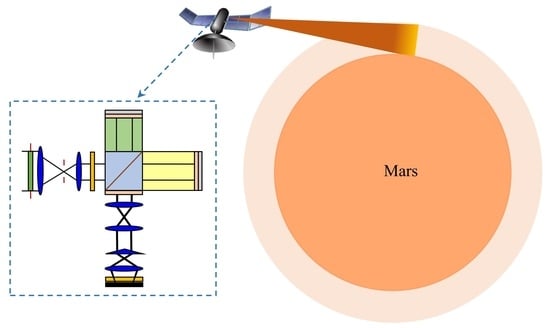
Novel Compact Polarized Martian Wind Imaging Interferometer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Principle
2.1. Photochemical Mechanism of O2 1.27 μm Dayglow and Nightglow on Mars
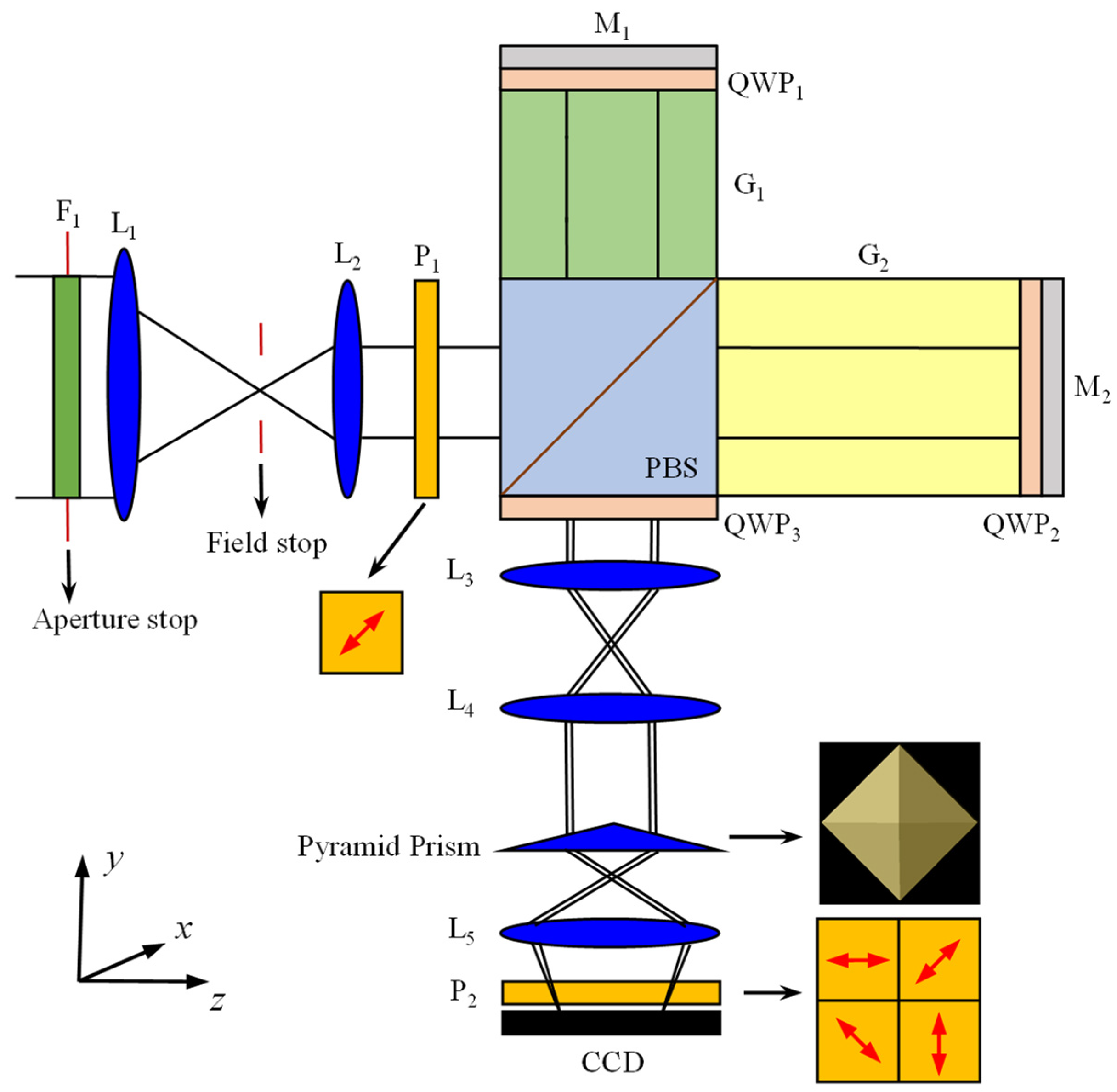
2.2. Principle of Polarized Martian Wind Imaging Interferometer
3. Design, Simulation, and Analysis of Polarized Martian Wind Imaging Interferometer
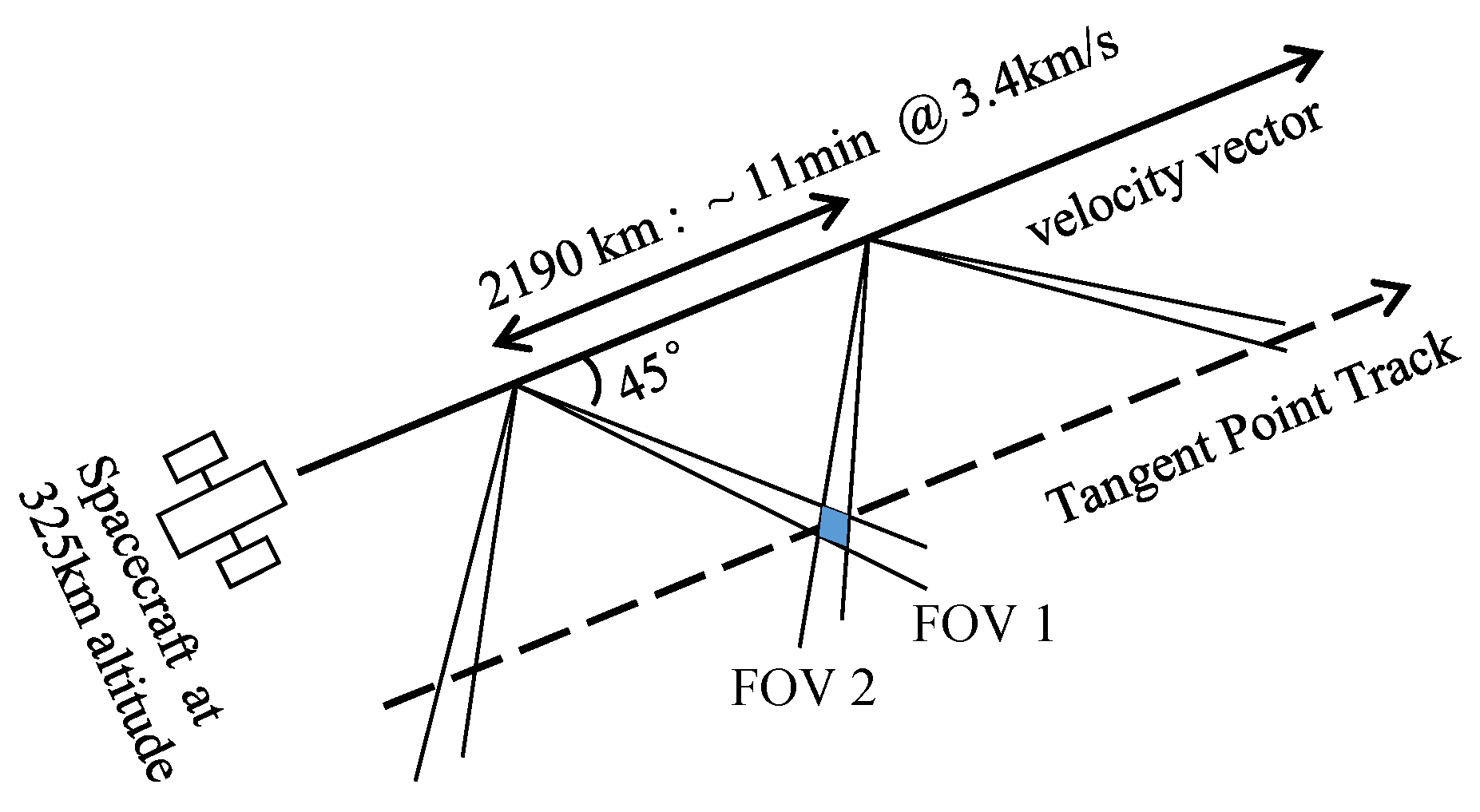
3.1. Description of Instrumentation Parameter and Observation Modes
3.2. Selection of Instrument Optical Path Difference (OPD)
3.3. All-Solid-State Arm Glass Compensation Design
3.4. Design and Simulation of FP Etalon
3.5. Pyramid Prism
3.6. Wind Field Measurement Simulation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The proposed compact polarized solid-state Mars wind imaging interferometer scheme is capable of high-precision Mars wind field measurement. An OPD of 8.6 cm can achieve a measurement accuracy of 5 m/s for Martian atmospheric wind velocity and 5 K for temperature measurement, as validated through theoretical analysis and simulations.
- The designed pyramid prism with a wedge angle of 5.7° has a negligible impact on the polarization state of the incident light, making it suitable for aperture segmentation in the polarized Mars wind imaging interferometer.
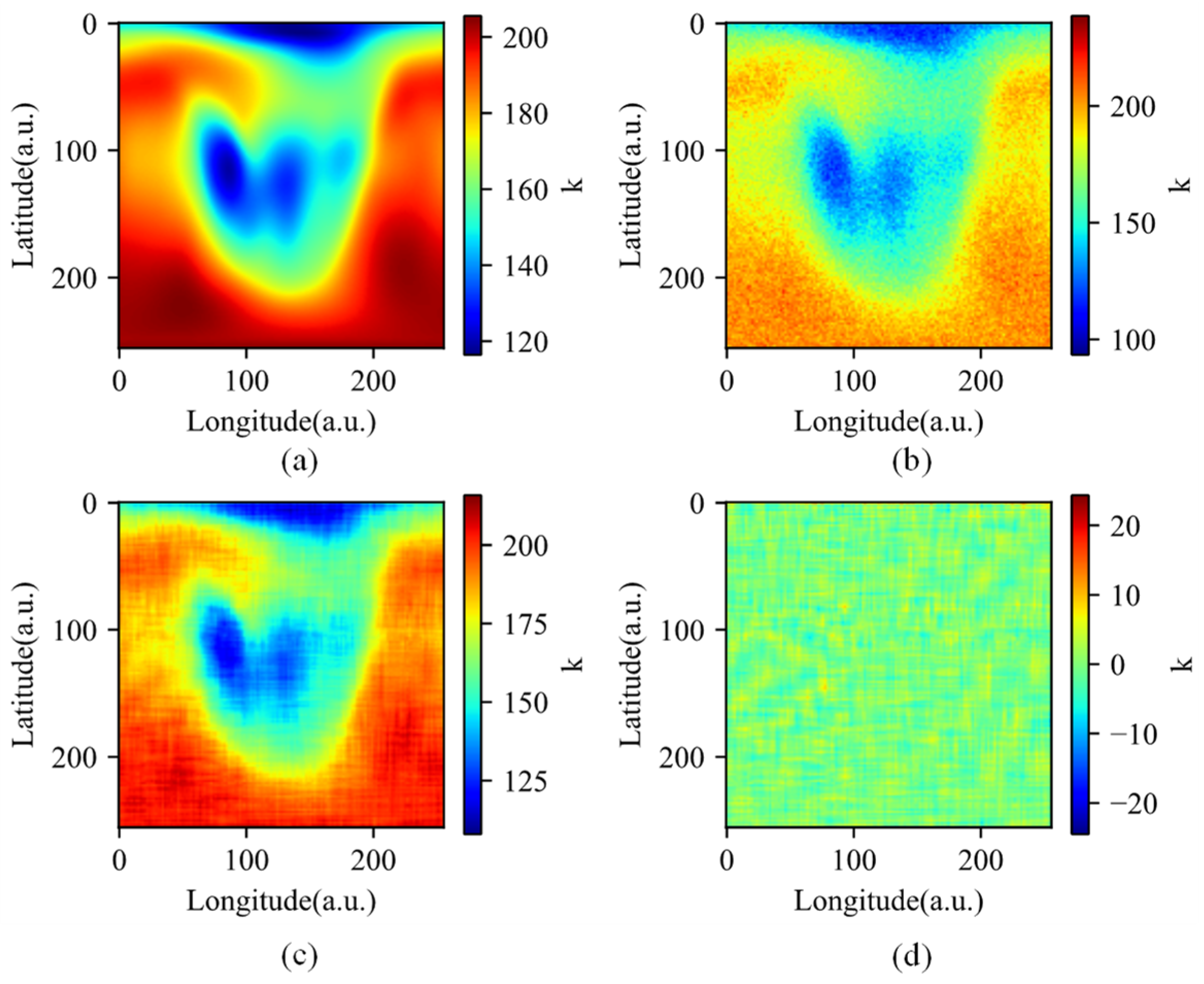
- Denoising of the wind field interferogram is necessary and can further enhance the accuracy of detecting Mars atmospheric wind veloctiy and temperature.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, N.; Xia, C.; Yu, T.; Zuo, X.; Sun, Y.; Yan, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Le, H.; Liu, L.; et al. Measurement of Martian atmospheric winds by the O2 1.27 μm airglow observations using Doppler Michelson Interferometry: A concept study. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 2027–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, W.G.; Tamppari, L.K.; Livesey, N.J.; Clancy, R.T.; Forget, F.; Hartogh, P.; Rafkin, S.C.R.; Chattopadhyay, G. Retrieval of wind, temperature, water vapor and other trace constituents in the Martian Atmosphere. Planet. Space Sci. 2018, 161, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, W.E.; Gault, W.A.; Rowlands, N.; Wang, S.; Shepherd, G.G.; Mcdade, I.C.; McConnell, J.C.; Michelangeli, D.V.; Caldwell, J.J. An imaging interferometer for satellite observations of wind and temperature on Mars, the Dynamic Atmosphere Mars Observer (DYNAMO). In Proceedings of the Applications of Photonic Technology, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 17 February 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhleman, D.O.; Clancy, R.T. Microwave spectroscopy of the Mars atmosphere. Appl. Opt. 1995, 34, 6067–6080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasai, Y.; Sagawa, H.; Kuroda, T.; Manabe, T.; Ochiai, S.; Kikuchi, K.-I.; Nishibori, T.; Baron, P.; Mendrok, J.; Hartogh, P.; et al. Overview of the Martian atmospheric submillimetre sounder FIRE. Planet. Space Sci. 2012, 63–64, 62–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, P.B.; Abreu, V.J.; Dobbs, M.E.; Gell, D.A.; Grassl, H.J.; Skinner, W.R. The high-resolution Doppler imager on the Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 10713–10723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, G.G.; Thuillier, G.; Gault, W.A.; Solheim, B.H.; Hersom, C.; Alunni, J.M.; Brun, J.-F.; Brune, S.; Charlot, P.; Cogger, L.L. WINDII, the wind imaging interferometer on the Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1993, 98, 10725–10750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gault, W.A.; Shepherd, G.G.; Thuillier, G.; Solheim, B.H.; Hersom, C.H.; Brun, J.-F.; Brune, S.; Gore, J. WIND Imaging Interferometer (WINDII) on the upper-atmosphere research satellite. In Proceedings of the Instrumentation for Planetary and Terrestrial Atmospheric Remote Sensing, San Diego, CA, USA, 29 June 1992; Volume 1745. [Google Scholar]
