Monitoring and Comparative Analysis of Hohhot Subway Subsidence Using StaMPS-PS Based on Two DEMS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area, Data
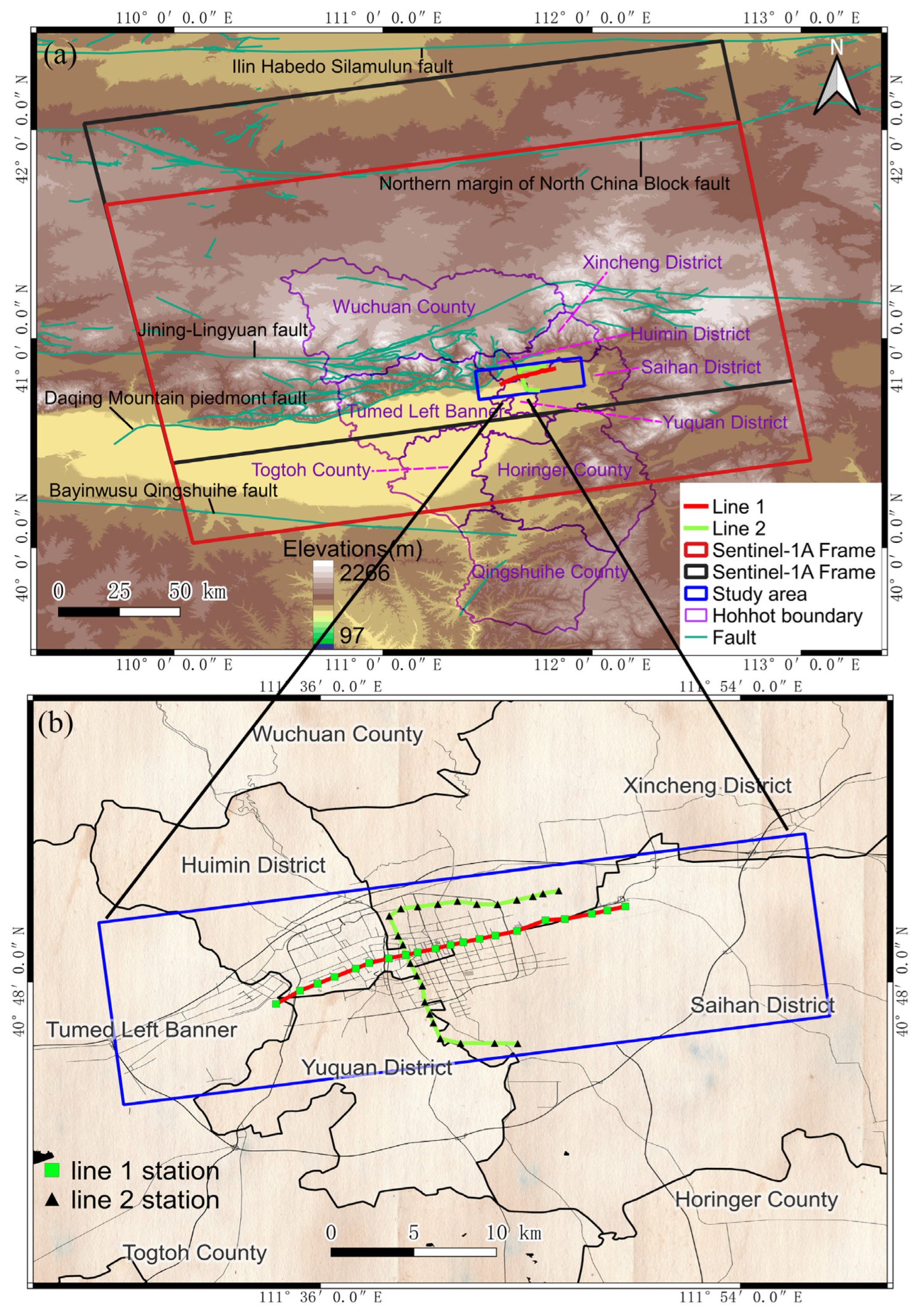
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
3. Data Processing and Methods
3.1. Data Processing
3.2. StaMPS-PS
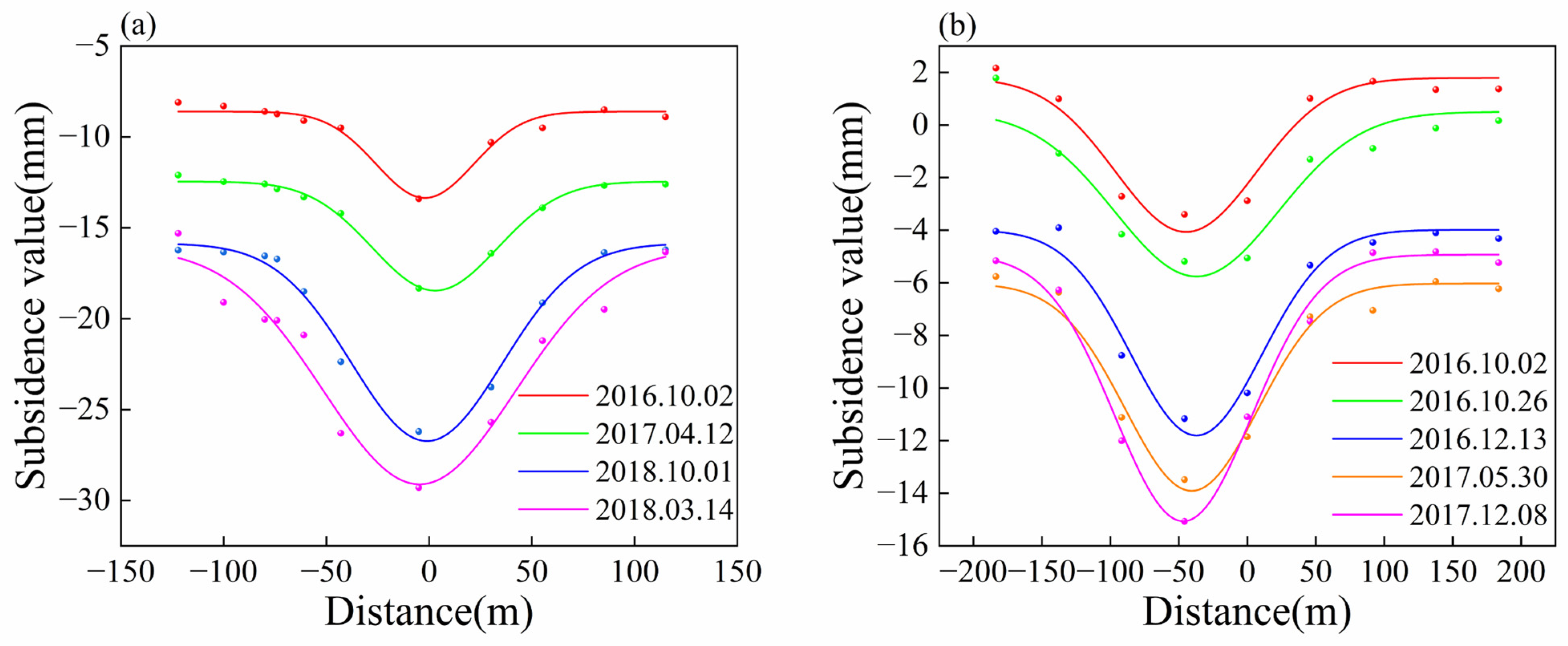
3.3. Peck Formula
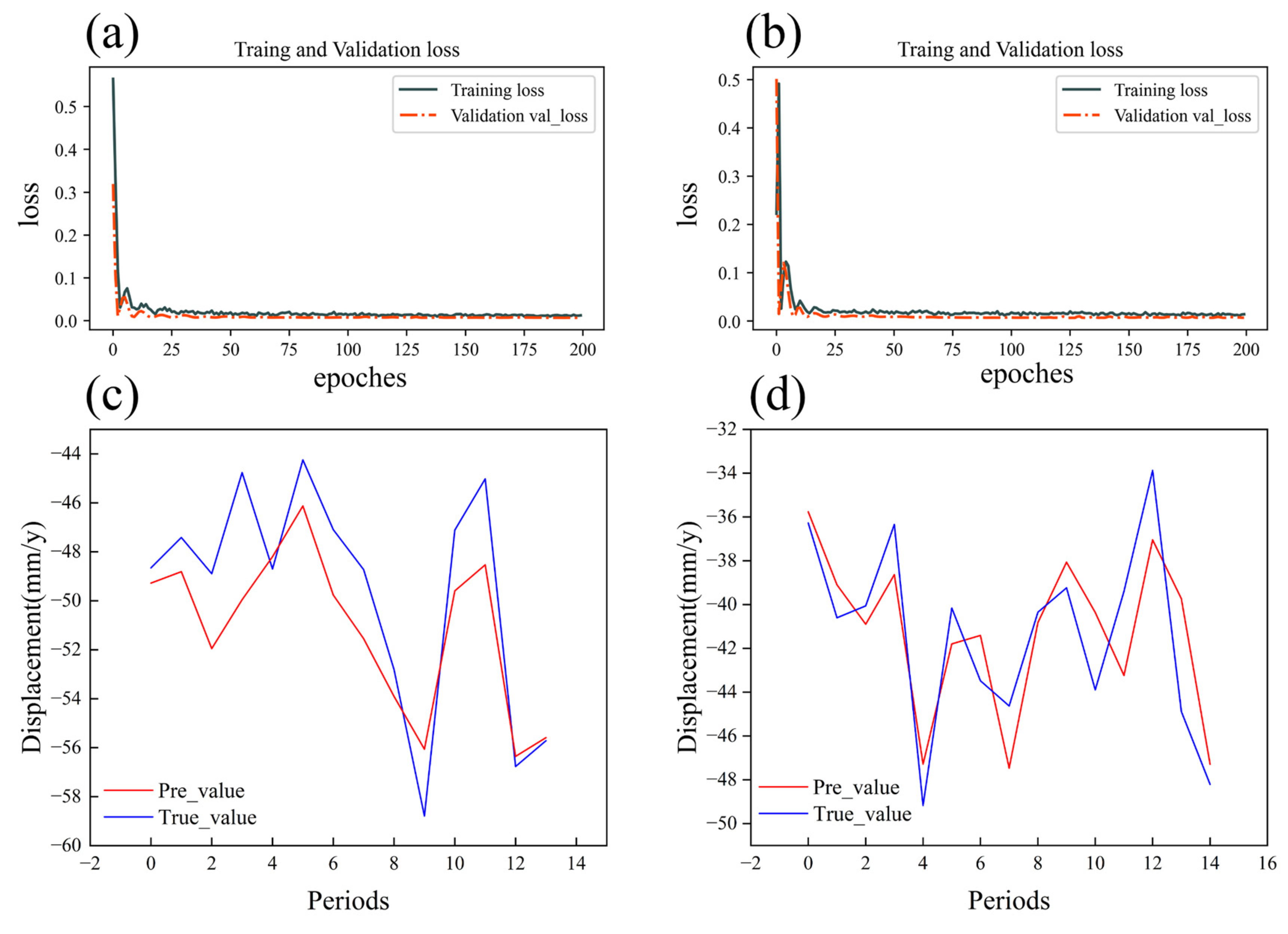
3.4. LSTM Model
4. Results and Validation
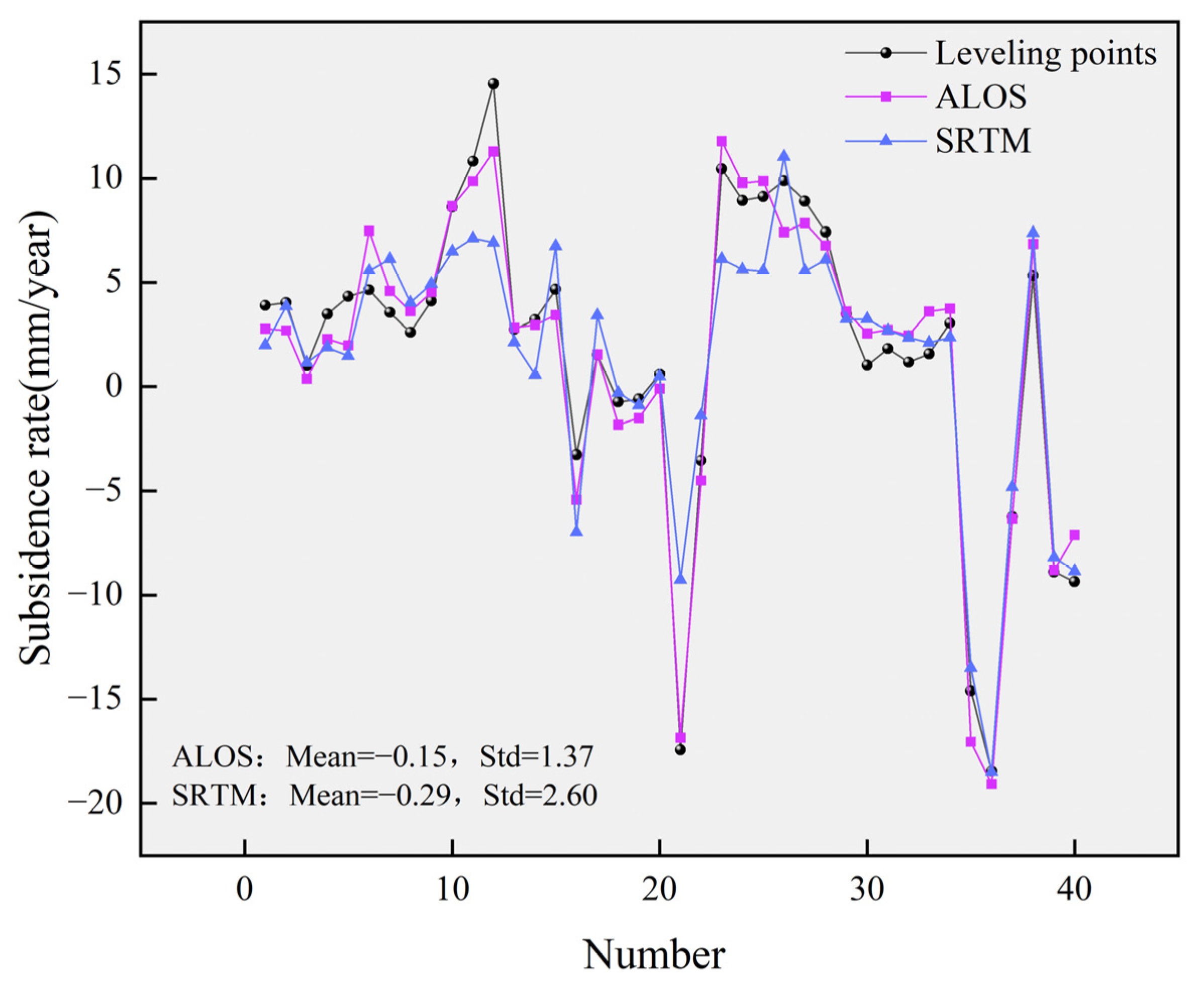
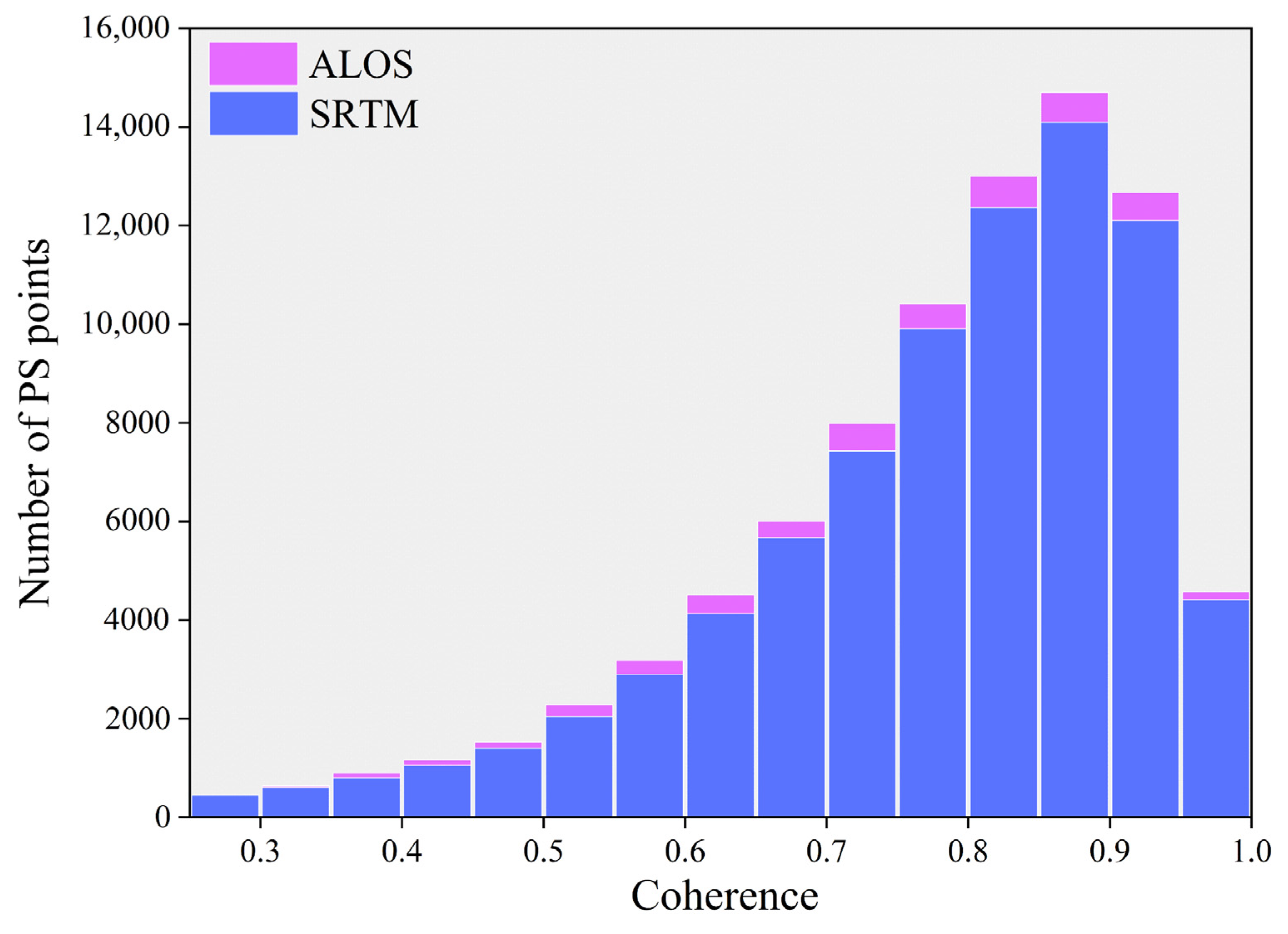
4.1. StaMPS-PS Results and Validation
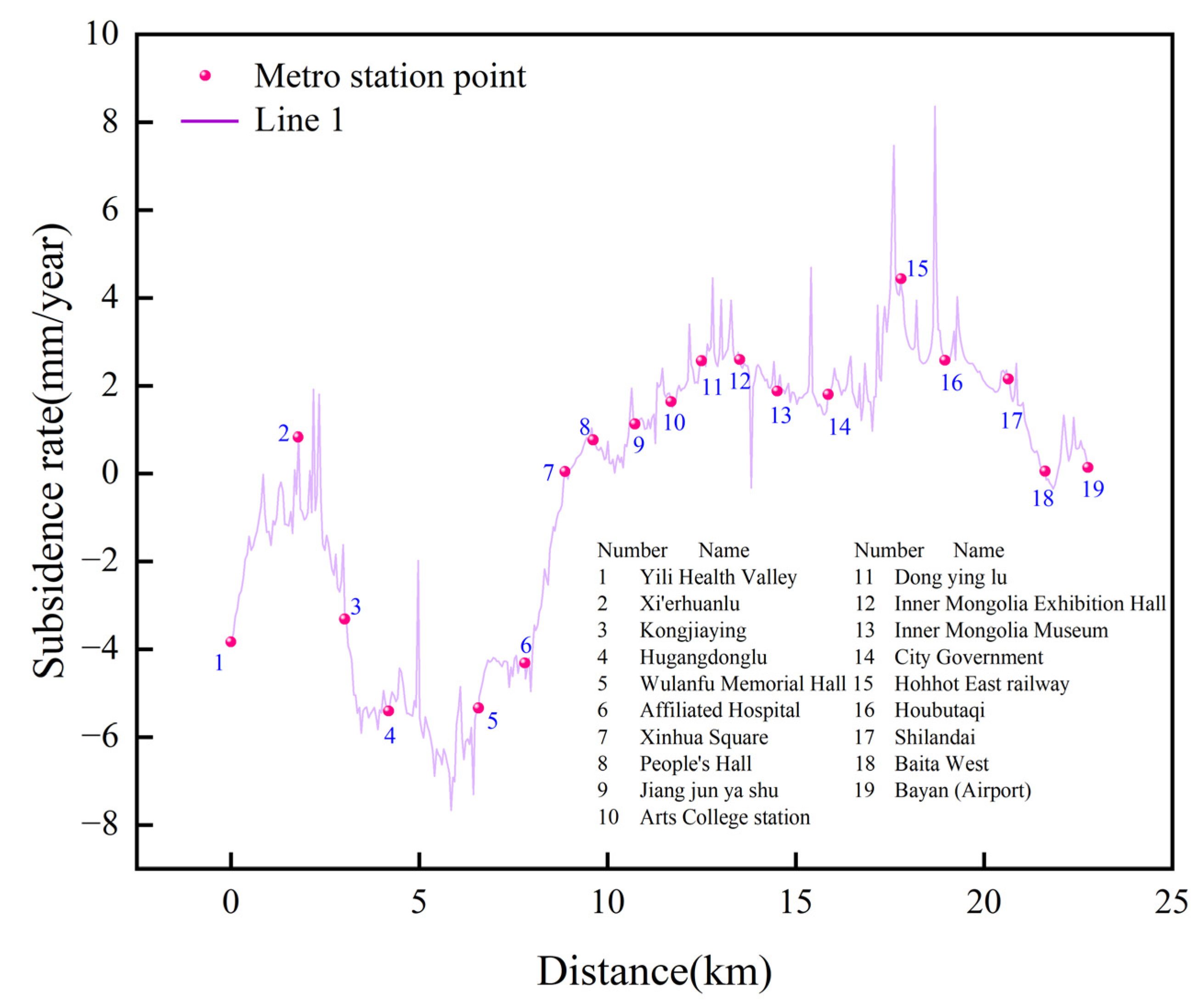
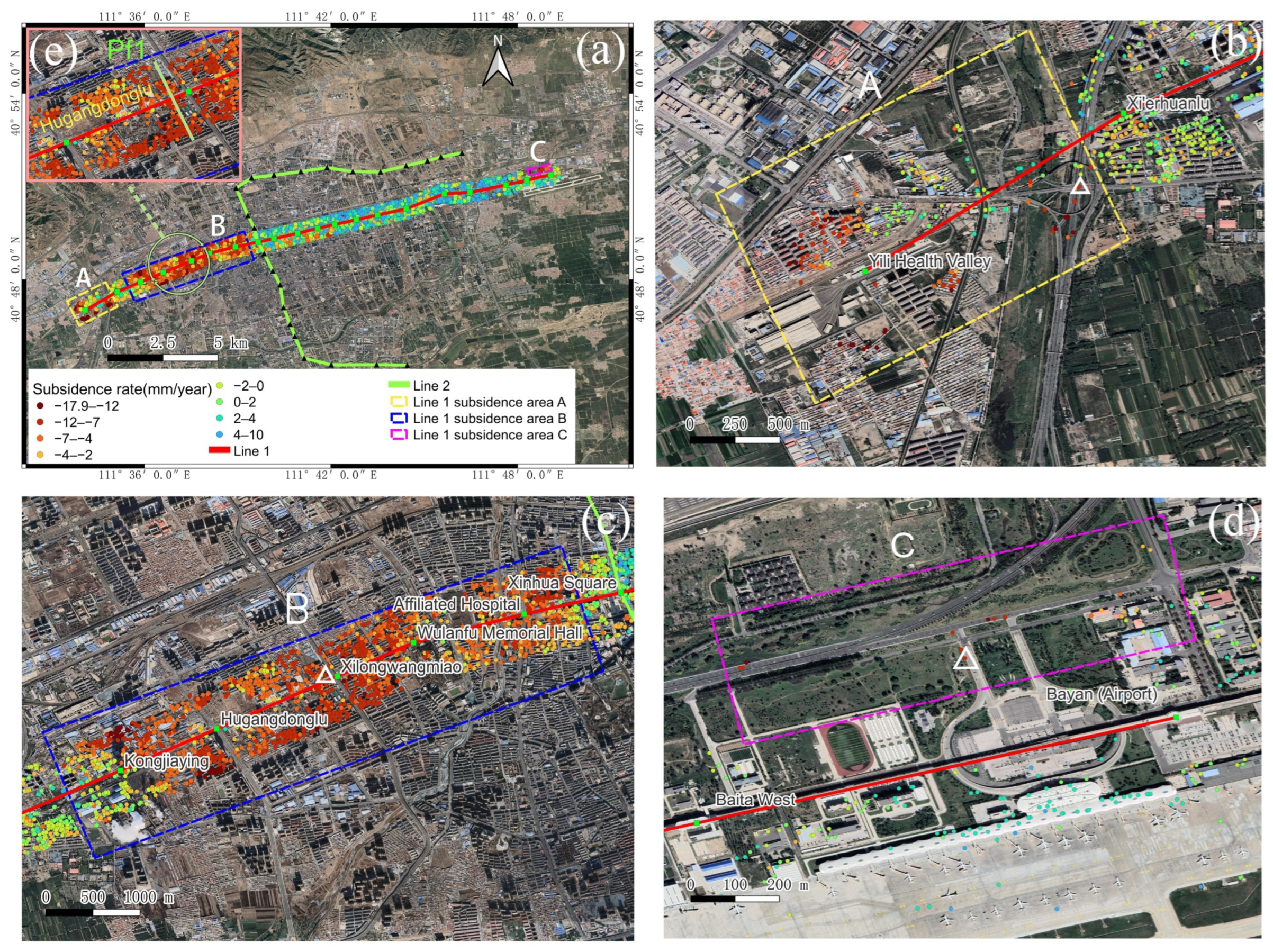
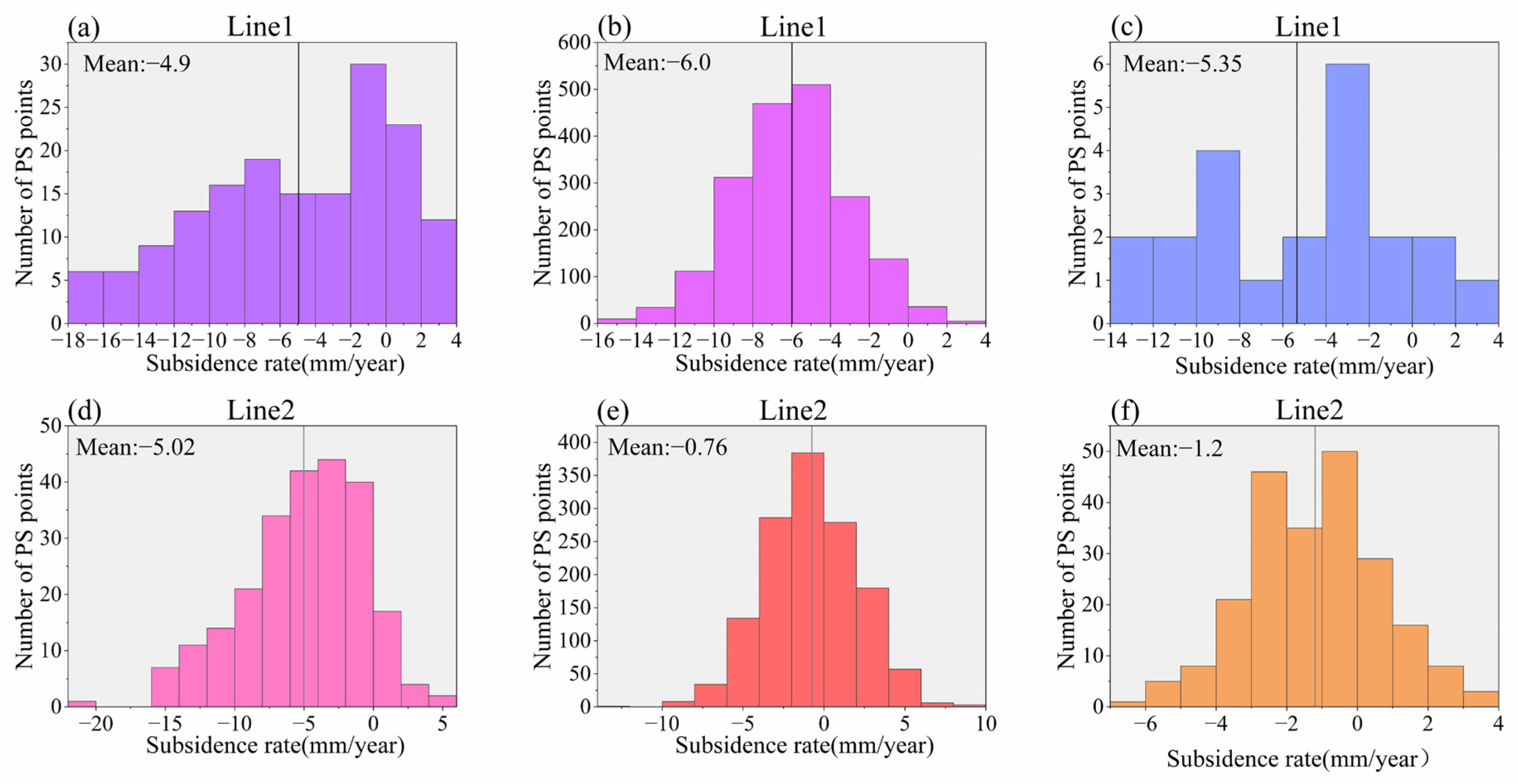
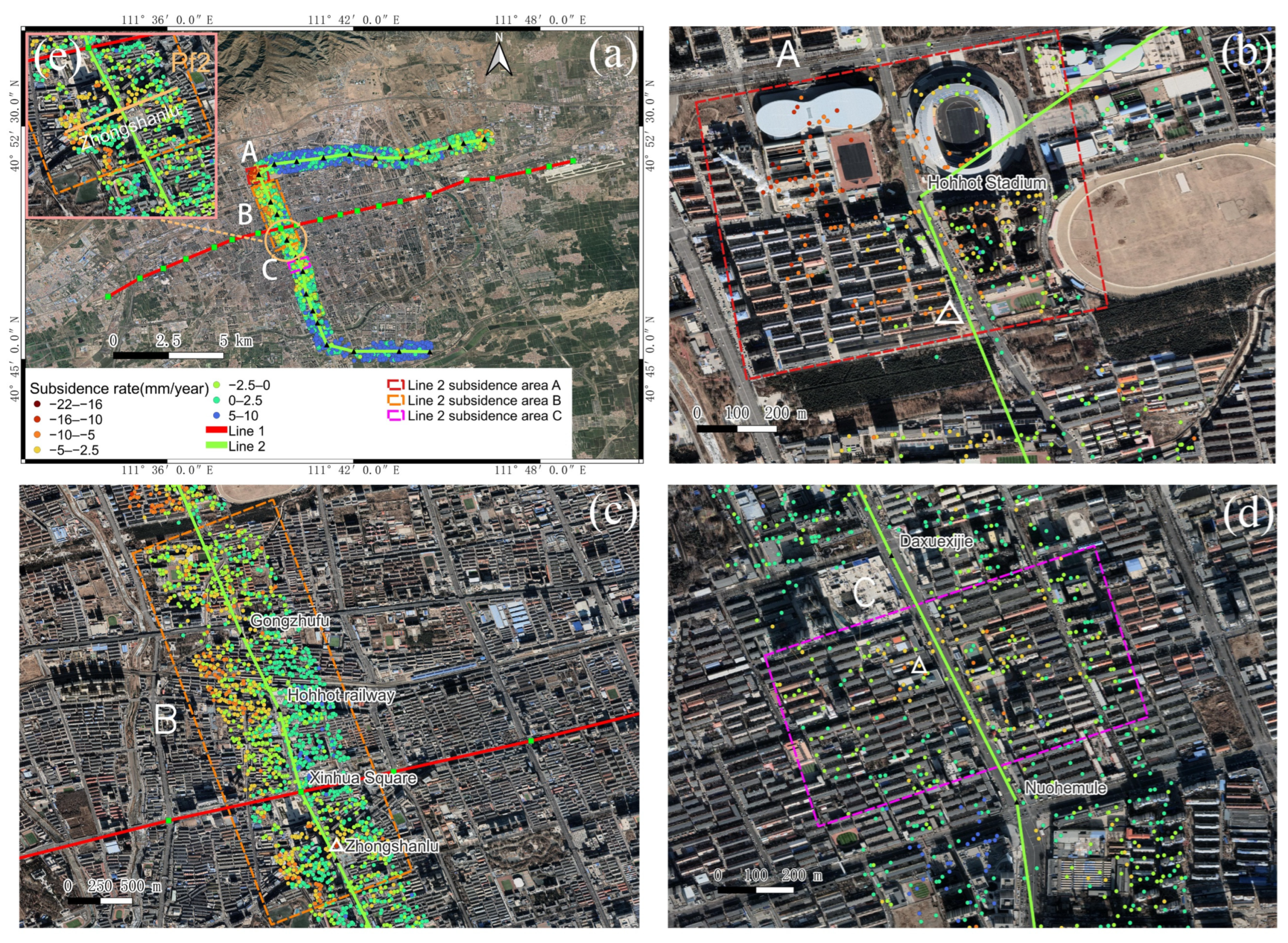
4.2. Monitoring Results of Line 1
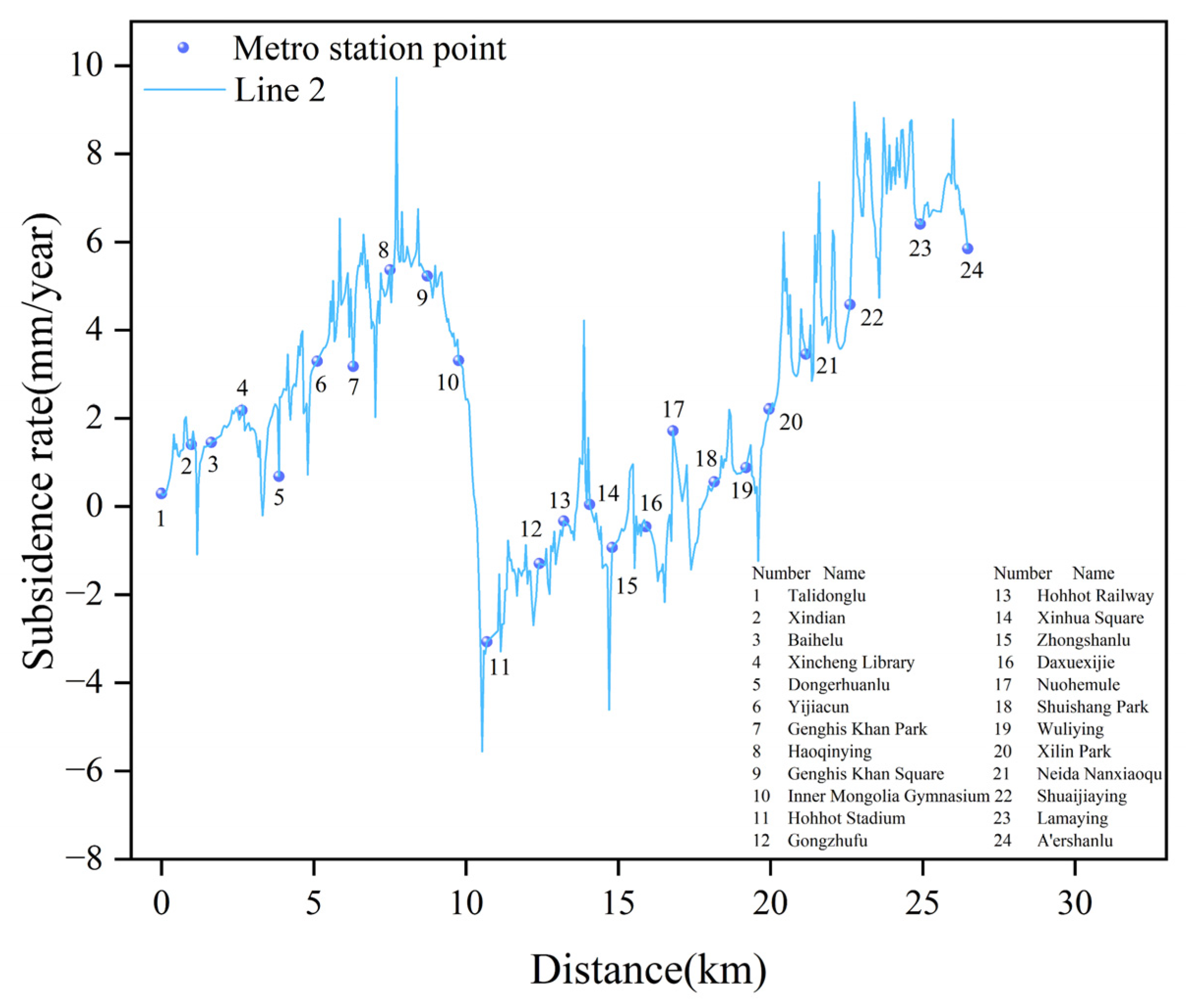
4.3. Monitoring Results of Line 2
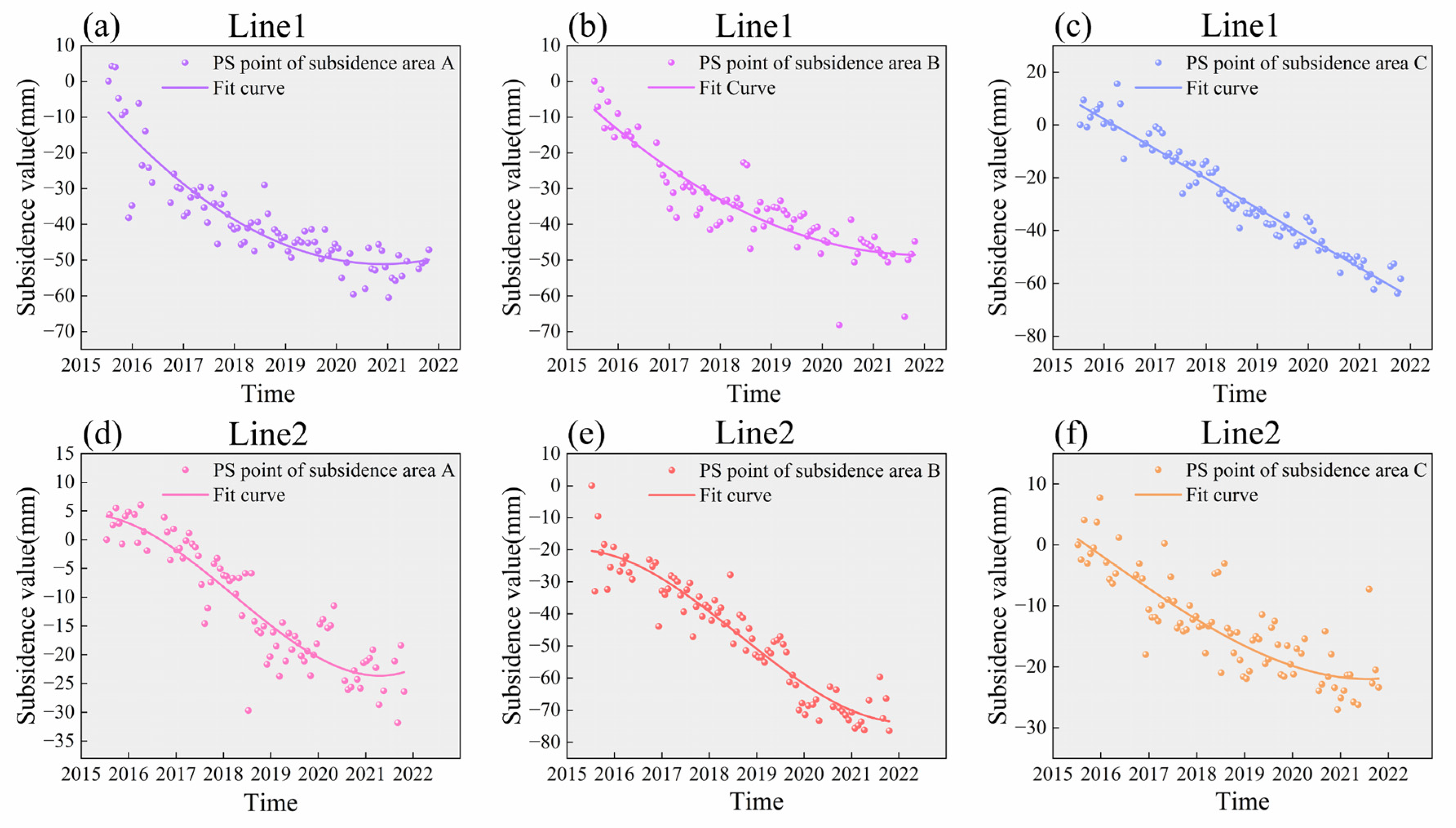
4.4. Spatial and Temporal Analysis of Subway Subsidence
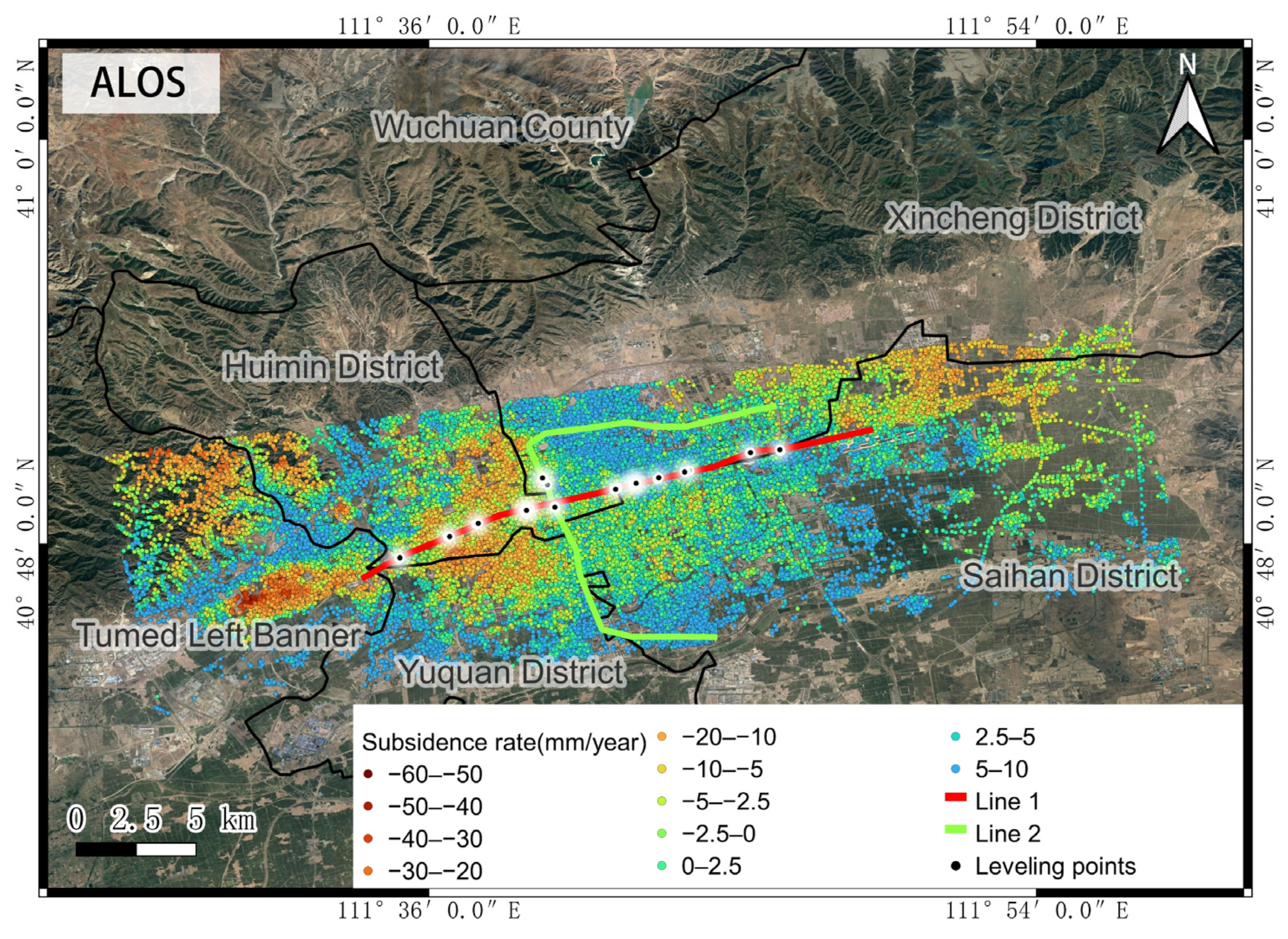
4.4.1. Spatial Analysis of Subway Subsidence
4.4.2. Time Series Analysis of Subway Subsidence
5. Discussion
5.1. Causes of Settlement along Subway Lines
5.2. Effect of Two External DEMs on StaMPS-PS
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, F.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z. Ground Subsidence Geo-Hazards Induced by Rapid Urbanization: Implications from InSAR Observation and Geological Analysis. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Qin, Y.; Feng, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, K. Safety Risks and Protection Measures for City Wall during Construction and Operation of Xi’an Metro. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2020, 34, 04020003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Stanus, Y.; Lombaert, G.; Degrande, G. Influence of Tunnel and Soil Parameters on Vibrations from Underground Railways. J. Sound Vib. 2009, 327, 70–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; He, P.; Zhang, H.; Ma, C. Analysis on the Safety of a Concrete-Masonry Structure near to Shield Tunnel Excavation. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Business Management and Electronic Information, Guangzhou, China, 13–15 May 2011; Volume 4, pp. 889–892. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, R. Response of the Groundwater Environment to Rapid Urbanization in Hohhot, the Provincial Capital of Western China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, M. Sequential InSAR Time Series Deformation Monitoring of Land Subsidence and Rebound in Xi’an, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmutoğlu, Y. Surface Subsidence Induced by Twin Subway Tunnelling in Soft Ground Conditions in Istanbul. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2011, 70, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qie, Z.; Yan, H. A Causation Analysis of Chinese Subway Construction Accidents Based on Fault Tree Analysis-Bayesian Network. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 887073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavvadas, M.J. Monitoring Ground Deformation in Tunnelling: Current Practice in Transportation Tunnels. Eng. Geol. 2005, 79, 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hu, F. Monitoring Ground Subsidence along the Shanghai Maglev Zone Using TerraSAR-X Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Doin, M.-P.; Lopez-Quiroz, P.; Tupin, F.; Fruneau, B.; Pinel, V.; Trouve, E. Mexico City Subsidence Measured by InSAR Time Series: Joint Analysis Using PS and SBAS Approaches. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 1312–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Dang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H.; Yan, S. Underground Coal Fires Identification and Monitoring Using Time-Series InSAR with Persistent and Distributed Scatterers: A Case Study of Miquan Coal Fire Zone in Xinjiang, China. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 164492–164506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, Z.; Feng, G.; Wang, Q.; Hu, J. Monitoring Surface Deformation over Permafrost with an Improved SBAS-InSAR Algorithm: With Emphasis on Climatic Factors Modeling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, L.; Feng, G.; Lu, Z.; Sun, Q. On the Accuracy of Topographic Residuals Retrieved by MTInSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib, O.-C.; Shimon, W.; Sarah, K.; Tonian, R. Detection of Sinkhole Activity in West-Central Florida Using InSAR Time Series Observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsironi, V.; Ganas, A.; Karamitros, I.; Efstathiou, E.; Koukouvelas, I.; Sokos, E. Kinematics of Active Landslides in Achaia (Peloponnese, Greece) through InSAR Time Series Analysis and Relation to Rainfall Patterns. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlögl, M.; Gutjahr, K.; Fuchs, S. The Challenge to Use Multi-Temporal InSAR for Landslide Early Warning. Nat. Hazards 2022, 112, 2913–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serkhane, A.; Benfedda, A.; Guettouche, M.S.; Bouhadad, Y. InSAR Derived Co-Seismic Deformation Triggered by the Mihoub (Tell Atlas of Algeria) 28 May 2016 (Mw = 5.4) Earthquake Combined to Geomorphic Features Analysis to Identify the Causative Active Fault. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2022, 188, 104476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Xu, X.; Chen, S. Coseismic Slip Model of the 2021 Maduo Earthquake, China from Sentinel-1 InSAR Observation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Liang, K.; Li, H.; Jiang, W. Coseismic Displacement and Slip Distribution of the 21 May 2021 Mw 6.1 Earthquake in Yangbi, China Derived from InSAR Observations. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 857739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Qiu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, D.; Ma, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Tang, B. Efficient Identification and Monitoring of Landslides by Time-Series InSAR Combining Single- and Multi-Look Phases. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Torres, E.A.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Novelo-Casanova, D.A.; Solano-Rojas, D.; Havazli, E.; Salazar-Tlaczani, L. Risk Assessment of Land Subsidence and Associated Faulting in Mexico City Using InSAR. Nat. Hazards 2022, 112, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Tapete, D. Urban Growth and Land Subsidence: Multi-Decadal Investigation Using Human Settlement Data and Satellite InSAR in Morelia, Mexico. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 152211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Perissin, D.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Y. L- and X-Band Multi-Temporal InSAR Analysis of Tianjin Subsidence. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7933–7951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Gong, H.; Yu, J.; Li, X.; Ke, Y. Stable Pointwise Target Detection Method and Small Baseline Subset INSAR Used in Beijing Subsidence Monitoring. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2016, 20, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.G.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, S.; Meng, L.; Liu, J.; Cui, Y. Dynamic Analysis of Urban Ground Subsidence in Beijing Based on the Permanent Scattering InSAR Technology. JARS 2018, 12, 026001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Feng, G.; Li, Z.; Shan, X.; Du, Y.; Wang, H. Spatio-Temporal Error Sources Analysis and Accuracy Improvement in Landsat 8 Image Ground Displacement Measurements. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Feng, G.; Xu, B.; Yu, Y.; Li, Z.; Du, Y.; Zhu, J. Deriving Spatio-Temporal Development of Ground Subsidence Due to Subway Construction and Operation in Delta Regions with PS-InSAR Data: A Case Study in Guangzhou, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yang, M.; Dong, J.; Liao, M. Investigating Deformation along Metro Lines in Coastal Cities Considering Different Structures with InSAR and SBM Analyses. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 115, 103099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wang, R.; Li, M.; Liao, M. A PSI Targets Characterization Approach to Interpreting Surface Displacement Signals: A Case Study of the Shanghai Metro Tunnels. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 280, 113150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espiritu, K.W.; Reyes, C.J.; Benitez, T.M.; Tokita, R.C.; Galvez, L.J.; Ramirez, R. Sentinel-1 Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) Reveals Continued Ground Deformation in and around Metro Manila, Philippines, Associated with Groundwater Exploitation. Nat. Hazards 2022, 114, 3139–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, B.; Schmidt, D.; Simoni, A. The Influence of External Digital Elevation Models on PS-InSAR and SBAS Results: Implications for the Analysis of Deformation Signals Caused by Slow Moving Landslides in the Northern Apennines (Italy). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 2618–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducret, G.; Doin, M.-P.; Grandin, R.; Lasserre, C.; Guillaso, S. DEM Corrections Before Unwrapping in a Small Baseline Strategy for InSAR Time Series Analysis. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torun, A.T.; Ekercin, S.; Algancı, U.; Yılmaztürk, F. Evaluating the Effect of External DEMs on the Accuracy of InSAR DEM Generation. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2023, 51, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Feng, G.; Li, Z.; Peng, X.; Zhu, J.; Ren, Z. Effects of External Digital Elevation Model Inaccuracy on StaMPS-PS Processing: A Case Study in Shenzhen, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Agrawal, R.; Mohan, S. Topographic Correction of ALOS-PALSAR Images Using InSAR-Derived DEM. Geocarto Int. 2015, 30, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Tan, Z.; Fan, X.; Chang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yin, X. Application of Life Cycle Assessment for Municipal Solid Waste Management Options in Hohhot, People’s Republic of China. Waste Manag. Res. 2021, 39, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, Z. Responses of Stream Geomorphic Indices to Piedmont Fault Activity in the Daqingshan Area of China. J. Earth Sci. 2020, 31, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; He, Z.; Ma, B.; Long, J.; Zhang, H.; Liang, K. Vertical Slip Rates of Normal Faults Constrained by Both Fault Walls: A Case Study of the Hetao Fault System in Northern China. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 816922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Liu, B.; Shi, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z. The Spatial Distribution and Hydrogeological Controls of Fluoride in the Confined and Unconfined Groundwater of Tuoketuo County, Hohhot, Inner Mongolia, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Nie, Z. Improving Assessment of Groundwater Sustainability with Analytic Hierarchy Process and Information Entropy Method: A Case Study of the Hohhot Plain, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 2353–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zebker, H. Two-Dimensional Phase Unwrapping with Use of Statistical Models for Cost Functions in Nonlinear Optimization. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 2001, 18, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Segall, P.; Zebker, H. Persistent Scatterer Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar for Crustal Deformation Analysis, with Application to Volcán Alcedo, Galápagos. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2007, 112, B07407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H.; Segall, P.; Kampes, B. A New Method for Measuring Deformation on Volcanoes and Other Natural Terrains Using InSAR Persistent Scatterers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L23611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A. A Multi-Temporal InSAR Method Incorporating Both Persistent Scatterer and Small Baseline Approaches. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L16302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H.A. Phase Unwrapping in Three Dimensions with Application to InSAR Time Series. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 2007, 24, 2737–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, M.; Motagh, M. Psinsar Improvement Using Amplitude Dispersion Index Optimization of Dual Polarimetry Data. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, XL-1-W5, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in Interferometric Radar Echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.X.; Zhao, W.; Yu, J.J. Predication and Analysis on Ground Settlement Induced by Shielding Tunneling Construction. AMR 2011, 261–263, 1156–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Bai, L.; Bai, W. Multi-Scale and Multi-Dimensional Time Series InSAR Characterizing of Surface Deformation over Shandong Peninsula, China. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ding, L.; Luo, H. Non-Linear Description of Ground Settlement over Twin Tunnels in Soil. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2014, 42, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Feng, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Xie, R. Coastal Subsidence Monitoring Associated with Land Reclamation Using the Point Target Based SBAS-InSAR Method: A Case Study of Shenzhen, China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Dong, J.; Zhong, G.; Sun, X. Prediction of Sea Surface Temperature Using Long Short-Term Memory. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1745–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, P.; Li, T.; Yan, Y. Space-Time Residual LSTM Architechture for Distant Speech Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 11th International Symposium on Chinese Spoken Language Processing (ISCSLP), Taipei, Taiwan, 26–29 November 2018; pp. 379–383. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Z.; Yan, J.; Demir, I. A Rainfall-Runoff Model with LSTM-Based Sequence-to-Sequence Learning. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR025326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, J.; Cui, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, R.; Cao, Q.; Li, J.; Dai, W.; Bao, H.; et al. Large-Scale Land Subsidence Monitoring and Prediction Based on SBAS-InSAR Technology with Time-Series Sentinel-1A Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Si, X.; Hu, C.; Zhang, J. A Review of Recurrent Neural Networks: LSTM Cells and Network Architectures. Neural Comput. 2019, 31, 1235–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Qiu, H.; Yang, D.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Tang, B.; Sun, K.; Cao, M. Surface Multi-Hazard Effect of Underground Coal Mining. Landslides 2023, 20, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qiu, H.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, S.; Yang, D.; Tang, B. The Post-Failure Spatiotemporal Deformation of Certain Translational Landslides May Follow the Pre-Failure Pattern. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No | Reference Image | Secondary Image | Perp_B (m) | Temp_B (Days) | No | Reference Image | Secondary Image | Perp_B (m) | Temp_B (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2018.06.18 | 2015.07.16 | 75.22 | −1068 | 43 | 2018.06.18 | 2018.08.29 | −40.27 | 72 |
| 2 | 2018.06.18 | 2015.08.09 | −73.44 | −1044 | 44 | 2018.06.18 | 2018.09.22 | 18.99 | 96 |
| 3 | 2018.06.18 | 2015.09.02 | −5.11 | −1020 | 45 | 2018.06.18 | 2018.10.16 | −103.51 | 120 |
| 4 | 2018.06.18 | 2015.09.26 | 24.28 | −996 | 46 | 2018.06.18 | 2018.11.09 | 92.64 | 144 |
| 5 | 2018.06.18 | 2015.10.20 | −55.77 | −972 | 47 | 2018.06.18 | 2018.12.03 | 46.35 | 168 |
| 6 | 2018.06.18 | 2015.11.13 | 61.74 | −948 | 48 | 2018.06.18 | 2018.12.27 | −42.91 | 192 |
| 7 | 2018.06.18 | 2015.12.07 | 11.16 | −924 | 49 | 2018.06.18 | 2019.01.20 | 51.08 | 216 |
| 8 | 2018.06.18 | 2015.12.31 | −37.09 | −900 | 50 | 2018.06.18 | 2019.02.13 | −14.76 | 240 |
| 9 | 2018.06.18 | 2016.02.17 | −14.09 | −852 | 51 | 2018.06.18 | 2019.03.09 | −37.40 | 264 |
| 10 | 2018.06.18 | 2016.03.12 | −16.58 | −828 | 52 | 2018.06.18 | 2019.04.02 | −23.01 | 288 |
| 11 | 2018.06.18 | 2016.04.05 | −10.00 | −804 | 53 | 2018.06.18 | 2019.04.26 | −135.11 | 312 |
| 12 | 2018.06.18 | 2016.04.29 | −36.87 | −780 | 54 | 2018.06.18 | 2019.05.20 | 32.02 | 336 |
