A Robust InSAR Phase Unwrapping Method via Improving the pix2pix Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. pu-pix2pix
2.1. The Principle of Phase Unwrapping
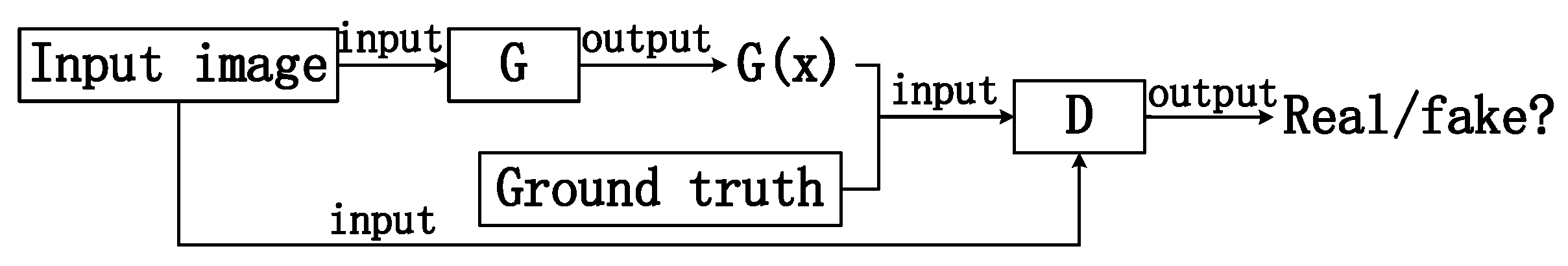
2.2. pix2pix Model
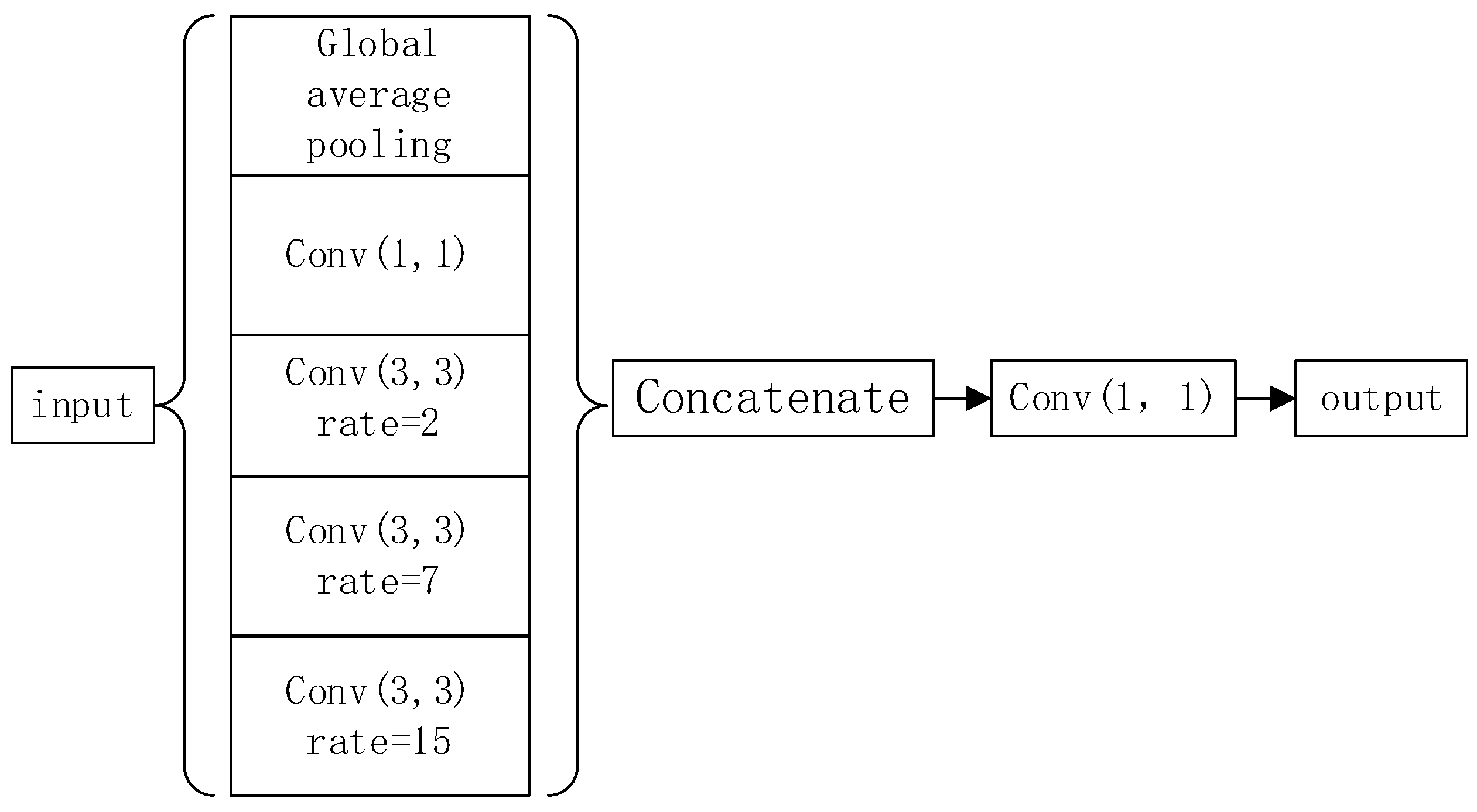
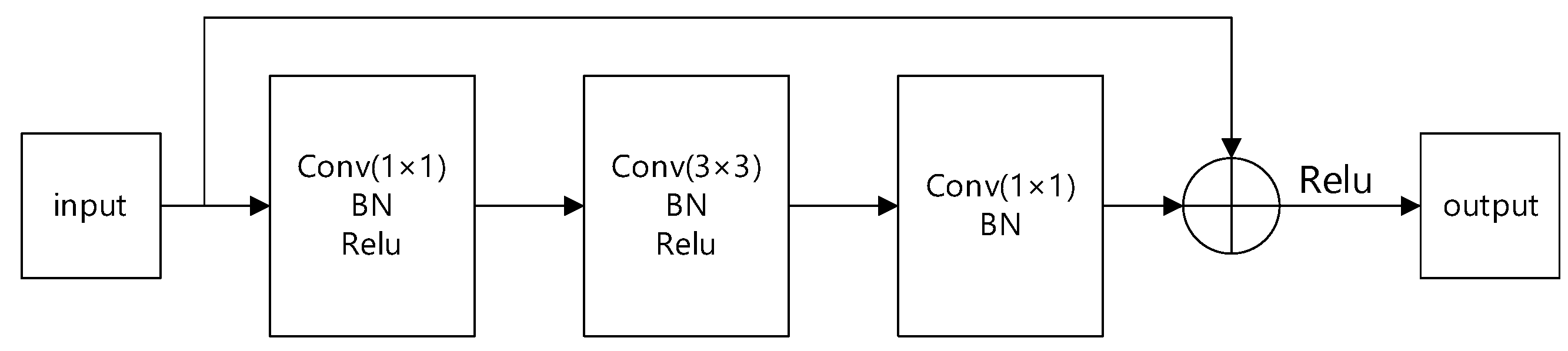
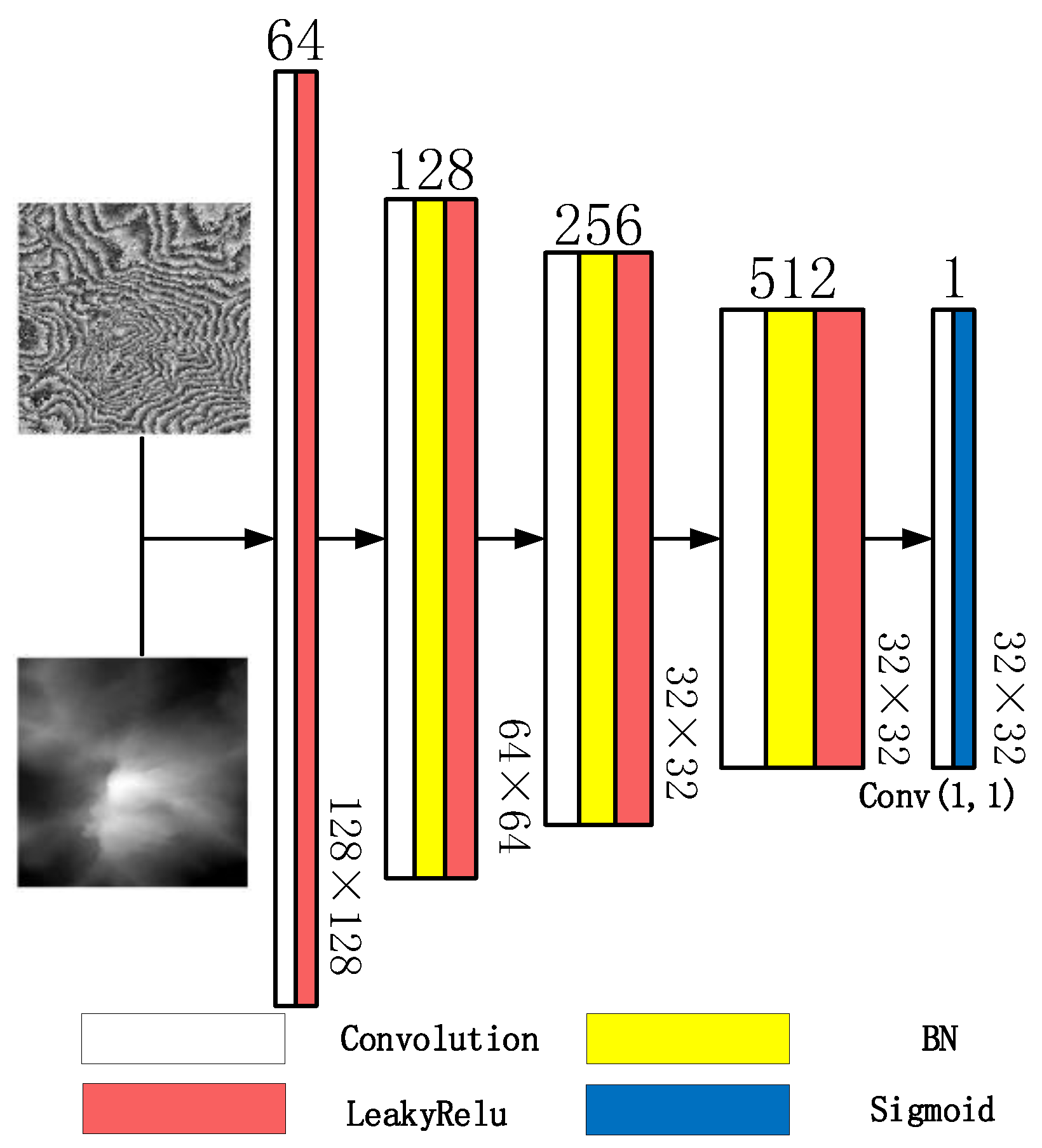
2.3. The Structure of pu-pix2pix
2.4. Loss Function
3. Experiments and Results
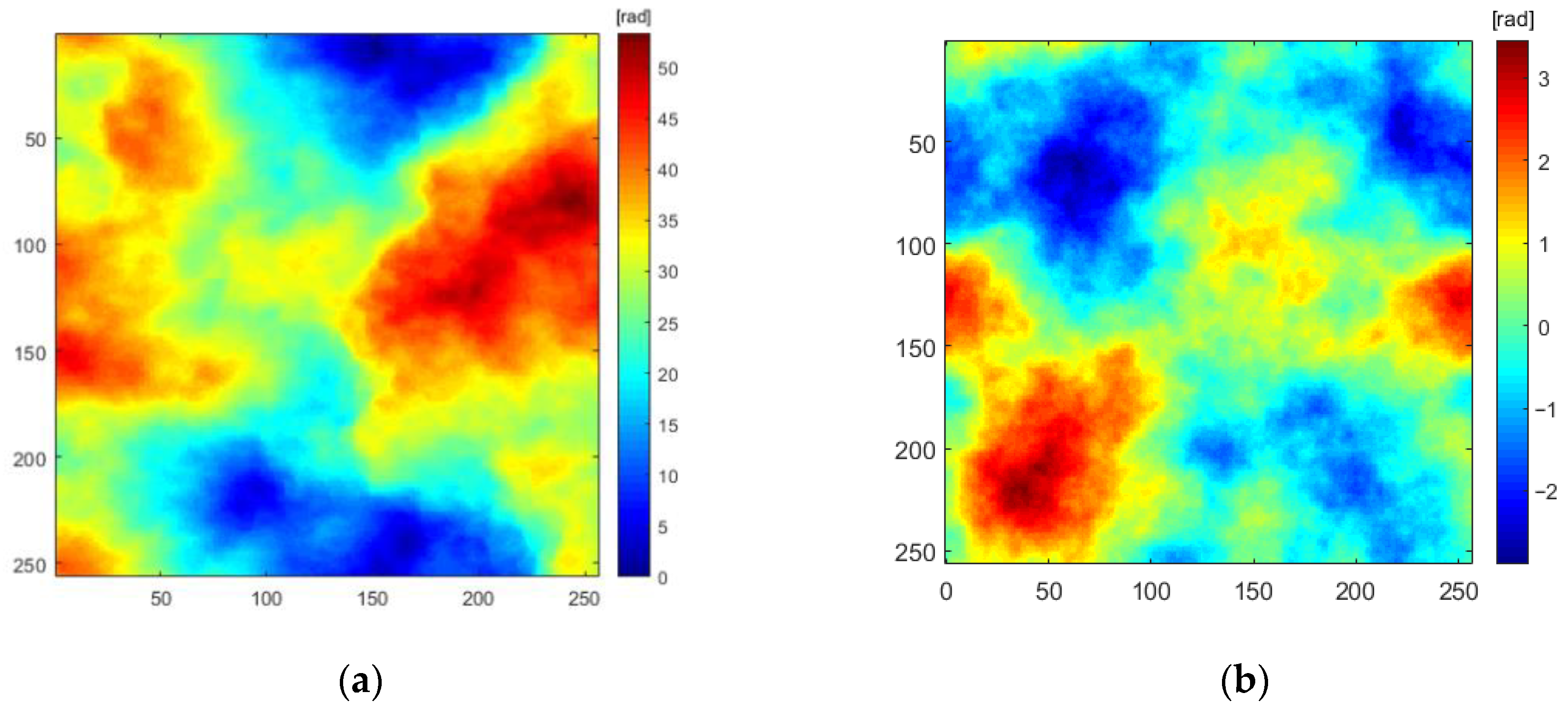
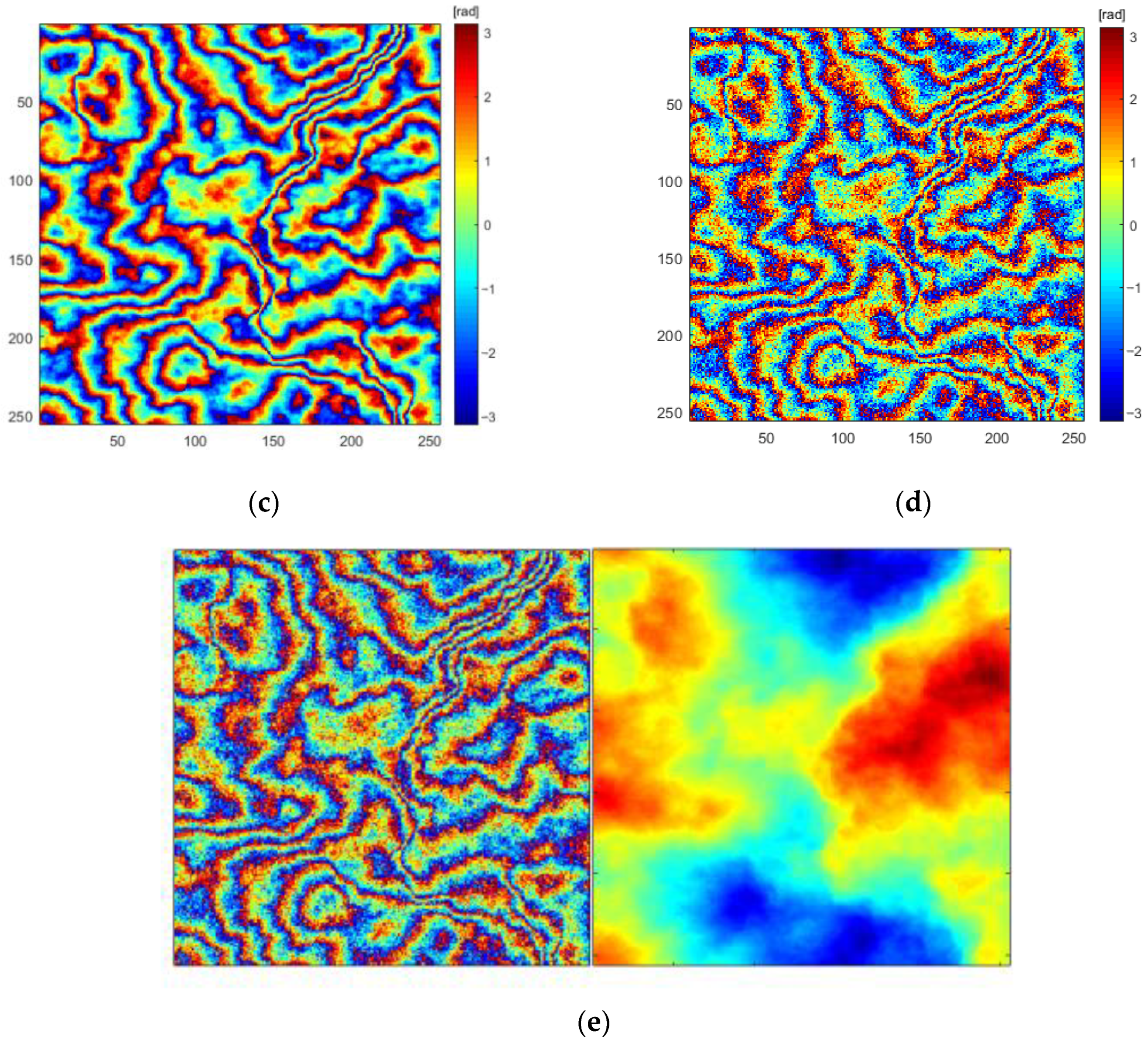
3.1. Dataset Generation
- (1)
- Simulate the topography phase. There are two methods for this: one is to specify the size and elevation range of the row and column, and generate an analog digital elevation model according to the random polynomial to obtain the topography phase image; the other is to use the existing DEM (digital elevation model) data, then simulate the oblique range imaging process of dual-antenna SAR sensors, specify the baseline length, and obtain a phase image containing only terrain errors, which is considered to be a true terrain phase image.
- (2)
- Simulate the atmospheric phase noise. The power spectrum inversion method is used to simulate this atmospheric phase noise. Its basic principle is to filter the complex Gauss random number matrix with a power spectrum function consistent with atmospheric turbulence, and then use the inverse Fourier transform to obtain the atmospheric phase noise.
- (3)
- Phase rewrapped. To perform the phase rewrapped operation, combine the terrain phase result with the atmospheric phase, and wrap the phase value to .
- (4)
- Add noise. The gamma distribution is used to simulate the InSAR phase noise, and the wrapped phase image is noised to obtain the wrapped phase image with noise.
- (5)
- Merge the images. To meet the input conditions of the pu-pix2pix model’s paired image training, first cut the phase diagram and the wrapped phase diagram with noise to 256 × 256 size, and then combine them into multiple 256 × 512 size images.