- Bird, J.C.; Liang, F.; Solheim, B.H.; Shepherd, G.G. A polarizing Michelson interferometer for measuring thermospheric winds. Meas. Sci. Technol. 1995, 6, 1368–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gault, W.A.; Brown, S.; Moise, A.; Liang, D.; Sellar, G.; Shepherd, G.G.; Wimperis, J. ERWIN: An E-region wind interferometer. Appl. Opt. 1996, 35, 2913–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gault, W.A.; Mcdade, I.C.; Shepherd, G.G.; Mani, R.; Brown, S.; Gregory, P.; Scott, A.; Rochon, Y.J.; Evans, W.F.J. SWIFT: An infrared Doppler Michelson interferometer for measuring stratospheric winds. In Proceedings of the Sensors, Systems, and Next-Generation Satellites V, Toulouse, France, 12 December 2001; SPIE: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 476–481. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, W.E.; Gault, W.A.; Shepherd, G.G.; Rowlands, N. The Waves Michelson interferometer: A visible/near-IR interferometer for observing middle atmosphere dynamics and constituents. In Proceedings of the Sensors, Systems, and Next-Generation Satellites V, Toulouse, France, 12 December 2001; SPIE: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 100–111. [Google Scholar]
- Kristoffersen, S.K.; Ward, W.E.; Langille, J.; Gault, W.A.; Power, A.; Miller, I.; Scott, A.; Arsenault, D.; Favier, M.; Losier, V.; et al. Wind imaging using simultaneous fringe sampling with field-widened Michelson interferometers. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 6627–6641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babcock, D.D. Mesospheric Imaging Michelson Interferometer Instrument Development and Observations. Ph.D. Thesis, York University, Toronto, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Langille, J.A. The Michelson Interferometer for Airglow Dynamics Imaging: Implementation, Characterzation and Testing. Ph.D. Thesis, University of New Brunswick, Fredericton, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, T.; Langille, J.A.; Ward, W.E.; Gault, W.A.; Scott, A.; Bell, A.; Touahiri, D.; Zheng, S.H.; Zhang, C. A compact static birefringent interferometer for the measurement of upper atmospheric winds: Concept, design and lab performance. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 6213–6232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortland, D.A.; Hays, P.B.; Skinner, W.R.; Yee, J.