Integrated Approach for the Study of Urban Expansion and River Floods Aimed at Hydrogeomorphic Risk Reduction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
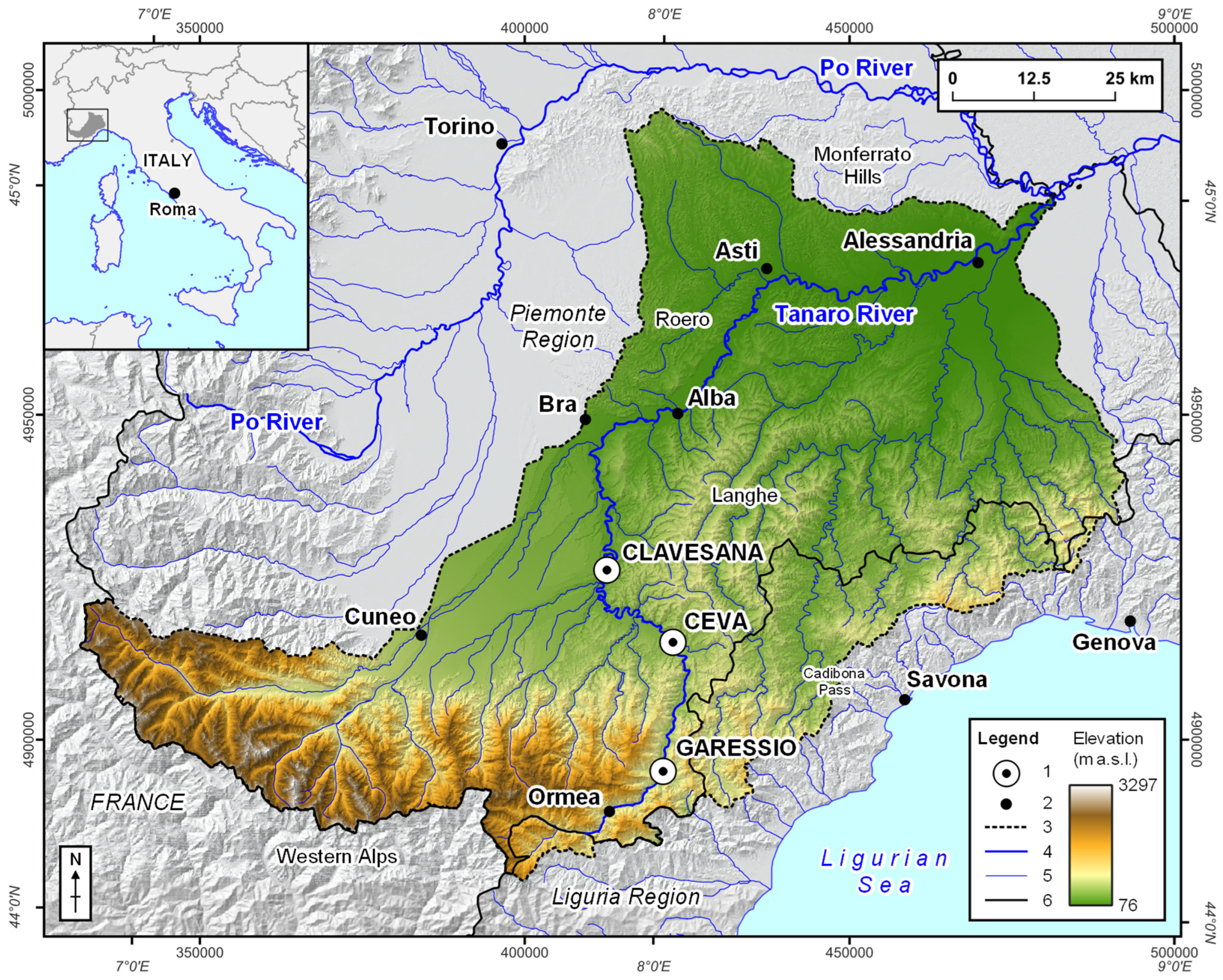
2. Study Area
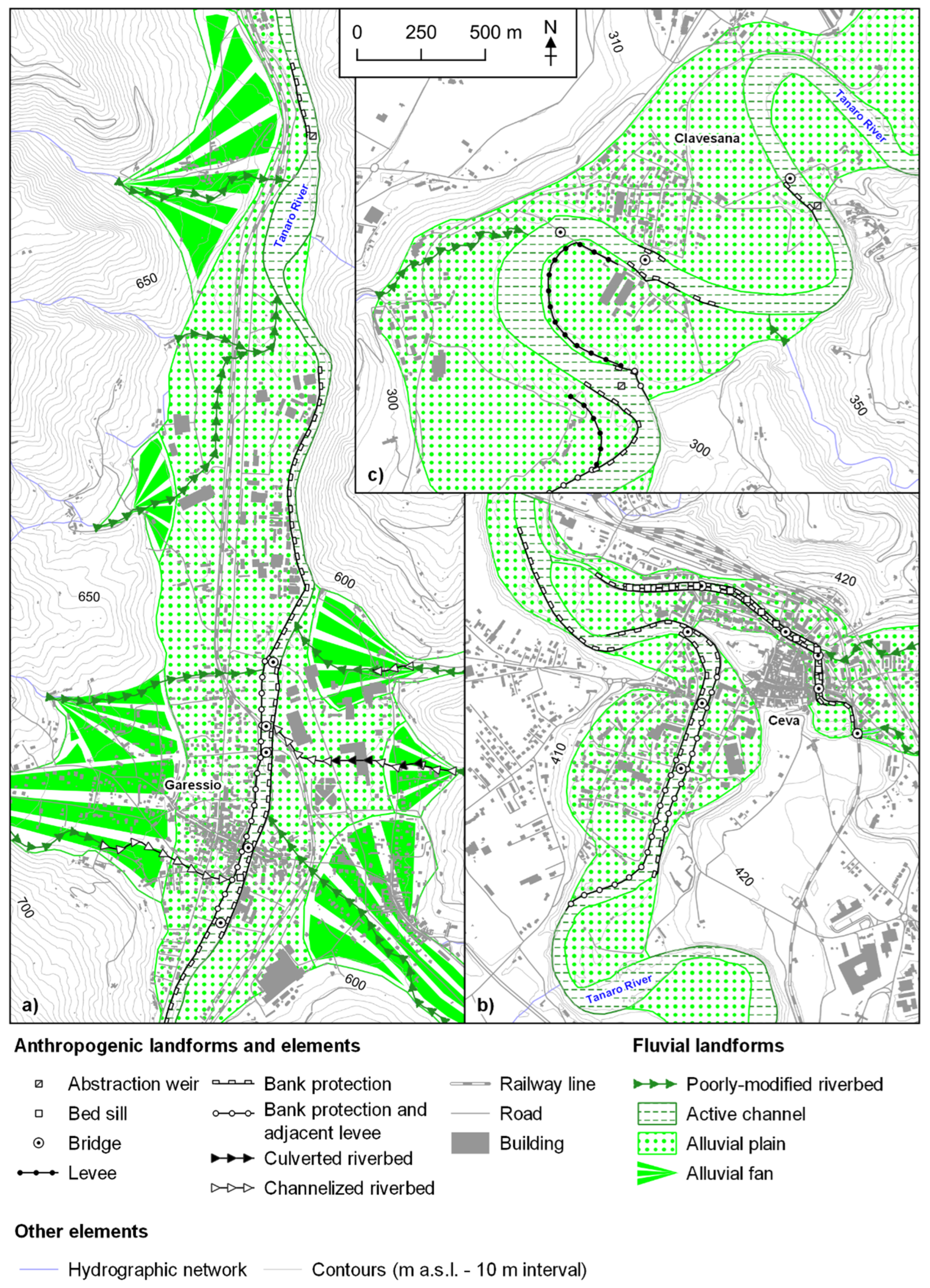
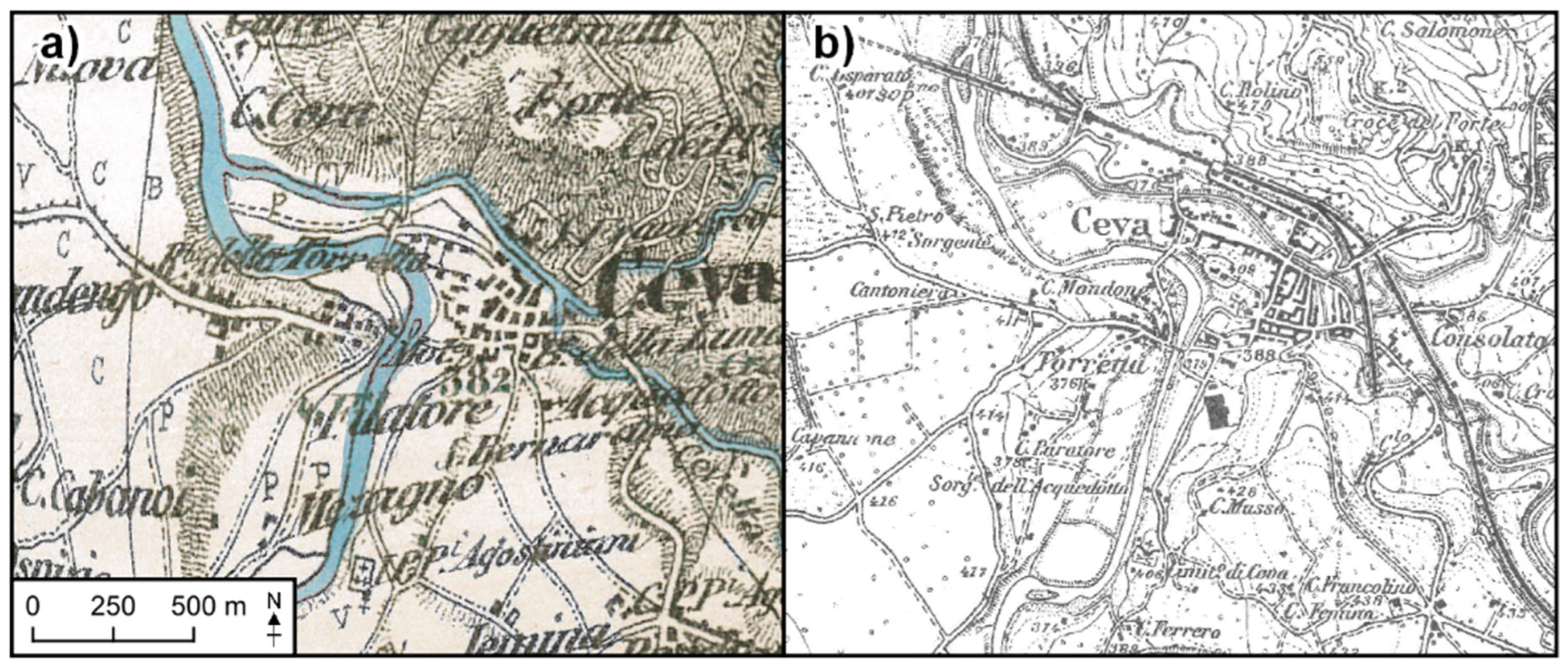
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
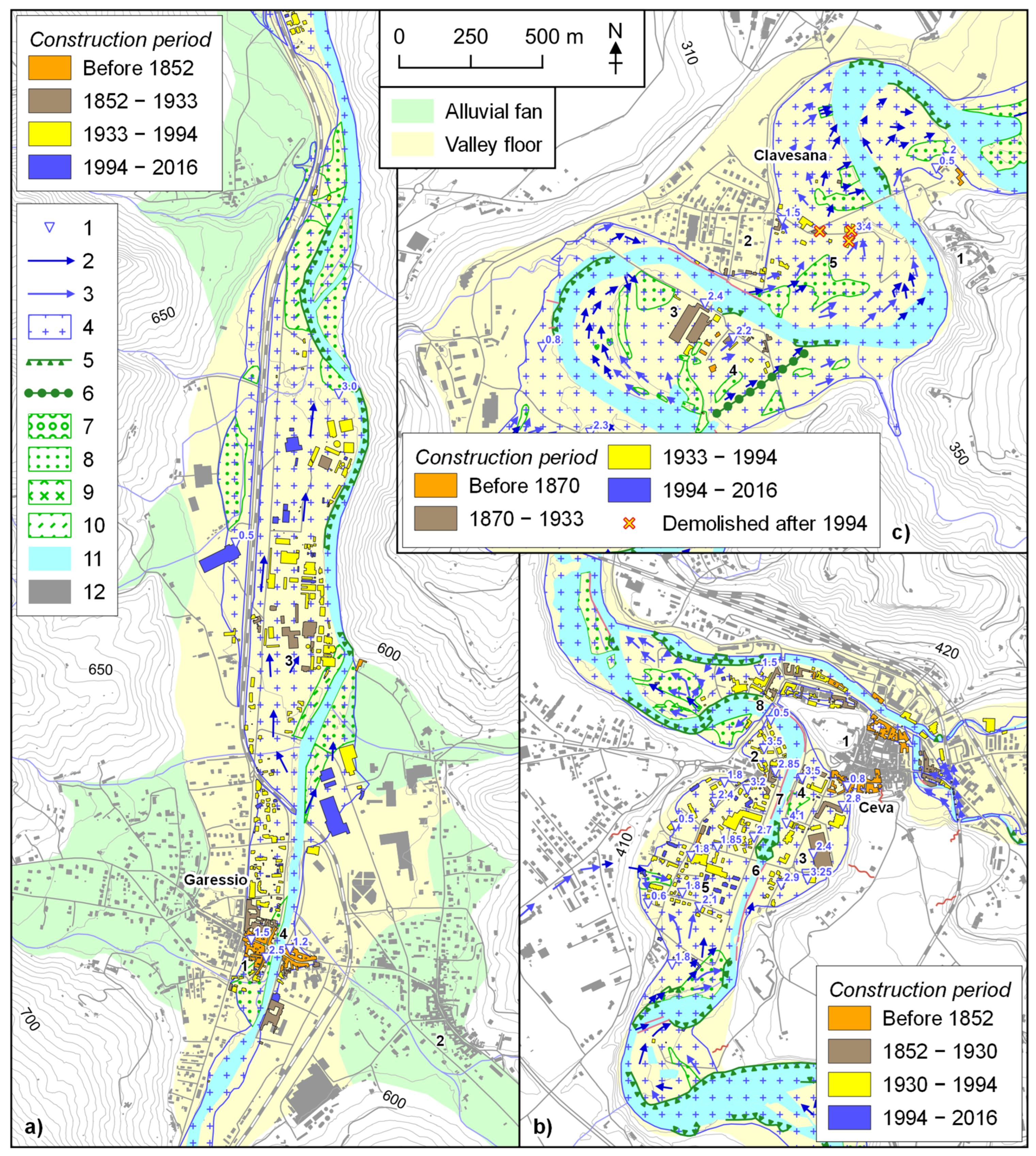
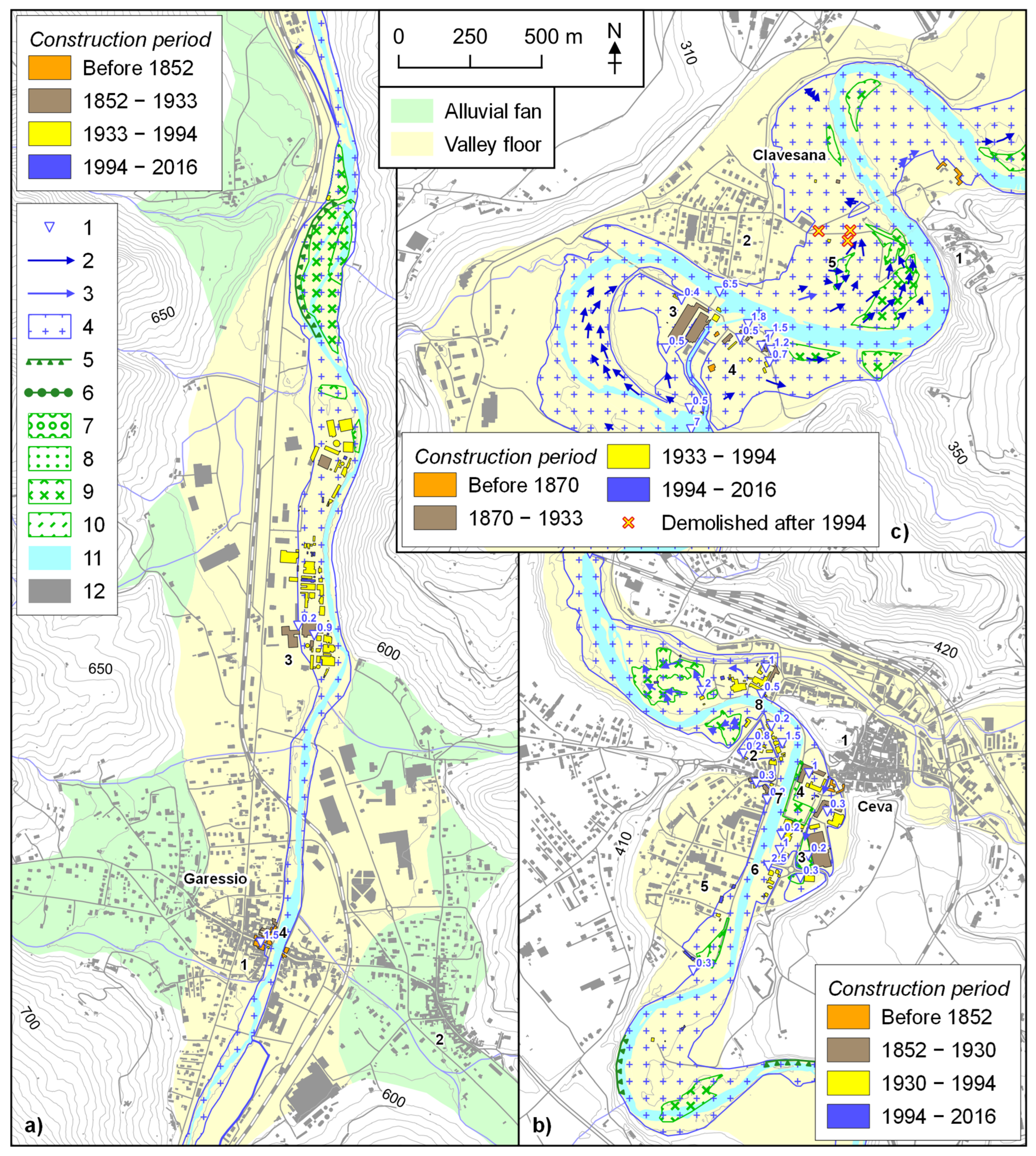
4.1. Urban Expansion
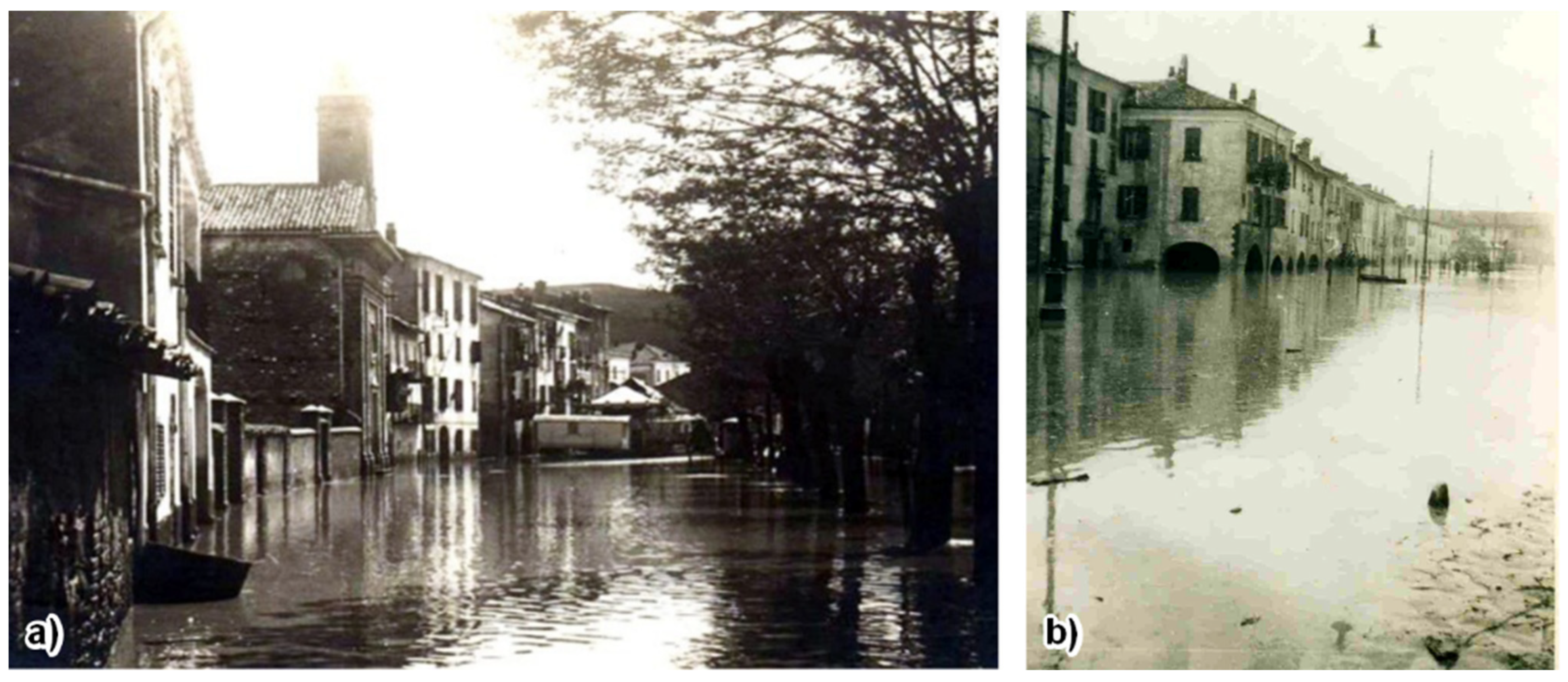
4.2. Historical Floods of the Tanaro River
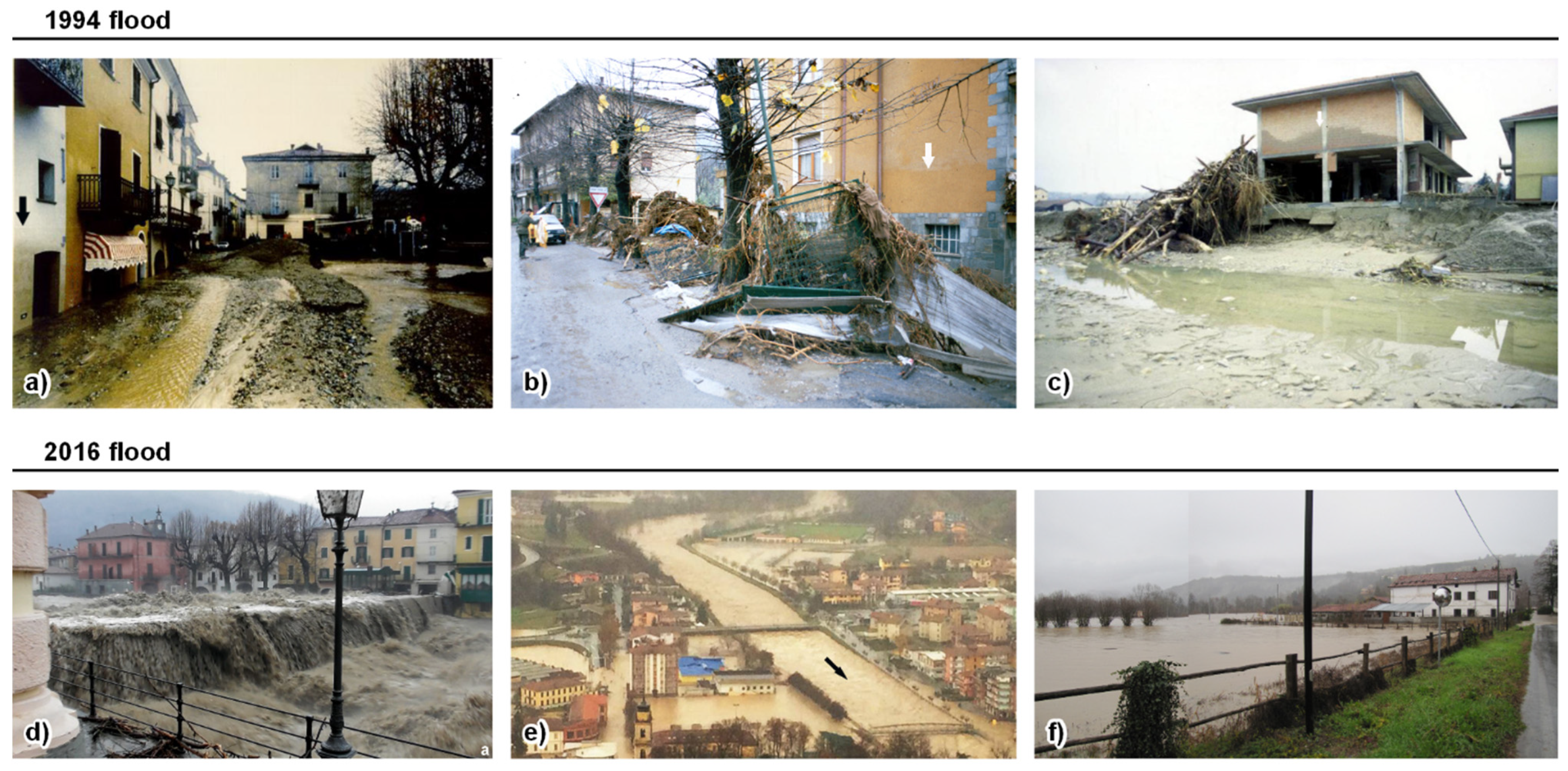
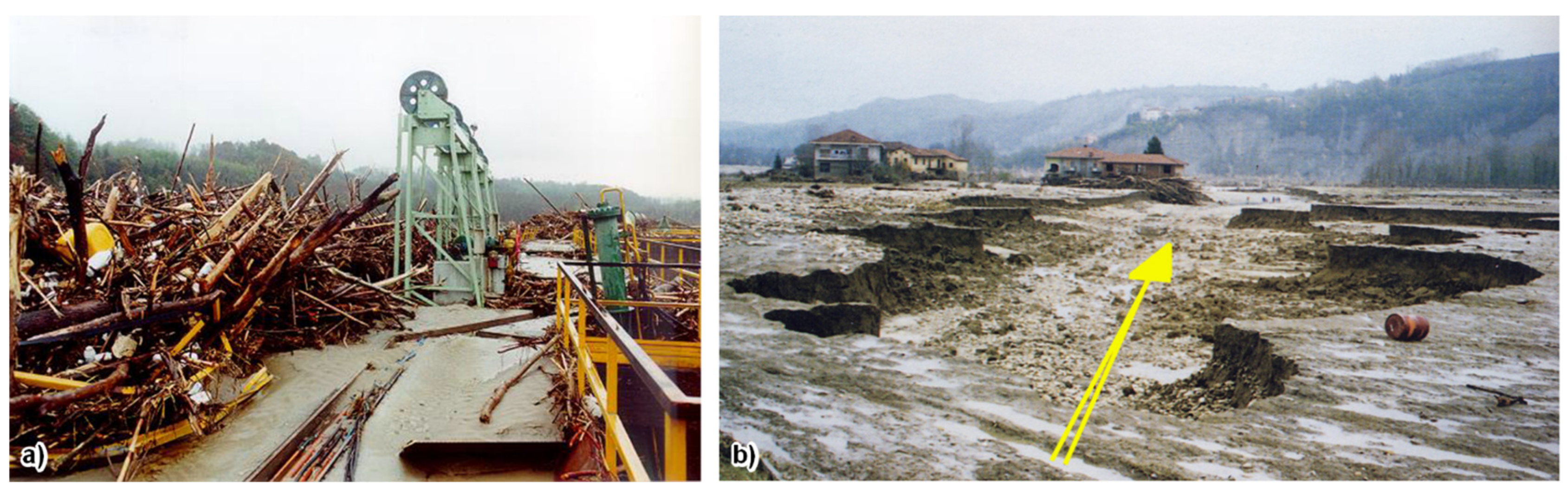
4.3. The 1994 and 2016 High-Magnitude Floods
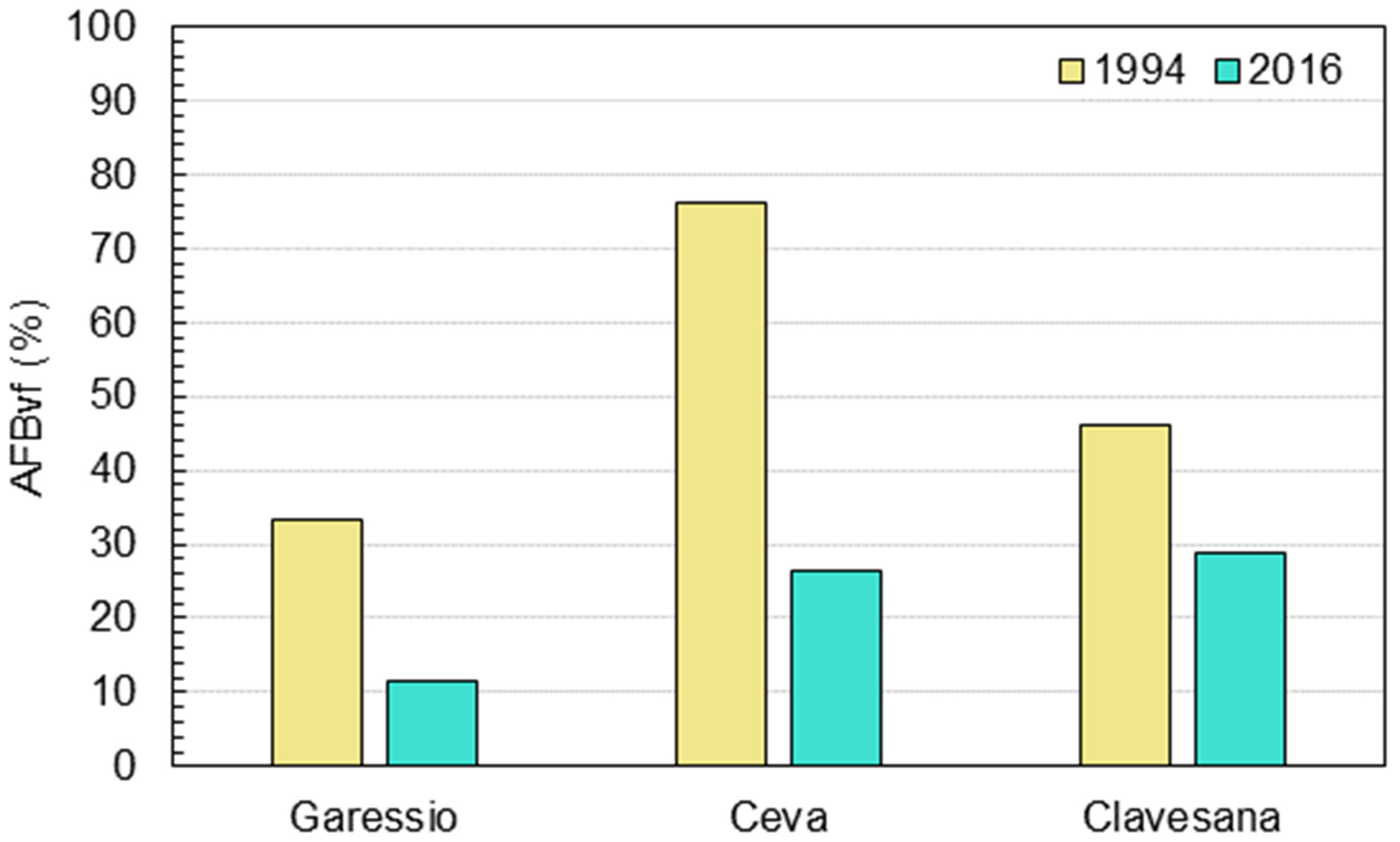
4.4. Building Inundation Analysis
5. Discussion
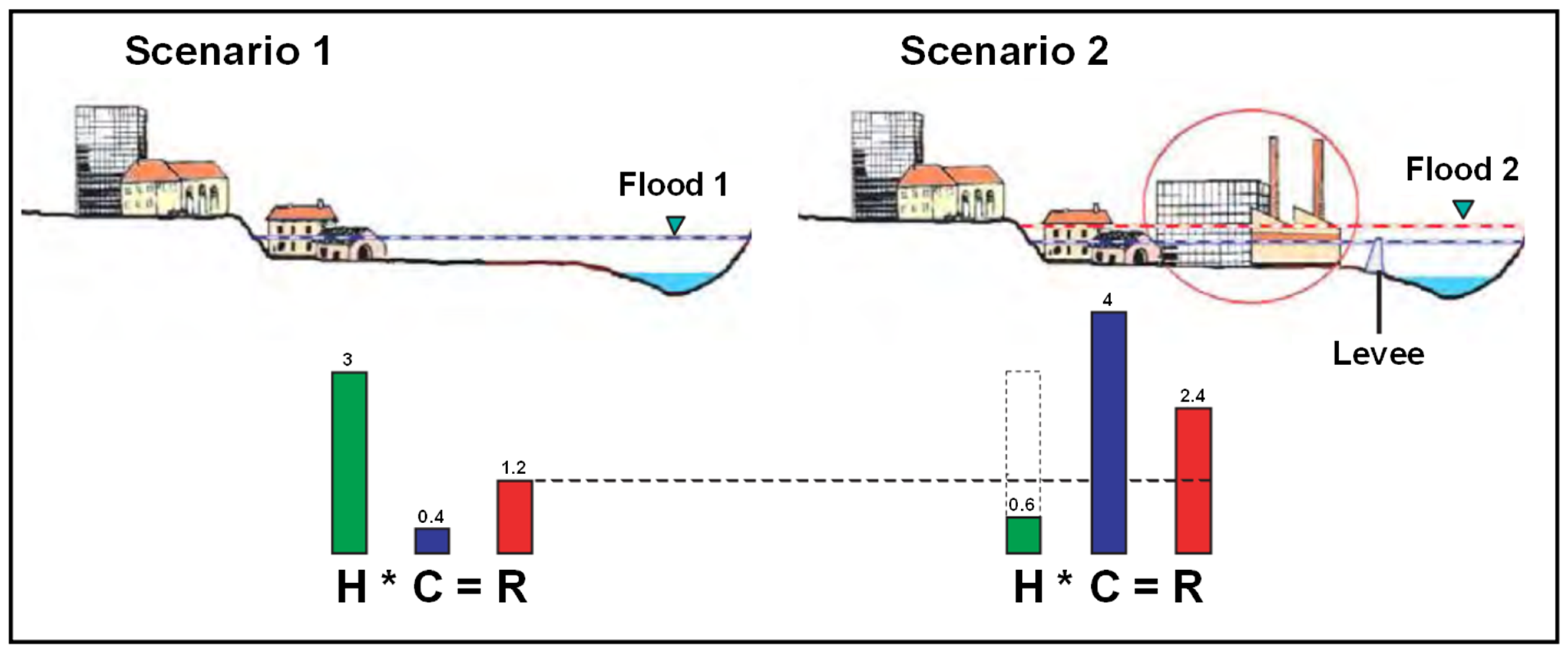
5.1. Urban Expansion and Floods
5.2. Recommendations for Urban Expansion
5.3. Integrated Approach and Metrics to Investigate Urbanization and Floods
