Abstract
In order to investigate the abundance of and temporal variation in nitrogen dioxide (NO2) in the troposphere and validate the corresponding satellite products during a normal year and the lockdown period of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Lhasa, a city on the Tibetan Plateau (TP), ground-based remote-sensing measurements captured by applying multi-axis differential optical absorption spectroscopy (MAX-DOAS) were recorded from August 2021 to March 2023 at the Lhasa site (91.14°E, 29.66°N; 3552.5 m altitude). The NO2 differential slant column densities (dSCDs) were retrieved from the spectra of scattered solar light at different elevation angles. Then, the tropospheric NO2 vertical column densities (VCDs) were calculated with the geometric approximation method. Based on the retrieved tropospheric NO2 VCDs, we found that the pattern of monthly variation in tropospheric NO2 VCDs in Lhasa presented two peaks, one in winter and one around May. According to the monthly means of tropospheric NO2 VCDs during the COVID-19 lockdown, the NO2 background level in Lhasa was estimated to be 0.53 × 1015 molecules·cm−2. For diurnal variations in tropospheric NO2 VCDs, the morning and evening peaks disappeared during the COVID-19 lockdown period. The east–west direction (i.e., along the river valley) was the main path of NO2 transport and dispersion in Lhasa, but the tropospheric NO2 VCDs were little dependent on the wind direction or wind speed during the COVID-19 lockdown. The correlation coefficient of tropospheric NO2 VCDs was R = 0.33 (R = 0.43), with the averaged relative deviation of −28% (99%) for the TROPOMI (GEMS) relative to ground-based MAX-DOAS. The monthly deviations of tropospheric NO2 VCDs between ground-based MAX-DOAS and the satellite showed a dependence on NO2 abundance, with the maxima of the monthly positive deviations during the COVID-19 lockdown period. The GEMS could not capture the strong and systematic diurnal variation in tropospheric NO2 VCDs in the “normal” year well. During the COVID-19 lockdown, the GEMS (>2 × 1015 molecules·cm−2) overestimated the hourly levels measured by ground-based MAX-DOAS (<1.6 × 1015 molecules·cm−2). As a whole, these results are beneficial to understanding the influences of anthropogenic activities on NO2 background levels in Lhasa and to learning the accuracy of satellite products over the TP, with its high altitude and complex terrain.
1. Introduction
As one of the major air pollutants, tropospheric nitrogen dioxide (NO2) affects the production of secondary atmospheric pollutants, such as ozone (O3), peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN), and secondary aerosol [1]. Tropospheric NO2 is harmful to human health, for instance, inducing respiratory disease [2]. Tropospheric NO2 originates from natural processes (microbial activities in soils, lighting in the atmosphere, etc.) and human activities (transportation, residential energy, industry, etc.) [3,4,5,6]. Tropospheric NO2 is mainly removed by photolysis and the photochemical reaction with free radicals or O3 [7]. Therefore, long-term observations of tropospheric NO2 are essential to monitor the conditions and characteristics of the atmospheric environment, which are quite useful to formulate scientific emission-controlling measures for improving air quality.
As one of six criteria for air pollutants, the surface in situ hourly NO2 concentrations in Lhasa have been released online by China’s Ministry of Environmental Protection since January 2013 [8]. These air quality data are widely used to reveal the spatiotemporal variations and formation mechanisms of air pollution. Through a cluster analysis of the annual and diurnal variations in the gaseous and particulate pollutants in 31 provincial capital cities, it was found that Lhasa is a slightly polluted city [8,9]. In western China, the meteorological conditions in winter tend to be unfavorable to pollutant dispersion and dilution, and the reduction in transport emissions is crucial for reducing NO2 [10]. Among six cities on the Tibetan Plateau (TP), the anthropogenic activities in Lhasa are the strongest, so attention should be paid to local emissions in addition to long-range transport pollutants [11]. A comparison of NO2 mixing ratios in Lhasa in the summers between 1998 and 2012 showed that the emission of NO2 is increasing and its inter-correlations with other trace gases (for example, carbon oxide and sulfur dioxide) are changing [12]. These findings are related to accelerated social and economic development, such as rapid urbanization, the development of the tourism industry, and the change in energy structure [13]. To prevent the spread of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Lhasa took emergency lockdown measures starting on 13 August 2022. The lockdown of production and living activities caused a pronounced reduction in the local emission of primary air pollutants. This presented a great opportunity to investigate the background condition of air pollution in Lhasa during the COVID-19 lockdown period.
Tropospheric NO2 vertical column density (VCD) is an important indicator reflecting the air quality. Tropospheric NO2 VCDs are usually measured by satellite or ground-based remote sensing [14,15,16,17]. As a kind of ground-based remote-sensing technique, multi-axis differential optical absorption spectroscopy (MAX-DOAS) is widely used to retrieve tropospheric NO2 VCDs, which are also applied in the validation of a satellite product [18,19,20]. However, there are few reports of MAX-DOAS observations over the TP. The NO2 levels and monthly variations were estimated via this technique at Waliguan, a global atmospheric background station located in the northeastern TP [21]. Stratospheric NO2 VCDs were retrieved from the zenith DOAS spectra at Golmud station in the northern TP [22]. The NO2 profiles for the northern slope of Mount Everest were derived from MAX-DOAS observations to investigate the characteristics of NO2 vertical distributions in the southern TP [23]. Mobile MAX-DOAS observations were also performed to study the spatial distributions of tropospheric NO2 VCDs during the summer over the Three Rivers’ source region in the TP [24]. Ground-based MAX-DOAS was applied to monitor the short-term variation in tropospheric NO2 in Lhasa [25]. To the best of our knowledge, relatively long-term variations in tropospheric NO2 VCDs, especially those during the COVID-19 outbreak in 2022, have not been reported yet. Currently, the validations of satellite products, especially for the new-generation geostationary satellites monitoring the atmospheric composition over the TP, are the focus of the remote-sensing community [14].
In this study, we performed ground-based MAX-DOAS measurements in Lhasa from 8 August 2021, covering the COVID-19 pandemic from 13 August to 13 December 2022. In the process, we retrieved the tropospheric NO2 VCDs from the spectra of scattered solar light, investigated the characteristics of the temporal evolution of tropospheric NO2 VCDs, and validated the tropospheric NO2 satellite products over Lhasa. The remainder of this article is structed as follows. Section 2 introduces the measurement site and instruments, the methods (including a spectral analysis and tropospheric NO2 VCD retrieval), and tropospheric NO2 satellite products. Section 3 presents the monthly and diurnal variations in tropospheric NO2 VCDs, the relationship to wind, and a comparison with the satellite products. Finally, we provide a discussion and conclusions in Section 4 and Section 5, respectively.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site and Instruments
The fieldwork was performed from 8 August 2021 to 20 March 2023 at the Lhasa meteorological station (91.14°E, 29.66°N; 3552.5 m above sea level), located in the downtown of the capital of Tibet Autonomous Region. The world famous Potala Palace is about 1.5 km away from the southwest of Lhasa station. Low buildings are distributed mainly over 3 km within Lhasa, containing several temples (such as Jokhang temple and Ramoche temple) with incense biofuel burning due to religious activities. The Lhasa city is within a flat river valley over the TP, i.e., with the mountains located to the south and north of the site. The Lhasa River, as a tributary of the Yarlung Zangbo River, runs through the southern part of the Lhasa city from the east to west. The major roads are built along an east–west direction. The national nature reserve of Lalu wetland is about 3 km away to the northwest of the Lhasa site. The Duilongdeqing district, mainly containing light and logistics industries, is about 13 km west of the Lhasa site. The railway station and airport are located to the southwest of the Lhasa site at distances of about 7.5 km and 45 km, respectively. The site is dominated by a monsoon temperate semi-arid plateau climate, characterized by strong solar radiation, a long period of sunny weather and low rainfall. The rainy season is concentrated in June through September with frequent night rain. It is cold and dry in winter. The operational meteorological observations, such as surface wind, are performed at this station. For more details about the natural conditions and human activities surrounding the site, please refer to previous studies [12,13,25].
