Distribution of Grazing Paths and Their Influence on Mountain Vegetation in the Traditional Grazing Area of the Tien-Shan Mountains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
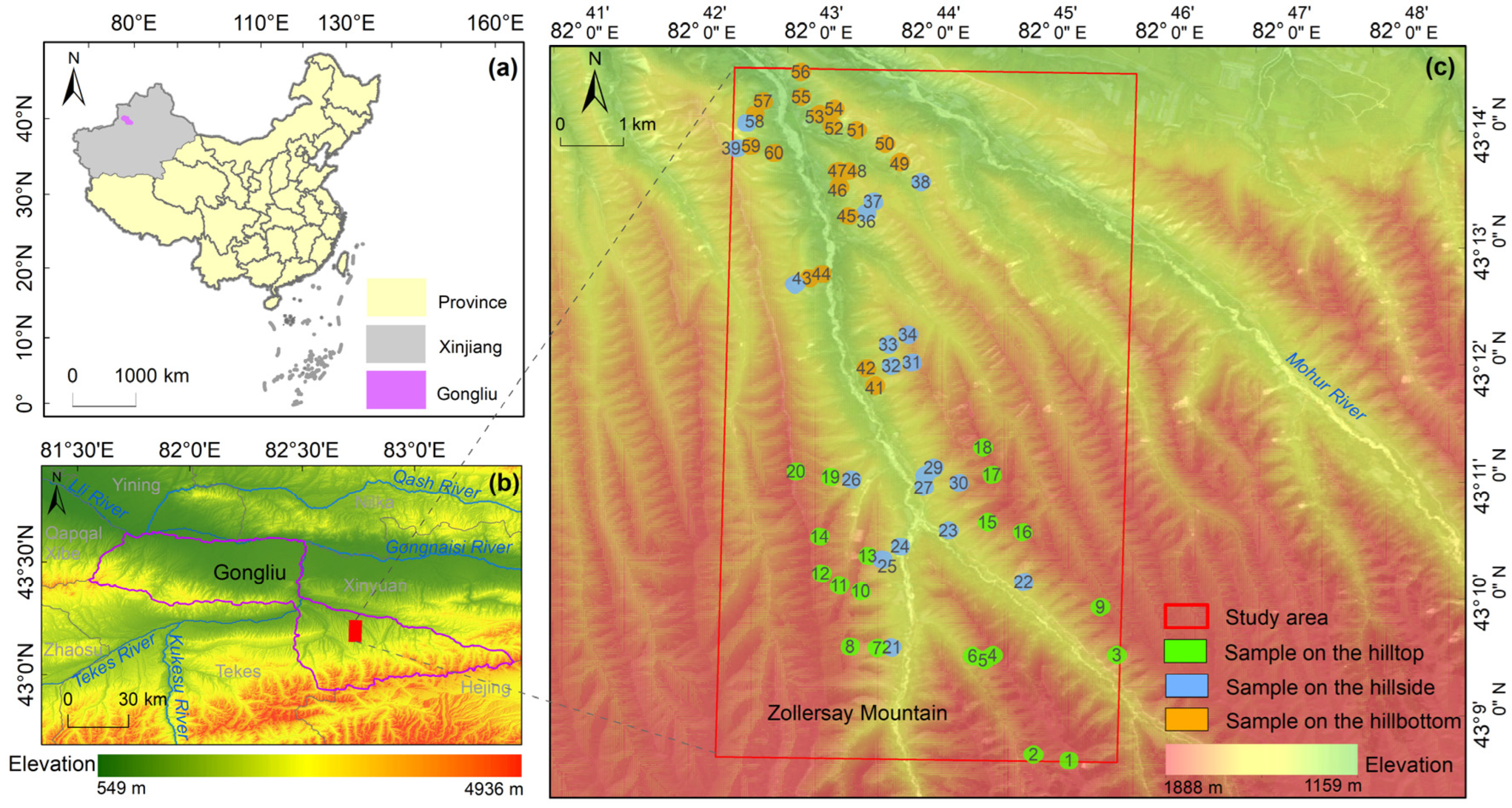
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Processing
2.2.1. Image Data
2.2.2. Sample Data
2.3. Study Method
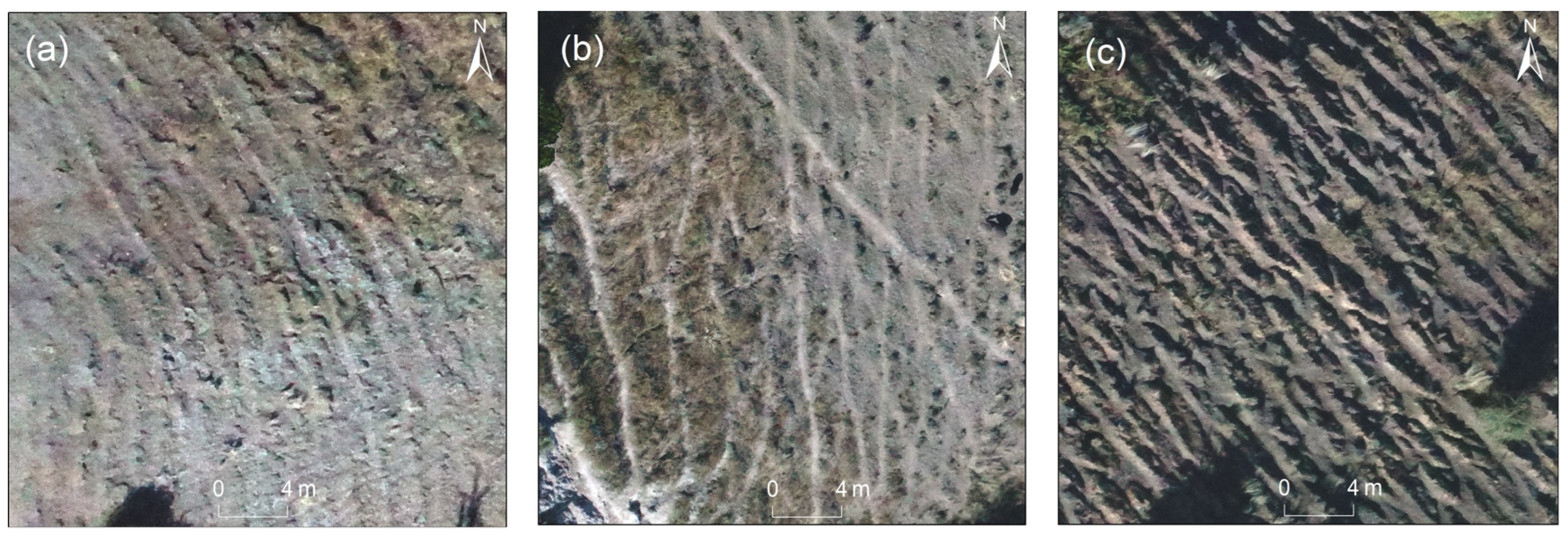
2.3.1. Extraction of the Grazing Path
2.3.2. Parameter Extraction of the Grazing Path
Amplitude of the Grazing Path
Tortuosity of the Grazing Path
Number of Plane Bends
Density of the Grazing Path
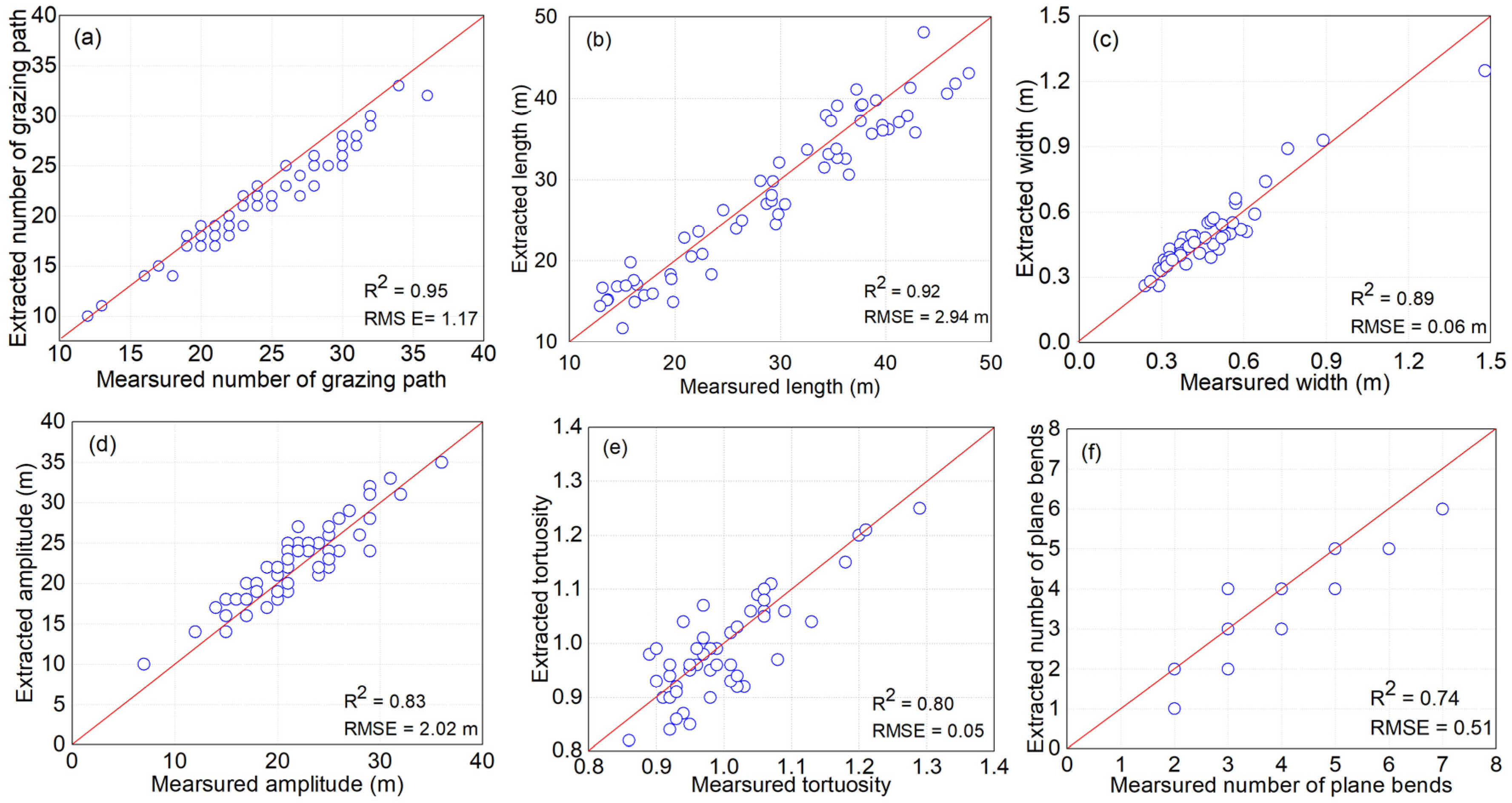
Accuracy Evaluation
2.3.3. Grassland Quality Characteristics
Grassland Quality Index (IGQ)
Grass Vegetation Coverage (GVC)
2.3.4. Correlation of Grazing Paths with Montane Vegetation
The Impact of the Grazing Path on Grassland
The Effect of the Grazing Path on the Malus sieversii Tree
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Grazing Path
3.1.1. Quantitative Characteristics of the Grazing Path
3.1.2. Morphological Characteristics of the Grazing Path
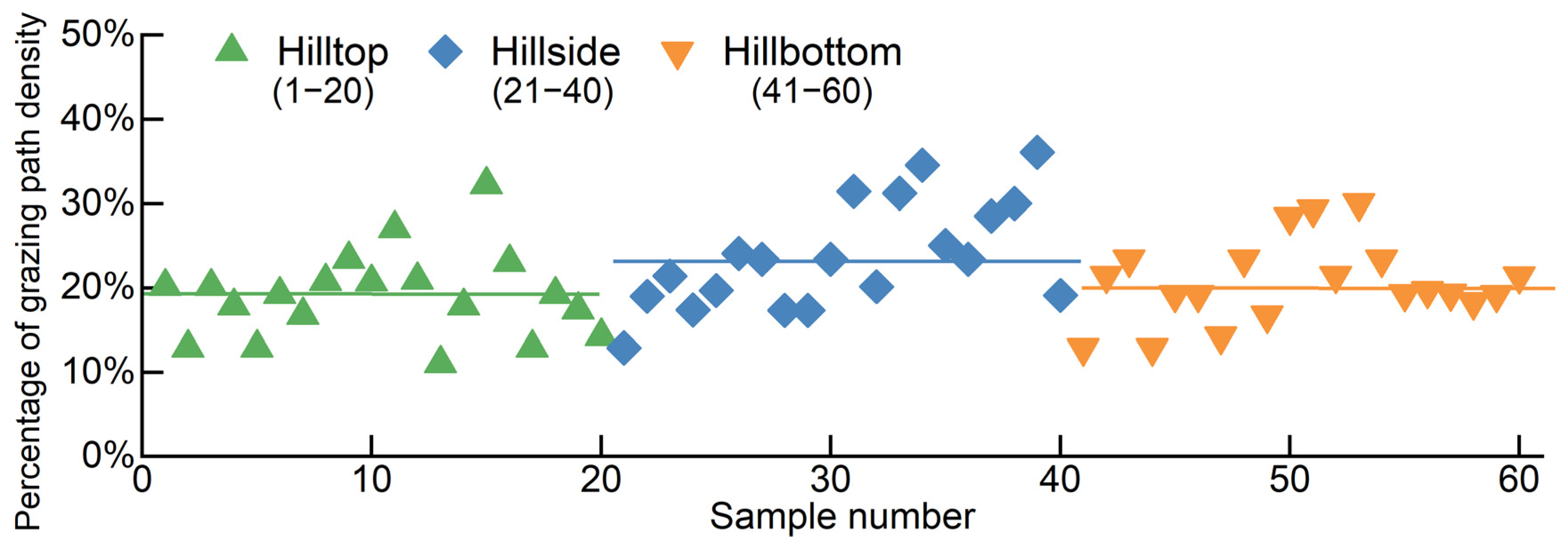
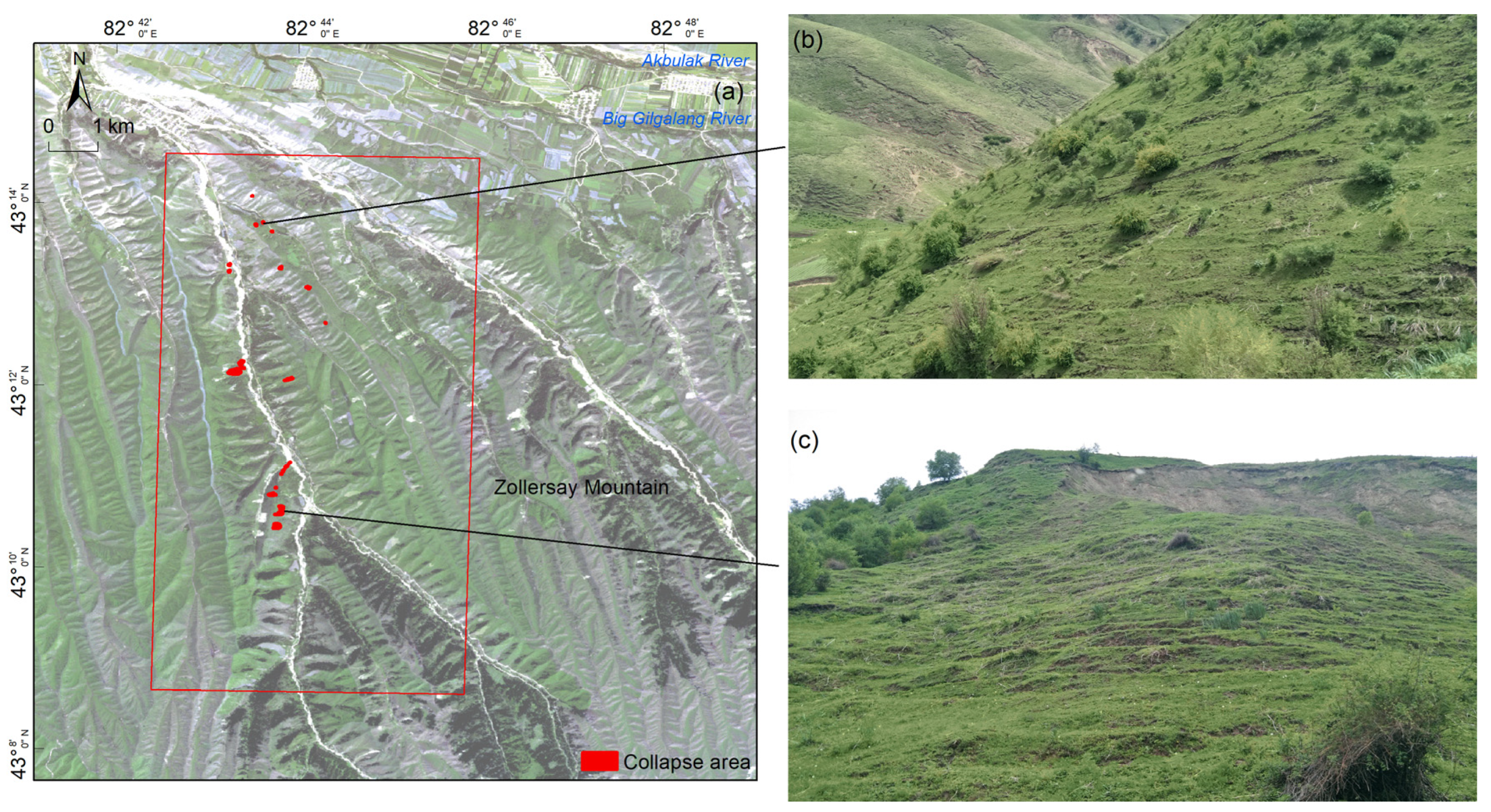
3.1.3. Distribution Characteristics of the Grazing Path
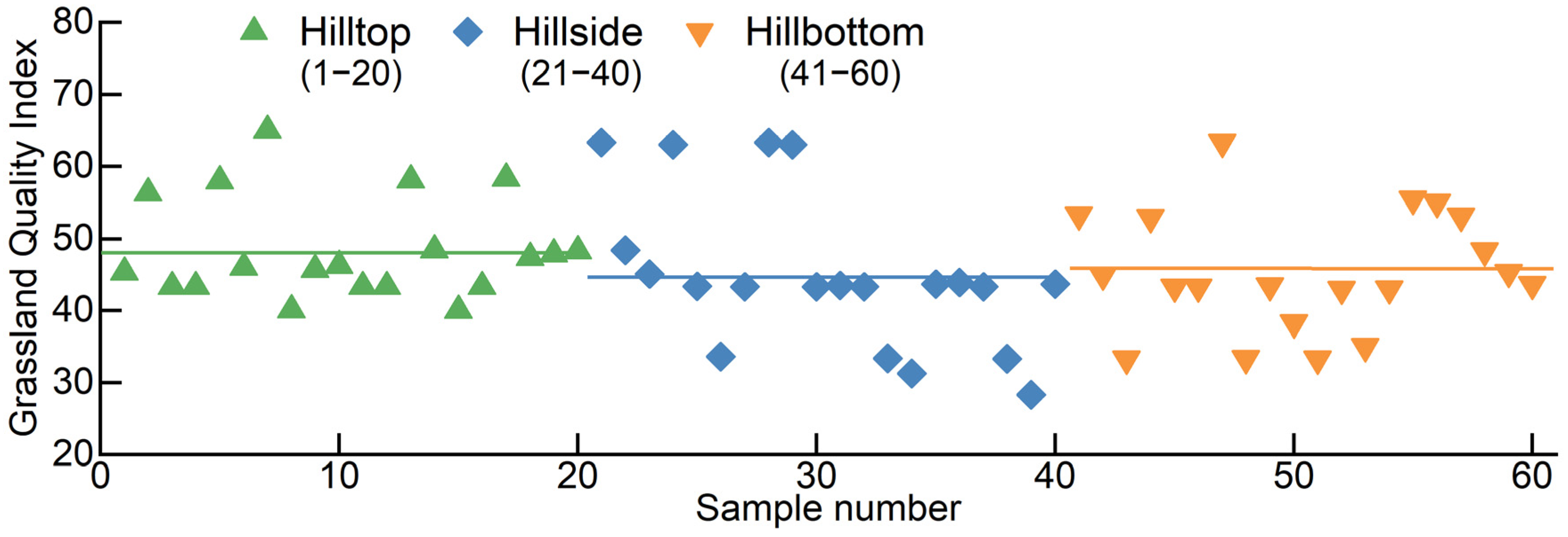
3.2. Influence of the Grazing Path on Grassland Degradation
3.2.1. Effect of the Grazing Path on IGQ
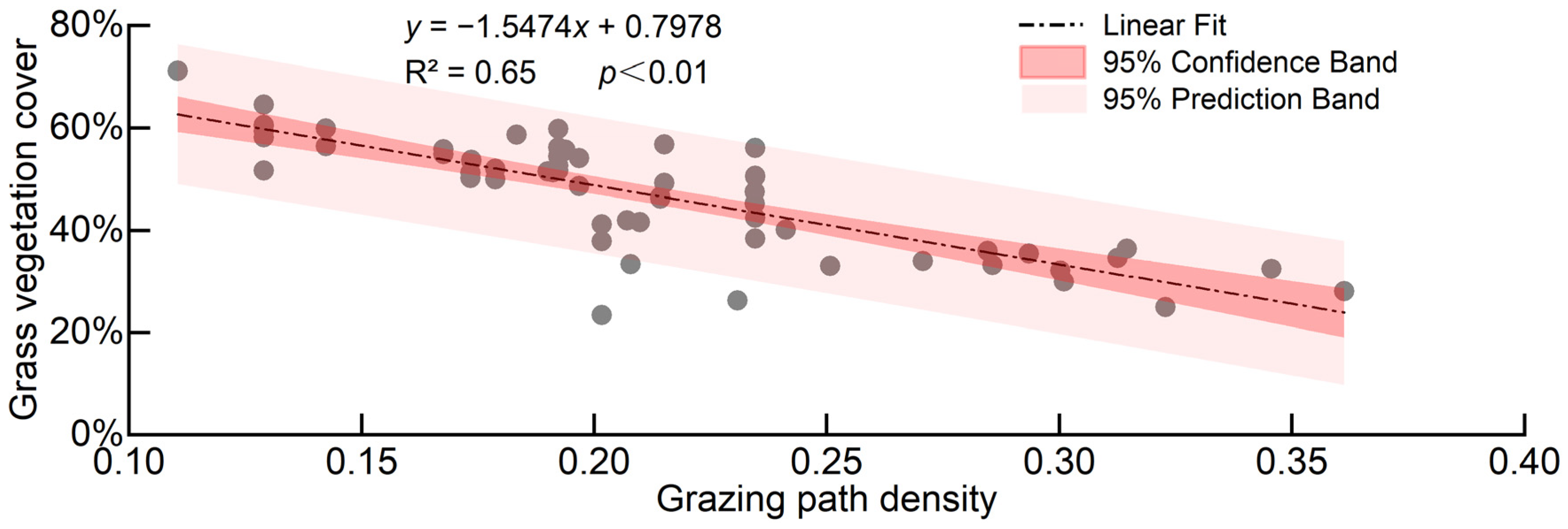
3.2.2. Effect of the Grazing Path on GVC
3.3. Effect of the Grazing Path on Malus sieversii
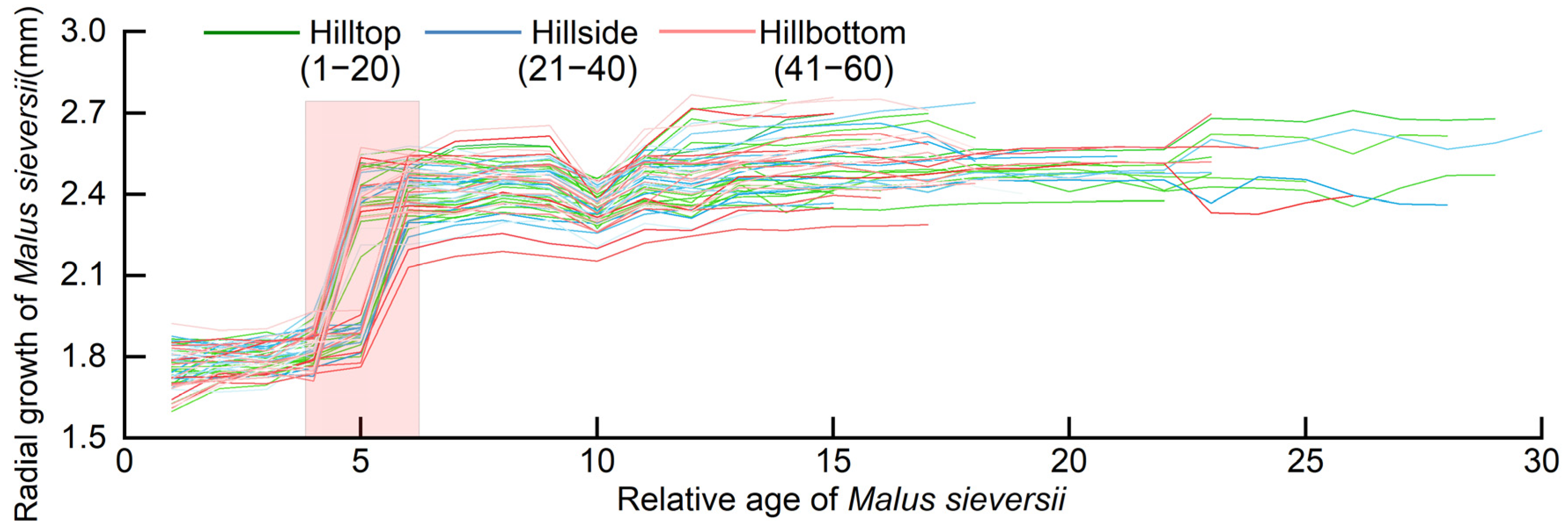
3.3.1. Changes in Radial Growth of Malus sieversii
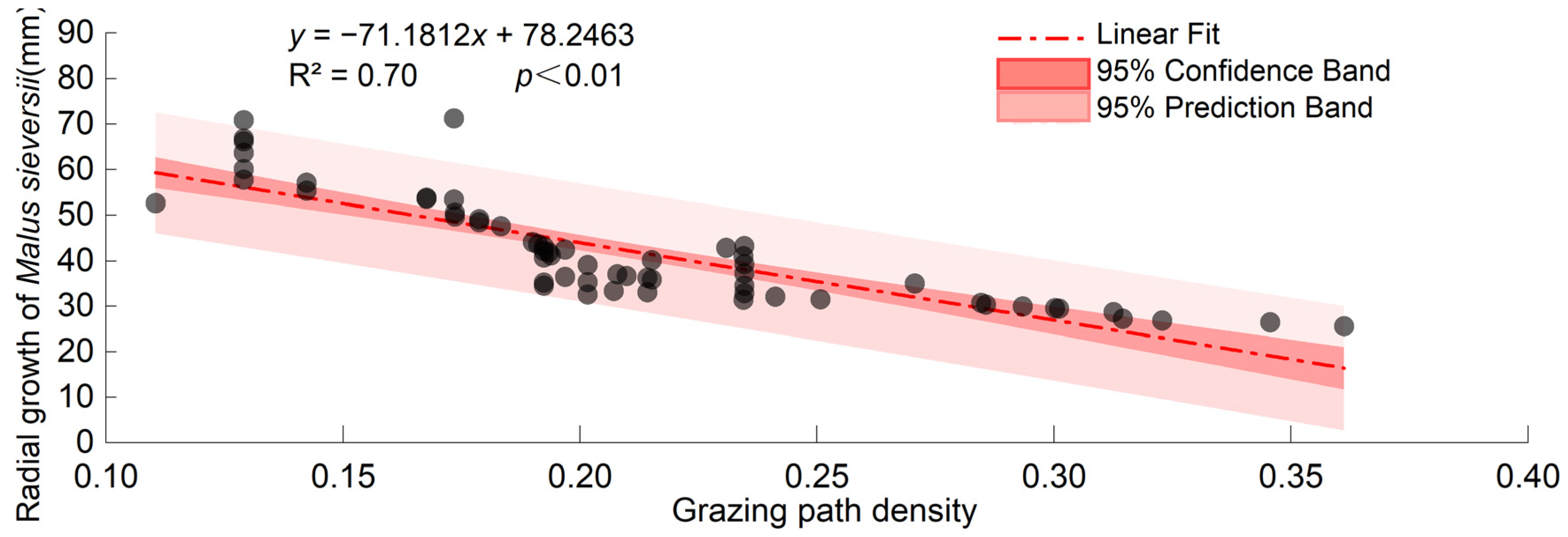
3.3.2. Relationship between the Grazing Path and Radial Growth of Malus sieversii
4. Discussion
4.1. Evolution of Grazing Path Characteristics
4.2. Mechanisms of Grazing Path Action on Montane Vegetation
4.3. Remodeling Effect of Grazing Paths on Mountainous Terrain
