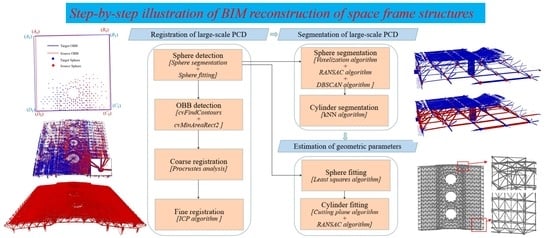
Semi-Automated BIM Reconstruction of Full-Scale Space Frames with Spherical and Cylindrical Components Based on Terrestrial Laser Scanning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Relevant Work
2.1. PCD Registration
2.2. PCD Segmentation
2.3. 3D Reconstruction of Structural Components
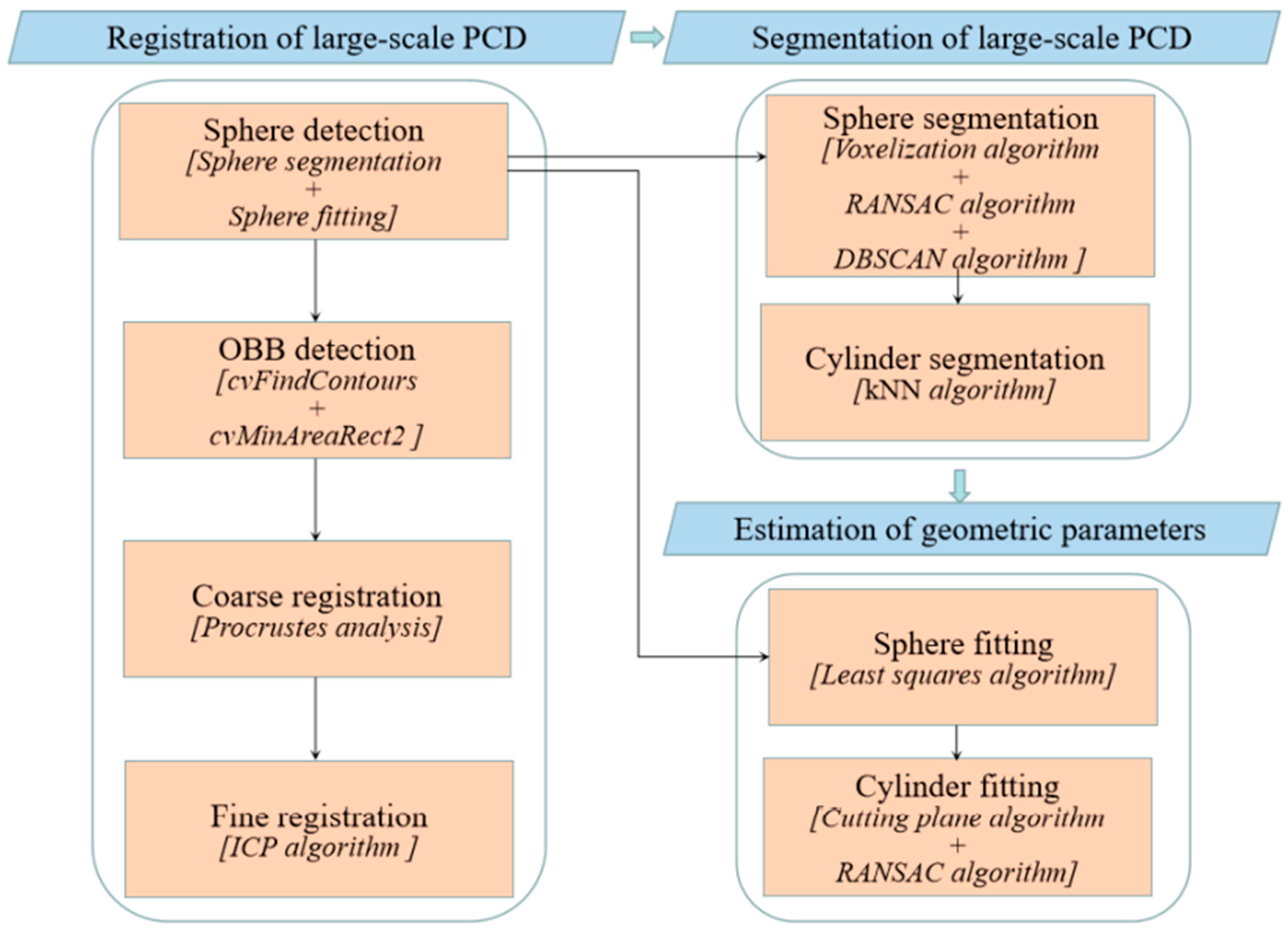
3. Methodology
3.1. Registration of Large-Scale PCD
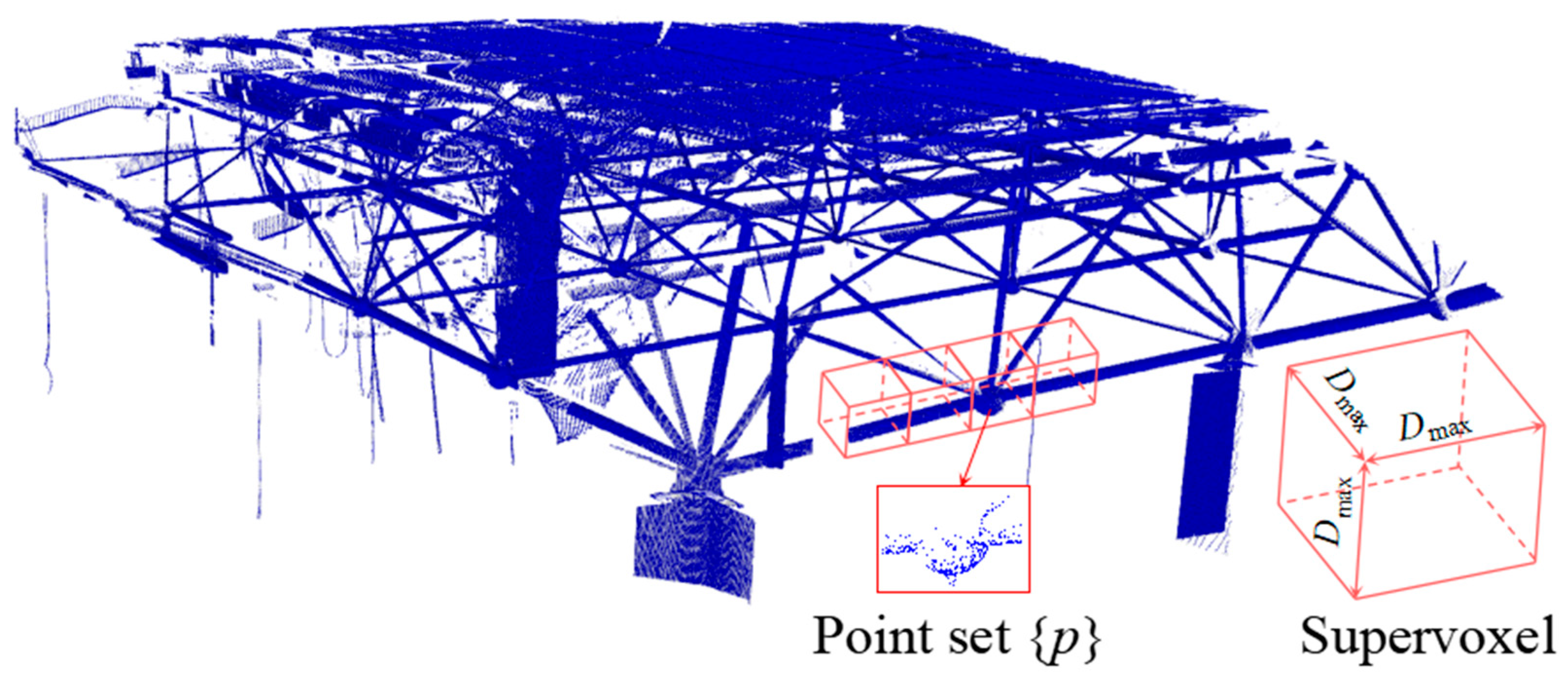
3.2. Segmentation of Large-Scale PCD
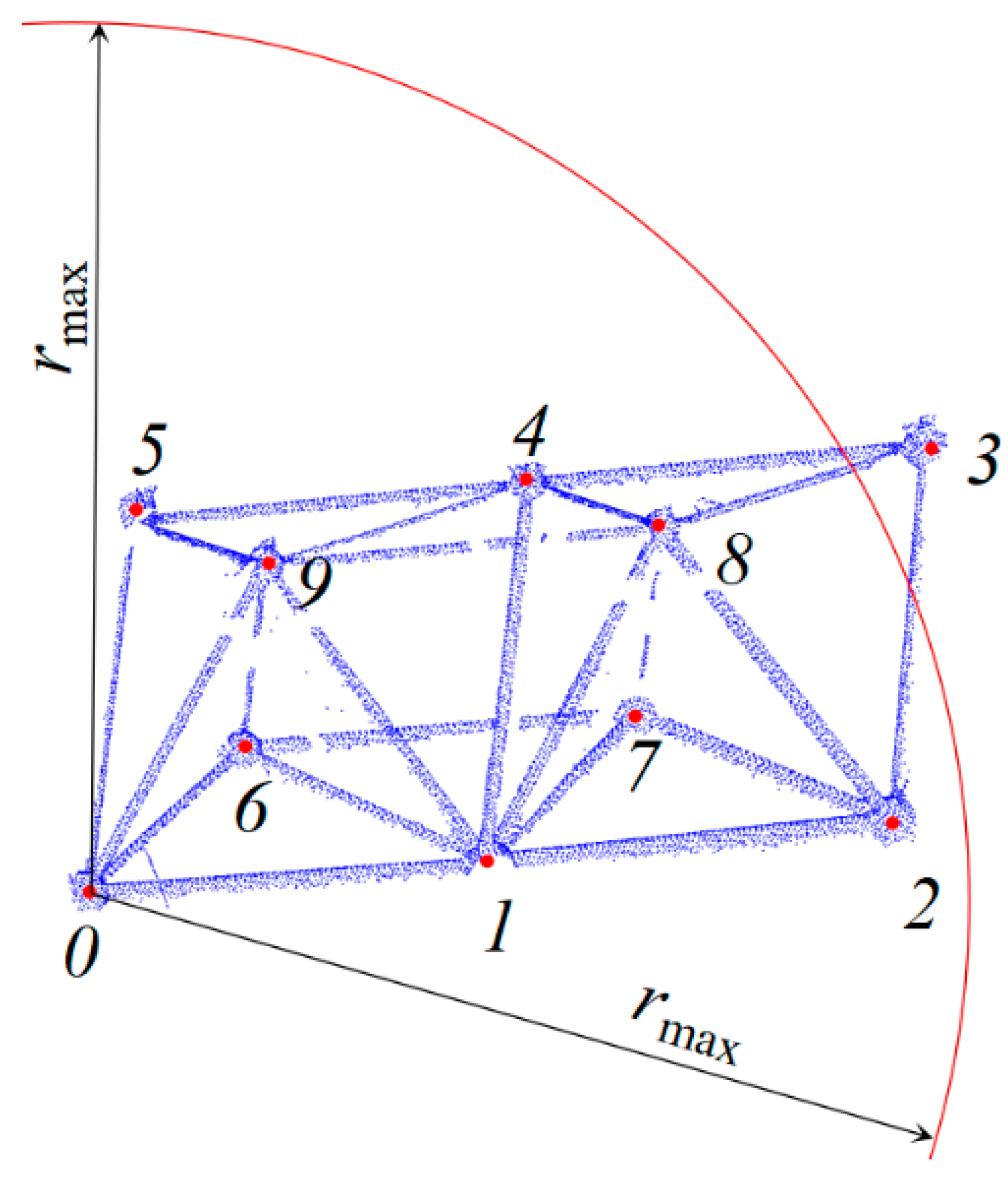
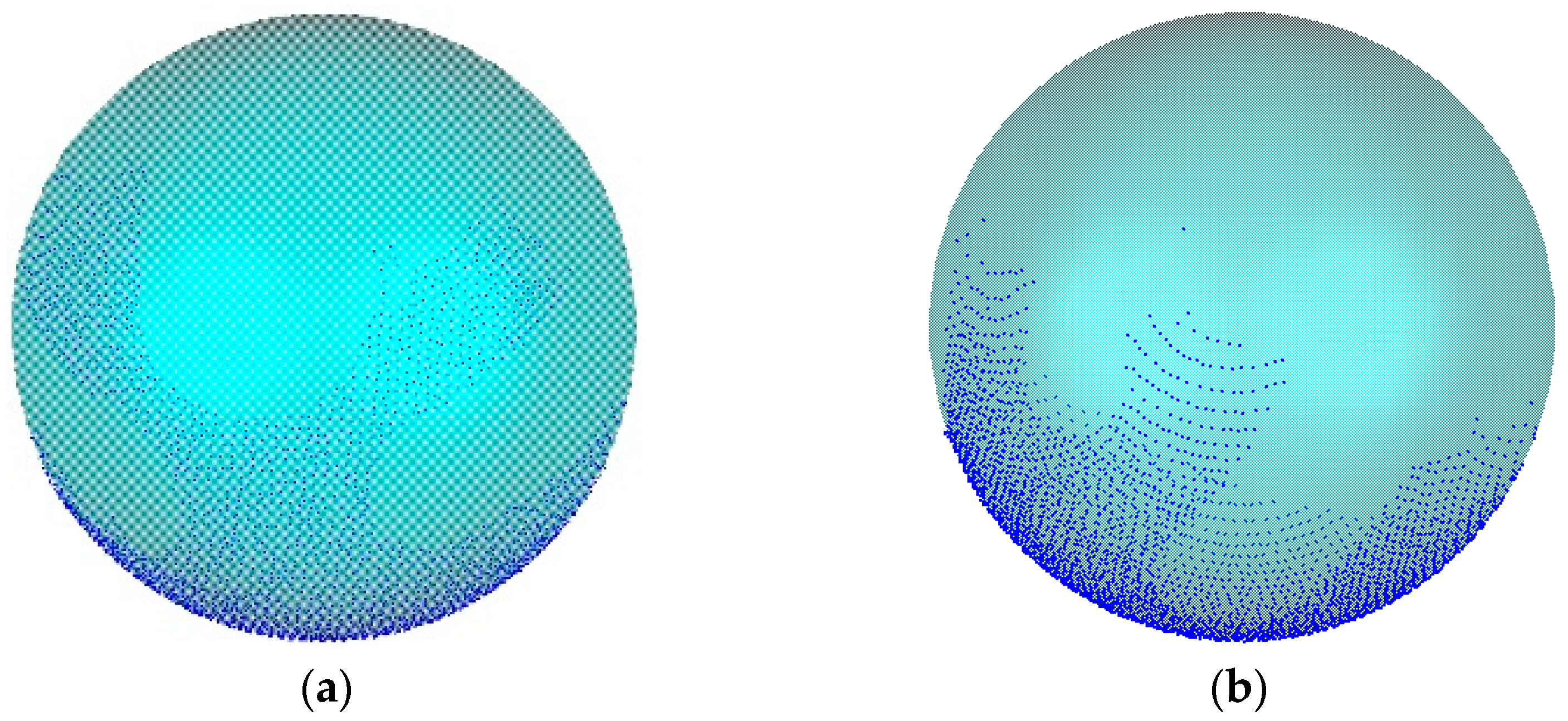
3.2.1. Sphere
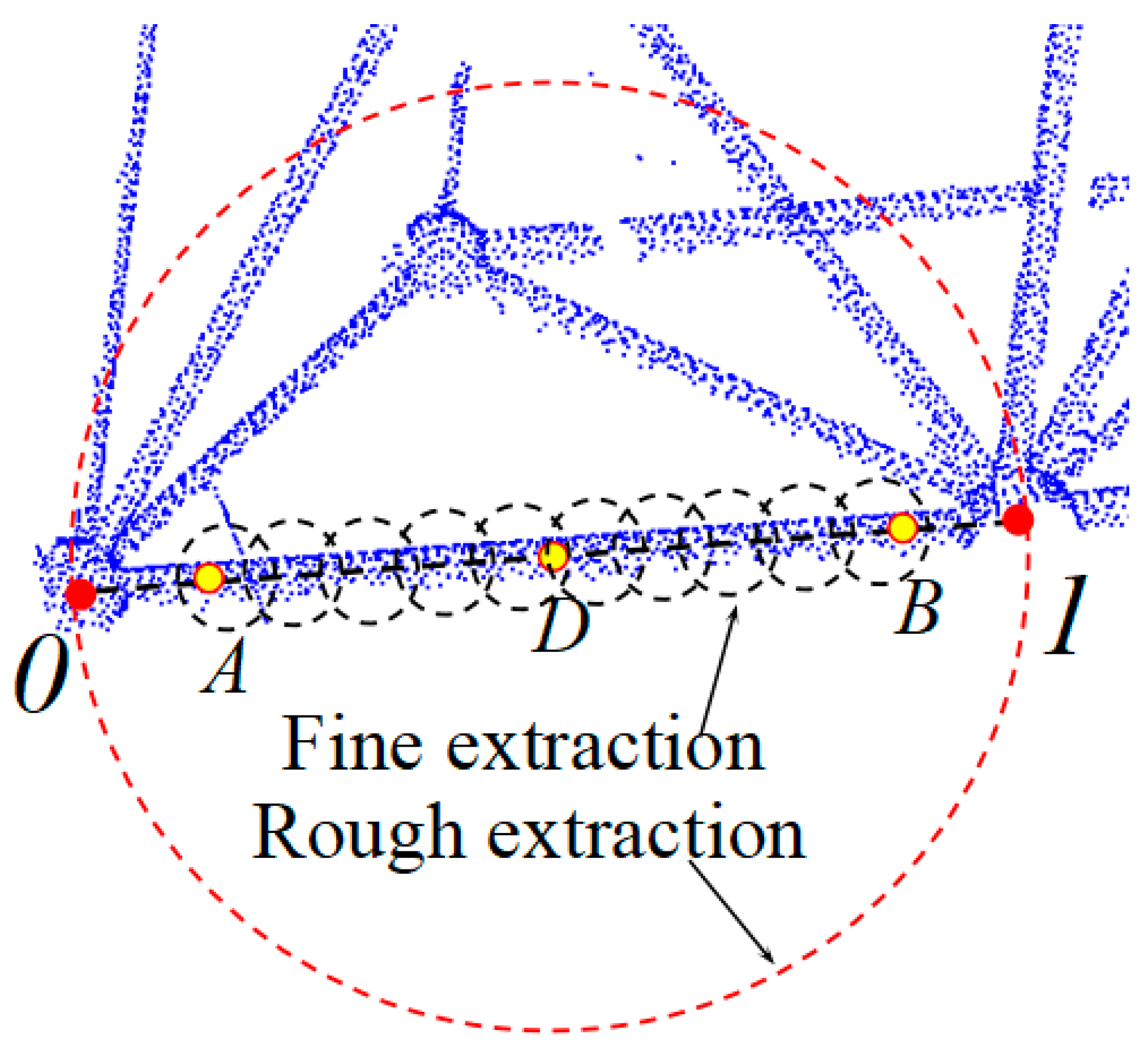
3.2.2. Cylinder
3.3. Estimation of Geometric Parameters
3.3.1. Sphere
3.3.2. Cylinder
4. An Application in Full-Scale Space Frame Structures
4.1. Data Collection
4.2. Results and Discussion
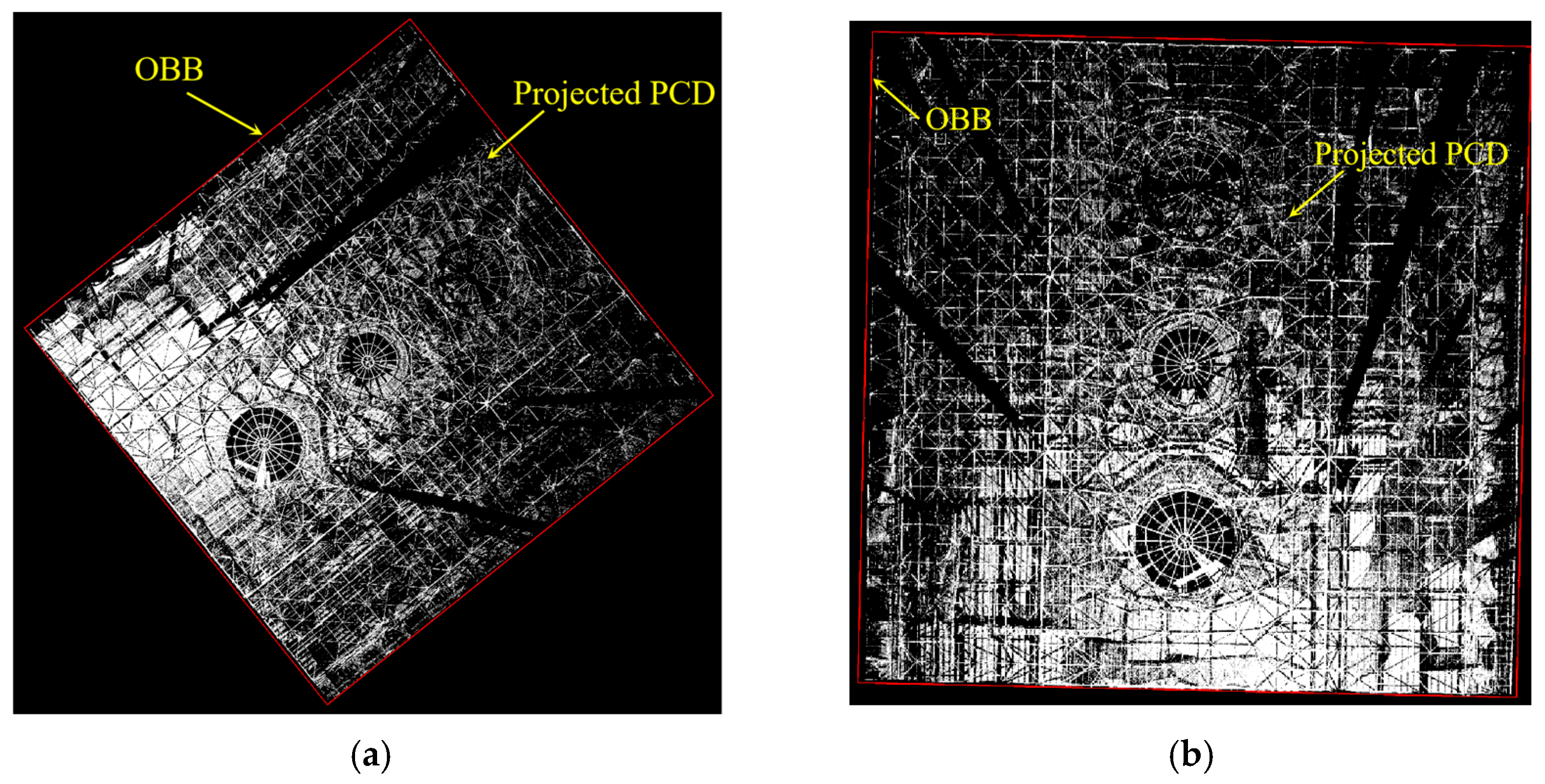
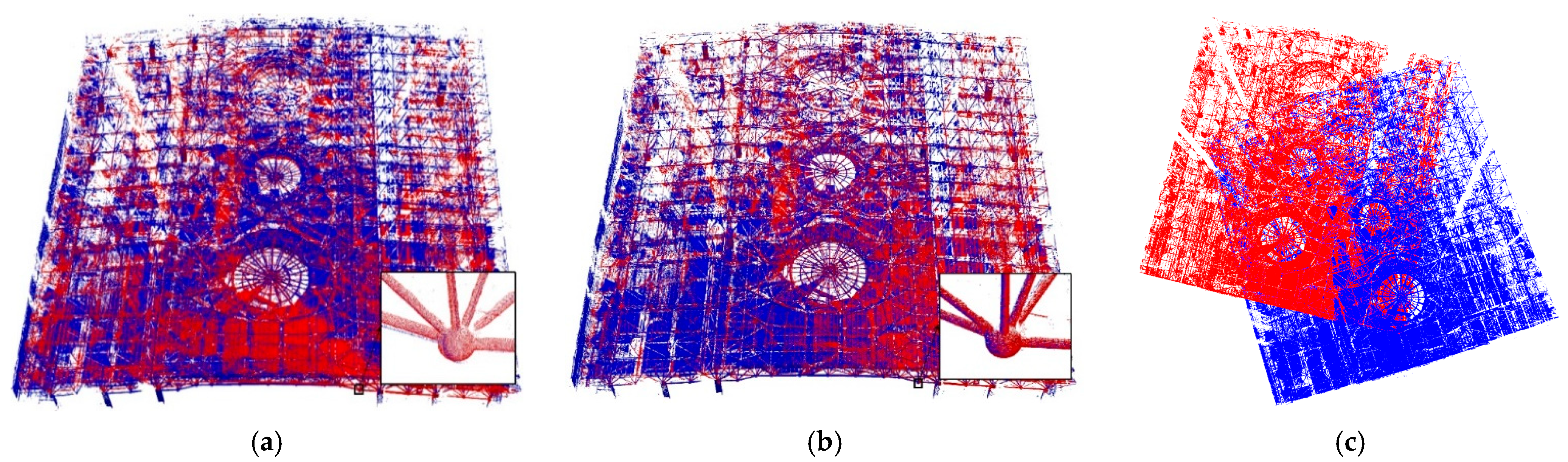
4.2.1. Registration of Large-Scale PCD
4.2.2. Segmentation of Large-Scale PCD
4.2.3. BIM Reconstruction
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The proposed TO–ICP enables the automatic registration of PCD of space frames with high accuracy;
- (2)
- The total computation time of the proposed VR-eSphere and FE-eCylinder is approximately half that of the curvature-based feature detection methods;
- (3)
- Although manual modeling is required for undetected components, the proposed BIM reconstruction approach significantly improves the efficiency of obtaining the as-built BIM model of full-scale space frame structures with cylindrical and spherical components. The effectiveness and reliability of the method are demonstrated by its application in the actual space frame structure.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Sheikh, A. Approximate dynamic analysis of space trusses. Eng. Struct. 2000, 22, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toğan, V.; Daloğlu, A.T. Optimization of 3d trusses with adaptive approach in genetic algorithms. Eng. Struct. 2006, 28, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, W.V.; Bezerra, L.M.; Freitas, C.S.; Bonilla, J.; Silva, R. Use of Natural Fiber and Recyclable Materials for Spacers in Typical Space Truss Connections. J. Struct. Eng. 2021, 147, 04021112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Liao, W.; Huang, Y.; Lu, X. Intelligent beam layout design for frame structure based on graph neural networks. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 63, 105499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, C.; Yan, J.; Feng, J.; Sareh, P. Intelligent computational design of scalene-faceted flat-foldable tessellations. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2022, 9, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Fan, W.; Chen, Y.; Feng, J.; Sareh, P. Structural symmetry recognition in planar structures using convolutional neural networks. Eng. Struct. 2020, 260, 114227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yan, J.; Sareh, P.; Feng, J. Nodal flexibility and kinematic indeterminacy analyses of symmetric tensegrity structures using orbits of nodes. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 155, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, S. Building information modeling (BIM): Trends, benefits, risks, and challenges for the AEC industry. Leadersh. Manag. Eng. 2011, 11, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.; Wilsmann, J.; Kang, D. Use of as-built building information modeling. In Proceedings of the Construction Research Congress 2010: Innovation for Reshaping Construction Practice, Banff, AB, Canada, 8–10 May 2010; pp. 538–548. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, P.; Huber, D.; Akinci, B.; Lipman, R.; Lytle, A. Automatic reconstruction of as-built building information models from laser-scanned point clouds: A review of related techniques. Autom. Constr. 2010, 19, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, S. A review of 3D reconstruction techniques in civil engineering and their applications. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2018, 37, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Kim, M.-K. Applications of 3D point cloud data in the construction industry: A fifteen-year review from 2004 to 2018. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2019, 39, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Sun, J. Deep learning based point cloud registration: An overview. Virtual Real. Intell. Hardw. 2020, 2, 222–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Wu, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, Y. Registration of laser scanning point clouds: A review. Sensors 2018, 18, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Adan, A.; Akinci, B.; Huber, D. Automatic creation of semantically rich 3D building models from laser scanner data. Autom. Constr. 2013, 31, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaleiro, M.; Riveiro, B.; Arias, P.; Caamaño, J.C.; Vilán, J.A. Automatic 3D modelling of metal frame connections from LiDAR data for structural engineering purposes. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 96, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laefer, D.F.; Truong-Hong, L. Toward automatic generation of 3D steel structures for building information modelling. Autom. Constr. 