A Prediction Method of Ionospheric hmF2 Based on Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
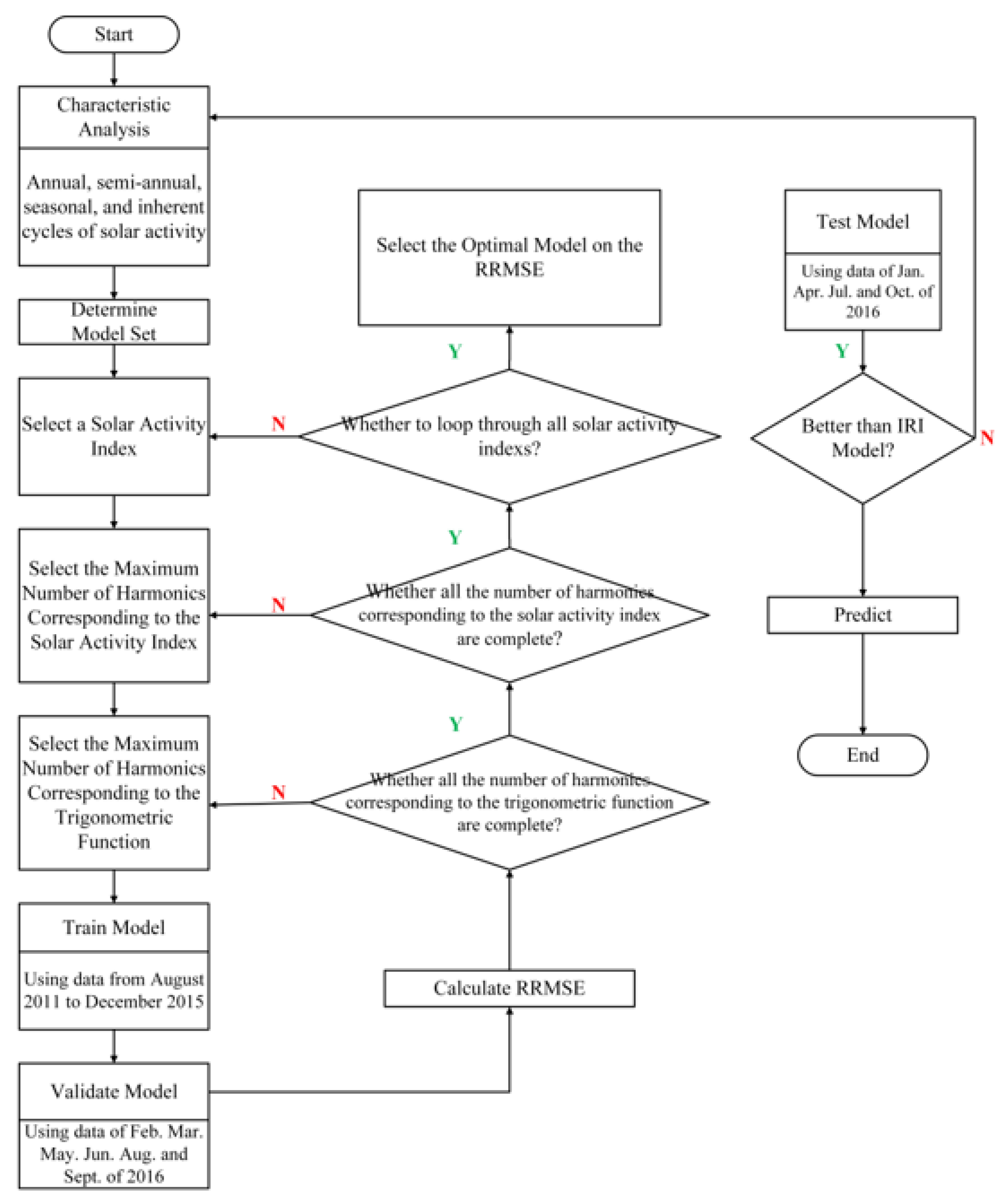
2.1. Method
2.2. Data
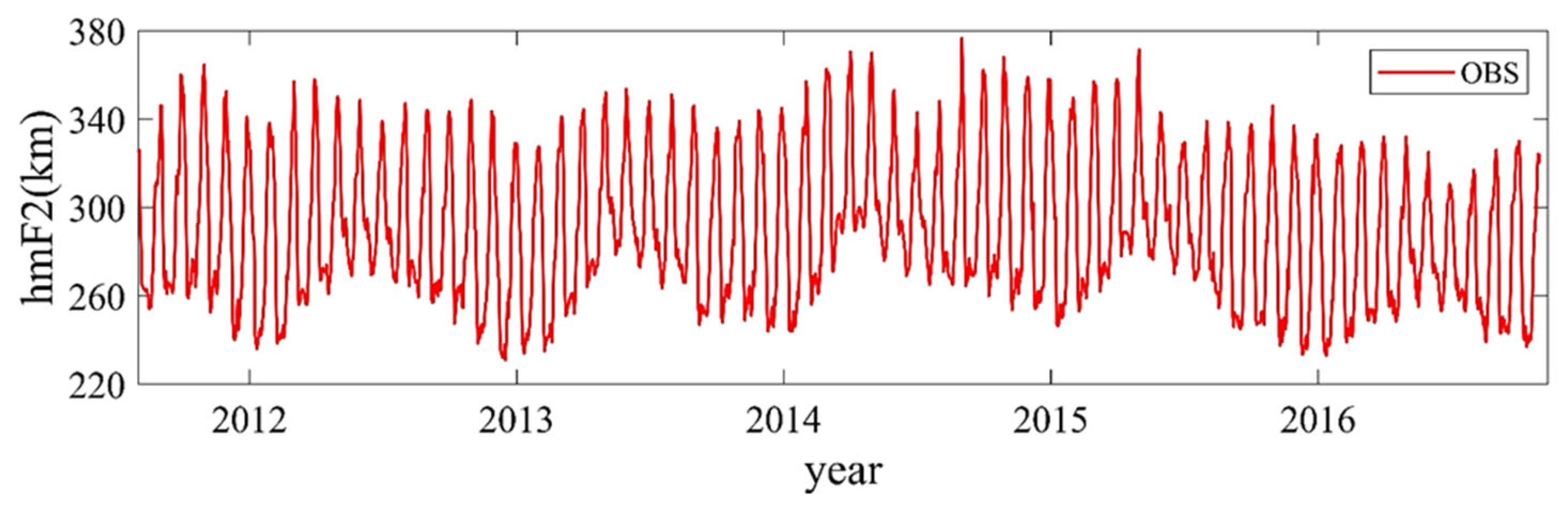
2.2.1. Ionospheric hmF2
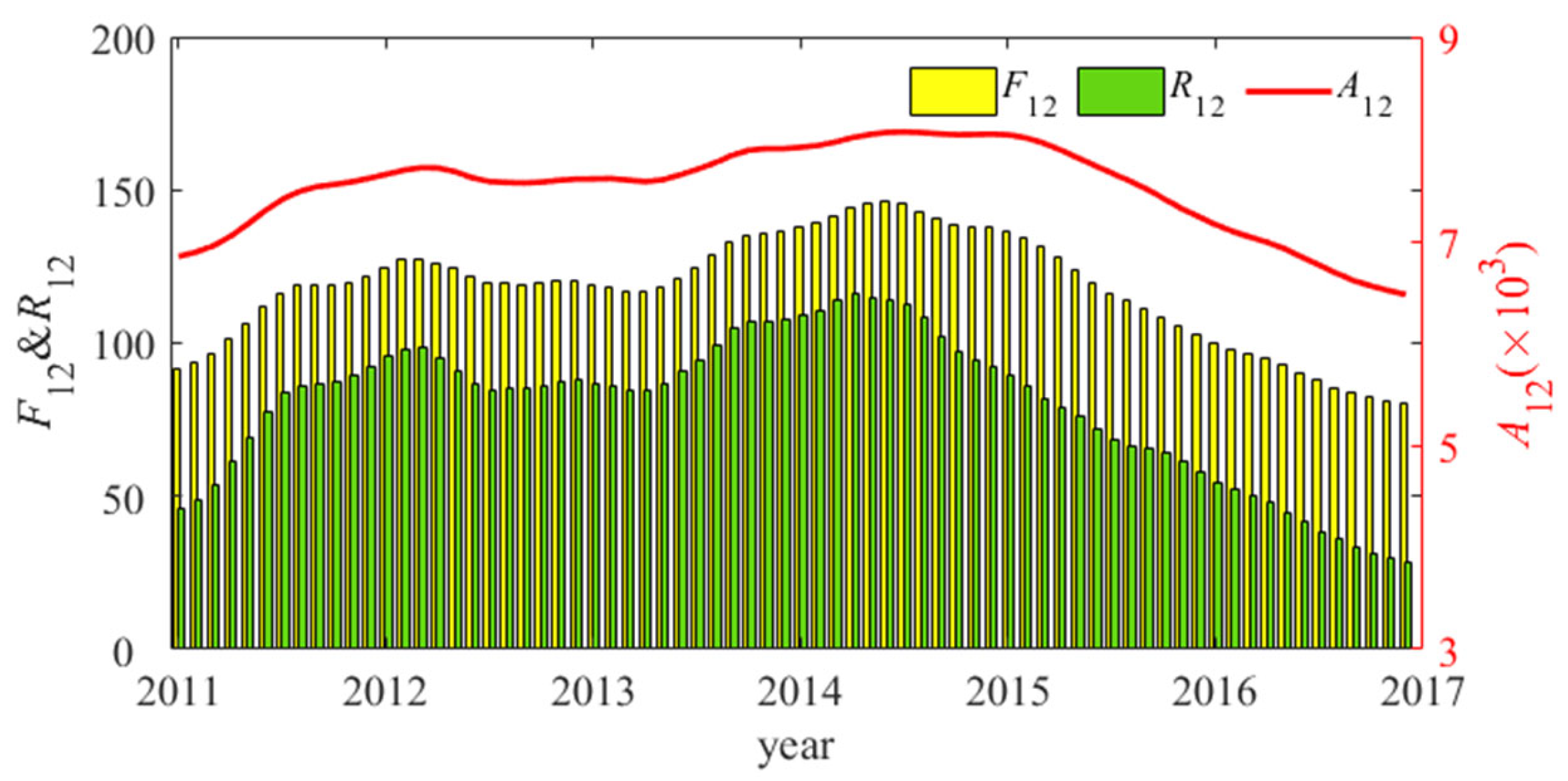
2.2.2. Solar Activity Index
3. Results
3.1. Model Determination
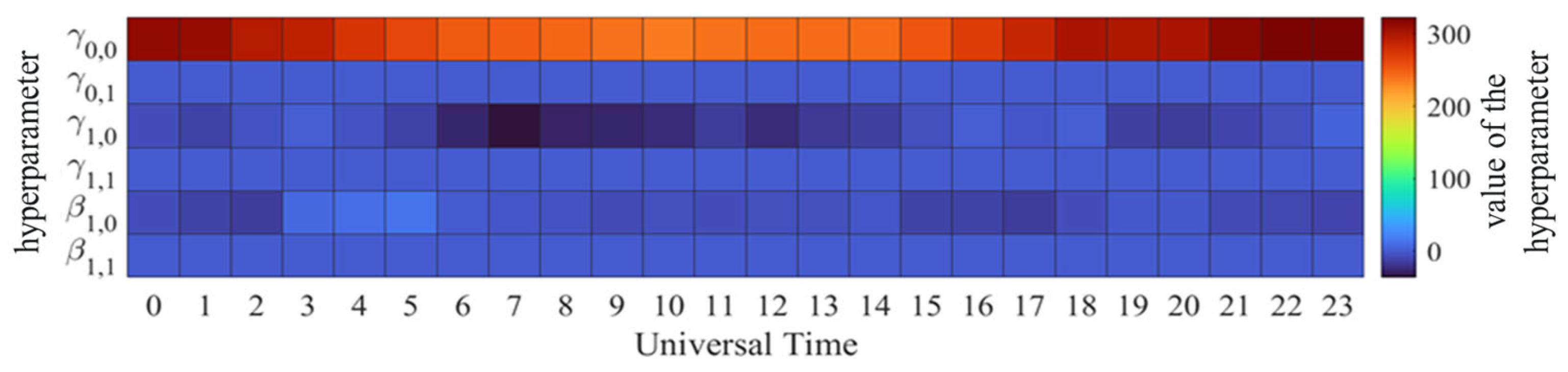
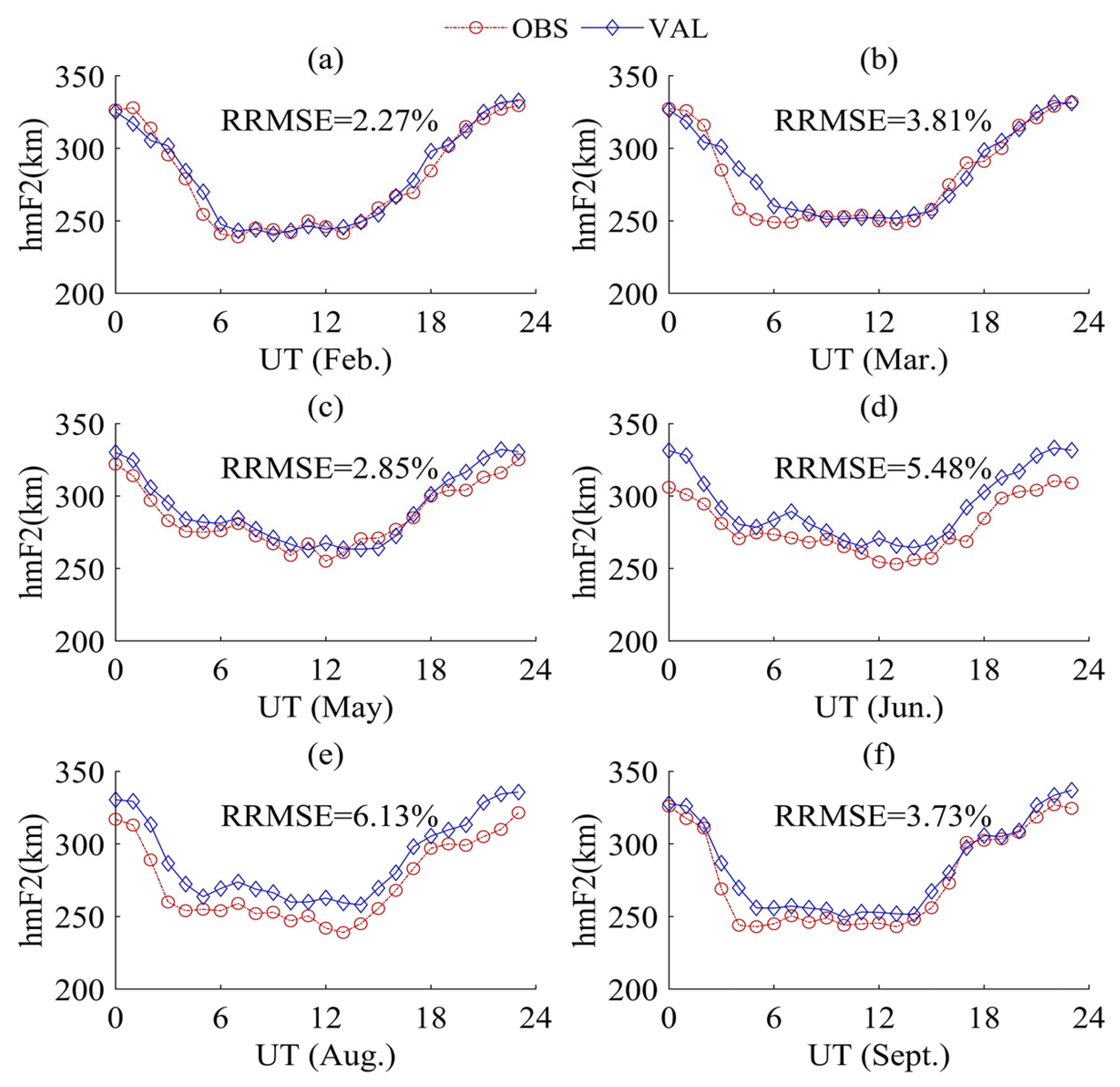
3.2. Results Analysis
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sezen, U.; Sahin, O.; Arikan, F.; Arikan, O. Estimation of hmF2 and foF2 Communication Parameters of Ionosphere F2-Layer Using GPS Data and IRI-Plas Model. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 5264–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagouri, I.; Goncharenko, L.; Shim, J.S.; Belehaki, A.; Buresova, D.; Kuznetsova, M.M. Assessment of current capabilities in modeling the ionospheric climatology for space weather applications: foF2 and hmF2. Space Weather 2018, 16, 1930–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ITU. ITU-R P.1240, ITU-R Methods of Basic MUF, Operational MUF and Ray-Path Prediction; ITU: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Zhang, L.; Rahman, T.; Su, D. Prediction of the HF Ionospheric Channel Stability Based on the Modified ITS Model. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 3321–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Wang, G.; Tian, G.; Li, W.; Su, D.; Rahman, T. The HF Channel EM Parameters Estimation Under a Complex Environment Using the Modified IRI and IGRF Model. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 59, 1778–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikan, F.; Sezen, U.; Gulyaeva, T.L.; Cilibas, O. Online, automatic, ionospheric maps: IRI-PLAS-MAP. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 2106–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishbeth, H.; Edwards, R. Modeling the F2 layer peak height in terms of atmospheric pressure. Radio Sci. 1990, 25, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, T.V.; Sridhar, M.; Ratnam, D.V.; Harsha, P.B.S.; Srivani, I. A Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory-Based Ionospheric foF2 and hmF2 Models for a Single Station in the Low Latitude Region. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, L.; Mikhailov, A.V.; Scotto, C.; Sabbagh, D. Testing of the Method Retrieving a Consistent Set of Aeronomic Parameters with Millstone Hill ISR Noontime hmF2 Observations. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 1698–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, F.; Li, X. Evaluation of foF2 and hmF2 Parameters of IRI-2016 Model in Different Latitudes over China under High and Low Solar Activity Years. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 860. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Shi, Y.; Yang, C. Investigation of Two Prediction Models of Maximum Usable Frequency for HF Communication Based on Oblique- and Vertical-Incidence Sounding Data. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilitza, D.; Mckinnell, L.A.; Reinisch, B.; Rowell, T.F. The international reference ionosphere today and in the future. J. Geod. 2011, 85, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.L.; Liu, C.; Wan, W.; Liu, L.; Ning, B. A global model of the ionospheric F2 peak height based on EOF analysis. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 3203–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.L.; Liu, C.; Wan, W.; Liu, L.; Ning, B. Evaluation of global modeling of M(3000)F2 and hmF2 based on alternative empirical orthogonal function expansions. Adv. Space Res. 2010, 46, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wan, W.; Xiong, B.; Ren, Z.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Ning, B.; Liu, L. Modeling Chinese ionospheric layer parameters based on EOF analysis. Space Weather 2015, 13, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Themens, D.R.; Jayachandran, P.T.; Galkin, I.; Hall, C. The Empirical Canadian High Arctic Ionospheric Model (E-CHAIM): NmF2 and hmF2. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 9015–9031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai, G.V.; Tulasi, R.S. An Artificial Neural Network based Ionospheric Model to predict NmF2 and hmF2 using long-term data set of FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC radio occultation observations: Preliminary results. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 11743–11755. [Google Scholar]
