Analysis and Validation of the Aerosol Optical Depth of MODIS Products in Gansu Province, Northwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. In Situ Observation Data
2.2.2. MODIS Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Wavelength Matching
2.3.2. Space-Time Matching
2.3.3. Verification Method
3. Results
3.1. Overall Validation Analysis
3.2. Validation Analysis of Different Underlying Surfaces
3.3. Validation Analysis for Different Seasons
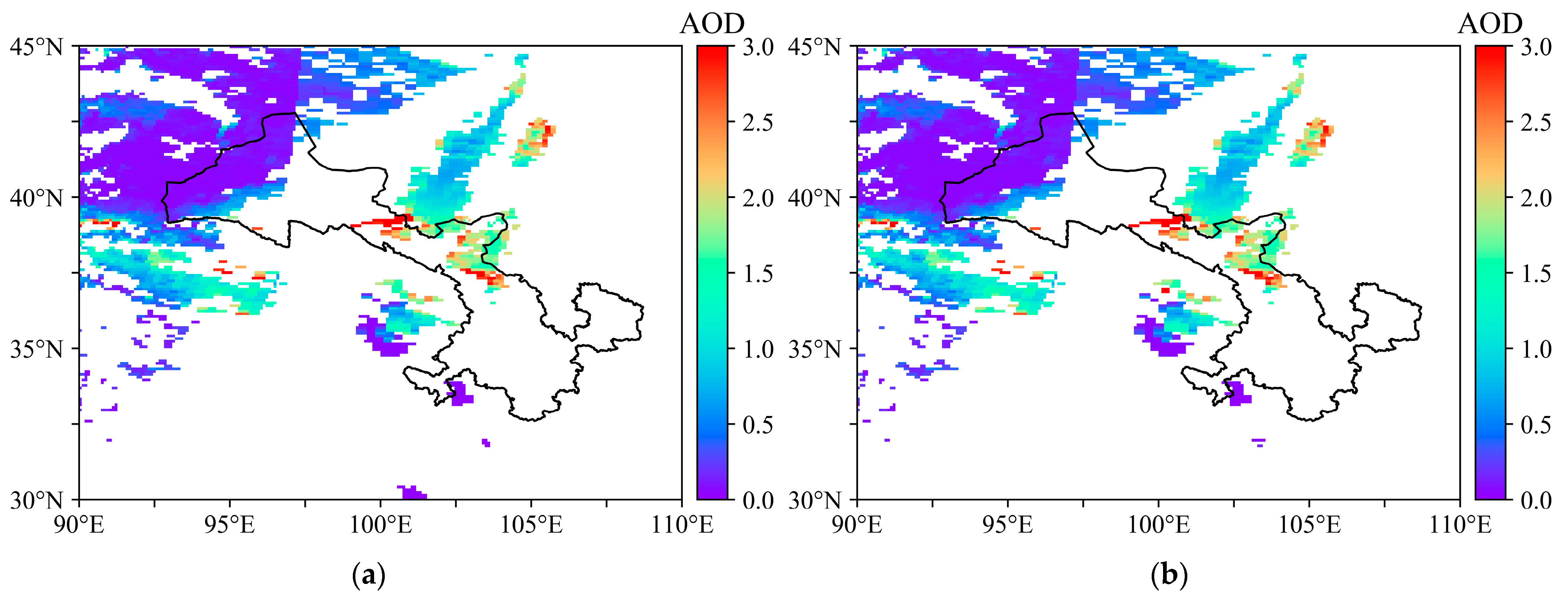
3.4. Comparison of MODIS Product Images during Typical Polluted Atmospheric Conditions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The spatial sampling windows of the DB algorithm and the DB–DT combined algorithm of MODIS C6 AOD are more representative of the AOD values in Gansu Province when set at 30 km × 30 km, and the inversion accuracy of the DB algorithm dataset for AOD in this region is better than that of the DB–DT combined algorithm dataset on the whole. The inversion accuracy is highest when the spatial sampling window of the DB algorithm AOD is set at 30 km × 30 km, and the lowest inversion accuracy is with the DB–DT combined algorithm AOD with the sampling window set at 70 km × 70 km. The dynamic database of surface reflectance and the improved cloud pollution image element procedure established in the DB algorithm greatly improve the DB algorithm AOD inversion accuracy.
- (2)
- In the comparison of the inversion effect of different sub-surfaces, the MODIS C6 DB algorithm AOD product still maintains high inversion accuracy, especially when the spatial sampling window is set at 30 km × 30 km. The DB algorithm is almost unaffected by the surface differences in inversion accuracy.