2017, 74, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Cheng, J.C.; Wang, Q. Semi-automated generation of parametric BIM for steel structures based on terrestrial laser scanning data. Autom. Constr. 2020, 112, 103037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besl, P.J.; McKay, N.D. A method for registration of 3-D shapes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1992, 14, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, H.; Campbell, D.; Jia, Y. Go-ICP: A globally optimal solution to 3D ICP point-set registration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 38, 241–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoso, F.A.; Austin, K.J.; McAree, P.R. How do ICP variants perform when used for scan matching terrain point clouds? Robot. Auton. Syst. 2017, 87, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellado, N.; Aiger, D.; Mitra, N.J. Super 4pcs fast global point cloud registration via smart indexing. Comput. Graph. Forum 2014, 33, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosché, F. Plane-based registration of construction laser scans with 3D/4D building models. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2021, 26, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, R.B.; Blodow, N.; Beetz, M. Fast point feature histograms (FPFH) for 3D registration. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; pp. 3212–3217. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Lyu, S. Detecting image region duplication using SIFT features. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics: Speech and Signal Processing, Dallas, TX, USA, 14–19 March 2010; pp. 1706–1709. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.M.; Brady, J.M. SUSAN—A new approach to low level image processing. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1997, 23, 45–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Li, W.; Yuan, Y.; Pan, J. Fully affine invariant SURF for image matching. Neurocomputing 2012, 85, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, Y.; Goforth, H.; Srivatsan, R.A.; Lucey, S. Pointnetlk: Robust & efficient point cloud registration using pointnet. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7163–7172. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Wan, G.