- Tulasi, R.S.; Sai, G.V.; Mitra, A.; Reinisch, B. The improved two-dimensional artificial neural network-based ionospheric model (ANNIM). J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2018, 123, 5807–5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, D.; He, C.; Hu, A.; Zhang, K. Advanced Machine Learning Optimized by The Genetic Algorithm in Ionospheric Models Using Long-Term Multi-Instrument Observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokoué, E. Model Selection for Optimal Prediction in Statistical Machine Learning. Not. Am. Math. Soc. 2020, 67, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, C.; An, W. Regional Refined Long-term Predictions Method of Usable Frequency for HF Communication Based on Machine Learning over Asia. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2022, 70, 4040–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, Q.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C. An Explainable Dynamic Prediction Method for Ionospheric foF2 Based on Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Burns, A.G.; Solomon, S.C. Annual/semiannual variation of the ionosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1928–1933. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.H. Machine Learning, 2nd ed.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Available online: https://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/stp/space-weather/solar-data/ (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- Afraimovich, E.L.; Astafyeva, E.I.; Oinats, A.V. Global electron content: A new conception to track solar activity. Ann. Geophys. 2008, 26, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunspot Number. Available online: https://www.sidc.be/silso/datafiles (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- Data of Hydrogen Emission at 121.6 nm. Available online: https://lasp.colorado.edu/lisird/composite_timeseries.html (accessed on 27 April 2022).
- Tapping, K.F. The 10.7cm solar radio flux (F10.7). Space Weather 2013, 11, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.C.; Qian, L.; Burns, A.G. The anomalous ionosphere between solar cycles 23 and 24. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2013, 118, 6524–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.M. Ionospheric Model Research Based on Intelligent Information Processing Technology; Tianjin University: Tianjin, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W. Study on Regional Ionospheric Characteristics Based on Ground-Based GPS and Occultation Technology; Wuhan University: Wuhan, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, W. Comparison of Different Detection Scenarios of Lyman-α. In Highlights in Science, Engineering and Technology; Darcy & Roy Press: Portland, OR, USA, 2023; Volume 38, pp. 850–855. [Google Scholar]
- Perna, L.; Pezzopane, M. foF2 vs solar indices for the Rome station: Looking for the best general relation which is able to describe the anomalous minimum between cycles 23 and 24. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2016, 148, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, F.; Bai, H.M.; Cao, Y.B.; Chen, Q.; Ma, J.G. A regional model for the prediction of M(3000)F2 over East Asia. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 65, 2036–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Reference Ionosphere. Available online: http://IRImodel.org/IRI-2016 (accessed on 18 April 2022).


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Yu, Q.; Shi, Y.; Yang, C. A Prediction Method of Ionospheric hmF2 Based on Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123154
Wang J, Yu Q, Shi Y, Yang C. A Prediction Method of Ionospheric hmF2 Based on Machine Learning. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(12):3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123154
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jian, Qiao Yu, Yafei Shi, and Cheng Yang. 2023. "A Prediction Method of Ionospheric hmF2 Based on Machine Learning" Remote Sensing 15, no. 12: 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123154
APA StyleWang, J., Yu, Q., Shi, Y., & Yang, C. (2023). A Prediction Method of Ionospheric hmF2 Based on Machine Learning. Remote Sensing, 15(12), 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123154






