Spatiotemporal Analysis of Landscape Ecological Risk and Driving Factors: A Case Study in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
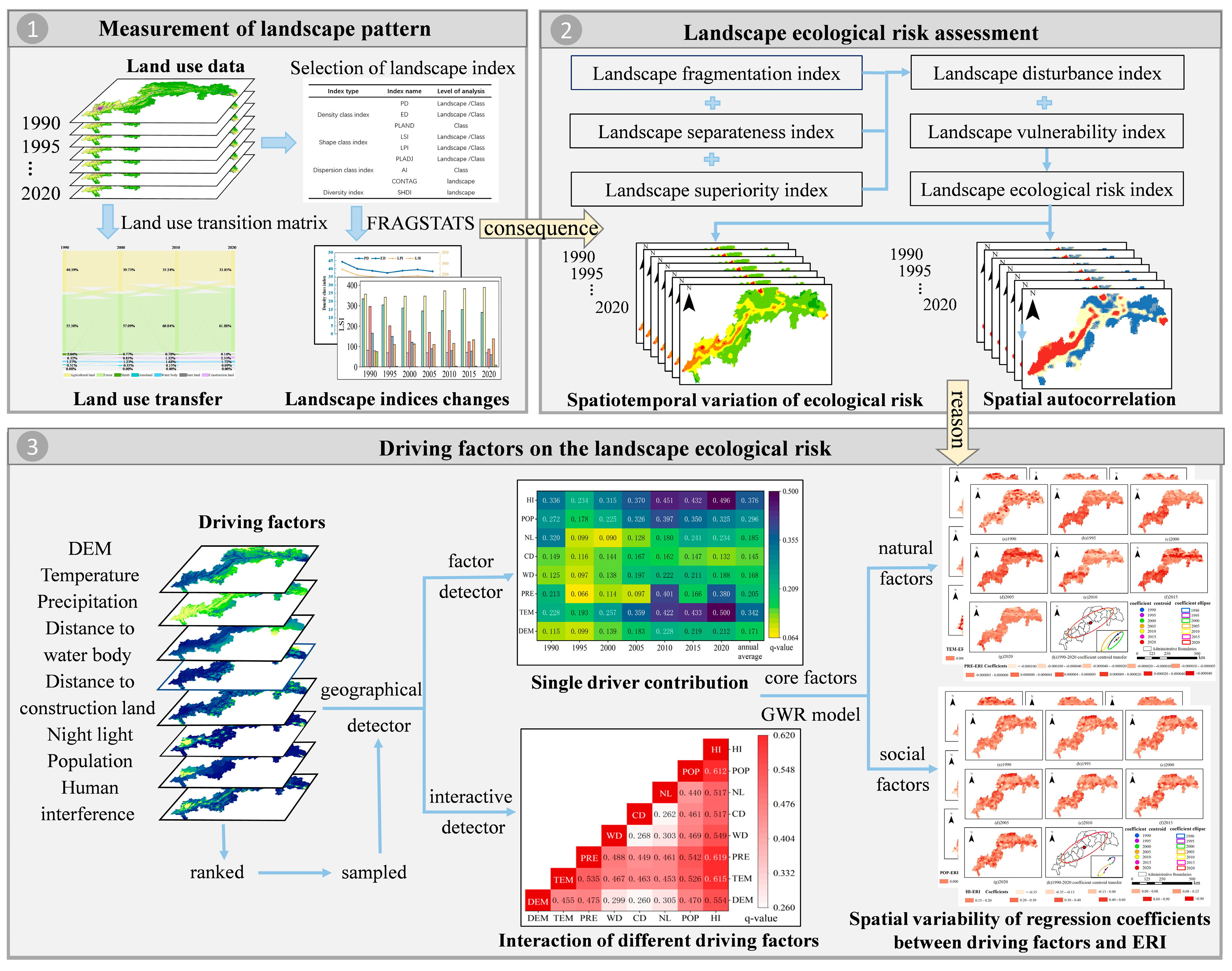
2. Materials and Methods
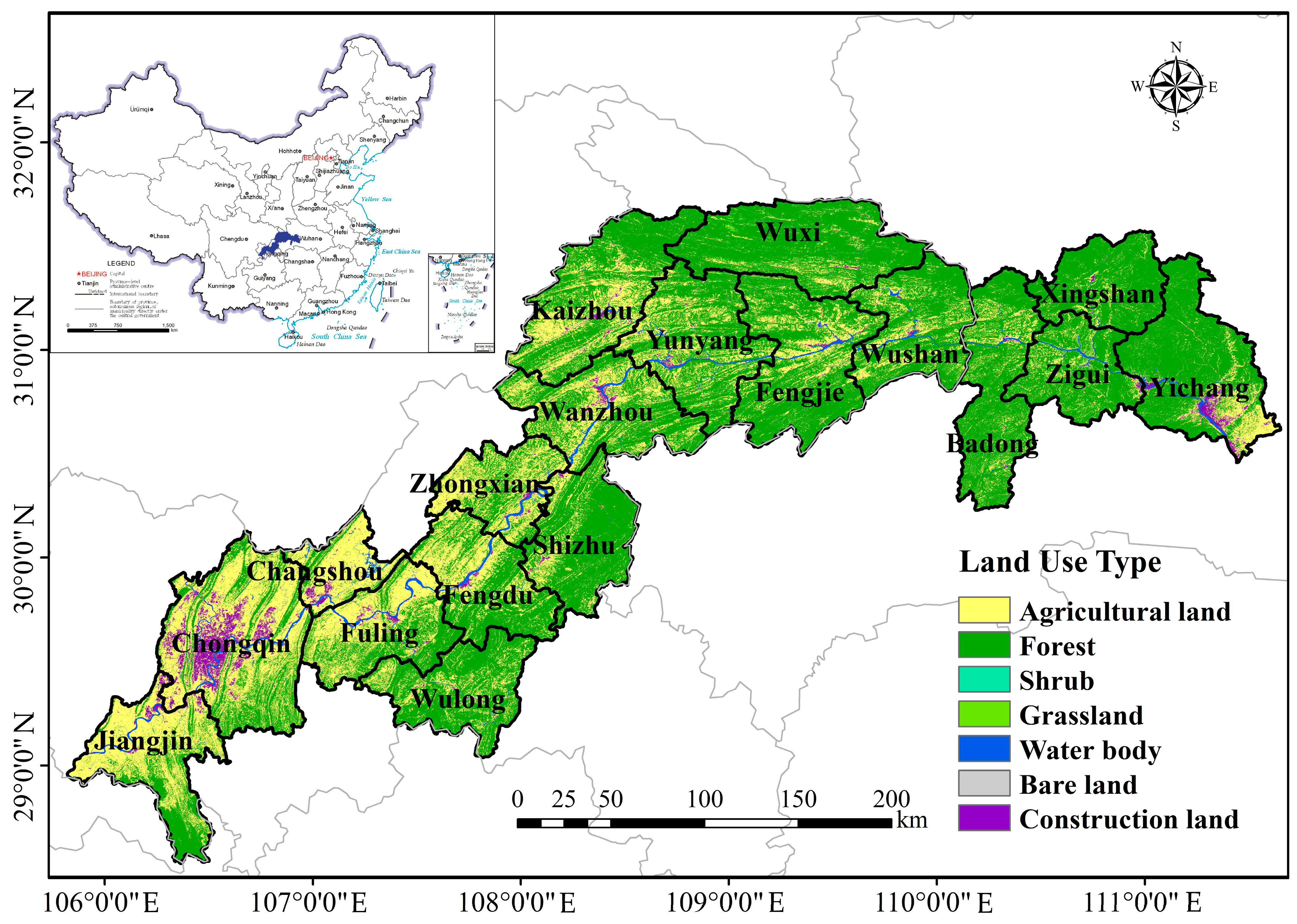
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Descriptions
2.3. Research Methodology
2.3.1. Land Use Transfer Matrix
2.3.2. Selection and Calculation of Landscape Indices
2.3.3. Quantification of Landscape Ecological Risk
2.3.4. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
2.3.5. Standard Deviation Ellipse
2.3.6. Selection and Calculation of Driving Factors
2.3.7. Geographical Detector
2.3.8. Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR) Model
3. Results
3.1. Landscape Pattern Characteristics
3.1.1. Land Use Transfer
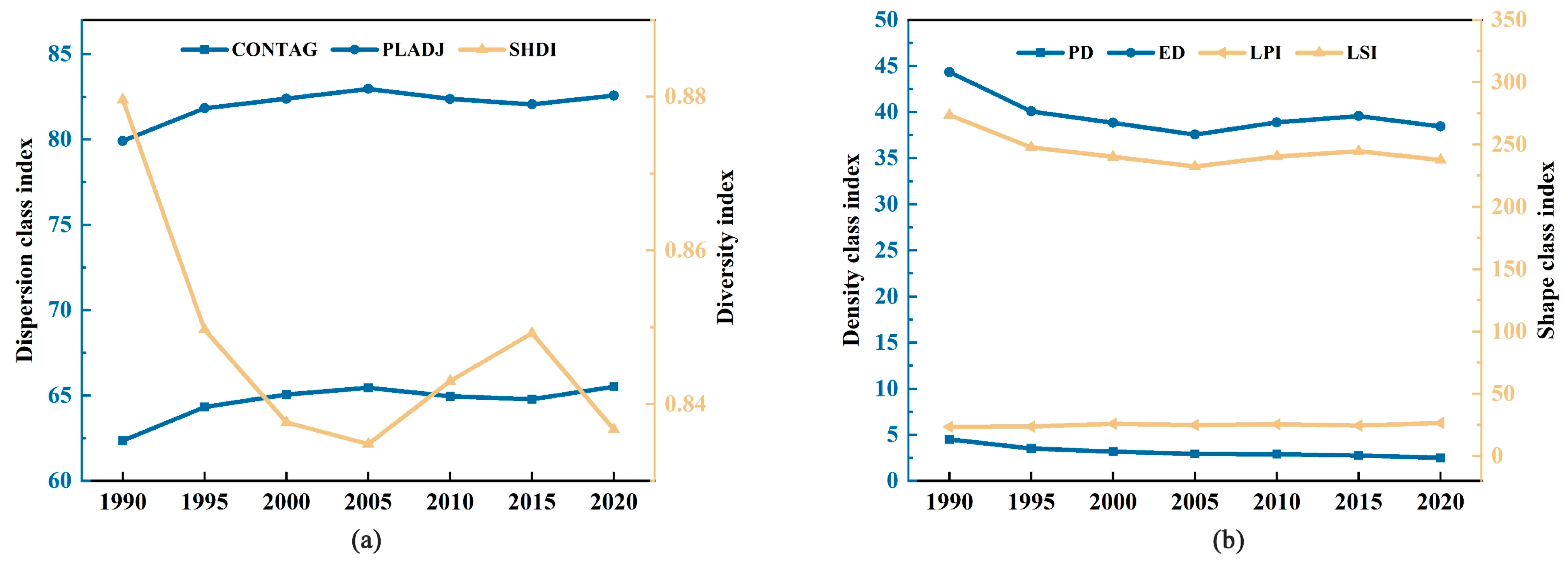
3.1.2. Landscape Index Change
3.2. Landscape Ecological Risk Characteristics
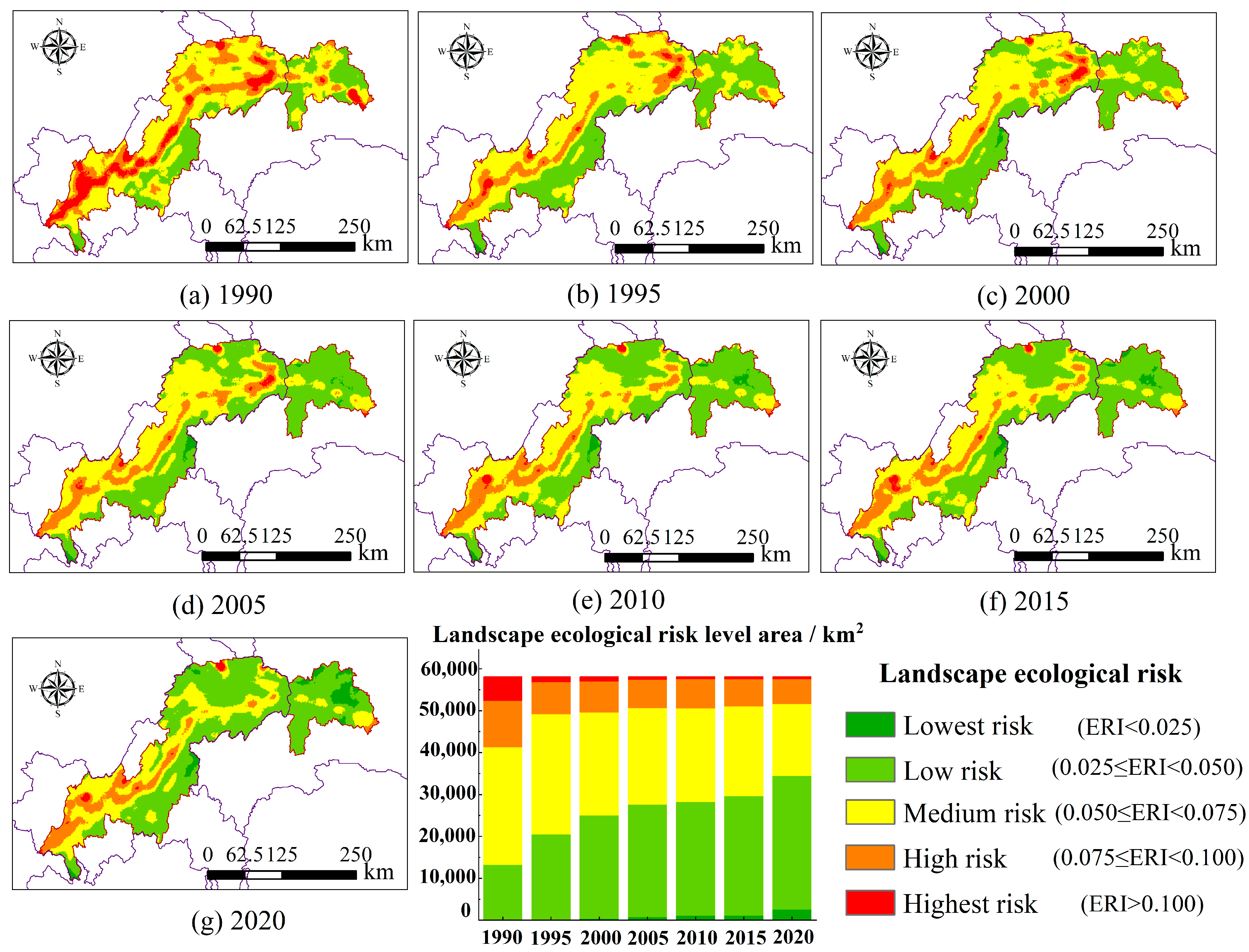
3.2.1. Spatiotemporal Changes of Landscape Ecological Risk
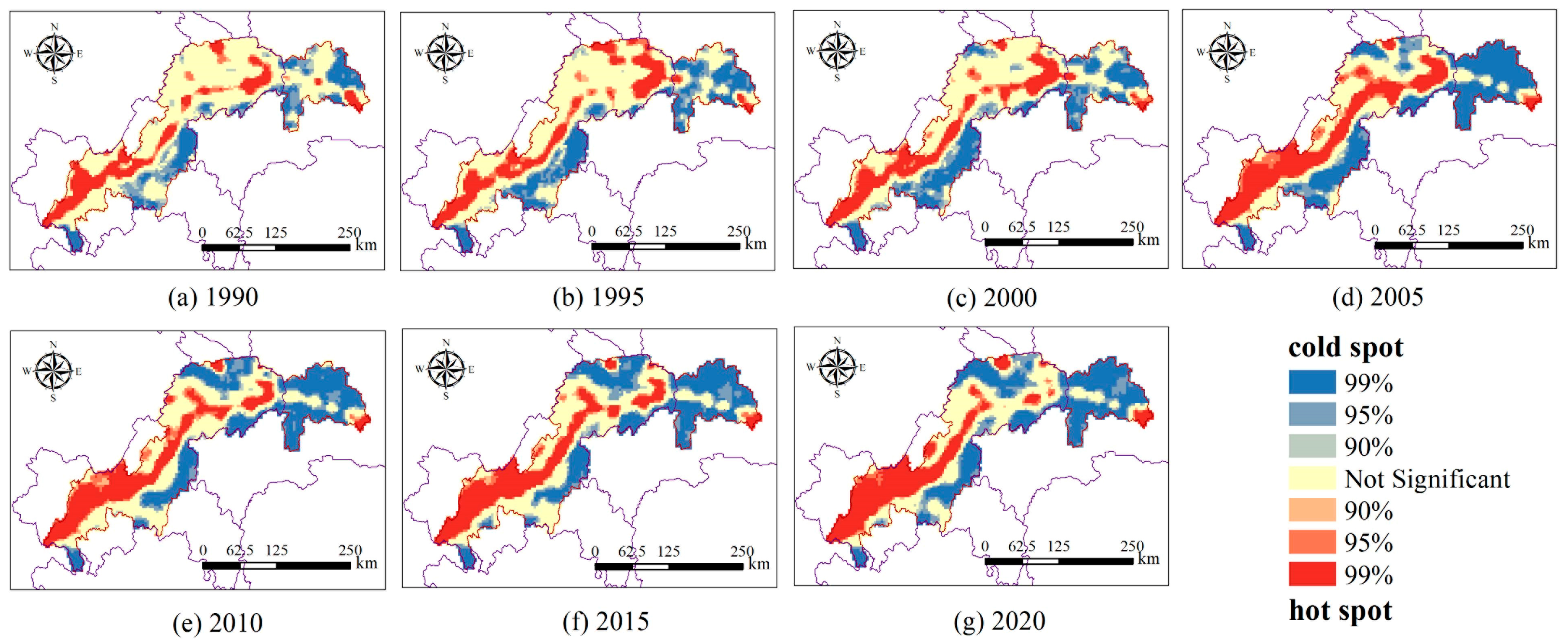
3.2.2. Spatial Autocorrelation of Landscape Ecological Risk
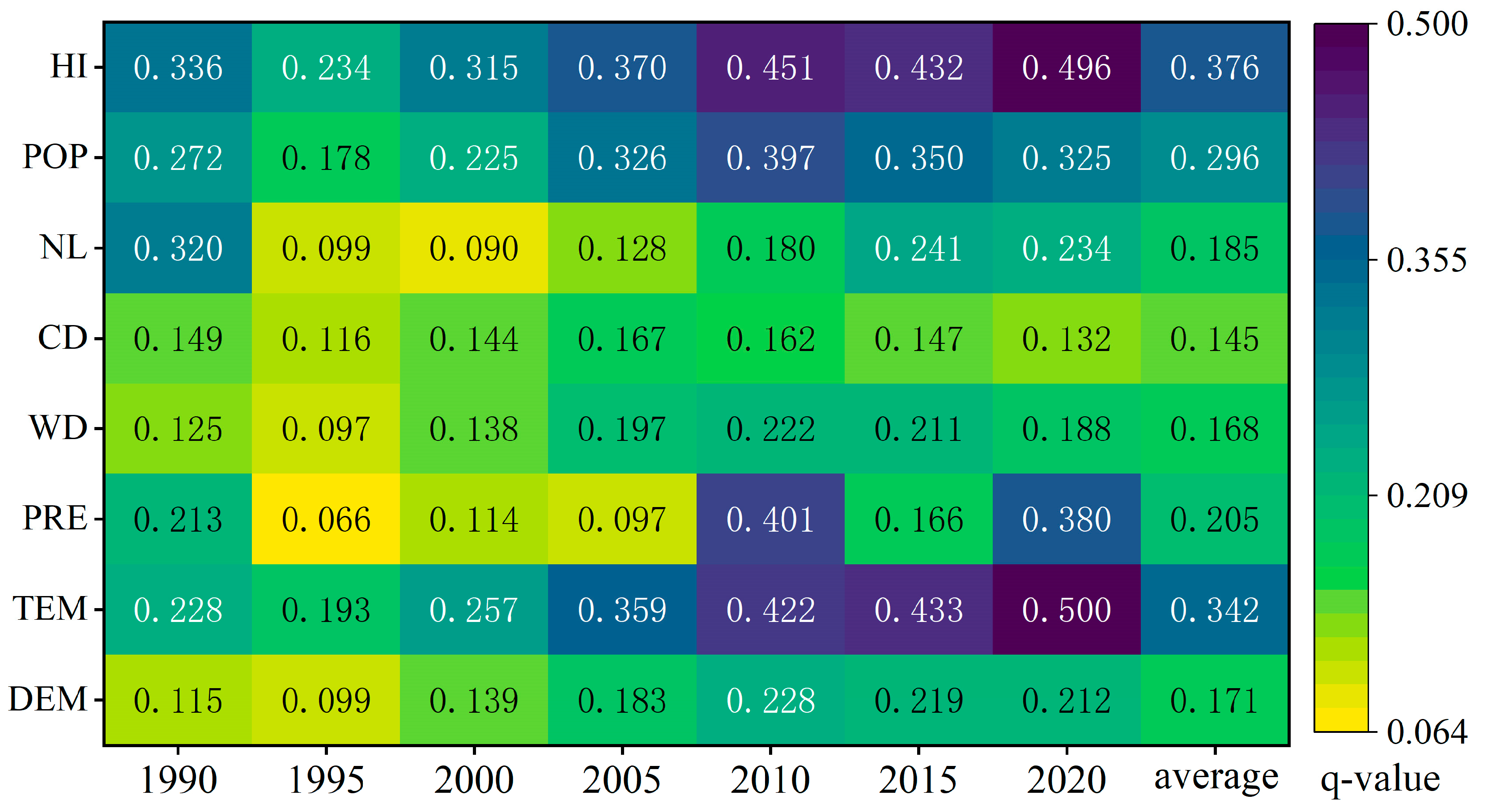
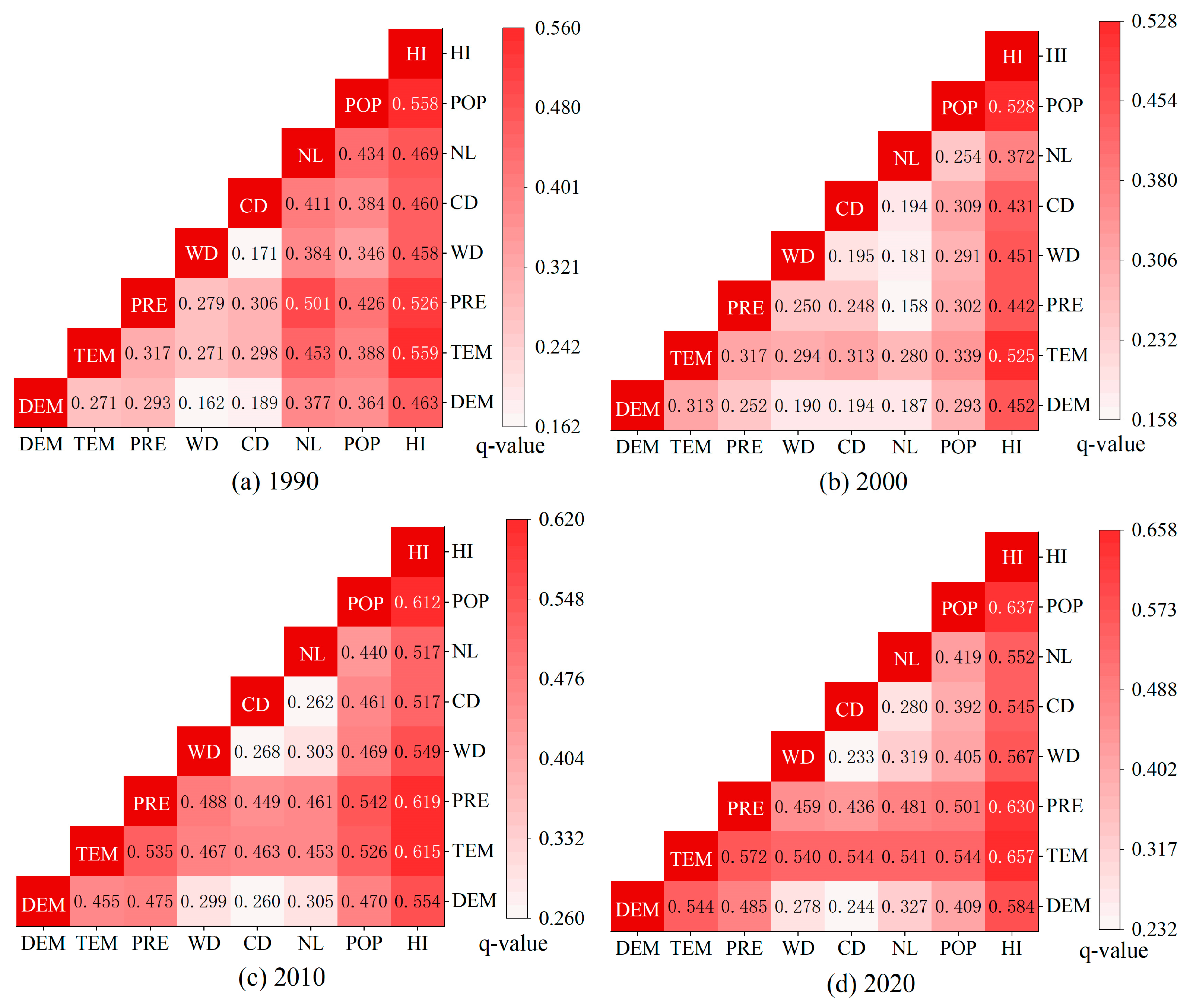
3.3. Analysis of Landscape Ecological Risk Driving Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Landscape Pattern and Landscape Ecological Risk Change Characteristics
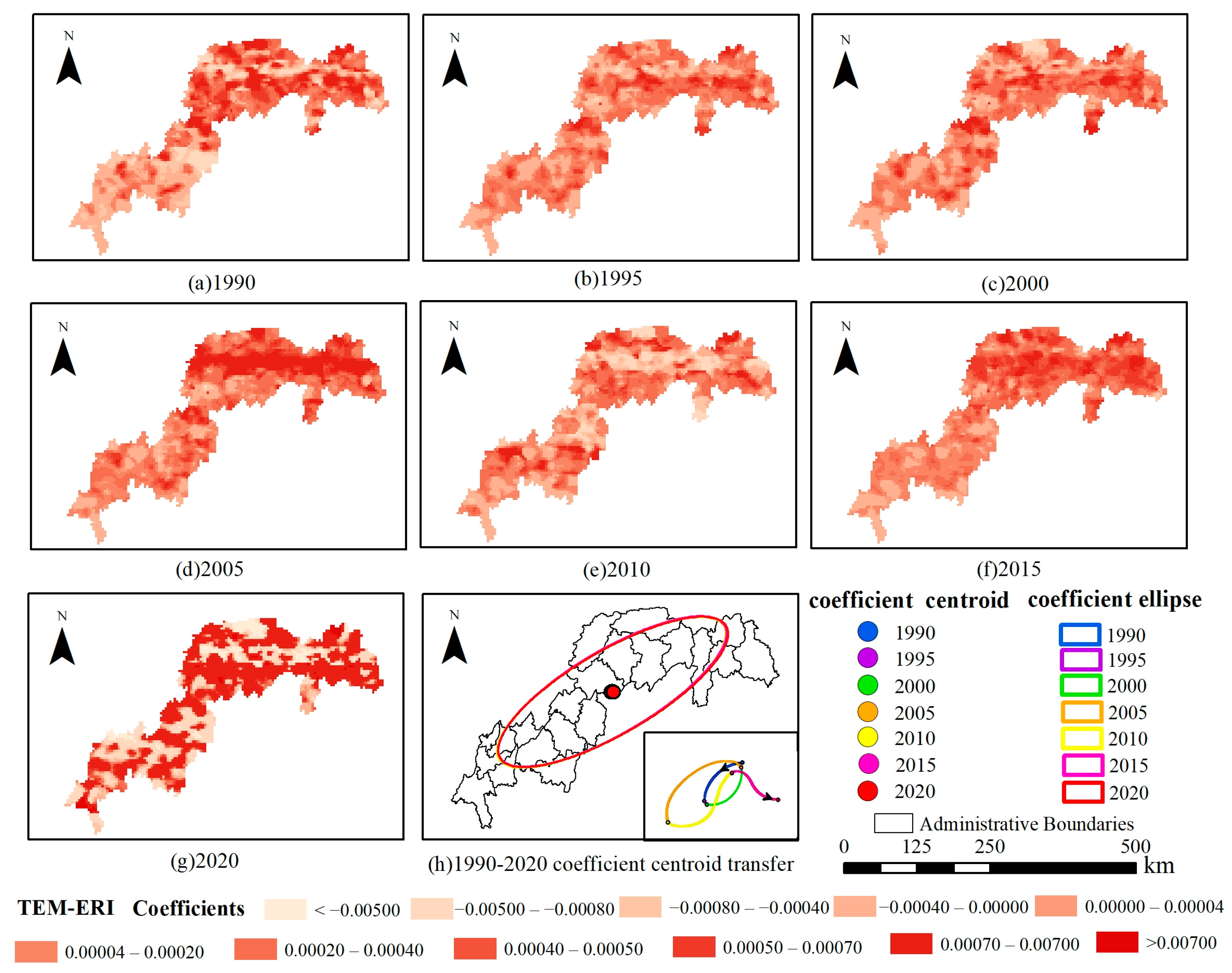
4.2. Spatial Response of Landscape Ecological Risk to Drivers
4.3. Limitations and Generalized Contributions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, X.; Li, J.; Ma, Q. Integrating green infrastructure, ecosystem services and nature-based solutions for urban sustainability: A comprehensive literature review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 98, 104843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafortezza, R.; Sanesi, G. Nature-based solutions: Settling the issue of sustainable urbanization. Environ. Res. 2019, 172, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimian, H.; Zou, W.; Chen, Y.; Xia, J.; Wang, Z. Landscape ecological risk assessment and driving factor analysis in Dongjiang river watershed. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Shi, L.; Liu, B. Risks assessment and driving forces of urban environmental accident. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 340, 130710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Dong, Z.; Yan, Y.; Tang, L. Ecological risk assessment models for simulating impacts of land use and landscape pattern on ecosystem services. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hope, B.K. An examination of ecological risk assessment and management practices. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 983–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, P.; Shekhar, A.; Kumar, A. Quantifying Temperature and Precipitation Change Caused by Land Cover Change: A Case Study of India Using the WRF Model. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 766328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Geng, L.; Li, M. The impact of climate change on aeolian desertification: A case of the agro-pastoral ecotone in northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesshöver, C.; Assmuth, T.; Irvine, K.N.; Rusch, G.M.; Waylen, K.A.; Delbaere, B.; Haase, D.; Jones-Walters, L.; Keune, H.; Kovacs, E.; et al. The science, policy and practice of nature-based solutions: An interdisciplinary perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1215–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, S. Construction of landscape ecological network based on landscape ecological risk assessment in a large-scale opencast coal mine area. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 125523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Cao, A. Analysis of the heterogeneity of landscape risk evolution and driving factors based on a combined GeoDa and Geodetector model. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chang, A.C.; Chen, W.; Zhou, W.; Feng, Q. A framework for the urban eco-metabolism model—Linking metabolic processes to spatial patterns. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Yeh, C.; Huang, S. Energy hierarchy and landscape sustainability. Landscape Ecol. 2013, 28, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Xie, S.; Sun, R.; Cheng, X. Impacts of landscape multifunctionality change on landscape ecological risk in a megacity, China: A case study of Beijing. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, D. Impacts of road network expansion on landscape ecological risk in a megacity, China: A case study of Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Zhao, C.; Chang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zang, F. Spatial-temporal pattern analysis of landscape ecological risk assessment based on land use/land cover change in Baishuijiang National nature reserve in Gansu Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 124, 107454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, M. Assessing landscape eco-risk associated with hilly construction land exploitation in the southwest of China: Trade-off and adaptation. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 62, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Dong, B.