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFB | Area of flooded buildings |
| AFBcp | Areas of flooded buildings refer to construction periods |
| AFBvf | Area of flooded buildings out of the total area of buildings located within the valley floor |
| AFBvf_cp | Area of flooded buildings out of the total area of buildings located within the valley floor with reference to construction periods |
| BA | Building area |
| BAvf | Building area over the valley floor |
| BAvf Ratio | Building area over the valley floor ratio |
| BE Rate | Rate of building expansion |
| BEvf Rate | Rate of building expansion over the valley floor |
| CAFB | Cumulative area of flooded buildings |
| CBA | Cumulative building area |
| CBAvf | Cumulative building area over the valley floor |
References
- Barredo, J.I. Major Flood Disasters in Europe: 1950–2005. Nat. Hazards 2007, 42, 125–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathrellos, G.D.; Skilodimou, H.D.; Soukis, K.; Koskeridou, E. Temporal and Spatial Analysis of Flood Occurrences in the Drainage Basin of Pinios River (Thessaly, Central Greece). Land 2018, 7, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaume, E.; Borga, M.; Llassat, M.C.; Maouche, S.; Lang, M.; Diakakis, M. Mediterranean Extreme Floods and Flash Floods. In The Mediterranean Region under Climate Change; Allevi, Ed.; Sub-chapter 1.3.4; A scientific update; Coll. Synthèses; IRD Editions: Marseille, France, 2016; pp. 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Gaume, E.; Bain, V.; Bernardara, P.; Newinger, O.; Barbuc, M.; Bateman, A.; Blaškovičová, L.; Blöschl, G.; Borga, M.; Dumitrescu, A.; et al. A Compilation of Data on European Flash Floods. J. Hydrol. 2009, 367, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldsen, T.R.; Macdonald, N.; Lang, M.; Mediero, L.; Albuquerque, T.; Bogdanowicz, E.; Brázdil, R.; Castellarin, A.; David, V.; Fleig, A.; et al. Documentary Evidence of Past Floods in Europe and Their Utility in Flood Frequency Estimation. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, L.; Borga, M.; Preciso, E.; Gaume, E. Characterisation of Selected Extreme Flash Floods in Europe and Implications for Flood Risk Management. J. Hydrol. 2010, 394, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, M.I.; Viviroli, D.; Sikorska, A.E.; Vannier, O.; Favre, A.-C.; Seibert, J. Flood Type Specific Construction of Synthetic Design Hydrographs. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 1390–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nied, M.; Pardowitz, T.; Nissen, K.; Ulbrich, U.; Hundecha, Y.; Merz, B. On the Relationship between Hydro-Meteorological Patterns and Flood Types. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 3249–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters. EM-DAT The International Disasters Database. Available online: https://www.emdat.be/ (accessed on 9 May 2023).
