Improved Identification for Point-Distributed Coded Targets with Self-Adaption and High Accuracy in Photogrammetry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Previous Work
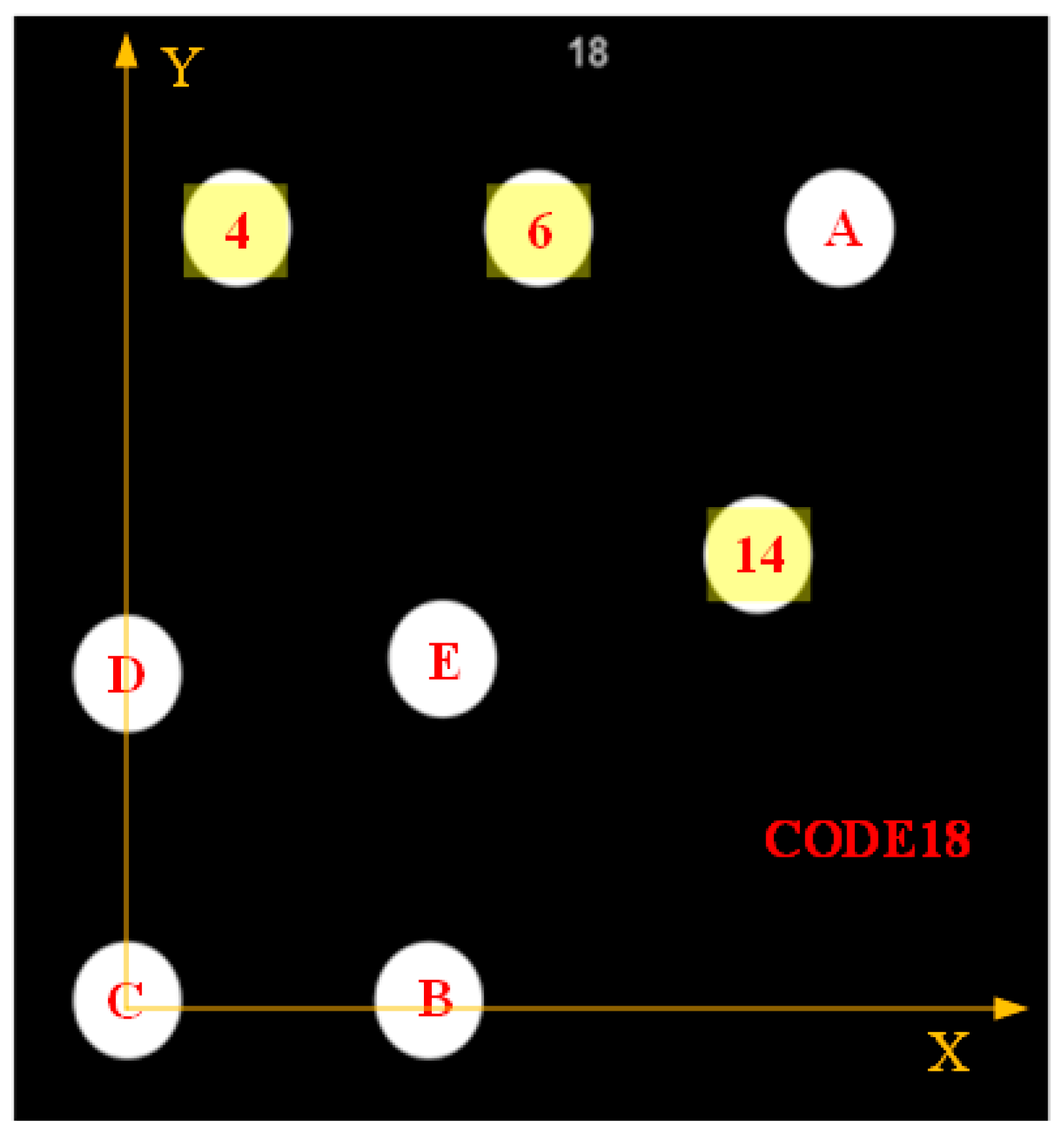
2.1.1. The Structure of a GCT
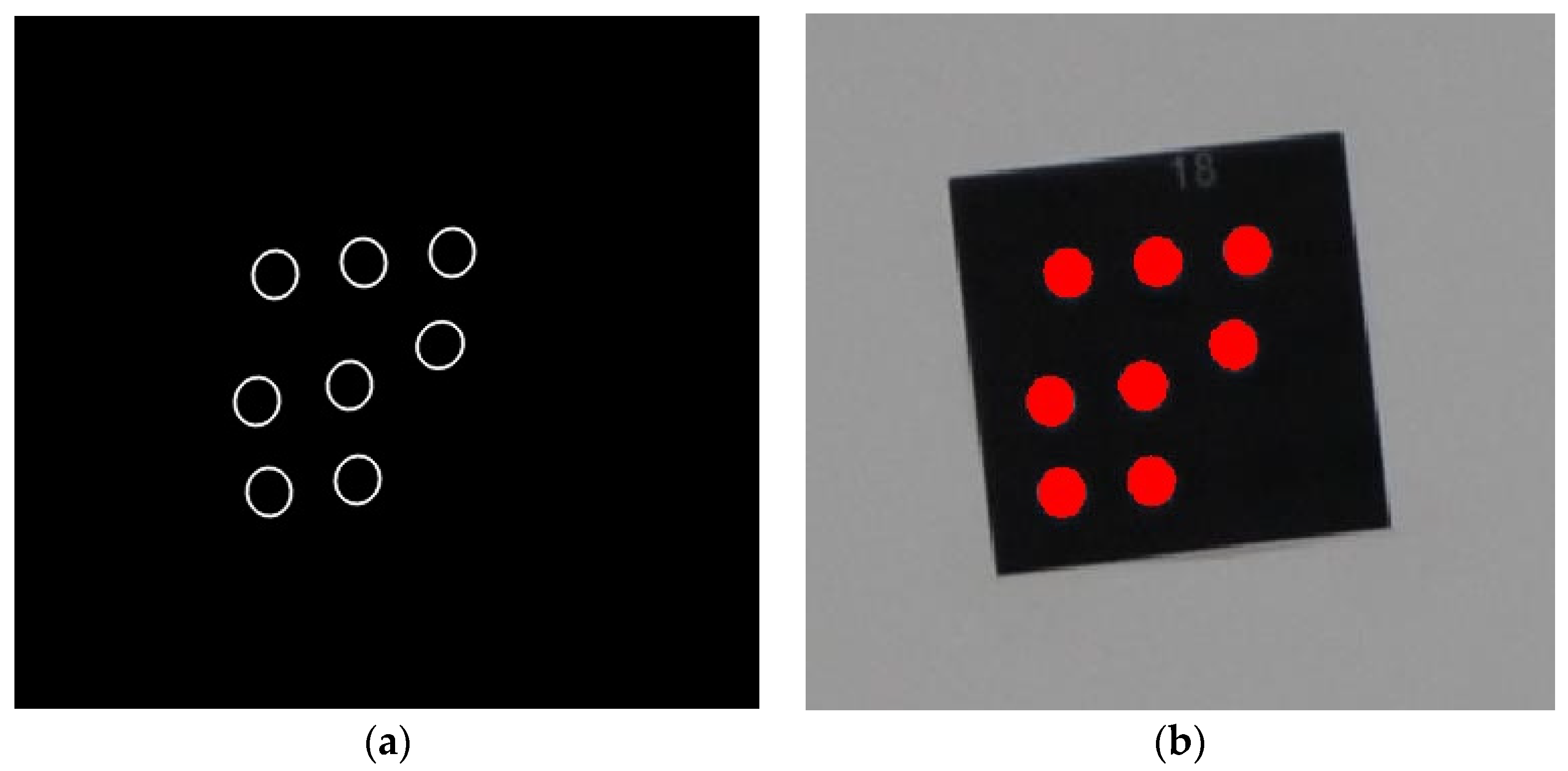
2.1.2. Round Target Extraction and Center Positioning
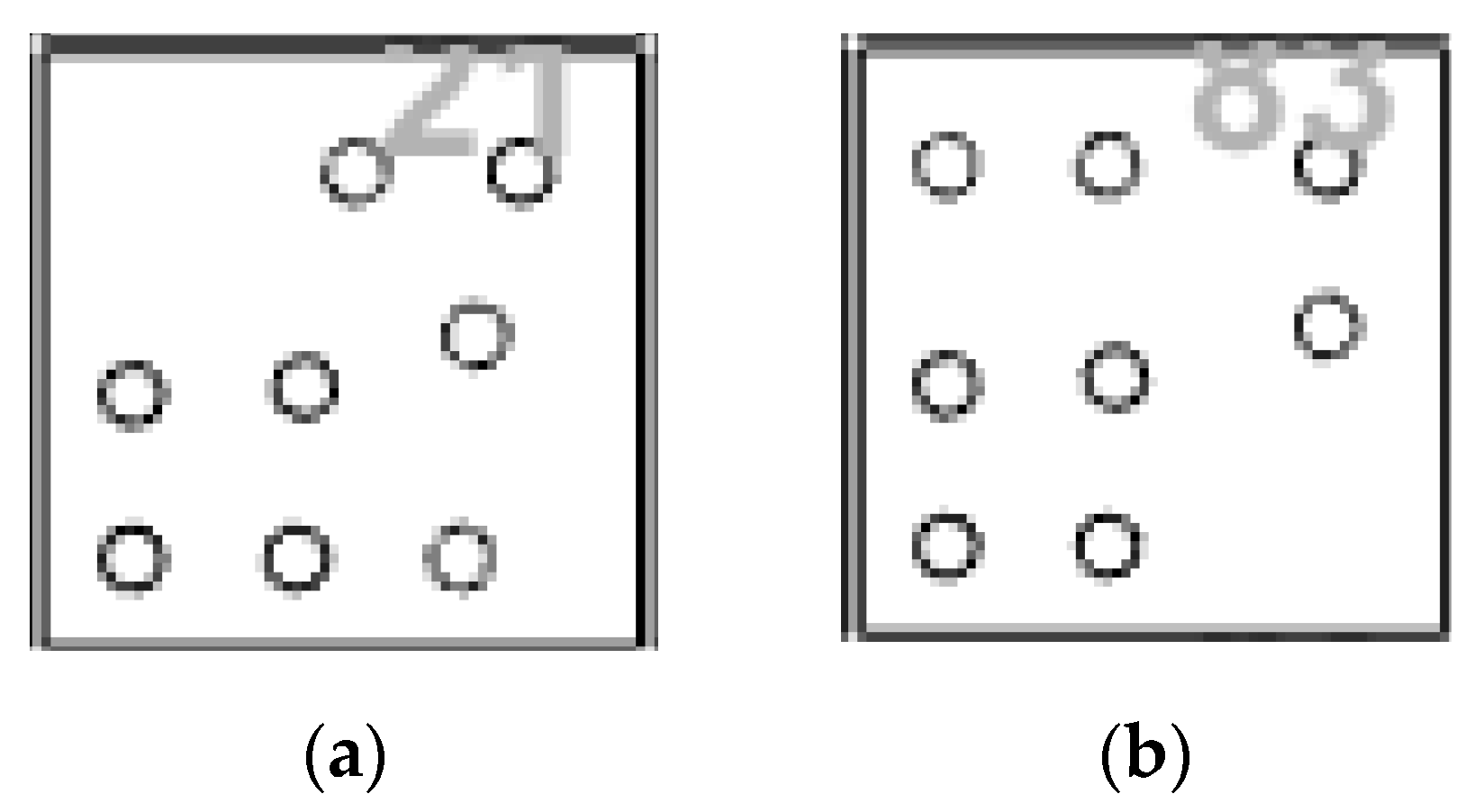
2.1.3. Template Point Recognition
2.1.4. Decoding Point Determination
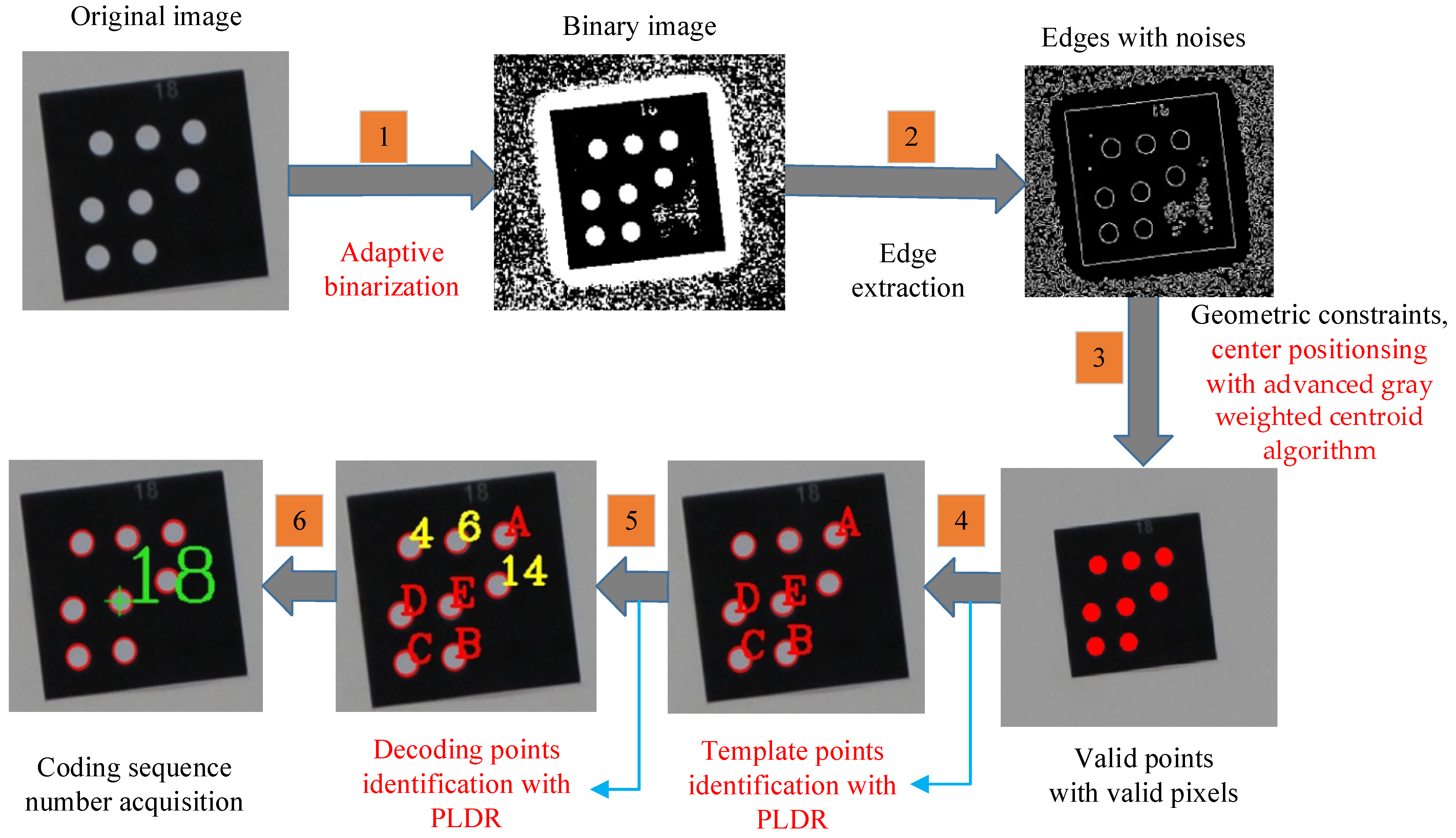
2.1.5. Identification Process of GCTs
2.1.6. Existing Problems
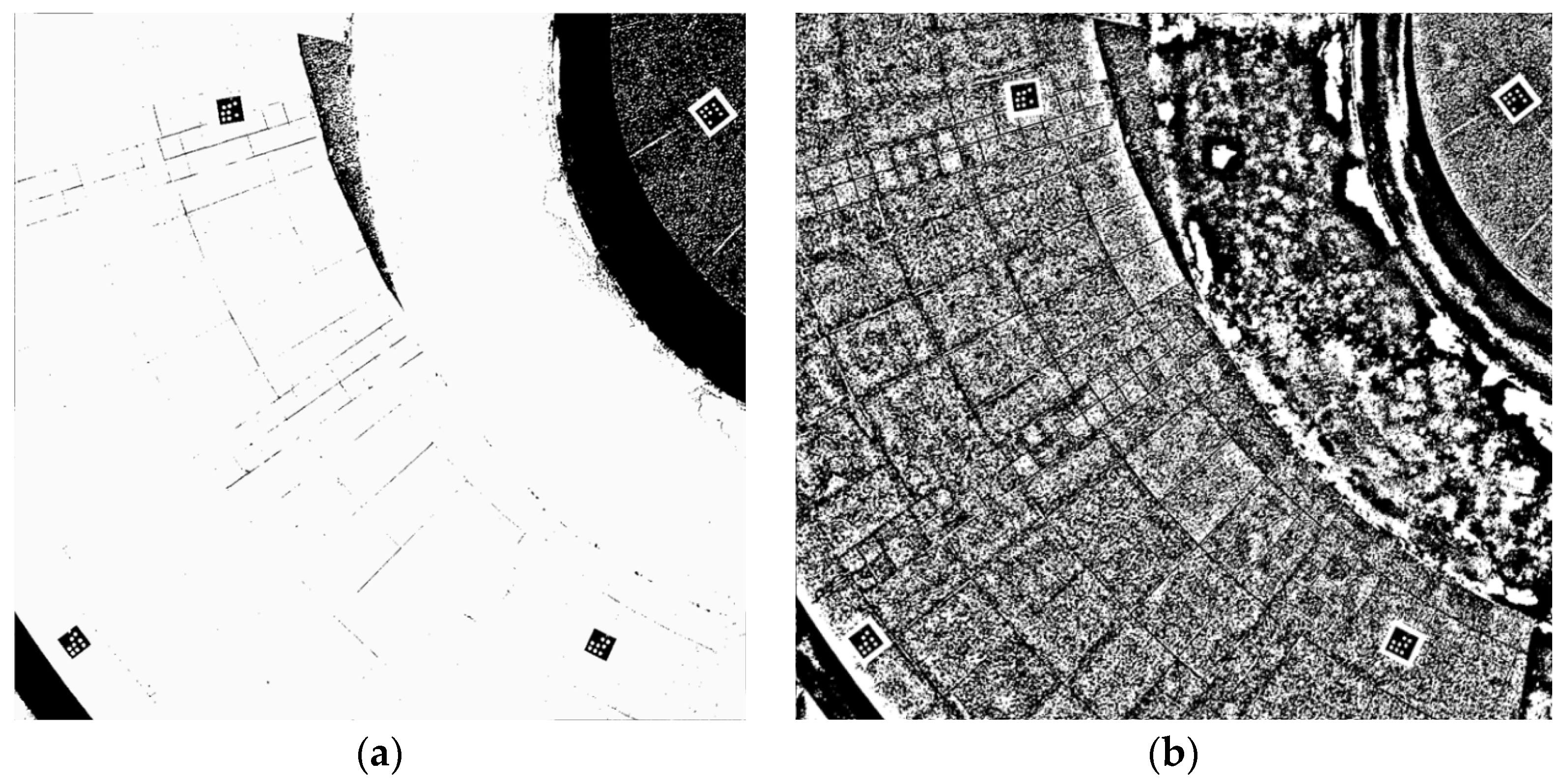
2.2. Adaptive Binarization for Edge Detection
2.3. More Precise Ellipse-Center Localization
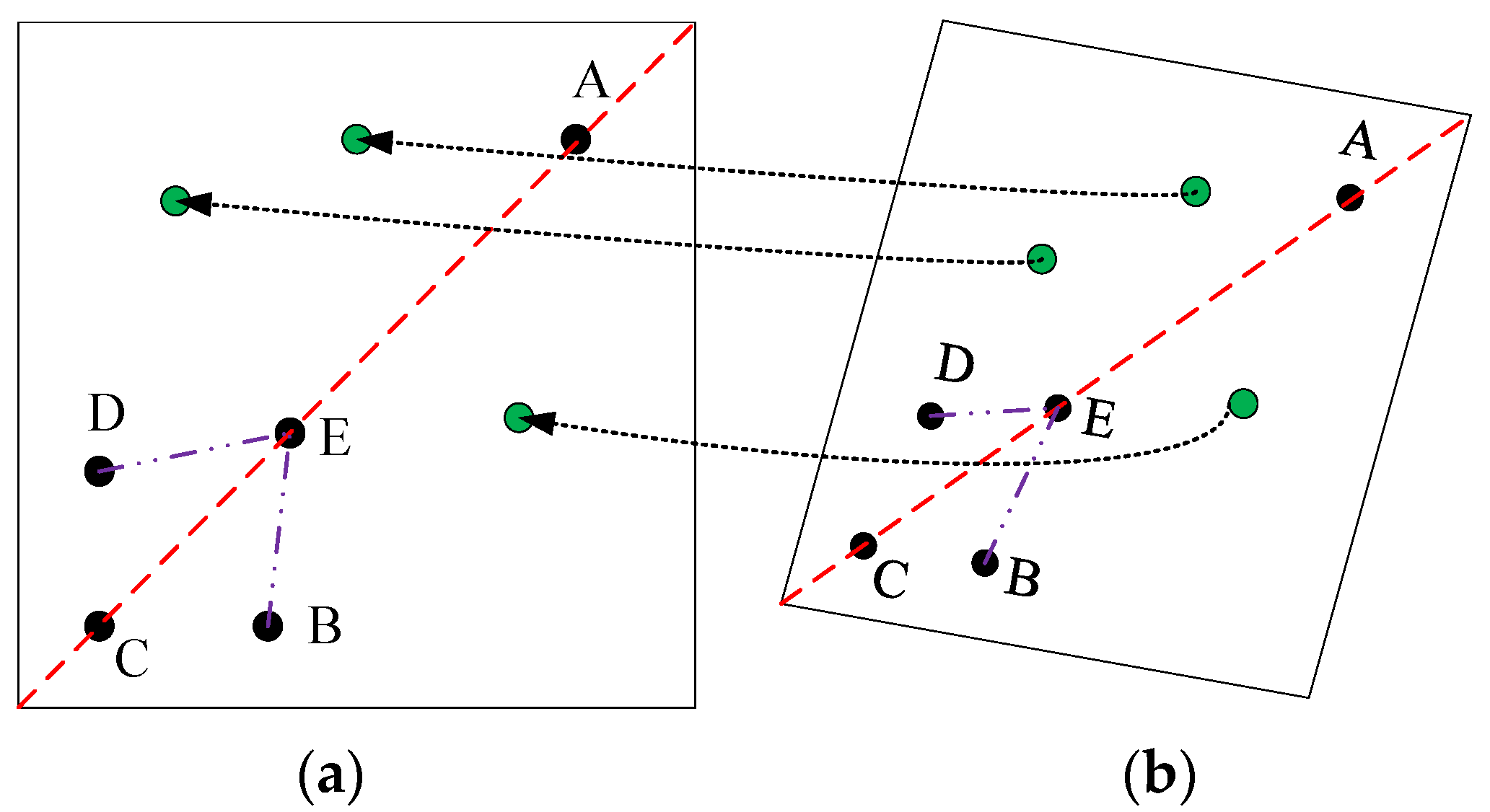
2.4. The Invariance Theory of PLDR
2.4.1. The Invariance of the PLDR for Line Matching
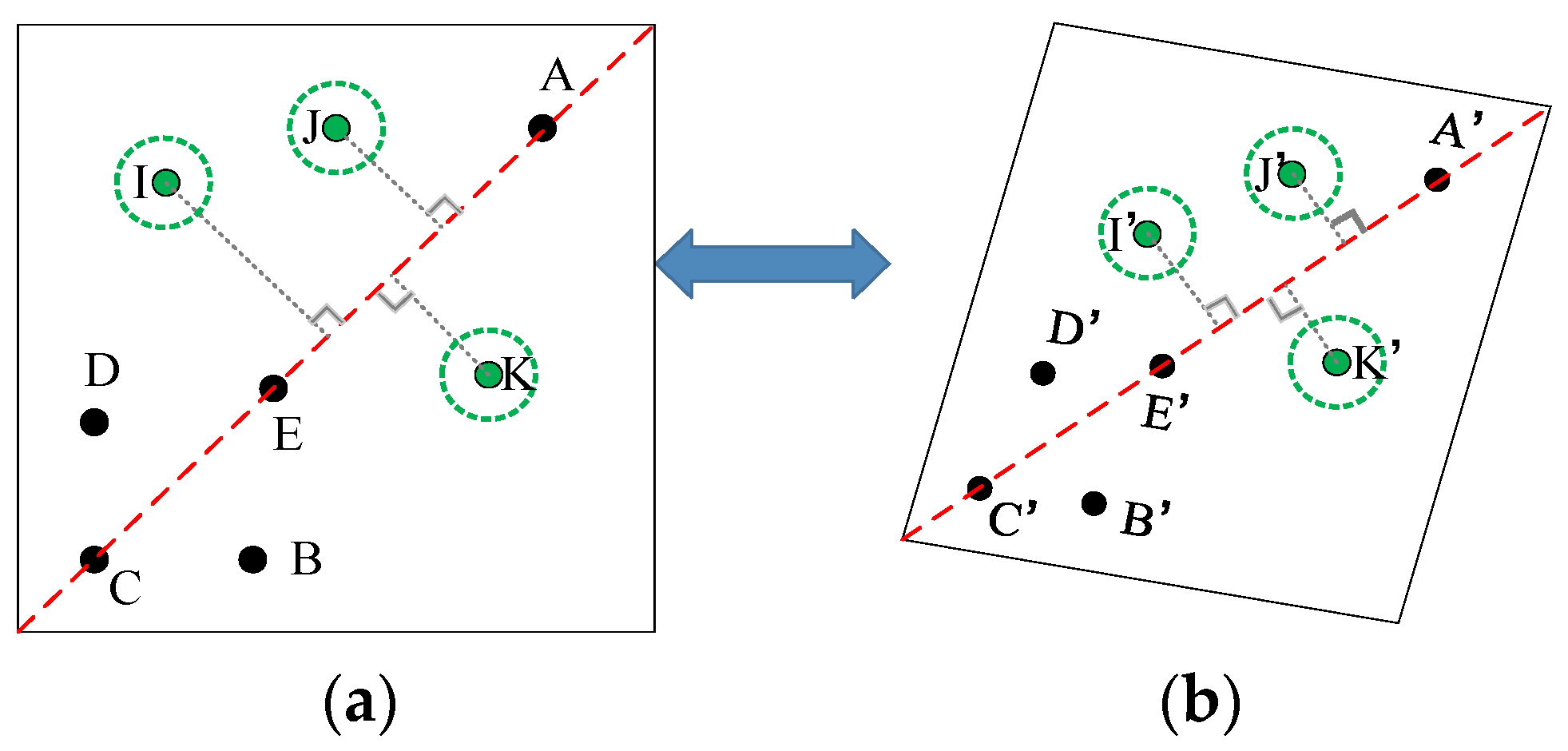
2.4.2. The Invariance of the PLDR for Template Point Recognition
2.4.3. The Invariance of the PLDR for Decoding Point Determination
2.5. The Identification Process of the Improved IPCT
3. Results
3.1. Experiment for Indoor Scenes
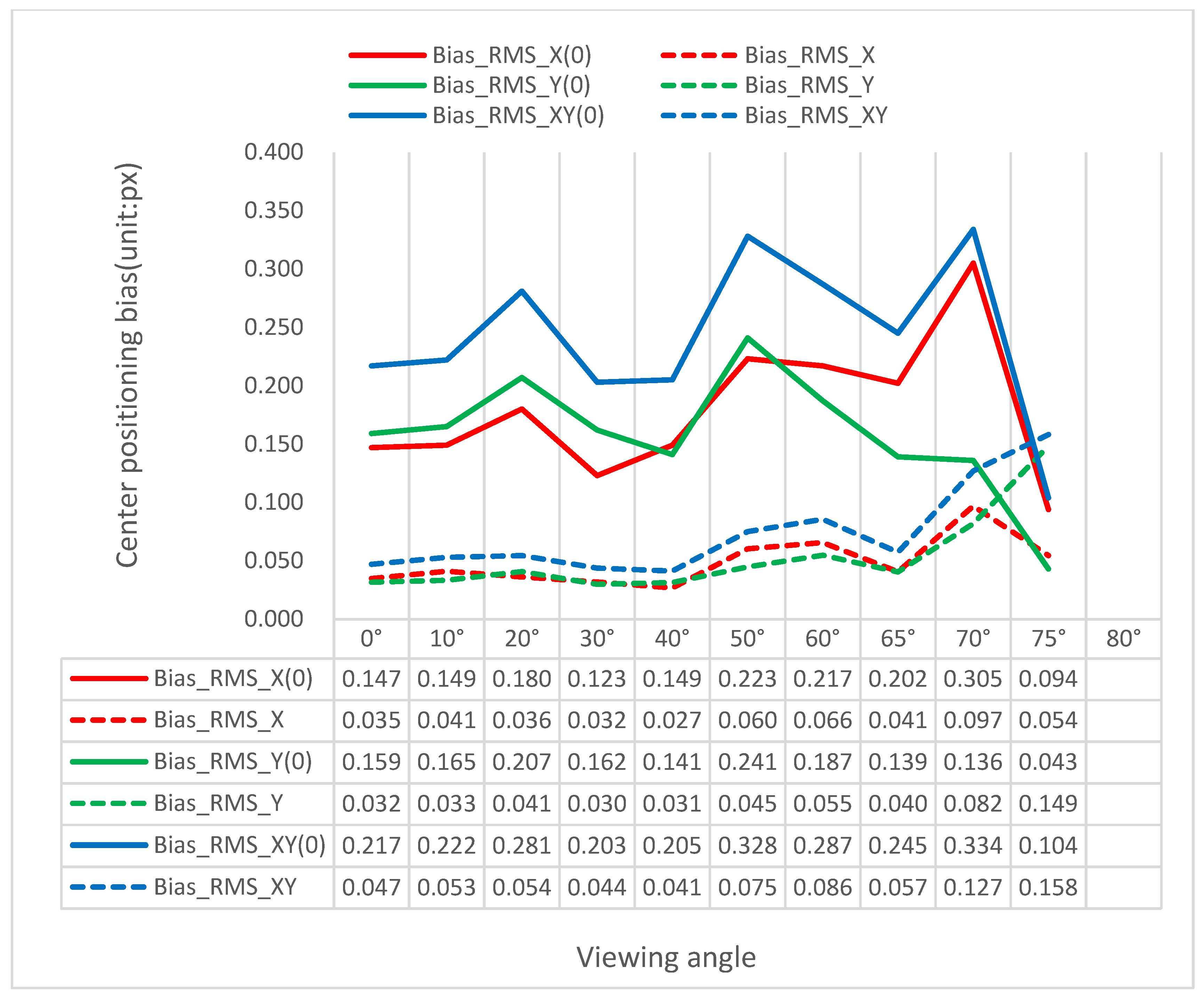
3.1.1. Experiments with Different Viewing Angles of Medium-Sized GCTs
3.1.2. Experiments with Small-Sized GCTs
3.1.3. Experiments with Mixed GCTs
3.2. Experiment for Outdoor Scenes
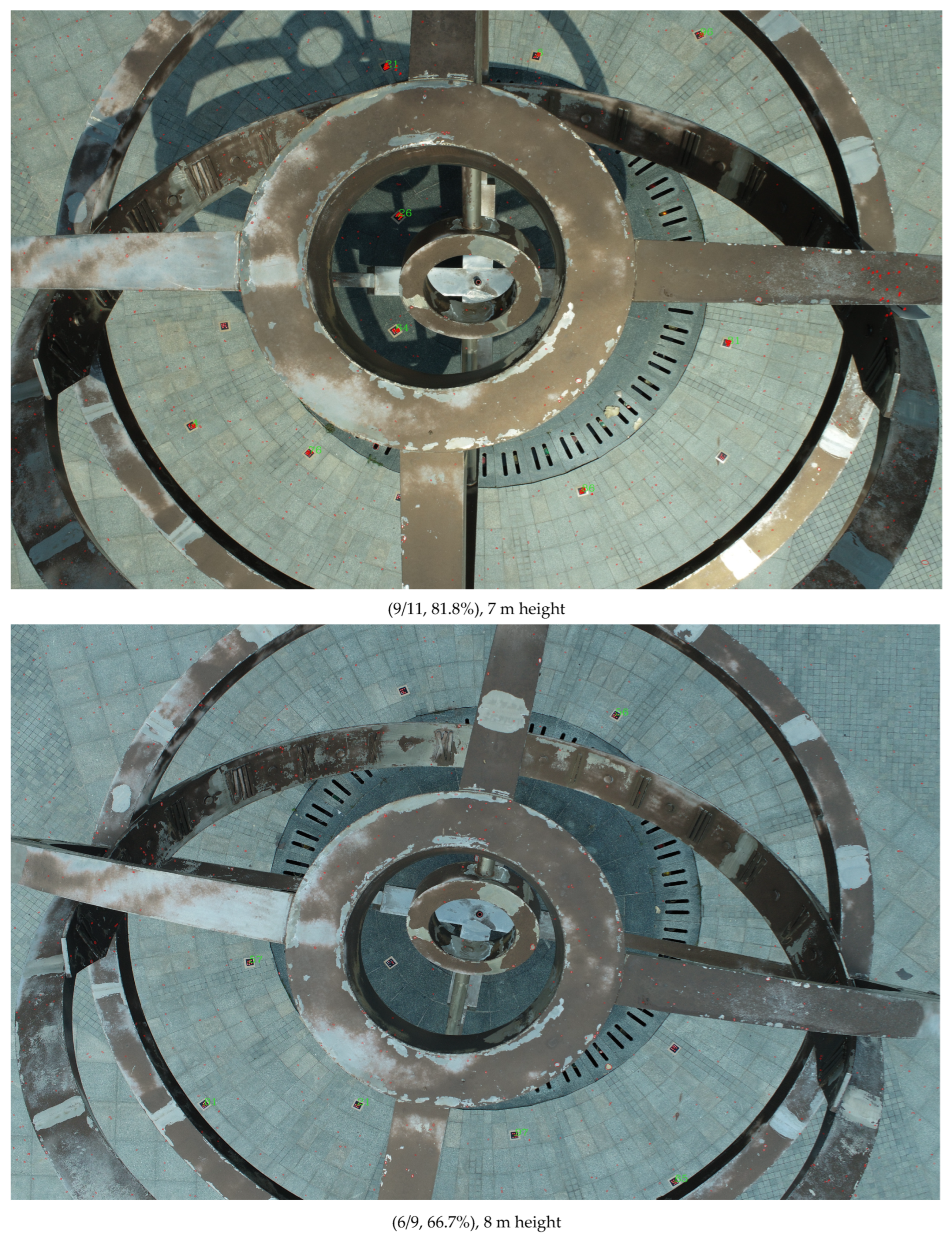
3.3. Experiment for UAV Scenes
4. Discussion
4.1. The Precision of Ellipse-Center Localization
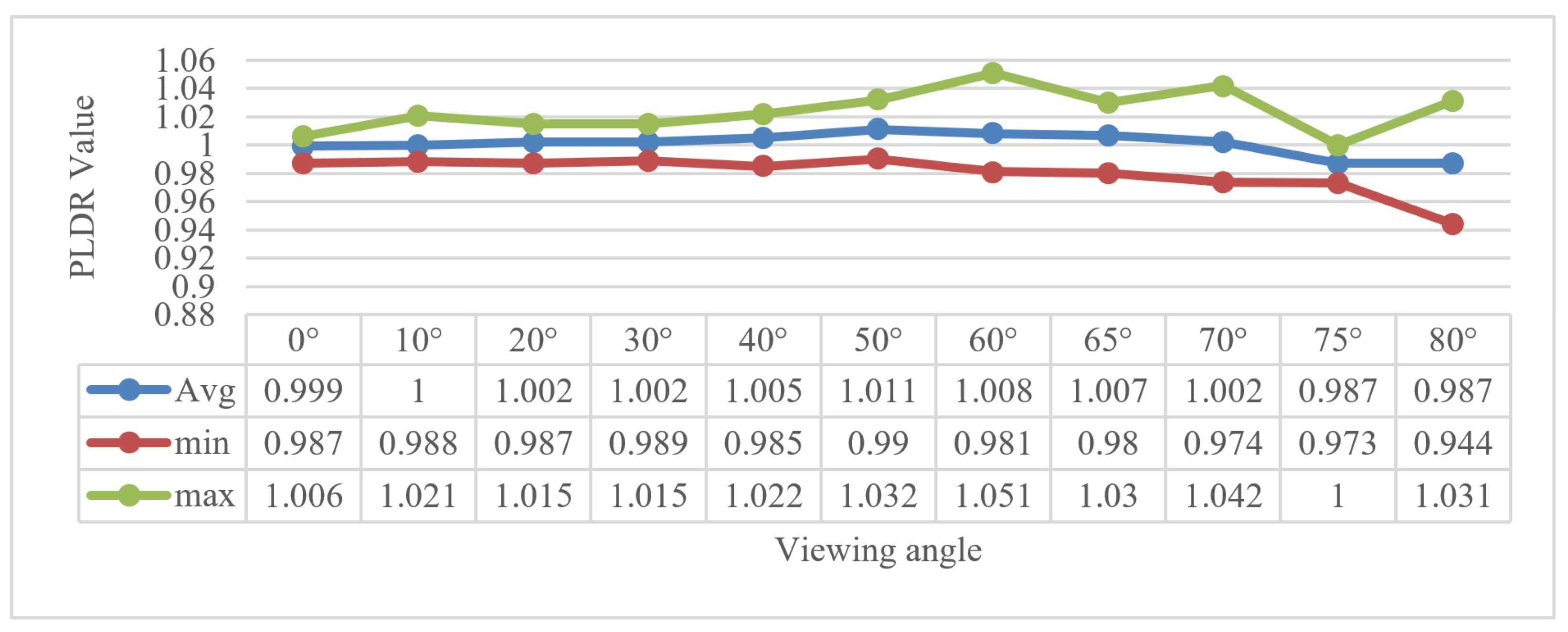
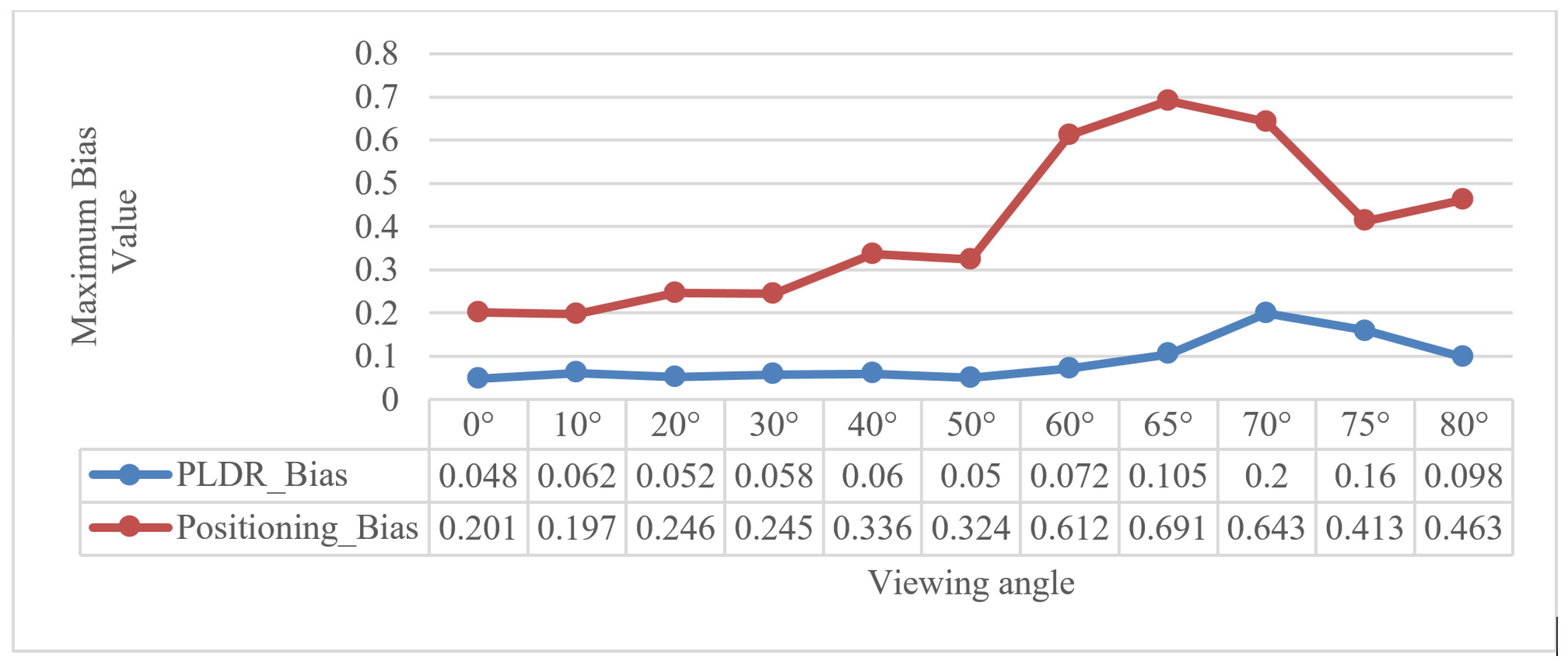
4.2. The Robustness of the PLDR
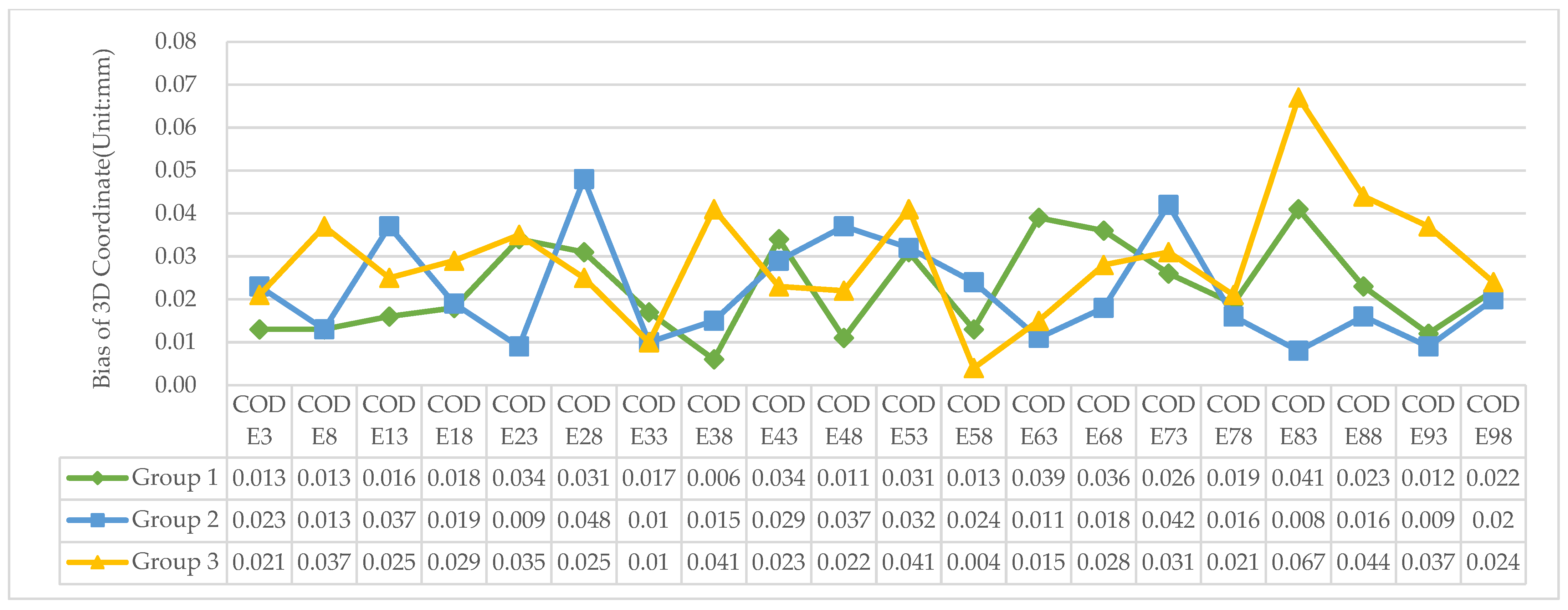
4.3. The Precision Validation of 3D Measurement
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GSI | Geodetic Systems Inc. |