The commercial Mini MAX-DOAS from Hoffmann Messtechnik GmbH in Germany, which was set up on the roof of a four-storied building, was used to collect the spectra of scattered sunlight at 12 elevation angles (1°, 2°, 3°, 4°, 5°, 6°, 8°, 10°, 15°, 30°, 45°, and 90°). The same instrument had been used in previous measurements at Gucheng [26], Waliguan [21] and Longfengshan stations [20], respectively. The instrument consists of an entrance optical lens, fiber-coupled spectrograph, as well as collecting and controlling electronics, which are sealed in a metal box with a volume of 3 L. A telescope and a stepper motor are mounted outside the box. The box can be rotated on the whole in the vertical direction to make the telescope point to different-elevation viewing angles with a fixed azimuth angle of 211°. The spectrograph covers a wavelength range of roughly 290–447 nm, operating at a stable detector temperature lower than the air temperature. The operating detector temperatures in Lhasa were set as −10 °C in winter and 0 °C in other seasons. At a specific operating temperature, the spectra of dark current (DC) and electronic offset (OS) were manually collected to correct each measurement spectrum. A laptop with professional software was used to control the instrument automatically. It takes about 12 min to perform a sequence of elevation angles because the integration time of one individual spectrum is ~1 min.
2.2. Spectral Analysis
The method of differential optical absorption spectroscopy (DOAS) was proposed in the 1970s on the basis of the Beer–Lambert law, which can be used to retrieve the differential slant column densities (dSCDs) of atmospheric trace gases (such as NO2) from scattered sunlight spectra [27]. This process is achieved by a spectral fit, i.e., minimizing the differences between measured and simulated spectra (Figure 1a). The retrieved dSCDs of a target trace gas, i.e., NO2 in this article, represent the differences in the integrated concentration along the effective light path (SCD) between the atmospheric measurement spectrum and the Fraunhofer reference spectrum (FRS) [18,28]. The FRS, selected from the measured spectra, usually includes two schemes, i.e., so-called “fixed FRS” and “sequential FRS” [24,29]. The former corresponds to a fixed spectrum at the 90° elevation angle at noon, which is used for all measured spectra to minimize the tropospheric and stratospheric contributions. The latter is defined as the time-interpolated spectrum between two zenith spectra measured before and after the time of the current off-zenith elevation angle. Comparisons in previous studies have shown that the signal-to-noise ratios are higher and the fitting errors are smaller when using the sequential FRS rather than the fixed FRS, which can be attributed to more similar instrument properties and similar atmospheric conditions in a short time between a specific measurement spectrum and the corresponding sequential FRS [24]. Therefore, we used the scheme of “sequential FRS” in this study. Table 1 lists the final optimal fit settings for the NO2 spectral analyses. In practice, the retrieval of NO2 dSCDs was achieved with the QDOAS software (version 3.0), developed by the Royal Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy (BIRA-IASB) [30]. The QDOAS software includes multiple functions, such as DC and OS corrections of the measured spectra, spectral calibration of the FRS, convolution of the cross-sections of the trace gases, and spectral fit. Figure 1 shows an example of the spectral fit for NO2 dSCDs from a measured spectrum at the 15° elevation angle and the 53.92° solar zenith angle (SZA) at 3:43 UTC on 19 February 2022 in Lhasa. The reason for choosing this spectrum as an example of spectral fit is that its root mean square (RMS) of the spectral fitting residual is close to the RMS’s median of all spectra during the observation period. During the quality control of NO2 dSCDs, we applied filters to balance the results’ quality and the remaining data amount. With the filters of SZA < 75° and RMS < 0.003 [20], we kept 75.60% of the NO2 dSCDs relative to the original QDOAS output. For all the filtered NO2 dSCDs, the means of RMS and relative spectral-fit errors are 1.37 × 10−3 and 10.6%, respectively.
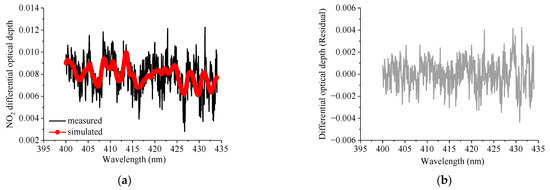
Figure 1.
Example of the spectral fit for NO2 at 3:43 UTC on 19 February 2022 in Lhasa at the 15° elevation angle and 53.92° SZA. (a) Black curves and red curves with symbols indicate the measured and simulated differential absorption spectral structures for NO2, respectively. The derived NO2 dSCD is 1.35 × 1016 molec·cm−2. (b) The root mean square (RMS) of the spectral-fitting residuals between measured and fitted spectra is 1.32 × 10−3 for NO2.

Table 1.
Fit settings for the NO2 spectral analyses.
2.3. Tropospheric NO2 VCDs
Tropospheric NO2 VCDs are calculated with the aforementioned filtered NO2 dSCDs. When adopting the scheme of “sequential FRS”, the NO2 dSCDs retrieved from measured spectra can be treated as tropospheric dSCDs (shown as dSCDTrop) [18]. For convenient comparison between different measurements, the air mass factor (AMF), which is independent of solar position, observation geometry and effective light path length, is usually used to convert the SCDs to VCDs. The total AMF can be split into two parts, i.e., the tropospheric AMFTrop and stratospheric AMFStra [35]. The VCDTrop can be expressed as the following:
If ,
Via further formula derivation with Equations (1) and (2), the VCDTrop can be written as:
where:
The AMF can be accurately simulated by an atmospheric radiative transfer model with various input information or simply estimated by the so-called “geometric approximation”. A previous study for the TP indicated that the “geometric approximation” method is suitable for the VCD’s calculation of tropospheric NO2, which is mainly distributed in the lower troposphere [24]. When adopting the “geometric approximation” method, the can be expressed as follows:
Then, Equation (3) becomes:
More details about the applicability of the “geometric approximation” method can be found in our previous research papers [24,35]. In this study, we calculated NO2 VCDTrop according to the dSCDs at the 15° elevation angle. In this situation, the typical errors caused by the geometric approximation method are less than 20% for NO2 [24].
2.4. Satellite Product
2.4.1. Tropospheric NO2 by TROPOMI
The TROPOspheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) is the sole payload of the Sentinel-5 Precursor (S-5 P) satellite, launched by the European Space Agency (ESA) on 13 October 2017. The S-5 P satellite flies in a near-polar sun-synchronous orbit, with the local transit time of 13:30 at the ascending node. The TROPOMI can effectively monitor the global distributions of several trace gases in the atmosphere, including tropospheric NO2, and also allows the observation of aerosol and cloud [36]. The TROPOMI covers multi-wavelength segments of the ultraviolet-visible, near-infrared, and shortwave infrared spectral ranges. It achieves daily global coverage with a 108° field of view at nadir. Since 6 August 2019, the TROPOMI has performed the measurement in the spatial resolution of 5.5 × 3.5 km2 at nadir. To obtain the tropospheric NO2 VCDs, a total NO2 SCD is firstly retrieved from the Level-1b radiance and irradiance spectra measured by the TROPOMI using DOAS method. Then, total NO2 SCDs are separated into the stratospheric SCDs and the tropospheric SCDs based on the information coming from a data assimilation system. Finally, the NO2 SCDs are converted into corresponding VCDs by using a look-up table of altitude-dependent AMFs. In this study, we use a kind of TROPOMI Level-2 NO2 product named “S5P_L2__NO2____HiR” [37]. According to the official recommendations for the data product usage, the flag of ‘quality assurance value’ (i.e., the variable of ‘qa_value’ in data product file) is used to filter the tropospheric NO2 VCDs for each individual observation, with the filtering condition of qa_value > 0.5. For comparison, the valid TROPOMI tropospheric NO2 VCDs within a 0.05° × 0.05° cell of the Lhasa observation site are averaged to ensure spatial consistency, and the filtered MAX-DOAS tropospheric NO2 VCDs within ± 1.5 h of the TROPOMI overpass time are also averaged to ensure consistency in time. Finally, 578 data pairs in total are applied in the comparison between the two datasets.
