Quantification of Aquarius, SMAP, SMOS and Argo-Based Gridded Sea Surface Salinity Product Sampling Errors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Observations
2.2. Model
2.3. Method
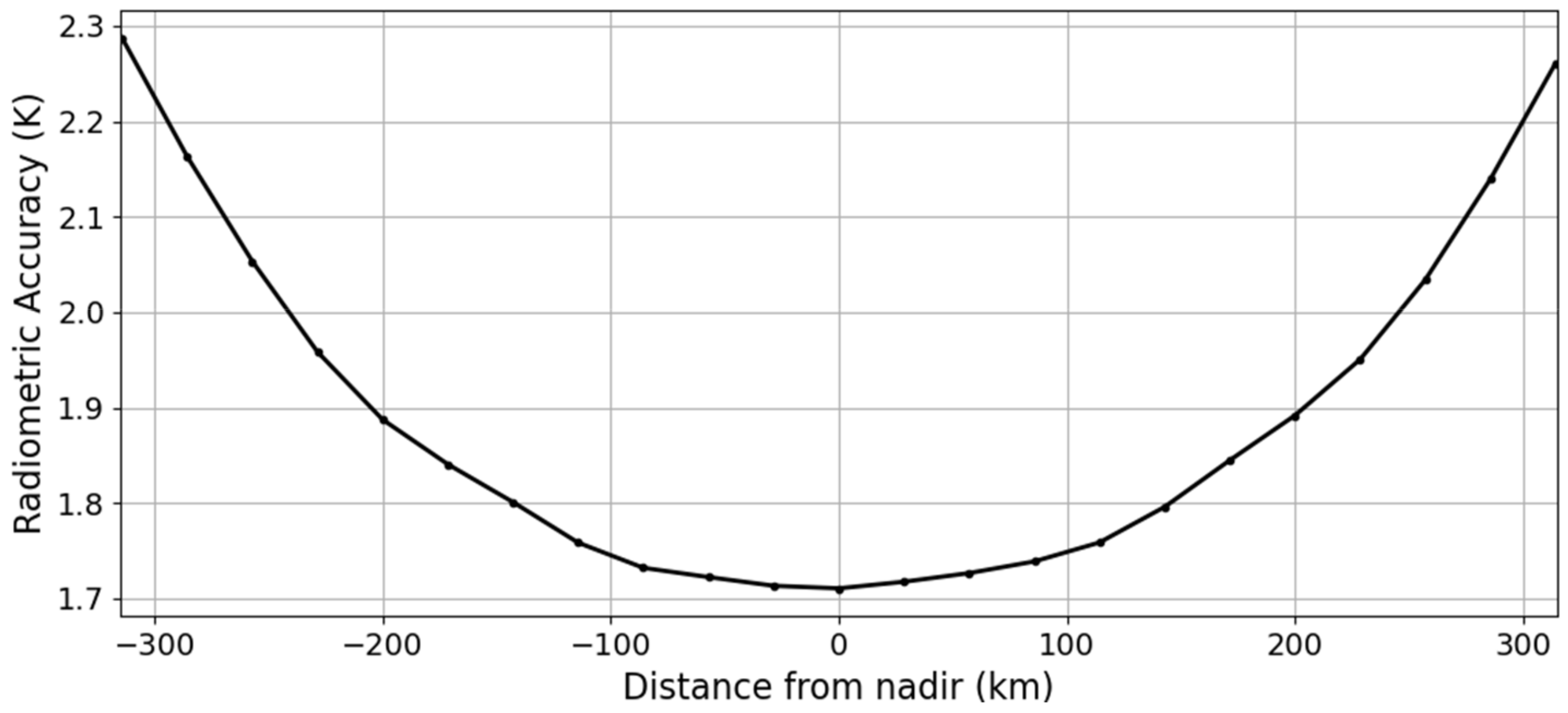
2.3.1. Level 2 and 3 Aquarius and SMAP Simulations
2.3.2. Level 2 and 3 SMOS Simulations
2.3.3. Argo Single Float and Gridded Products Simulations
2.3.4. Model Fields
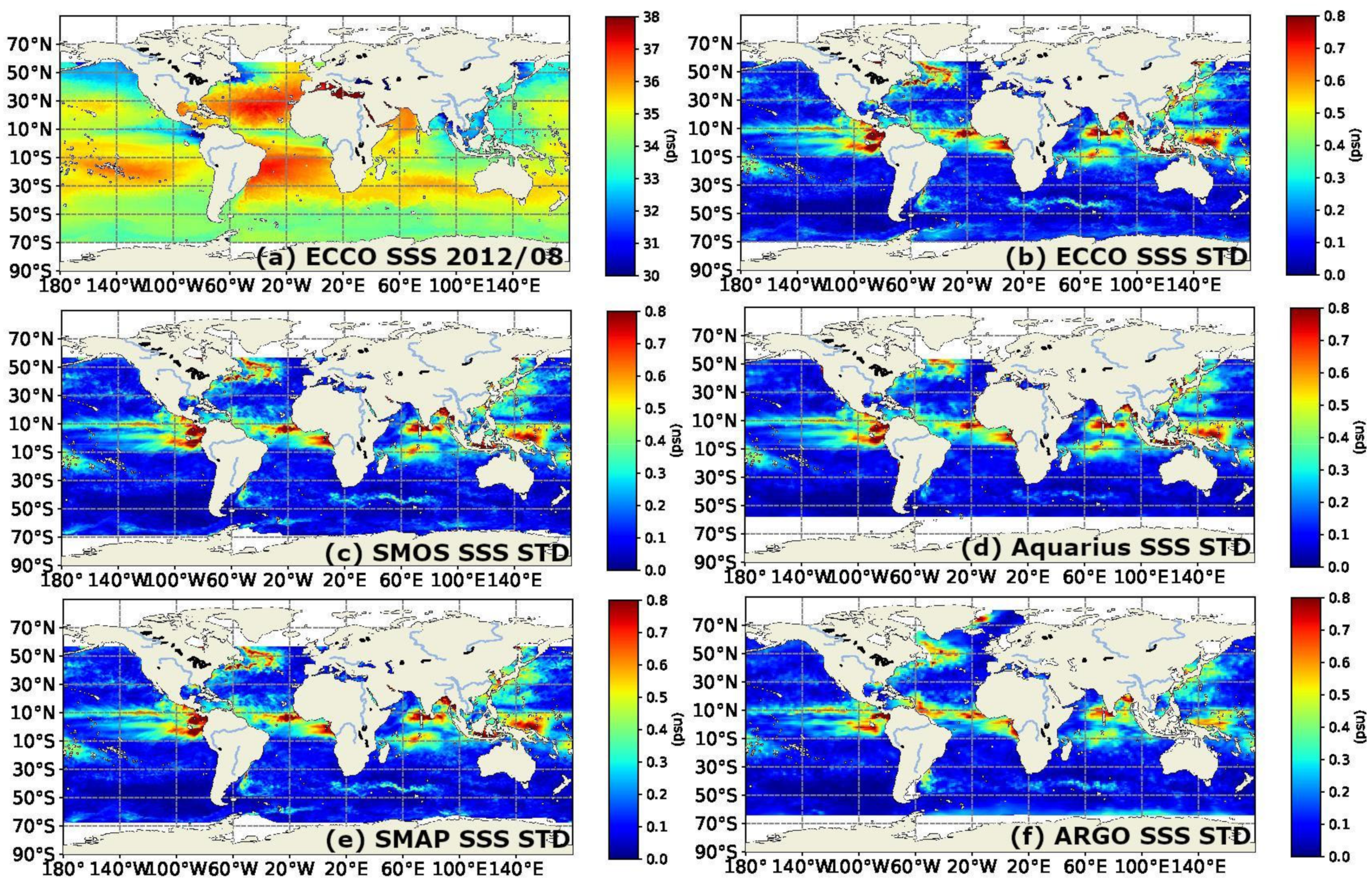
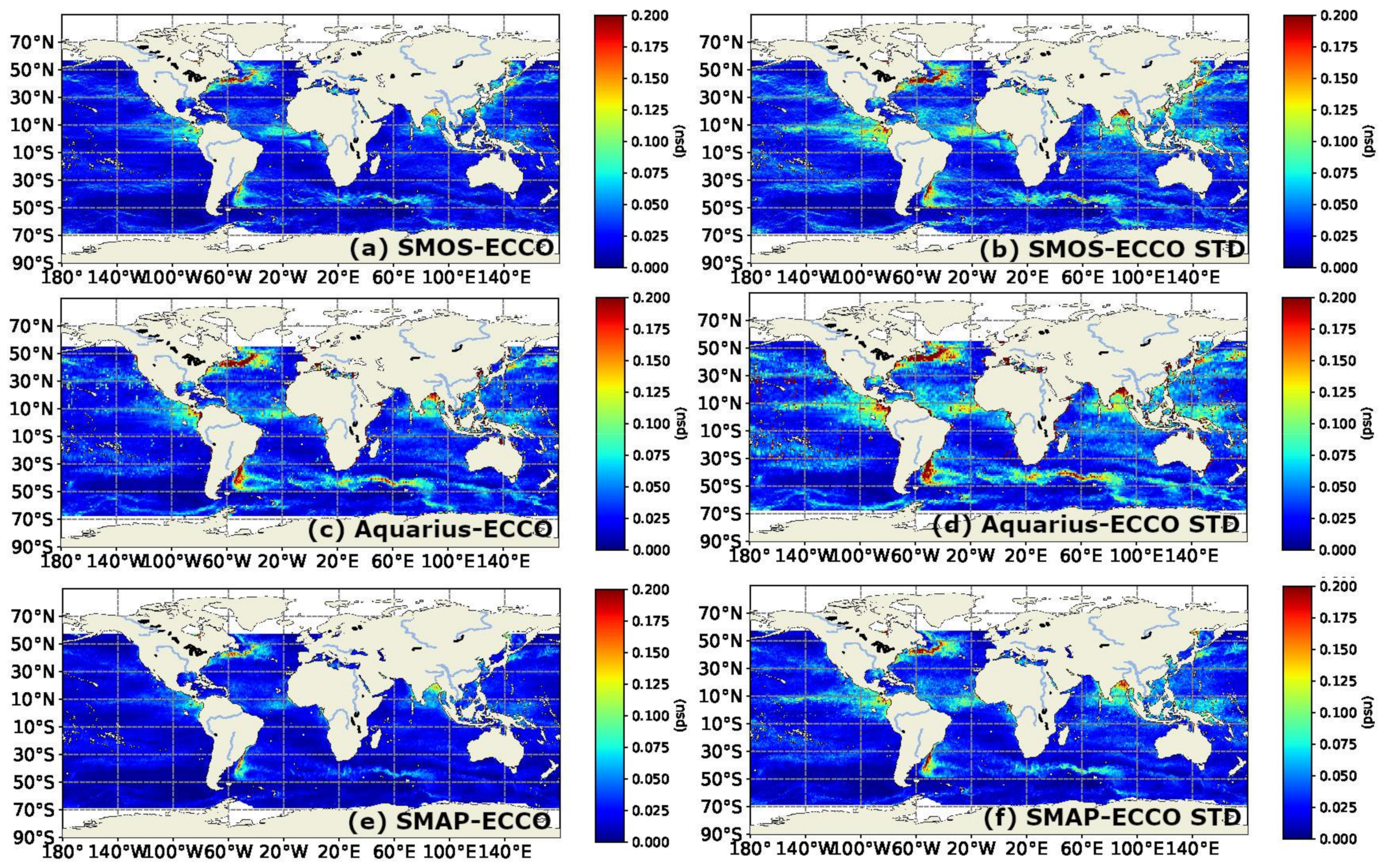
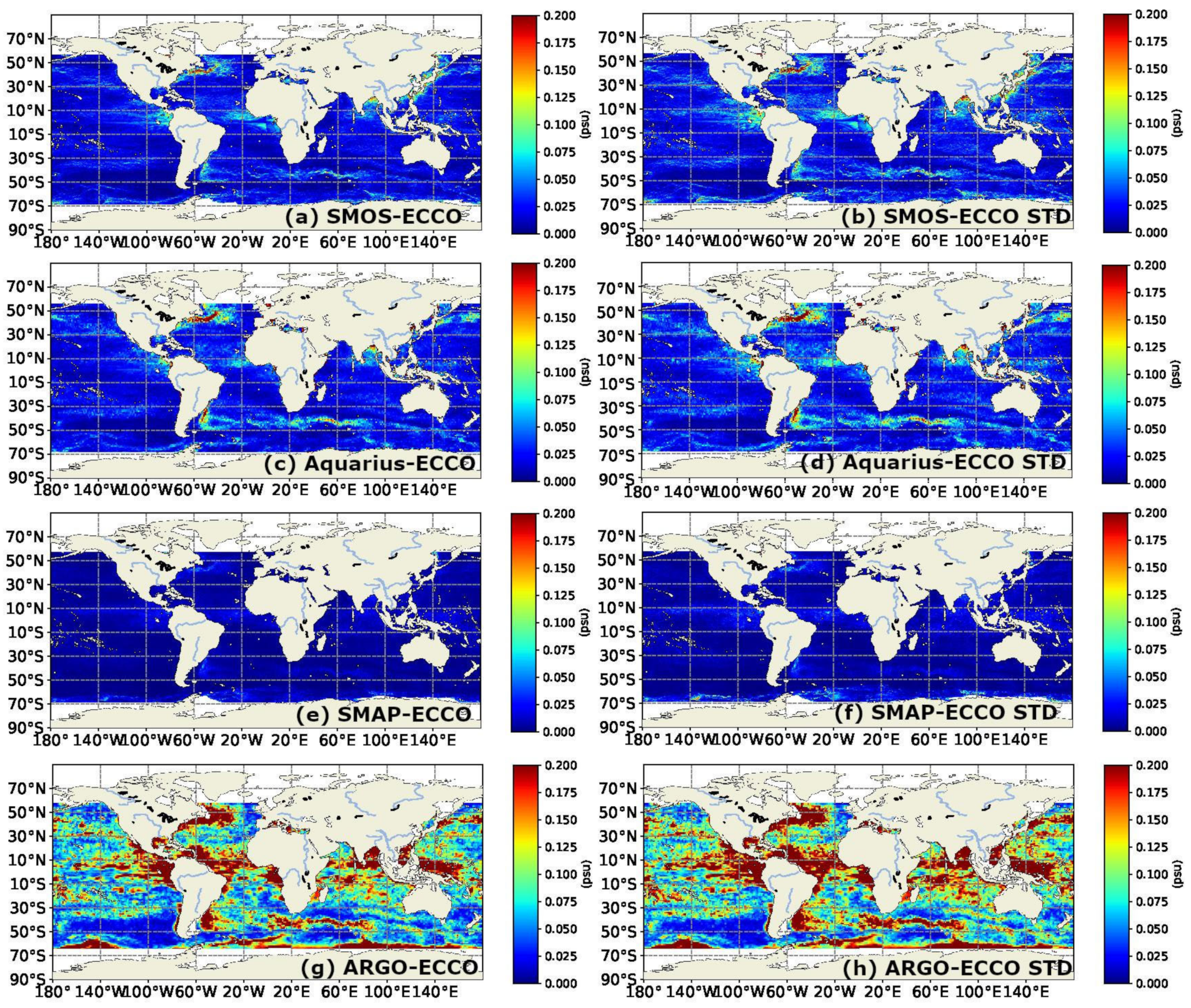
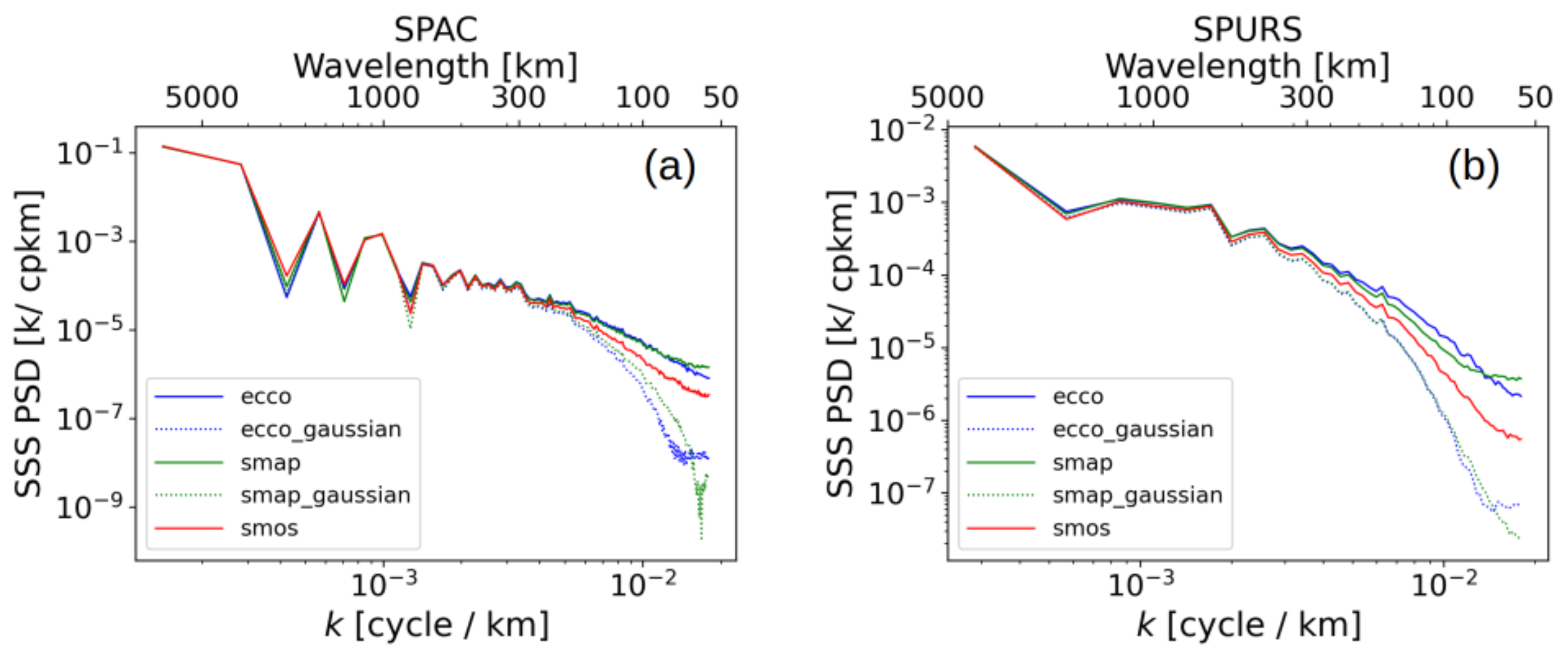
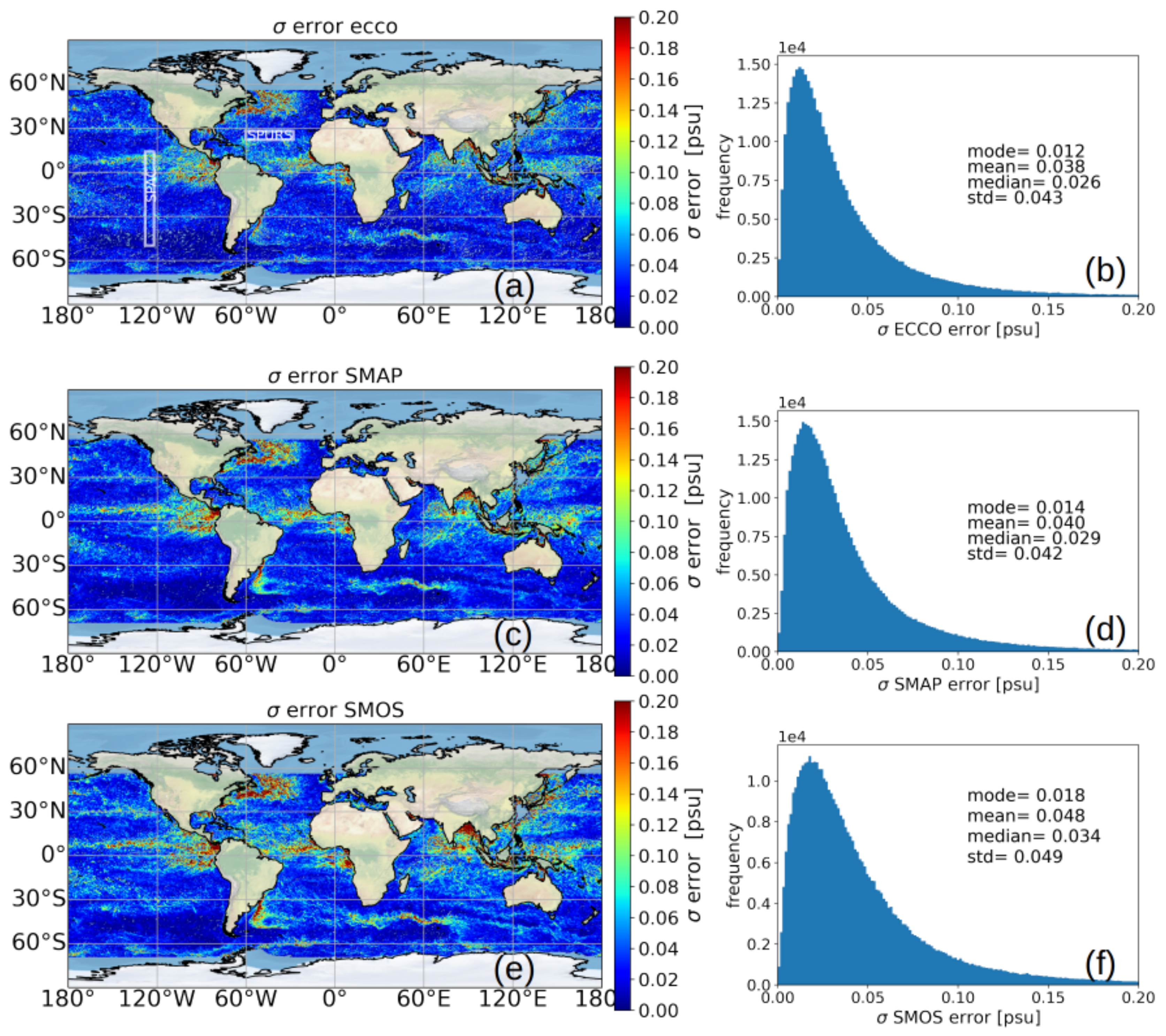
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Font, J.; Camps, A.; Borges, A.; Martin-Neira, M.; Boutin, J.; Reul, N.; Kerr, Y.; Hahne, A.; Mecklenburg, S. SMOS: The challenging sea surface salinity measurement from space. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reul, N.; Chapron, B.; Lee, T.; Donlon, C.; Boutin, J.; Alory, G. Sea surface salinity structure of the meandering Gulf Stream revealed by SMOS sensor. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 3141–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerloef, G.; DeCharon, A.; Lindstrom, E. Ocean Salinity and the Aquarius/SAC-D Mission: A New Frontier in Ocean Remote Sensing. J. Mar. Technol. Soc. 2013, 47, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G.; O’Neill, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Crow, W.T.; Edelstein, W.N.; Entin, J.K.; Goodman, S.D.; Jackson, T.J.; Johnson, J.; et al. The Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) Mission. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradova, N.; Lee, T.; Boutin, J.; Drushka, K.; Fournier, S.; Sabia, R.; Stammer, D.; Bayler, E.; Reul, N.; Gordon, A.; et al. Satellite Salinity Observing System: Recent Discoveries and the Way Forward. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnichenko, O.; Hacker, P.; Maximenko, N.; Lagerloef, G.; Potemra, J. Optimum interpolation analysis of Aquarius Sea surface salinity. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 602–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, J.; Reul, N.; Koehler, J.; Martin, A.; Catany, R.; Guimbard, S.; Rouffi, F.; Vergely, J.L.; Arias, M.; Chakroun, M.; et al. Satellite-Based Sea Surface Salinity Designed for Ocean and Climate Studies. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2021, 126, e2021JC017676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo, E.; González-Haro, C.; Hoareau, N.; Umbert, M.; González-Gambau, V.; Martínez, J.; Gabarró, C.; Turiel, A. Nine years of SMOS sea surface salinity global maps at the Barcelona Expert Center. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 857–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, T.; Wentz, F.J.; Manaster, A.; Lindsley, R. Remote Sensing Sytems SMAP Ocean Surface Salinities, Version 4.0; Validated Release; Remote Sensing Systems: Santa Rosa, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roemmich, D.; Gilson, J. The 2004–2008 mean and annual cycle of temperature, salinity, and steric height in the global ocean from the Argo Program. Prog. Oceanogr. 