average RSEI was 0.62, 0.66, 0.64, 0.66, and 0.60 in 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020, respectively. To further quantitatively analyze the spatial and temporal changes of the RSEI in different periods, it was divided into five classes of poor (RSEI < 0.2), fair (0.2 ≤ RSEI < 0.4), moderate (0.4 ≤ RSEI < 0.6), good (0.6 ≤ RSEI < 0.8), and excellent (RSEI ≥ 0.8) in the YREBML (Figure 3A). Its spatial characteristics showed that the RSEI was overall higher in the middle reaches of the YREB than in the lower reaches, and higher in the south than in the north. The areas with good and excellent ecological environment were mainly distributed in northwestern Hubei, Jiangxi, and Zhejiang, while the areas with poor and fair ecological environment were distributed in the southeastern and eastern regions of the YREBML. In addition, urbanized areas such as Shanghai and Jiangsu had a poor ecological environment.
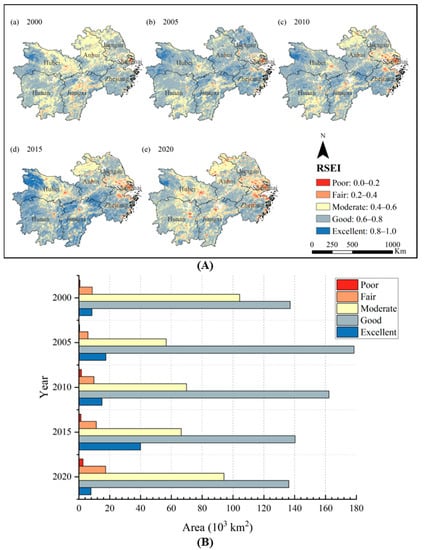
Figure 3.
Spatial and temporal changes of RSEI in the YREBML during 2000 and 2020: (A) Spatial patterns of the RSEI; (B) RSEI area statistics of different categories. Note: Datum: D_WGS_1984; Projection: WGS_1984_UTM_Zone_50N; Representation scale: 1:17,000,000; Nominal scale: 1:250.
The overall RSEI was at moderate and good levels in the YREBML. However, there were significant differences between years. The areas with poor and fair RSEI accounted for 0.29% and 3.34% of the area of the YREBML in 2000, respectively (Figure 3B). In 2005, the regional ecological environment quality improved significantly, and the proportion of areas with poor and fair eco-environment was only 0.18% and 2.27%, respectively. In particular, the RSEI of Jiangsu and Anhui improved by 13.73% and 13.61%, respectively, during 2000–2005. However, due to rapid urbanization, industrialization, and human activities, the RSEI of Shanghai decreased by 6.27% during 2000–2005. In 2010, the regional ecological quality declined, and the poor, fair, and medium areas gradually expanded, accounting for 0.63%, 3.77%, and 27.04% of the area of the YREBML, respectively. Compared with 2005, the RSEI in the lower reaches of the YREB decreased significantly, and the RSEI of Anhui, Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Zhejiang decreased by 4.94%, 13.06%, 14.09%, and 2.22%, respectively. The areas with excellent eco-environment gradually expanded in 2015, accounting for 15.43% of the total area of the region, mainly in Jiangxi and Zhejiang. However, eco-environment quality decreased in the YREBML in 2020. The areas with poor, fair, and moderate eco-environment expanded, accounting for 1.05%, 6.72%, and 36.47% of the total area, respectively. The areas with poor and fair eco-environment in Shanghai and Jiangsu continued to expand to distant suburban dispersal in 2020. In terms of the urbanized areas, the areas with poor and fair eco-environment showed an increasing trend in Hubei, Hunan, and Jiangxi, especially Wuhan, Changsha, Nanchang, and Xiaogan in 2020.