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Higgins, C.G. Grazing-step terracettes and their significance. Z. Fur Geomorphol. 1982, 26, 459–472. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, B.; Sun, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, M.; Ni, X.; Luo, K.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, H.; Li, F.; Wu, X.B. Livestock tracks transform resource distribution on terracette landscapes of the Loess Plateau. Ecosphere 2016, 7, e01337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T. Soil erosion on yak-grazing steps in the Langtang Himal, Nepal. Mt. Res. Dev. 1994, 14, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apollo, M.; Andreychouk, V.; Bhattarai, S.S. Short-term impacts of livestock grazing on vegetation and track formation in a high mountain environment: A case study from the Himalayan Miyar Valley (India). Sustainability 2018, 10, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, M.; Shimamura, M.; Ushiyama, M.; Fukuyama, M. Characteristics of cattle tracks on steep grassland in relation to cattle behavior and land conservation. Jarq-Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 1988, 22, 200–205. [Google Scholar]
- Hiltbrunner, D.; Schulze, S.; Hagedorn, F.; Schmidt, M.W.; Zimmmermann, S. Cattle trampling alters soil properties and changes soil microbial communities in a Swiss sub-alpine pasture. Geoderma 2012, 170, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachica, M.; Prieto, C.; Aguilera, J. The energy costs of walking on the level and on negative and positive slopes in the Granadina goat (Capra hircus). Br. J. Nutr. 1997, 77, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Cheng, H.; Sun, G.; Li, F.; Wu, X.B. Multi-parallel structure and a generalized conceptual model of livestock track network. Catena 2022, 216, 106380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarah, P.; Sachs, E.; Zhevelev, H.; Fragin, A.G.; Shaked-Weiss, A. Trampling routes modified size distribution of Sarcopoterium spinosum in semiarid rangelands. Catena 2018, 160, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarah, P.; Zonana, M. Livestock redistribute runoff and sediments in semi-arid rangeland areas. Solid Earth 2015, 6, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavi, I.; Yizhaq, H.; Osem, Y.; Argaman, E. Positive impacts of livestock and wild ungulate routes on functioning of dryland ecosystems. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 13684–13691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.X.; Gong, Y.B.; Zheng, J.K.; Zhang, X.H.; Jiang, G.Z.; Yue, Y.J.; Zuo, Q.; Liu, M. Relationships between grazing-path and Berberis aggregate population characteristics in upper reaches of Minjiang River, Southwest China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 24, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, J.; Higgins, C.; Gardiner, V. (Eds.) Dimensions of grazing-step terracettes and their significance. In International Geomorphology 1986: Proceedings of the First International Conference on Geomorphology; John Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Shuang, T.; Jinrong, W. Characterization of livestock foraging and trampling tracks in Xinjiang mountain grasslands based on ground-based photogrammetry. Chin. Xinjiang Environ. Prot. 2013, 35, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H. The Resource Selection, Movement Characteristics and Vegetation Effects of Goats in the Hilly Loess Plateau. Ph.D. Thesis, Lanzhou Uinversity, Lanzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Study on Development of Goat Track Landscape and Succession of Plant Community in Semi-Arid Hilly Region of Loess Plateau. Ph.D. Thesis, Lanzhou Uinversity, Lanzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Milchunas, D.G.; Lauenroth, W.K. Quantitative effects of grazing on vegetation and soils over a global range of environments: Ecological Archives M063-001. Ecol. Monogr. 1993, 63, 327–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belsky, A.J. Does herbivory benefit plants? A review of the evidence. Am. Nat. 1986, 127, 870–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönbach, P.; Wan, H.; Gierus, M.; Bai, Y.; Müller, K.; Lin, L.; Susenbeth, A.; Taube, F. Grassland responses to grazing: Effects of grazing intensity and management system in an Inner Mongolian steppe ecosystem. Plant Soil 2011, 340, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, F. Effects of different grazing intensities on grassland production in China: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Jiao, F.; Li, Y.; Kallenbach, R.L. Anthropogenic disturbances are key to maintaining the biodiversity of grasslands. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milchunas, D.G.; Sala, O.E.; Lauenroth, W.K. A generalized model of the effects of grazing by large herbivores on grassland community structure. Am. Nat. 1988, 132, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaughton, S. Compensatory plant growth as a response to herbivory. Oikos 1983, 40, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, N. Degradation of river ecological quality in Tibet plateau with overgrazing: A quantitative assessment using biotic integrity index improved by random forest. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Yu, K.; Ren, Z.; Xu, G.; Cheng, S.; Wang, F.; Ma, Y. Distribution of soil organic carbon impacted by land-use changes in a hilly watershed of the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hou, F.; Angerer, J.P.; Yi, S. Effects of topography and land-use patterns on the spatial heterogeneity of terracette landscapes in the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, L.; Allsopp, N. Rehabilitation of rangelands in Paulshoek, Namaqualand: Understanding vegetation change using biophysical manipulations. J. Arid Environ. 2007, 70, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fan, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, L. Effects of grazing exclusion on biomass growth and species diversity among various grassland types of the Tibetan Plateau. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Shi, S.; Cao, W. Six years of grazing exclusion is the optimum duration in the alpine meadow-steppe of the north-eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köbel, M.; Listopad, C.; Príncipe, A.; Nunes, A.; Branquinho, C. Temporary grazing exclusion as a passive restoration strategy in a dryland woodland: Effects over time on tree regeneration and on the shrub community. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 483, 118732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouinard, A.; Filion, L. Detrimental effects of white-tailed deer browsing on balsam fir growth and recruitment in a second-growth stand on Anticosti Island, Québec. Ecoscience 2001, 8, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Ling, H.; Zhang, G.; Yan, J.; Han, F. Unreasonable human disturbance shifts the positive effect of climate change on tree-ring growth of Malus sieversii in the origin area of world cultivated apples. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Song, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Maimaiti, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J. Wild apples are not that wild: Conservation status and potential threats of Malus sieversii in the mountains of Central Asia biodiversity hotspot. Diversity 2022, 14, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.M.; Li, Y.G.; Maisupova, B.; Zhou, X.B.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.L.; Yin, B.F.; Zang, Y.X.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, Y.M. Effects of growth decline on twig functional traits of wild apple trees in two long-term monitoring plots in Yili Valley: Implication for their conservation. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 33, e01998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X.; Jia, X. Spatial Distribution Pattern of Root Sprouts under the Canopy of Malus Sieversii in a Typical River Valley on the Northern Slopes of the Tianshan Mountain. Forests 2022, 13, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicke, M.; Burrough, P.A. Using fractal dimensions for characterizing tortuosity of animal trails. Physiol. Entomol. 1988, 13, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Wang, G.; Du, G.Z. Succession of the artificial grasslands in the mountain grassland area of gannan district gansu. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 1990, 14, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Jin, B.; Luo, K.; Pei, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, J.; Yang, Q.; Sun, G. Vegetation Response to Goats Grazing Intensity in Semiarid Hilly Grassland of the Loess Plateau, Lanzhou, China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.; Guo, Y. Effects of Grazing Intensity on Plant Community and Species Diversity of Temperate Steppe in Lhasa River Valley. Chin. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2019, 27, 668–674. [Google Scholar]