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, X.; Yuan, P.; Song, S. Deepvcp: An end-to-end deep neural network for point cloud registration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Trimble, Trimble RealWorks. Available online: https://geospatial.trimble.com/products-and-solutions/trimble-realworks (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Geomagic, Geomagic Wrap. Available online: https://www.3dsystems.com/software/geomagic-wrap (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- ClearEdge3D. EdgeWise. Available online: https://www.clearedge3d.com/products/edgewise (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Jung, J.; Hong, S.; Jeong, S.; Kim, S.; Cho, H.; Hong, S.; Heo, J. Productive modeling for development of as-built BIM of existing indoor structures. Autom. Constr. 2014, 42, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.K.; Holi, P.; Lee, S.K.; Chai, Y.H. An adaptive approach for the reconstruction and modeling of as-built 3D pipelines from point clouds. Autom. Constr. 2017, 75, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.J.; Wang, Q.; Park, J.H. Geometric quality inspection of prefabricated MEP modules with 3D laser scanning. Autom. Constr. 2020, 111, 103053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.; Bischof, L. Seeded region growing. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1994, 16, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, P.; Chaudhuri, B.B. A survey of Hough Transform. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 993–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, S.; Vosselman, G. Automatic extraction of building features from terrestrial laser scanning. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2006, 36, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel, R.; Wahl, R.; Klein, R. Efficient RANSAC for point-cloud shape detection. Comput. Graph. Forum 2007, 26, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzaina, A.; Nixon, M.S.; Carter, J.N. Sphere detection in kinect point clouds via the 3d hough transform. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns, York, UK, 27–29 August 2013; pp. 290–297. [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima, K.; Kanai, S.; Date, H. As-built modeling of piping system from terrestrial laser-scanned point clouds using normal-based region growing. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2014, 1, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.; Kim, C.; Kim, C. Fully automated as-built 3D pipeline extraction method from laser-scanned data based on curvature computation. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2015, 29, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.H.P.; Choi, Y. Comparison of point cloud data and 3D CAD data for on-site dimensional inspection of industrial plant piping systems. Autom. Constr. 2018, 91, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, J.; Feng, L.; Zhou, Y.; Qi, H.; Chen, Y.F. Automatic modeling of prefabricated components with laser-scanned data for virtual trial assembly. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2021, 36, 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaleiro, M.; Riveiro, B.; Arias, P.; Caamaño, J. Algorithm for beam deformation modeling from lidar data. Measurement 2015, 76, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y. Dimensional accuracy and structural performance assessment of spatial structure components using 3D laser scanning. Autom. Constr. 2018, 96, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiger, D.; Mitra, N.J.; Cohen-Or, D. 4-points congruent sets for robust pairwise surface registration. In Proceedings of the SIGGRAPH’08: Special Interest Group on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 11–15 August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bradski, G.; Kaehler, A. Learning OpenCV: Computer Vision with the OpenCV Library; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2008; Available online: https://opencv.org/ (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Case, F.; Beinat, A.; Crosilla, F.; Alba, I.M. Virtual trial assembly of a complex steel structure by Generalized Procrustes Analysis techniques. Autom. Constr. 2014, 37, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabassi, E.A.; Papaioannou, G.; Theoharis, T. A fast depth-buffer-based voxelization algorithm. J. Graph. Tools 1999, 4, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louhichi, S.; Gzara, M.; Abdallah, H.B. A density based algorithm for discovering clusters with varied density. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Computer Applications and Information Systems, Hammamet, Tunisia, 17–19 January 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Zong, M.; Zhu, X.; Wang, R. Efficient kNN Classification with Different Numbers of Nearest Neighbors. IEEE Trans. Neural. Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 29, 1774–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faro. Faro Focus Laser Scanner User Manual. 2019. Available online: https://www.faro.com/en/Products/Hardware/Focus-Laser-Scanners (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Li, D.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Y.; Cheng, G.; Dong, B.; Chen, Y.F. 3D model-based scan planning for space frame structures considering site conditions. Autom. Constr. 2022, 140, 104363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 50205-2020; Standard for Acceptance of Construction Quality of Steel Structures. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of PRC: Beijing, China, 2020. Available online: https://www.chinesestandard.net/China/Chinese.aspx/GB50205-2020 (accessed on 25 March 2023).





