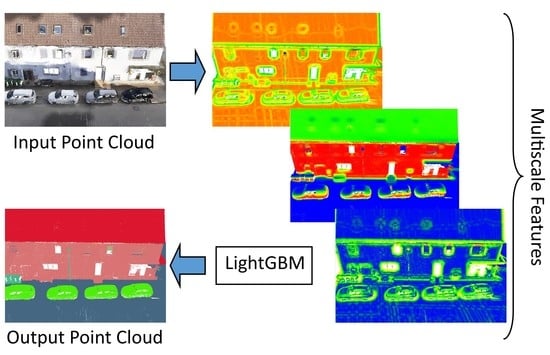
Classification of Large-Scale Mobile Laser Scanning Data in Urban Area with LightGBM
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We are one of the first studies using LightGBM in 3D PCC as we are showing its effectiveness compared with Random Forest (RF) in mobile LiDAR datasets, as we compare it with DL methods.
- Our feature set achieved competitive results even though they are lightweight features.
- Our feature calculation implementation is comparatively faster than previous studies, even though our multiscale sampling method produces an irregular point cloud, which leads to less information loss.
2. Related Works
2.1. Classification with Hand-Crafted Features
2.2. Classification with Deep Features
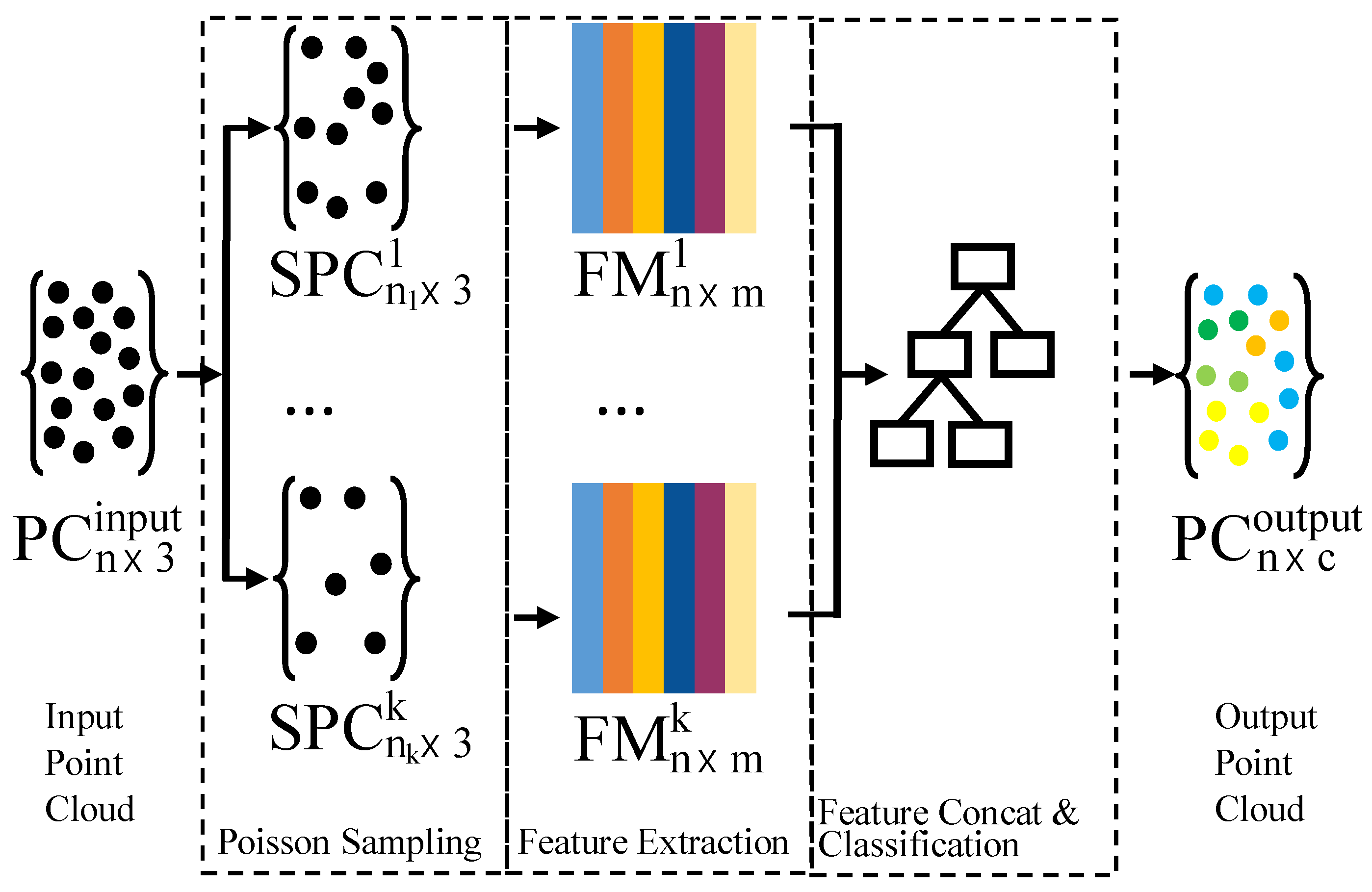
3. Methodology
3.1. Multi-Scale Sampling
3.2. Neighborhood Definition
3.3. Feature Extraction
3.4. Classification
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. Datasets
4.1.1. Paris-rue-Madame Database
4.1.2. Paris-rue-Cassette Database
4.1.3. Toronto-3D Mobile LiDAR Dataset
4.2. Implementation
4.3. Evaluation
4.4. Experiments and Discussion
4.4.1. Paris–rue–Madame and Paris–rue–Cassette Databases
4.4.2. Toronto-3D
4.5. Comparison with the Previous Studies
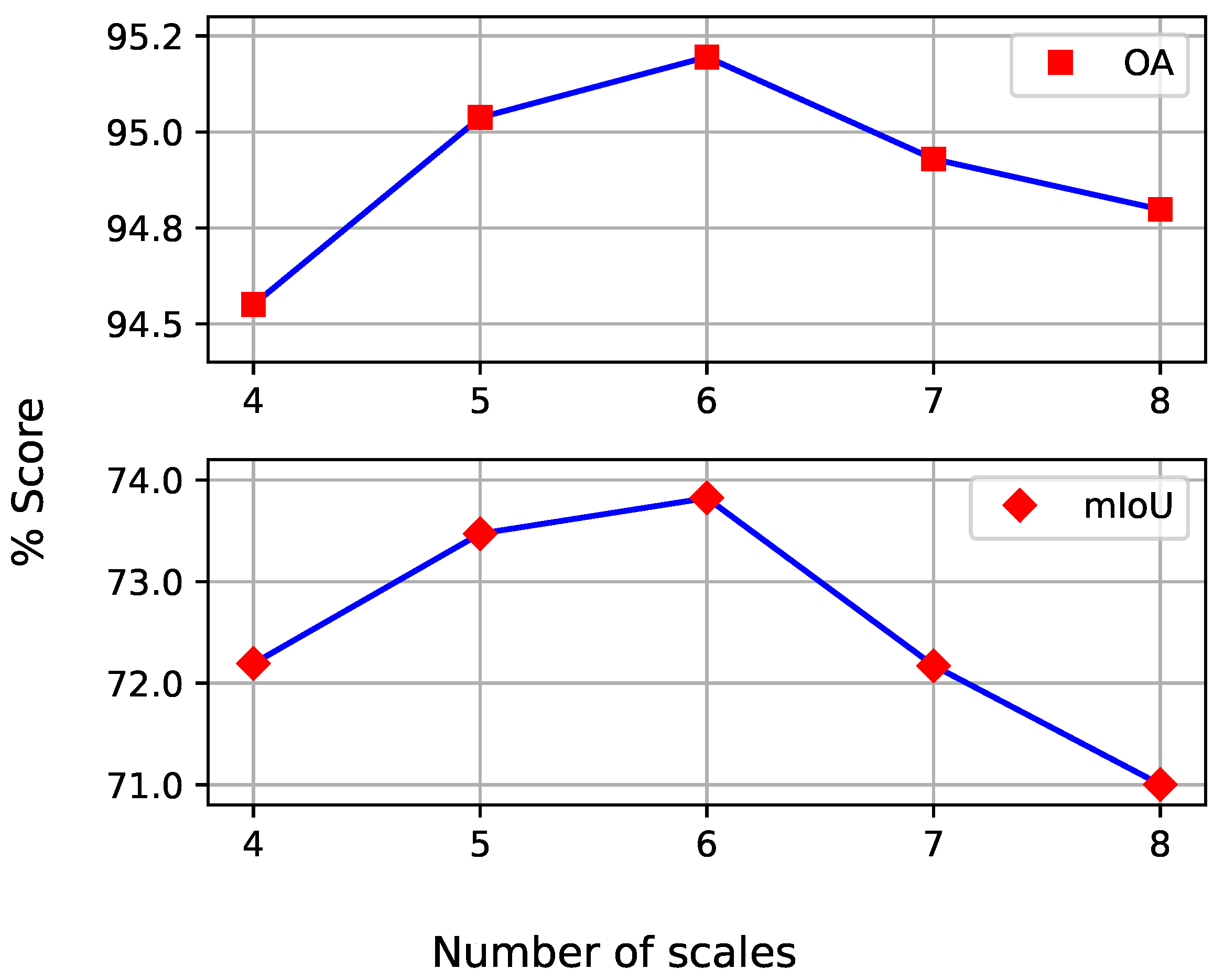
4.6. Ablation Study
4.6.1. Impact of Training Point Selection
4.6.2. Sampling Methods
4.6.3. Multi-Scale Levels
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Puente, I.; González-Jorge, H.; Martínez-Sánchez, J.; Arias, P. Review of mobile mapping and surveying technologies. Measurement 2013, 46, 2127–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhong, Z.; Liu, F.; Chapman, M.A.; Cao, D.; Li, J. Deep Learning for LiDAR Point Clouds in Autonomous Driving: A Review. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 3412–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Peethambaran, J.; Chen, D. LiDAR Point Clouds to 3-D Urban Models: A Review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 606–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wen, C.; Dai, Y.; Yu, S.; Liu, M. Urban 3D modeling with mobile laser scanning: A review. Virtual Real. Intell. Hardw. 2020, 2, 175–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Oude Elberink, S.; Vosselman, G. Semantic labelling of road furniture in mobile laser scanning data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, 42, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Ma, L.; Wu, R.; Luo, Z.; Wang, C. Rapid Urban Roadside Tree Inventory Using a Mobile Laser Scanning System. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 3690–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; You, S. Pole-like object detection and classification from urban point clouds. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 3032–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Yan, W.; Yu, Y.; Zhong, L.; Li, D. Robust Traffic-Sign Detection and Classification Using Mobile LiDAR Data With Digital Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 1715–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Hossain, S.; Lang, H.; Lin, X. A review of high-definition map creation methods for autonomous driving. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 122, 106125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Tian, J.; Reinartz, P. 3D change detection—Approaches and applications. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 122, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voelsen, M.; Schachtschneider, J.; Brenner, C. Classification and Change Detection in Mobile Mapping LiDAR Point Clouds. PFG—J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Geoinf. Sci. 2021, 89, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhu, X.X. Linking Points With Labels in 3D: A Review of Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2020, 8, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Bennamoun, M. Deep Learning for 3D Point Clouds: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 4338–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, H.; Goulette, F.; Deschaud, J.E.; Marcotegui, B.; LeGall, Y. Semantic Classification of 3D Point Clouds with Multiscale Spherical Neighborhoods. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Verona, Italy, 5–8 September 2018; pp. 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinmann, M.; Jutzi, B.; Hinz, S.; Mallet, C. Semantic point cloud interpretation based on optimal neighborhoods, relevant features and efficient classifiers. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 105, 286–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodu, N.; Lague, D. 3D terrestrial lidar data classification of complex natural scenes using a multi-scale dimensionality criterion: Applications in geomorphology. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 68, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Shan, J. Graph attention convolution for point cloud semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 10296–10305. [Google Scholar]
- Niemeyer, J.; Rottensteiner, F.; Soergel, U. Contextual classification of lidar data and building object detection in urban areas. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 87, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomley, R.; Jutzi, B.; Weinmann, M. Classification of airborne laser scanning data using geometric multi-scale features and different neighbourhood types. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, 3, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, B.; Huang, X.; Zhang, F.; Sohn, G. Classification of airborne laser scanning data using JointBoost. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 100, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinmann, M.; Schmidt, A.; Mallet, C.; Hinz, S.; Rottensteiner, F.; Jutzi, B. Contextual classification of point cloud data by exploiting individual 3D neigbourhoods. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, 2, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hackel, T.; Wegner, J.D.; Schindler, K. Fast Semantic Segmentation of 3D Point Clouds with Strongly Varying Density. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, 3, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demantké, J.; Mallet, C.; David, N.; Vallet, B. Dimensionality based scale selection in 3D lidar point clouds. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2012, 38, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blomley, R.; Weinmann, M. Using multi-scale features for the 3D semantic labeling of airborne laser scanning data. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, 4, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chehata, N.; Guo, L.; Mallet, C. Airborne lidar feature selection for urban classification using random forests. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Workshop Laserscanning’09, Paris, France, 1–2 September 2009; pp. 207–212. [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann, M.; Urban, S.; Hinz, S.; Jutzi, B.; Mallet, C. Distinctive 2D and 3D features for automated large-scale scene analysis in urban areas. Comput. Graph. 2015, 49, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.F.; Sun, S.J.; Song, X.Y.; Xiao, G.Q. 3D Point Cloud Descriptors in Hand-crafted and Deep Learning Age: State-of-the-Art. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1802.02297. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD ’16, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.Y. Lightgbm: A highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Bentéjac, C.; Csörgő, A.; Martínez-Muñoz, G. A comparative analysis of gradient boosting algorithms. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 1937–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Maji, S.; Kalogerakis, E.; Learned-Miller, E. Multi-view convolutional neural networks for 3d shape recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 945–953. [Google Scholar]
- Tatarchenko, M.; Park, J.; Koltun, V.; Zhou, Q.Y. Tangent convolutions for dense prediction in 3d. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3887–3896. [Google Scholar]
- Boulch, A.; Le Saux, B.; Audebert, N. Unstructured point cloud semantic labeling using deep segmentation networks. 3dor@ Eurographics 2017, 3, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Riegler, G.; Osman Ulusoy, A.; Geiger, A. Octnet: Learning deep 3d representations at high resolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3577–3586. [Google Scholar]
- Maturana, D.; Scherer, S. Voxnet: A 3d convolutional neural network for real-time object recognition. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 922–928. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Shan, J.; He, L. MSNet: Multi-Scale Convolutional Network for Point Cloud Classification. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 652–660. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. Pointnet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Yang, B.; Xie, L.; Rosa, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Trigoni, N.; Markham, A. Randla-net: Efficient semantic segmentation of large-scale point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11108–11117. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Jiang, L.; Fu, C.W.; Jia, J. Pointweb: Enhancing local neighborhood features for point cloud processing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5565–5573. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Bu, R.; Sun, M.; Wu, W.; Di, X.; Chen, B. Pointcnn: Convolution on x-transformed points. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Qi, Z.; Fuxin, L. Pointconv: Deep convolutional networks on 3d point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9621–9630. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, H.; Qi, C.R.; Deschaud, J.E.; Marcotegui, B.; Goulette, F.; Guibas, L.J. Kpconv: Flexible and deformable convolution for point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6411–6420. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Ding, R.; Zhao, H.; Qi, X. Paconv: Position adaptive convolution with dynamic kernel assembling on point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 3173–3182. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sarma, S.E.; Bronstein, M.M.; Solomon, J.M. Dynamic graph cnn for learning on point clouds. ACM Trans. Graph. (Tog) 2019, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engel, N.; Belagiannis, V.; Dietmayer, K. Point transformer. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 134826–134840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.H.; Cai, J.X.; Liu, Z.N.; Mu, T.J.; Martin, R.R.; Hu, S.M. Pct: Point cloud transformer. Comput. Vis. Media 2021, 7, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Jiang, L.; Jia, J.; Torr, P.H.; Koltun, V. Point transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 16239–16248. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.; Lu, Z. A Review of Deep Learning-Based Semantic Segmentation for Point Cloud. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 179118–179133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, R.L. Stochastic Sampling in Computer Graphics. Acm Trans. Graph. 1986, 5, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kölle, M.; Laupheimer, D.; Schmohl, S.; Haala, N.; Rottensteiner, F.; Wegner, J.D.; Ledoux, H. The Hessigheim 3D (H3D) benchmark on semantic segmentation of high-resolution 3D point clouds and textured meshes from UAV LiDAR and Multi-View-Stereo. ISPRS Open J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 1, 100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharroubi, A.; Van Wersch, L.; Billen, R.; Poux, F. Tesserae3d: A Benchmark for Tesserae Semantic Segmentation in 3D Point Clouds. In SPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences; Copernicus: Goettingen, Germany, 2021; Volume V-2-2021, pp. 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna, A.; Marcotegui, B.; Goulette, F.; Deschaud, J.E. Paris-rue-Madame database: A 3D mobile laser scanner dataset for benchmarking urban detection, segmentation and classification methods. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Applications and Methods ICPRAM 2014, Angers, France, 6–8 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vallet, B.; Brédif, M.; Serna, A.; Marcotegui, B.; Paparoditis, N. TerraMobilita-iQmulus urban point cloud analysis benchmark. Comput. Graph. 2015, 49, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, W.; Qin, N.; Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Du, J.; Cai, G.; Yang, K.; Li, J. Toronto-3D: A Large-Scale Mobile LiDAR Dataset for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Roadways. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- PDAL Contributors. PDAL: The Point Data Abstraction Library. 2022. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2616780 (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Butler, H.; Chambers, B.; Hartzell, P.; Glennie, C. PDAL: An open source library for the processing and analysis of point clouds. Comput. Geosci. 2021, 148, 104680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, R.B.; Cousins, S. 3D is here: Point Cloud Library (PCL). In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, K.; Hu, Q.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.; Li, L.; Ji, S. Continuous Mapping Convolution for Large-Scale Point Clouds Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, B.; Lee, A.; Hong, M. Semantic Segmentation of Large-Scale Outdoor Point Clouds by Encoder–Decoder Shared MLPs with Multiple Losses. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Dong, Z.; Yang, B. A point-based deep learning network for semantic segmentation of MLS point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 175, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Tan, W.; Yu, Y.; Chapman, M.A. Multi-Scale Point-Wise Convolutional Neural Networks for 3D Object Segmentation From LiDAR Point Clouds in Large-Scale Environments. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhong, Z.; Cao, D.; Li, J. TGNet: Geometric Graph CNN on 3-D Point Cloud Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 3588–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Sum of eigenvalues | |
| Linearity | |
| Planarity | |
| Sphericity | |
| Omnivariance | |
| Eigenentropy | |
| Surface variation | |
| Anisotropy | |
| Absolute Moment (6) | |
| Vertical moment (2) | |
| Verticality | |
| Height range | |
| Height above min | |
| Height below max | |
| Average height | |
| Height variance | |
| Density |
| Datasets | Classes | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Facade | Ground | Cars | Mtrcl | T.Signs | Pedest. | Veg. | ||
| Paris–rue–Madame | 9978.43 | 8024.30 | 1835.38 | 10.05 | 98.87 | 15.48 | - | 19,962.51 |
| Paris–rue–Cassette | 7027.02 | 4229.64 | 368.27 | 40.33 | 46.1 | 24.0 | 212.13 | 11,947.49 |
| Datasets | Classes | Total | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Road | Road Mrk. | Natural | Building | U.Line | Pole | Car | Fence | ||
| Training | 35,391.89 | 1449.31 | 4650.92 | 18,252.78 | 589.86 | 743.58 | 4311.63 | 356.46 | 65,746.43 |
| Testing | 6305.46 | 296.14 | 1921.65 | 883.71 | 85.04 | 154.25 | 323.00 | 18.26 | 9987.52 |
| Class Name | Precision | Recall | F1-Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Facade | 99.10 | 99.36 | 99.23 |
| Ground | 99.38 | 97.99 | 98.68 |
| Cars | 97.61 | 99.41 | 98.50 |
| Pedest. | 80.27 | 99.91 | 88.94 |
| Mtrcl. | 69.22 | 99.13 | 81.49 |
| T.Signs | 70.19 | 99.39 | 82.19 |
| Average | 85.96 | 99.20 | 91.50 |
| Class Name | Precision | Recall | F1-Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Facade | 99.91 | 97.94 | 98.61 |
| Ground | 99.51 | 99.05 | 99.28 |
| Cars | 92.64 | 98.88 | 95.65 |
| Mtrcl. | 68.51 | 99.47 | 81.07 |
| T.Signs | 43.83 | 97.92 | 60.49 |
| Pedest. | 42.49 | 99.06 | 59.36 |
| Veg. | 87.37 | 98.85 | 92.74 |
| Average | 76.32 | 98.74 | 83.93 |
| Class Name | Precision | Recall | F1-Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Road | 99.43 | 95.03 | 97.18 |
| Road Mrk. | 50.09 | 93.27 | 65.17 |
| Natural | 97.71 | 97.07 | 97.39 |