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Peng, L.; Fang, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, S. Study on landscape ecological risk assessment of Hooded Crane breeding and overwintering habitat. Environ. Res. 2020, 187, 109649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Yu, K.; Zeng, Z.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. Assessing the dynamic landscape ecological risk and its driving forces in an island city based on optimal spatial scales: Haitan Island, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Xie, P.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J. Urban thermal environment dynamics and associated landscape pattern factors: A case study in the Beijing metropolitan region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 173, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, S.; Wei, B.; Zhou, X. Characterizing Production–Living–Ecological Space Evolution and Its Driving Factors: A Case Study of the Chaohu Lake Basin in China from 2000 to 2020. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Ge, J.; Gao, J.; Meng, B.; Li, Y.; Yin, J.; Liu, J.; Feng, Q.; Liang, T. Ecological Risk Assessment and Impact Factor Analysis of Alpine Wetland Ecosystem Based on LUCC and Boosted Regression Tree on the Zoige Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Feng, C.; Yu, Q.; Han, R.; Guo, L. Contradiction or coordination? The spatiotemporal relationship between landscape ecological risks and urbanization from coupling perspectives in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Pan, Z.; Liu, D.; Guo, X. Exploring the regional differences of ecosystem health and its driving factors in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Wen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, W. Landslide susceptibility mapping using hybrid random forest with GeoDetector and RFE for factor optimization. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 101211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Gao, X.; Zhao, X.; Wu, P. Scale effect and spatially explicit drivers of interactions between ecosystem services—A case study from the Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Zhan, L.; Yao, M.; Yang, L. A geographically weighted regression model augmented by Geodetector analysis and principal component analysis for the spatial distribution of PM2.5. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 56, 102106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Chen, X.; Xue, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Li, D. Modeling the spatially heterogeneous relationships between tradeoffs and synergies among ecosystem services and potential drivers considering geographic scale in Bairin Left Banner, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Xiong, Q.; Yang, Z. Effects