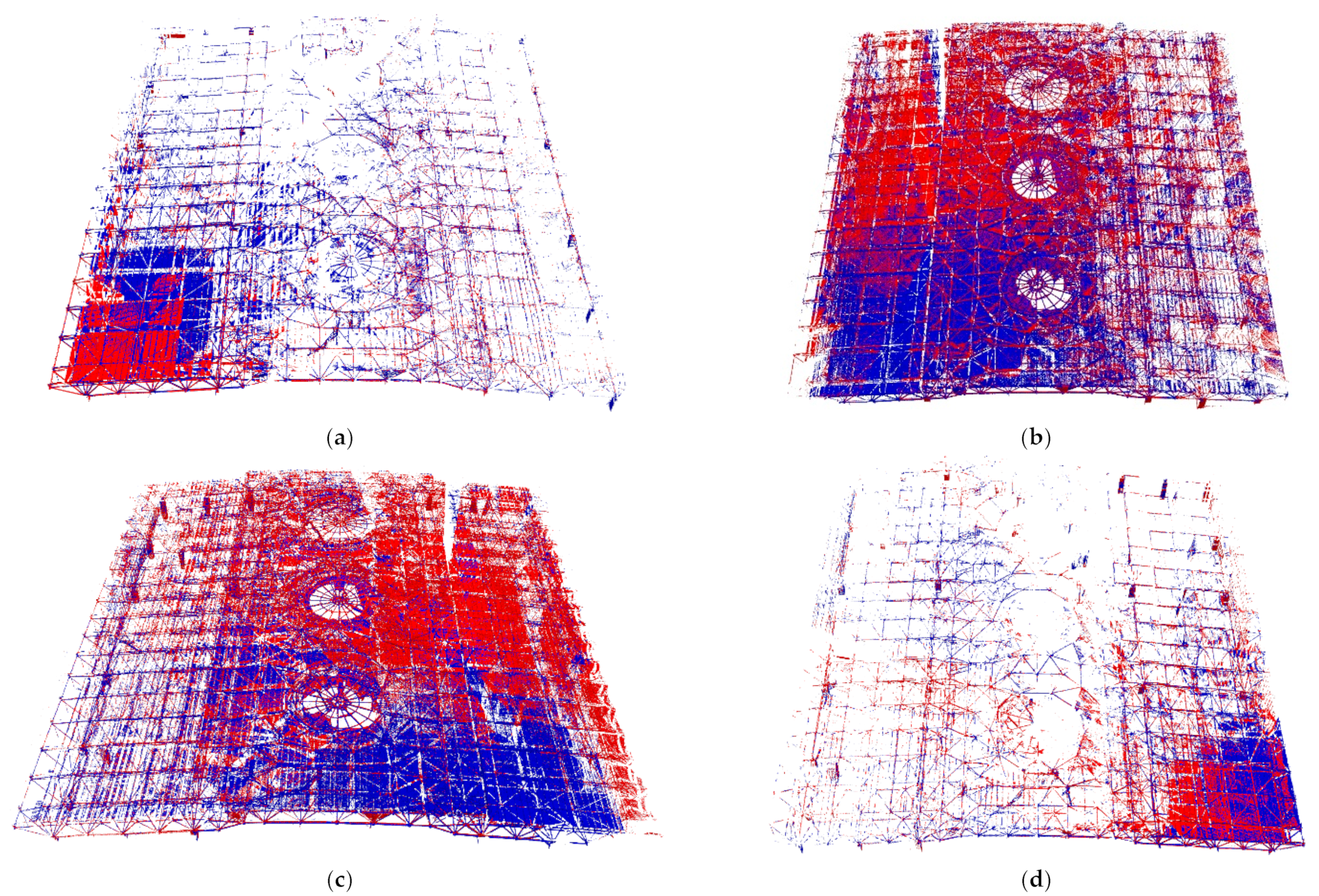
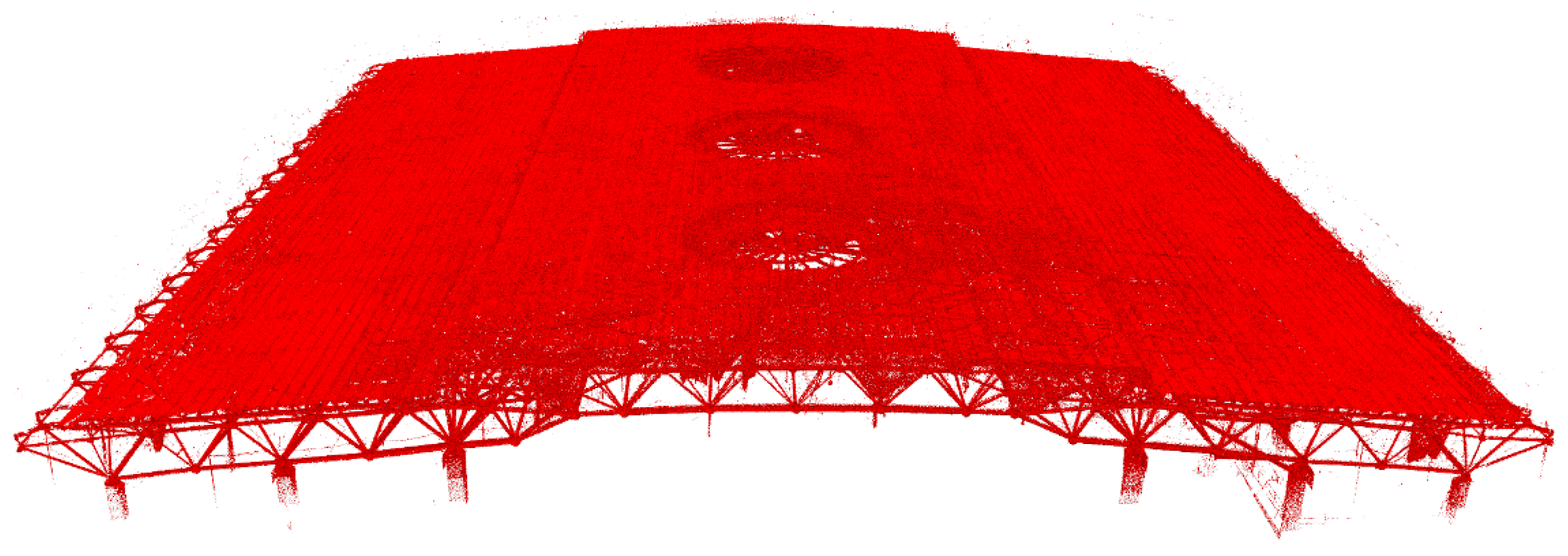

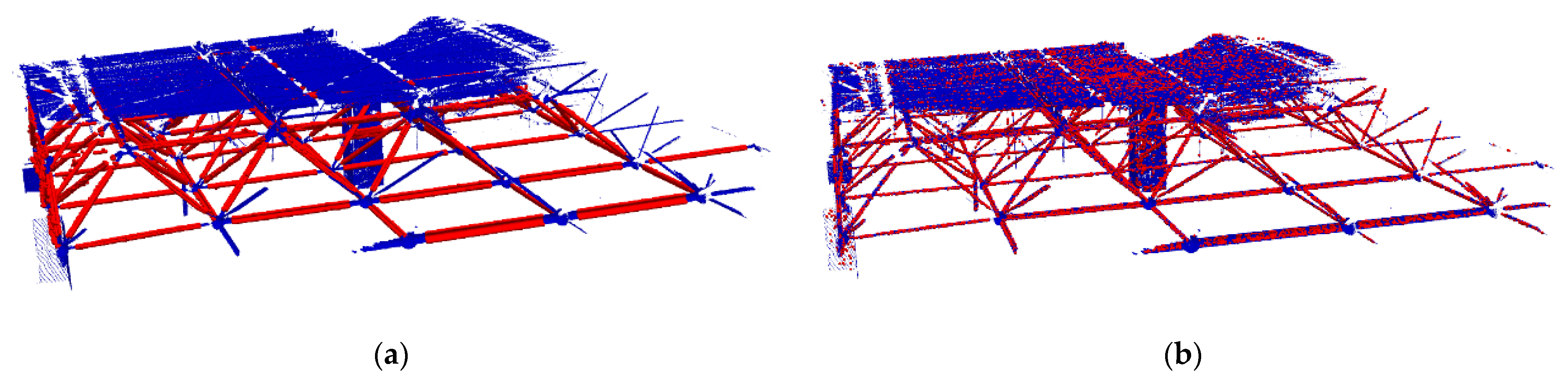
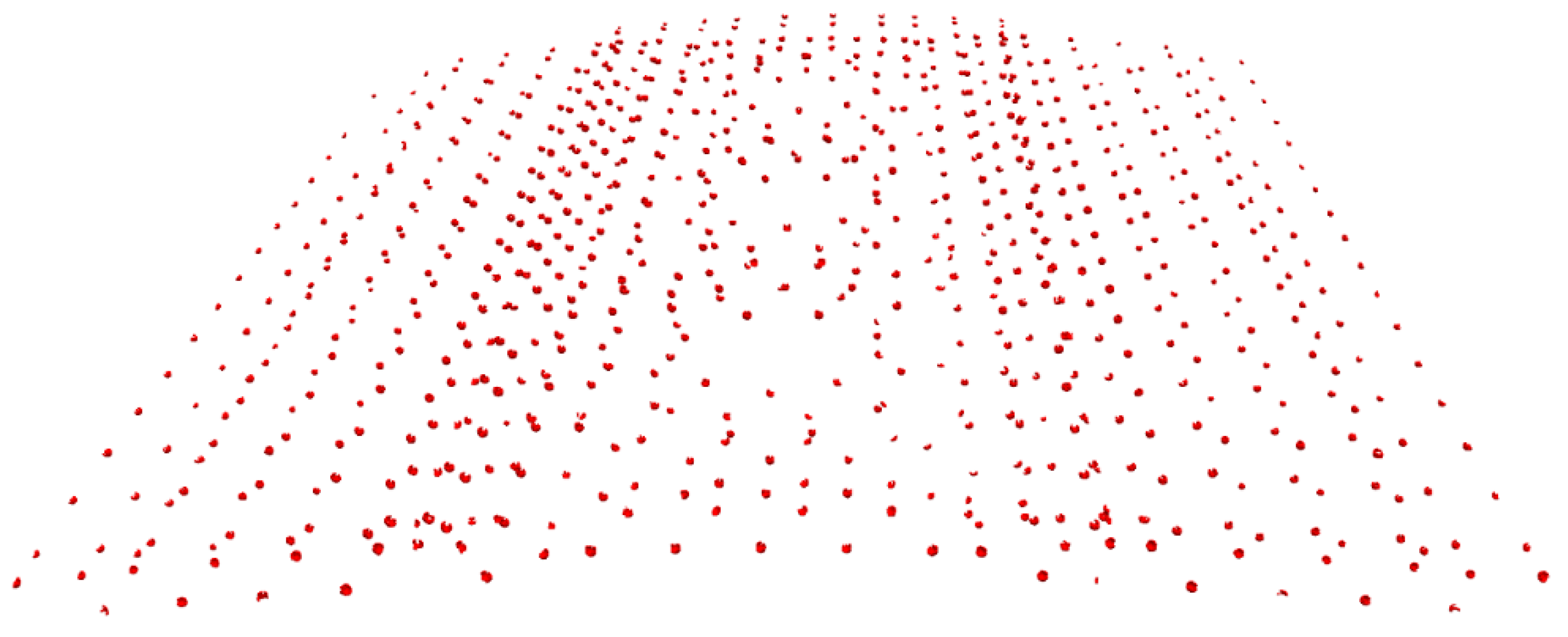

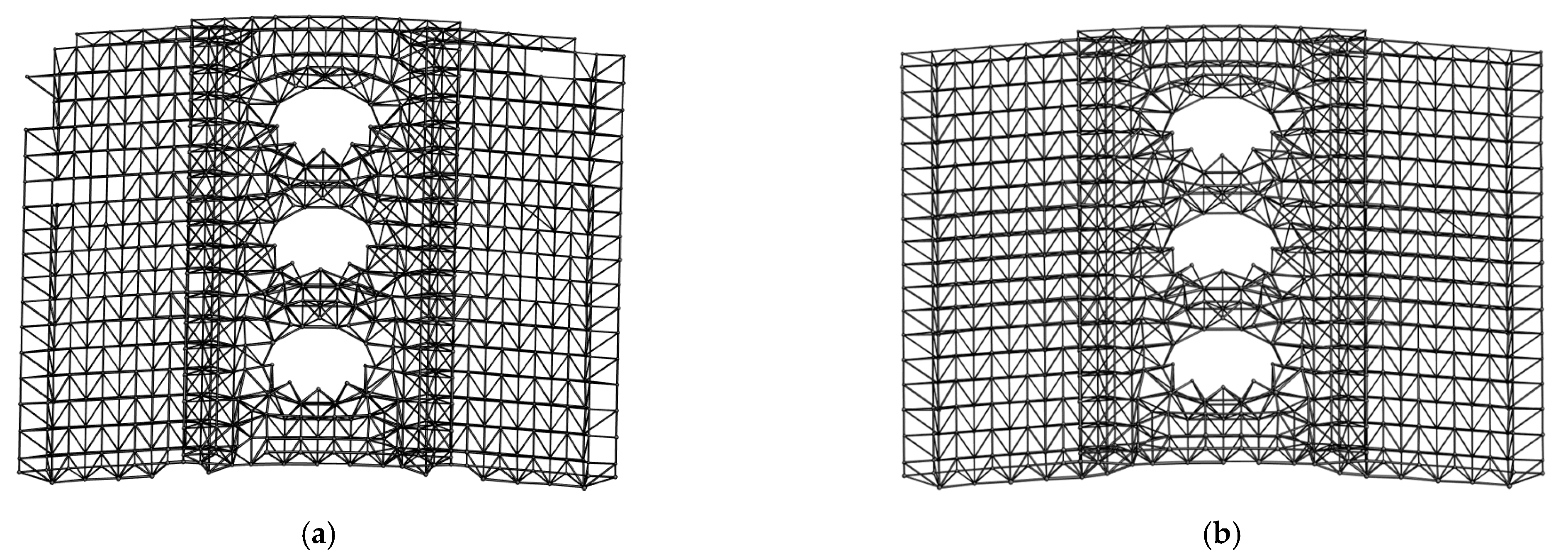
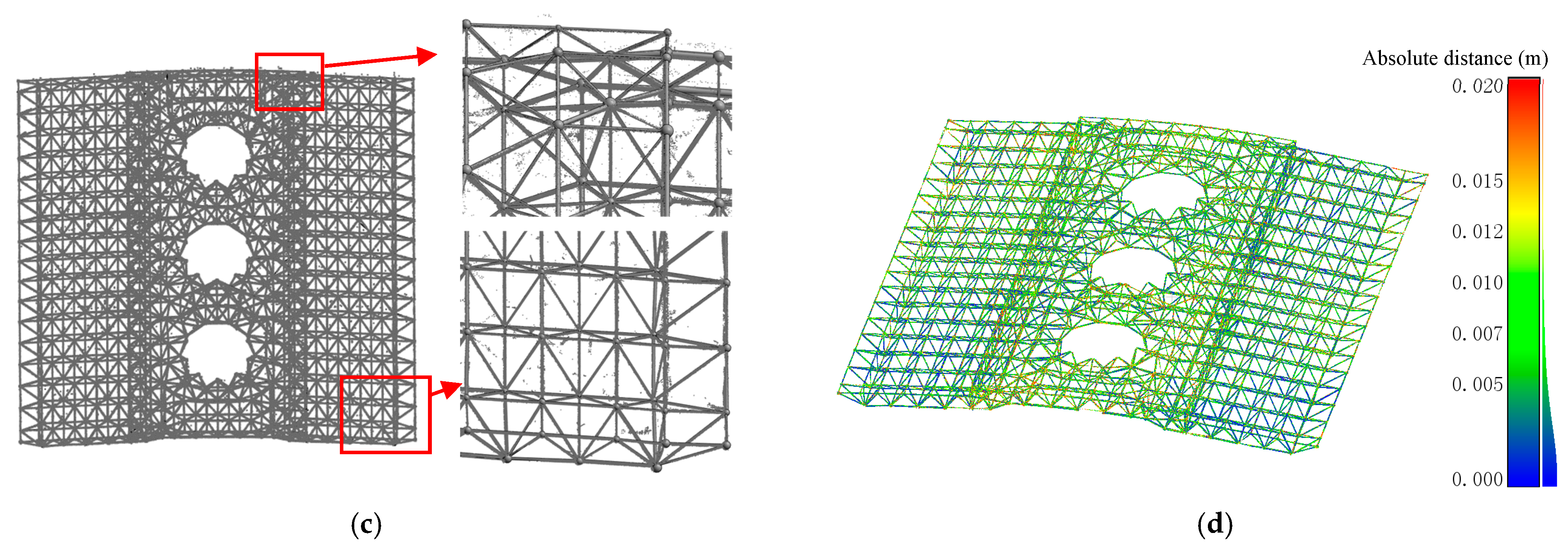
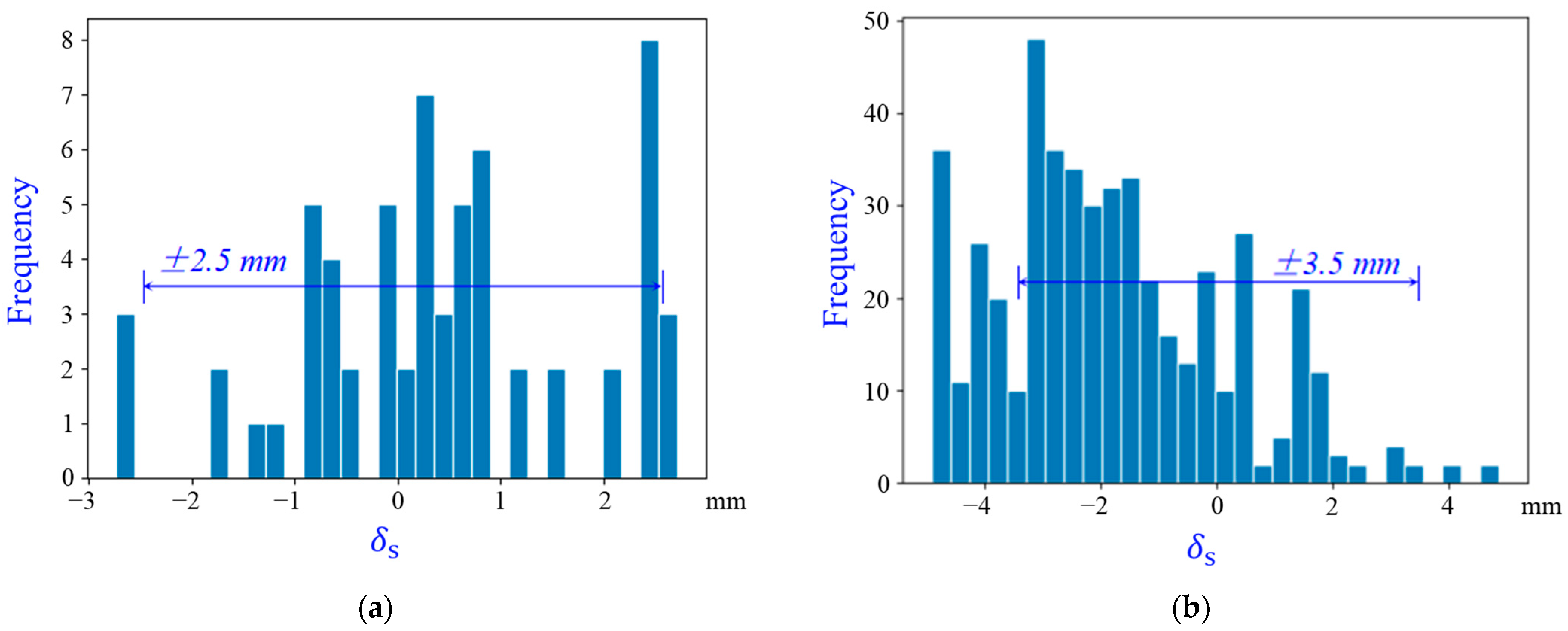
| Location | Original/Sampling Points | Location | Original/Sampling Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | 13,988,195/5,368,352 | #2 | 16,275,140/7,570,197 |
| #3 | 15,392,697/7,544,656 | #4 | 13,397,295/9,125,325 |
| #5 | 13,707,609/9,275,676 | #6 | 12,143,921/7,807,302 |
| #7 | 21,742,499/9,807,240 | #8 | 59,541,256/14,504,592 |
| #9 | 58,729,766/15,087,340 | #10 | 59,910,220/14,766,215 |
| #11 | 48,133,412/14,796,388 | #12 | 37,703,339/12,295,436 |
| #13 | 56,738,434/14,511,595 | #14 | 54,680,413/14,092,693 |
| #15 | 36,803,597/13,461,163 | #16 | 13,339,396/6,231,241 |
| #17 | 13,152,792/5,565,005 | #18 | 13,997,682/5,975,098 |
| #19 | 18,719,062/11,503,259 | #20 | 18,436,252/12,229,958 |