- Hall, J.; Arheimer, B.; Borga, M.; Brázdil, R.; Claps, P.; Kiss, A.; Kjeldsen, T.R.; Kriaučiūnienė, J.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Lang, M.; et al. Understanding Flood Regime Changes in Europe: A State-of-the-Art Assessment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 2735–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, H.F.; Slack, J.R. Streamflow Trends in the United States. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najibi, N.; Devineni, N. Recent Trends in the Frequency and Duration of Global Floods. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2018, 9, 757–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pörtner, H.-O.; Roberts, D.C.; Adams, H.; Adelekan, I.; Adler, C.; Adrian, R.; Aldunce, P.; Ali, E.; Ara Begum, R.; Bednar-Friedl, B.; et al. Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. In Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg2/ (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Merz, B.; Aerts, J.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Baldi, M.; Becker, A.; Bichet, A.; Blöschl, G.; Bouwer, L.M.; Brauer, A.; Cioffi, F.; et al. Floods and Climate: Emerging Perspectives for Flood Risk Assessment and Management. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 1921–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viglione, A.; Merz, B.; Viet Dung, N.; Parajka, J.; Nester, T.; Blöschl, G. Attribution of Regional Flood Changes Based on Scaling Fingerprints. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 5322–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casale, R.; Pedroli, G.B.; Samuels, P. Ribamod—River Basin Modelling, Management and Flood Mitigation—Concerted Action. Introduction. Proceedings of the First Workshop Current Policy and Practice on Flood Mitigation; European Commission, Directorate—General for Science, Research and Development; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, K.J. The Human Role in Changing River Channels. Geomorphology 2006, 79, 172–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogger, M.; Agnoletti, M.; Alaoui, A.; Bathurst, J.C.; Bodner, G.; Borga, M.; Chaplot, V.; Gallart, F.; Glatzel, G.; Hall, J.; et al. Land Use Change Impacts on Floods at the Catchment Scale: Challenges and Opportunities for Future Research. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 5209–5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cencetti, C.; De Rosa, P.; Fredduzzi, A. Geoinformatics in Morphological Study of River Paglia, Tiber River Basin, Central Italy. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luino, F.; Turconi, L.; Petrea, C.; Nigrelli, G. Uncorrected Land-Use Planning Highlighted by Flooding: The Alba Case Study (Piedmont, Italy). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 2329–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandarino, A.; Maerker, M.; Firpo, M. ‘The Stolen Space’: A History of Channelization, Reduction of Riverine Areas and Related Management Issues. The Lower Scrivia River Case Study (NW Italy). Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2019, 14, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccati, A.; Mandarino, A.; Perasso, L.; Robbiano, A.; Luino, F.; Faccini, F. Large-Scale Geomorphology of the Entella River Floodplain (Italy) for Coastal Urban Areas Management. J. Maps 2021, 17, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano Notivoli, R.; Mora Mur, D.; Ollero Ojeda, A.; Sánchez Fabre, M.; Sanz, P.; Saz Sánchez, M.Á. Floodplain Occupation and Flooding in the Central Pyrenees. Cuad. Investig. Geográfica Geogr. Res. Lett. 2017, 43, 309–328. [Google Scholar]
- Wyzga, B. Changes in the Magnitude and Transformation of Flood Waves Subsequent to the Channelization of the Raba River, Polish Carpathians. Earth Surf. Process Landf. 1996, 21, 749–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedient, P.B.; Huber, W.C.; Vieux, B.E. Hydrology and Floodplain Analysis: International Edition; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schober, B.; Hauer, C.; Habersack, H. Floodplain Losses and Increasing Flood Risk in the Context of Recent Historic Land Use Changes and Settlement Developments: Austrian Case Studies. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2020, 13, e12610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.L.; Maslin, M.A. Defining the Anthropocene. Nature 2015, 519, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalasiewicz, J.; Waters, C.N.; Summerhayes, C.P.; Wolfe, A.P.; Barnosky, A.D.; Cearreta, A.; Crutzen, P.; Ellis, E.; Fairchild, I.J.; Gałuszka, A.; et al. The Working Group on the Anthropocene: Summary of Evidence and Interim Recommendations. Anthropocene 2017, 19, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajjur, S.B.; Al-Ghamdi, S.G. Exploring Urban Growth–Climate Change–Flood Risk Nexus in Fast Growing Cities. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ayala, D.; Wang, K.; Yan, Y.; Smith, H.; Massam, A.; Filipova, V.; Pereira, J.J. Flood Vulnerability and Risk Assessment of Urban Traditional Buildings in a Heritage District of Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 2221–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, Z. Quantifying Land-Use Change Impacts on the Dynamic Evolution of Flood Vulnerability. Land Use Policy 2017, 65, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentschler, J.; Salhab, M.; Jafino, B.A. Flood Exposure and Poverty in 188 Countries. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, G.; Hudson, P.F. Flood Hazards: The Context of Fluvial Geomorphology. In Geomorphological Hazards and Disaster Prevention; Goudie, A.S., Alcántara-Ayala, I., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; pp. 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas Palom, A.; Saurí Pujol, D.; Olcina Cantos, J. Sustainable Land Use Planning in Areas Exposed to Flooding: Some International Experiences. In Floods; Vinet, F., Ed.; ISTE Press Ltd.: London, UK; Elsevier Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, C.J.; Bennett, E.M.; Cassell, K.; Hanes, D.M.; Minor, E.C.; Paerl, H.; Raymond, P.A.; Vargas, R.; Vidon, P.G.; Wollheim, W.; et al. The Impact of Flooding on Aquatic Ecosystem Services. Biogeochemistry 2018, 141, 439–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament and Council. Directive 2007/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2007 on the Assessment and Management of Flood Risks; Official Journal L 288, 6/11/2007; European Parliament: Brussels, Belgium, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament and Council. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy; Official Journal L 327, 22/12/2000; European Parliament: Brussels, Belgium, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bertsch, R.; Glenis, V.; Kilsby, C. Building Level Flood Exposure Analysis Using a Hydrodynamic Model. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 156, 105490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudashiru, R.B.; Sabtu, N.; Abustan, I.; Balogun, W. Flood Hazard Mapping Methods: A Review. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, I.; Kuleshov, Y. Flood Vulnerability Assessment and Mapping: A Case Study for Australia’s Hawkesbury-Nepean Catchment. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayenew, W.A.; Kebede, H.A. GIS and Remote Sensing Based Flood Risk Assessment and Mapping: The Case of Dikala Watershed in Kobo Woreda Amhara Region, Ethiopia. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2023, 18, 100243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak, S.; Rajan, G.; Jairaj, P.G. Geospatial Approach for Assessment of Vulnerability to Flood in Local Self Governments. Geoenvironmental Disasters 2020, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amen, A.R.M.; Mustafa, A.; Kareem, D.A.; Hameed, H.M.; Mirza, A.A.; Szydłowski, M.; Saleem, B.K.M. Mapping of Flood-Prone Areas Utilizing GIS Techniques and Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Duhok, Kurdistan Region of Iraq. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, G.; Giustarini, L.; Tarpanelli, A.; Jarihani, B.; Martinis, S. Flood Modeling and Prediction Using Earth Observation Data. Surv. Geophys. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastry, A.; Carter, E.; Coltin, B.; Sleeter, R.; McMichael, S.; Eggleston, J. Mapping Floods from Remote Sensing Data and Quantifying the Effects of Surface Obstruction by Clouds and Vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 291, 113556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccini, F.; Luino, F.; Paliaga, G.; Roccati, A.; Turconi, L. Flash Flood Events along the West Mediterranean Coasts: Inundations of Urbanized Areas Conditioned by Anthropic Impacts. Land 2021, 10, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, R.; Verburg, P.H.; Clevers, J.G.P.W.; Herold, M. The Potential of Old Maps and Encyclopaedias for Reconstructing Historic European Land Cover/Use Change. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 59, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.V.; Moore, R.; Hancher, M.; Turubanova, S.A.; Tyukavina, A.; Thau, D.; Stehman, S.V.; Goetz, S.J.; Loveland, T.R.; et al. High-Resolution Global Maps of 21st-Century Forest Cover Change. Science 2013, 342, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaim, D.; Kozak, J.; Kolecka, N.; Ziółkowska, E.; Ostafin, K.; Ostapowicz, K.; Gimmi, U.; Munteanu, C.; Radeloff, V.C. Broad Scale Forest Cover Reconstruction from Historical Topographic Maps. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 67, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luino, F.; Paliaga, G.; Roccati, A.; Sacchini, A.; Turconi, L.; Faccini, F. Anthropogenic changes in the alluvial plains of the Tyrrhenian Ligurian basins. Rend. Online Della Soc. Geol. Ital. 2019, 48, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandarino, A.; Pepe, G.; Cevasco, A.; Brandolini, P. Quantitative Assessment of Riverbed Planform Adjustments, Channelization, and Associated Land Use/Land Cover Changes: The Ingauna Alluvial-Coastal Plain Case (Liguria, Italy). Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Musso, N.M.; Capolongo, D.; Caldara, M.; Surian, N.; Pennetta, L. Channel Changes and Controlling Factors over the Past 150 Years in the Basento River (Southern Italy). Water 2020, 12, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäyrä, J.; Kivinen, S.; Keski-Saari, S.; Poikolainen, L.; Kumpula, T. Utilizing Historical Maps in Identification of Long-Term Land Use and Land Cover Changes. Ambio 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliaga, G.; Luino, F.; Turconi, L.; Marincioni, F.; Faccini, F. Exposure to Geo-Hydrological Hazards of the Metropolitan Area of Genoa, Italy: A Multi-Temporal Analysis of the Bisagno Stream. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zhou, Y.; Güneralp, B.; Li, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, H. Increasing Global Urban Exposure to Flooding: An Analysis of Long-Term Annual Dynamics. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 153012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, L.; Hong, Y.; Chen, H.-X.; Feng, S.-J. Flood Hazards in Urban Environment. Georisk Assess. Manag. Risk Eng. Syst. Geohazards 2023, 17, 241–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugianto, S.; Deli, A.; Miswar, E.; Rusdi, M.; Irham, M. The Effect of Land Use and Land Cover Changes on Flood Occurrence in Teunom Watershed, Aceh Jaya. Land 2022, 11, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheater, H.; Evans, E. Land Use, Water Management and Future Flood Risk. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, S251–S264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Holden, J.; Kirkby, M. The Impact of Land-Cover Change on Flood Peaks in Peatland Basins. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 3477–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwagrzyk, M.; Kaim, D.; Price, B.; Wypych, A.; Grabska, E.; Kozak, J. Impact of Forecasted Land Use Changes on Flood Risk in the Polish Carpathians. Nat. Hazards 2018, 94, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsova, D. Coupling Land Use Change Modeling with Climate Projections to Estimate Seasonal Variability in Runoff from an Urbanizing Catchment Near Cincinnati, Ohio. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2014, 3, 1256–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, F.L.; Raj Pradhan, N.; Downer, C.W.; Zahner, J.A. Relative Importance of Impervious Area, Drainage Density, Width Function, and Subsurface Storm Drainage on Flood Runoff from an Urbanized Catchment. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W12503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brath, A.; Montanari, A.; Moretti, G. Assessing the Effect on Flood Frequency of Land Use Change via Hydrological Simulation (with Uncertainty). J. Hydrol. 2006, 324, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollis, G.E. The Effect of Urbanization on Floods of Different Recurrence Interval. Water Resour. Res. 1975, 11, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrow, T.; Merz, B. Trends in Flood Magnitude, Frequency and Seasonality in Germany in the Period 1951–2002. J. Hydrol. 2009, 371, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woltemade, C.J.; Hawkins, T.W.; Jantz, C.; Drzyzga, S. Impact of Changing Climate and Land Cover on Flood Magnitudes in the Delaware River Basin, USA. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2020, 56, 507–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemas, V. Remote Sensing of Floods and Flood-Prone Areas: An Overview. J. Coast. Res. 2014, 31, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogherotto, R.; Fantini, A.; Raffaele, F.; Di Sante, F.; Dottori, F.; Coppola, E.; Giorgi, F. A Combined Hydrological and Hydraulic Modelling Approach for the Flood Hazard Mapping of the Po River Basin. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2022, 15, e12755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgi, M.; Turner, M.G. Factors and Processes Shaping Land Cover and Land Cover Changes Along the Wisconsin River. Ecosystems 2002, 5, 184–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreadis, K.M.; Wing, O.E.J.; Colven, E.; Gleason, C.J.; Bates, P.D.; Brown, C.M. Urbanizing the Floodplain: Global Changes of Imperviousness in Flood-Prone Areas. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 104024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandarino, A.; Faccini, F.; Terrone, M.; Paliaga, G. Anthropogenic Landforms and Geo-Hydrological Hazards of the Bisagno Stream Catchment (Liguria, Italy). J. Maps 2021, 17, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandarino, A.; Luino, F.; Turconi, L.; Faccini, F. Urban Geomorphology of a Historical City Straddling the Tanaro River (Alessandria, NW Italy). J. Maps 2021, 17, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandarino, A.; Pepe, G.; Maerker, M.; Cevasco, A.; Brandolini, P. Short-Term GIS Analysis for the Assessment of the Recent Active-Channel Planform Adjustments in a Widening, Highly Altered River: The Scrivia River, Italy. Water 2020, 12, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piana, P.; Faccini, F.; Luino, F.; Paliaga, G.; Sacchini, A.; Watkins, C. Geomorphological Landscape Research and Flood Management in a Heavily Modified Tyrrhenian Catchment. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiepolo, M.; Galligari, A. Urban Expansion-Flood Damage Nexus: Evidence from the Dosso Region, Niger. Land Use Policy 2021, 108, 105547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domeneghetti, A.; Carisi, F.; Castellarin, A.; Brath, A. Evolution of Flood Risk over Large Areas: Quantitative Assessment for the Po River. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandolini, P.; Mandarino, A.; Paliaga, G.; Faccini, F. Anthropogenic Landforms in an Urbanized Alluvial-Coastal Plain (Rapallo City, Italy). J. Maps 2021, 17, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandarino, A. Morphological Adjustments of the Lower Orba River (NW Italy) since the Mid-Nineteenth Century. Geomorphology 2022, 410, 108280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorpio, V.; Piégay, H. Is Afforestation a Driver of Change in Italian Rivers within the Anthropocene Era? CATENA 2021, 198, 105031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Li, D. The Analysis of the Impact of Land-Use Changes on Flood Exposure of Wuhan in Yangtze River Basin, China. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 2507–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccati, A.; Luino, F.; Turconi, L.; Piana, P.; Watkins, C.; Faccini, F. Historical Geomorphological Research of a Ligurian Coastal Floodplain (Italy) and Its Value for Management of Flood Risk and Environmental Sustainability. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beretta, R.; Ravazzani, G.; Maiorano, C.; Mancini, M. Simulating the Influence of Buildings on Flood Inundation in Urban Areas. Geosciences 2018, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakakis, M.; Deligiannakis, G.; Pallikarakis, A.; Skordoulis, M. Identifying Elements That Affect the Probability of Buildings to Suffer Flooding in Urban Areas Using Google Street View. A Case Study from Athens Metropolitan Area in Greece. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2017, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Brenner, C.; Peche, A.; Yang, J.; Feuerhake, U.; Sester, M. Determination of Building Flood Risk Maps from LiDAR Mobile Mapping Data. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2022, 93, 101759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yu, J.; Wang, Q.; Yue, Q. Understanding the Effects of Digital Elevation Model Resolution and Building Treatment for Urban Flood Modelling. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 42, 101122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivumäki, L.; Alho, P.; Lotsari, E.; Käyhkö, J.; Saari, A.; Hyyppä, H. Uncertainties in Flood Risk Mapping: A Case Study on Estimating Building Damages for a River Flood in Finland. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2010, 3, 166–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal, N.C.; Zapata, R.E.; Pagán, I.; López, R.; Agudelo, J. Building Damage Due to Riverine and Coastal Floods. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2010, 136, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzarin, T.; Defina, A.; Viero, D.P. Assessing 40 Years of Flood Risk Evolution at the Micro-Scale Using an Innovative Modeling Approach: The Effects of Urbanization and Land Planning. Geosciences 2023, 13, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.B.; Ali, S.A.; Bielecka, E.; Calka, B.; Orych, A.; Parvin, F.; Łupikasza, E. Flood Vulnerability and Buildings’ Flood Exposure Assessment in a Densely Urbanised City: Comparative Analysis of Three Scenarios Using a Neural Network Approach. Nat. Hazards 2022, 113, 1043–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luino, F.; Arattano, M.; Brunamonte, F. Vulnerability of Urban Areas to Flooding: Events in the North-West Italy, November 1994. In Proceedings of the Sexto Congreso Nacional y Conferencia Internacional de Geologia Ambiental y Ordenacion del Territorio, Granada, Spain, 22–25 April 1996; Volume 3, pp. 309–327. [Google Scholar]