2009, 82, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, S.A.; Martin, M.J.; Rayner, N.A. EN4: Quality controlled ocean temperature and salinity profiles and monthly objective analyses with uncertainty estimates. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 6704–6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, T.; Wentz, F.J.; Le Vine, D.M. The salinity retrieval algorithms for the NASA Aquarius Version 5 and SMAP Version 3 releases. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerloef, G.; Colomb, F.R.; Le Vine, D.; Wentz, F.; Yueh, S.; Ruf, C.; Lilly, J.; Gunn, J.; Chao, Y.; Decharon, A.; et al. The Aquarius/SAC-D mission: Designed to meet the salinity remote- sensing challenge. Oceanography 2008, 21, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, F.M. Subfootprint variability of sea surface salinity observed during the SPURS-1 and SPURS-2 field campaigns. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, J.; Chao, Y.; Asher, W.E.; Delcroix, T.; Drucker, R.; Drushka, K.; Kolodziejczyk, N.; Lee, T.; Reul, N.; Reverdin, G.; et al. Satellite and in situ salinity: Understanding near-surface stratification and subfootprint variability. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 1391–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradova, N.T.; Ponte, R.M. Small-scale variability in sea surface salinity and implications for satellite-derived measurements. J. Atmos. Oceanic Tech. 2013, 30, 2689–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, F.M.; Fournier, S.; Brodnitz, S.; Ulfsax, K.; Zhang, H. Matchup Characteristics of Sea Surface Salinity Using a High-Resolution Ocean Model. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T. Consistency of Aquarius sea surface salinity with Argo products on various spatial and temporal scales. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 3857–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradova, N.T.; Ponte, R.M.; Fukumori, I.; Wang, O. Estimating satellite salinity errors for assimilation of Aquarius and SMOS data into climate models. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 4732–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcroix, T.; McPhaden, M.J.; Dessier, A.; Gouriou, Y. Time and space scales for sea surface salinity in the tropical oceans. Deep. Sea Res. Part I 2005, 52, 787–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradova, N.T.; Ponte, R.M. Assessing temporal aliasing in satellite-based salinity measurements. J. Atmos. Oceanic Tech. 2012, 29, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, T.; Wentz, F.; Manaster, A.; Lindsey, R. NASA/RSS SMAP Salinity: Version 4.0 Validated Release, Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD). Remote Sens. Syst. Tech. Rep. 2019, 82219, 55. Available online: https://data.remss.com/smap/SSS/Release_V4.0.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- Marshall, J.; Adcroft, A.; Hill, C.; Perelman, L.; Heisey, C. A finite-volume, incompressible Navier Stokes model for studies of the ocean on parallel computers. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1997, 102, 5753–5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forget, G.; Campin, J.-M.; Heimbach, P.; Hill, C.N.; Ponte, R.M.; Wunsch, C. ECCO version 4: An integrated framework for non-linear inverse modeling and global ocean state estimation. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 3071–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, C.B.; Gille, S.T.; Chereskin, T.K.; Menemenlis, D. Seasonality of submesoscale dynamics in the kuroshio extension. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 11304–11311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, L.-L.; Qiu, B.; Menemenlis, D.; Farrar, J.; Chao, Y.; Thompson, A.F.; Flexas, M.M.; Farrar, T. An observing system simulation experiment for the calibration and validation of the surface water ocean topography sea surface height measurement using in situ platforms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2018, 35, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Chen, S.; Klein, P.; Wang, J.; Torres, H.; Fu, L.-L.; Menemenlis, D. Seasonality in transition scale from balanced to unbalanced motions in the world ocean. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2018, 48, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, A.C.; Arbic, B.K.; Alford, M.H.; Ansong, J.K.; Farrar, J.T.; Menemenlis, D.; O’Rourke, A.K.; Richman, J.G.; Shriver, J.F.; Voet, G.; et al. Spectral decomposition of internal gravity wave sea surface height in global models. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 7803–7821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Wang, J.; Klein, P.; Thompson, A.F.; Menemenlis, D. Ocean submesoscales as a key component of the global heat budget. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbic, B.K.; Alford, M.H.; Ansong, J.K.; Buijsman, M.C.; Ciotti, R.B.; Farrar, J.T.; Hallberg, R.W.; Henze, C.E.; Hill, C.N.; Luecke, C.A.; et al. Primer on Global Internal Tide and Internal Gravity Wave Continuum Modeling in HYCOM and MITgcm. In New Frontiers in Operational Oceanography; Chassignet, E., Pascual, A., Tintoré, J., Verron, J., Eds.; GODAE OceanView: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 307–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps, A.; Corbella, I.; Bara, J.; Torres, F. Radiometric sensitivity computation in aperture synthesis interferometric radiometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuusela, M.; Stein, M.L. Locally stationary spatio-temporal interpolation of Argo profiling float data. Proc. R. Soc. A 2018, 474, 20180400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Kuusela, M.; Giglio, D.; Gray, A. Spatio-Temporal Local Interpolation of Global Ocean Heat Transport Using Argo Floats: A Debiased Latent Gaussian Process Approach. Ann. Appl. Stat. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2105.09707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekking, F.M.; Kraaikamp, C.; Lopuhaä, H.P.; Meester, L.E. A Modern Introduction to Probability and Statistics: Understanding Why and How; Springer: London, UK, 2005; Volume 488, ISBN 978-1-85233-896-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gambau, V.; Turiel, A.; González-Haro, C.; Martínez, J.; Olmedo, E.; Oliva, R.; Martín-Neira, M. Triple collocation analysis for two error-correlated datasets: Application to l-band brightness temperatures over land. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoareau, N.; Portabella, M.; Lin, W.; Ballabrera-Poy, J.; Turiel, A. Error characterization of sea surface salinity products using triple collocation analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 5160–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratheesh, S.; Mankad, B.; Basu, S.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, R. Assessment of satellite-derived sea surface salinity in the Indian Ocean. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 10, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menemenlis, D.; Campin, J.M.; Heimbach, P.; Hill, C.; Lee, T.; Nguyen, A.; Schodlok, M.; Zhang, H. ECCO2: High resolution global ocean and sea ice data synthesis. Mercator Ocean. Q. Newsl. 2008, 31, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Argo. Argo Float Data and Metadata from Global Data Assembly Centre (Argo GDAC); Seanoe: Plouzané, France, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
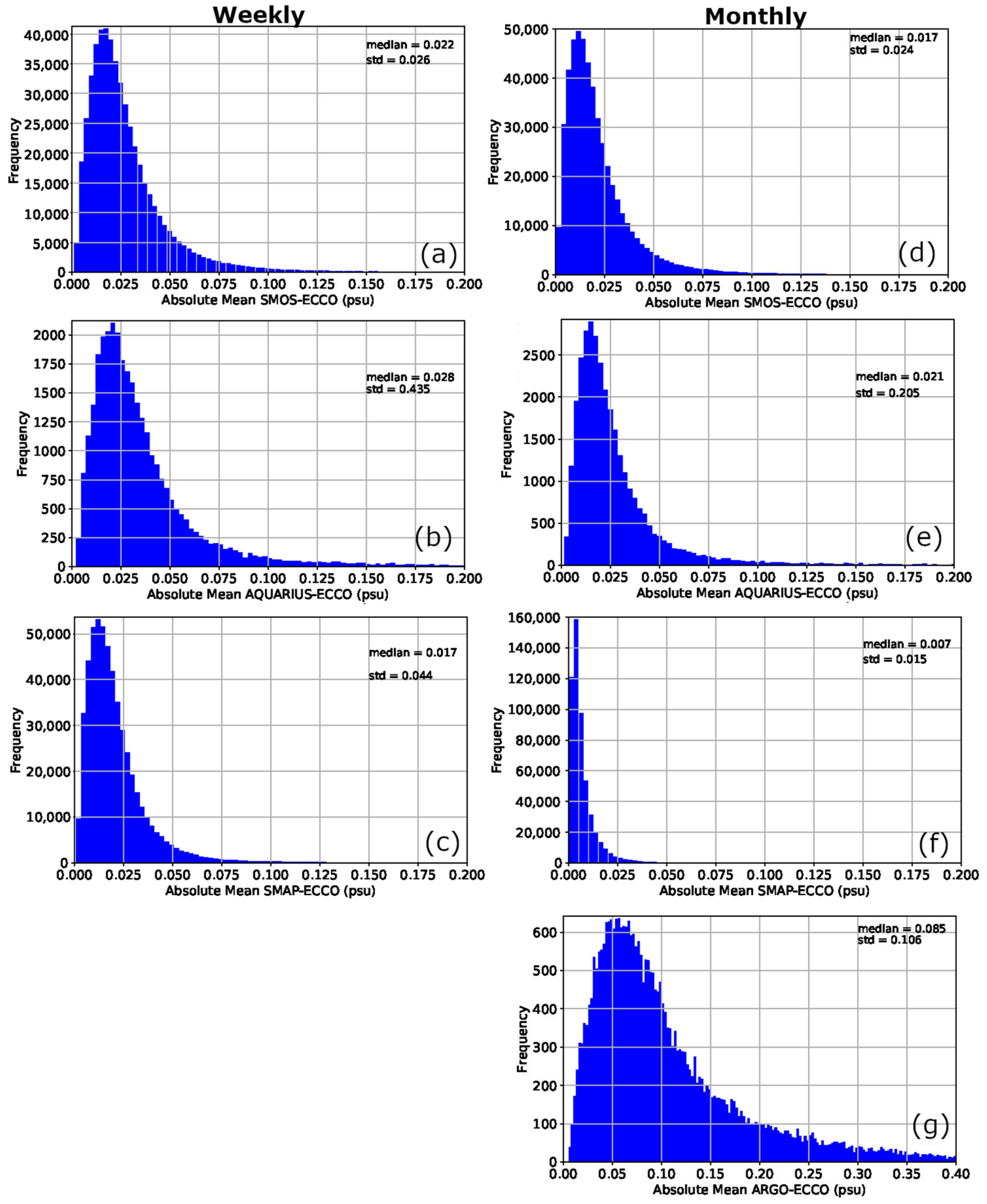
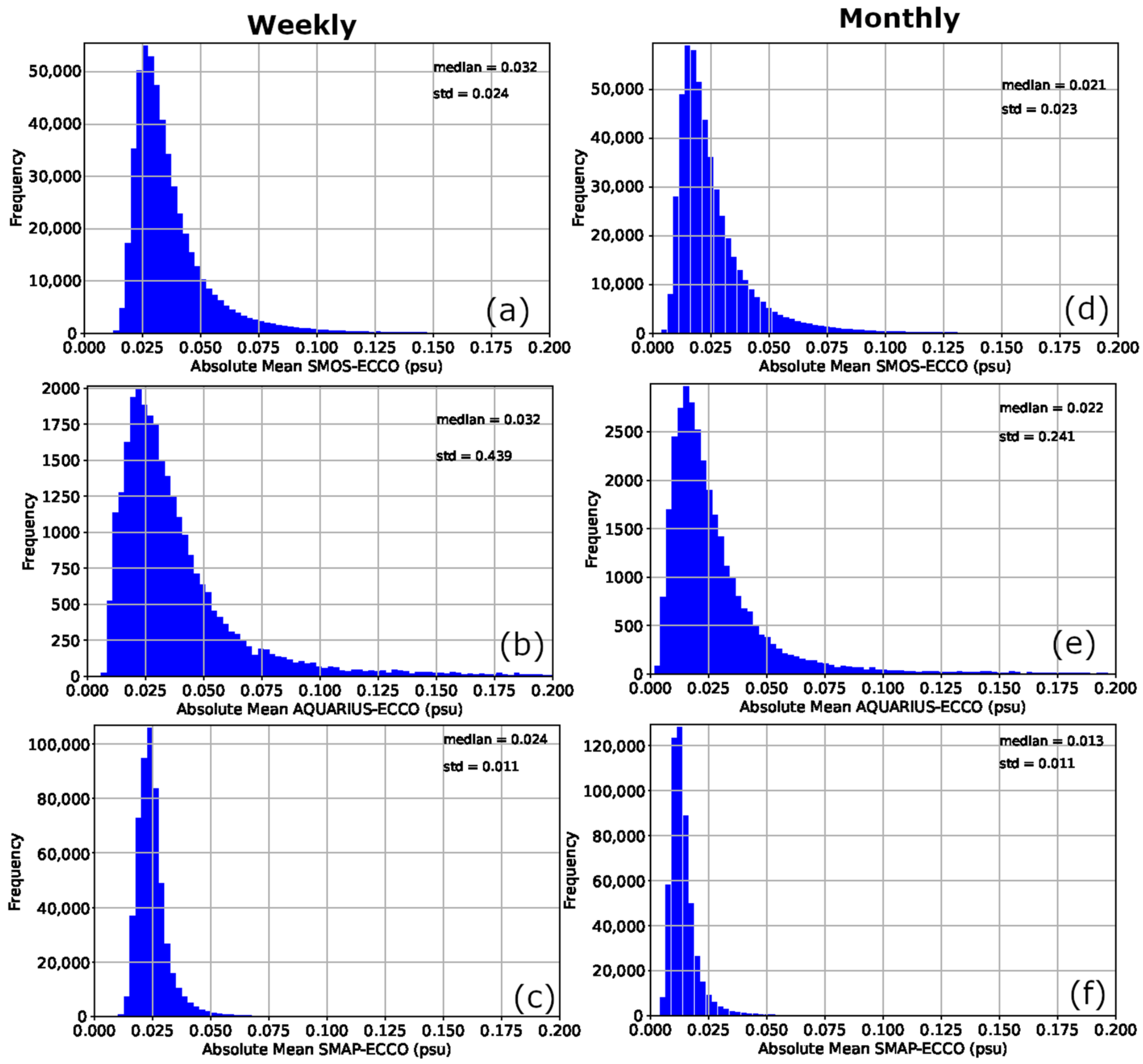
| First Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Median | Std | IQR | |
| SMAP-ECCO (psu) | 0.022 | 0.017 | 0.044 | 0.016 |
| SMOS-ECCO (psu) | 0.028 | 0.022 | 0.026 | 0.020 |
| Aquarius-ECCO (psu) | 0.087 | 0.028 | 0.435 | 0.027 |
| CTC Analysis | ||||
| mean | median | std | IQR | |