of Ecological Restoration Measures on Soil Erosion Risk in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area Since the 1980s. GeoHealth 2020, 4, e2020GH000274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Che, A. Establishing a monitoring network for an impoundment-induced landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Landslides 2009, 6, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tan, Y.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; Su, W. Impacts of China’s Three Gorges Dam Project on net primary productivity in the reservoir area. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 4656–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yu, L.; Xiang, S.; Gao, M. GIS-based ecological risk assessment and ecological zoning in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 4654–4664. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Wu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, M. Ecological risk assessment of the Three Gorges reservoir landscape based on ecological plots. Ecol. Environ. Monit. Three Gorges. 2022, 7, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Wang, Z. Landscape ecological risk assessment and its driving factors of multi-mountainous city. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Dong, C.; Kang, X.; Qian, X.; Gu, L. Spatiotemporal evolution of land cover changes and landscape ecological risk assessment in the Yellow River Basin, 2015–2020. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 332, 117149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ding, X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Z.; Wang, S. Evaluation of net anthropogenic nitrogen inputs in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuba, N. Research note: Sankey diagrams for visualizing land cover dynamics. Landsc. Urban Plan 2015, 139, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Li, T. Analysis of spatiotemporal changes in cultural heritage protected cities and their influencing factors: Evidence from China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 151, 110327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gao, M. The spatial granularity effect, changing landscape patterns, and suitable landscape metrics in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, 1995–2015. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Xu, J.; Peng, Y.; Xin, J.; Peng, N.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, C.; Wu, Y.; et al. Impacts of landscape patterns on plant species diversity at a global scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 896, 165193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.A.; Li, Y.; Jia, L.; Ji, Y.; Hu, G. Ecological risk assessment and ecological security pattern optimization in the middle reaches of the Yellow River based on ERI+MCR model. J. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 823–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. Evolution of habitat quality and association with land-use changes in mountainous areas: A case study of the Taihang Mountains in Hebei Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiong, N.; Sun, L.; Xu, J. Impacts of Land Use Changes on Net Primary Productivity in Urban Agglomerations under Multi-Scenarios Simulation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, P.; Cui, L.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Y.; Miao, D. Study on the spatial variation of China’s territorial ecological space based on the standard deviation ellipse. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 982734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Kang, Y.; Li, W.; Guo, F. Spatial correlation of factors affecting CO2 emission at provincial level in China: A geographically weighted regression approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, K.; Qian, H.; Gao, Y.; Fang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, W.; Ren, W. Characterization of soil salinization and its driving factors in a typical irrigation area of Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, M.; Huang, C.; Wang, P.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, Z.; Xiao, W.; Huang, Z.; Liu, C. Impacts of forest restoration on soil erosion in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Xi, J.; Cao, Y.; Feng, X.; Qiao, X. Anticipation of migration and psychological stress and the Three Gorges Dam project, China. Soc. Sci. Med. 2007, 65, 1012–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhou, Z.; Teng, M.; Wu, C.; Wang, P. Effects of climate, land use and land cover changes on soil loss in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Geogr. Sustain. 2020, 1, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Liang, S.; Feng, L.; He, T.; Song, X.; Zhang, L. Temperature changes in Three Gorges Reservoir Area and linkage with Three Gorges Project. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 4866–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, C.; Yang, Y.; Huang, C.; Wang, M.; Tan, W. Coordination of economic development and ecological conservation during spatiotemporal evolution of land use/cover in eco-fragile areas. Catena 2023, 226, 107097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Huang, X.; Peng, C.; Zhou, Z.; Teng, M.; Wang, P. Land use/cover change in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China: Reconciling the land use conflicts between development and protection. Catena 2019, 175, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, L.; Hu, D. Evaluation of urban green space in terms of thermal environmental benefits using geographical detector analysis. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2021, 105, 102610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Gao, G.; Fu, B. Spatiotemporal changes and driving forces of ecosystem vulnerability in the Yangtze River Basin, China: Quantification using habitat-structure-function framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Mou, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Tian, T.; He, Q. Evolution and Prediction of Cultivated Land Landscape Pattern in Multi level Watersheds of Chongqing Based on ANN-CA Model. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 30, 379–387. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zheng, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Ming, G. The spatiotemporal distribution and evolution characteristics of paddy fields in the Chongqing section of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area from 1990 to 2015. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2022, 43, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Peng, H.; Xu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Z. Impact of Land Use Changes on the Surface Runoff and Nutrient Load in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, J.; Liao, T.; Liang, X.; Tian, H. Simulating urban expansion and its impact on functional connectivity in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Fu, D. Landscape change patterns at three stages of the construction and operation of the TGP. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, M.; Li, L.; Ouyang, S.; Wang, N.; La, L.; Liu, C.; Xiao, W. Identifying and analyzing ecosystem service bundles and their socioecological drivers in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Mantgem, P.J.; Stephenson, N.L.; Byrne, J.C.; Daniels, L.D.; Franklin, J.F.; Fulé, P.Z.; Harmon, M.E.; Larson, A.J.; Smith, J.M.; Taylor, A.H.; et al. Widespread Increase of Tree Mortality Rates in the Western United States. Sci. Am. Assoc. Adv. Sci. 2009, 323, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germain, S.J.; Lutz, J.A. Climate warming may weaken stabilizing mechanisms in old forests. Ecol. Monogr. 2022, 92, e1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Piao, S.; Li, L.; Chen, A.; Wang, X.; Ciais, P.; Huang, L.; Lian, X.; Peng, S.; Zeng, Z.; et al. Divergent hydrological response to large-scale afforestation and vegetation greening in China. Sci Adv. 2018, 4, r4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimpour Golroudbary, V.; Zeng, Y.; Mannaerts, C.M.; Su, Z.B. Detecting the effect of urban land use on extreme precipitation in the Netherlands. Weather. Clim. Extrem. 