The Detection of Green Tide Biomass by Remote Sensing Images and In Situ Measurement in the Yellow Sea of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sources
2.1. Study Area
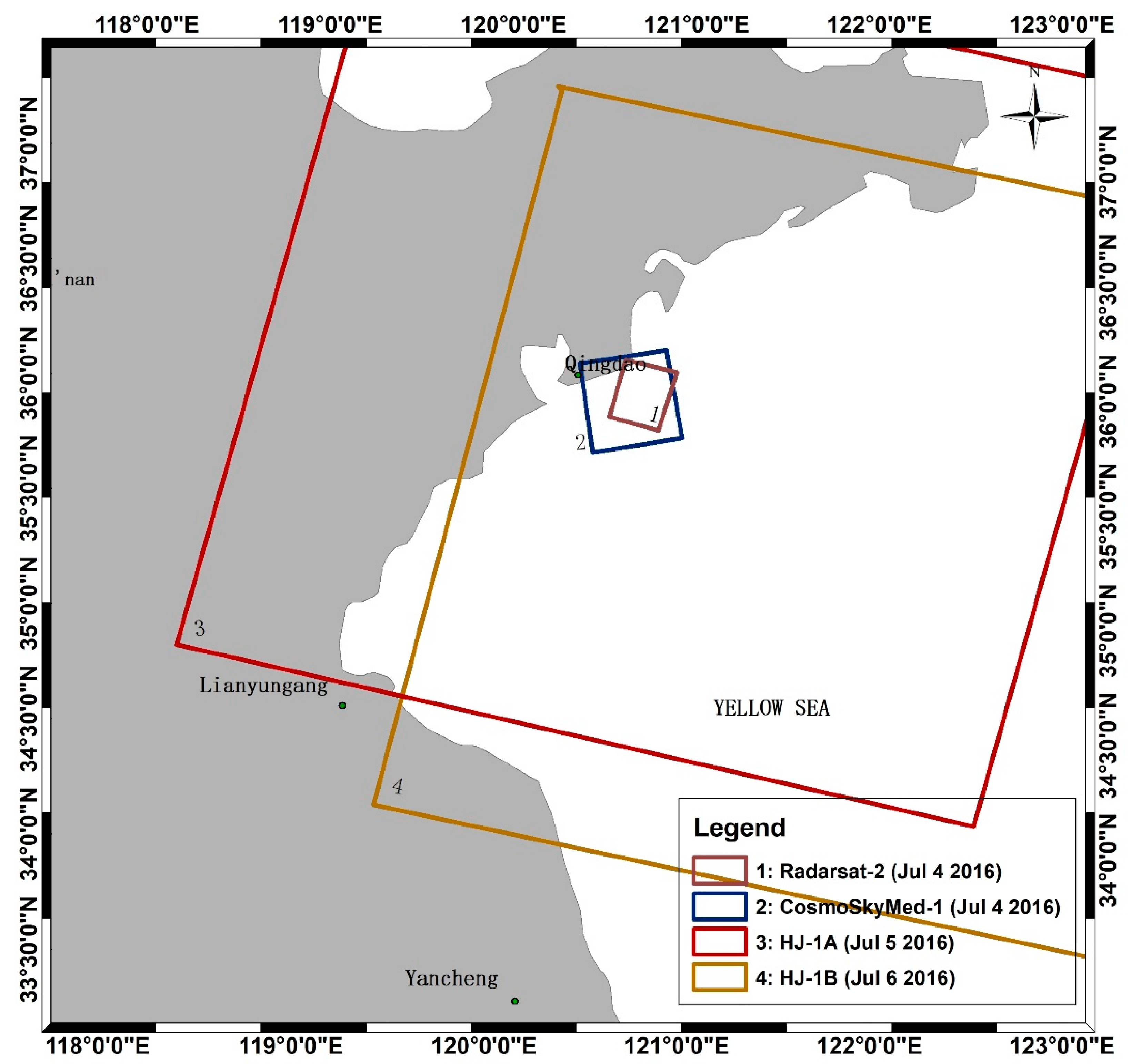
2.2. SAR Images
2.3. Optical Images
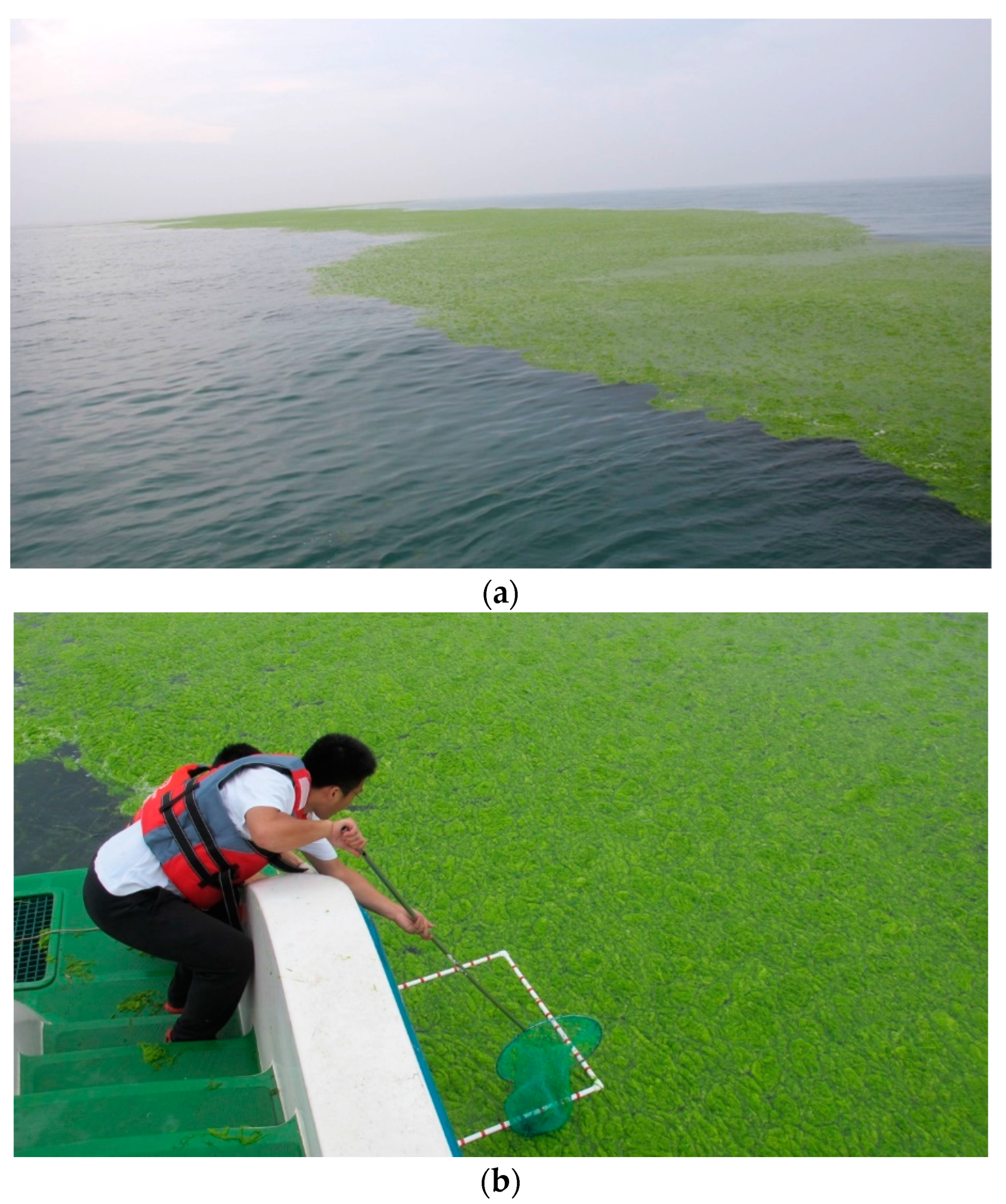
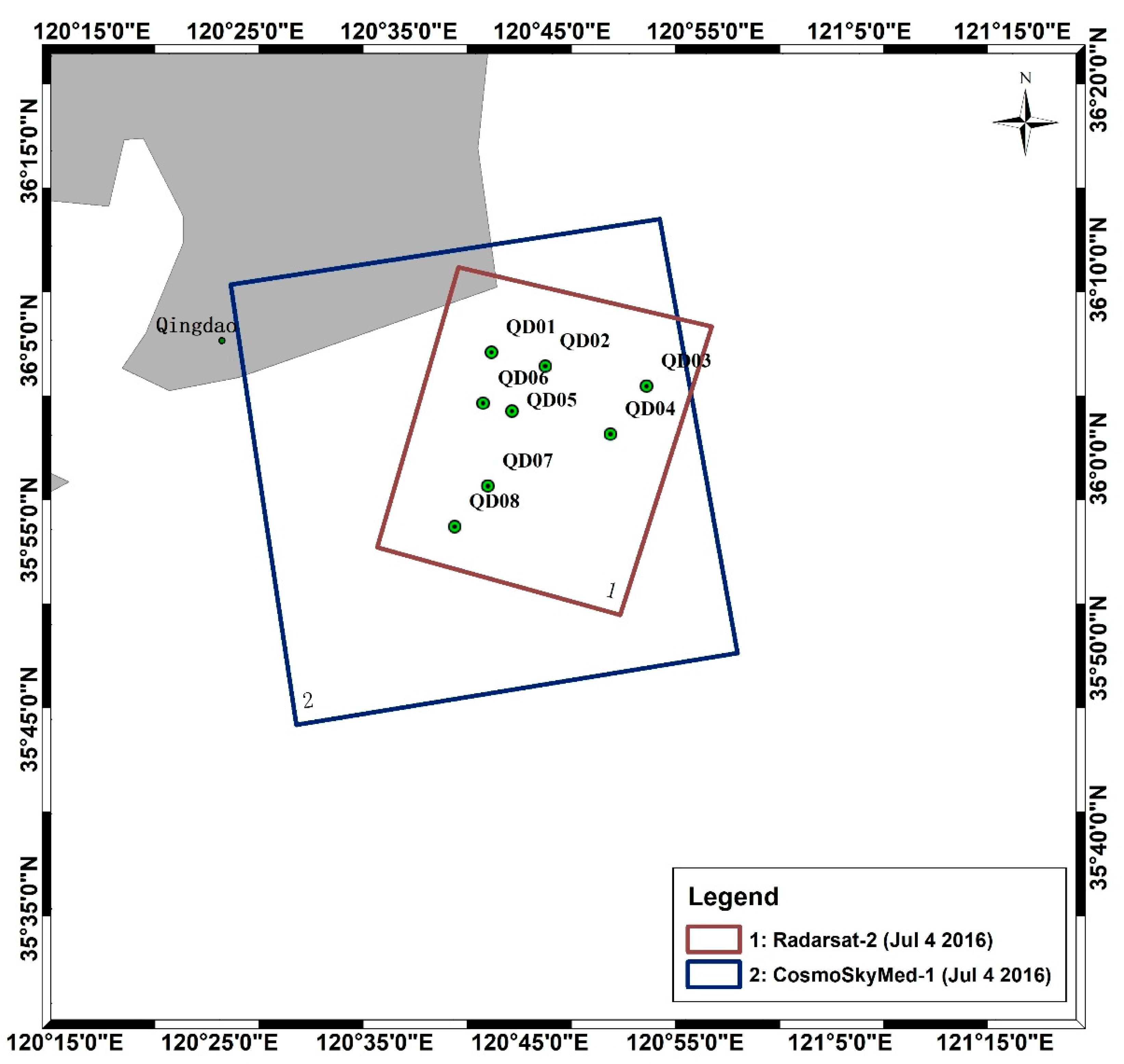
2.4. Synchronization Campaign Experiment
3. Experiment and Results
3.1. Tracing MABs by Diversified Time Series Images
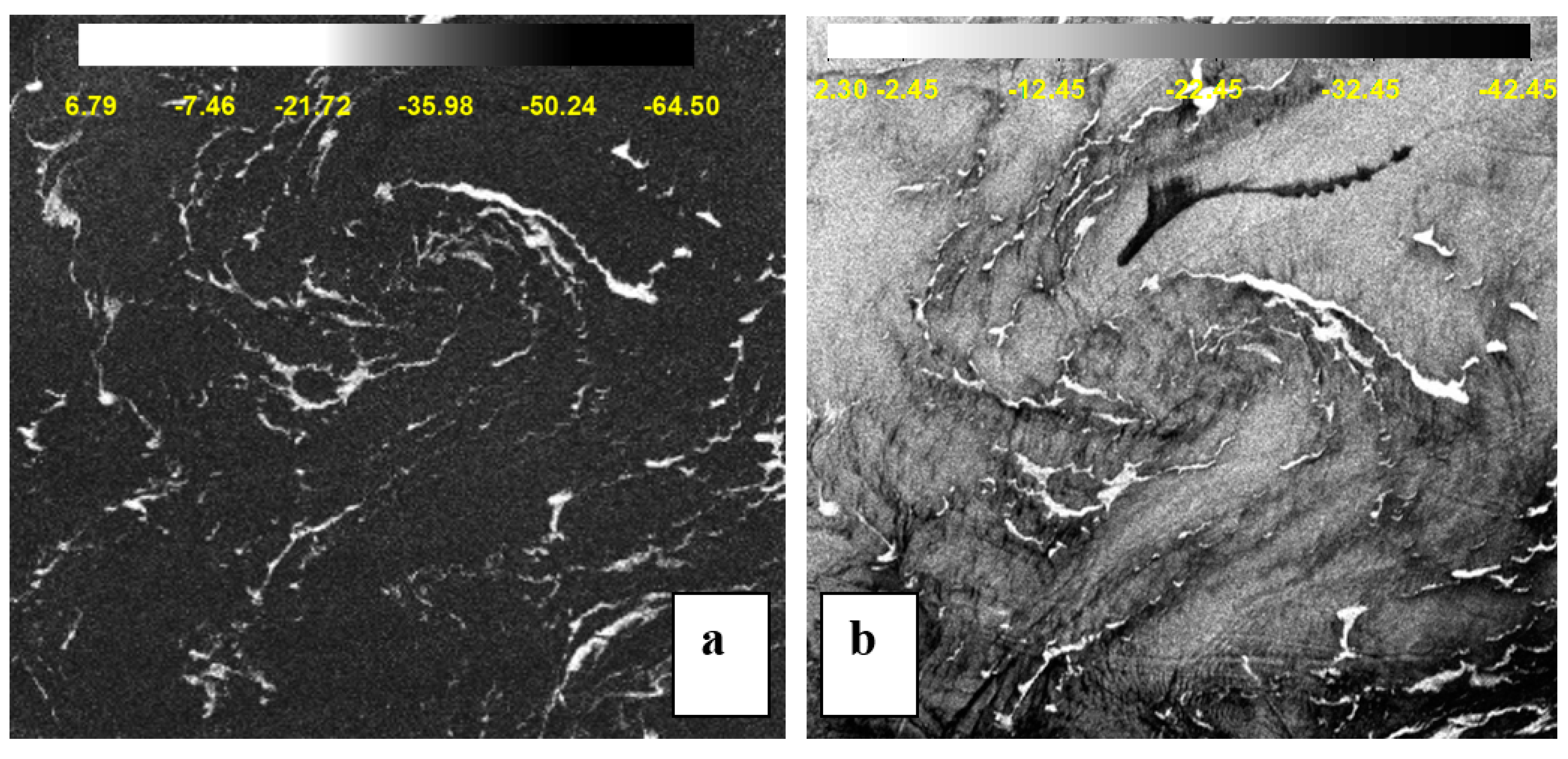
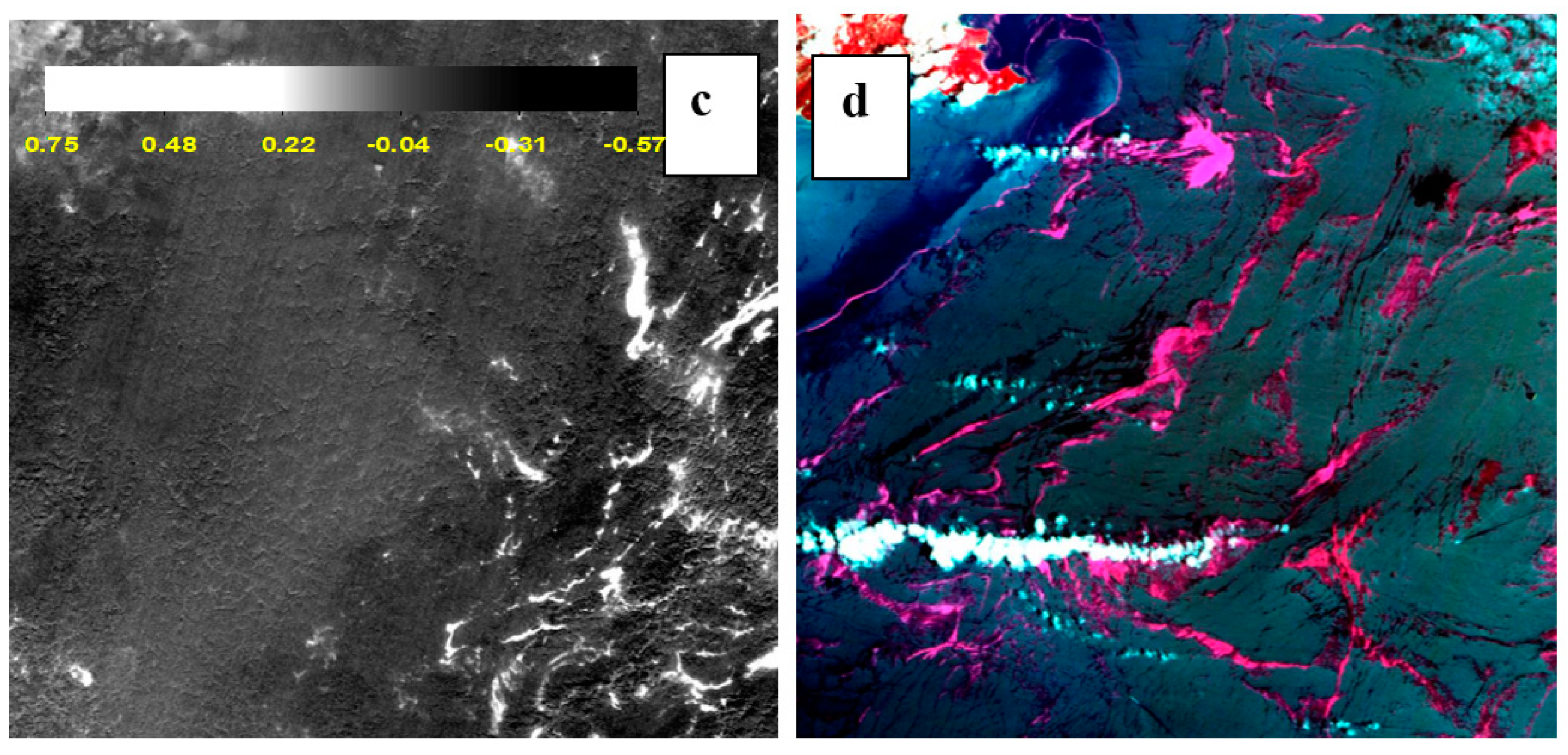
3.2. Features of Macroalgae versus Oil Spills in SAR Image
3.3. Floating Algae Index of Polarimetric SAR
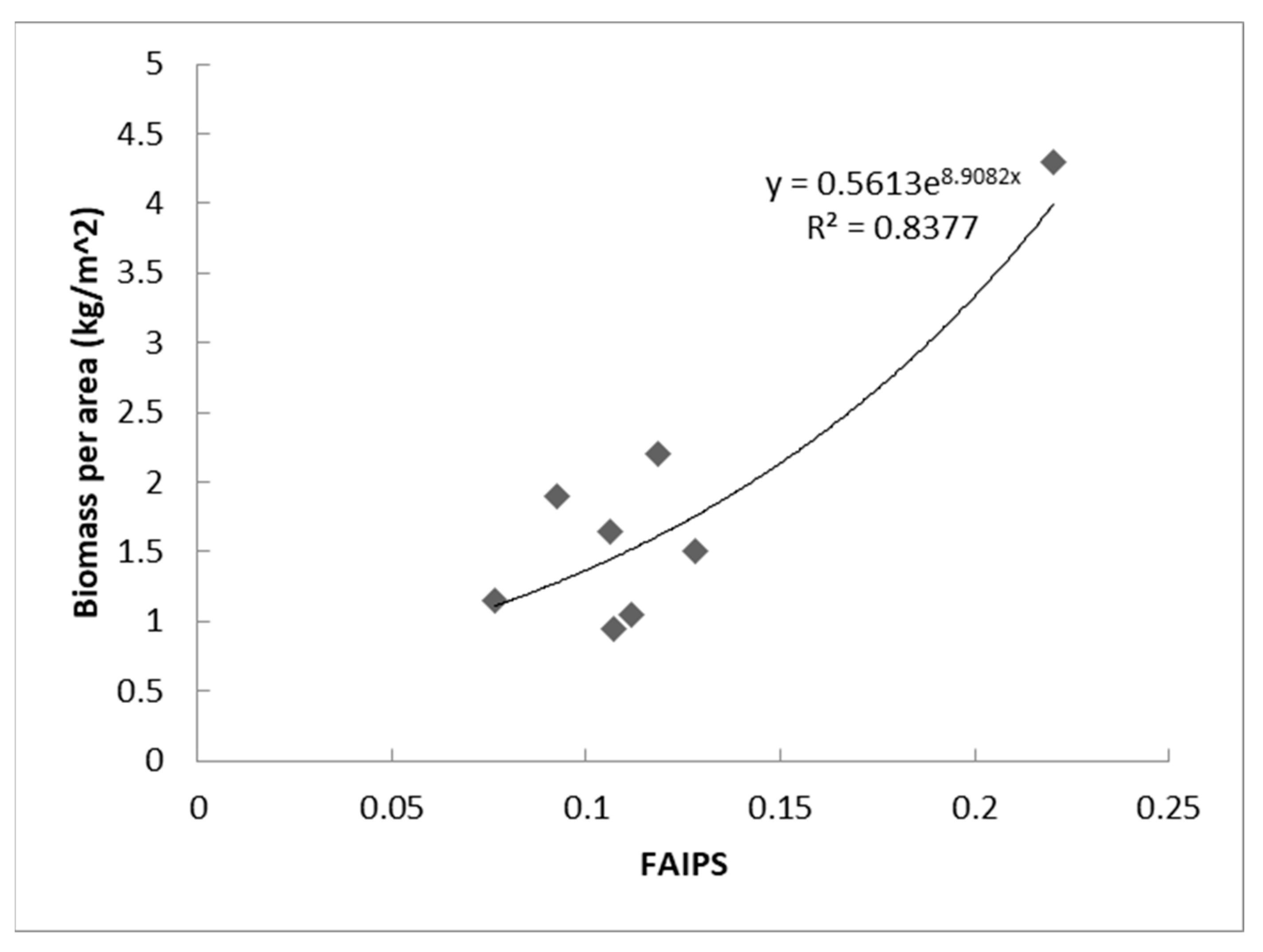
3.4. Floating Algae Biomass Evaluation Model
4. Discussions
4.1. Challenge of the Synchronization Experiment
4.2. Macroalgae Biomass Assessment by Means of Remote Sensing Images
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gade, M.; Rud, O.; Barale, V.; Snaith, H.M.; Jolly, G.W. Multisensor Studies of Oceanic Phaenomena in European Marginal Waters: Algae Blooms in the Baltic Sea and a River Plume in the Mediterranean. Eur. Space Agency 2000, 114, 1844–1855. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, R.A.; Fearns, P.; Keesing, J.K.; Liu, D. Quantification of Floating Macroalgae Blooms Using the Scaled Algae Index. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesing, J.K.; Liu, D.; Fearns, P.; Garcia, R. Inter- and Intra-Annual Patterns of Ulva Prolifera Green Tides in the Yellow Sea during 2007–2009, Their Origin and Relationship to the Expansion of Coastal Seaweed Aquaculture in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1169–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, Y.; Qi, X.; Tian, W.; Wen, B. Natural Marine Oil Seepage Detection and Evaluation with SAR. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Digital Earth: Data Processing and Applications, Beijing, China, 9–12 September 2009; Volume 7841, p. 78411L. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Keesing, J.K.; Dong, Z.; Zhen, Y.; Di, B.; Shi, Y.; Fearns, P.; Shi, P. Recurrence of the World’s Largest Green-Tide in 2009 in Yellow Sea, China: Porphyra Yezoensis Aquaculture Rafts Confirmed as Nursery for Macroalgal Blooms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Green Macroalgae Blooms in the Yellow Sea during the Spring and Summer of 2008. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2009, 114, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.H.; Wang, M.; Shon, J.K. Satellite Observations of Optical and Biological Properties in the Korean Dump Site of the Yellow Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Hu, C. Mapping Macroalgal Blooms in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea Using HJ-1 and Landsat Data: Application of a Virtual Baseline Reflectance Height Technique. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Ju, L.; Chen, M. Interannual Variability of Ulva Prolifera Blooms in the Yellow Sea. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 4099–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetacek, V.; Zingone, A. Green and Golden Seaweed Tides on the Rise. Nature 2013, 504, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Fan, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, D. Who Made the World’s Largest Green Tide in China?—An Integrated Study on the Initiation and Early Development of the Green Tide in Yellow Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Fu, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Song, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, G.; Shi, X.; Wang, X.; Zhu, M. Temporal Variation of Green Macroalgal Assemblage on Porphyra Aquaculture Rafts in the Subei Shoal, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.W.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.E.; Jia, Y.J.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Z.L.; Meng, J.M. Satellite Monitoring of Massive Green Macroalgae Bloom (GMB): Imaging Ability Comparison of Multi-Source Data and Drifting Velocity Estimation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 5513–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Keesing, J.K.; He, P.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y. The World’s Largest Macroalgal Bloom in the Yellow Sea, China: Formation and Implications. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 129, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, D.A.; Arvanitidis, C.; Blight, A.J.; Chatzinikolaou, E.; Guy-Haim, T.; Kotta, J.; Orav-Kotta, H.; Queirós, A.M.; Rilov, G.; Somerfield, P.J.; et al. Macroalgal Blooms Alter Community Structure and Primary Productivity in Marine Ecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2712–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Tosi, L.; Braga, F.; Gao, X.; Gao, M. Interpreting the Progressive Eutrophication behind the World’s Largest Macroalgal Blooms with Water Quality and Ocean Color Data. Nat. Hazards 2015, 78, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Hu, C.; Tang, D.; Tian, L.; Tang, S.; Wang, X.H.; Lou, M.; Gao, X. World’s Largest Macroalgal Blooms Altered Phytoplankton Biomass in Summer in the Yellow Sea: Satellite Observations. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12297–12313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Wu, L.; Tian, L.; Cui, T.; Li, L.; Kong, F.; Gao, X.; Wu, M. Remote Sensing of Early-Stage Green Tide in the Yellow Sea for Floating-Macroalgae Collecting Campaign. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huo, Y.; Wu, H.; Yu, K.; Kim, J.K.; Yarish, C.; Qin, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, R.; He, P. The Origin of the Ulva Macroalgal Blooms in the Yellow Sea in 2013. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 89, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Liu, Y.; Sun, C.; Wei, X.; Li, H.; Han, Z. A Study of the Environmental Factors Influencing the Growth Phases of Ulva Prolifera in the Southern Yellow Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.h.; Zhang, X.w.; Mao, Y.z.; Liang, C.w.; Xu, D.; Zou, J.; Zhuang, Z.m.; Wang, Q.y. “Green Tides” Are Overwhelming the Coastline of Our Blue Planet: Taking the World’s Largest Example. Ecol. Res. 2011, 26, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Keesing, J.K.; Xing, Q.; Shi, P. World’s Largest Macroalgal Bloom Caused by Expansion of Seaweed Aquaculture in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, X. Cruise Observation of Ulva Prolifera Bloom in the Southern Yellow Sea, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Pang, S.; Chopin, T.; Gao, S.; Shan, T.; Zhao, X.; Li, J. Understanding the Recurrent Large-Scale Green Tide in the Yellow Sea: Temporal and Spatial Correlations between Multiple Geographical, Aquacultural and Biological Factors. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 83, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.B.; Choi, B.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, Y.G. Tracing Floating Green Algae Blooms in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea Using GOCI Satellite Data and Lagrangian Transport Simulations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Qi, M.; Tang, H.; Han, X. Spatial and Temporal Nutrient Variations in the Yellow Sea and Their Effects on Ulva Prolifera Blooms. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Peng, K.; Xiao, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Fu, M.; Fan, S.; Zhu, M.; Li, R. Effects of Temperature on the Germination of Green Algae Micro-Propagules in Coastal Waters of the Subei Shoal, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. New Techniques for Radar Target Scattering Signature Measurement and Processing, 1st ed.; National Defense Industry Press of China: Beijing, China, 2017; ISBN 987-7-118-11418-8. [Google Scholar]
- Hedley, J.; Russell, B.; Randolph, K.; Dierssen, H. A Physics-Based Method for the Remote Sensing of Seagrasses. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 174, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Pang, I.C.; Moon, I.J.; Ryu, J.H. On Physical Factors That Controlled the Massive Green Tide Occurrence along the Southern Coast of the Shandong Peninsula in 2008: A Numerical Study Using a Particle-Tracking Experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, 116, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.J.; Liu, F.; Shan, T.F.; Xu, N.; Zhang, Z.H.; Gao, S.Q.; Chopin, T.; Sun, S. Tracking the Algal Origin of the Ulva Bloom in the Yellow Sea by a Combination of Molecular, Morphological and Physiological