2.4.2. Tropospheric NO2 by GEMS
The Geostationary Environment Monitoring Spectrometer (GEMS) is onboard the GEO-COMPSAT-2B satellite, launched on 18 February 2020 by the Arianespace Ariane 5 rocket [38]. The UV-visible hyper spectrometer for the GEMS measures the atmospheric composition including NO2, sulfur dioxide (SO2), ozone (O3), formaldehyde (HCHO), and aerosols over East and Southeast Asia [39]. The GEMS, developed by the National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER), firstly achieves the geostationary air quality mission with high temporal resolution (8 observations over East Asia per day) [40]. The nominal spatial resolution is typically 7 km × 8 km for gases in the eastern and central scan domain, but the north–south spatial resolution can exceed 25 km in the western side. The whole field of view (FOV) covers a latitude range of 5–45°N and a longitude range of 80–152°E. There are four scan scenarios (i.e., Half East, Half Korea, Full Central, and Full West) moving from the east to west. The hourly GEMS observation includes the 30 min to scan the full coverage and another 30 min to transmit data to the ground data center. Owing to the seasonal variation in subsolar points relative to the Earth, there are about 10 hourly observations per day in summer and 6 in winter. The basic three steps of the GEMS tropospheric NO2 algorithm are similar to those described in Section 2.4.1. The details of the satellite, retrieval, and product can be found on the GEMS homepage (https://nesc.nier.go.kr/en/html/index.do, accessed on 21 July 2023). The official GEMS tropospheric NO2 VCDs (product version: v2.0.0), requested by the SFTP service, were used in this study. In addition, the hourly GEMS tropospheric NO2 VCDs within 0.05° of the Lhasa observation site were averaged for comparison with the corresponding means of ground-based MAX-DOAS measurements during the 30 min GEMS scan. Finally, there were 3090 data pairs in total between the two datasets.
3. Results
3.1. Monthly Variations in NO2 VCDs
Using the aforementioned filtered data, we firstly calculated the daytime hourly averaged NO2 VCDs, which were used to statistically obtain NO2 monthly variations at the Lhasa station. Figure 2 shows the monthly variation in the tropospheric NO2 VCDs from August 2021 to March 2023. Both the mean and median tropospheric NO2 VCDs present the same annual cycles, with the maximum (4.04 × 1015 molecules·cm−2) around December 2021 and minimum (0.53 × 1015 molecules·cm−2) in September 2022 during our observation period. The NO2 VCDs show the peak in winter, similar to surface NO2 in situ measurements in Lhasa [11,12,13], but there is another peak for the NO2 VCDs around May. The lower value in October 2021 was partly because of less tourism activity, with Lhasa moving into the cold season. The peak in December 2021 was probably related to the increase in winter heating emissions. Local minimum values appeared in February 2022, which were probably connected with the migrants leaving Lhasa, such as those returning home for the Spring Festival. Then, the NO2 VCDs began to increase and reached high values in the warm seasons (April–July 2022), which were partly connected with many people coming to Lhasa for business or summer tourism. The dramatic decline in NO2 VCDs from July to August in 2022 and the extreme minimum around September 2022 should be particularly noted. To a large extent, this was created by the COVID-19 outbreak in Lhasa, and then some emergent lockdown measures were taken from 13 August to 13 December 2022 in order to prevent the COVID-19 pandemic. Correspondingly, the local emissions of primary air pollutants were strongly reduced. After lifting the lockdown, another local minimum of the NO2 VCDs appeared in January 2023, probably with a cause similar to that of the minimum in February 2022. In addition, the rather low levels of NO2 VCDs were not only less than those at the Longfengshan and Shangdianzi regional background stations [20,28] but also significantly lower than those in megacities (such as Beijing) [35,41]. This can be attributed to the higher site altitude with a thin tropospheric air column and relatively fewer anthropogenic emissions in Lhasa.
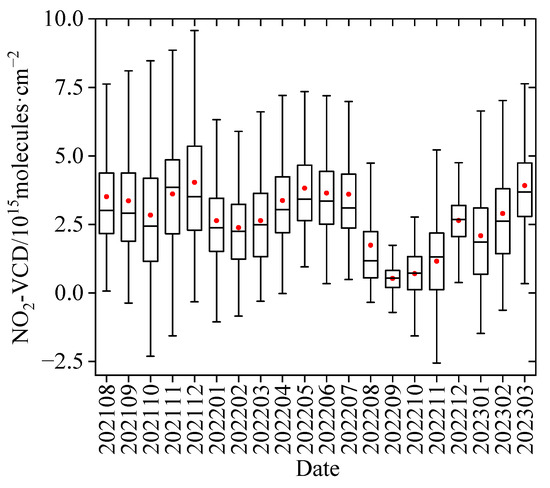
Figure 2.
Monthly variation in the tropospheric NO2 VCDs in Lhasa from August 2021 to March 2023. Upper (lower) error bars and black boxes are the maxima (minima) and the 25th (75th) percentiles of the hourly NO2 VCDs grouped in each month, respectively. The hyphens inside the boxes and the red dots are the medians and the mean values, respectively.
3.2. Diurnal Variations in NO2 VCDs
Due to the COVID-19 lockdown covering the late summer, autumn, and early winter of 2022, we preferred to choose representative months to analyze the diurnal variations in tropospheric NO2 VCDs in different seasons in this study. Figure 3 shows the averaged diurnal variations in tropospheric NO2 VCDs in April, July, October and January (the averaged diurnal variations in tropospheric NO2 VCDs in four seasons are shown in Figure A1). It should be noted that we eliminated one outlier (2.63 × 1016 molecules·cm−2) at 17:00 Beijing time (BJT = UTC + 8; we use BJT in this article unless otherwise specified) on 29 July 2022, which was larger than the mean plus three times the standard deviation. Due to different lengths of the sunshine duration in different seasons, the longest available time period for MAX-DOAS measurements appeared in July, and the shortest in January. The diurnal variation patterns of tropospheric NO2 VCDs were different in different seasons, owing to the complex interplay of source emissions, atmospheric photochemical reactions, and dynamic processes [28,35,42,43]. In April and July, the highest tropospheric NO2 VCDs occurred in the morning and late afternoon with the minimum around 16:00 BJT. In July, there was another small peak around 14:00 BJT. In October 2021, tropospheric NO2 VCDs had a maximum at 10:00 BJT and a minimum at 17:00 BJT. However, the diurnal cycle of tropospheric NO2 in October 2022 was absolutely different. The tropospheric NO2 maintained a very low level with a slightly decreasing trend and without morning and evening peaks. Figure 3 also shows the apparent differences in level and diurnal pattern of tropospheric NO2 between the ‘normal’ and ‘lockdown’ conditions. In January, the diurnal patterns of tropospheric NO2 are similar between 2022 and 2023, i.e., a decreasing trend from the early morning to the late evening. However, except during the morning, the levels of tropospheric NO2 VCDs are significantly lower in January 2023 (i.e., after COVID-19 pandemic) than those in January 2022 (i.e., during a normal year). As a whole, these results imply that the characteristics of tropospheric NO2 diurnal variation are closely related to local anthropogenic activities in Lhasa.