- Mandarino, A.; Luino, F.; Faccini, F. Flood-Induced Ground Effects and Flood-Water Dynamics for Hydro-Geomorphic Hazard Assessment: The 21–22 October 2019 Extreme Flood along the Lower Orba River (Alessandria, NW Italy). J. Maps 2021, 17, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonasera, M.; Ferrero, A.M.; Fubelli, G.; Masciocco, L.; Nocera, A.; Viviani, E. Pericolosità idrologica della città di Ceva (CN). Geol. Dell’ambiente 2020, 1, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Luino, F. Flooding Vulnerability of a Town in the Tanaro Basin: The Case of Ceva (Piedmont—Northwest Italy). In Palaeofloods, Historical Floodsand Climatic Variability: Applications in Flood Risk Assessment, Proceedings of the PHEFRA Workshop, Barcelona, 16–19 October 2002; Thorndycraft, V.R., Benito, G., Barriendos, M., Llasat, M.C., Eds.; PHEFRA: Barcelona, Spain, 2003; pp. 321–326. [Google Scholar]
- Luino, F. The Flood and Landslide Event of November 4–6 1994 in Piedmont Region (Northwestern Italy): Causes and Related Effects in Tanaro Valley. Phys. Chem. Earth Part Solid Earth Geod. 1999, 24, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicótina, L.; Alessi Celegon, E.; Rinaldo, A.; Marani, M. On the Impact of Rainfall Patterns on the Hydrologic Response. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W12401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siviglia, A.; Federici, B.; Becchi, I.; Rinaldi, M. Sediment Transport and Morphodynamics of the Tanaro River, Northwestern Italy. IAHS-AISH Publ. 2004, 288, 308–315. [Google Scholar]
- Taboni, B.; Licata, M.; Buleo Tebar, V.; Bonasera, M.; Umili, G. Proposal for Flood Risk Mitigation in the Upper Tanaro Valley (Western Alps—North-Western Italy). Geosciences 2022, 12, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares da Costa, R.; Mazzoli, P.; Bagli, S. Limitations Posed by Free DEMs in Watershed Studies: The Case of River Tanaro in Italy. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AdBDPo. Piano Stralcio per l’Assetto Idrogeologico—Relazione Generale; Autorità di Bacino Distrettuale del Fiume Po: Parma, Italy, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri, C.; Carrapa, B.; Di Giulio, A.; Wijbrans, J.; Murrell, G.R. Provenance of Oligocene Synorogenic Sediments of the Ligurian Alps (NW Italy): Inferences on Belt Age and Cooling History. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2003, 92, 758–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Atri, A.; Piana, F.; Barale, L.; Bertok, C.; Martire, L. Geological Setting of the Southern Termination of Western Alps. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2016, 105, 1831–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federico, L.; Crispini, L.; Scarsi, M.; Capponi, G.; Piazza, M. Late Orogenic Tectonics in the Ligurian Alps (Italy): Constraints from Syntectonic Sedimentary Deposits at the Top of an Exhumed Plate Interface. J. Maps 2022, 18, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federico, L.; Crispini, L.; Dabove, G.M.; Piazza, M.; Capponi, G. Stratigraphic vs Structural Contacts in a Late Orogenic Basin: The Case of the Tertiary Piedmont Basin in the Sassello Area (Ligurian Alps, Italy). J. Maps 2016, 12, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molli, G.; Crispini, L.; Malusà, M.; Mosca, P.; Piana, F.; Federico, L. Geology of the Northern Apennine-Western Alps Junction Area: A Regional Review. J. Virtual Explor. 2010, 36, 3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, G.; Cevasco, A.; Piazza, M.; Macciò, R.; Arrighetti, F.; Casagli, N. On the Efficiency and Effectiveness of Automatic Deep Drainage Systems during an Extreme Rainfall Event: The Mendatica Landslide Case Study (Western Liguria, Italy). Landslides 2021, 18, 3799–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piana, F.; Barale, L.; Bertok, C.; d’Atri, A.; Irace, A.; Mosca, P. The Alps-Apennines Interference Zone: A Perspective from the Maritime and Western Ligurian Alps. Geosciences 2021, 11, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piana, F.; Fioraso, G.; Irace, A.; Mosca, P.; d’Atri, A.; Barale, L.; Falletti, P.; Monegato, G.; Morelli, M.; Tallone, S.; et al. Geology of Piemonte Region (NW Italy, Alps–Apennines Interference Zone). J. Maps 2017, 13, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regione Piemonte. Piano di Tutela Delle Acque; Regione Piemonte: Torino, Italy, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Luino, F.; Turconi, L.; Silvestro, C.; Tropeano, D.; Vigna, B. L’evento Alluvionale nel Piemonte Meridionale. In L’Evento Alluvionale del 2–3 Ottobre 2020 in Piemonte; Luino, F., Ed.; Geologia dell’Ambiente, 28; Società Italiana di Geologia Ambientale (SIGEA): Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- AVI Project Database. Inventory of Areas Affected by Landslides and Floods in Italy. National Research Council, National Group for Prevention of Hydrological Hazards. Available online: https://avi.gndci.cnr.it/ (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Biancotti, A. Geomorfologia dell’Alta Langa (Piemonte meridionale). Mem. Della Soc. Ital. Sci. Nat. E Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. Milano 1981, 22, 58–104. [Google Scholar]
- Tropeano, D. Evento Alluvionale del Novembre 1994 in Piemonte. Interventi Di Studio Effettuati dall’IRPI-CNR di Torino: Sintesi delle Osservazioni. GEAM 1995, XXXII, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- ARPA Piemonte. Eventi Alluvionali in Piemonte—Evento del 21–25 Novembre 2016; Agenzia Regionale per la Protezione Ambientale: Torino, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bellardone, G.; Colombo, I.; Forlati, F.; Giampani, C.; Oberti, R.; Piccini, C.; Ramsco, M.; Susella, G. Cronistoria del processo di piena. In Eventi Alluvionali in Piemonte 2–6 Novembre 1994, 8 Luglio 1996, 7–10 Ottobre 1996; Susella, G., Ed.; Regione Piemonte: Torino, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Cat Berro, D.; Mercalli, L.; Luino, F.; Turconi, L.; Savio, G. L’alluvione del 21–26 Novembre 2016 in Piemonte e Liguria: Analisi meteorologica ed effetti sul territorio. Nimbus 2019, 27, 4–51. [Google Scholar]
- Forlati, F.; Moletta, G.; Susella, G. Considerazioni sul processo di piena lungo il fiume Tanaro. In Eventi Alluvionali in Piemonte 2–6 Novembre 1994, 8 Luglio 1996, 7–10 Ottobre 1996; Regione Piemonte: Torino, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, A.P.; Shellberg, J.G.; Knight, J.; Spencer, J. Alluvial Gully Erosion: An Example from the Mitchell Fluvial Megafan, Queensland, Australia. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 1951–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, B.; Fiorini, L.; Marucci, A.; Zullo, F. The Urbanization Run-Up in Italy: From a Qualitative Goal in the Boom Decades to the Present and Future Unsustainability. Land 2020, 9, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, B.; Zullo, F. Land Urbanization in Central Italy: 50 Years of Evolution. J. Land Use Sci. 2014, 9, 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horacio, J.; Ollero, A.; Noguera, I.; Fernández-Pasquier, V. Flooding, Channel Dynamics and Transverse Infrastructure: A Challenge for Middle Ebro River Management. J. Maps 2019, 15, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczykiewicz, T.; Skonieczna, M. Rainfall Flooding in Urban Areas in the Context of Geomorphological Aspects. Geosciences 2020, 10, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleari, S. Natural Disasters in Italy: Do We Invest Enough in Risk Prevention and Mitigation? Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 75, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, E.; Rousselle, J.; Lacroix, J. Flood Damage Reduction Program (FDRP) in Québec: Case Study of the Chaudiére River. Nat. Hazards 2003, 28, 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaler, T.; Fuchs, S. Financial Recovery Schemes in Austria: How Planned Relocation Is Used as an Answer to Future Flood Events. Environ. Hazards 2020, 19, 268–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysiak, J.; Testella, F.; Bonaiuto, M.; Carrus, G.; De Dominicis, S.; Ganucci Cancellieri, U.; Firus, K.; Grifoni, P. Flood Risk Management in Italy: Challenges and Opportunities for the Implementation of the EU Floods Directive (2007/60/EC). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 2883–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audisio, C.; Turconi, L. Urban Floods: A Case Study in the Savigliano Area (North-Western Italy). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 2951–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collenteur, R.A.; de Moel, H.; Jongman, B.; Di Baldassarre, G. The Failed-Levee Effect: Do Societies Learn from Flood Disasters? Nat. Hazards 2015, 76, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turconi, L.; Tropeano, D.; Savio, G.; Bono, B.; De, S.K.; Frasca, M.; Luino, F. Torrential Hazard Prevention in Alpine Small Basin through Historical, Empirical and Geomorphological Cross Analysis in NW Italy. Land 2022, 11, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, M.R.; Wesselink, A.; Brandimarte, L.; Di Baldassarre, G.; Rahman, M.M. The Levee Effect along the Jamuna River in Bangladesh. Water Int. 2019, 44, 496–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, R.L.; Wohl, E.E.; Morrison, R.R. Levees Don’t Protect, They Disconnect: A Critical Review of How Artificial Levees Impact Floodplain Functions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turconi, L.; Casazza, M.; Bono, B.; Luino, F. Increasing Geohydrological Instability in a Valley of the Italian Central Alps: A Study in the Anthropocene. J. Maps 2022, 19, 2145917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CIRF. La Riqualificazione Fluviale in Italia. Linee Guida, Strumenti Ed Esperienze per Gestire i Corsi d’acqua e Il Territorio; Nardini, A., Sansoni, G., Eds.; Mazzanti Editori: Venezia, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, A.; Bruwier, M.; Archambeau, P.; Erpicum, S.; Pirotton, M.; Dewals, B.; Teller, J. Effects of Spatial Planning on Future Flood Risks in Urban Environments. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 225, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntelekos, A.A.; Oppenheimer, M.; Smith, J.A.; Miller, A.J. Urbanization, Climate Change and Flood Policy in the United States. Clim. Change 2010, 103, 597–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, B. Flood Management under Rapid Urbanisation and Industrialisation in Flood-Prone Areas: A Need for Serious Consideration. Irrig. Drain. 2006, 55 (Suppl. S1), S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olcina, J.; Sauri, D.; Hernández, M.; Ribas, A. Flood Policy in Spain: A Review for the Period 1983-2013. Disaster Prev. Manag. 2016, 25, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.B.; Johnstone, W.M.; Lence, B.J. Wood Frame Building Response to Rapid-Onset Flooding. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2011, 12, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, W.M.; Lence, B.J. Assessing the Value of Mitigation Strategies in Reducing the Impacts of Rapid-Onset, Catastrophic Floods. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2009, 2, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannata, P.G. Acque, fiumi, pianificazioni dei bacini idrografici: L’uso del suolo come difesa. In Proceedings of the Congress Fiumi, Paesaggio, Difesa del Suolo. Superare le Emergenze, Cogliere le Opportunità, Florence, Italy, 10–11 May 2006; Ercolini, M., Ed.; Firenze University Press: Firenze, Italy, 2007; pp. 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Burby, R.J. Flood Insurance and Floodplain Management: The US Experience. Glob. Environ. Change Part B Environ. Hazards 2001, 3, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priest, S.J.; Penning-Rowsell, E.C.; Suykens, C. Promoting Adaptive Flood Risk Management: The Role and Potential of Flood Recovery Mechanisms. E3S Web Conf. 2016, 7, 17005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surminski, S.; Aerts, J.C.J.H.; Botzen, W.J.W.; Hudson, P.; Mysiak, J.; Pérez-Blanco, C.D. Reflections on the Current Debate on How to Link Flood Insurance and Disaster Risk Reduction in the European Union. Nat. Hazards 2015, 79, 1451–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botzen, W.J.W.; Aerts, J.C.J.H.; van den Bergh, J.C.J.M. Willingness of Homeowners to Mitigate Climate Risk through Insurance. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 2265–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crichton, D. Role of Insurance in Reducing Flood Risk. Geneva Pap. Risk Insur.-Issues Pract. 2008, 33, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ruig, L.T.; Haer, T.; de Moel, H.; Brody, S.D.; Botzen, W.J.W.; Czajkowski, J.; Aerts, J.C.J.H. How the USA Can Benefit from Risk-Based Premiums Combined with Flood Protection. Nat. Clim. Change 2022, 12, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, I.; Llasat, M.C. Policy and Systems of Flood Risk Management: A Comparative Study between Japan and Spain. Nat. Hazards 2017, 87, 919–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesselaar, M.; Botzen, W.J.W.; Robinson, P.J.; Aerts, J.C.J.H.; Zhou, F. Charity Hazard and the Flood Insurance Protection Gap: An EU Scale Assessment under Climate Change. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 193, 107289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, A.H.; Brown, T.J.; Price, S.J.; Ford, J.R.; Waters, C.N. Humans Are the Most Significant Global Geomorphological Driving Force of the 21st Century. Anthr. Rev. 2018, 5, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meresa, H.; Tischbein, B.; Mekonnen, T. Climate Change Impact on Extreme Precipitation and Peak Flood Magnitude and Frequency: Observations from CMIP6 and Hydrological Models. Nat. Hazards 2022, 111, 2649–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.G.; Tooth, S.; Bullard, J.E.; Thomas, D.S.G.; Chiverrell, R.C.; Plater, A.J.; Murton, J.; Thorndycraft, V.R.; Tarolli, P.; Rose, J.; et al. The geomorphology of the Anthropocene: Emergence, status and implications. Earth Surf. Process Landf. 2017, 42, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamm, O.; Saaremäe, E.; Rahkema, K.; Jaagus, J.; Tamm, T. The Intensification of Short-Duration Rainfall Extremes Due to Climate Change—Need for a Frequent Update of Intensity–Duration–Frequency Curves. Clim. Serv. 2023, 30, 100349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Year | City | Datum Description | Scale | Data Source for GIS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1852 | Garessio, Ceva | Historical map, ‘Gran Carta degli Stati Sardi in Terraferma’ | 1:50,000 | Digital image ** |
| 1870 | Clavesana | Historical map, ‘Gran Carta degli Stati Sardi in Terraferma’ | 1:50,000 | Digital image ** |
| 1930 | Ceva | Historical map of the Military Geographic Institute of Italy | 1:25,000 | Digital image ** |
| 1933 | Garessio, Clavesana | Historical map of the Military Geographic Institute of Italy | 1:25,000 | Digital image ** |
| 1991 * | Garessio, Ceva, Clavesana | Orthophotos (B/W) | Regional Geoportal WMS | |
| 1991 * | Garessio, Ceva, Clavesana | Regional map ‘Carta Tecnica Regionale’ | 1:10,000 | Digital image ** |
| 1994 | Garessio, Ceva, Clavesana | Aerial photographs (B/W) | 1:10,000 | Digital image ** |
| 2015 * | Garessio, Ceva, Clavesana | Orthophotos (C) | Regional Geoportal WMS | |
| 2016 | Garessio, Ceva, Clavesana | Regional map, ‘Banca Dati Territoriale di Riferimento degli Enti—BDTRE’ | 1:10,000 | Regional Geoportal WMS |
| 2016 | Clavesana, Ceva | Orthophotos (C) | Regional Geoportal WMS | |
| 2017 * | Garessio, Ceva, Clavesana | Building vector layer of the regional database | 1:10,000 | Regional Geoportal WFS |
| 2017 * | Garessio, Ceva, Clavesana | Google Earth images (C) | Google Earth |
| City | Construction Period | BA | CBA | BE Rate | BAvf | CBAvf | BEvf Rate | BAvf Ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ha) | (%) | (ha) | (%) | (ha/yr) | (ha) | (%) | (ha) | (%) | (ha/yr) | (%) | ||
| Garessio * | Before 1852 | 5.0 | 13.8 | 5.0 | 13.8 | 4.2 | 14.1 | 4.2 | 14.1 | 83.1 | ||
| 1852–1933 | 5.2 | 14.1 | 10.2 | 27.9 | 0.06 | 4.7 | 16.0 | 8.9 | 30.1 | 0.06 | 91.7 | |
| 1933–1994 | 18.4 | 50.1 | 28.6 | 78.0 | 0.30 | 15.9 | 53.6 | 24.8 | 83.7 | 0.26 | 86.7 | |
| 1994–2016 | 8.1 | 22.0 | 36.6 | 100.0 | 0.37 | 4.8 | 16.3 | 29.7 | 100.0 | 0.22 | 60.0 | |
| Total | 36.6 | 29.7 | 81.0 | |||||||||
| Ceva | Before 1852 | 4.6 | 11.2 | 4.6 | 11.2 | 1.0 | 7.9 | 1.0 | 7.9 | 20.9 | ||
| 1852–1930 | 5.2 | 12.4 | 9.8 | 23.6 | 0.07 | 3.3 | 26.7 | 4.3 | 34.5 | 0.04 | 63.7 | |
| 1930–1994 | 21.3 | 51.4 | 31.1 | 75.0 | 0.33 | 7.1 | 57.5 | 11.3 | 92.1 | 0.11 | 33.2 | |
| 1994–2016 | 10.4 | 25.0 | 41.5 | 100.0 | 0.47 | 1.0 | 7.9 | 12.3 | 100.0 | 0.04 | 9.4 | |
| Total | 41.5 | 12.3 | 29.7 | |||||||||
| Clavesana | Before 1870 | 1.3 | 14.0 | 1.3 | 14.0 | 0.4 | 8.0 | 0.4 | 8.0 | 32.2 | ||
| 1870–1933 | 2.3 | 24.5 | 3.6 | 38.5 | 0.04 | 1.6 | 30.5 | 2.0 | 38.5 | 0.03 | 69.6 | |
| 1933–1994 | 3.9 | 41.9 | 7.5 | 80.4 | 0.06 | 3.0 | 56.7 | 5.0 | 95.2 | 0.05 | 75.9 | |
| 1994–2016 | 1.8 | 19.6 | 9.4 | 100.0 | 0.08 | 0.3 | 4.8 | 5.3 | 100.0 | 0.01 | 13.6 | |
| Total | 9.4 | 5.3 | 56.0 | |||||||||
| Date | Garessio | Ceva | Clavesana | Date | Garessio | Ceva | Clavesana |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13–14 January 1610 | Very high | 18 September 1907 | High | ||||
| 6 November 1612 | Low | 28 September 1907 | Medium | ||||
| 18 August 1665 | Medium | 3 October 1907 | Medium | ||||
| 21 April 1716 | High | 16 October 1907 | Medium | ||||
| 25 July 1716 | High | 3 March 1914 | Medium | ||||
| 30 October 1744 | High | 9 September 1914 | Medium | ||||
| 27 July 1747 | High | 14 September 1914 | High | ||||
| 9–13 October 1791 | High | 23 September 1920 | Low | ||||
| 19 November 1791 | Medium | 15–16 May 1926 | Medium | High | |||
| 1 October 1792 | High | 21–22 November 1926 | Low | ||||
| 19 April 1796 | High | 11 November 1951 | High | ||||
| 28 July 1798 | Medium | 13–16 June 1957 | Medium | ||||
| 26 May 1879 | Medium | 18 December 1960 | Medium | ||||
| 3 November 1843 | High | 8 November 1962 | High | High | |||
| 17 October 1885 | Medium | 3 November 1968 | Medium | ||||
| 21 November 1885 | Medium | 19 November 1970 | Low | ||||
| October–November * 1885 | Medium | 14–15 October 1976 | Medium | ||||
| 10–11 November 1886 | Very high | Very high | 5–6 November 1994 | Very high | Very high | Very high | |
| 18 May 1890 | Medium | 24–25 November 2016 | Very high | Very high | Very high | ||
| 28 October 1896 | Low | 2–3 October 2020 | Very high | Very high | Very high | ||
| 1 November 1906 | Medium |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mandarino, A.; Faccini, F.; Luino, F.; Bono, B.; Turconi, L. Integrated Approach for the Study of Urban Expansion and River Floods Aimed at Hydrogeomorphic Risk Reduction. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4158. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174158
Mandarino A, Faccini F, Luino F, Bono B, Turconi L. Integrated Approach for the Study of Urban Expansion and River Floods Aimed at Hydrogeomorphic Risk Reduction. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(17):4158. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174158
Chicago/Turabian StyleMandarino, Andrea, Francesco Faccini, Fabio Luino, Barbara Bono, and Laura Turconi. 2023. "Integrated Approach for the Study of Urban Expansion and River Floods Aimed at Hydrogeomorphic Risk Reduction" Remote Sensing 15, no. 17: 4158. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174158
APA StyleMandarino, A., Faccini, F., Luino, F., Bono, B., & Turconi, L. (2023). Integrated Approach for the Study of Urban Expansion and River Floods Aimed at Hydrogeomorphic Risk Reduction. Remote Sensing, 15(17), 4158. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174158