- (3)
- From the seasonal analysis, it can be seen that the DB algorithm has less seasonal variability in the AOD inversion accuracy in Gansu and has inversion advantages in spring, autumn and winter, while the DB–DT combined algorithm has a better inversion effect than the DB algorithm only in winter. The inversion effect of both algorithms on AOD is influenced by the spatial sampling window setting.
- (4)
- From the distribution of MODIS AOD product images during typical polluted atmospheric conditions, we can see that both the DB algorithm AOD of MODIS C6 and the DB–DT combined algorithm AOD can monitor the distribution characteristics of AOD in northwest and central Gansu, but the monitoring effect in southeast Gansu is poor; meanwhile, there is a discontinuity of AOD distribution in northwest Gansu.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- King, M.D.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Menzel, W.P.; Tanre, D. Remote sensing of cloud, aerosol, and water vapor properties from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (MODIS). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 2–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.; Kaufman, Y.; Nakajima, T. Remote sensing of tropospheric aerosols from space: Past, present and future. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 80, 2229–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.F.; Zhou, X.J.; Li, W.L. Advances in the study of atmosphere aerosol radiative forcing and climate change. Adv. Earth Sci. 1998, 13, 572–581. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, D.P.; Qian, Y. Decreasing trends in sunshine duration over China for 1954–1998: Indication of increased haze pollution. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 38–1–38–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.B.; Kang, W.M.; Zhao, T.L.; Luo, Y.X.; Duan, C.C.; Chen, J. Long-term trends in sunshine duration over Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau in Southwest China for 1961–2005. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L15707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Li, F.; Ramana, M.V.; Praveen, P.S.; Kim, D.; Corrigan, C.E.; Nguyen, H.; Stone, E.A.; Schauer, J.J.; Carmichael, G.R. Atmospheric brown clouds: Hemispherical and regional variations in long-range transport, absorption, and radiative forcing. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2007, 112, D22S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, M.; Trüssel, B.; Ohmura, A.; Charles, N.L.; Gert, K.L.; Ellsworth, G.D.; Tsvetkov, A. Global dimming and brightening: An update beyond 2000. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanhill, G. A perspective on global warming, dimming, and brightening. EOS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2007, 88, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.C.; Dickinson, R.E.; Liang, S.L. Clear sky visibility has decreased over land globally from 1973 to 2007. Science 2009, 323, 1468–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Q.; Niu, F.; Fan, J.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y. Long-term impacts of aerosols on the vertical development of clouds and precipitation. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 12, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Wang, T.J.; Shu, L.; Zhuang, B.; Jiang, Z.; Liao, J.; Yin, C. The Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Aerosol-Cloud-Precipitation Interactions during summer in East Asia. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 39, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, K.; Che, H.Z.; Chen, Q.; Zeng, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Long, Q.; Sun, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liao, T. Water vapor variation and the effect of aerosols in China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 165, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Liu, J.; Jiao, D.; Zha, Y.; Cao, S. Evaluation of MODIS DT, DB, and MAIAC Aerosol Products over Different Land Cover Types in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, X.X.; Wu, D.; Brasseur, G. Lung cancer mortality and exposure to atmospheric aerosol particles in Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2375–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, K.; Thomas, W.; Peters, A.; Ries, L.; Cyrys, J. Influences of the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull volcanic plume on air quality in the northern Alpine region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 8555–8575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gao, X.M.; Xie, Z.Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, W. Spatio-temporal characteristics of aerosol optical depth over Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei-Shanxi-Shandong region during 2000–2013. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2015, 35, 1506–1511. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.F.; Ye, H. Monitoring the changes of urban heat island seasonal dynamics in the process of urbanization by remote sensing. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2009, 18, 1817–1821. [Google Scholar]
- Twomey, S.A. The Influence of Pollution on the Shortwave Albedo of Clouds. Atmos. Sci. 1977, 34, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofala, J.; Amann, M.; Gyarfas, F.; Schoepp, W.; Boudri, J.C.; Hordijk, L.; Kroeze, C.; Li, J.; Dai, L.; Panwar, T.S. Cost-effective control of SO2 emissions in Asia. J. Environ. Manag. 2004, 72, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Dai, J.; Yu, X.; Yao, Z.; Xu, X.; Yang, X.; Du, C. Inverse relations between amounts of air pollution and orographic precipitation. Science 2007, 315, 1396–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T. AERONET-A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xia, X.; Goloub, P.; Holben, B.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.C.; Wang, H.; Blarel, L.; et al. Ground-based aerosol climatology of China: Aerosol optical depths from the China aerosol remote sensing network (CARSNET) 2002–2013. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 7619–7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Li, C.; Tang, X.; Li, H.; Geng, F.; Wu, Y. Validation of MODIS derived aerosol optical depth over the Yangtze River Delta in China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 8, 1649–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, X.X.; Qu, J.J.; Che, H. Validation of MODIS aerosol optical depth product over China using CARSNET measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5970–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.X.; Chen, J.; Zheng, X.B.; Zhao, T.L. Climatology of aerosol optical depth over China from recent 10 years of MODIS remote sensing data. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2012, 21, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D. The MODIS Aerosol Algorithm, Products, and Validation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 947–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichoku, C.; Remer, L.A.; ECK, T.F. Quantitative evaluation and intercomparison of morning and afternoon Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aerosol measurements from Terra and Aqua. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 10, 454–459. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, R.C.; Leptoukh, G.G.; Kazhn, R.; Zubko, V.; Remer, L.A. A Critical Look at Deriving Monthly Aerosol Optical Depth from Satellite Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2942–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Yoon, S.C.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.Y. Seasonal and monthly variations of columnar aerosol optical properties over East Asia determined from multi-year MODIS, LIDAR and AERONET Sun/Sky radiometer measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 1634–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyewa, Z.D.; Balogun, E.E. Wavelength dependence of aerosol optical depth and the fit of the Angstrom law. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2003, 74, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.C.; Mao, J.T.; Kai-Hon Lau, A. Characteristics of Aerosol Optical Depth Distributions over Sichuan Basin Derived from MODIS Data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2003, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.C.; Mao, J.T.; Kai-Hon Lau, A. Remote Sensing of High Spatial Resolution Aerosol Optical Depth with MODIS Data over Hong Kong. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 29, 335–342. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, J.X.; Li, C.C. Spatial Distributions and Changes of Aerosol Optical Depth over Eastern and Central China. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2010, 46, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Sayer, A.M.; Munchak, L.A.; Hsu, N.C.; Levy, R.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.J. MODIS Collection 6 aerosol products: Comparison between Aqua’s e-Deep Blue, Dark Target, and “merged” data sets, and usage recommendations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 119, 13965–13989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.Z.; Qi, B.; Zhao, H.; Xia, X.; Philippe, G.; Oleg, D.; Victor, E.; Emilio, C.A.; Luc, B.; Wu, Y. Aerosol optical properties and instantaneous radiative forcing based on high temporospatial resolution CARSNET ground-based measurements over eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 18, 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Reid, J.S. A decadal regional and global trend analysis of the aerosol optical depth using a data-assimilation grade over-water MODIS and Level2 MISR aerosol products. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10949–10963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.W.; Liu, W.Q.; Zhang, Y.J.; Lu, Y.H.; Liu, J.G.; Zhao, N.J.; Han, D.W.; Liu, W.Q.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y.H. Influence of temperature and relative humidity upon aerosol mass concentrations vertical distributions. J. Grad. Sch. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2007, 24, 619–624. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Peng, Y.; Sun, L. MODIS Collection 6.1aerosol optical depth products over land and ocean: Validation and comparison. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 201, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.B.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.L.; Wang, T.T.; Tao, J.H.; Wang, P.; Ma, S.L.; Xu, B.B.; Fan, M. Validation and analysis of MODIS aerosol optical depth products over China. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 4190–4202. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.Q. Remote Sensing Based Validation of MODIS C6 Aerosol Products in Land Areas of China. Henan Sci. Technol. 2023, 42, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, Y.T.; Zhang, B.; Huang, H. Regional Difference Analysis of Climate Change in Gansu Province in Recent 58 Years and Its Impact on Circulation. Plateau Meteorol. 2022, 41, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Ichoku, C.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Remer, L.A.; Chu, D.A.; Lau, W.K.M. Global aerosol remote sensing from MODIS. Adv. Space Res. 2004, 34, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ångström, A. The parameters of atmospheric turbidity. Tellus 1964, 16, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichoku, C.; Chu, D.A.; Mattoo, S.M. A spatio-temporal approach for global validation and analysis of MODIS aerosol products. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, MOD121–MOD124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Remer, L.A.; Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S. Validation of MODIS 3 km land aerosol optical depth from NASA’s EOS Terra and Aqua missions. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 3145–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.B.; Zhang, L.; Jiao, S.M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, C. Evaluation of the MODIS aerosol products and analysis of the retrieval errors in China. Plateau Meteorol. 2016, 35, 810–822. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.N.; Wu, S.C.; Xu, F.F.; Wang, Z.; Tao, S.; Ma, J.J. Comparison and Analysis of Three Versions of MODIS Aerosol Product in China Region. J. Atmos. Environ. Opt. 2016, 11, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.Y.; Bao, Y.S.; Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L. Comparison of FY-3A/MERSI, MODIS C5.1, C6 and AERONET aerosol optical depth in China. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2018, 76, 449–460. [Google Scholar]