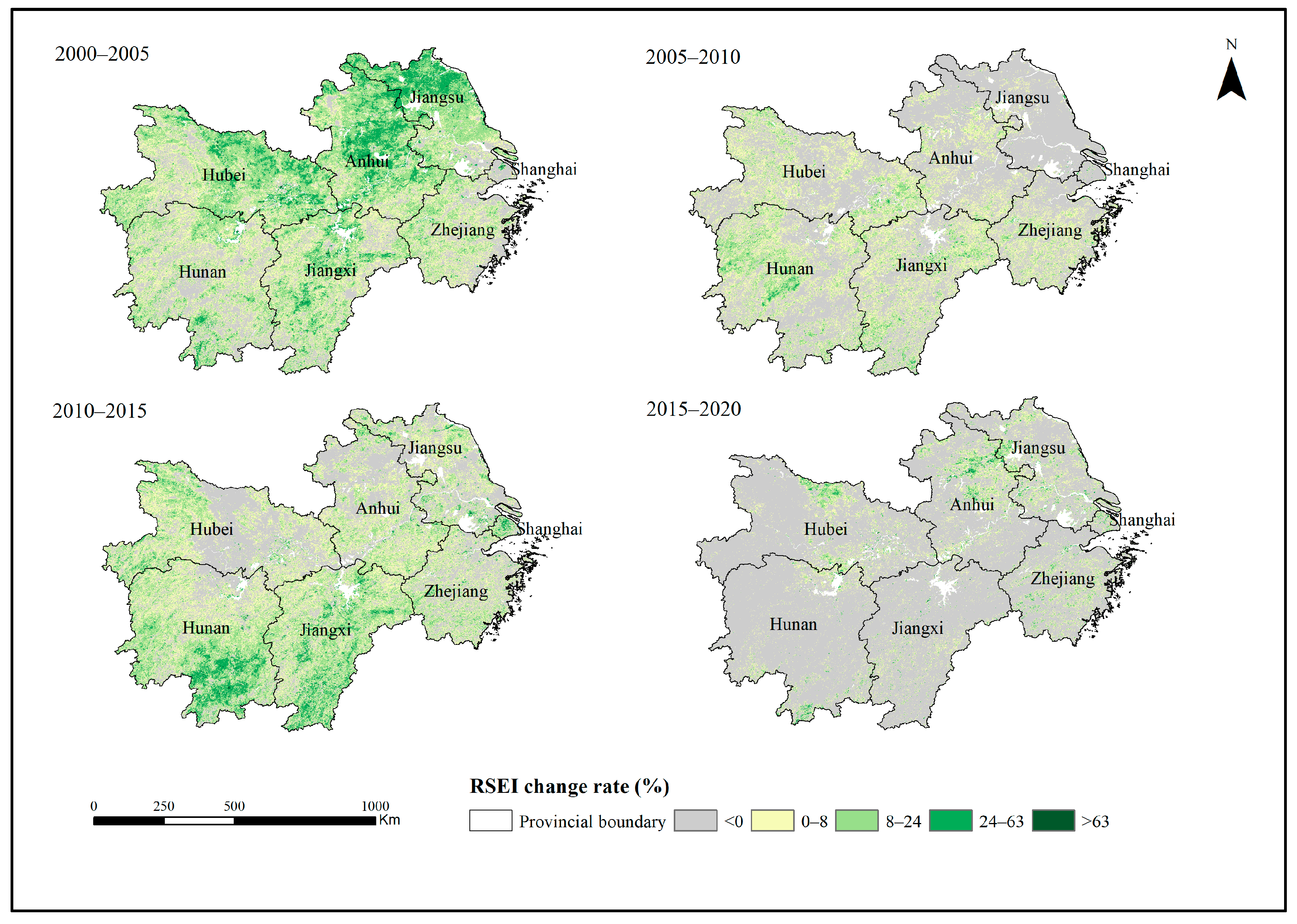
This study calculated the RSEI change rate to further understand the changes in the ecological environment quality of the YREBML from 2000 to 2020 (Figure 4). The results showed that there was a significantly decreasing trend of RSEI in this region during 2005–2010 and 2015–2020. More than 50% of grids had RSEI change rates below zero during 2005–2010, and they were mainly in Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Anhui. This was mainly due to the large-scale urban development and industrial land construction in the lower reaches of the YREB, which has led to an increase in surface temperatures and bare soil area, reducing ecological environment quality. More than 80% of grids had RSEI change rates below zero during 2015–2020, and they were mainly in Hunan, Hubei, Jiangxi, Jiangsu, and Shanghai. The proportion of area that experienced ecological environment degradation from 2015 to 2020 was 82.24%, which was much higher than the degraded area proportion of 59.99% from 2005 to 2010. Development planning of urban groups in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River was proposed in 2015 to promote the economic development of Hubei, Hunan, and Jiangxi. The average annual growth of the regional economy of the middle reaches of YREB from 2015 to 2019 was 8.2%, which was higher than the average annual growth of the regional economy of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration of 7.7%. In addition, the significant growth of urban impervious surfaces led to a decline in ecological environment quality in this region. However, the ecological environment improvement areas were distributed in Hunan and Jiangxi during 2010 and 2015. In 2010–2015, the eco-environment improvement area accounted for 63.72% of the total area, which was larger than the eco-environment degradation area of 36.28%.
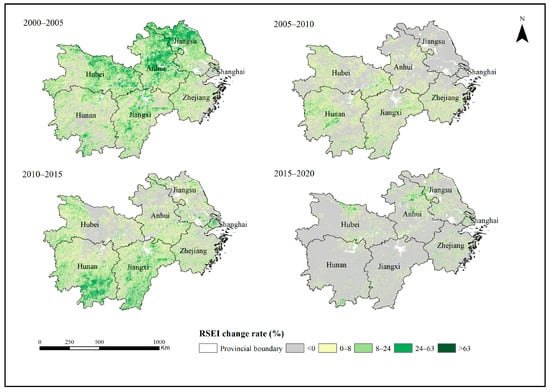
Figure 4.
Distribution of RSEI change rate in the YREBML, 2000–2005, 2005–2010, 2010–2015, and 2015–2020. Note: Datum: D_WGS_1984; Projection: WGS_1984_UTM_Zone_50N; Representation scale: 1:17,000,000; Nominal scale: 1:250.