-H. Remote sensing of mesospheric temperature and O2(1Σ) band volume emission rates with the high-resolution Doppler imager. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 1821–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D. Research on the Data Retrieval and Calibration of the Upper Atmosphere Wind and Temperature Measuring Fabry-Perot Interferometer. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Killeen, T.; Wu, Q.; Solomon, S.; Ortland, D.; Skinner, W.; Niciejewski, R.; Gell, D. TIMED Doppler Interferometer: Overview and recent results. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2006, 111, A10S01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englert, C.R.; Babcock, D.D.; Harlander, J.M. Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne spectroscopy (DASH): Concept and experimental demonstration. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 7297–7307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Feng, Y.; Wen, Z.; Di, F. Doppler Asymmetric Spatial Heterodyne Interferometry for Wind Measurement in Middle and Upper Atmosphere (Invited). Acta Photonica Sin. 2022, 51, 0851516. [Google Scholar]
- Englert, C.R.; Harlander, J.M.; Brown, C.M.; Marr, K.D.; Miller, I.J.; Stump, J.E.; Hancock, J.; Peterson, J.Q.; Kumler, J.; Morrow, W.H.; et al. Michelson Interferometer for Global High-Resolution Thermospheric Imaging (MIGHTI): Instrument Design and Calibration. Space Sci. Rev. 2017, 212, 553–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, B.J.; Chau, J.L.; He, M.; Englert, C.R.; Harlander, J.M.; Marr, K.D.; Makela, J.J.; Clahsen, M.; Li, G.; Ratnam, M.V.; et al. Validation of ICON-MIGHTI Thermospheric Wind Observations: 2. Green-Line Comparisons to Specular Meteor Radars. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2020JA028947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, P.; Zhang, C.; Ward, W.E.; Zhu, H.; Dai, H. Compensation optimization for a static Mars wind imaging Michelson interferometer. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2021, 142, 106589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yan, T.; Mu, T.; He, Y. Theoretical Model and Design of A Novel Static Polarization Wind Imaging Interferometer (NSPWII). ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, V-1-2020, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yan, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Ward, W.; Kristoffersen, S. Static wind imaging Michelson interferometer for the measurement of stratospheric wind fields. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 29411–29426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noxon, J.F.; Traub, W.A.; Carleton, N.P.; Connes, P. Detection of O2 dayglow emission from Mars and the Martian ozone abundance. Astron. J. 1976, 207, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnopolsky, V.A. Mapping of Mars O2 1.27 μm dayglow at four seasonal points. Icarus 2003, 165, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnopolsky, V.A. Photochemistry of the martian atmosphere: Seasonal, latitudinal, and diurnal variations. Icarus 2006, 185, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnopolsky, V.A. Seasonal variations of photochemical tracers at low and middle latitudes on Mars: Observations and models. Icarus 2009, 201, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guslyakova, S.; Fedorova, A.A.; Lefèvre, F.; Korablev, O.I.; Montmessin, F.; Bertaux, J.L. O2(a1Δg) dayglow limb observations on Mars by SPICAM IR on Mars-Express and connection to water vapor distribution. Icarus 2014, 239, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorova, A.; Korablev, O.; Perrier, S.; Bertaux, J.-L.; Lefevre, F.; Rodin, A. Observation of O2 1.27 μm dayglow by SPICAM IR: Seasonal distribution for the first Martian year of Mars Express. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, E09S07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, F.; Zasova, L.V.; D’aversa, E.; Bellucci, G.; Carrozzo, F.G.; Gondet, B.; Bibring, J.P. O2 1.27 μm emission maps as derived from OMEGA/MEx data. Icarus 2009, 204, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorova, A.A.; Lefèvre, F.; Guslyakova, S.; Korablev, O.; Bertaux, J.L.; Montmessin, F.; Reberac, A.; Gondet, B. The O2 nightglow in the martian atmosphere by SPICAM onboard of Mars-Express. Icarus 2012, 219, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertaux, J.L.; Gondet, B.; Lefèvre, F.; Bibring, J.P.; Montmessin, F. First detection of O2 1.27 μm nightglow emission at Mars with OMEGA/MEX and comparison with general circulation model predictions. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, E00J04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guslyakova, S.; Fedorova, A.; Lefèvre, F.; Korablev, O.; Montmessin, F.; Trokhimovskiy, A.; Bertaux, J.L. Long-term nadir observations of the O2 dayglow by SPICAM IR. Planet. Space Sci. 2016, 122, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnopolsky, V.A. Photochemical mapping of Mars. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 1997, 102, 13313–13320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd Clancy, R.; Smith, M.D.; Lefèvre, F.; McConnochie, T.H.; Sandor, B.J.; Wolff, M.J.; Lee, S.W.; Murchie, S.L.; Toigo, A.D.; Nair, H.; et al. Vertical profiles of Mars 1.27 µm O2 dayglow from MRO CRISM limb spectra: Seasonal/global behaviors, comparisons to LMDGCM simulations, and a global definition for Mars water vapor profiles. Icarus 2017, 293, 132–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Fu, D.; Feng, Y.; Li, J.; Hao, X.; Li, F. Simulation and application of the emission line O19P18 of O2(a1Δg) dayglow near 1.27 μm for wind observations from limb-viewing satellites. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 16984–16999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasnopolsky, V.A. Spectroscopy and Photochemistry of Planetary Atmospheres and Ionospheres: Mars, Venus, Titan, Triton and Pluto; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019; Volume 23. [Google Scholar]
- Crisp, D.; Meadows, V.S.; Bézard, B.; Bergh, C.d.; Maillard, J.P.; Mills, F.P. Ground-based near-infrared observations of the Venus nightside: 1.27-μm O2(a1Δg) airglow from the upper atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 4577–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Rong, P.; Yan, T.; Chen, Z. Influence of the tilted arm glass on the temperature and wind velocity inversion for a static wind imaging interferometer. Opt. Commun. 