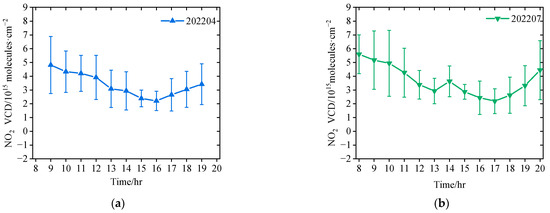
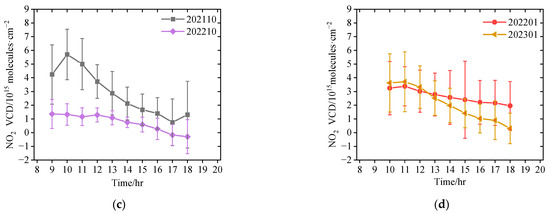
Figure 3.
Diurnal variation in the hourly averaged tropospheric NO2 VCDs in Lhasa in representative month of different seasons, i.e., (a) April, (b) July, (c) October, and (d) January. The error bars denote the standard deviations for each grouped hour. The numbers in the legends refer to the observation time, with the first four digits for year and the last two digits for month, respectively.
3.3. Relationship to Wind
In this section, we explore the relationship of tropospheric NO2 VCDs to the wind in the representative months of different seasons (the corresponding figures to different seasons can be found in Figure A2, Figure A3 and Figure A4). Considering that tropospheric NO2 commonly exponentially decreases with height (with scale heights of usually a few hundred meters) [23], the ground wind data are usually used to investigate the dependences of the tropospheric NO2 column on wind [28,44]. According to the wind roses in 16 wind direction sectors (Figure 4), we can see that the wind directions were mainly distributed in the W, WSW, and E during the daytime effective observation period, conforming to the typical terrain of river valley in Lhasa. The dominant wind directions changed with different months, i.e., with western and eastern wind in spring and summer, WSW wind in autumn, and eastern wind in winter, due to the differences in the atmospheric large-scale circulation (such as monsoon) affecting Lhasa in different seasons [45]. Most of the wind speeds were concentrated in the range of 1–4 m·s−1, and wind speeds higher than 6 m·s−1 were rare (mainly in winter). The tropospheric NO2 VCDs were strongly dependent on the wind (Figure 5). In all months, larger NO2 VCDs appeared along with weak wind, indicating the potential influence of local source emissions (such as traffic emissions) in Lhasa on the tropospheric NO2 levels. When under the lockdown of anthropogenic activities, the tropospheric NO2 in Lhasa sharply deceased to very low levels without the dependences of wind direction and wind speed, as can be seen in Figure 5e. When wind speeds were higher than 3 m·s−1, the tropospheric NO2 VCDs were strongly dependent on the wind direction in July 2022 (Figure 5d). In this case, the higher NO2 VCDs were distributed in the sections of N, SE, and SW, respectively. Furthermore, we explored the influence of air mass transport via weighted NO2 VCDs (Figure A5), which denote the tropospheric NO2 VCDs multiplied by the corresponding wind frequency [28]. Although the dominant transport directions varied with seasons, the larger weighted NO2 VCDs essentially occurred in the sections of W, WSW and E, implying that the east–west direction (i.e., along the river valley) is the main transport path and the mountains to the south and north of the Lhasa city block the transport of air masses with less air pollutants to Lhasa. Therefore, the winds, affected by the terrain, influence the NO2 transport and dispersion in Lhasa significantly.
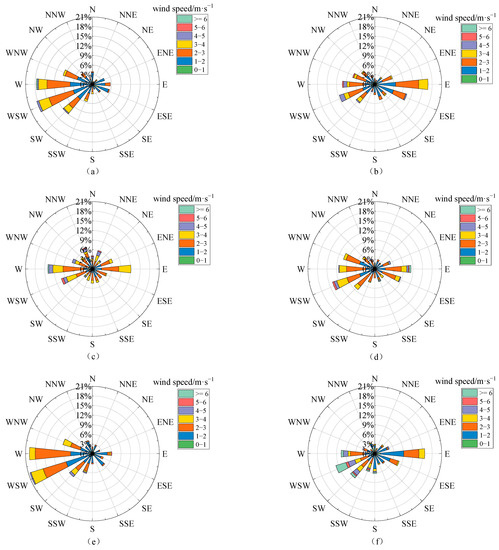
Figure 4.
The roses for wind frequency and wind speed in 16 wind direction sectors at Lhasa station during the daytime of the observation period in the representative month of different seasons, i.e., (a) October 2021, (b) January 2022, (c) April 2022, (d) July 2022, (e) October 2022, and (f) January 2023.
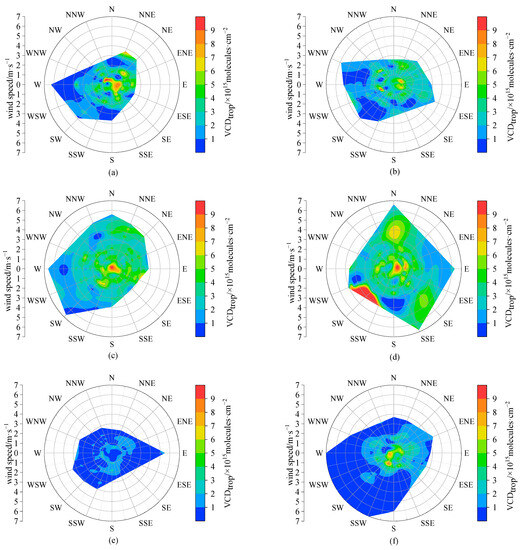
Figure 5.
The roses of hourly tropospheric NO2 VCDs in 16 wind direction sectors at Lhasa station during the daytime of observation period in the representative month of different seasons, i.e., (a) October 2021, (b) January 2022, (c) April 2022, (d) July 2022, (e) October 2022, and (f) January 2023.
3.4. Comparison with the TROPOMI and GEMS Products
The MAX-DOAS measurement is performed on the ground, but the satellites (TROPOMI and GEMS) detect atmospheric NO2 from the space. Meanwhile, TROPOMI scans the atmosphere in a near-polar sun-synchronous orbit once a day and the GEMS achieves eight observations per day in a geostationary orbit. To validate the satellite NO2 products over the Tibetan Plateau, we compared the tropospheric NO2 VCDs between the ground-based MAX-DOAS measurements and two satellite measurements, i.e., TROPOMI and GEMS, respectively. Based on the aforementioned data pairs (Section 2.4), the monthly medians of tropospheric NO2 VCDs were separately calculated for the three datasets. In a linear regression analysis (Figure 6a) [46], the correlation coefficient (R = 0.53) of ground-based MAX-DOAS with the TROPOMI was smaller than that (R = 0.73) with the GEMS, with averaged relative deviations of −51% and −13% for the TROPOMI and the GEMS, respectively, relative to the ground-based MAX-DOAS measurement. Furthermore, the averaged GEMS NO2 VCD (2.73 × 1015 molecules·cm−2) was significantly larger than that (1.14 × 1015 molecules·cm−2) observed by the TROPOMI during the fieldwork period on the whole. The differences in the levels and their correlations with ground MAX-DOAS measurement between the two satellite NO2 products are partly connected with the fact that the GEMS contained more data pairs (Section 2.4) including larger NO2 VCDs in the morning, relative to the TROPOMI. Meanwhile, both the slopes of linear fit were smaller than unity (Figure 6a), indicating that the two satellites overestimated (underestimated) the tropospheric NO2 VCDs in low-level (high-level) months. Figure 6b presents the absolute deviations (AD) and relative deviations (RD) of the monthly median tropospheric NO2 VCDs for the TROPOMI and the GEMS relative to the ground-based MAX-DOAS measurement, respectively. For both the TROPOMI and the GEMS, the AD and RD show similar seasonal variation patterns. The maxima of monthly positive AD and RD appear during the COVID-19 lockdown period, specifically in October and November 2022 for the TROPOMI and in September for the GEMS, respectively. The AD and RD depend on the tropospheric NO2 abundance, and their monthly variations show a reverse phase of that of the tropospheric NO2 VCDs (Figure 2). Similarly, previous studies for urban, suburban, rural and remote stations found apparent station dependence, i.e., usually negative deviations in the unban condition and positive deviations in the remote condition for satellite tropospheric NO2 products [14]. The possible reasons for our finding are: (1) the ground-based MAX-DOAS is more sensitive to the NO2 in the lower troposphere, while the satellite’s sensitivity is higher in the upper troposphere; (2) the layer of high NO2 concentration was close to the surface in the ‘normal’ urban condition, but the relative NO2 profile had its maximum at higher altitudes during the lockdown period in Lhasa.