| 13 | 2018.06.18 | 2016.05.23 | 47.17 | −756 | 55 | 2018.06.18 | 2019.06.13 | 51.09 | 360 |
| 14 | 2018.06.18 | 2016.10.02 | 46.62 | −624 | 56 | 2018.06.18 | 2019.07.07 | 1.10 | 384 |
| 15 | 2018.06.18 | 2016.10.26 | −23.25 | −600 | 57 | 2018.06.18 | 2019.07.31 | 48.62 | 408 |
| 16 | 2018.06.18 | 2016.11.19 | −57.42 | −576 | 58 | 2018.06.18 | 2019.08.24 | −115.89 | 432 |
| 17 | 2018.06.18 | 2016.12.13 | 94.01 | −552 | 59 | 2018.06.18 | 2019.09.17 | 6.33 | 456 |
| 18 | 2018.06.18 | 2017.01.06 | 23.64 | −528 | 60 | 2018.06.18 | 2019.10.11 | 51.58 | 480 |
| 19 | 2018.06.18 | 2017.01.30 | −5.35 | −504 | 61 | 2018.06.18 | 2019.11.04 | −64.72 | 504 |
| 20 | 2018.06.18 | 2017.02.23 | 37.50 | −480 | 62 | 2018.06.18 | 2019.11.28 | 59.01 | 528 |
| 21 | 2018.06.18 | 2017.03.19 | −36,91 | −456 | 63 | 2018.06.18 | 2019.12.22 | 51.29 | 552 |
| 22 | 2018.06.18 | 2017.04.12 | −31.74 | −432 | 64 | 2018.06.18 | 2020.01.15 | −12.63 | 576 |
| 23 | 2018.06.18 | 2017.05.06 | −108.20 | −408 | 65 | 2018.06.18 | 2020.02.08 | 60.78 | 600 |
| 24 | 2018.06.18 | 2017.05.30 | −25.93 | −384 | 66 | 2018.06.18 | 2020.03.15 | −76.36 | 636 |
| 25 | 2018.06.18 | 2017.06.23 | 31.09 | −360 | 67 | 2018.06.18 | 2020.04.08 | 59.22 | 660 |
| 26 | 2018.06.18 | 2017.07.17 | −45.08 | −336 | 68 | 2018.06.18 | 2020.05.02 | −45.93 | 684 |
| 27 | 2018.06.18 | 2017.08.10 | 17.95 | −312 | 69 | 2018.06.18 | 2020.07.25 | −38.84 | 768 |
| 28 | 2018.06.18 | 2017.09.03 | 12.96 | −288 | 70 | 2018.06.18 | 2020.08.18 | 27.81 | 792 |
| 29 | 2018.06.18 | 2017.09.27 | −81.84 | −264 | 71 | 2018.06.18 | 2020.09.11 | −112.47 | 816 |
| 30 | 2018.06.18 | 2017.10.21 | 41.75 | −240 | 72 | 2018.06.18 | 2020.10.05 | −34.57 | 840 |
| 31 | 2018.06.18 | 2017.11.14 | 58.51 | −216 | 73 | 2018.06.18 | 2020.10.29 | 47.23 | 864 |
| 32 | 2018.06.18 | 2017.12.08 | 44.06 | −192 | 74 | 2018.06.18 | 2020.11.22 | −42.23 | 888 |
| 33 | 2018.06.18 | 2018.01.01 | 159.21 | −168 | 75 | 2018.06.18 | 2020.12.16 | 31.85 | 912 |
| 34 | 2018.06.18 | 2018.01.25 | −19.82 | −144 | 76 | 2018.06.18 | 2021.01.09 | 82.91 | 936 |
| 35 | 2018.06.18 | 2018.02.18 | 2.79 | −120 | 77 | 2018.06.18 | 2021.02.02 | −29.08 | 960 |
| 36 | 2018.06.18 | 2018.03.14 | 37.47 | −96 | 78 | 2018.06.18 | 2021.02.26 | 41.30 | 984 |
| 37 | 2018.06.18 | 2018.04.07 | 1.15 | −72 | 79 | 2018.06.18 | 2021.03.22 | −12.94 | 1008 |
| 38 | 2018.06.18 | 2018.05.01 | 63.16 | −48 | 80 | 2018.06.18 | 2021.04.15 | −18.37 | 1032 |
| 39 | 2018.06.18 | 2018.05.25 | −81.31 | −24 | 81 | 2018.06.18 | 2021.05.21 | −44.71 | 1068 |
| 40 | 2018.06.18 | 2018.06.18 | 0 | 0 | 82 | 2018.06.18 | 2021.08.13 | 45.03 | 1152 |
| 41 | 2018.06.18 | 2018.07.12 | 73.01 | 24 | 83 | 2018.06.18 | 2021.09.06 | 8.84 | 1176 |
| 42 | 2018.06.18 | 2018.08.05 | −18.30 | 48 | 84 | 2018.06.18 | 2021.09.30 | −87.07 | 1200 |