3.3. Spatial Pattern of Ecological Resilience
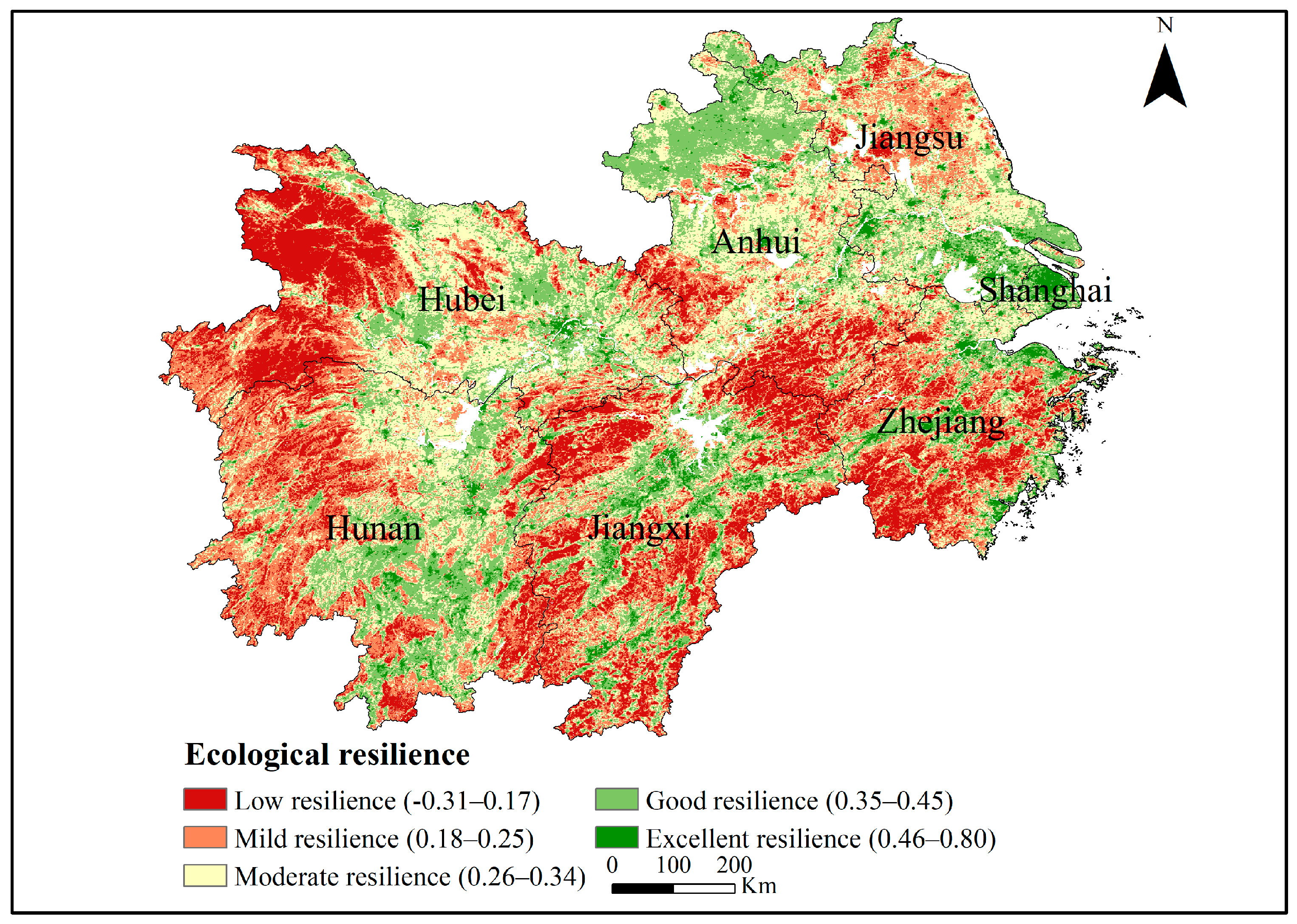
The ecological resilience ranged from −0.31 to 0.80 in the YREBML. The natural break is a systematic cluster analysis method, which starts from the possible similarity and affinity between the objects, and classifies and groups them according to the degree of similarity or correlation of various characteristic signs between the objects. It is widely applied in vulnerability or resilience classification [48,49,50,51]. Therefore, the ecological resilience was further classified with the natural break method (Figure 5). Ecological resilience refers to the ability of an ecosystem to maintain its normal functions and services under internal and external forces. High ecological resilience means fewer changes after being subjected to damage caused by an ecological disturbance and it being much easier for the ecosystem to recover. The results showed that the spatial pattern of ecological resilience was characterized by high resilience in the north and east, and low resilience in the south and west. High ecological resilience areas (>0.35) covered 40.48% of the whole region and were mainly concentrated in the middle reaches of the YREB, accounting for 23.28% of the total area. This was because these regions had fewer changes of RSEI under the influence of factors such as climate change and human activities. However, low ecological resilience areas (<0.25) covered 25.17% of the whole region and were distributed in Jiangsu and Zhejiang, accounting for 10.85% of the total area. Due to economic development, climate change, and human activities, the RSEI in these regions changed dramatically during 2000 and 2020, indicating that the eco-environment was damaged by an ecological disturbance. It is worth noting that Shanghai had higher ecological resilience than other regions. This was because the RSEI in Shanghai was relatively stable from 2000 to 2020, with an average value of 0.44.