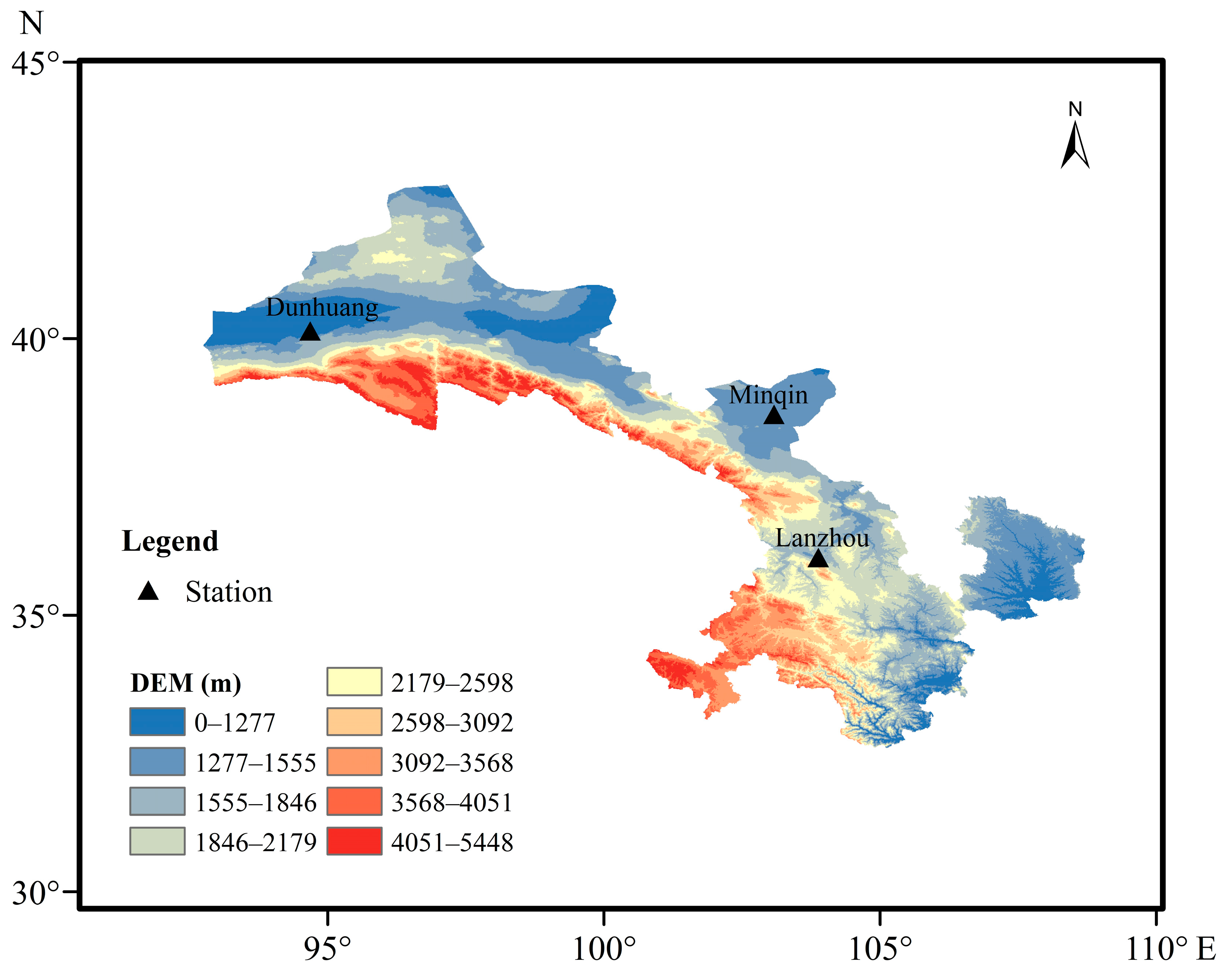

| Stations | Longitude & Latitude | Elevation |
|---|---|---|
| Lanzhou | 36.04° N, 103.88° E | 1517.2 m |
| Dunhuang | 40.14° N, 94.68° E | 1137.5 m |
| Minqin | 38.63° N, 103.08° E | 1367.5 m |
| Stations | Sampling Window | DB | DB–DT Combined | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | RMSE | N | R | RMSE | N | ||
| Lanzhou | 30 km × 30 km | 0.929 | 0.179 | 237 | 0.884 | 0.193 | 254 |
| 50 km × 50 km | 0.882 | 0.183 | 273 | 0.858 | 0.187 | 282 | |
| 70 km × 70 km | 0.837 | 0.192 | 286 | 0.878 | 0.199 | 296 | |
| 90 km × 90 km | 0.879 | 0.190 | 298 | 0.832 | 0.200 | 303 | |
| Dunhuang | 30 km × 30 km | 0.929 | 0.171 | 364 | 0.920 | 0.177 | 364 |
| 50 km × 50 km | 0.914 | 0.181 | 386 | 0.919 | 0.178 | 387 | |
| 70 km × 70 km | 0.887 | 0.183 | 416 | 0.887 | 0.188 | 418 | |
| 90 km × 90 km | 0.883 | 0.180 | 418 | 0.906 | 0.179 | 422 | |
| Minqin | 30 km × 30 km | 0.933 | 0.182 | 323 | 0.929 | 0.184 | 324 |
| 50 km × 50 km | 0.917 | 0.188 | 352 | 0.916 | 0.198 | 354 | |
| 70 km × 70 km | 0.898 | 0.197 | 361 | 0.877 | 0.205 | 366 | |
| 90 km × 90 km | 0.905 | 0.191 | 372 | 0.921 | 0.180 | 371 | |
| Seasons | DB | |||||||||||
| 30 km × 30 km | 50 km × 50 km | 70 km × 70 km | 90 km × 90 km | |||||||||
| R | RMSE | N | R | RMSE | N | R | RMSE | N | R | RMSE | N | |
| Spring | 0.938 | 0.161 | 258 | 0.930 | 0.169 | 281 | 0.922 | 0.206 | 292 | 0.925 | 0.200 | 301 |
| Summer | 0.868 | 0.195 | 253 | 0.809 | 0.199 | 269 | 0.730 | 0.226 | 283 | 0.771 | 0.218 | 295 |
| Autumn | 0.846 | 0.170 | 239 | 0.896 | 0.175 | 262 | 0.841 | 0.178 | 277 | 0.840 | 0.175 | 279 |
| Winter | 0.917 | 0.186 | 174 | 0.904 | 0.187 | 199 | 0.833 | 0.203 | 211 | 0.851 | 0.197 | 213 |
| Seasons | DB–DT Combined | |||||||||||
| 30 km × 30 km | 50 km × 50 km | 70 km × 70 km | 90 km × 90 km | |||||||||
| R | RMSE | N | R | RMSE | N | R | RMSE | N | R | RMSE | N | |
| Spring | 0.899 | 0.190 | 261 | 0.901 | 0.202 | 280 | 0.845 | 0.219 | 299 | 0.887 | 0.200 | 301 |
| Summer | 0.828 | 0.275 | 261 | 0.804 | 0.277 | 281 | 0.683 | 0.225 | 295 | 0.817 | 0.271 | 300 |
| Autumn | 0.839 | 0.180 | 246 | 0.861 | 0.185 | 262 | 0.819 | 0.201 | 277 | 0.869 | 0.211 | 281 |
| Winter | 0.945 | 0.153 | 174 | 0.934 | 0.172 | 200 | 0.906 | 0.197 | 209 | 0.917 | 0.197 | 214 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, F.; Ma, W.; Wang, S.; Feng, C.; Kong, X.; Liu, H. Analysis and Validation of the Aerosol Optical Depth of MODIS Products in Gansu Province, Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2972. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15122972
Huang F, Ma W, Wang S, Feng C, Kong X, Liu H. Analysis and Validation of the Aerosol Optical Depth of MODIS Products in Gansu Province, Northwest China. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(12):2972. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15122972
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Fangfang, Weiqiang Ma, Suichan Wang, Chao Feng, Xiaoyi Kong, and Hao Liu. 2023. "Analysis and Validation of the Aerosol Optical Depth of MODIS Products in Gansu Province, Northwest China" Remote Sensing 15, no. 12: 2972. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15122972
APA StyleHuang, F., Ma, W., Wang, S., Feng, C., Kong, X., & Liu, H. (2023). Analysis and Validation of the Aerosol Optical Depth of MODIS Products in Gansu Province, Northwest China. Remote Sensing, 15(12), 2972. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15122972