| V-STARS | Video-simultaneous triangulation and resection system |
| SCT | Schneider circular coded target |
| GCT | GSI-coded target |
| IPCT | Identification for point-distributed coded target |
| I-IPCT | Improved IPCT |
| PLDR | Point–line distance ratio |
| UAV | Unmanned aerial vehicle |
| SIFT | Scale invariant feature transform |
| P2-Invariant | Projective and permutation invariant |
Appendix A





References
- Wang, Y.M.; Yu, S.Y.; Ren, S.; Cheng, S.; Liu, J.Z. Close-range industrial photogrammetry and application: Review and outlook. AOPC 2020 Opt. Ultra Precis. Manuf. Test. 2020, 11568, 152–162. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, M.; Zakariyaeinejad, Z.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Ahmadabadian, A.H. A new method for automatic and accurate coded target recognition in oblique images to improve augmented reality precision. Trans. GIS 2022, 26, 1509–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Guo, Y.; Wang QLiu, Y.; Liu, J.; Song, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, H. A Novel Capacity Expansion and Recognition Acceleration Method for Dot-dispersing Coded Targets in Photogrammetry. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 33, 125016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Su, X.; Guo, X.; Suo, T.; Yu, Q. A Novel Concentric Circular Coded Target, and Its Positioning and Identifying Method for Vision Measurement under Challenging Conditions. Sensors 2021, 21, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan-Ley, M.; Olague, G.; Altamirano-Gomez, G.E.; Clemente, E. Self-localization of an uncalibrated camera through invariant properties and coded target location. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, D239–D245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Fang, S.; Kong, B.; Li, Y. Design of a color coded target for vision measurements. Optik 2014, 125, 3727–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Zhang, X.; Fayek, S.; Yin, Z. A table method for coded target decoding with application to 3-D reconstruction of soil specimens during triaxial testing. Acta Geotech. 2021, 16, 3779–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurník, J.; Zatočilová, A.; Paloušek, D. Circular coded target system for industrial applications. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2021, 32, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, V.; Khosravi, M.; Ahmadi, M.; Noori, N.; Haghshenas, S.; Hosseininaveh, A.; Varshosaz, M. The performance evaluation of multi-image 3D reconstruction software with different sensors. Measurement 2018, 120, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.T.; Sinnreich, K. Optical 3-D measurement systems for quality control in industry. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1993, 29, 56–59. Available online: http://www.isprs.org/proceedings/xxix/congress/part5/56_xxix-part5.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Fraser, C.S. Innovations in Automation for Vision Metrology Systems. Photogramm. Rec. 1997, 15, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.agisoft.com/features/professional-edition/ (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- Liba, N.; Metsoja, K.; Järve, I.; Miljan, J. Making 3D models using close-range photogrammetry: Comparison of cameras and software. Int. Multidiscip. Sci. GeoConf. SGEM 2019, 19, 561–568. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.D.; Dold, J. V-STARS—A system for digital industrial photogrammetry. In Optical 3-D Measurement Techniques III; Gruen, A., Kahmen, H.Ž., Eds.; Wichmann Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 12–21. Available online: http://gancell.com/papers/S%20Acceptance%20Test%20Results%20-%20metric%20version.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2022).
- Why V-STARS? Available online: https://www.geodetic.com/v-stars/ (accessed on 27 October 2022).
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, X.; Zhang, H. A Robust and Effective Identification Method for Point-Distributed Coded Targets in Digital Close-Range Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Wu, F.; Hu, Z. Robust line matching through line–point invariants. Pattern Recognit. 2012, 45, 794–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Baig, M.H.A.; Wang, G.; He, L.; Cui, T. Line matching of wide baseline images in an affine projection space. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 41, 632–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, W.; Burge, M.J. Scale-Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT). In Digital Image Processing: An Algorithmic Introduction; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 709–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meer, P.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lenz, R. Correspondence of coplanar features through p2-invariant representations. In Proceedings of the Joint European-US Workshop on Applications of Invariance in Computer Vision, Ponta Delgada, Portugal, 9–14 October 1993; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 473–492. [Google Scholar]
- Bergamasco, F.; Albarelli, A.; Torsello, A. Pi-Tag: A fast image-space marker design based on projective invariants. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2012, 24, 1295–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, S.; Akimoto, K.; Ohnishi, Y.; Miura, S. Semi-automated tunnel measurement by vision metrology using coded-targets. In Modern Tunneling Science and Technology, 1st ed.; Adachi, T., Tateyama, K., Kimura, M., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 285–288. [Google Scholar]
- Tushev, S.; Sukhovilov, B.; Sartasov, E. Robust coded target recognition in adverse light conditions. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Industrial Engineering, Applications and Manufacturing (ICIEAM), Moscow, Russia, 15–18 May 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kanatani, K.; Sugaya, Y.; Kanazawa, Y. Ellipse Fitting for Computer Vision: Implementation and Applications. Synth. Lect. Comput. Vis. 2016, 6, 1–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setan, H.; Ibrahim, M.S. High Precision Digital Close Range Photogrammetric System for Industrial Application Using V-STARS: Some Preliminary Result. In Proceedings of the International Geoinformation Symposium, Bogotá, Colombia, 24–26 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.; Ma, J.; Su, Z.; Li, C. Robust circular marker localization under non-uniform illuminations based on homomorphic filtering. Measurement 2020, 170, 108700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Fan, X.; Luo, Z.; Song, L.; Qiu, T. A Fast Ellipse Detector Using Projective Invariant Pruning. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3665–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, C.S.; Edmundson, K.L. Design and implementation of a computational processing system for off-line digital close-range photogrammetry. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2000, 55, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kharaz, A.A.; Chong, A. Reliability of a close-range photogrammetry technique to measure ankle kinematics during active range of motion in place. Foot 2020, 46, 101763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Ali, F.; Zhou, B.; Li, S.; Yu, Y.; Yang, T.; Liu, X.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, K. A novel approach of efficient 3D reconstruction for real scene using unmanned aerial vehicle oblique photogrammetry with five cameras. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 99, 107804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Lv, L.; Liu, J.; Wan, J. Application of UAV oblique photography in real scene 3D modeling. ISPRS—Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, 43, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniaz, V.V.; Grodzitskiy, L.; Knyaz, V.A. Deep learning for coded target detection. ISPRS—Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, 44, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
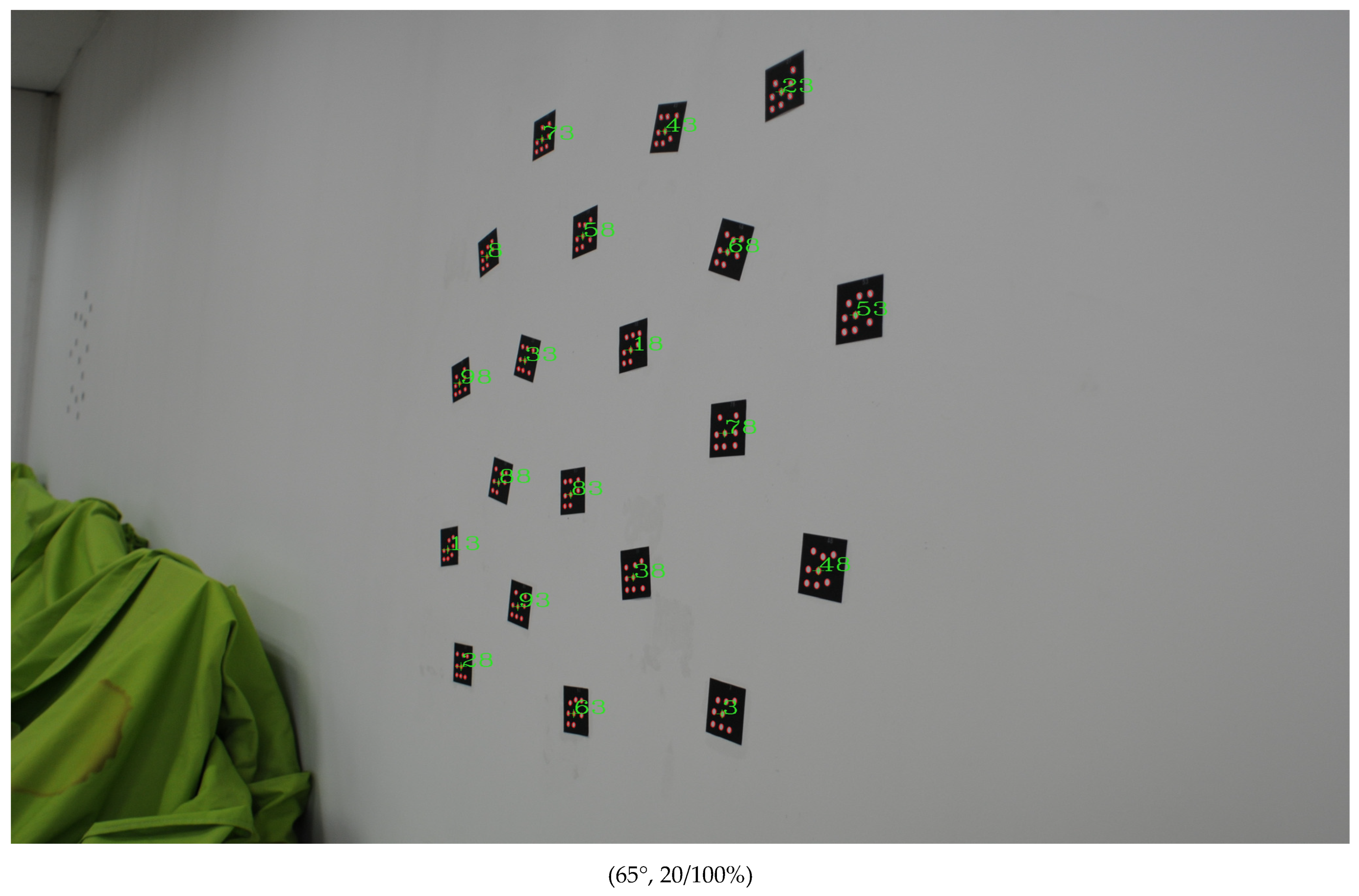









| Test Cases | Accurate Identification Rate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V-STARS | IPCT | I-IPCT | ||
| Indoors with medium-sized GCTs | 0° | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| 10° | 100% | 100% | 100% | |
| 20° | 100% | 100% | 100% | |
| 30° | 100% | 100% | 100% | |
| 40° | 100% | 100% | 100% | |
| 50° | 85% | 100% | 100% | |
| 60° | 75% | 100% | 100% | |
| 65° | 100% | 85% | 100% | |
| 70° | 70% | 65% | 75% | |
| 75° | 80% | 5% | 30% | |