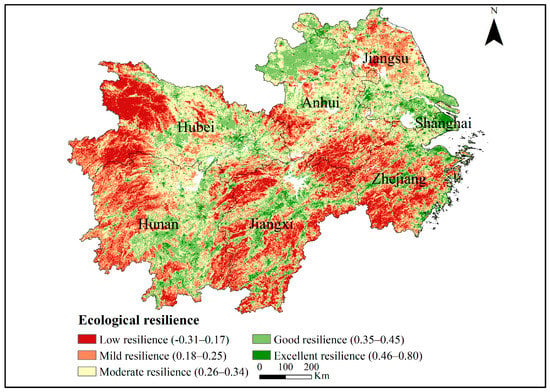
Figure 5.
Spatial pattern of ecological resilience in the YREBML during 2000–2020. Note: Datum: D_WGS_1984; Projection: WGS_1984_UTM_Zone_50N; Representation scale: 1:7,000,000; Nominal scale: 1:100.
3.4. Driving Factors of Ecological Resilience
In terms of the goodness-of-fit index of the hypothetical model, Chi-square/df was equal to 2.560, less than 3; GFI, AGFI, NFI, and CFI were equal to 0.969, 0.941, 0.978, and 0.986, respectively, all greater than 0.9; SRMR was equal to 0.029, less than 0.05; and RMSEA was equal to 0.059, less than 0.08 (Table 4). The above parameters showed that the goodness of fit and the model fitness of the hypothetical model were relatively good.

Table 4.
The goodness-of-fit index of the hypothetical model.
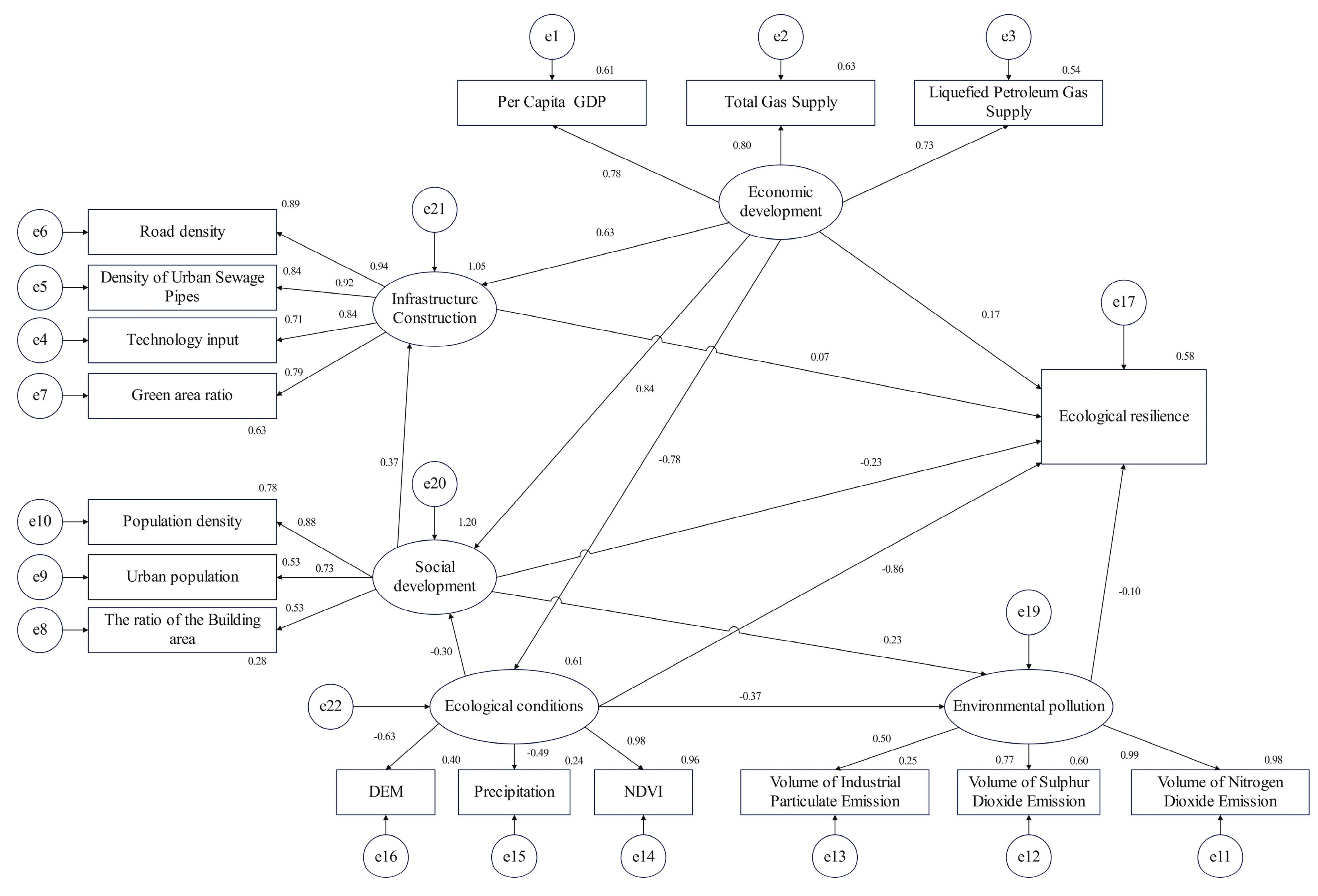
The SEM was constructed based on ecological resilience theory, and the results verified related hypotheses, while social development and infrastructure development did not have significant effects on resilience, and hypotheses H2 and H3 were rejected (Figure 6). The influence paths of each subsystem on ecological resilience showed that economic development had a significant positive influence on ecological resilience (Table 5). This indicated that the greater the economic development, the higher the ecological resilience, which directly proved the importance of economic development on ecological resilience improvement. Natural disaster risk had a significant negative effect on resilience. Areas with concentrated rainfall and high topographic relief were more prone to disaster events, leading to a decrease in ecological resilience. In addition, environmental pollution had a significant negative effect on resilience and serious environmental pollution led to lower ecological resilience. Therefore, strengthening environmental protection is extremely critical to ecological resilience improvement.