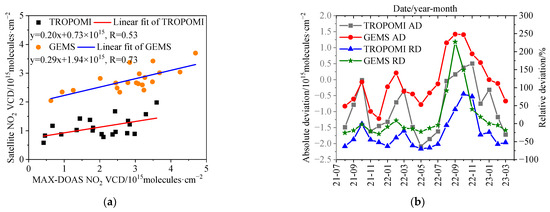
Figure 6.
Comparing the seasonal cycle of tropospheric NO2 VCDs between the ground-based MAX-DOAS measurement and satellite products. (a) Linear fit of the monthly medians of tropospheric NO2 VCDs between ground-based MAX-DOAS and two satellites (i.e., TROPOMI and GEMS), respectively. (b) Relative to the ground-based MAX-DOAS, the absolute deviations (AD) and relative deviations (RD) of monthly medians of tropospheric NO2 VCDs for TROPOMI and GEMS, respectively.
On the basis of the aforementioned comparison between satellite and ground-based MAX-DOAS measurements, the tropospheric NO2 VCDs were further selected for cases when the TROPOMI overpass time was within ±0.5 h of GEMS observations, producing 338 data pairs among the three datasets. In this situation, the means ± standard deviations of tropospheric NO2 VCDs for the ground-based MAX-DOAS, GEMS, and TROPOMI were 2.09 ± 1.33 × 1015 molecules·cm−2, 2.68 ± 0.56 × 1015 molecules·cm−2, and 1.04 ± 0.62 × 1015 molecules·cm−2 during the observation period, respectively. After eliminating the data samples under the condition of data pairs ≤3 in a specific month, the monthly medians of tropospheric NO2 VCDs were calculated and a corresponding linear regression analysis was carried out. The correlation coefficient was R = 0.33 (R = 0.43) between the TROPOMI (GEMS) and ground-based MAX-DOAS, with the averaged RD of −28% (99%) (Figure 7a). Figure 7b shows the updated monthly AD and RD of TROPOMI and GEMS tropospheric NO2 VCDs relative to the ground-based MAX-DOAS measurement. Both the GEMS and the TROPOMI overestimated or underestimated the tropospheric NO2 VCDs in different degrees on average, but they had similar monthly variation patterns for AD and RD. The large differences between the two satellite NO2 products cannot be fully understood at present. A large effort should be made to validate and improve the satellite tropospheric NO2 products for the TP in the future.
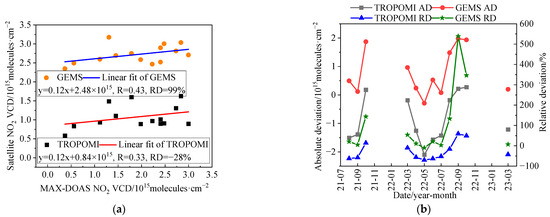
Figure 7.
Comparing the seasonal cycle of tropospheric NO2 VCDs for cases when the TROPOMI overpass time is within ± 0.5 h of GEMS observations. (a) Linear fit of the monthly medians of tropospheric NO2 VCDs between ground-based MAX-DOAS and two satellites (i.e., TROPOMI and GEMS), respectively. (b) Relative to the ground-based MAX-DOAS, the absolute deviations (AD) and relative deviations (RD) of monthly medians of tropospheric NO2 VCDs for TROPOMI and GEMS, respectively. The missing data are due to the data samples being ≤3 pairs in a specific month.
The GEMS satellite observes the same location on an hourly scale, providing the unique opportunity to investigate the diurnal variation in tropospheric NO2 VCDs from a satellite perspective. Figure 8a shows the diurnal cycle of tropospheric NO2 VCDs derived from data pairs of ground-based MAX-DOAS and the GEMS during the whole observation period (‘ALL’), the COVID-19 lockdown period (‘Lockdown’), and the period of lifting the COVID-19 lockdown (‘NoLockdown’). In the situations ‘All’ and ‘NoLockdown’, the diurnal patterns of tropospheric NO2 VCDs were different between ground-based MAX-DOAS and the GEMS. The former decreased gradually from 9:00 BJT to 16:00 BJT, but the latter fluctuated in a small range. This finding indicates that the GEMS does not capture the strong and systematic diurnal variation in the tropospheric NO2 VCD over Lhasa well. One possible explanation could be that the temporal variation in the NO2 layer height over Lhasa is not well-represented in the profile assumptions in the satellite retrieval.
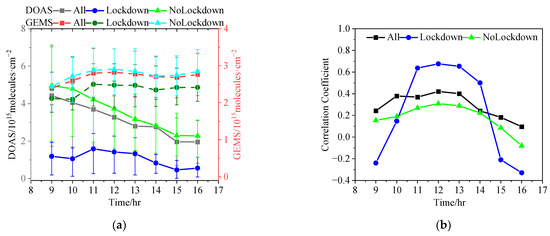
Figure 8.
Comparing the diurnal cycles of tropospheric NO2 VCDs between ground-based MAX-DOAS (abbreviated as DOAS in the figure) and GEMS satellite. (a) Averaged diurnal variation derived from the medians of tropospheric NO2 VCDs for three time periods, i.e., the whole observation period (‘ALL’), the COVID-19 lockdown period (‘Lockdown’), and the period of lifting the COVID-19 lockdown (‘NoLockdown’), respectively. (b) Correlation between the two datasets for each grouped hour during the three different time periods. The error bars denote the standard deviations for each grouped hour (BJT).
For the ‘Lockdown’ situation, both of the two datasets varied in a small range. However, the GEMS NO2 VCDs were larger than 2 × 1015 molecules·cm−2 and the ground-based MAX-DOAS NO2 VCDs were smaller than 1.6 × 1015 molecules·cm−2, indicating that the GEMS overestimated the tropospheric NO2 VCDs during the whole ‘Lockdown’ daytime. To further explore the consistency between the two datasets, we calculated the correlation coefficients in each grouped hour during the three different time periods (see Figure 8b). The diurnal patterns of correlation coefficient were similar for the three situations (‘All’, ‘Lockdown’, and ‘NoLockdown’), with the maximum correlation appearing around 12:00 BJT. It should be noted that a weak and even negative correlation tended to occur in the early morning and afternoon (local time). This is probably related to the large uncertainties of satellite observation under the condition of relatively low abundance and small variation range of tropospheric NO2 in Lhasa, especially during the COVID-19 lockdown period.
4. Discussion
The pattern of the monthly variation in the tropospheric NO2 VCDs in Lhasa presented two peaks within one year, which were different from a single winter peak in typical cities of eastern China [35]. With the background condition of very clean air over the Tibetan Plateau [21,24], this monthly cycle is closely connected with migration and seasonal living requirements. The peak around May was not detected by surface in situ measurement [11,12,13]. Probably, column observation by ground-based MAX-DOAS is a more appropriate way to monitor the NO2 levels of atmospheric pollution in Lhasa. Due to the COVID-19 lockdown, the tropospheric NO2 VCDs dramatically declined to the minimum during our observation period, further confirming that local emission sources have a potential effect on the NO2 levels in Lhasa.