2017, 17, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Zhu, J.; Lou, K.; Yang, L. Coupling coordination and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between urbanization and ecological environment in Shaanxi Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liang, L.; Sun, Z.; Wang, X. Spatiotemporal differentiation and the factors influencing urbanization and ecological environment synergistic effects within the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 243, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, W. Local Effects of Forests on Temperatures across Europe. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naudts, K.; Chen, Y.; McGrath, M.J.; Ryder, J.; Valade, A.; Otto, J.; Luyssaert, S. Europe’s forest management did not mitigate climate warming. Science 2016, 351, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, L.; Song, C.; Ai, D. Nature-based solutions for urban expansion: Integrating ecosystem services into the delineation of growth boundaries. Habitat Int. 2022, 124, 102575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





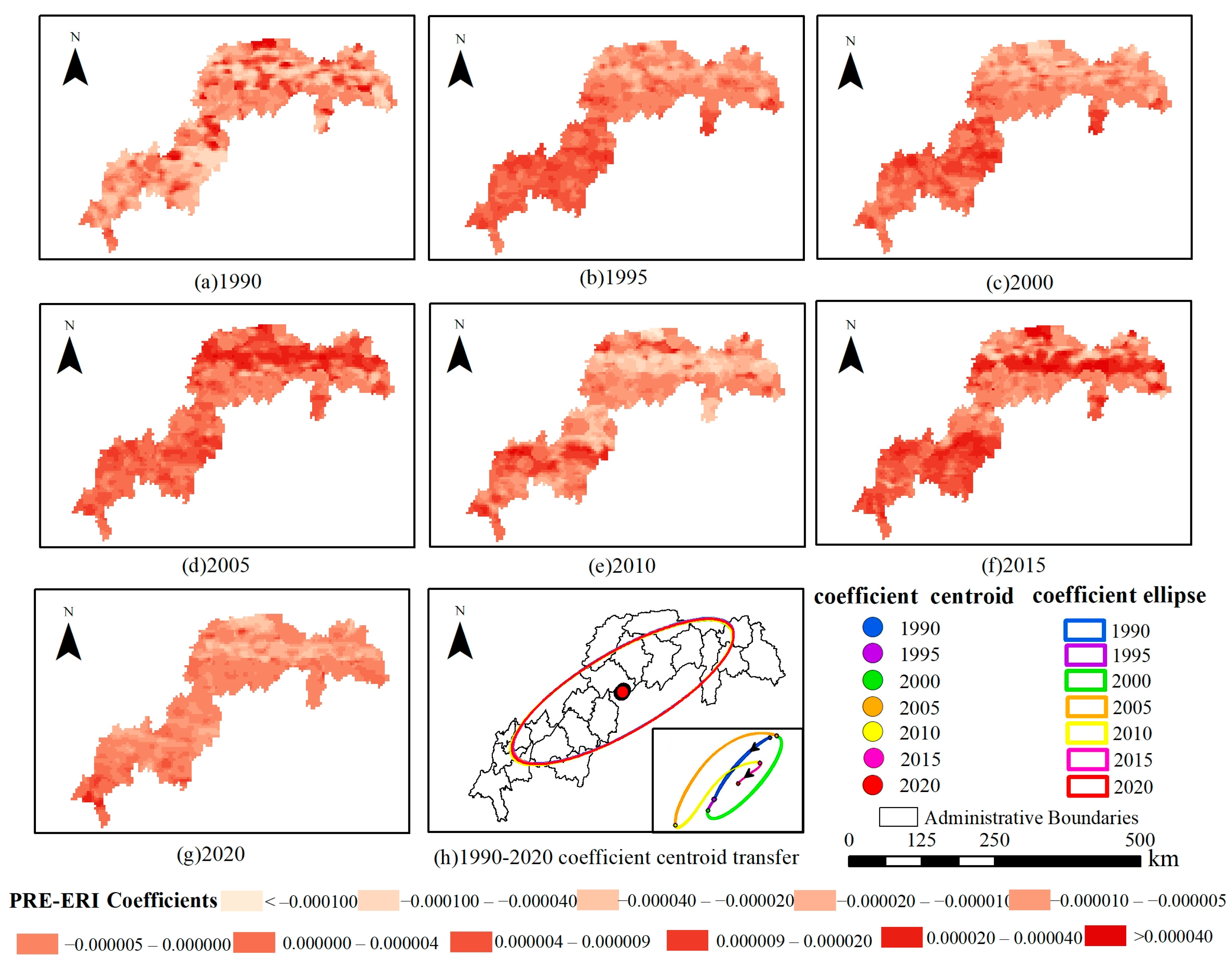
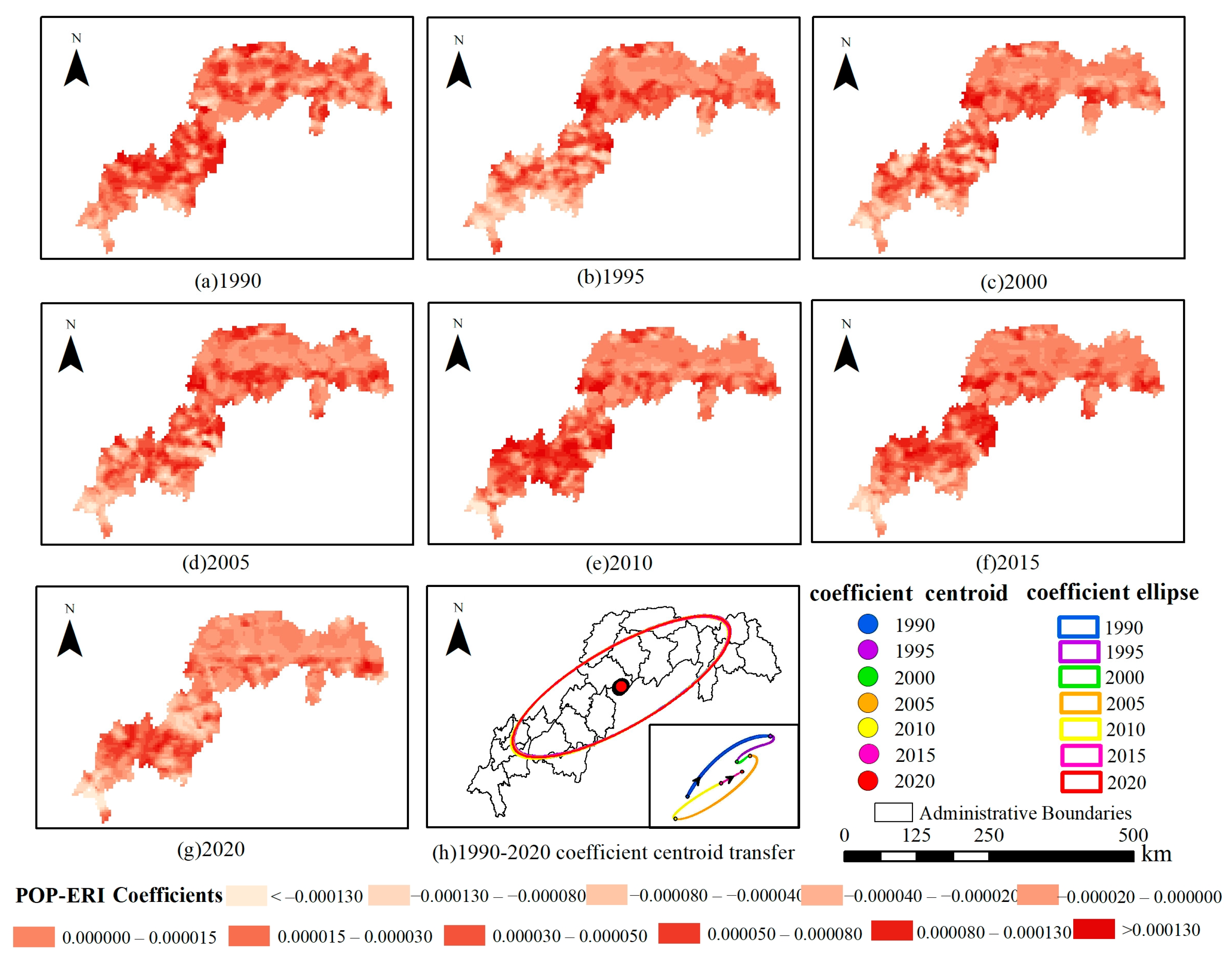
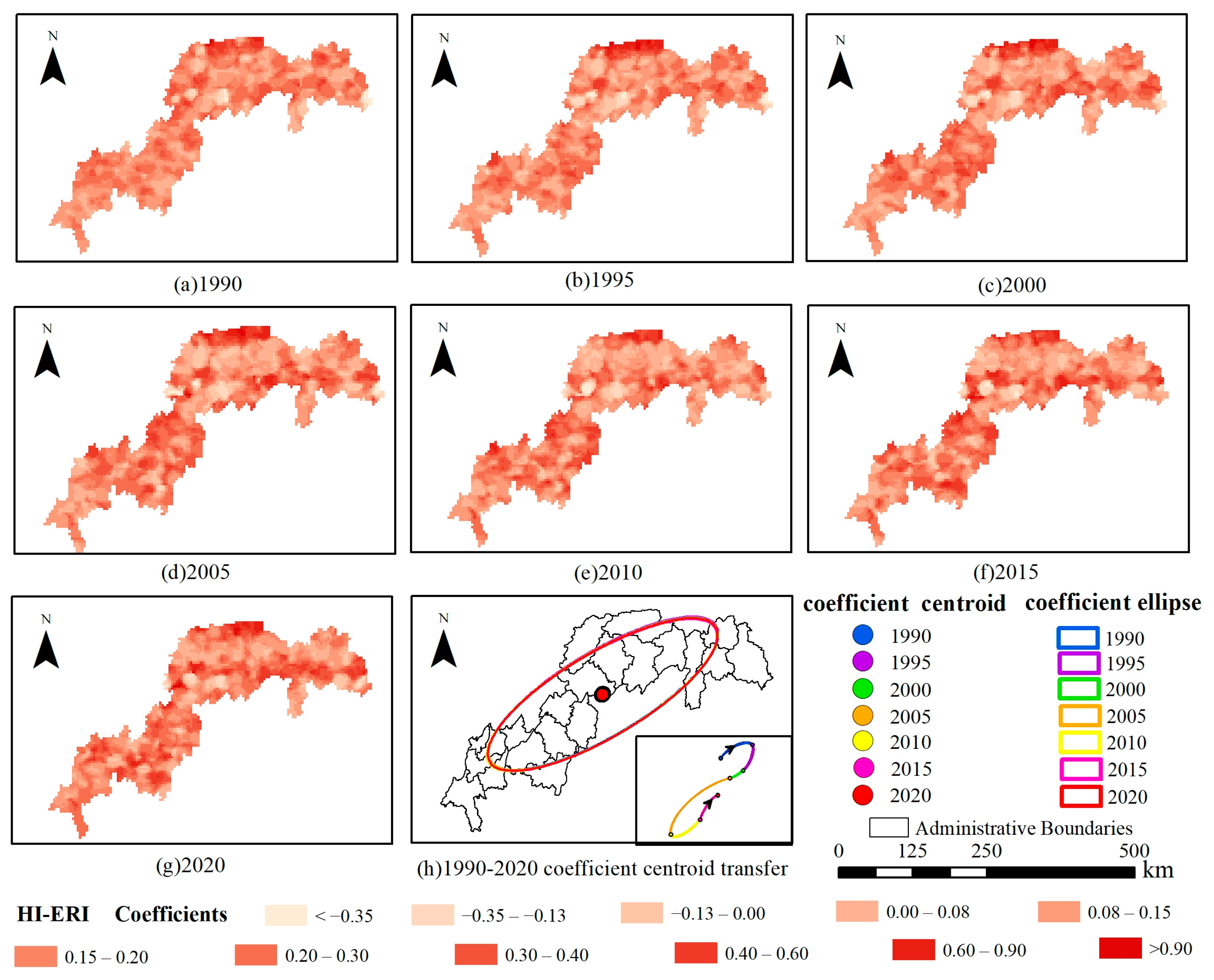
| Data Type | Data Description | Data Format | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Land use data | Annual China land cover data | Raster (30 m) | Annual China Land Cover Dataset from Wuhan University [37] |
| Natural factors data | Digital elevation model (DEM) | Raster (90 m) | China’s Geospatial Data Cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn/ (accessed on 26 August 2023)) |
| Annual average temperature (TEM) | Raster (1 km) | Resources and Environmental Sciences of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (https://www.resdc.cn/ (accessed on 26 August 2023)) | |
| Annual precipitation (PRE) | Raster (1 km) | Resources and Environmental Sciences of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (https://www.resdc.cn/ (accessed on 26 August 2023)) | |
| Social factors data | Annual artificial night light (NL) | Raster (1 km) | National Tibetan Plateau Data Center(http://data.tpdc.ac.cn/zh-hans/ (accessed on 26 August 2023)) |
| Population density (POP) | Raster (1 km) | Resources and Environmental Sciences of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (https://www.resdc.cn/ (accessed on 26 August 2023)) |
| Index Type | Index Name | Level of Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Density class index | Patch Density (PD) | Landscape/Class |