| 80° | 50% | 0% | 10% | |
| Indoors with small-sized GCTs | 0° | 100% | 95% | 100% |
| 30° | 100% | 100% | 100% | |
| 60° | 100% | 55% | 75% | |
| Indoors with mixed GCTs | 0° | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| 30° | 100% | 100% | 100% | |
| 60° | 50% | 100% | 100% | |
| Outdoors | Scene 1 | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Scene 2 | 100% | 100% | 100% | |
| Scene 3 | 90.9% | 90.9% | 100% | |
| UAV | 4 m | 75% | 100% | 100% |
| 7 m | 81.8% | 72.7% | 81.8% | |
| 8 m | 55.6% | 44.4% | 66.7% | |
| Coding | Center Positioning Coordinate (x,y) (Unit: px) | Positioning Bias (Unit: px) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serial Number | V-STARS | The Improved IPCT | |||
| 3 | (2950.418,2222.000) | (2950.430,2222.032) | −0.012 | −0.032 | 0.034 |
| 8 | (1266.945,670.800) | (1266.910,670.769) | 0.035 | 0.031 | 0.047 |
| 13 | (1116.764,1912.218) | (1116.745,1912.251) | 0.019 | −0.033 | 0.038 |
| 18 | (2365.036,1127.382) | (2365.085,1127.405) | −0.049 | −0.023 | 0.054 |
| 23 | (3019.909,412.727) | (3019.936,412.734) | −0.027 | −0.007 | 0.028 |
| 28 | (1307.745,2373.909) | (1307.781,2373.976) | −0.036 | −0.067 | 0.076 |
| 33 | (1650.145,1127.909) | (1650.124,1127.886) | 0.021 | 0.023 | 0.031 |
| 38 | (2470.600,1883.091) | (2470.627,1883.129) | −0.027 | −0.038 | 0.047 |
| 43 | (2463.727,401.327) | (2463.748,401.324) | −0.021 | 0.003 | 0.021 |
| 48 | (3299.764,1770.691) | (3299.834,1770.704) | −0.070 | −0.013 | 0.071 |
| 53 | (3372.509,1097.691) | (3372.512,1097.681) | −0.003 | 0.010 | 0.010 |
| 58 | (2002.491,686.655) | (2002.503,686.621) | −0.012 | 0.034 | 0.036 |
| 63 | (2165.400,2388.618) | (2165.397,2388.648) | 0.003 | −0.030 | 0.030 |