3.2. Performance Evaluation Index
3.3. Experimental Settings
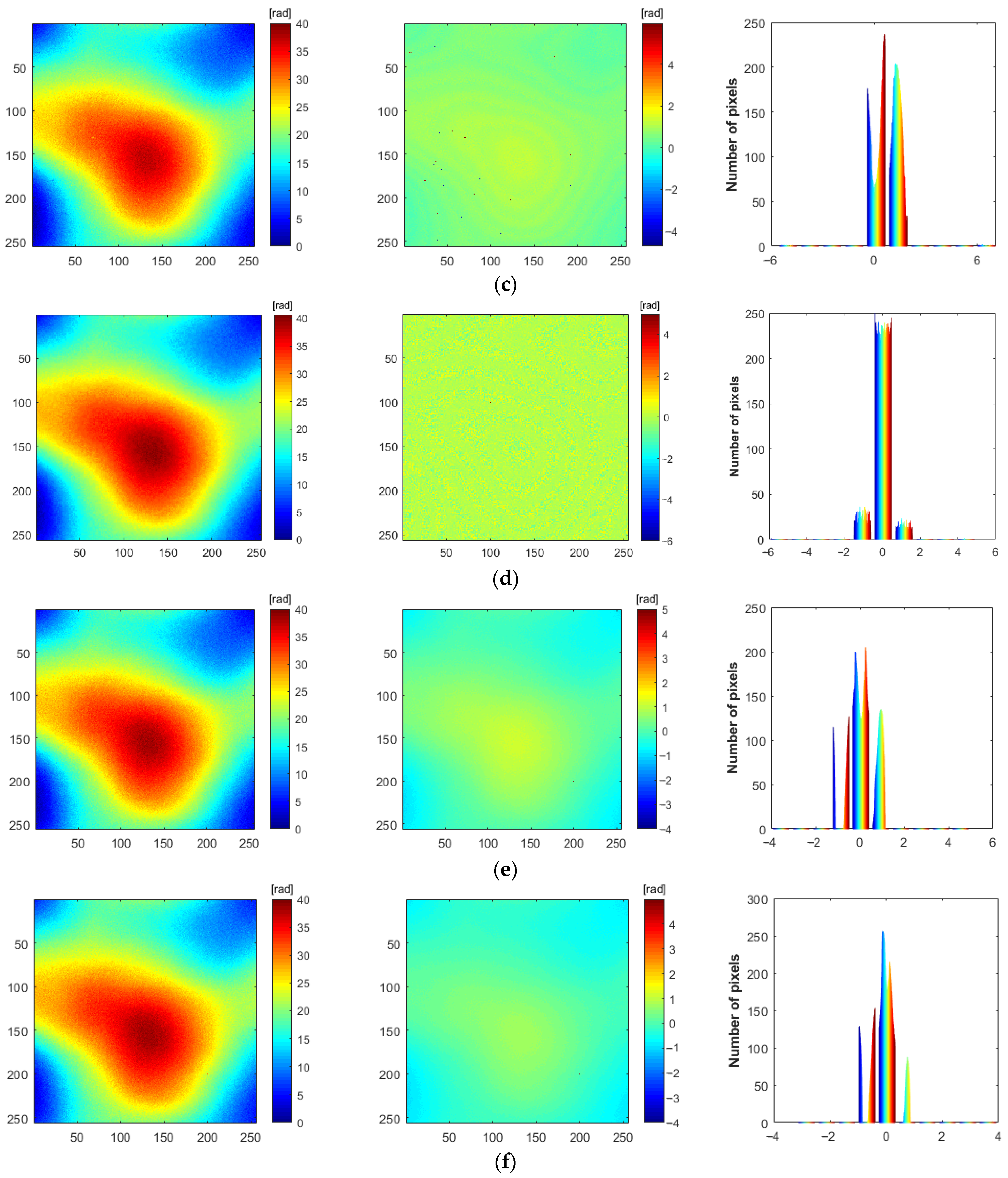
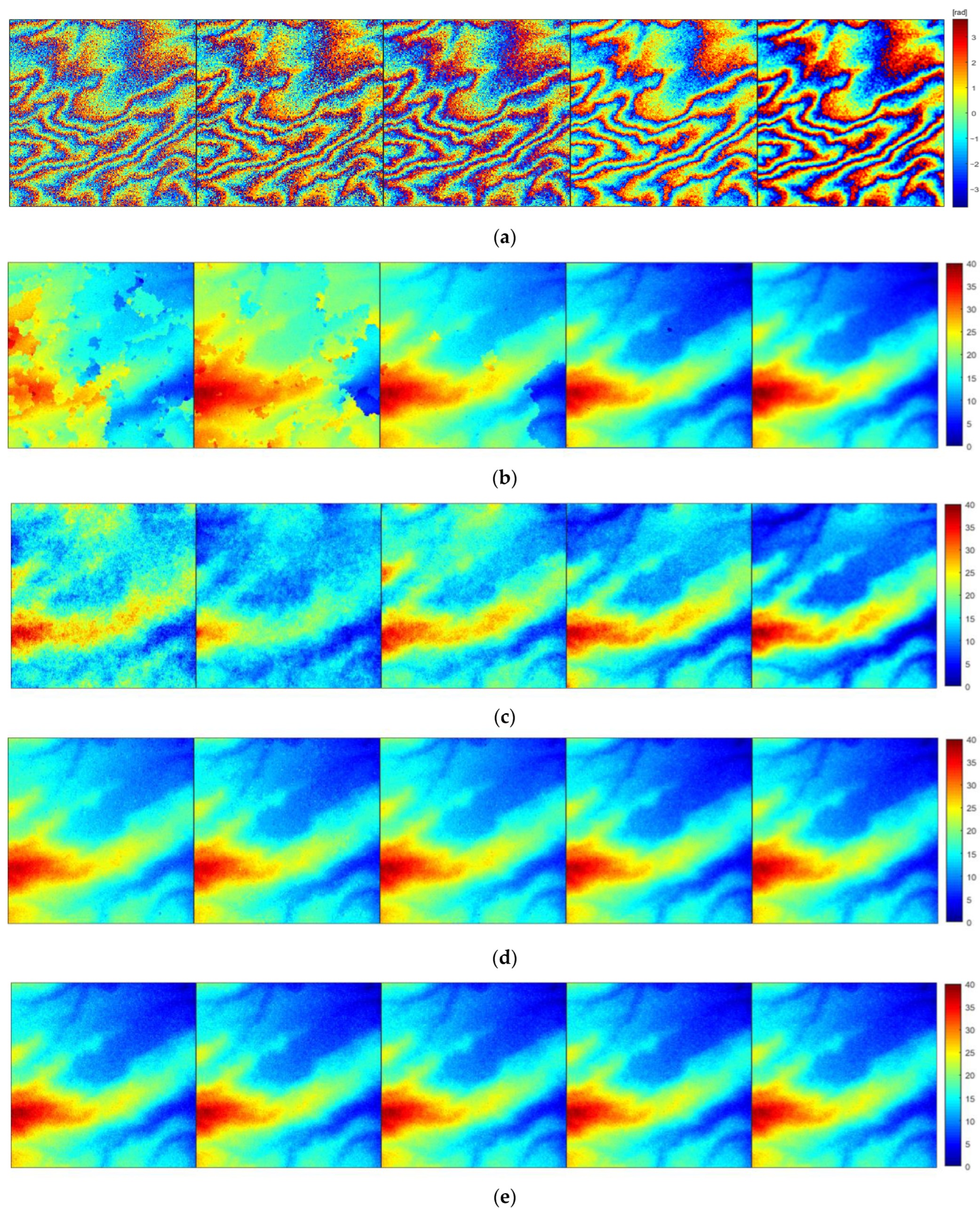
3.4. Analysis of Unwrapping Results Based on Simulated Data
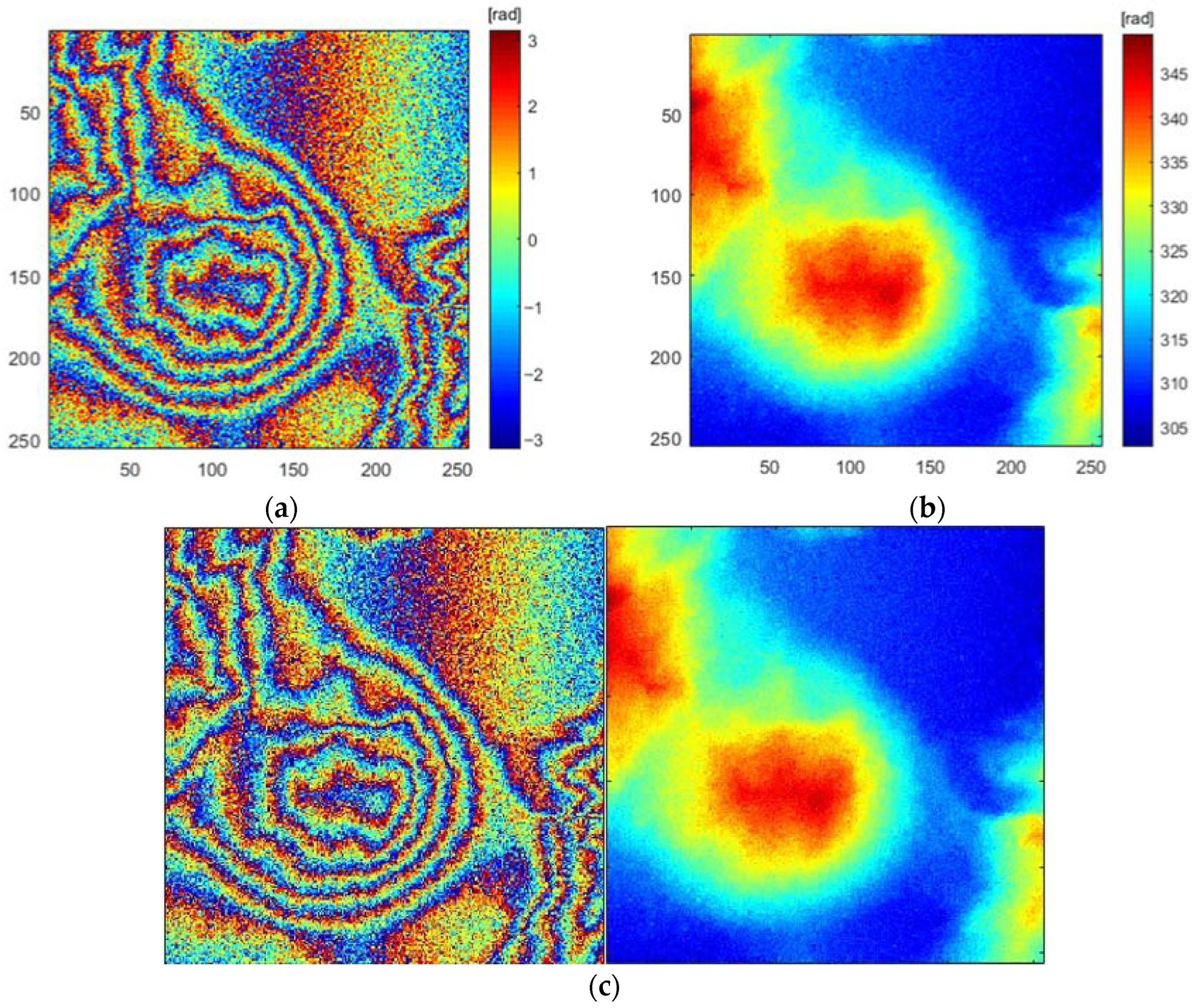
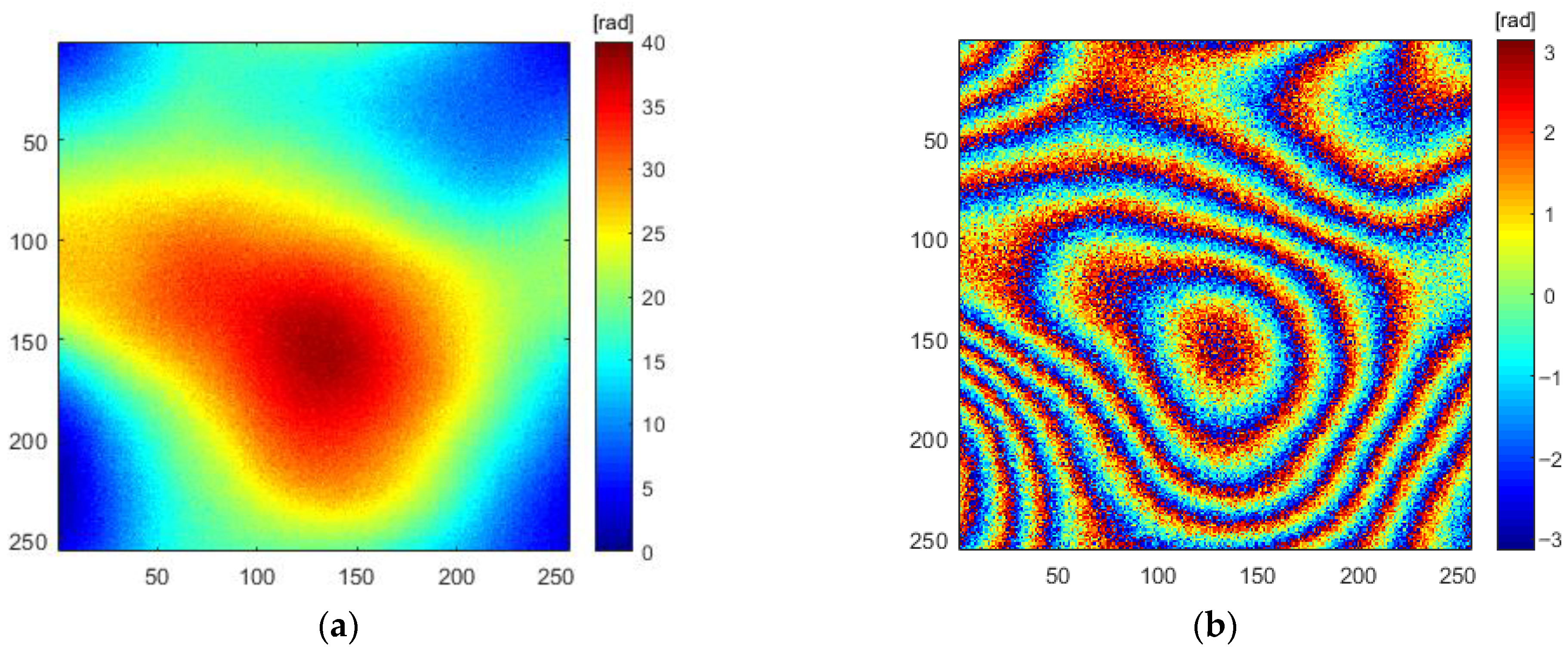
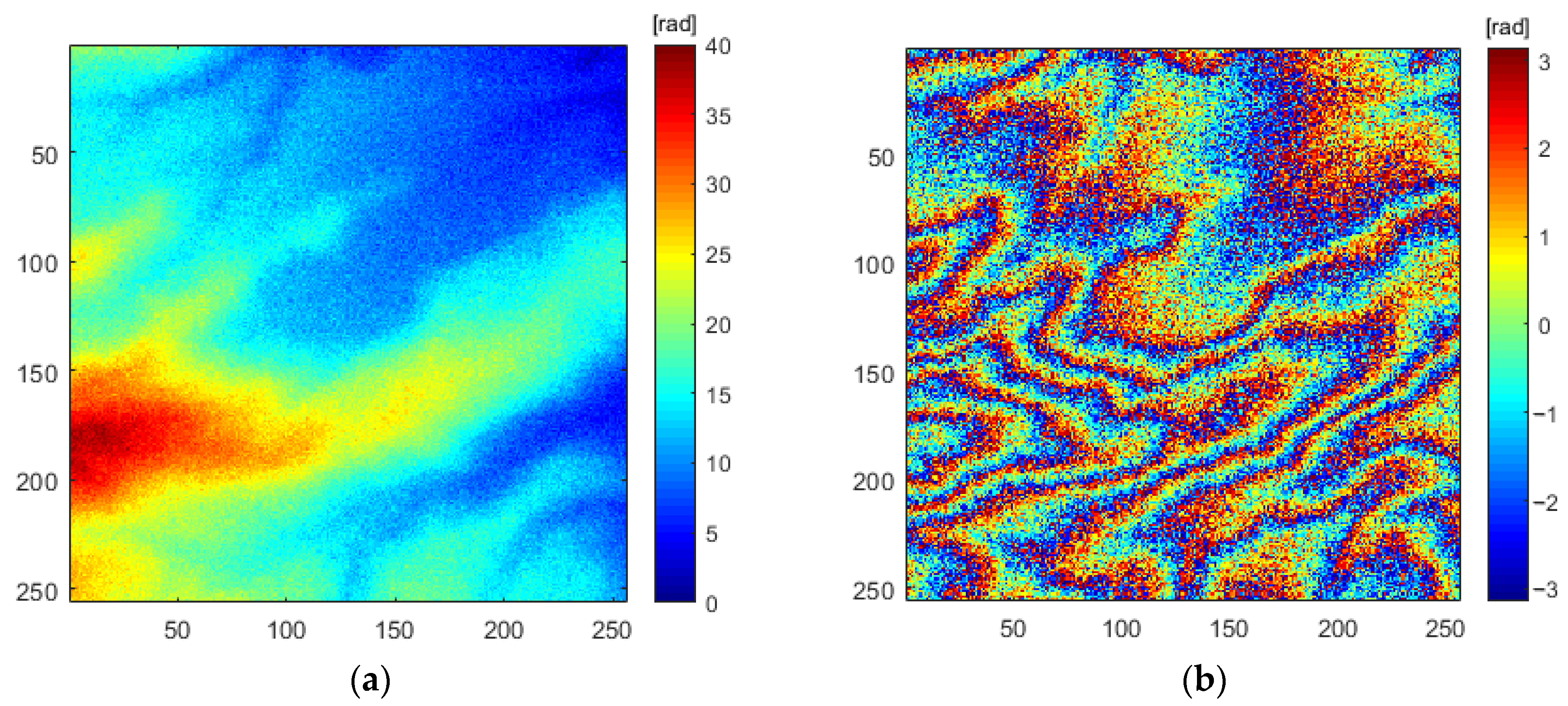
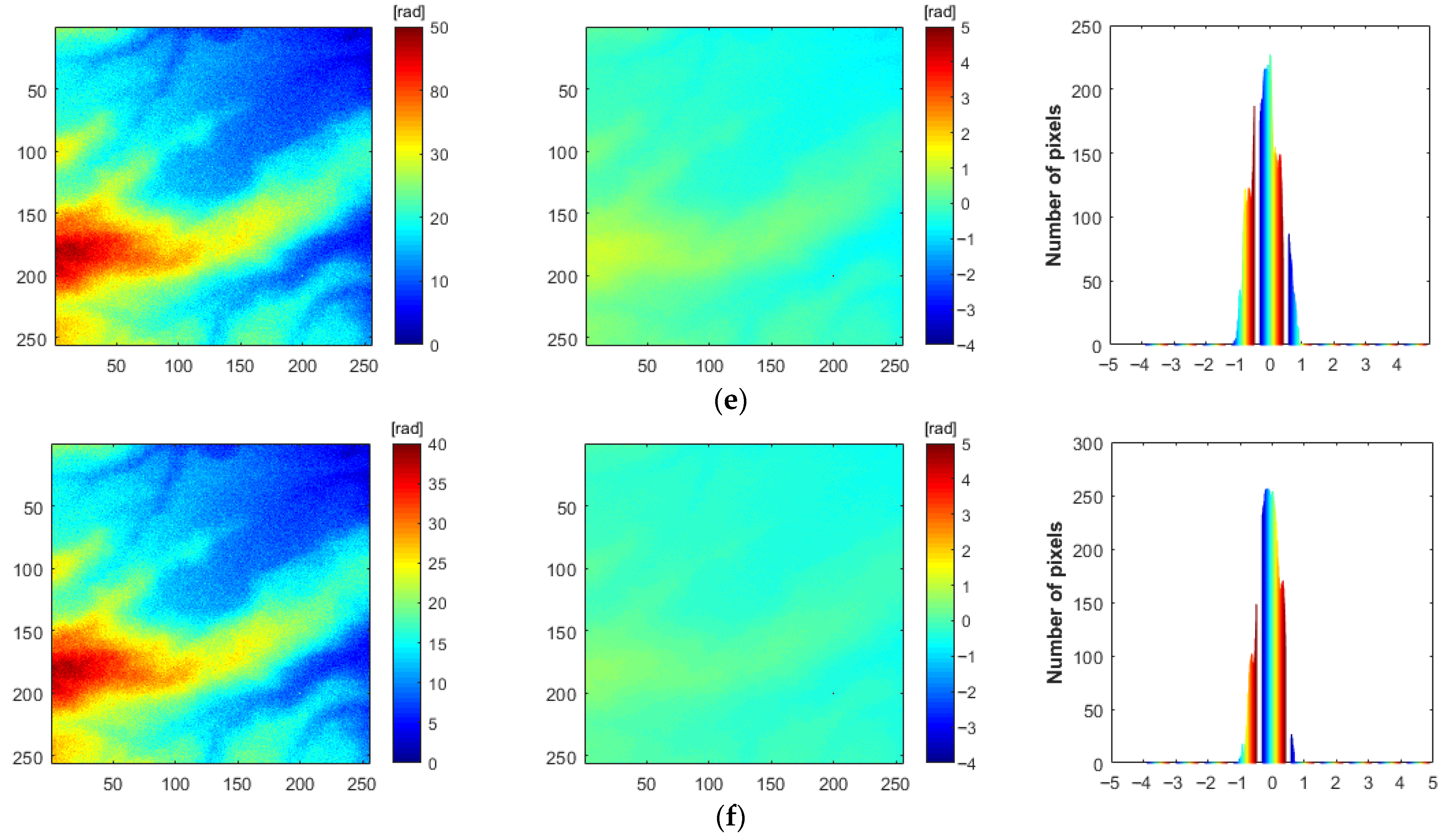
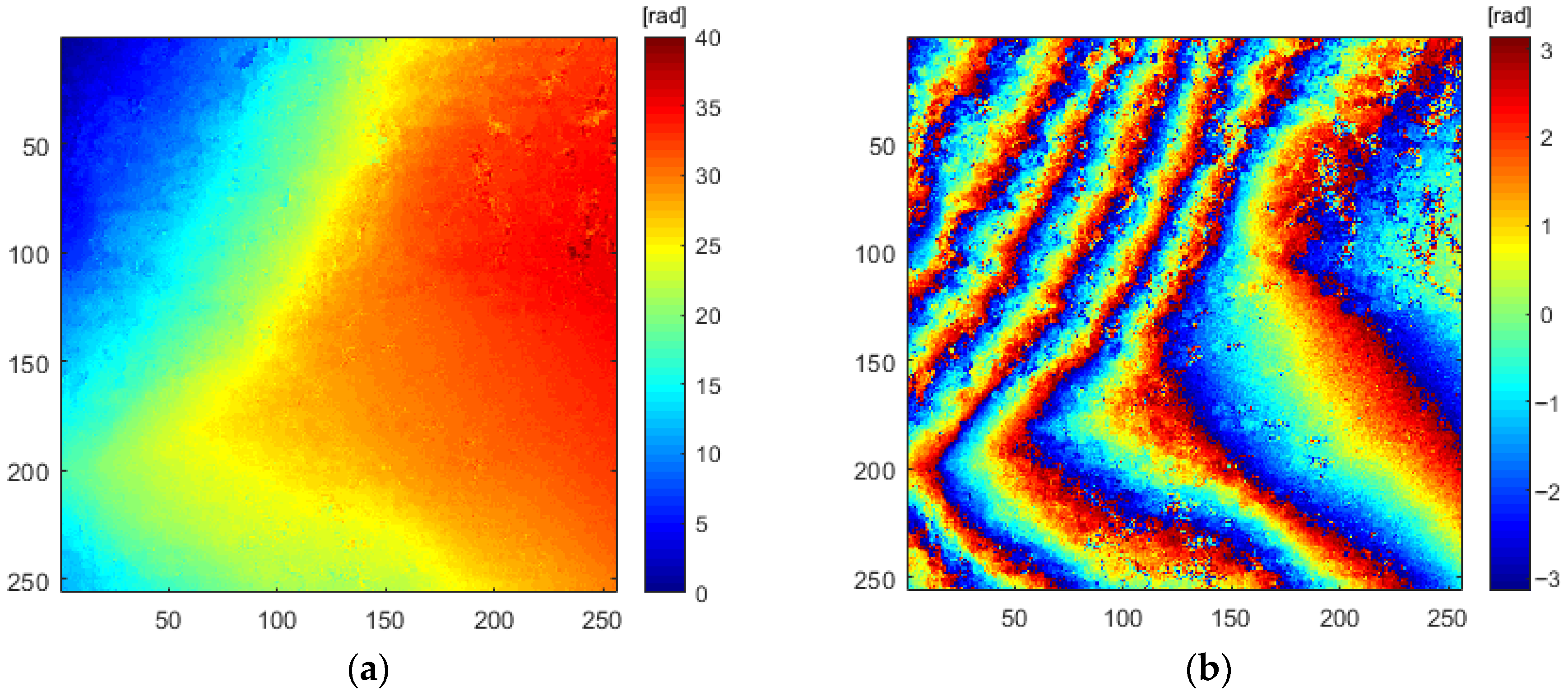
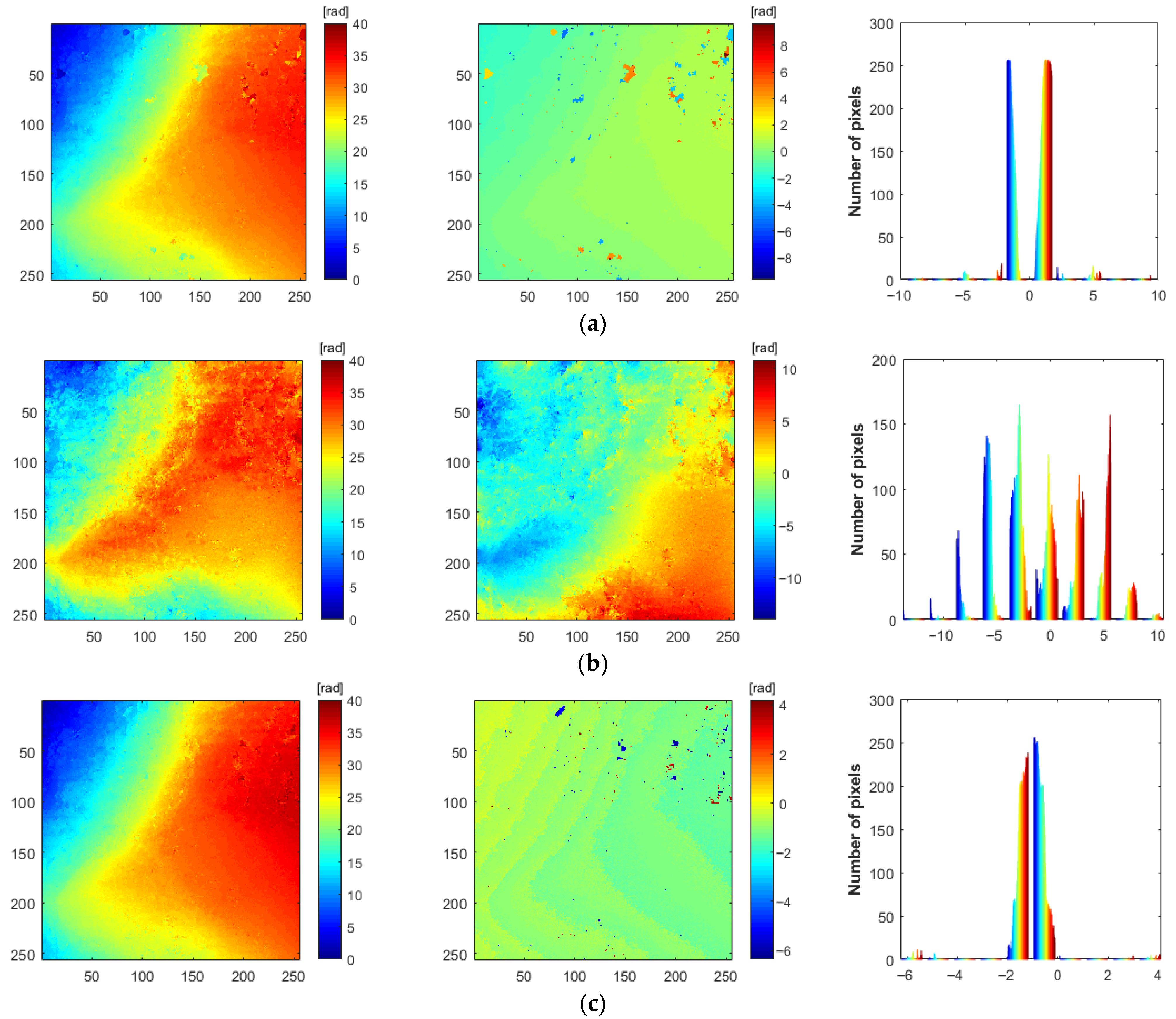
3.5. Analysis of Unwrapping Results Based on Real Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Itoh, K. Analysis of the phase unwrapping algorithm. Appl. Opt. 1982, 21, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A.; Werner, C.L. Satellite radar interferometry: Two-dimensional phase unwrapping. Radio Sci. 2016, 23, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Wei, X.; Huang, X. Two new practical methods for phase unwrapping. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience & Remote Sensing Symposium, Firenze, Italy, 10–14 July 1995; pp. 196–198. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, T.J. Consistent 2-D phase unwrapping guided by a quality map. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience & Remote Sensing Symposium, Lincoln, NE, USA, 31 May 1996; pp. 2057–2059. [Google Scholar]
- Quiroga, J.A.; González-Cano, A.; Bernabeu, E. Phase-unwrapping algorithm based on an adaptive criterion. Appl. Opt. 1995, 34, 2560–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Cumming, I. A region-growing algorithm for InSAR phase unwrapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, G.; Cheng, H.; Liu, W. InSAR Phase Unwrapping Using Least Squares Method with Integer Ambiguity Resolution and Edge Detection. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2012, 41, 441–448. [Google Scholar]
- Takajo, H.; Takahashi, T. Least-squares phase estimation from the phase difference. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1988, 5, 1818–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritt, M.D.; Shipman, J.S. Least-squares two-dimensional phase unwrapping using FFT’s. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 706–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, D.L. Least-square fitting a wave-front distortion estimate to an array of phase-difference measurements. Opt. Soc. Am. J. 1977, 67, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M. A novel phase unwrapping method based on network programming. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Zebker, H.A. Two-dimensional phase unwrapping with use of statistical models for cost functions in nonlinear optimization. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2001, 18, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Valadao, G. Phase Unwrapping via Graph Cuts. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.M.; Zeng, Q.N. Efficient and robust phase unwrapping algorithm based on unscented Kalman filter, the strategy of quantizing paths-guided map, and pixel classification strategy. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 9294–9307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.M.; Li, Y.H. Enhanced phase unwrapping algorithm based on unscented Kalman filter, enhanced phase gradient estimator, and path-following strategy. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 4049–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Pi, Y. Phase noise filtering and phase unwrapping method based on unscented Kalman filter. Syst. Eng. Electron. J. 2011, 22, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffeld, O.; Nies, H.; Knedlik, S.; Yu, W. Phase Unwrapping for SAR Interferometry—A Data Fusion Approach by Kalman Filtering. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 46, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Espla, J.J.; Martinez-Marin, T.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M. Using a Grid-Based Filter to Solve InSAR Phase Unwrapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 2, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Espla, J.J.; Martinez-Marin, T.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M. An Optimized Algorithm for InSAR Phase Unwrapping Based on Particle Filtering, Matrix Pencil, and Region-Growing Techniques. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Espla, J.J.; Martinez-Marin, T.