Kalman Filter, ANN-MLP, LSTM and ACO Methods Showing Anomalous GPS-TEC Variations Concerning Turkey’s Powerful Earthquake (6 February 2023)
Abstract
1. Introduction
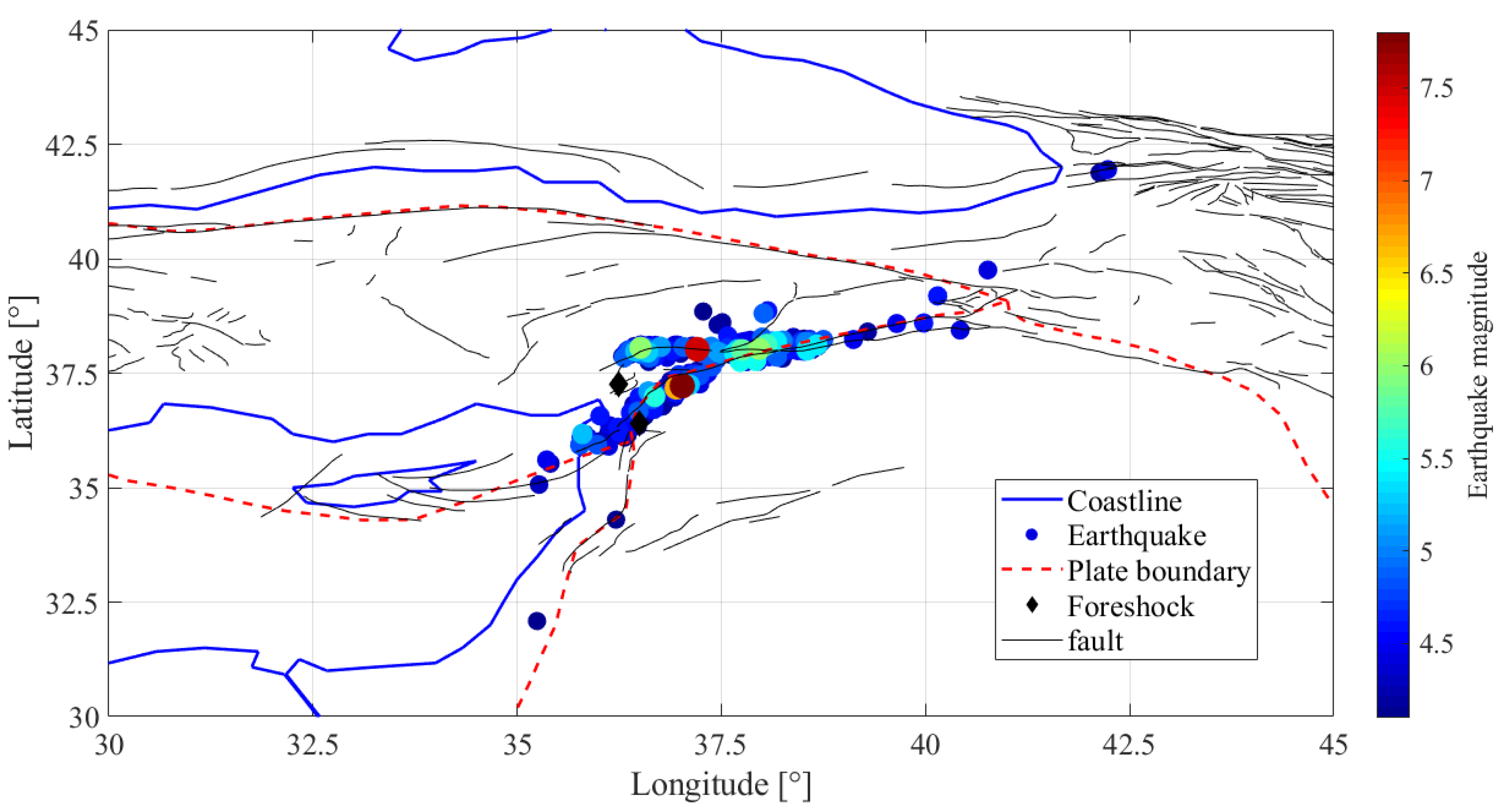
Case Study
2. Data
2.1. TEC Data
2.2. Solar–Geomagnetic Data
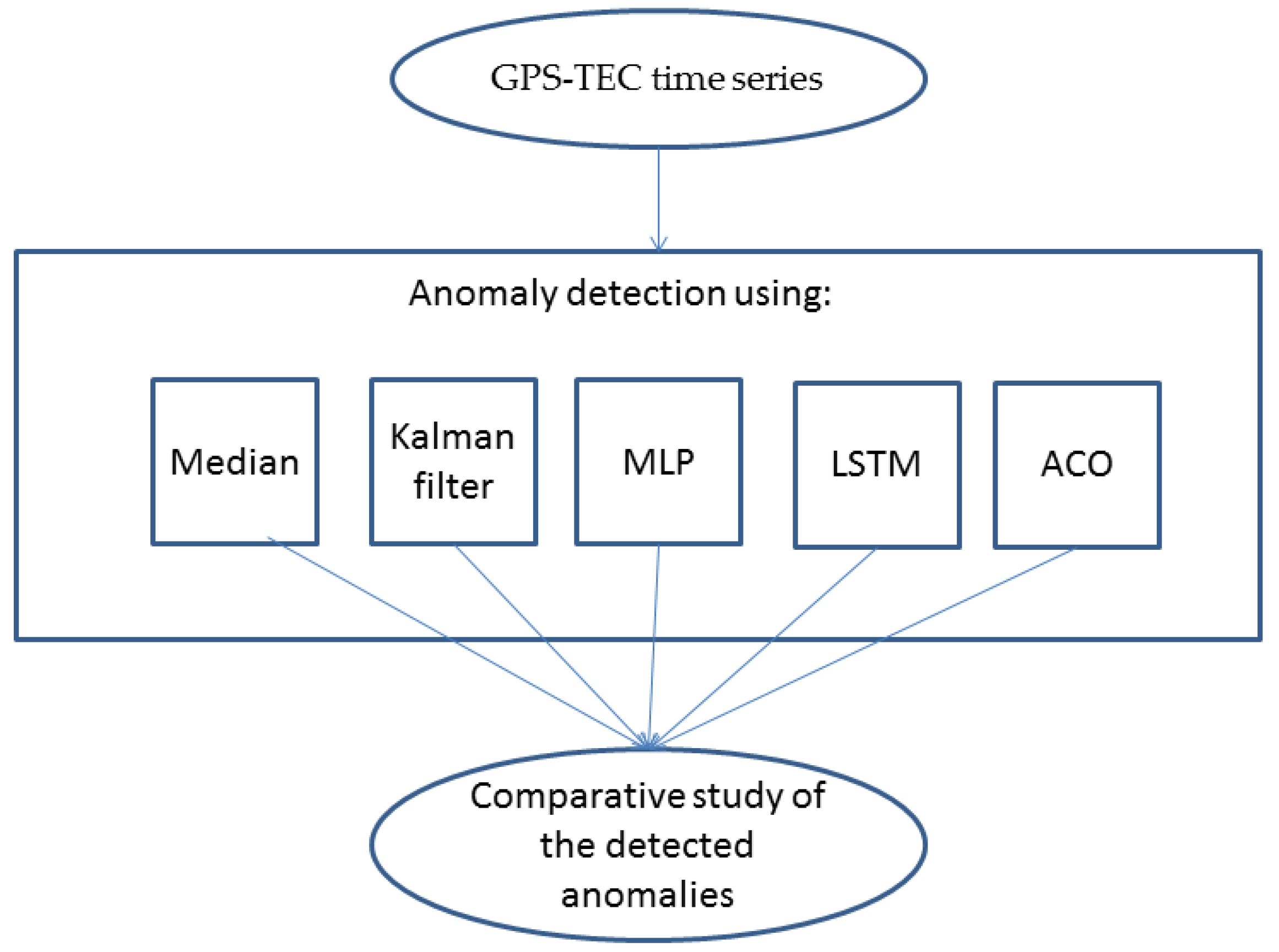
3. Methods
3.1. Median
3.2. Kalman Filter
3.3. ANN-MLP
3.4. LSTM
3.5. ACO
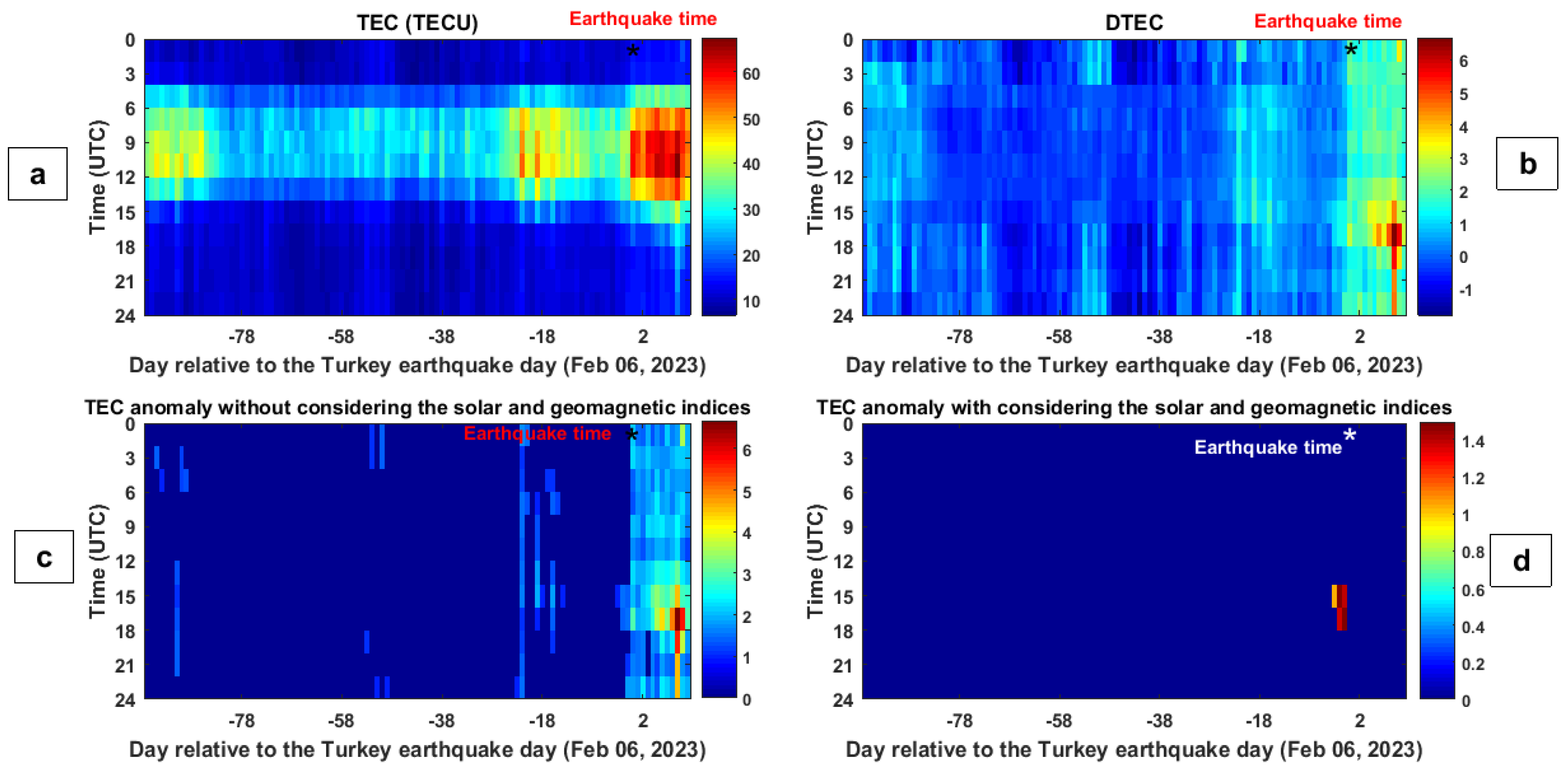
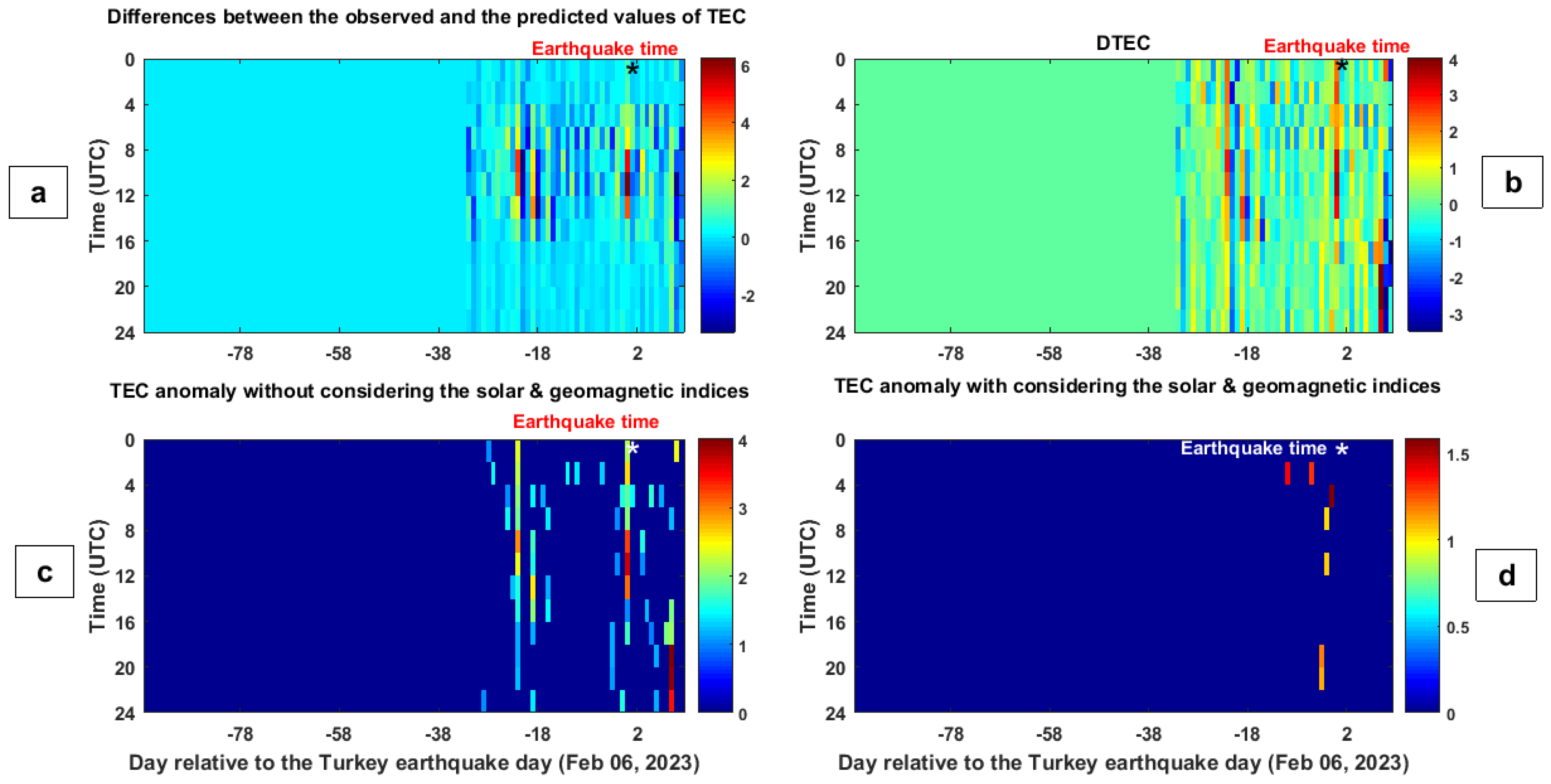
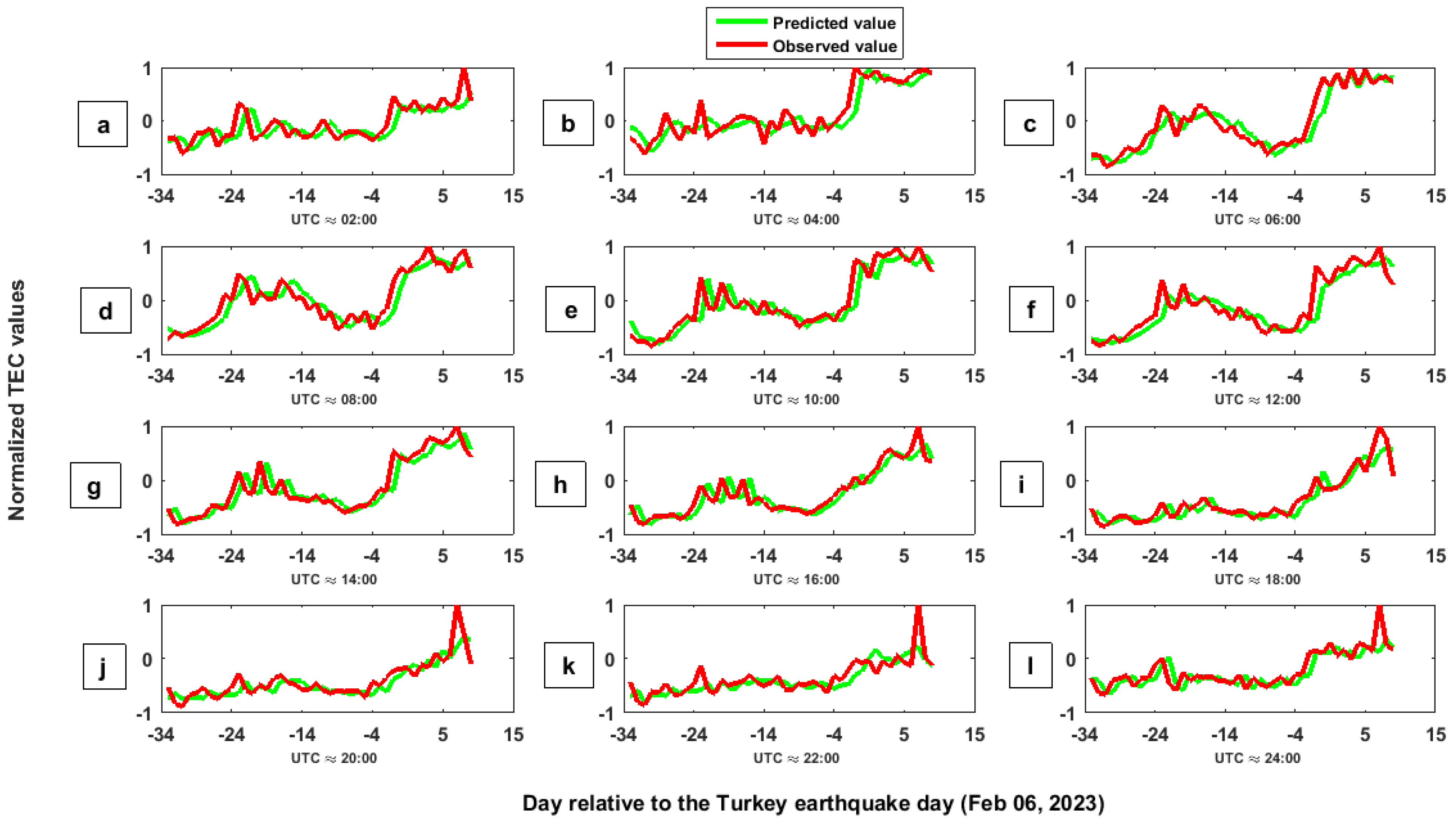
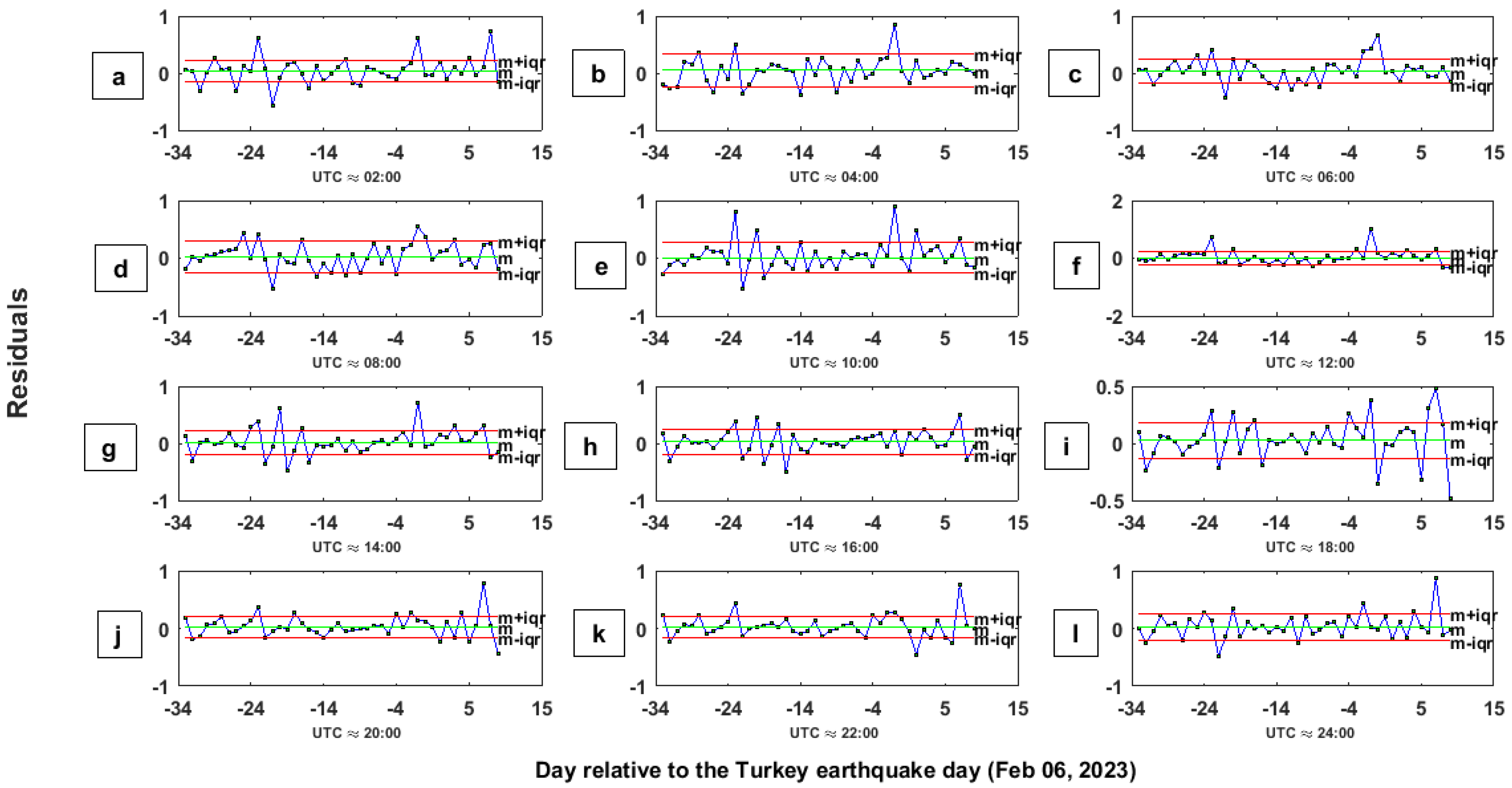
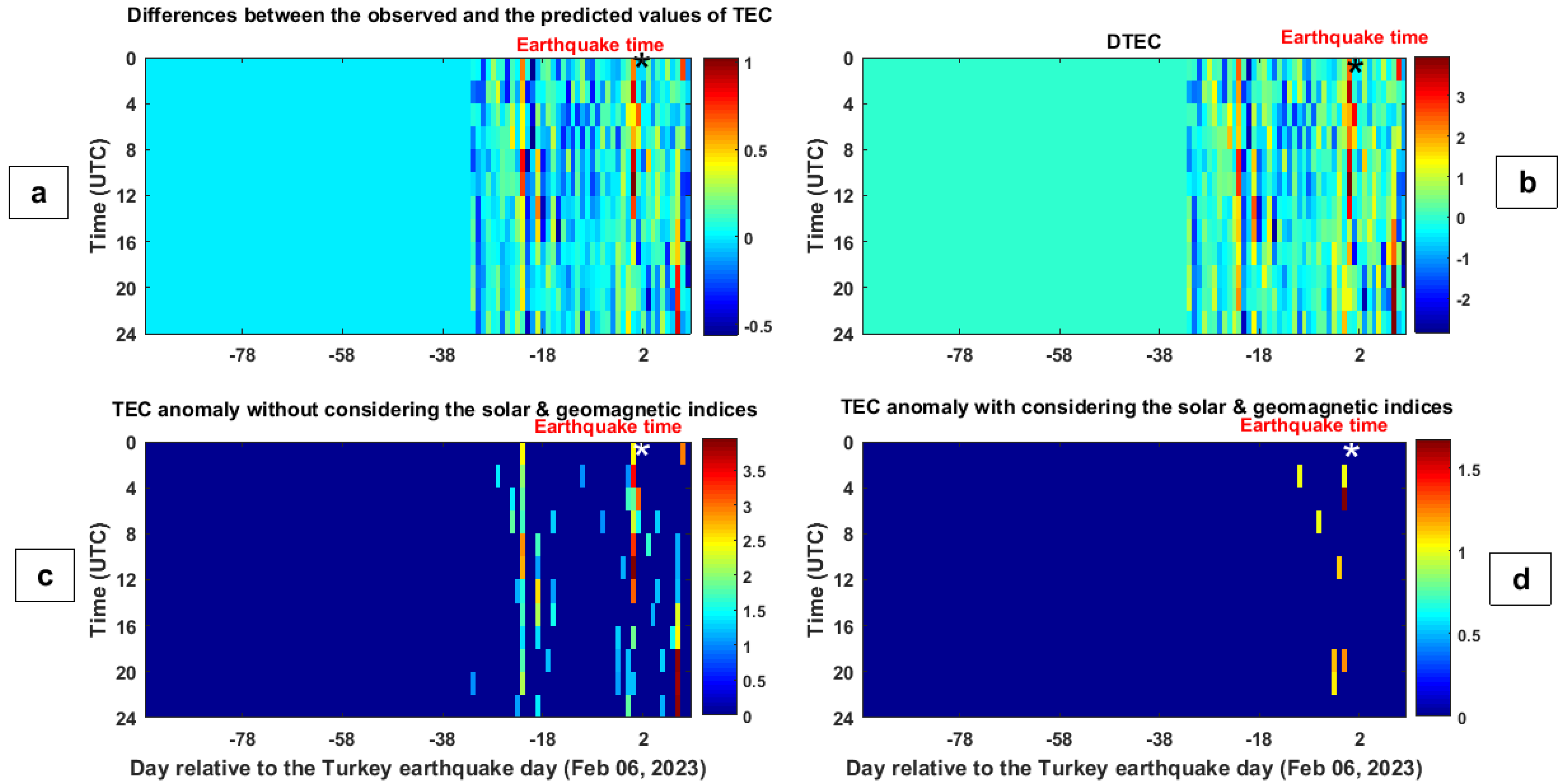
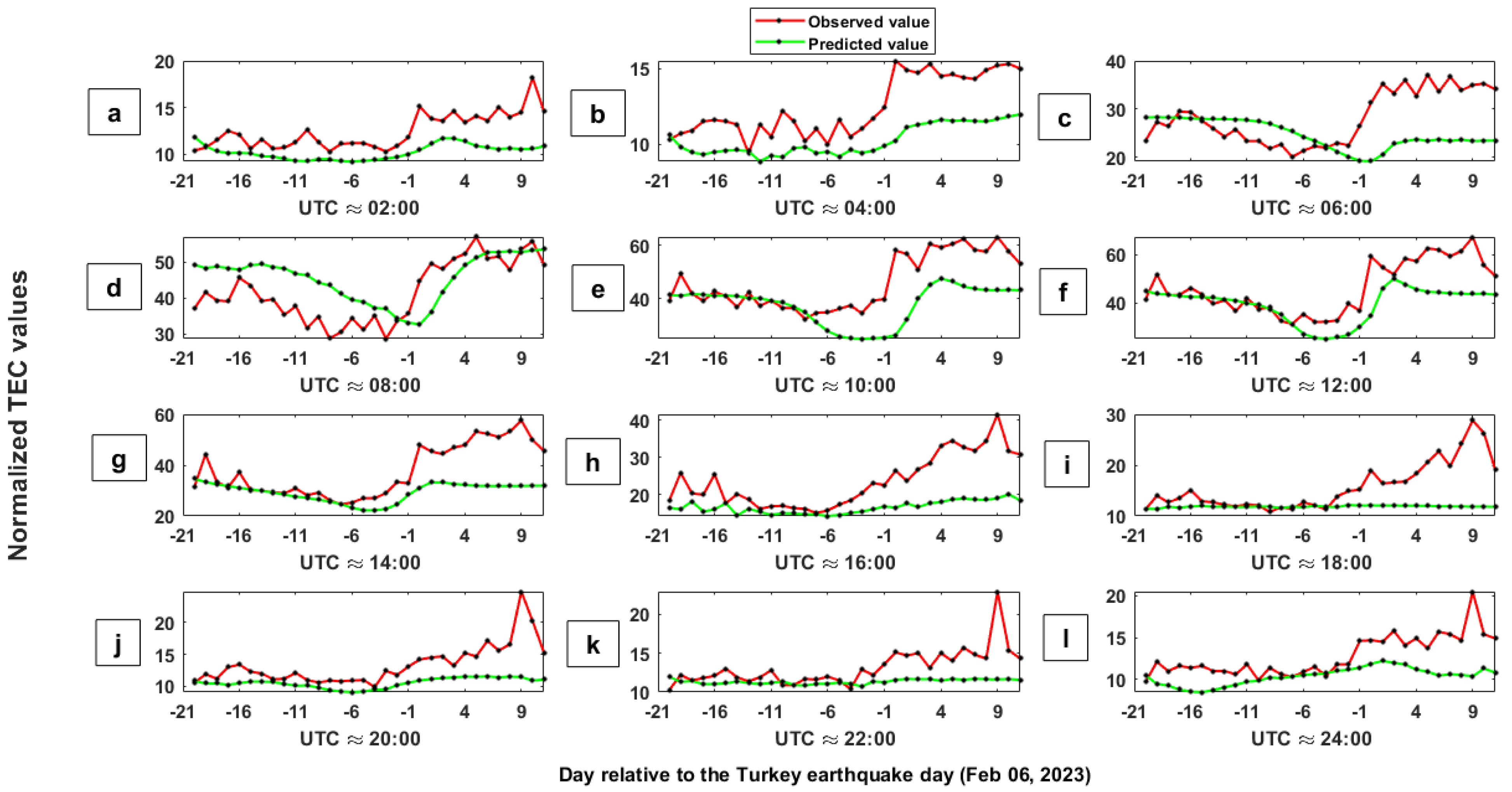
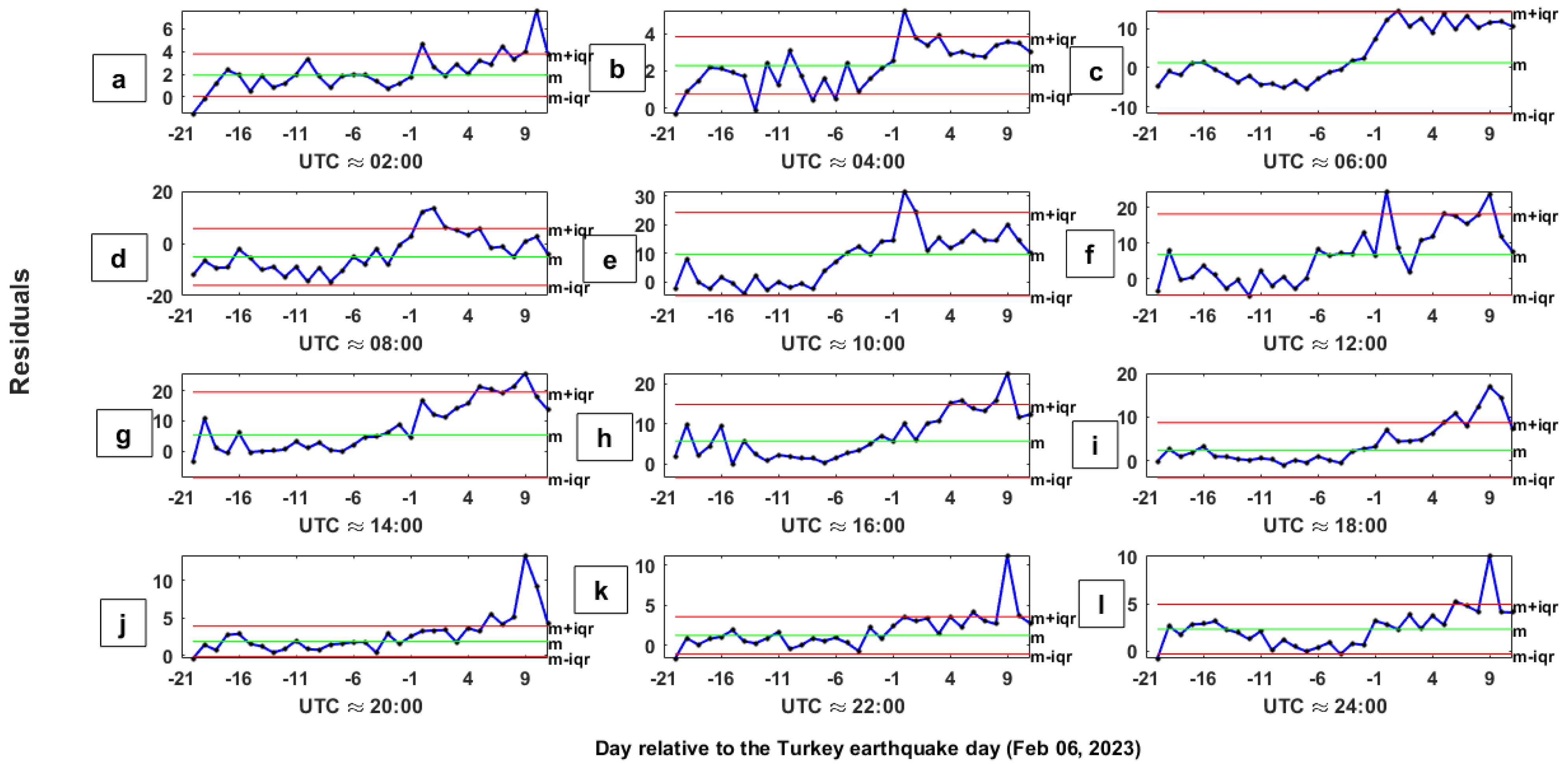
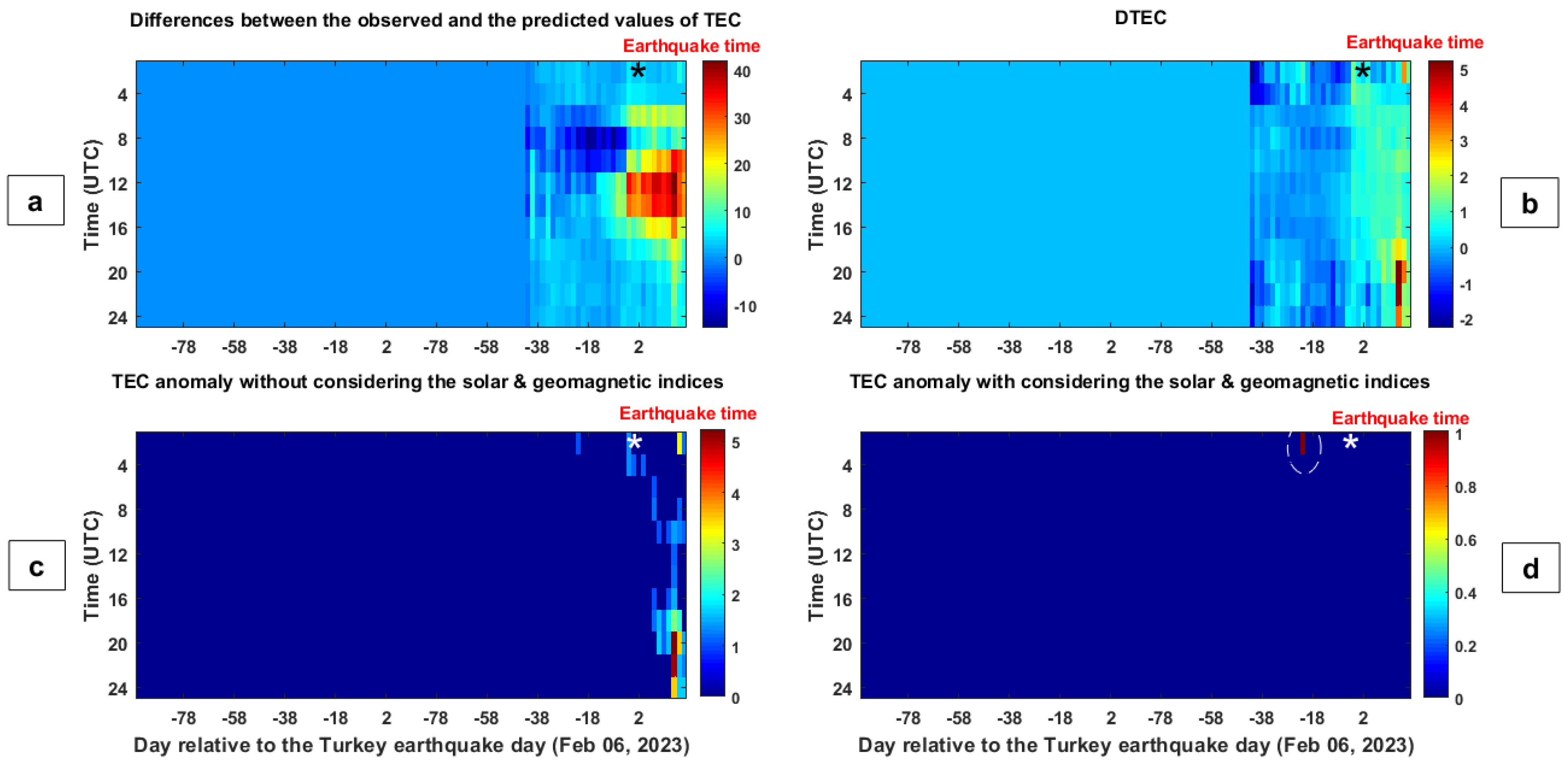
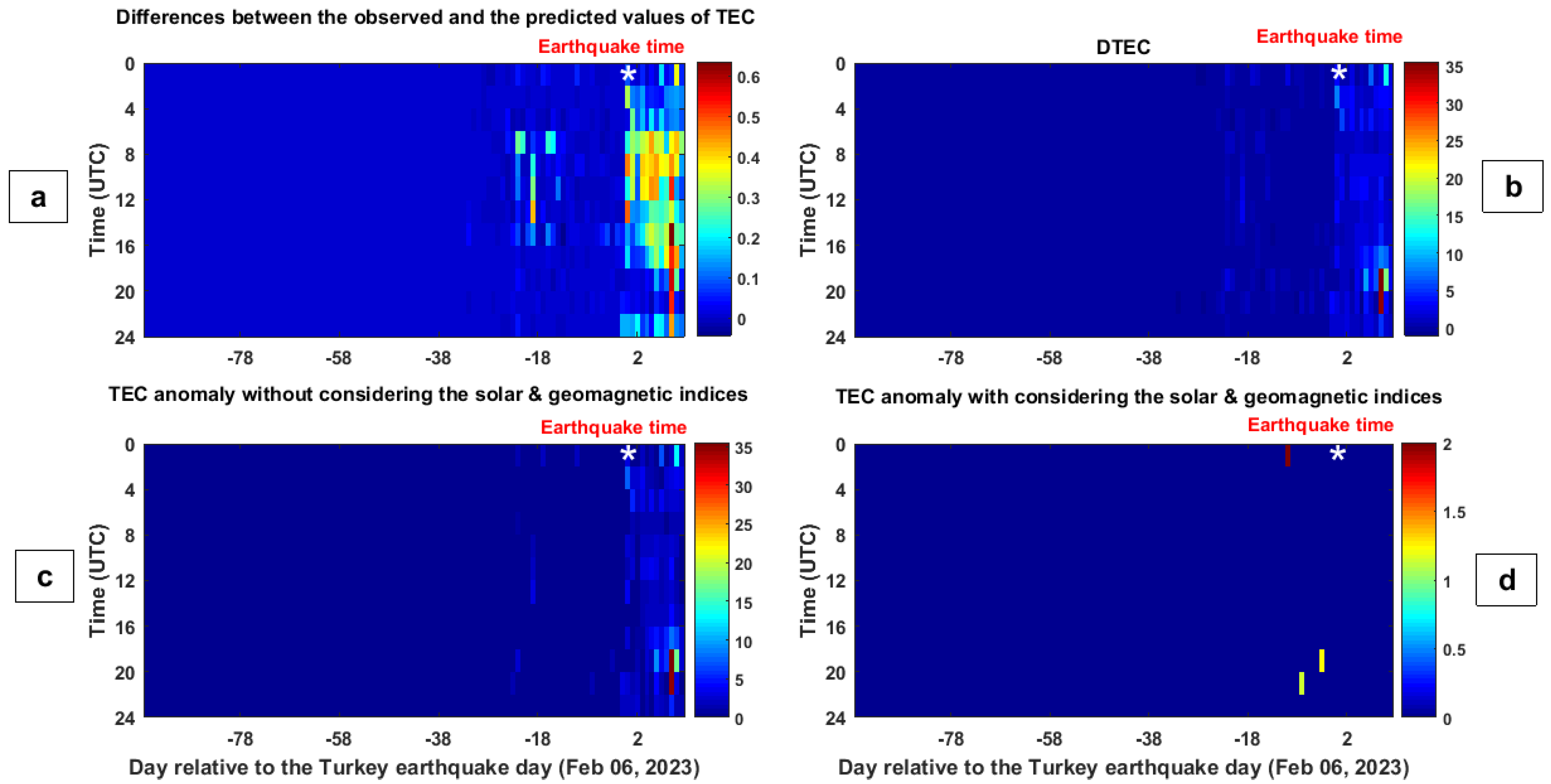
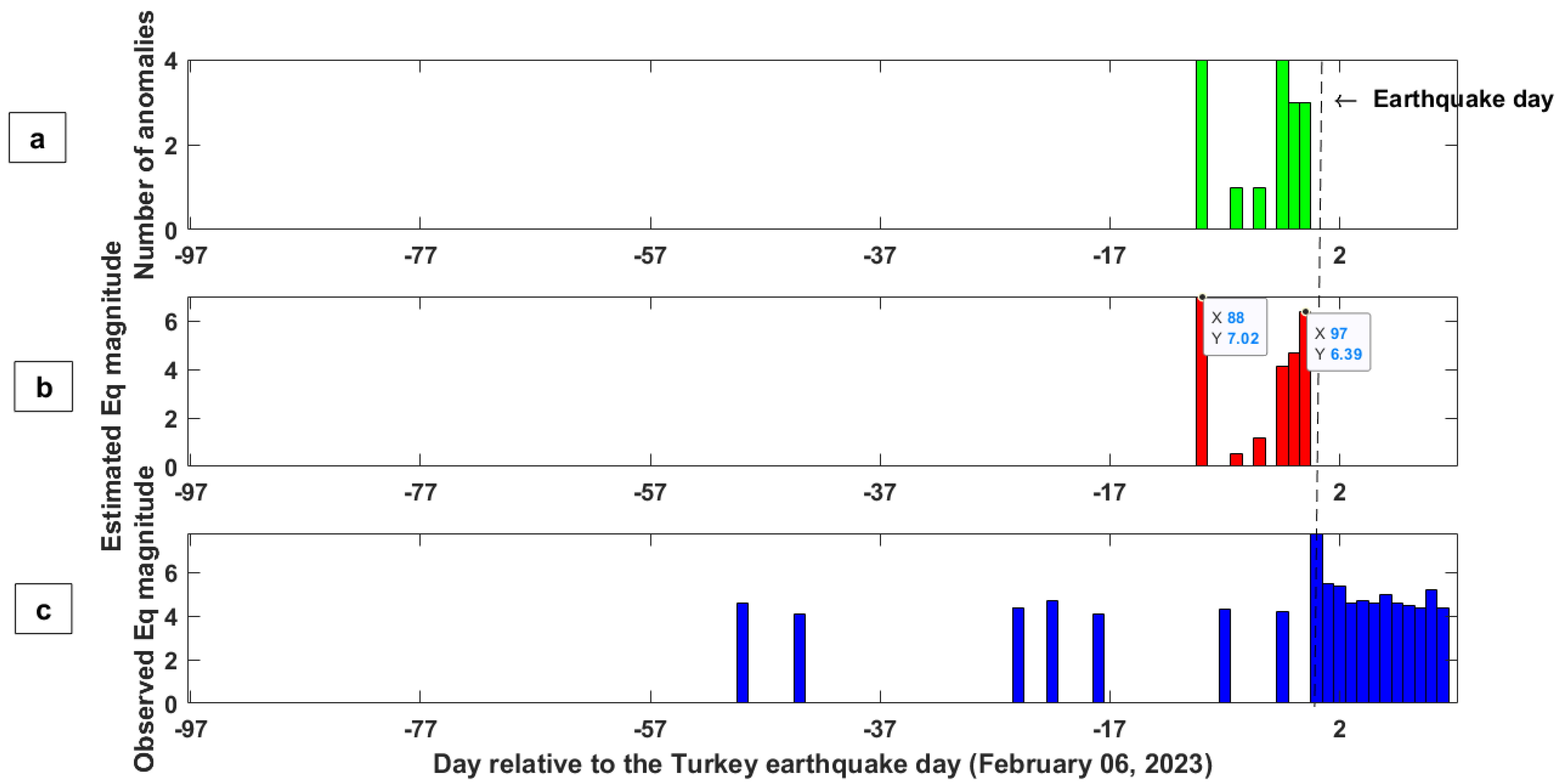
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garmaise, M.J.; Moskowitz, T.J. Catastrophic Risk and Credit Markets. J. Financ. 2009, 64, 657–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignan, A.; Ouillon, G.; Sornette, D.; Freund, F. Global Earthquake Forecasting System (GEFS): The Challenges Ahead. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2021, 230, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, A.; Marchetti, D.; Pavón-Carrasco, F.J.; Cianchini, G.; Perrone, L.; Abbattista, C.; Alfonsi, L.; Amoruso, L.; Campuzano, S.A.; Carbone, M.; et al. Precursory Worldwide Signatures of Earthquake Occurrences on Swarm Satellite Data. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, D.; De Santis, A.; Campuzano, S.A.; Zhu, K.; Soldani, M.; D’Arcangelo, S.; Orlando, M.; Wang, T.; Cianchini, G.; Di Mauro, D.; et al. Worldwide Statistical Correlation of Eight Years of Swarm Satellite Data with M5.5+ Earthquakes: New Hints about the Preseismic Phenomena from Space. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, D.; Zhu, K.; Yan, R.; ZeRen, Z.; Shen, X.; Chen, W.; Cheng, Y.; Fan, M.; Wang, T.; Wen, J.; et al. Ionospheric Effects of Natural Hazards in Geophysics: From Single Examples to Statistical Studies Applied to M5.5+ Earthquakes. In Proceedings of the 4th International Electronic Conference on Geosciences, Online, 1–15 December 2022; MDPI: Basel, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-I.; Huang, C.-S.; Liu, J.-Y. Statistical Evidences of Seismo-Ionospheric Precursors Applying Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve on the GPS Total Electron Content in China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 114, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genzano, N.; Filizzola, C.; Hattori, K.; Pergola, N.; Tramutoli, V. Statistical Correlation Analysis Between Thermal Infrared Anomalies Observed from MTSATs and Large Earthquakes Occurred in Japan (2005–2015). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2020JB020108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Parrot, M.; Pinçon, J.-L. Statistical Study on Variations of the Ionospheric Ion Density Observed by DEMETER and Related to Seismic Activities: Ionospheric Density and Seismic Activity. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 12421–12429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoondzadeh, M. Advances in Seismo-LAI Anomalies Detection within Google Earth Engine (GEE) Cloud Platform. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 69, 4351–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, V.; Bi, Y.; Wilkie, G. A Tool for Swarm Satellite Data Analysis and Anomaly Detection. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Han, P.; Hattori, K. Recent Advances and Challenges in the Seismo-Electromagnetic Study: A Brief Review. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, A.; Marchetti, D.; Spogli, L.; Cianchini, G.; Pavón-Carrasco, F.J.; Franceschi, G.D.; Di Giovambattista, R.; Perrone, L.; Qamili, E.; Cesaroni, C.; et al. Magnetic Field and Electron Density Data Analysis from Swarm Satellites Searching for Ionospheric Effects by Great Earthquakes: 12 Case Studies from 2014 to 2016. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, P.; Marchetti, D.; De Santis, A.; Zhang, X.; Shen, X. SafeNet: SwArm for Earthquake Perturbations Identification Using Deep Learning Networks. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essam, Y.; Kumar, P.; Najah Ahmed, A.; Ary Murti, M.; El-Shafie, A. Exploring the reliability of different artificial intelligence techniques in predicting earthquake for Malaysia. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 147, 106826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portillo, A.; Moya, L. Seismic Risk Regularization for Urban Changes Due to Earthquakes: A Case of Study of the 2023 Turkey Earthquake Sequence. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marhain, S.; Ahmed, A.N.; Murti, M.A.; Kumar, P.; El-Shafie, A. Investigating the application of artificial intelligence for earthquake prediction in Terengganu. Nat. Hazards 2021, 108, 977–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, X.; Tao, T.; Zhu, Y.; Qu, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, J.; Song, S. Source Model of the 2023 Turkey Earthquake Sequence Imaged by Sentinel-1 and GPS Measurements: Implications for Heterogeneous Fault Behavior along the East Anatolian Fault Zone. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murti, M.A.; Junior, R.; Ahmed, A.N.; Elshafie, A. Earthquake multi-classification detection based velocity and displacement data filtering using machine learning algorithms. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoondzadeh, M.; Marchetti, D. Study of the Preparation Phase of Turkey’s Powerful Earthquake (6 February 2023) by a Geophysical Multi-Parametric Fuzzy Inference System. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basili, R.; Danciu, L.; Beauval, C.; Sesetyan, K.; Vilanova, S.; Adamia, S.; Arroucau, P.; Atanackov, J.; Baize, S.; Canora, C.; et al. European Fault-Source Model 2020 (EFSM20): Online Data on Fault Geometry and Activity Parameters; Istituto Nazionale Di Geofisica e Vulcanologia (INGV): Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoondzadeh, M. Anomalous TEC variations associated with the powerful Tohoku earthquake of 11 March 2011. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 1453–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Chuo, Y.J.; Shan, S.J.; Tsai, Y.B.; Chen, Y.I.; Pulinets, S.A.; Yu, S.B. Pre-earthquake-ionospheric anomalies registered by continuous GPS TEC. Ann. Geophys. 2004, 22, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoondzadeh, M. A MLP neural network as an investigator of TEC time series to detect seismo-ionospheric anomalies. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 51, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoondzadeh, M.; De Santis, A.; Marchetti, D.; Shen, X. Swarm-TEC Satellite Measurements as a Potential Earthquake Precursor Together with Other Swarm and CSES Data: The Case of Mw7.6 2019 Papua New Guinea Seismic Event. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 820189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoondzadeh, M.; De Santis, A. Is the Apparent Correlation between Solar-Geomagnetic Activity and Occurrence of Powerful Earthquakes a Casual Artifact? Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klobuchar, J.A. Ionospheric Time-Delay Algorithm for Single-Frequency GPS Users. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1987, 23, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Cerdeira, R.; Orús-Pérez, R.; Breeuwer, E.; Lucas-Rodríguez, R.; Falcone, M. Innovation: The European Way. Performance of the Galileo Single-Frequency Ionospheric Correction during In-Orbit Validation. GPSworld 2014, 25, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, N.; Li, Z.; Huo, X. The BeiDou global broadcast ionospheric delay correction model (BDGIM) and its preliminary performance evaluation results. J. Inst. Navig. 2019, 66, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrovolsky, I.P.; Zubkov, S.I.; Miachkin, V.I. Estimation of the Size of Earthquake Preparation Zones. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1979, 117, 1025–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoondzadeh, M.; De Santis, A.; Marchetti, D.; Piscini, A.; Cianchini, G. Multi Precursors Analysis Associated with the Powerful Ecuador (MW = 7.8) Earthquake of 16 April 2016 Using Swarm Satellites Data in Conjunction with Other Multi-Platform Satellite and Ground Data. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 61, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoondzadeh, M.; De Santis, A.; Marchetti, D.; Wang, T. Developing a Deep Learning-Based Detector of Magnetic, Ne, Te and TEC Anomalies from Swarm Satellites: The Case of Mw 7.1 2021 Japan Earthquake. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, M. Optimization, Learning, and Natural Algorithms. Ph.D. Thesis, Politecnico di Milano, Milano, Italy, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Akhoondzadeh, M. Ant Colony Optimization detects anomalous aerosol variations associated with the Chile earthquake of 27 February 2010. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 1754–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoondzadeh, M.; Marchetti, D. Developing a Fuzzy Inference System Based on Multi-Sensor Data to Predict Powerful Earthquake Parameters. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, Y. Coupled Interaction of Earthquake Nucleation with Deep Earth Gases: A Possible Mechanism for Seismo-Electromagnetic Phenomena. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 191, 1210–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, F.; Ouillon, G.; Scoville, J.; Sornette, D. Earthquake Precursors in the Light of Peroxy Defects Theory: Critical Review of Systematic Observations. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2021, 230, 7–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulinets, S.; Ouzounov, D. Lithosphere–Atmosphere–Ionosphere Coupling (LAIC) Model—An Unified Concept for Earthquake Precursors Validation. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 41, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.L.; Lee, L.C.; Huba, J.D. An Improved Coupling Model for the Lithosphere-Atmosphere-Ionosphere System. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 3189–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Method | Anomalous Day and Time | DTEC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Day | UTC | ||
| Median | −1 | 16:00 | 39.8% |
| 18:00 | 48.6% | ||
| −2 | 16:00 | 49.6% | |
| 18:00 | 37.1% | ||
| −3 | 16:00 | 4.1% | |
| Kalman filter | −1 | 6:00 | 58.7% |
| −2 | 8:00 | 3.7% | |
| 12:00 | 6.2% | ||
| −3 | 20:00 | 18.9% | |
| 22:00 | 11% | ||