| 68 | (2833.673,856.636) | (2833.734,856.617) | −0.061 | 0.019 | 0.064 |
| 73 | (1645.036,253.364) | (1645.045,253.319) | −0.009 | 0.045 | 0.046 |
| 78 | (2885.182,1407.964) | (2885.242,1407.954) | −0.060 | 0.010 | 0.061 |
| 83 | (2052.600,1632.600) | (2052.636,1632.609) | −0.036 | −0.009 | 0.037 |
| 88 | (1510.909,1611.400) | (1510.934,1611.455) | −0.025 | −0.055 | 0.060 |
| 93 | (1728.127,2075.018) | (1728.090,2075.064) | 0.037 | −0.046 | 0.059 |
| 98 | (1108.182,1199.545) | (1108.207,1199.545) | −0.025 | 0.000 | 0.025 |
| RMSE | 0.035 | 0.032 | 0.047 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Cui, X.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y. Improved Identification for Point-Distributed Coded Targets with Self-Adaption and High Accuracy in Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2859. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112859
Liu Y, Cui X, Wang Q, Sun Y. Improved Identification for Point-Distributed Coded Targets with Self-Adaption and High Accuracy in Photogrammetry. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(11):2859. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112859
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yang, Ximin Cui, Qiang Wang, and Yanbiao Sun. 2023. "Improved Identification for Point-Distributed Coded Targets with Self-Adaption and High Accuracy in Photogrammetry" Remote Sensing 15, no. 11: 2859. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112859
APA StyleLiu, Y., Cui, X., Wang, Q., & Sun, Y. (2023). Improved Identification for Point-Distributed Coded Targets with Self-Adaption and High Accuracy in Photogrammetry. Remote Sensing, 15(11), 2859. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112859