In most cases, the diurnal variations in tropospheric NO2 VCDs in Lhasa presented two peaks, one in the early morning and another in the late afternoon. This is likely related to traffic emissions during the morning and evening rush hours. The time of the lowest NO2 VCDs during the daytime changed with month due to time differences in minimal SZA between seasons. The lowest NO2 levels during the diurnal cycle are partly caused by the photochemical loss under the strong solar radiation condition and also related to the favorable diffusion with the development of the planetary boundary layer. There were apparent differences in the diurnal pattern of tropospheric NO2 VCDs between the ‘normal’ and ‘COVID-19 lockdown’ conditions. During the COVID-19 lockdown period, the levels of tropospheric NO2 VCDs were close to the background concentration over the Tibetan Plateau [24].
The prevailing wind directions, i.e., western or eastern wind, are dependent on season and are affected by the landform of the river valley in Lhasa. The blocking effect of mountains in the south and north is not conducive to pollutant diffusion in the city river valley. The wind strongly affects the tropospheric NO2 VCDs, especially through source emissions along the river valley. In the future, the characteristics of the NO2 transport and dispersion along the river valley should be fully considered for designing the industry distributions in Lhasa. Although the tropospheric NO2 VCDs are very low at present in Lhasa, we should pay close attention to the increase in local sources with the city’s development [12], as well as the influence of long-distance transport on air pollution around the Tibetan Plateau in summer in future studies [47].
The comparison results for the tropospheric NO2 VCDs between ground-based MAX-DOAS and satellite (TROPOMI and GEMS) show that it is a challenge to precisely monitor NO2 in the lower troposphere using satellite over the TP, even in the plateau city of Lhasa. The small correlation coefficients, large deviations, and different diurnal patterns of tropospheric NO2 between ground-based MAX-DOAS and satellite are influenced by multiple complex factors, such as the difference in the sensitive altitudes of the two methods [14], low level and small variation range of tropospheric NO2, low signal-to-noise ratio (reduced due to measurement errors over mountain terrain [24]), and horizontal NO2 inhomogeneity [16,28]. The satellite retrieval of tropospheric NO2 should be further improved and validated over the TP in future studies. Before improving the satellite NO2 products and confirming their validity, we should use them with caution to investigate atmospheric chemical processes over the TP.
5. Conclusions
Ground-based MAX-DOAS measurements were conducted from August 2021 to March 2023 at Lhasa, an urban site in the south-central Tibetan Plateau (TP). To our knowledge, these are the first long-term measurements of this kind on the Tibetan Plateau. The NO2 differential slant column densities (dSCDs) were retrieved from the spectra of scattered solar light at different elevation angles using the DOAS technique. Then, the tropospheric NO2 vertical column densities (VCDs) were derived with the geometric approximation method. Based on the retrieved and filtered tropospheric NO2 VCDs, we investigated the characteristics of the tropospheric NO2 temporal evolution. The tropospheric NO2 VCDs were also applied to validate the corresponding TROPOMI and GEMS satellite products. The main findings are summarized as follows.
- The monthly variation pattern of the tropospheric NO2 VCDs in Lhasa presented two peaks, occurring in winter and around May. With the COVID-19 lockdown, the tropospheric NO2 VCDs dramatically declined to the minimum (0.53 × 1015 molecules·cm−2) in September 2022, which represents the NO2 background level in Lhasa city. Our dataset is thus very well-suited for the validation of atmospheric models centered on that region.
- Different from the diurnal variations in tropospheric NO2 VCDs under the ‘normal’ condition, there were no morning and evening peaks during the COVID-19 lockdown period, implying that local anthropogenic sources have apparent influences on the abundance and temporal evolution of tropospheric NO2 in Lhasa.
- Commonly, the east–west direction (i.e., along the river valley) was the main path of NO2 transport and dispersion in Lhasa. Under the condition of COVID-19 lockdown, the tropospheric NO2 VCDs were little dependent on the wind direction and wind speed.
- We also carried out the first validation of the novel GEMS satellite (as well as the TROPOMI satellite), utilizing its long-term observations over the Tibetan Plateau. Our ground-based measurements are especially well-suited for the validation of the GEMS observations because they also cover the diurnal variation in the tropospheric NO2 VCD. When the observations for the three datasets were available at the same time, the correlation coefficient of tropospheric NO2 VCDs was R = 0.33 (R = 0.43) with the averaged relative deviation of −28% (99%) for the TROPOMI (GEMS) relative to ground-based MAX-DOAS. Relative to the tropospheric NO2 VCDs measured by ground-based MAX-DOAS, the monthly deviations of satellite products had a dependence on NO2 abundance, with the maxima of monthly positive deviations occurring during the COVID-19 lockdown period. The GEMS could not capture the strong and systematic diurnal variation in tropospheric NO2 VCDs in the ‘normal’ year well. During the ‘Lockdown’ daytime, the GEMS (>2 × 1015 molecules·cm−2) overestimated the hourly levels measured by ground-based MAX-DOAS (<1.6 × 1015 molecules·cm−2).
As a whole, these conclusions are beneficial to further research on the atmospheric environment over the region with complex terrain and high altitude. More long-term ground-based MAX-DOAS measurements with smaller uncertainties are crucial for understanding the spatiotemporal evolution of air pollutants and satellite product validation in the future over the Tibetan Plateau.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.C., J.M. and T.W.; data curation, J.M. and H.H.; formal analysis, S.C.; funding acquisition, S.C. and G.P.; investigation, S.C., G.P., J.M., T.Y. and T.W.; methodology, S.C., J.M., H.H. and T.W.; project administration, S.C. and G.P.; resources, J.M., H.H., J.D. and T.W.; software, S.C., J.M. and T.W.; supervision, J.M.; validation, S.C., J.M. and T.W.; visualization, S.C. and G.P.; writing—original draft, S.C.; writing—review and editing, S.C., J.M. and T.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Nature Foundation of Tibet Autonomous Region (No. XZ202301ZR0011G) and the Fund of the State Key Laboratory of Applied Optics (No. SKLAO2021001A02).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request.
Acknowledgments
We thank the staff at the Lhasa Meteorological Bureau for supporting the measurements. We also thank NASA and NIER for providing the satellite products.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A
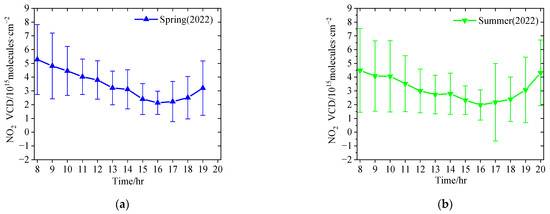
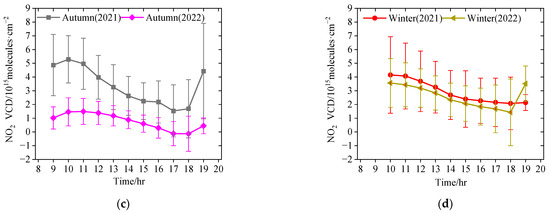
Figure A1.
Diurnal variation in the hourly averaged tropospheric NO2 VCDs in Lhasa in different seasons, i.e., (a) spring (March–May 2022), (b) summer (June–August 2022), (c) autumn (September–November 2021 and 2022), and (d) winter (December–February 2021 and 2022). The error bars denote the standard deviations for each grouped hour.
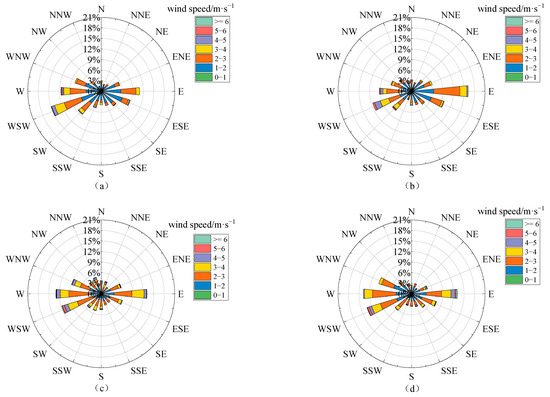
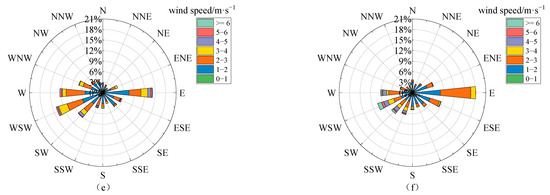
Figure A2.