| Buildings | 95.03 | 93.93 | 94.48 |
| Util. Line | 83.70 | 90.48 | 86.95 |
| Pole | 82.27 | 87.53 | 84.82 |
| Cars | 91.54 | 97.79 | 94.57 |
| Fence | 32.10 | 45.75 | 37.72 |
| Average | 78.98 | 87.61 | 82.29 |
| Study | Facade | Ground | Cars | Mtrcl. | T.Signs | Pedest. | Veg. | mIoU | OA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [14] | 98.22 | 96.62 | 95.37 | 61.55 | 67.43 | 77.86 | - | 82.84 | - |
| 97.27 | 97.77 | 84.94 | 58.99 | 12.71 | 35.31 | 71.48 | 65.50 | - | |
| [22] | 97.06 | 96.29 | 89.09 | 47.44 | 33.96 | 24.13 | - | 58.89 | 97.55 |
| 93.89 | 96.99 | 80.88 | 51.33 | 18.58 | 24.69 | 51.40 | 54.08 | 95.43 | |
| [15] | 91.81 | 84.88 | 55.48 | 9.44 | 4.90 | 1.63 | - | 31.68 | 88.62 |
| 86.65 | 95.75 | 47.31 | 17.12 | 14.29 | 9.06 | 24.63 | 35.30 | 89.60 | |
| Ours | 98.47 | 97.39 | 97.04 | 68.80 | 69.89 | 80.22 | - | 85.30 | 98.91 |
| 97.86 | 98.57 | 91.68 | 68.26 | 43.42 | 42.32 | 86.49 | 75.51 | 98.39 |
| Method | Road | Road Mrk. | Natural | Bldg | Util. Line | Pole | Car | Fence | mIoU | OA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PointNet++ SSG [39] | 89.27 | 0.00 | 69.0 | 54.1 | 43.7 | 23.3 | 52.0 | 3.0 | 41.81 | 84.88 |
| PointNet++ MSG [39] | 92.90 | 0.00 | 86.13 | 82.15 | 60.96 | 62.81 | 76.41 | 14.43 | 59.47 | 92.56 |
| DGCNN [46] | 93.88 | 0.00 | 91.25 | 80.39 | 62.40 | 62.32 | 88.26 | 15.81 | 61.79 | 94.24 |
| KPConv [44] | 94.62 | 0.06 | 96.07 | 91.51 | 87.68 | 81.56 | 85.66 | 15.72 | 69.11 | 95.39 |
| MS-PCNN [64] | 93.84 | 3.83 | 93.46 | 82.59 | 67.80 | 71.95 | 91.12 | 22.50 | 65.89 | 90.03 |
| TG-Net [65] | 93.54 | 0.00 | 90.83 | 81.57 | 65.26 | 62.98 | 88.73 | 7.85 | 61.34 | 94.08 |
| MS-TG-Net [57] | 94.41 | 17.19 | 95.72 | 88.83 | 76.01 | 73.97 | 94.24 | 23.64 | 70.50 | 95.71 |
| RandlaNet * [40] | 96.69 | 64.21 | 96.92 | 94.24 | 88.06 | 77.84 | 93.37 | 42.86 | 81.77 | 94.37 |
| MapConvSeg * [61] | 97.15 | 67.87 | 97.55 | 93.75 | 86.88 | 82.12 | 93.72 | 44.11 | 82.89 | 94.72 |
| [62] * | 92.84 | 27.43 | 89.90 | 95.27 | 85.59 | 74.50 | 44.41 | 58.30 | 71.03 | 83.60 |
| [63] ** | 92.20 | 53.80 | 92.80 | 86.00 | 72.20 | 72.50 | 75.70 | 21.20 | 70.80 | 93.60 |
| Ours | 94.52 | 48.34 | 94.91 | 89.54 | 75.92 | 73.64 | 89.69 | 23.24 | 73.85 | 95.12 |
| Metric | Poisson | Random | Voxel |
|---|---|---|---|
| mIoU | 74.01 | 70.91 | 73.39 |
| OA | 95.12 | 95.10 | 94.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sevgen, E.; Abdikan, S. Classification of Large-Scale Mobile Laser Scanning Data in Urban Area with LightGBM. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153787
Sevgen E, Abdikan S. Classification of Large-Scale Mobile Laser Scanning Data in Urban Area with LightGBM. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(15):3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153787
Chicago/Turabian StyleSevgen, Eray, and Saygin Abdikan. 2023. "Classification of Large-Scale Mobile Laser Scanning Data in Urban Area with LightGBM" Remote Sensing 15, no. 15: 3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153787
APA StyleSevgen, E., & Abdikan, S. (2023). Classification of Large-Scale Mobile Laser Scanning Data in Urban Area with LightGBM. Remote Sensing, 15(15), 3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153787