- Vila, B.; Torre, F.; Guibal, F.; Martin, J.L. Growth change of young Picea sitchensis in response to deer browsing. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 180, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Sun, G.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, M.; Ni, X.; Luo, K.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Wu, X.B. Goat track networks facilitate efficiency in movement and foraging. Landsc. Ecol. 2019, 34, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganskopp, D.; Cruz, R.; Johnson, D.E. Least-effort pathways: A GIS analysis of livestock trails in rugged terrain. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2000, 68, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, C.; Ruifrok, J.L.; van Klink, R.; Olff, H. Rewilding with large herbivores: The importance of grazing refuges for sapling establishment and wood-pasture formation. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 182, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjeljord, O.; Histøl, T.; Wam, H.K. Forest pasturing of livestock in Norway: Effects on spruce regeneration. J. For. Res. 2014, 25, 941–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, Q. Threshold effects of vegetation coverage on runoff and soil loss in the Loess Plateau of China: A meta-analysis. Geoderma 2022, 412, 115720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouri, M.H.; Zare, M.; Askarizadeh, D.; FakhreGhazi, M.; Salarian, T.; Miarrostami, S. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping for Subalpine Grassland Using Frequency Ratio and Landslide Index Model (Case Study: Masoleh Watershed, Iran). J. Rangel. Sci. 2013, 3, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Beck, R.; Pan, Q.; Zhao, M.; Hao, X. Soil physical and chemical properties in response to long-term cattle grazing on sloped rough fescue grassland in the foothills of the Rocky Mountains, Alberta. Geoderma 2019, 346, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Indicator | Detailed Parameter |