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M. A Particle Filter Approach for InSAR Phase Filtering and Unwrapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lan, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Xu, J.; Lee, H. Phase Unwrapping in InSAR: A Review. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 7, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, L.; Zhou, L.; Shi, J.; Wei, S. A Robust InSAR Phase Unwrapping Method via Phase Gradient Estimation Network. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Jiang, H.; Sun, Z.; Wang, R.; Han, Y. A Parallel InSAR Phase Unwrapping Method Based on Separated Continuous Regions. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yu, H.; Lan, Y.; Xing, M. Artificial Intelligence Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Phase Unwrapping: A Review. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 9, 10–28. [Google Scholar]
- Rouet-leduc, B.; Dalaison, M.; Johnson, P.A.; Jolivet, R. Deep learning InSAR: Atmospheric noise removal and small deformation signal extraction from InSAR time series using a convolutional autoencoder. Am. Geophys. Union Fall Meet. 2019, 2019, G21A-07. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Zimmer, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Kottayil, N.K.; Ghuman, P.; Cheng, I. DeepInSAR: A Deep Learning Framework for SAR Interferometric Phase Restoration and Coherence Estimation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sica, F.; Gobbi, G.; Rizzoli, P.; Bruzzone, L. Φ-Net: Deep Residual Learning for InSAR Parameters Estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 3917–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yu, H.; Yang, L. Deep Convolutional Neural Network-Based Robust Phase Gradient Estimation for Two-Dimensional Phase Unwrapping Using SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 4653–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qian, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X. An Improved Least Square Phase Unwrapping Algorithm Combined with Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 3384–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yu, H.; Yang, L.; Xing, M. Deep Learning-Based Branch-Cut Method for InSAR Two-Dimensional Phase Unwrapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, G.; Pascazio, V.; Schirinzi, G.; Vitale, S.; Xing, M.; Yu, H.; Zhou, L. Joint Phase Unwrapping and Speckle Filtering by Using Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 3376–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, R. A Deep Learning Based Method for Local Subsidence Detection and InSAR Phase Unwrapping: Application to Mining Deformation Monitoring. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020–2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–2 October 2020; pp. 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yu, H.; Pascazio, V.; Xing, M. PU-GAN: A One-Step 2-D InSAR Phase Unwrapping Based on Conditional Generative Adversarial Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoorthi, G.E.; Gorthi, S.; Gorthi, R.K.S.S. PhaseNet: A Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Two-Dimensional Phase Unwrapping. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 26, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tian, X.; Shao, J.; Luo, H.; Liang, R. Phase unwrapping in optical metrology via denoised and convolutional segmentation networks. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 14903–14912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoorthi, G.E.; Gorthi, R.K.S.S.; Gorthi, S. PhaseNet 2.0: Phase Unwrapping of Noisy Data Based on Deep Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4862–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, Z. The One Hundred Layers Tiramisu: Fully Convolutional DenseNets for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiglia, D.C.; Pritt, M. Two-Dimensional Phase Unwrapping: Theory, Algorithms, and Software; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Wang, R.; Deng, Y.K.; Chen, R.; Shao, Y.; Yuan, Z. A New Quality Map for 2-D Phase Unwrapping Based on Gray Level Co-Occurrence Matrix. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 11, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemao, Q.; Gao, W.; Wang, H. Windowed Fourier-filtered and quality-guided phase-unwrapping algorithm. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 5420–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Nets. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional Generative Adversarial Nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1784. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1611.07004. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, M.; Pascazio, V.; Yu, H. A Special Issue on Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry [From the Guest Editors]. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2020, 8, 6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Method | RMSE (Rad) | Time (s) |
|---|---|---|
| Quality guide | 5.5797 | 1.3982 |
| LS | 5.0503 | 1.1495 |
| MCF | 1.8911 | 3.2251 |
| U-net | 1.5424 | 0.1474 |
| pix2pix | 1.5514 | 0.1517 |
| pu-pix2pix | 1.5129 | 0.1526 |
| Method | The First Set of Real Data | The Second Set of Real Data | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE (Rad) | Time (s) | RMSE (Rad) | Time (s) | |
| Quality guide | 14.3751 | 1.4734 | 4.1260 | 1.3154 |
| LS | 13.0493 | 1.3549 | 9.6236 | 1.3241 |
| MCF | 2.7510 | 4.0452 | 2.8114 | 3.3454 |
| U-net | 2..9514 | 0.1621 | 2.5786 | 0.1579 |
| pix2pix | 2.2513 | 0.1645 | 2.1568 | 0.1631 |
| pu-pix2pix | 2.2207 | 0.1631 | 2.1321 | 0.1570 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Huang, G.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Lu, L.; Huo, W. A Robust InSAR Phase Unwrapping Method via Improving the pix2pix Network. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4885. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194885
Zhang L, Huang G, Li Y, Yang S, Lu L, Huo W. A Robust InSAR Phase Unwrapping Method via Improving the pix2pix Network. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(19):4885. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194885
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Long, Guoman Huang, Yutong Li, Shucheng Yang, Lijun Lu, and Wenhao Huo. 2023. "A Robust InSAR Phase Unwrapping Method via Improving the pix2pix Network" Remote Sensing 15, no. 19: 4885. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194885
APA StyleZhang, L., Huang, G., Li, Y., Yang, S., Lu, L., & Huo, W. (2023). A Robust InSAR Phase Unwrapping Method via Improving the pix2pix Network. Remote Sensing, 15(19), 4885. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194885