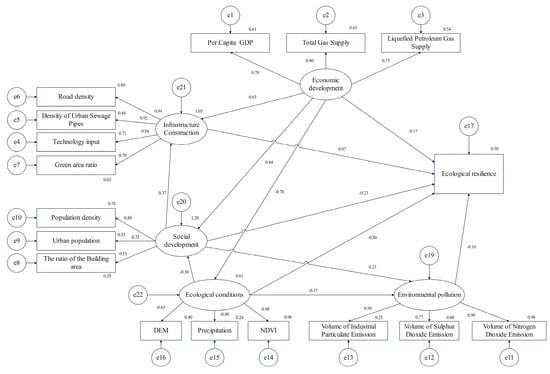
Figure 6.
Driving factors analysis of ecological resilience in the YREBML based on SEM.

Table 5.
SEM path coefficients for the identification of key driving factors of ecological resilience in the YREBML.
The direct, indirect, and total effect coefficients of the social development, economic growth, infrastructure construction, natural disaster risk, and environmental pollution subsystems on ecological resilience were calculated through the relationships among the latent variables and the modification of the SEM (Table 6). The direct effect could be expressed by the path coefficients between the variables, which represented the direct effect of a variable on ecological resilience. Indirect effects referred to the effect of a variable on ecological resilience through other variables. Each endogenous or exogenous variable usually had multiple pathways affecting ecological resilience, including both direct and indirect effects, and the total effect was the sum of the direct and indirect effects, representing the total effect of a variable on the ecological resilience. Natural disaster risk and economic development had the most significant direct and indirect effect on ecological resilience, with values of −0.899 and 0.468, respectively. Therefore, economic development and natural disaster risk had both direct and indirect effects on improving regional ecological resilience. In addition, the direct effect of environmental pollution on ecological resilience was −0.127, with no indirect effect. Environmental pollution, such as air and water pollution, directly affected regional ecological resilience. In conclusion, the key path to enhance ecological resilience depended on promoting economic growth and improving the ecological environment.

Table 6.
The effects of the five subsystems on ecological resilience in the YREBML.
4. Discussion
Since the implementation of YREB development strategy in China, the YREBML has become an important region for urbanization development and industrial clustering. However, rapid economic development, population agglomeration, climate change, and other human activities have led to a dramatical decrease of the ecological environment in this region. Therefore, this study detected spatial–temporal changes of the RSEI and further analyzed the spatial pattern of ecological resilience based on MODIS data from 2000 to 2020. Similar research is mostly based on Landsat data to construct the RSEI model [52,53,54,55]. In addition, most studies have used Landsat 5, 7, and 8 surface reflectance images to obtain long time series data on a small scale [56]. However, in terms of the YREBML, there are some missing data strips in Landsat products due to sensor problems. The overall accuracy of Landsat data for long time series is poor in this region. Thus, this study directly utilizes spatial–temporal continuous MODIS data and products, breaking the spatial–temporal limitations of the data sources. In terms of the research framework, based on the concepts of the RSEI, this study has provided an integrated approach to assess long-term ecological environment quality and construct the indicator of ecological resilience for facilitating regional planning. The improvement of the framework can quickly help detect dynamic and intuitive ecological environment changes and theoretically conceptualize and empirically explore the ecological resilience of urban systems.