Analyses. Mar. Environ. Res. 2010, 69, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelfsema, C.M.; Lyons, M.; Kovacs, E.M.; Maxwell, P.; Saunders, M.I.; Samper-Villarreal, J.; Phinn, S.R. Multi-Temporal Mapping of Seagrass Cover, Species and Biomass: A Semi-Automated Object Based Image Analysis Approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 150, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Guan, W.; Yang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Chen, Q. Drifting Trajectories of Green Algae in the Western Yellow Sea during the Spring and Summer of 2012. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Gao, Z.; Jiang, X.; Shang, W.; Ning, J.; Song, D.; Ai, J. A UAV and S2A Data-Based Estimation of the Initial Biomass of Green Algae in the South Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 128, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z. A New Assessment of the Algal Biomass of Green Tide in the Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 174, 113253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisco, B.; Li, K.; Tedford, B.; Charbonneau, F.; Yun, S.; Murnaghan, K. Compact Polarimetry Assessment for Rice and Wetland Mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 1949–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Li, X.; Pichel, W.G.; Muller-Karger, F.E. Detection of Natural Oil Slicks in the NW Gulf of Mexico Using MODIS Imagery. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L01604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. The First Sentinel-1 SAR Image of a Typhoon. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2015, 34, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, H. Remote Sensing of the China Seas. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 3919–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Fan, X.; Liu, H.; Xiao, J.; Ross, S.; Brisco, B.; Brown, R.; Staples, G. Rice Monitoring and Production Estimation Using Multitemporal RADARSAT. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunziata, F.; Migliaccio, M.; Li, X. Sea Oil Slick Observation Using Hybrid-Polarity SAR Architecture. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2015, 40, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Bian, X.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, Z. On the Detection of Oil Spill with China’s HJ-1C SAR Image. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 3, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Shao, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y. An Experiment for Oil Spill Recognition Using RADARSAT-2 Image. Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. Symp. 2010, 2761–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Perrie, W.; Li, X.; Pichel, W.G. Mapping Sea Surface Oil Slicks Using RADARSAT-2 Quad-Polarization SAR Image. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L10602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, A.; Rahman, A.F.; Warren, M.W.; Robeson, S.M. Mapping Spatial Distribution and Biomass of Coastal Wetland Vegetation in Indonesian Papua by Combining Active and Passive Remotely Sensed Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 183, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Li, D.; Chen, C.; Ge, J.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Liu, J.; Yu, F.; He, M.X. On the Recurrent Ulva Prolifera Blooms in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2010, 115, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Li, X.; Kong, F.; Yu, R.; Guo, Y.; Ren, Y. AlgaeNet: A Deep-Learning Framework to Detect Floating Green Algae From Optical and SAR Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 2782–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Perrie, W.; Liu, Q.; He, Y. Detection of Macroalgae Blooms by Complex SAR Imagery. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 78, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, M.S.; Alonso, L.; Moreno, J.F.; Cendrero Mateo, M.P.; de la Cruz, D.F.; Montoro, A. A RADARSAT-2 Quad-Polarized Time Series for Monitoring Crop and Soil Conditions in Barrax, Spain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1057–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Brisco, B.; Yun, S.; Touzi, R. Polarimetric Decomposition with RADARSAT-2 for Rice Mapping and Monitoring. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 38, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Ding, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Xu, M. Ocean Oil Spill Classification with RADARSAT-2 SAR Based on an Optimized Wavelet Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shao, Y.; Tian, W.; Bian, X. An Investigation into the Capability of Compact Polarized SAR to Classify Multi-Sea-Surface Characteristics. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 44, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, P.; Liu, X.; Tan, W.; Fu, W.; Li, C. A Hybrid Polarimetric Target Decomposition Algorithm with Adaptive Volume Scattering Model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Wang, X.S.; Sato, M. Uniform Polarimetric Matrix Rotation Theory and Its Applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 4756–4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W. Polarimetric Coherence Pattern: A Visualization and Characterization Tool for Pol SAR Data Investigation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.D.; Xiao, S.P.; Chen, S.W. Three-Dimension Polarimetric Correlation Pattern Interpretation Tool and Its Application. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buono, A.; Nunziata, F.; Migliaccio, M. Analysis of Full and Compact Polarimetric SAR Features over the Sea Surface. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1527–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zheng, W.; Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Pichel, W.G. Sea Surface Imprints of Coastal Mountain Lee Waves Imaged by Synthetic Aperture Radar. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, 116, C02014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.M.; Li, X.M.; Velotto, D.; Chen, K.S. Study of the Polarimetric Characteristics of Mud Flats in an Intertidal Zone Using C- and X-Band Spaceborne SAR Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 176, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, M.; Alpers, W.; Melsheimer, C.; Tanck, G. Classification of Sediments on Exposed Tidal Flats in the German Bight Using Multi-Frequency Radar Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1603–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Wal, D.; Herman, P.M.J. Regression-Based Synergy of Optical, Shortwave Infrared and Microwave Remote Sensing for Monitoring the Grain-Size of Intertidal Sediments. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 111, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Jackson, T.; Bindlish, R.; Lee, H.; Hong, S. Radar Vegetation Index for Estimating the Vegetation Water Content of Rice and Soybean. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Sui, Y. Automatic Extraction of Green Tide From GF-3 SAR Images Based on Feature Selection And. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 10598–10613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Wang, M.; Hu, C.; Holt, B. Remote Sensing of Environment on the Capacity of Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar in Detecting Floating Macroalgae and Other Floating Matters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 280, 113188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C. A Novel Ocean Color Index to Detect Floating Algae in the Global Oceans. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2118–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yun, S.; Wuyi, Y.; Xiaoping, Q.; Wei, T.; Shi’ang, W.; Junna, Y. Expression of Hydrocarbon on Sea Surface and Its Remote Sensing Detection: Taking the South China Sea Area as an Example. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2011, 38, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Sun, J.; Liu, Q.; Lian, Z.; Ren, J.S.; Bai, T.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Z. A Numerical Study of the Ulva Prolifera Biomass during the Green Tides in China—Toward a Cleaner Porphyra Mariculture. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 161, 111805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim Reanalysis: Configuration and Performance of the Data Assimilation System. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Shao, Y.; Tian, W.; Gong, H. Microwave Remote Sensing for Marine Monitoring: An Example of Enteromorpha Prolifera Bloom Monitoring. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 4530–4533. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-S.; Pottier, E. Polarimetric Radar Imaging; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. An Entropy Based Classification Scheme for Land Applications of Polarimetric SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zyl, J.J.; Zebker, H.A.; Elachi, C. Imaging Radar Polarization Signatures: Theory and Observation. Radio Sci. 1987, 22, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNairn, H.; Duguay, C.; Brisco, B.; Pultz, T. The Effect of Soil and Crop Residue Characteristics on Polarimetric Radar Response. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Long, D.G. Microwave Radar and Radiometric Sensing; The University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-0-472-11935-6. [Google Scholar]
- Raney, R.K. Hybrid Dual-Polarization Synthetic Aperture Radar. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, E.; Dabboor, M.; Pettinato, S.; Paloscia, S. Combining Machine Learning and Compact Polarimetry for Estimating Soil Moisture from C-Band SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shao, Y.; Tian, W.; Li, K. On the Classification of Mixed Floating Pollutants on the Yellow Sea of China by Using a Quad-Polarized SAR Image. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 12, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Hu, C.; Ming-Xia, H.E. Remote Estimation of Biomass of Ulva Prolifera Macroalgae in the Yellow Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cui, T.; Gong, J.; Liu, R.; Chen, X.; Liang, X. Remote Sensing Estimation of the Biomass of Floating Ulva Prolifera and Analysis of the Main Factors Driving the Interannual Variability of the Biomass in the Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J. Romote Sensing Estimation of the Green Tide Biomass in the Yellow Sea; Ocean University of China: Qingdao, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]

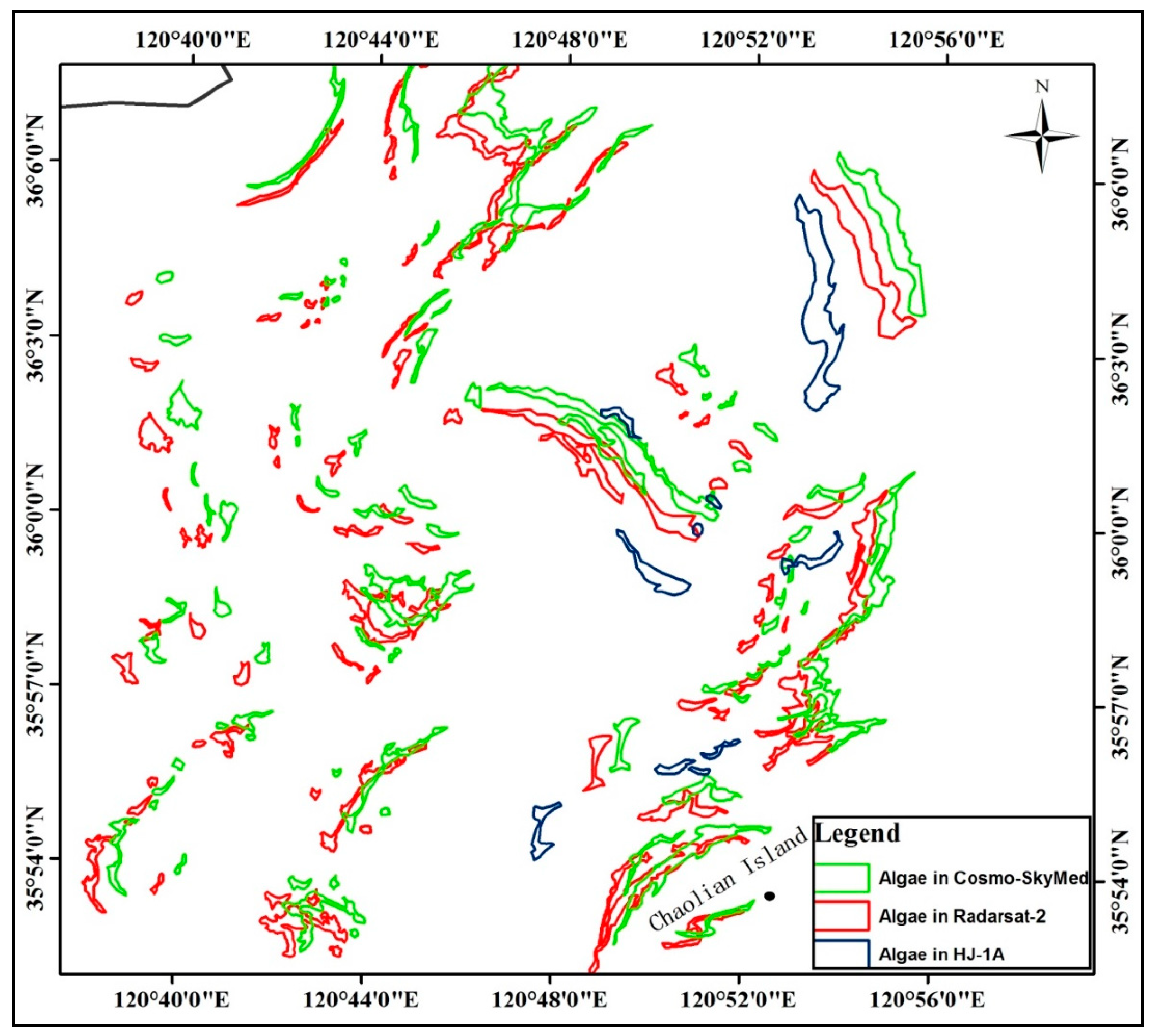
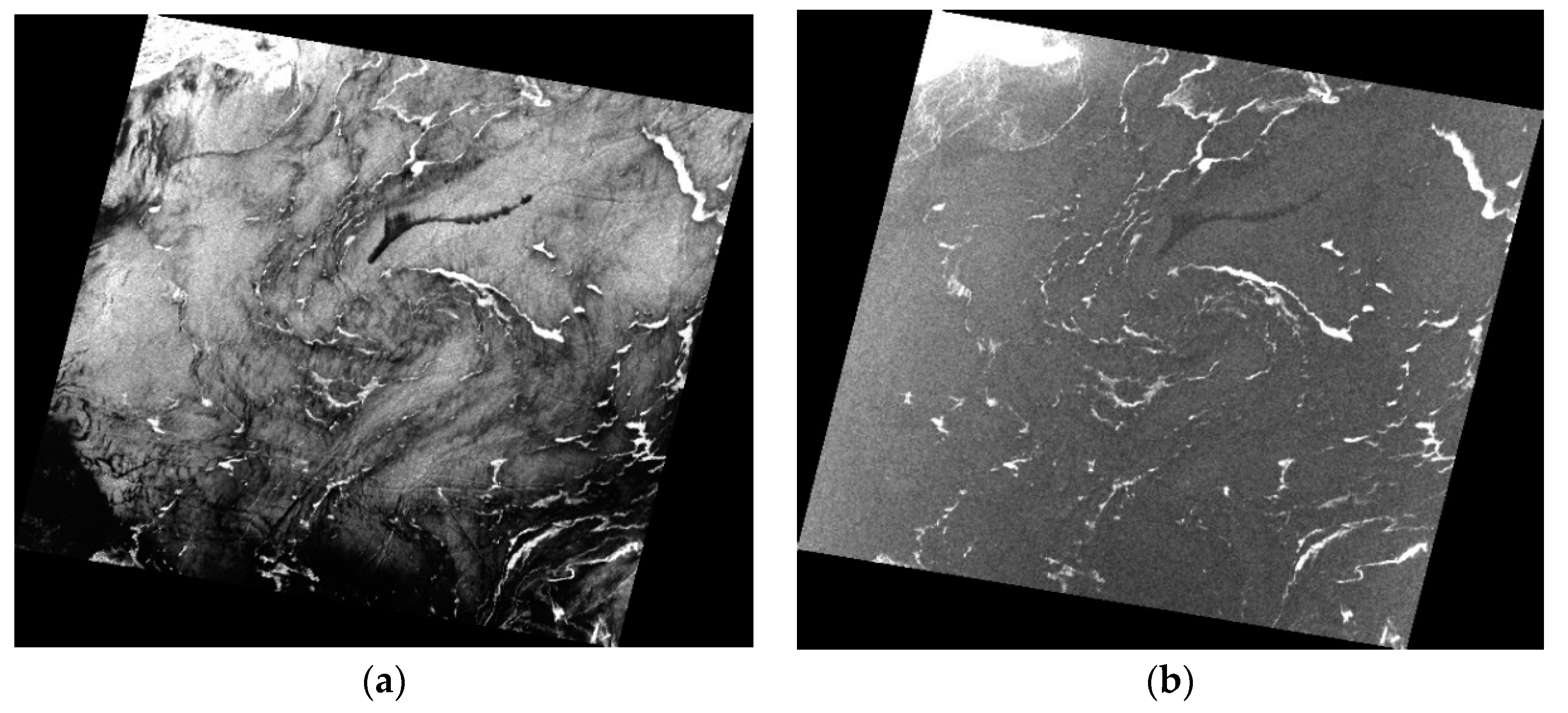
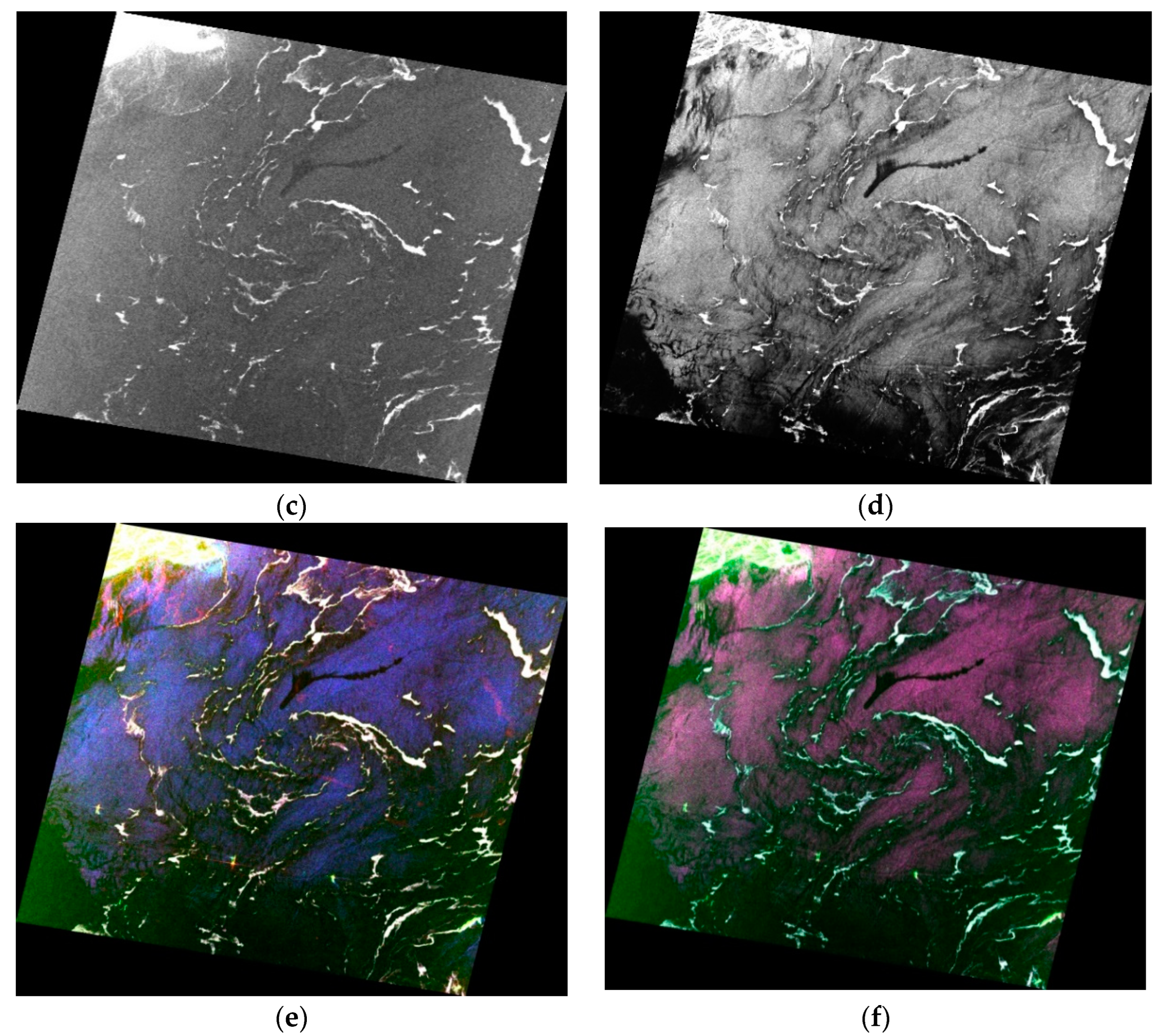
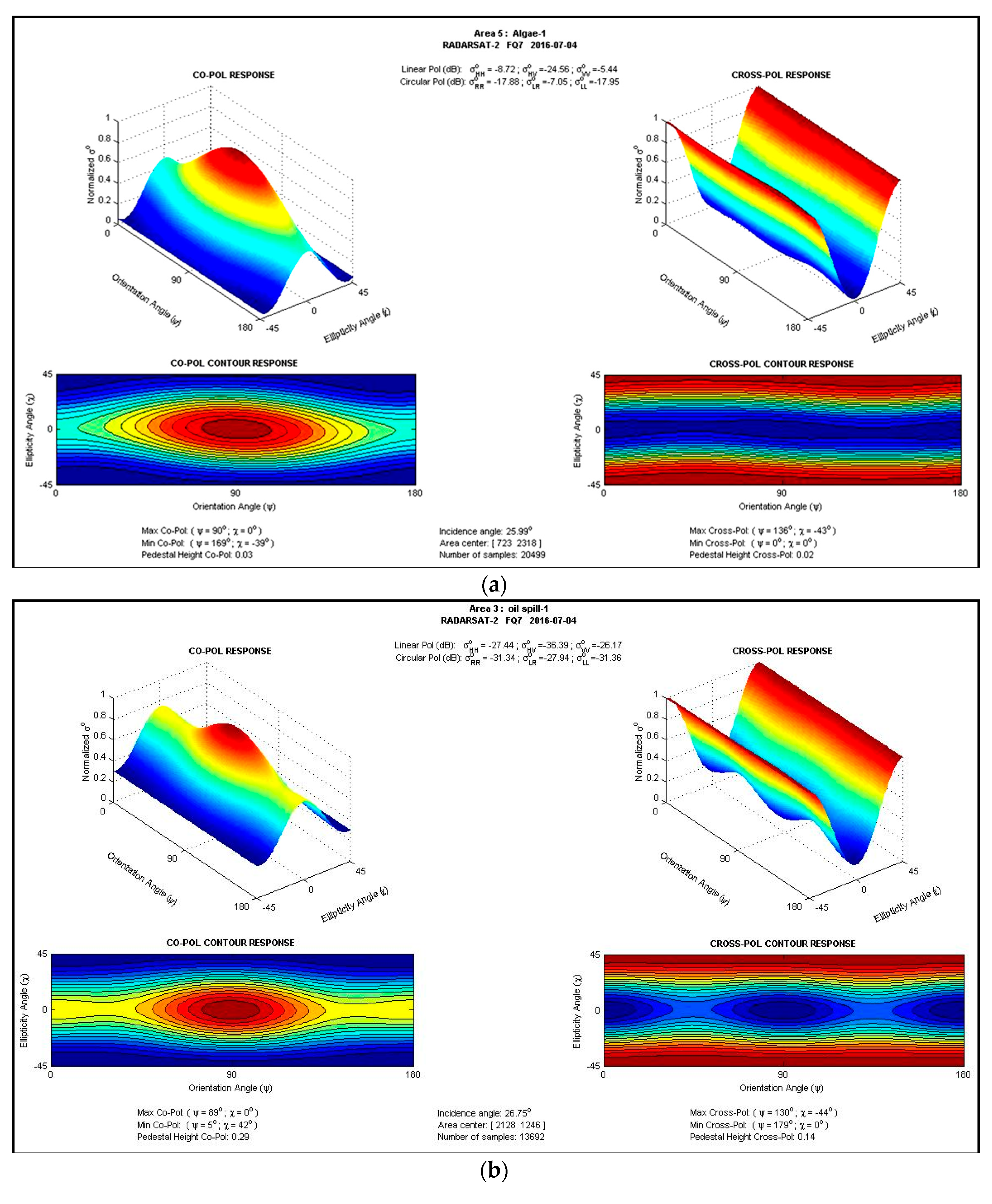
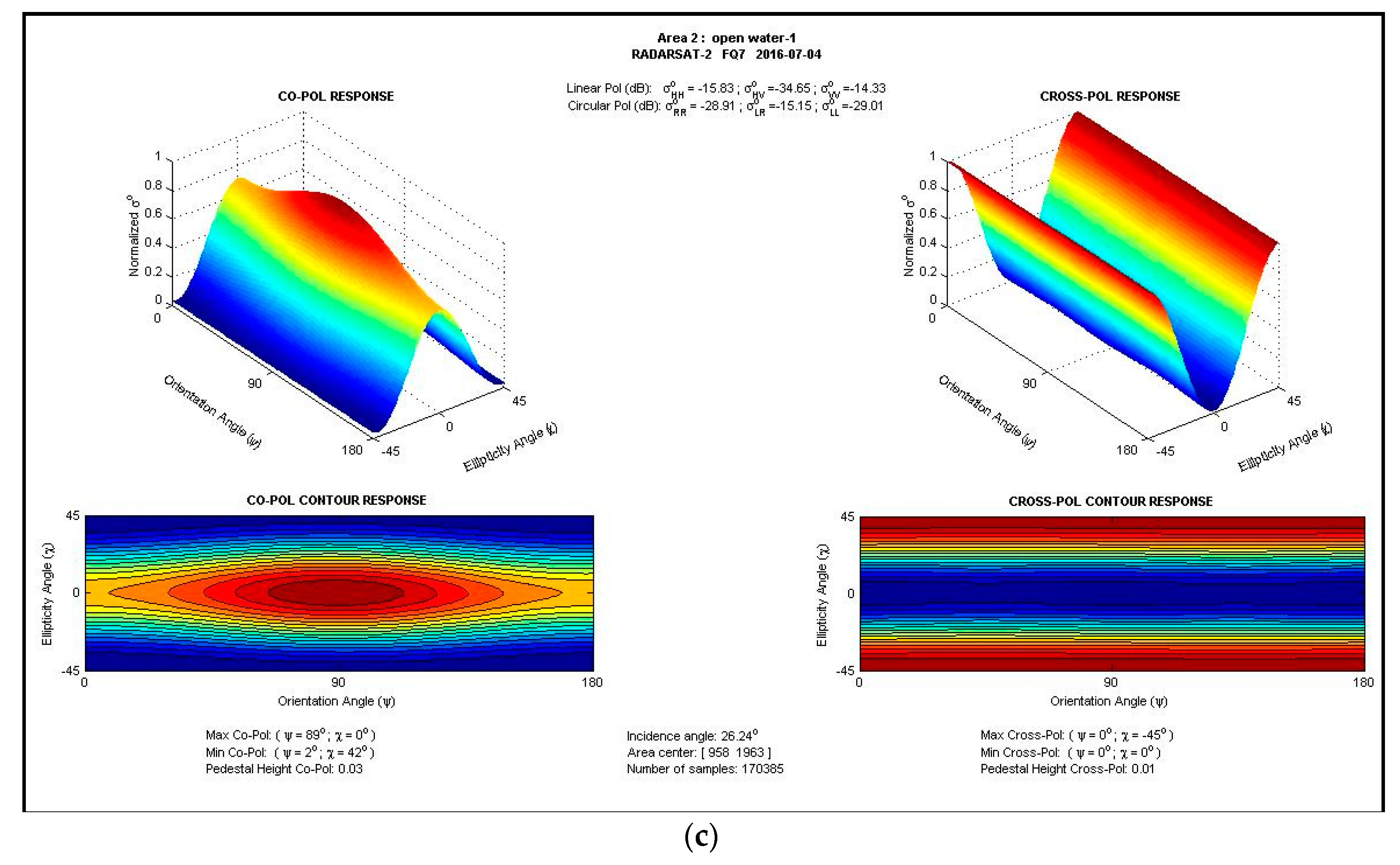
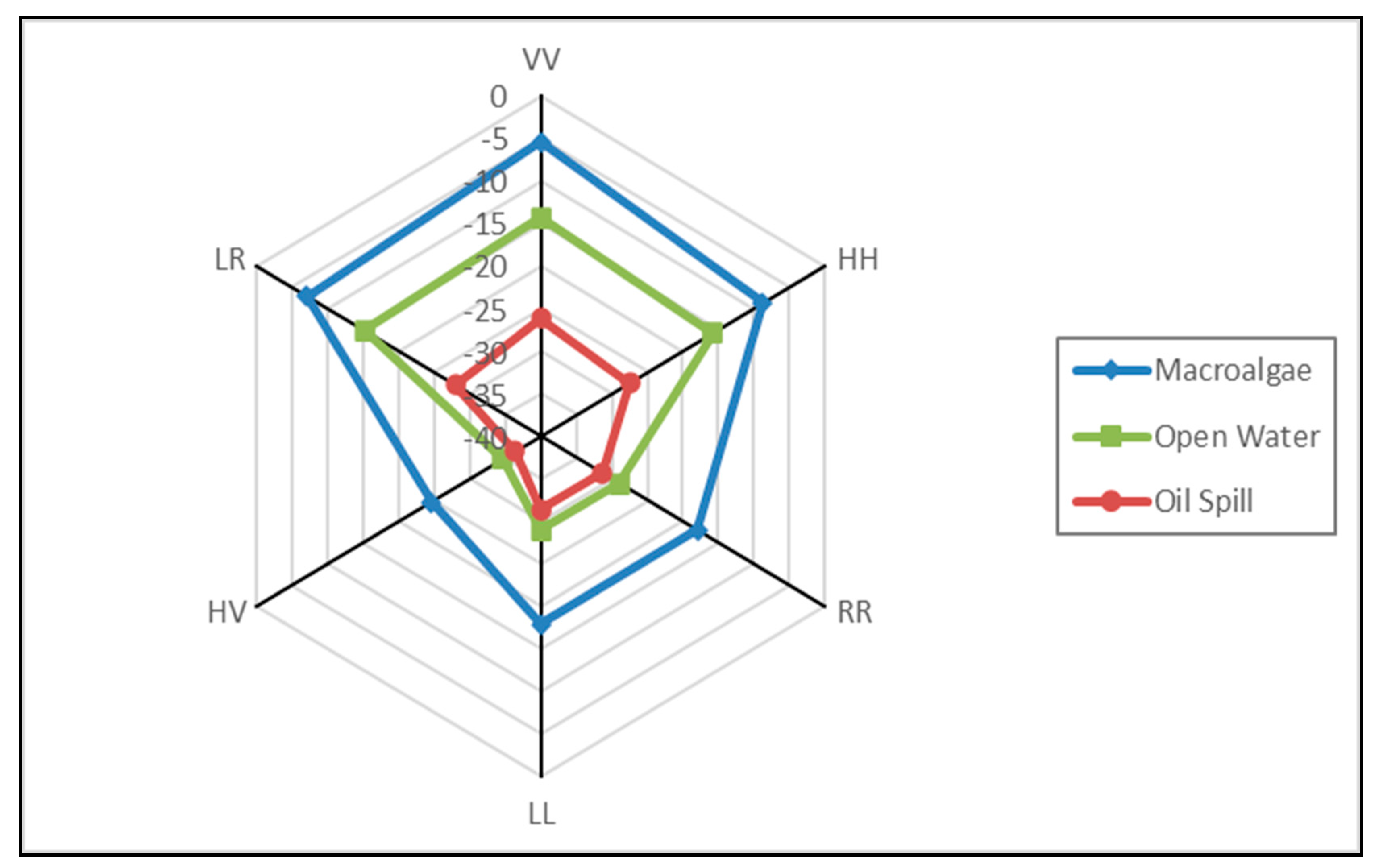
| Image Acquiring Time | Satellite Platform (Sensor) | Wave Band | Polarization (for SAR Image Only) | Spatial Resolution (m) | Swath (km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 July 2016 21:46:04 UTC | Cosmo-SkyMed-1 (SAR) | X | HH/VV | 15 | 45 |
| 4 July 2016 22:07:08 UTC | Radarsat-2 (SAR) | C | HH/HV/VV/VH | 8 | 25 |
| 5 July 2016 02:20:54 UTC | HJ-1A (CCD) | Visible/Infrared | - | 30 | 400 |
| 6 July 2016 02:12:15 UTC | HJ-1B (CCD) | Visible/Infrared | - | 30 | 400 |