| 85 | 2018.06.18 | 2021.10.24 | −21.89 | 1224 |
| DEM | Spatial Resolution (m) | Source | Date of Acquisition | Distribution Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALOS PALSAR DEM | 12.5 | https://vertex.daac.asf.alaska.edu, accessed on accessed on 20 October 2022 | 2000.02.11–2000.02.21 | 60°S–60°N |
| SRTM-1 arc DEM | 30 | http://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/, accessed on accessed on 22 October 2022 | 2008.12.22–2009.01.20 | 57°S–60°N |
| Date | R2 | RMSE | Smax (mm) | i (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016.10.02 | 0.9338 | 0.3039 | −4.8 | 23.8 |
| 2017.04.12 | 0.9914 | 0.1428 | −6.0 | 30.7 |
| 2018.01.01 | 0.9813 | 0.4643 | −11.0 | 39.4 |
| 2018.03.14 | 0.9191 | 0.9634 | −13.5 | 48.7 |
| Date | R2 | RMSE | Smax (mm) | i (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016.10.02 | 0.9102 | 0.4761 | −5.9 | 58 |
| 2016.10.26 | 0.8497 | 0.6767 | −6.3 | 67 |
| 2016.12.13 | 0.9499 | 0.4887 | −7.8 | 52 |
| 2017.05.30 | 0.9527 | 0.4794 | −7.9 | 51 |
| 2017.12.08 | 0.9816 | 0.3826 | −10.1 | 49 |
| Region | Model Parameters | Parameter Settings |
|---|---|---|
| affiliated hospital | Input_size | 13 |
| Output_size | 1 | |
| Hidden layers | 2 | |
| Hidden layer neurons | 50 | |
| Epoches | 200 | |
| Loss | MSE | |
| Optimizer | Adam | |
| Batch_size | 16 | |
| Dropout | 0.2 | |
| Learning_rate | 0.01 | |
| Hugangdonglu | Input_size | 12 |
| Output_size | 1 | |
| Hidden layers | 2 | |
| hidden layer neurons | 50 | |
| Epoches | 200 | |
| Loss | MSE | |
| Optimizer | Adam | |
| Batch_size | 32 | |
| Dropout | 0.2 | |
| Learning_rate | 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, S.; Li, P.; Li, H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, B. Monitoring and Comparative Analysis of Hohhot Subway Subsidence Using StaMPS-PS Based on Two DEMS. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4011. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15164011
Zhao S, Li P, Li H, Zhang T, Wang B. Monitoring and Comparative Analysis of Hohhot Subway Subsidence Using StaMPS-PS Based on Two DEMS. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(16):4011. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15164011
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Sihai, Peixian Li, Hairui Li, Tao Zhang, and Bing Wang. 2023. "Monitoring and Comparative Analysis of Hohhot Subway Subsidence Using StaMPS-PS Based on Two DEMS" Remote Sensing 15, no. 16: 4011. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15164011
APA StyleZhao, S., Li, P., Li, H., Zhang, T., & Wang, B. (2023). Monitoring and Comparative Analysis of Hohhot Subway Subsidence Using StaMPS-PS Based on Two DEMS. Remote Sensing, 15(16), 4011. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15164011