With the rapid urbanization and economic development in China, the YREBML region is still facing ecological and environmental challenges such as soil loss, reduction of wetland areas, degradation of wetland ecosystems, and wastewater pollution. The results revealed that the overall RSEI was at moderate and good levels in the YREBML. Its spatial characteristics showed that the RSEI was higher in the middle reaches of the YREB than in the lower reaches, and higher in the south than in the north. Similar research has also found that the overall ecological environment rank was mainly neutral and slightly good in the YREB [43,57]. Climate change, rapid urbanization, population agglomeration, and industrial clustering would bring greater pressure on the eco-environment [58,59]. Between 2000 and 2020, the ecological environment was better in 2005 and 2010, which was significantly related to temperature, precipitation, and vegetation cover. Specifically, the values of SWCI, NDVI, NDSIM, and LST showed increasing, increasing, decreasing, and increasing trends in 2005, respectively. Therefore, the improvement in the ecological environment of the YREBML may be influenced by the decrease in the surface bare soil area, increase in water vapor content, and increase in vegetation cover in 2005. In addition, the positive effect of the increase of SWCI and NDVI in 2015 was greater than the negative effect of NDSIM and LST, and the ecological index in this region showed an increasing trend. However, the RSEI decreased in the middle and lower reaches in 2010 and 2020. Due to the influence of climate change, urbanization, and human activities, the increase of urban surface temperatures and bare soil area led to a greater negative effect of NDSIM and LST than the positive effect of increased SWCI and NDVI. The above phenomenon indicated that with the increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme climate events, it would inevitably have a significant impact on the sustainable development of the ecological environment in the YREBML. Compared with the middle reaches, the lower reaches of the YREB had greater ecological pressures and faced the problem of ecosystem degradation, which requires the government to pay attention and take corresponding protection measures for improving ecological resilience.
Ecological environment quality is influenced by various factors, including the natural environment and human activities. This study mainly selected the four indicators of SWCI, NDVI, NDSIM, and LST to detect spatial–temporal changes of eco-environment quality. Compared with other studies, the optimized NDSIM used the red and green bands to calculate the building index, which were more sensitive to the built-up land [23]. Moreover, SWCI was more sensitive to humidity. Therefore, the improved NDSIM and SWCI can better characterize the interactions among the ecosystem factors, and the comprehensive ecological index is more representative. The ecological resilience evaluation method based on the dynamic change of the RSEI can solve the problems of the number of indicators, the overlap between various indicators, and the lack of objectivity in the previous resilience assessment research. The driving analysis based on SEM showed that high-quality economic development, natural disaster risk mitigation, and ecological environmental protection were key elements to enhance ecological resilience. It indicated that industrial transformation and industrial structure optimization were required in the YREBML to achieve high-quality economic development. In terms of natural disaster risk, the cities should further monitor and assess regional natural disaster risk, and combine structural and non-structural measures to mitigate this risk. Finally, the government should increase investment in environmental protection and propose ecological protection policies to improve ecological environment quality.
This study proposed an integrated assessment framework that combined the RSEI and ecological resilience, which can be used for large-scale and long time series ecological monitoring and resilience management studies, such as wetland ecosystems, mining areas, and urban systems. However, this study also has some limitations that need to be tackled in future research. In addition to natural environmental factors, the influence of human environment factors on ecological resilience should also be considered, such as population, economic development, building density, regional governance level, and environmental policies. In terms of uncertainty, it existed in the acquisition of remote sensing data and data processing processes. As for remotely sensed images acquired by sensors with specific physical parameters, the complexity of the surface landscape distribution and the size of the surface cells together directly affected the uncertainty of the remotely sensed data. The processing of the four indices, including removing clouds and anomalous values, also increased uncertainty in this study. The number of samples in SEM also further affected the results of the driver analysis. In addition, the RSEI model should be improved to detect the eco-environment accurately and provide effective data support for eco-environment monitoring and management in future research.
5. Conclusions
This study improved the RSEI model based on MODIS data in the YREBML, promoting the scope and scale of model applications. Considering the effect of the four indicators of NDVI, SWCI, NDSIM, and LST on the eco-environment, this study assessed spatial–temporal changes of the RSEI and further analyzed spatial patterns of ecological resilience and its driving factors in the YREBML during 2000–2020. The results showed that the LST and NDSIM had a negative effect on ecological environment quality; however, the SWCI and NDVI had a positive effect. The overall RSEI was at moderate and good levels in the YREBML during 2000–2020, accounting for more than 85% of the total area. Its spatial characteristics showed that the RSEI was higher in the middle reaches of the YREB than in the lower reaches, and higher in the south than in the north. In addition, there was a significantly decreasing trend of RSEI in this region during 2005–2010 and 2015–2020, mainly in Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Anhui. The increased NDSIM and LST and decreased NDVI had a negative effect on the RSEI, resulting in ecological environment degradation. Moreover, the spatial pattern of ecological resilience was characterized by high resilience in the north and east, and low resilience in the south and west, indicating that economic development, climate change, and human activities would further affect ecological resilience of urban systems. Economic development had a significant positive effect on ecological resilience, while natural disaster risk and environmental pollution had a significant negative effect on resilience. The key path to enhance ecological resilience depends on promoting economic growth and improving the ecological environment. The study provided a new evaluation perspective for the comprehensive evaluation of regional large-scale ecological environment quality based on MODIS data and its spatial and temporal variation pattern exploration. It also provided data and decision support for ecological environment monitoring and management.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.L.; methodology, Z.L. and L.P.; formal analysis, L.P. and H.W.; data curation, L.P. and H.W.; writing—original draft preparation, L.P. and Z.L.; writing—review and editing, Z.L.; visualization, Z.L. and H.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41890824 and 71804175, M-0369).