The roses for wind frequency and wind speed in 16 wind direction sectors at Lhasa station during the daytime of the observation period in (a) autumn (September–November) 2021, (b) winter (December 2021–February 2022) 2021, (c) spring (March–May) 2022, (d) summer (June–August) 2022, (e) autumn (September–November) 2022, and (f) winter (December 2022–February 2023) 2022.
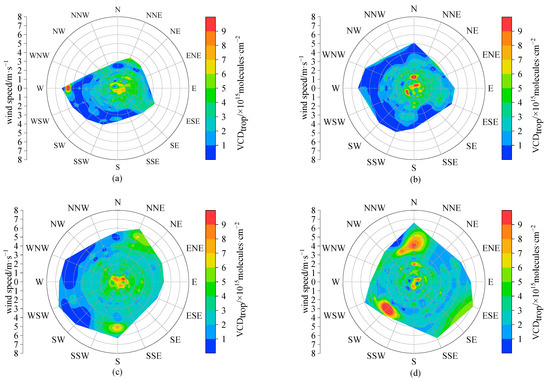
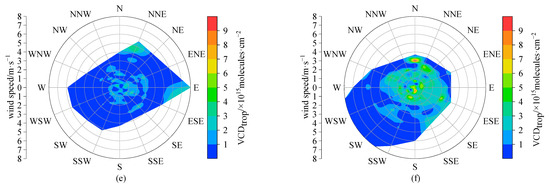
Figure A3.
The roses of hourly tropospheric NO2 VCDs in 16 wind direction sectors at Lhasa station during the daytime of the observation period in (a) autumn (September–November) 2021, (b) winter (December 2021–February 2022) 2021, (c) spring (March–May) 2022, (d) summer (June–August) 2022, (e) autumn (September–November) 2022, and (f) winter (December 2022–February 2023) 2022.
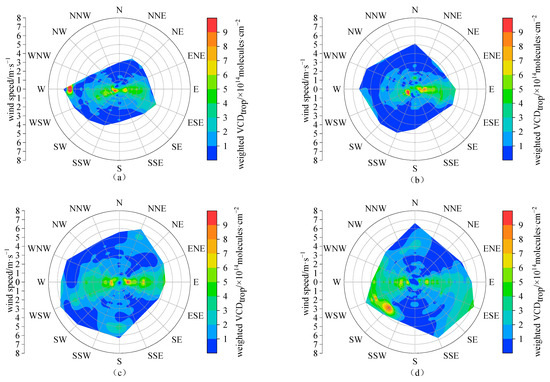
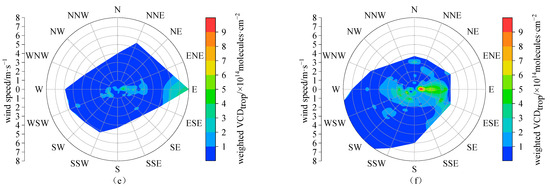
Figure A4.
The roses of hourly tropospheric NO2 VCDs weighted by wind frequency in 16 wind direction sectors at Lhasa station during the daytime of the observation period in (a) autumn (September–November) 2021, (b) winter (December 2021–February 2022) 2021, (c) spring (March–May) 2022, (d) summer (June–August) 2022, (e) autumn (September–November) 2022, and (f) winter (December 2022–February 2023) 2022.
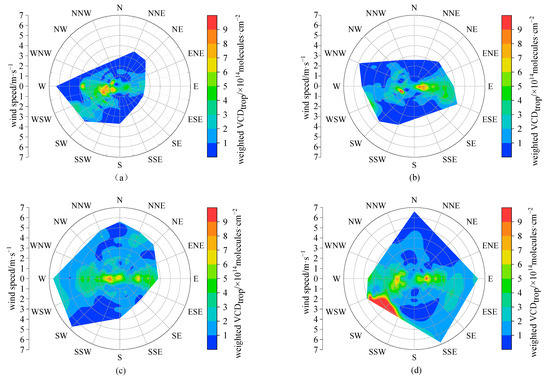
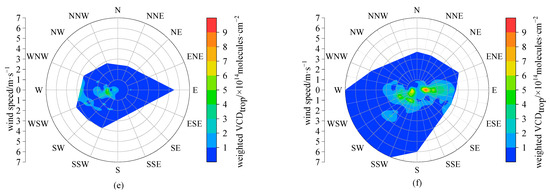
Figure A5.
The roses of hourly tropospheric NO2 VCDs weighted by wind frequency in 16 wind direction sectors at Lhasa station during the daytime of the observation period in the representative month of different seasons, i.e., (a) October 2021, (b) January 2022, (c) April 2022, (d) July 2022, (e) October 2022, and (f) January 2023.
References
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, C.; Li, B.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, C. Spatiotemporal neural network for estimating surface NO2 concentrations over north China and their human health impact. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Zhou, X. The study of the cycle of nitrogen oxides in the troposphere. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 1993, 4, 92–99. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.S.; Köhler, I.; Grobler, E.; Rohrer, F.; Sausen, R.; Gallardo-Klenner, L.; Olivier, J.G.J.; Dentener, F.J.; Bouwman, A.F. Estimations of global NOX emissions and their uncertainties. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 1735–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granier, C.; Bessagnet, B.; Bond, T.; D’Angiola, A.; Denier van der Gon, H.; Frost, G.J.; Heil, A.; Kaiser, J.W.; Kinne, S.; Klimont, Z.; et al. Evolution of anthropogenic and biomass burning emissions of air pollutants at global and regional scales during the 1980–2010 period. Clim. Change 2011, 109, 163–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimblecombe, P.; Chu, M.; Liu, C.-H.; Fu, Y.; Wei, P.; Ning, Z. Roadside NO2/NOX and primary NO2 from individual vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 295, 119562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, M. Atmospheric Environmental Chemistry; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Yu, Y.; Yin, D.; He, J.; Liu, N.; Qu, J.; Xiao, J. Annual and diurnal variations of gaseous and particulate pollutants in 31 provincial capital cities based on in situ air quality monitoring data from China National Environmental Monitoring Center. Environ. Int. 2016, 86, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Zhao, S.; Qu, J. Spatial and seasonal variations of gaseous and particulate matter pollutants in 31 provincial capital cities, China. Air Qual. Atmos Health 2017, 10, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ji, Z.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Lee, S.-Y. Spatiotemporal variations of air pollutants in western China and their relationship to meteorological factors and emission sources. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Kang, S.; Yang, J.; Pu, T.; Li, C.; Guo, J.; Tripathee, L. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Gaseous and Particulate Pollutants in Six Sites in Tibet, China, during 2016–2017. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Lin, W.L.; Deji, Y.Z.; La, B.; Tsering, P.M.; Xu, X.B.; Wang, W. Surface gas pollutants in Lhasa, a highland city of Tibet-current levels and pollution implications. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 10721–10730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; de Foy, B.; Wu, K.; Feng, C.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Q. Gaseous and particulate pollutants in Lhasa, Tibet during 2013–2017: Spatial variability, temporal variations and implications. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Park, J.; Hong, H.; Van Roozendael, M.; Hendrick, F.; Wang, T.; Wang, P.; et al. POMINO-GEMS: A Research Product for Tropospheric NO2 Columns from Geostationary Environment Monitoring Spectrometer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Luo, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Si, F.; Xi, L.; Zhou, H.; Liu, W. Tropospheric NO2 Pollution Monitoring with the GF-5 Satellite Environmental Trace Gases Monitoring Instrument over the North China Plain during Winter 2018–2019. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoelst, T.; Compernolle, S.; Pinardi, G.; Lambert, J.-C.; Eskes, H.J.; Eichmann, K.-U.; Fjæraa, A.M.; Granville, J.; Niemeijer, S.; Cede, A.; et al. Ground-based validation of the Copernicus Sentinel-5P TROPOMI NO2 measurements with the NDACC ZSL-DOAS, MAX-DOAS and Pandonia global networks. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 481–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xing, C.; Hu, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhao, S.; Gao, M. Stereoscopic hyperspectral remote sensing of the atmospheric environment: Innovation and prospects. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 226, 103958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hönninger, G.; Friedeburg, C.V.; Platt, U. Multi axis differential optical absorption spectroscopy (MAX-DOAS). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2004, 4, 231–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xing, C.; Hu, Q.; Li, Q.; Liu, H.; Hong, Q.; Tan, W.; Ji, X.; Lin, H.; Lu, C.; et al. Ground-based Hyperspectral Stereoscopic Remote Sensing Network: A Promising Strategy to Learn Coordinated Control of O3 and PM2.5 over China. Engineering 2021, 19, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cheng, S.; Ma, J.; Xu, X.; Lv, J.; Jin, J.; Guo, J.; Yu, D.; Dai, X. MAX-DOAS Measurements of Tropospheric NO2 and HCHO Vertical Profiles at the Longfengshan Regional Background Station in Northeastern China. Sensors 2023, 23, 3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Dörner, S.; Donner, S.; Jin, J.; Cheng, S.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, P.; Zhang, G.; et al. MAX-DOAS measurements of NO2, SO2, HCHO, and BrO at the Mt. Waliguan WMO GAW global baseline station in the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 6973–6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Ma, J.; Zheng, X.; Gu, M.; Donner, S.; Dörner, S.; Zhang, W.; Du, J.; Li, X.; Liang, Z.; et al. Retrieval of O3, NO2, BrO and OClO Columns from Ground-Based Zenith Scattered Light DOAS Measurements in Summer and Autumn over the Northern Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Liu, C.; Wu, H.; Lin, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Gao, M. Ground-based vertical profile observations of atmospheric composition on the Tibetan Plateau (2017–2019). Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 4897–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Cheng, X.; Ma, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; Lv, J.; Bai, G.; Chen, B.; Ma, S.; Ziegler, S.; et al. Mobile MAX-DOAS observations of tropospheric NO2 and HCHO during summer over the Three Rivers’ Source region in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 3655–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, G.; Cheng, S.; Li, S.; Lü, J.; Chen, H.; Ma, J. Spectral inversion and variation characteristics of tropospheric NO2 column density in Lhasa, Tibet. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2023, 43, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Ma, J.; Lin, W.; Zhao, H.; Shaiganfar, R.; Beirle, S.; Wagner, T. MAX-DOAS measurements and satellite validation of tropospheric NO2 and SO2 vertical column densities at a rural site of North China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 133, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, U.; Stutz, J. Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy, Principles and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Ma, J.; Cheng, W.; Yan, P.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, L.; Yang, P. Tropospheric NO2 vertical column densities retrieved from ground-based MAX-DOAS measurements at Shangdianzi regional atmospheric background station in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 80, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Puķīte, J.; Wagner, T.; Donner, S.; Beirle, S.; Hilboll, A.; Vrekoussis, M.; Richter, A.; Apituley, A.; Piters, A.; et al. Vertical Profiles of Tropospheric Ozone From MAX-DOAS Measurements During the CINDI-2 Campaign: Part 1-Development of a New Retrieval Algorithm. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 10637–10670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danckaert, T.; Fayt, C.; Roozendael, M.V.; Smedt, I.D.; Letocart, V.; Merlaud, A.; Pinardi, G. QDOAS Software User Manual; Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vandaele, A.C.; Hermans, C.; Simon, P.C.; Carleer, M.; Colin, R.; Fally, S.; Mérienne, M.F.; Jenouvrier, A.; Coquart, B. Measurements of the NO2 absorption cross-section from 42000 cm−1 to 10000 cm−1 (238–1000 nm) at 220 K and 294 K. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 1998, 59, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyansky, O.L.; Kyuberis, A.A.; Zobov, N.F.; Tennyson, J.; Yurchenko, S.N.; Lodi, L. ExoMol molecular line lists XXX: A complete high-accuracy line list for water. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 480, 2597–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serdyuchenko, A.; Gorshelev, V.; Weber, M.; Chehade, W.; Burrows, J.P. High spectral resolution ozone absorption cross-sections—Part 2: Temperature dependence. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalman, R.; Volkamer, R. Temperature dependent absorption cross-sections of O2-O2 collision pairs between 340 and 630 nm and at atmospherically relevant pressure. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 15371–15381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Z.; Beirle, S.; Jin, J.L.; Shaiganfar, R.; Yan, P.; Wagner, T. Tropospheric NO2 vertical column densities over Beijing: Results of the first three years of ground-based MAX-DOAS measurements (2008–2011) and satellite validation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 1547–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veefkind, J.P.; Aben, I.; McMullan, K.; Förster, H.; Vries, J.d.; Otter, G.; Claas, J.; Eskes, H.J.; Haan, J.F.d.; Kleipool, Q.; et al. TROPOMI on the ESA Sentinel-5 Precursor: A GMES mission for global observations of the atmospheric composition for climate, air quality and ozone layer applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESA; KNMI. Sentinel-5P TROPOMI Tropospheric NO2 1-Orbit L2 5.5 km × 3.5 km. 2021. Available online: https://sentinels.copernicus.eu/web/sentinel/data-products/-/asset_publisher/fp37fc19FN8F/content/sentinel-5-precursor-level-2-nitrogen-dioxide (accessed on 6 July 2023).
- Kang, M.; Ahn, M.-H.; Liu, X.; Jeong, U.; Kim, J. Spectral Calibration Algorithm for the Geostationary Environment Monitoring Spectrometer (GEMS). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.J. Introducing the geostationary environment monitoring spectrometer. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2018, 12, 044005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeong, U.; Ahn, M.-H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, R.J.; Lee, H.; Song, C.H.; Choi, Y.-S.; Lee, K.-H.; Yoo, J.-M.; et al. New Era of Air Quality Monitoring from Space: Geostationary Environment Monitoring Spectrometer (GEMS). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 101, E1–E22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrick, F.; Müller, J.-F.; Clémer, K.; Wang, P.; Mazière, M.D.; Fayt, C.; Gielen, C.; Hermans, C.; Ma, J.Z.; Pinardi, G.; et al. Four years of ground-based MAX-DOAS observations of HONO and NO2 in the Beijing area. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 765–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, C.; Lin, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Wu, H.; Liu, C. Variations of Urban NO2 Pollution during the COVID-19 Outbreak and Post-Epidemic Era in China: A Synthesis of Remote Sensing and In Situ Measurements. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvir, A.; Javed, Z.; Jian, Z.; Zhang, S.; Bilal, M.; Xue, R.; Wang, S.; Bin, Z. Ground-Based MAX-DOAS Observations of Tropospheric NO2 and HCHO During COVID-19 Lockdown and Spring Festival Over Shanghai, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lampel, J.; Xie, P.; Beirle, S.; Li, A.; Wu, D.; Wagner, T. Ground-based MAX-DOAS observations of tropospheric aerosols, NO2, SO2 and HCHO in Wuxi, China, from 2011 to 2014. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2189–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Hou, X.; Kang, H. Analysis of the seasonal ozone budget and the impact of the summer monsoon on the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 2029–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ju, T.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, F.; Zhang, G. Analysis of spatiotemporal variation of formaldehyde column concentration in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its influencing factors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 55233–55251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.B.; Zhang, H.L.; Lin, W.L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.Y.; Jia, S.H. First simultaneous measurements of peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) and ozone at Nam Co in the central Tibetan Plateau: Impacts from the PBL evolution and transport processes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 5199–5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).