|---|---|
| Number of rotors | 4 |
| Satellite positioning module | GPS/GLONASS dual-mode |
| Image sensor | 1 inch CMOS, effective pixels: 20 million |
| Lens | FOV 84°, 8.8 mm/24 mm (35 mm format equivalence), f/2.8–f/11 with autofocus (focusing distance: 1 m–infinity) |
| Location | Metrics | Maximum Value | Minimum Value | Mean Value | Variance | Standard Deviation | Standard Error | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hilltop | Number | 30.00 | 14.00 | 21.05 | 18.37 | 4.18 | 0.96 | 21.05 ± 2.01 |
| Width (m) | 1.64 | 0.32 | 0.62 | 0.07 | 0.27 | 0.06 | 0.62 ± 0.13 | |
| Length (m) | 48.45 | 14.36 | 32.75 | 142.61 | 11.64 | 2.67 | 32.75 ± 5.59 | |
| Hillside | Number | 33.00 | 18.00 | 24.05 | 22.58 | 4.63 | 1.06 | 24.05 ± 2.22 |
| Width (m) | 0.95 | 0.37 | 0.51 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.51 ± 0.06 | |
| Length (m) | 50.61 | 15.01 | 27.25 | 120.01 | 10.68 | 2.45 | 27.25 ± 5.13 | |
| Hillbottom | Number | 29.00 | 10.00 | 20.60 | 28.15 | 5.17 | 1.19 | 20.60 ± 2.48 |
| Width (m) | 0.83 | 0.28 | 0.44 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.44 ± 0.05 | |
| Length (m) | 53.63 | 19.40 | 35.47 | 93.51 | 9.42 | 2.16 | 35.47 ± 4.53 |
| Location | Morphological Characteristics | Maximum Value | Minimum Value | Mean Value | Variance | Standard Deviation | Standard Error | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hilltop | Amplitude (m) | 31.00 | 11.00 | 24.00 | 25.53 | 4.92 | 1.13 | 24.00 ± 2.36 |
| Tortuosity | 1.26 | 1.02 | 1.09 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 1.09 ± 0.03 | |
| Number of plane bends | 7.00 | 3.00 | 4.85 | 0.77 | 0.85 | 0.20 | 4.85 ± 0.41 | |
| Hillside | Amplitude (m) | 35.00 | 15.00 | 27.00 | 28.96 | 5.24 | 1.20 | 27.00 ± 2.52 |
| Tortuosity | 1.74 | 0.89 | 1.13 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 1.13 ± 0.09 | |
| Number of plane bends | 8.00 | 2.00 | 4.25 | 1.36 | 1.13 | 0.26 | 4.25 ± 0.54 | |