| Target PCD | Source PCD | eR (°) * | eT (mm) | Computation Time (s) ** | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ex | ey | ez | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| #1 | #2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0001 | 6558 | 12 | 6 | 120 |
| #8 | #9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.00004 | 3882 | 30 | 35 | 119 |
| #12 | #13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0002 | 3715 | 27 | 19 | 113 |
| #17 | #18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.00008 | 5981 | 11 | 4 | 119 |
| Item | Sphere | Cylinder | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recall (%) | 94.4% | 94.1% | 94.1% |
| Items | Allowable Errors |
|---|---|
| Ds <= 300 mm | ±1.5 mm |
| 300 mm < Ds <= 500 mm | ±2.5 mm |
| 500 mm < Ds <= 800 mm | ±3.5 mm |
| Ds > 800 mm | ±4.0 mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, G.; Liu, J.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.F. Semi-Automated BIM Reconstruction of Full-Scale Space Frames with Spherical and Cylindrical Components Based on Terrestrial Laser Scanning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2806. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112806
Cheng G, Liu J, Li D, Chen YF. Semi-Automated BIM Reconstruction of Full-Scale Space Frames with Spherical and Cylindrical Components Based on Terrestrial Laser Scanning. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(11):2806. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112806
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Guozhong, Jiepeng Liu, Dongsheng Li, and Y. Frank Chen. 2023. "Semi-Automated BIM Reconstruction of Full-Scale Space Frames with Spherical and Cylindrical Components Based on Terrestrial Laser Scanning" Remote Sensing 15, no. 11: 2806. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112806
APA StyleCheng, G., Liu, J., Li, D., & Chen, Y. F. (2023). Semi-Automated BIM Reconstruction of Full-Scale Space Frames with Spherical and Cylindrical Components Based on Terrestrial Laser Scanning. Remote Sensing, 15(11), 2806. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112806