2021, 495, 127118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, W.E. The Design and Implementation of the Wide-Angle Michelson Interferometer to Observe Thermospheric Winds. Ph.D. Thesis, York University, Toronto, Canada, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Langille, J.A.; Ward, W.E.; Scott, A.; Arsenault, D.L. Measurement of two-dimensional Doppler wind fields using a field widened Michelson interferometer. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 1617–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuillier, G.; Shepherd, G.G. Fully compensated Michelson interferometer of fixed-pathdifference. Appl. Opt. 1985, 24, 1599–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millour, E.; Forget, F.; Spiga, A.; Vals, M.; Zakharov, V.; Navarro, T.; Montabone, L.; Lefevre, F.; Montmessin, F.; Chaufray, J.-Y.; et al. The Mars Climate Database (MCD Version 5.3). In Proceedings of the 19th EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, 23–28 April 2017; EGU: Munich, Germany, 2017; p. 12247. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, P. Measurement of visibility and phase steps of a static wind imaging interferometer assisted by deep learning. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 3533–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

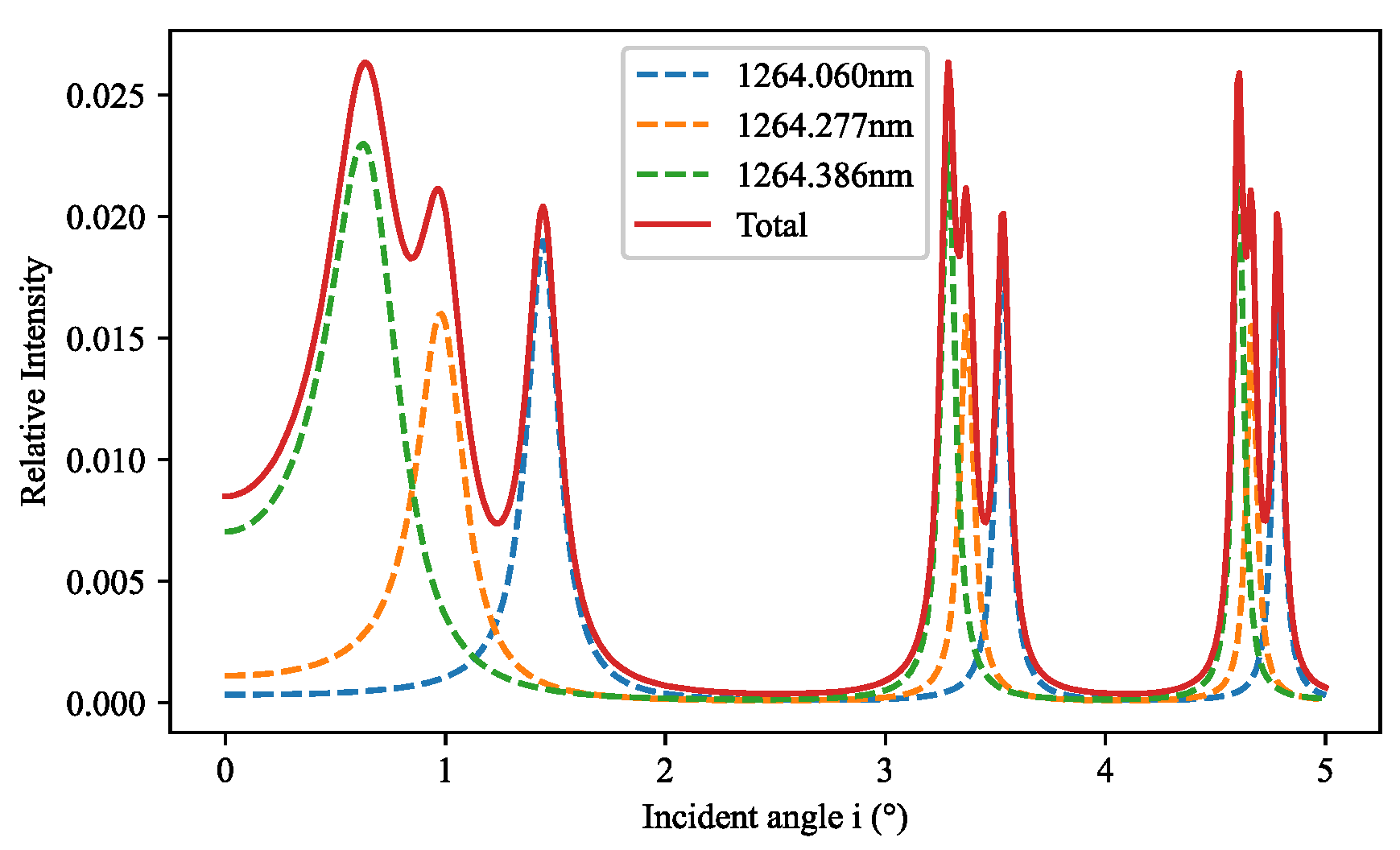
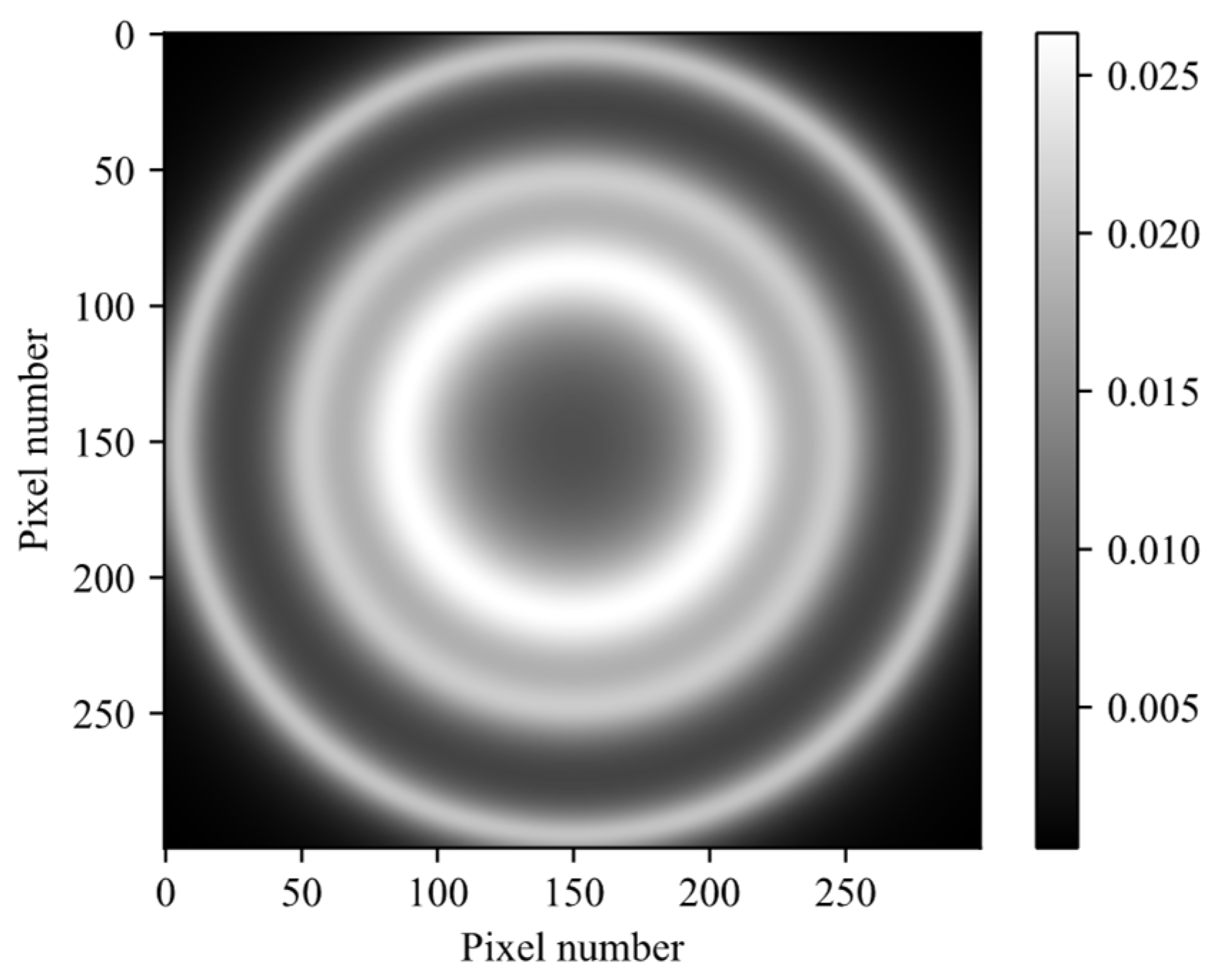
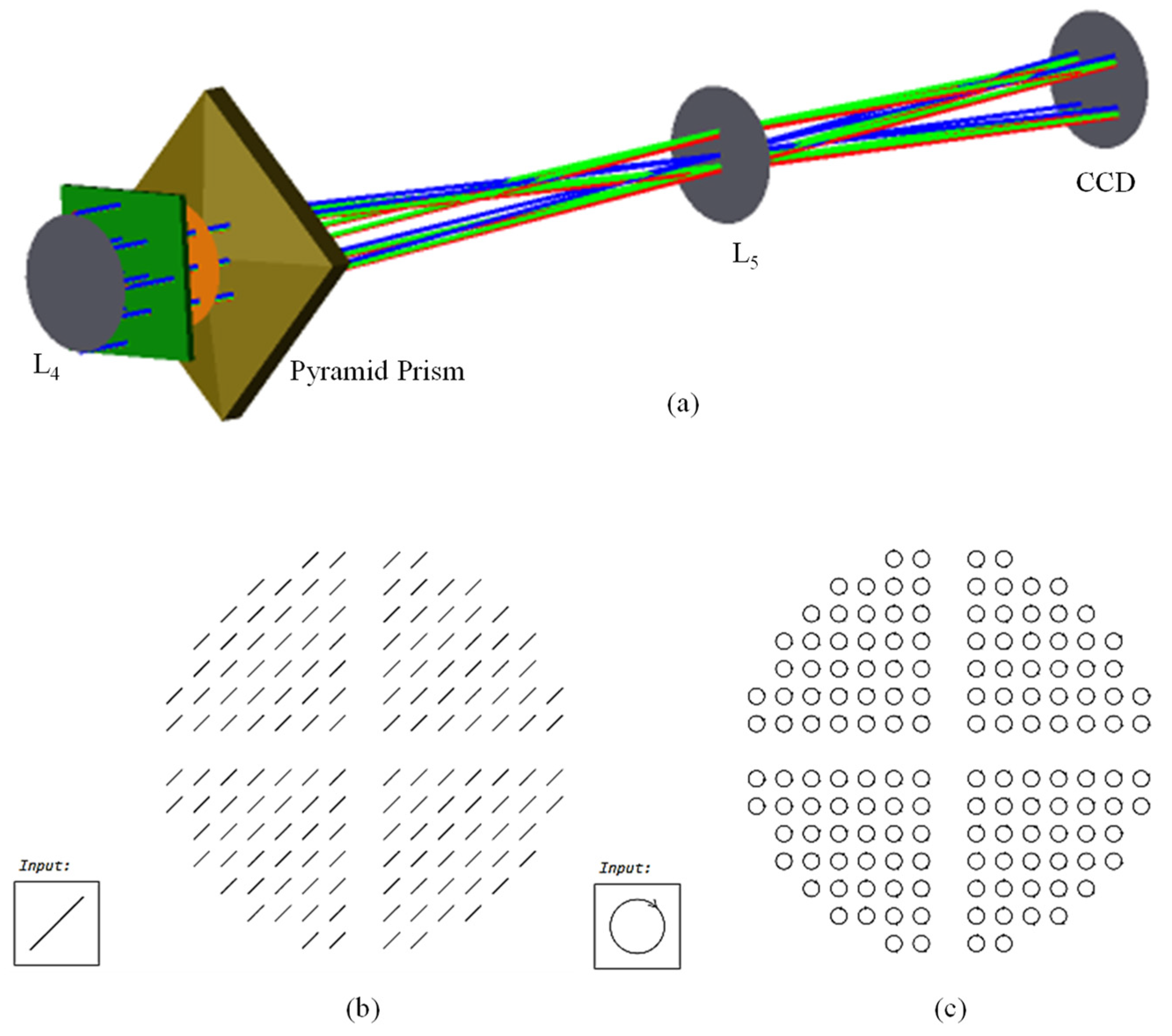

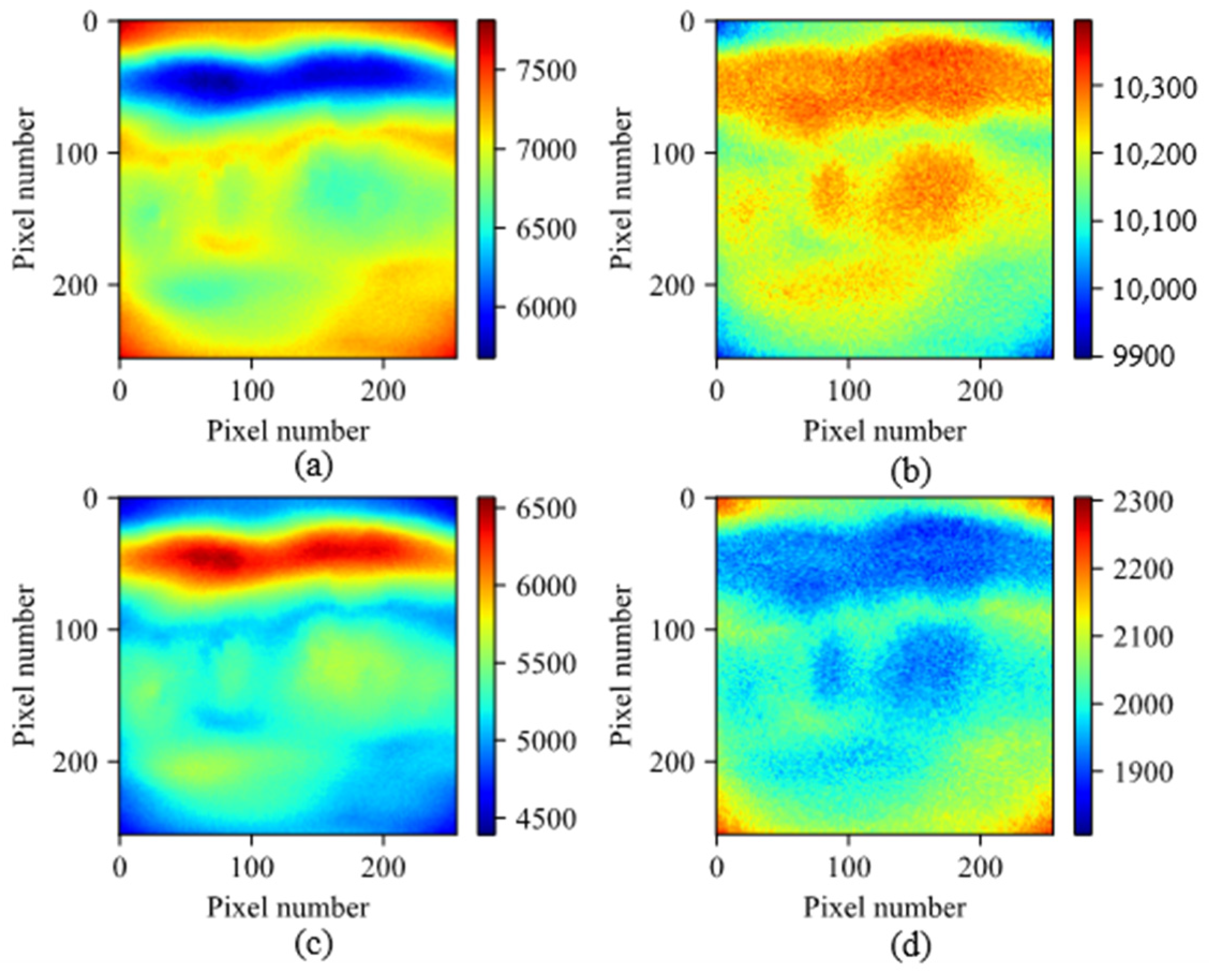
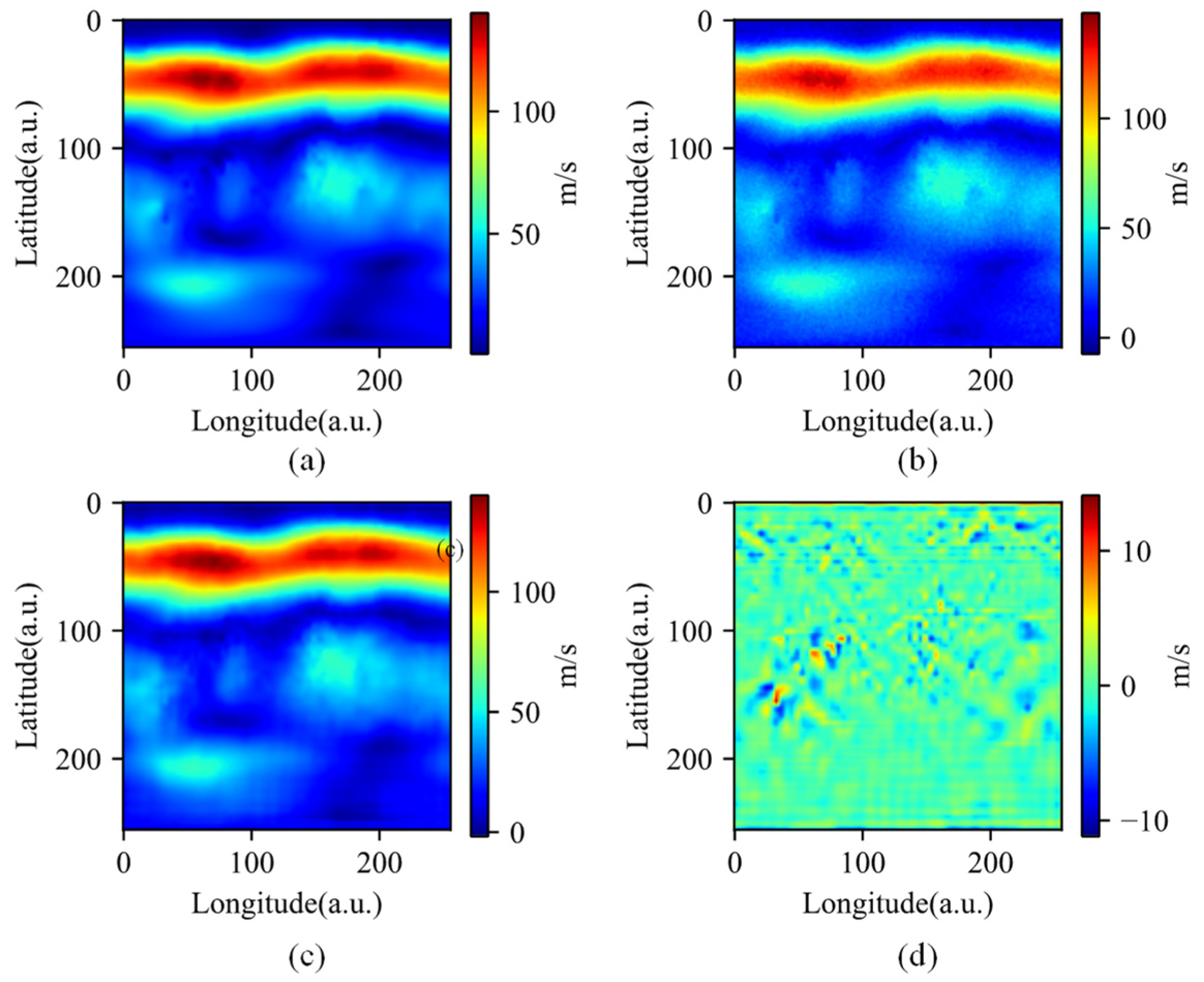
| Line | Wavelength in Vacuum (nm) | Relative Intensity at 225 K | dI/dT at 225 K (%/K) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RQ (9) | 1264.060 | 0.019 | −0.016 |
| SR (3) | 1264.277 | 0.017 | −0.340 |
| RR (9) | 1264.386 | 0.023 | −0.016 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Mean satellite height | 325 km |
| Orbit eccentricity (Elliptical orbit) | 0.0072 |
| Orbit inclination | 70° |
| Azimuth of FOVs | FOV1: 45°, FOV2: 135° |
| Declination | 21.75° |
| vertical resolution | 1 km |
| Focal length of system | 108 mm, F/2 |
| Field of view | 2° × 2° |