| Hillbottom | Amplitude (m) | 34.00 | 15.00 | 24.00 | 24.66 | 4.84 | 1.11 | 24.00 ± 2.32 |
| Tortuosity | 1.18 | 1.01 | 1.08 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 1.08 ± 0.02 | |
| Number of plane bends | 8.00 | 1.00 | 4.50 | 2.30 | 1.48 | 0.34 | 4.50 ± 0.71 |
| Characteristics of the Grazing Path | Linear Equations in One Element | R2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| number | y = −0.0334x + 46.913 | 0.0003 | 0.89 |
| length | y = −0.1522x + 49.94 | 0.0082 | 0.49 |
| width | y = −2.228x + 48.626 | 0.0008 | 0.83 |
| amplitude | y = 0.7311x + 42.929 | 0.0103 | 0.44 |
| tortuosity | y = −0.0334x + 46.913 | 0.0003 | 0.89 |
| number of plane bends | y = −0.2632x + 54.557 | 0.1119 | <0.01 |
| density | y = 0.5546x + 45.892 | 0.0002 | 0.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, X.; Huang, T.; Chen, M.; Han, N.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X. Distribution of Grazing Paths and Their Influence on Mountain Vegetation in the Traditional Grazing Area of the Tien-Shan Mountains. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3163. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123163
Jia X, Huang T, Chen M, Han N, Liu Y, Chen S, Zhang X. Distribution of Grazing Paths and Their Influence on Mountain Vegetation in the Traditional Grazing Area of the Tien-Shan Mountains. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(12):3163. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123163
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Xiang, Tiecheng Huang, Mengyu Chen, Ning Han, Yihao Liu, Shujiang Chen, and Xiaoli Zhang. 2023. "Distribution of Grazing Paths and Their Influence on Mountain Vegetation in the Traditional Grazing Area of the Tien-Shan Mountains" Remote Sensing 15, no. 12: 3163. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123163
APA StyleJia, X., Huang, T., Chen, M., Han, N., Liu, Y., Chen, S., & Zhang, X. (2023). Distribution of Grazing Paths and Their Influence on Mountain Vegetation in the Traditional Grazing Area of the Tien-Shan Mountains. Remote Sensing, 15(12), 3163. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123163