| −5 | 4:00 | 30.2% | |
| −10 | 4:00 | 38.9% | |
| ANN-MLP | −1 | 6:00 | 67.5% |
| 8:00 | 0.8% | ||
| 20:00 | 21.2% | ||
| −2 | 12:00 | 11.7% | |
| −3 | 20:00 | 14.3% | |
| 22:00 | 5.3% | ||
| −6 | 8:00 | 0.3% | |
| −10 | 4:00 | 1.5% | |
| LSTM | −10 | 2:00 | 1.1% |
| ACO | −3 | 20:00 | 25% |
| −7 | 22:00 | 14.29% | |
| −10 | 2:00 | 100% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akhoondzadeh, M. Kalman Filter, ANN-MLP, LSTM and ACO Methods Showing Anomalous GPS-TEC Variations Concerning Turkey’s Powerful Earthquake (6 February 2023). Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3061. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123061
Akhoondzadeh M. Kalman Filter, ANN-MLP, LSTM and ACO Methods Showing Anomalous GPS-TEC Variations Concerning Turkey’s Powerful Earthquake (6 February 2023). Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(12):3061. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123061
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkhoondzadeh, Mehdi. 2023. "Kalman Filter, ANN-MLP, LSTM and ACO Methods Showing Anomalous GPS-TEC Variations Concerning Turkey’s Powerful Earthquake (6 February 2023)" Remote Sensing 15, no. 12: 3061. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123061
APA StyleAkhoondzadeh, M. (2023). Kalman Filter, ANN-MLP, LSTM and ACO Methods Showing Anomalous GPS-TEC Variations Concerning Turkey’s Powerful Earthquake (6 February 2023). Remote Sensing, 15(12), 3061. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123061