Data Availability Statement
All data and materials are available upon request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the reviewers for their thoughtful comments that helped improve the quality of this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. The effect of urbanization on environmental pollution in rapidly developing urban agglomerations. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B. Ecological effects of new-type urbanization in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Feng, K. Coupling analysis of urbanization and energy-environment efficiency: Evidence from Guangdong province. Appl. Energy 2019, 254, 113650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Yu, S. Losses of natural coastal wetlands by land conversion and ecological degradation in the urbanizing Chinese coast. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.A.; Canh, N.P.; Le, T.N.L. Environmental degradation & role of financialisation, economic development, industrialisation and trade liberalisation. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, B.; Tzeremes, P.G.; Tzeremes, N.G. Energy consumption, economic growth and environmental degradation in OECD countries. Econ. Model 2020, 84, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunsolo, A.; Ellis, N.R. Ecological grief as a mental health response to climate change-related loss. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.; Xie, P.; He, W.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Khanal, R. Spatiotemporal change of ecologic environment quality and human interaction factors in three gorges ecologic economic corridor, based on RSEI. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, R.; Venkatakrishnan, P.; Balaji, N. Intelligent based novel embedded system based IoT enabled air pollution monitoring system. Microprocess. Microsy. 2020, 77, 103172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, H.; Shakeri, A.; Rezaei, M.; Dashti Barmaki, M.; Shahraki, M. Application of water quality index (WQI) and hydro-geochemistry for surface water quality assessment, chahnimeh reservoirs in the Sistan and Baluchestan province. Iran. J. Environ. Health 2019, 11, 575–586. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Marinello, F. Exploration of eco-environment and urbanization changes in coastal zones: A case study in China over the past 20 years. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 119, 106847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Deng, H. Evaluating urban resource and environment carrying capacity by using an innovative indicator system based on eco-civilization—A case study of Guiyang. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 6941–6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, P.; Huang, J.; Zhou, H.; Fang, C.; Zhan, Y.; Huang, W. Local and telecoupling coordination degree model of urbanization and the eco-environment based on RS and GIS: A case study in the Wuhan urban agglomeration. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; He, S.; Niu, R. Eco-environmental assessment model of the mining area in Gongyi, China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, R.; Saputra, A.M.W.; Wijayanto, A.W.; Caesarendra, W. Eco-environment vulnerability assessment using remote sensing approach in East Kalimantan, Indonesia. Remote Sens. Appl. 2022, 27, 100791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, Q.; Shao, Y.; Sun, S.; Xiao, L.; Guo, J. Ecological environment assessment based on land use simulation: A case study in the Heihe River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 133928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Jiang, W. Evaluation of the spatiotemporal variations in the eco-environmental quality in China based on the remote sensing ecological index. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boori, M.S.; Choudhary, K.; Paringer, R.; Kupriyanov, A. Eco-environmental quality assessment based on pressure-state-response framework by remote sensing and GIS. Remote Sens. Appl. 2021, 23, 100530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orusa, T.; Orusa, R.; Viani, A.; Carella, E.; Borgogno Mondino, E. Geomatics and EO data to support wildlife diseases assessment at landscape level: A pilot experience to map infectious keratoconjunctivitis in chamois and phenological trends in Aosta Valley (NW Italy). Remote Sens. Appl. 2020, 12, 3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliry, S.I.; Pekkan, E.; Avdan, U. GIS-Based Water Budget Estimation of the Kizilirmak River Basin using GLDAS-2.1 Noah and CLSM Models and Remote Sensing Observations. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2022, 50, 1191–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H. Ecological Water Demand of Taitema Lake in the Lower Reaches of the Tarim River and the Cherchen River. Remote Sens. Appl. 2022, 14, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. A remote sensing index for assessment of regional ecological changes. China Environ. Sci. 2013, 33, 889–897. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Guan, H.; Shi, T.; Hu, X. Detecting ecological changes with a remote sensing based ecological index (RSEI) produced time series and change vector analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Sharifi, A.; Schlör, H. Integrated social-ecological-infrastructural management for urban resilience. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 181, 106268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. Resilience and stability of ecological systems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1973, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentoni, D.; Pinkse, J.; Lubberink, R. Linking sustainable business models to socio-ecological resilience through cross-sector partnerships: A complex adaptive systems view. Bus. Soc. 2021, 60, 1216–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komugabe-Dixson, A.F.; de Ville, N.S.; Trundle, A.; McEvoy, D. Environmental change, urbanisation, and socio-ecological resilience in the Pacific: Community narratives from Port Vila, Vanuatu. Ecosyst. Serv. 2019, 39, 100973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, E.R. Properties and projects: Reconciling resilience and transformation for adaptation and development. World Dev. 2019, 122, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldbeck, N.; Angeloudis, P.; Ochieng, W.Y. Resilience assessment for interdependent urban infrastructure systems using dynamic network flow models. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2019, 188, 62–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslehi, S.; Reddy, T.A. Sustainability of integrated energy systems: A performance-based resilience assessment methodology. Appl. Energy 2018, 228, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, S.; Xu, X.; Luo, J. Integrated Natural Disasters Urban Resilience Evaluation: The Case of China. Nat. Hazards 2021, 107, 2105–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cui, Z.; Lin, J.; Xie, J.; Su, K. The coupling relationship between urbanization and ecological resilience in the Pearl River Delta. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 44–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yin, L.; Zhang, S.; Liang, K. Estimation on wetland loss and its restoration potential in Modern Yellow River Delta, Shandong Province of China. Chinese Chin. J. Popul. Resour. 2015, 13, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, I.M.; Darling, E.S. Rethinking Ecosystem Resilience in the Face of Climate Change. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Lv, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, J. Ecological resilience assessment of an arid coal mining area using index of entropy and linear weighted analysis: A case study of Shendong Coalfield, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiault, L.; Marshall, P.; Gelcich, S.; Collin, A.; Chlous, F.; Claudet, J. Mapping social–ecological vulnerability to inform local decision making. Conserv. Biol. 2018, 32, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, N.; Becerro, M.A.; Sanabria-Fernandez, J.A.; Martín-López, B. Assessing social-ecological vulnerability of coastal systems to fishing and tourism. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, F. Critical natural capital revisited: Ecological resilience and sustainable development. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhu, X.; Wu, H.; Li, Z. Assessment of Urban Ecological Resilience and Its Influencing Factors: A Case Study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration of China. Land 2022, 11, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, J.; Shirkey, G.; John, R.; Wu, S.R.; Park, H.; Shao, C. Applications of structural equation modeling (SEM) in ecological studies: An updated review. Ecol. Process. 2016, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Structural Equation Modeling. In Models and Methods for Management Science; Management for Professionals; Zhang, H., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Peng, F.L.; Qiao, Y.K.; Zhang, J.B. Evaluating disaster prevention benefits of underground space from the perspective of urban resilience. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 58, 102206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Fu, L.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Li, F.; Deng, Z.; Xie, Y. Spatiotemporal change detection of ecological quality and the associated affecting factors in Dongting Lake Basin, based on RSEI. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 302, 126995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Qiao, Y.; Shi, T.; Zhou, Q. Study on coupling coordination and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between economic development and ecological environment of cities along the Yellow River Basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 6898–6912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yang, W.; Huang, R. The multidimensional differences and driving forces of ecological environment resilience in China. Environ. Impact Assess. 2023, 98, 106954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullick, M.R.A.; Nur, R.M.; Alam, M.J.; Islam, K.A. Observed trends in temperature and rainfall in Bangladesh using pre-whitening approach. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2019, 172, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hedny, S.M.; Muhaimeed, A.S. Drought monitoring for Northern Part of Iraq using temporal NDVI and rainfall indices. In Environmental Remote Sensing and GIS in Iraq; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 301–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Shi, X.; Li, X.; Yan, J. Geographical indication agricultural products, livelihood capital, and resilience to meteorological disasters: Evidence from kiwifruit farmers in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 65832–65847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environme Leite, J.B.; Mantovani, J.R.S.; Dokic, T.; Yan, Q.; Chen, P.C.; Kezunovic, M. Resiliency assessment in distribution networks using GIS-based predictive risk analytics. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 34, 4249–4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Hao, X.; Hua, D.; Hao, H. Assessment of ecosystem resilience in Central Asia. J. Arid Environ. 2021, 195, 104625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Shi, S.; Reheman, Y.; Li, S. Measurement of urban flood resilience using a quantitative model based on the correlation of vulnerability and resilience. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 82, 103344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariken, M.; Zhang, F.; Liu, K.; Fang, C.; Kung, H.T. Coupling coordination analysis of urbanization and eco-environment in Yanqi Basin based on multi-source remote sensing data. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, S.; Rao, X.; Lin, X.; Li, R. Landsat TM/OLI-Based Ecological and Environmental Quality Survey of Yellow River Basin, Inner Mongolia Section. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Xu, W.; Lu, N.; Huang, S.; Wu, C.; Wang, L.; Dai, F.; Kou, W. Assessment of spatial–temporal changes of ecological environment quality based on RSEI and GEE: A case study in Erhai Lake Basin, Yunnan province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boori, M.S.; Choudhary, K.; Paringer, R.; Kupriyanov, A. Spatiotemporal ecological vulnerability analysis with statistical correlation based on satellite remote sensing in Samara, Russia. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 285, 112138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, P.; Xia, J.; Qi, K.; Wang, W.; Cai, W.; Chen, N. Research and analysis of ecological environment quality in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River Basin between 2000 and 2019. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Meng, F.; Fu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal change and driving factors of the Eco-Environment quality in the Yangtze River Basin from 2001 to 2019. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; He, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Predicting the joint effects of future climate and land use change on ecosystem health in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Appl. Geogr. 2020, 124, 102293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, H.; Li, Z.; Shan, Y. Decoupling of economic growth from CO2 emissions in Yangtze River Economic Belt cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).