| Edge Density (ED) | Landscape/Class | |
| Percentage of Landscape (PLAND) | Class | |
| Shape class index | Landscape Shape Index (LSI) | Landscape/Class |
| Largest Patch Index (LPI) | Landscape/Class | |
| Dispersion class index | Proportion of Like Adjacencies (PLADJ) | Landscape/Class |
| Aggregation Index (AI) | Class | |
| Contagion Index (CONTAG) | landscape | |
| Diversity index | Shannon’s Diversity Index (SHDI) | landscape |
| Index Name | Formula |
|---|---|
| Landscape fragmentation index Ci | ni: number of patches of landscape type i; Ai: Total area of landscape type i |
| Landscape separateness index Ni | li: distance index for landscape type i A: total area of landscape |
| Landscape superiority index Di | Qi: number of risk cells where patch i occurs/total risk cells Li: Area of patch i/total area of the risk cells |
| Landscape disturbance index Si | a + b + c = 1, assign values of 0.6, 0.3, and 0.1 respectively |
| Landscape Vulnerability Index Fi | Assigning vulnerability indices to different land use types (Bare land = 7; Water body = 6; Agricultural land = 5; Grassland = 4; Shrub = 3; Forest = 2; Construction land = 1). The landscape vulnerability index obtained after normalization |
| Landscape loss index Ri |
| Years | 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.444 | 0.413 | 0.408 | 0.418 | 0.464 | 0.480 | 0.495 | |
| -scores | 37.093 | 34.464 | 34.045 | 34.895 | 38.700 | 40.070 | 41.298 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Landscape Ecological Risk and Driving Factors: A Case Study in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4884. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194884
Yan Z, Wang Y, Wang Z, Zhang C, Wang Y, Li Y. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Landscape Ecological Risk and Driving Factors: A Case Study in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(19):4884. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194884
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Zhiyi, Yunqi Wang, Zhen Wang, Churui Zhang, Yujie Wang, and Yaoming Li. 2023. "Spatiotemporal Analysis of Landscape Ecological Risk and Driving Factors: A Case Study in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China" Remote Sensing 15, no. 19: 4884. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194884
APA StyleYan, Z., Wang, Y., Wang, Z., Zhang, C., Wang, Y., & Li, Y. (2023). Spatiotemporal Analysis of Landscape Ecological Risk and Driving Factors: A Case Study in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Remote Sensing, 15(19), 4884. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194884