| ECCO (psu) | 0.038 | 0.026 | 0.043 | 0.033 |
| SMAP (psu) | 0.040 | 0.029 | 0.042 | 0.034 |
| SMOS (psu) | 0.048 | 0.034 | 0.049 | 0.041 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fournier, S.; Bingham, F.M.; González-Haro, C.; Hayashi, A.; Ulfsax Carlin, K.M.; Brodnitz, S.K.; González-Gambau, V.; Kuusela, M. Quantification of Aquarius, SMAP, SMOS and Argo-Based Gridded Sea Surface Salinity Product Sampling Errors. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020422
Fournier S, Bingham FM, González-Haro C, Hayashi A, Ulfsax Carlin KM, Brodnitz SK, González-Gambau V, Kuusela M. Quantification of Aquarius, SMAP, SMOS and Argo-Based Gridded Sea Surface Salinity Product Sampling Errors. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(2):422. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020422
Chicago/Turabian StyleFournier, Séverine, Frederick M. Bingham, Cristina González-Haro, Akiko Hayashi, Karly M. Ulfsax Carlin, Susannah K. Brodnitz, Verónica González-Gambau, and Mikael Kuusela. 2023. "Quantification of Aquarius, SMAP, SMOS and Argo-Based Gridded Sea Surface Salinity Product Sampling Errors" Remote Sensing 15, no. 2: 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020422
APA StyleFournier, S., Bingham, F. M., González-Haro, C., Hayashi, A., Ulfsax Carlin, K. M., Brodnitz, S. K., González-Gambau, V., & Kuusela, M. (2023). Quantification of Aquarius, SMAP, SMOS and Argo-Based Gridded Sea Surface Salinity Product Sampling Errors. Remote Sensing, 15(2), 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020422