| Number of Sampling Station | Time of Sampling | Latitude (N) | Longitude (E) | Color of Sample | Genus Identified | Wet Biomass (kg/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QD01 | 4 July 2016 22:56:48UTC | 36°05′01.7″ | 120°41′32.2″ | Green-Yellow | Ulva prolifera | 2.2 |
| QD02 | 4 July 2016 23:12:27UTC | 36°04′22.0″ | 120°45′03.2″ | Green-Yellow | Ulva prolifera | 4.3 |
| QD03 | 4 July 2016 23:33:45UTC | 36°03′24.8″ | 120°51′40.1″ | Green-Yellow | Ulva prolifera | 1.9 |
| QD04 | 4 July 2016 23:49:55UTC | 36°00′50.4″ | 120°49′23.2″ | Green-Yellow | Ulva prolifera | 1.65 |
| QD05 | 5 July 2016 00:07:42UTC | 36°01′56.6″ | 120°42′57.1″ | Green-Yellow | Ulva prolifera | 0.95 |
| QD06 | 5 July 2016 00:19:04UTC | 36°02′19.5″ | 120°41′05.3″ | Green-Yellow | Ulva prolifera | 1.05 |
| QD07 | 5 July 2016 00:40:23UTC | 35°57′57.3″ | 120°41′31.2″ | Green-Yellow | Ulva prolifera | 1.15 |
| QD08 | 5 July 2016 00:53:45UTC | 35°55′46.0″ | 120°39′25.3″ | Green-Yellow | Ulva prolifera | 1.5 |
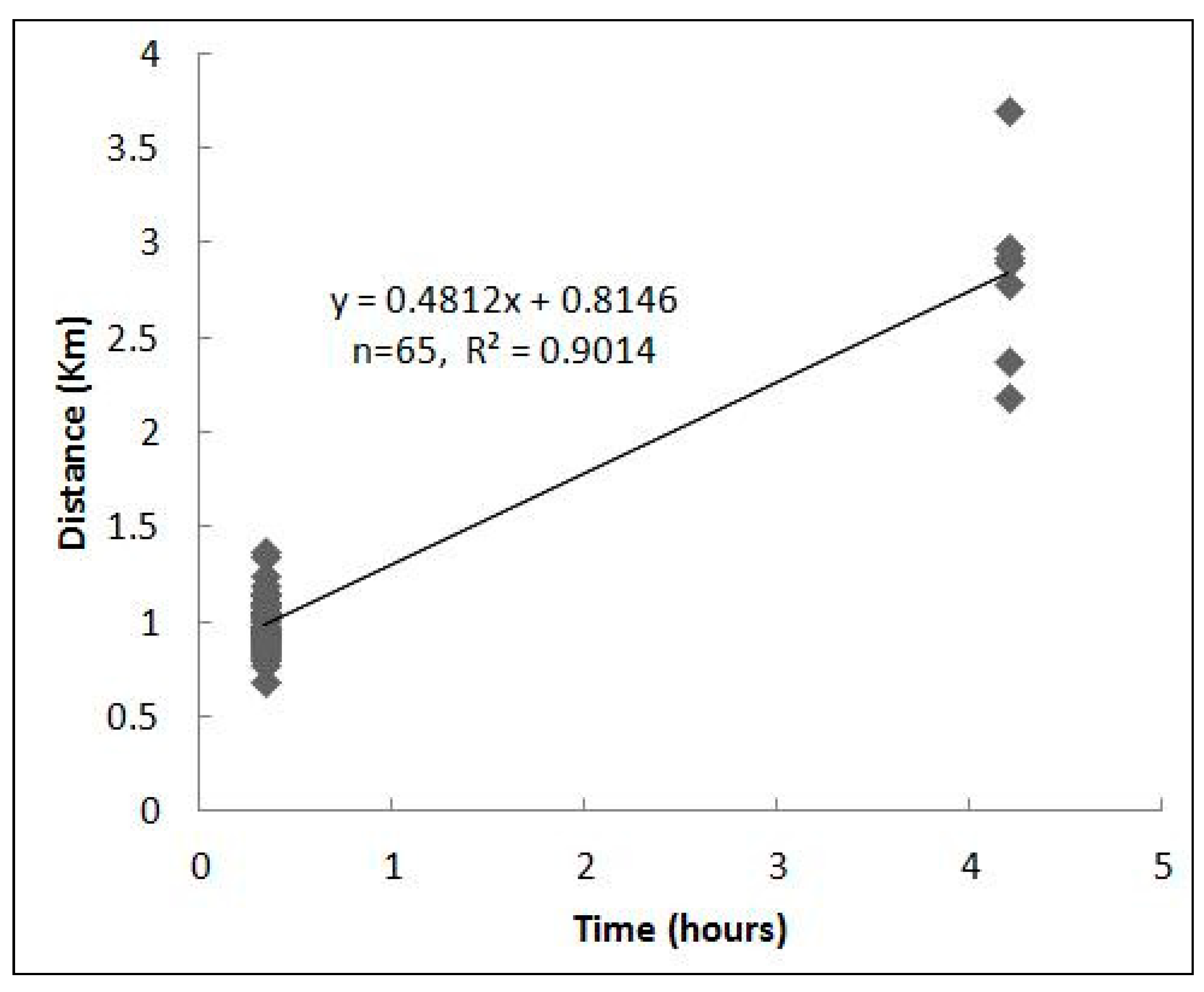
| Sample Station | Wet Biomass per Area (kg/m2) | Time Delay from Radarsat-2 Polarimetric SAR Image Acquisition Time to the Sample Time of the Station (min) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QD01 | 2.2 | 50 | 0.1960 | 0.0343 | 0.2789 | 0.1186 |
| QD02 | 4.3 | 65 | 0.2612 | 0.0435 | 0.3848 | 0.2201 |
| QD03 | 1.9 | 87 | 0.1714 | 0.0271 | 0.2484 | 0.0924 |
| QD04 | 1.65 | 103 | 0.1849 | 0.0310 | 0.2642 | 0.1060 |
| QD05 | 0.95 | 121 | 0.1861 | 0.0319 | 0.2656 | 0.1072 |
| QD06 | 1.05 | 132 | 0.1867 | 0.0301 | 0.2735 | 0.1115 |
| QD07 | 1.15 | 153 | 0.1574 | 0.0265 | 0.2240 | 0.0763 |
| QD08 | 1.5 | 167 | 0.2018 | 0.0344 | 0.2912 | 0.1279 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Yuan, J.; Mi, X.; Shao, Y. The Detection of Green Tide Biomass by Remote Sensing Images and In Situ Measurement in the Yellow Sea of China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3625. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143625
Tian W, Wang J, Zhang F, Liu X, Yang J, Yuan J, Mi X, Shao Y. The Detection of Green Tide Biomass by Remote Sensing Images and In Situ Measurement in the Yellow Sea of China. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(14):3625. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143625
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Wei, Juan Wang, Fengli Zhang, Xudong Liu, Jian Yang, Junna Yuan, Xiaofei Mi, and Yun Shao. 2023. "The Detection of Green Tide Biomass by Remote Sensing Images and In Situ Measurement in the Yellow Sea of China" Remote Sensing 15, no. 14: 3625. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143625
APA StyleTian, W., Wang, J., Zhang, F., Liu, X., Yang, J., Yuan, J., Mi, X., & Shao, Y. (2023). The Detection of Green Tide Biomass by Remote Sensing Images and In Situ Measurement in the Yellow Sea of China. Remote Sensing, 15(14), 3625. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143625