| Hor/Ver pixels of each FOV | 125/125 |
| Hor/Ver pixels per bin | 5/5 |
| The detected range of atmospheric altitude | 10~60 km |
| Symbols | Meaning | Value |
|---|---|---|
| c | Velocity of light | 3 × 108 m/s |
| Reference wavelength | 1264.277 nm | |
| U | Instrument visibility | 0.9 |
| V | Emission line visibility | Equation (27) |
| Integrated emission rate | 1~200 MR for dayglow | |
| A | Aperture area | 22.9 cm2 |
| The solid angle subtended by each bin on the detector | 3.83 × 10−7 sr | |
| Optical system transmittance | 0.15 | |
| CCD quantum efficiency | 0.8 | |
| t | Integration time | 10 s |
| N | The number of pixels in a bin | 25 |
| Dark current signal per pixel of CCD | 6 electrons | |
| Readout noise of CCD | 40 electrons rms |
| Parameters | Glass 1 | Glass 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Glass | H-ZlaF2A | H-K8 |
| Thickness (mm) | 84.34 | 71.24 |
| Refractive index @ 1264 nm | 1.7792 | 1.5028 |
| Filter | Bandwidth (nm) | Free Spectral Range (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| Narrowband Interference filter | 2.0 | None |
| F-P Etalon | 0.1 | 2.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yan, T.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z. Novel Compact Polarized Martian Wind Imaging Interferometer. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4881. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194881
Zhang C, Wang Y, Zhang B, Yan T, Chen Z, Chen Z. Novel Compact Polarized Martian Wind Imaging Interferometer. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(19):4881. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194881
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chunmin, Yanqiang Wang, Biyun Zhang, Tingyu Yan, Zeyu Chen, and Zhengyi Chen. 2023. "Novel Compact Polarized Martian Wind Imaging Interferometer" Remote Sensing 15, no. 19: 4881. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194881
APA StyleZhang, C., Wang, Y., Zhang, B., Yan, T., Chen, Z., & Chen, Z. (2023). Novel Compact Polarized Martian Wind Imaging Interferometer. Remote Sensing, 15(19), 4881. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194881