Current Status and Challenges of BDS Satellite Precise Orbit Products: From a View of Independent SLR Validation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. LRAs Onboard BDS Satellites
2.2. SLR Observations of BDS Satellites
2.3. SLR Validation Method
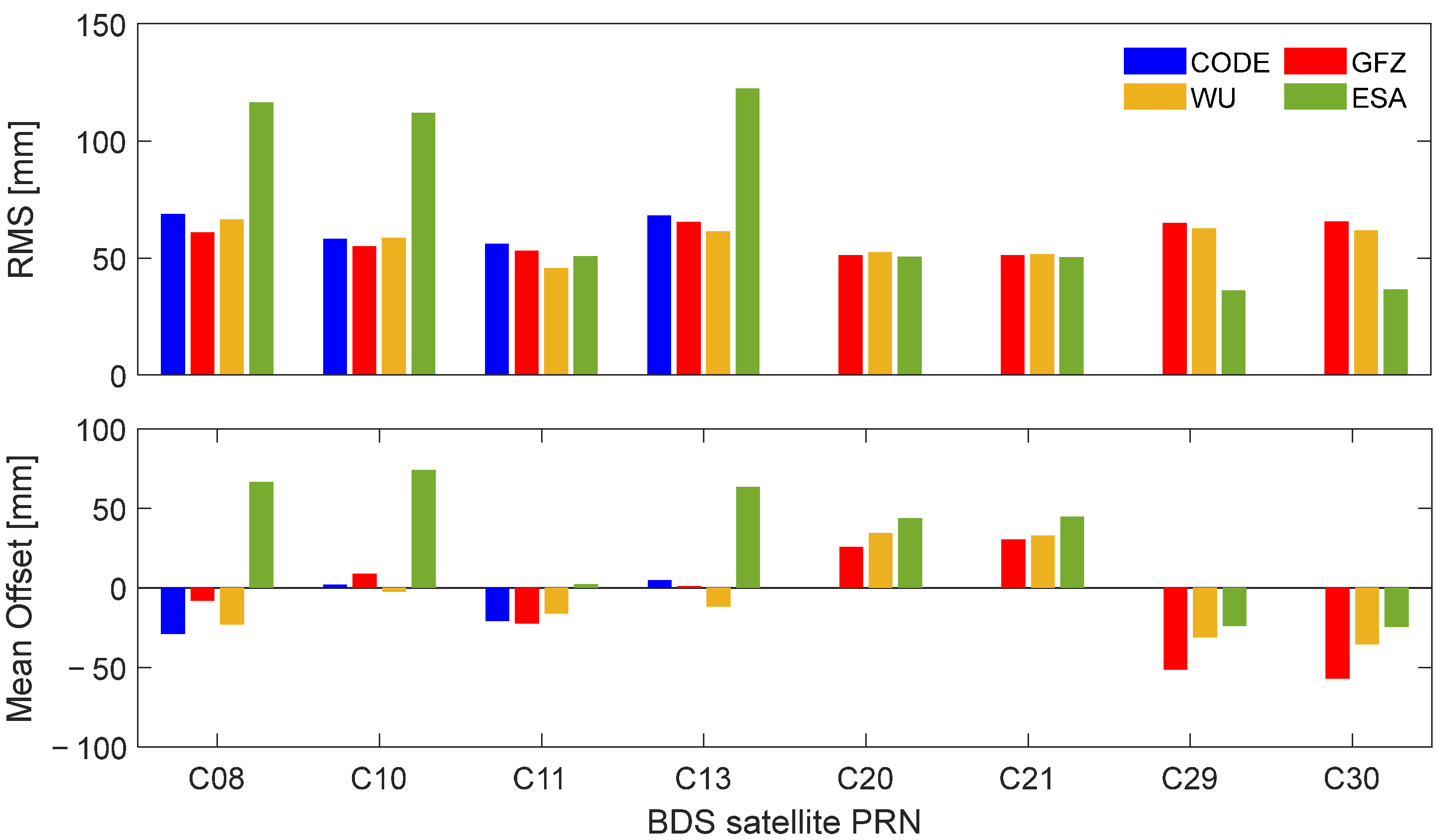
3. Results
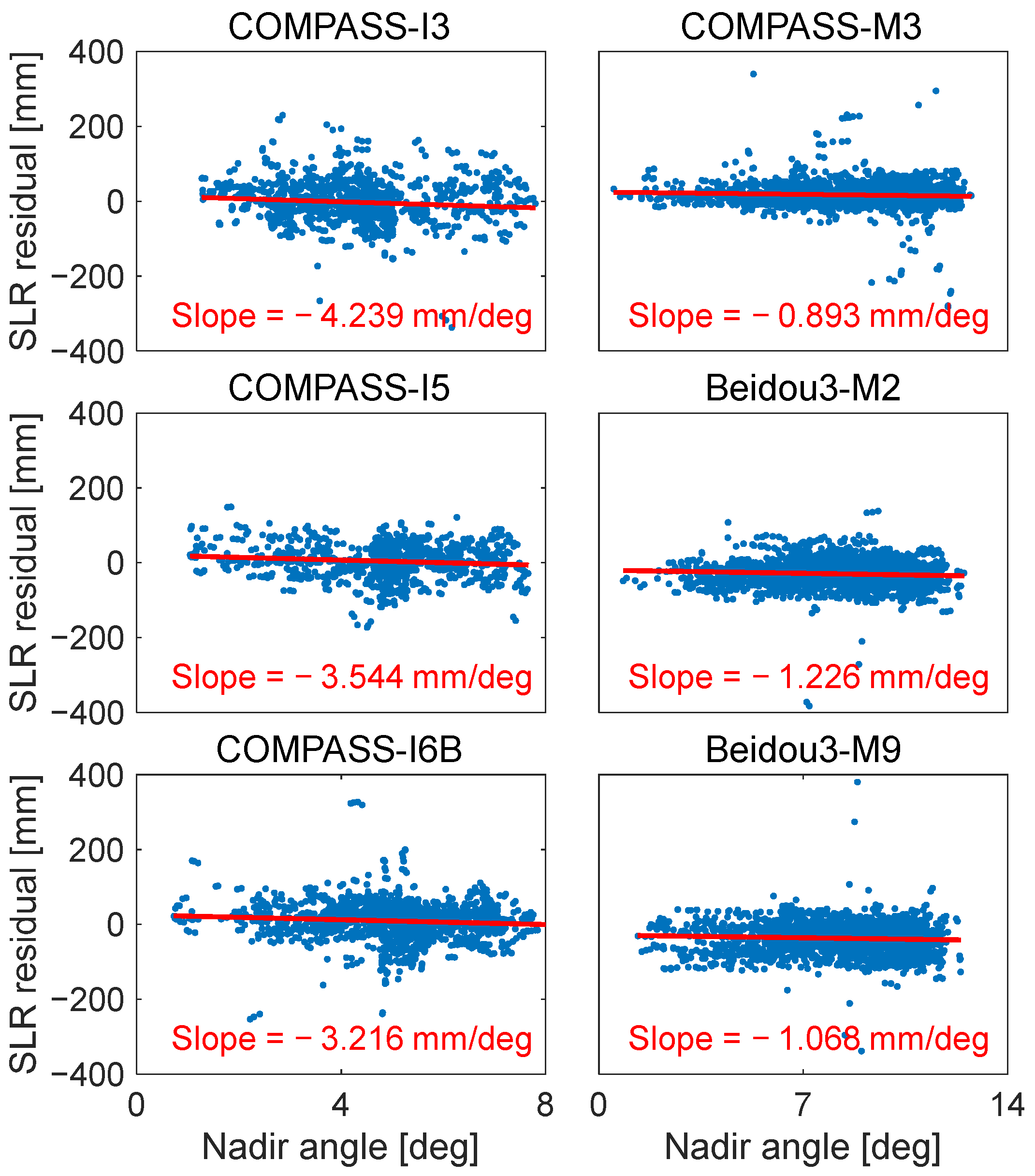
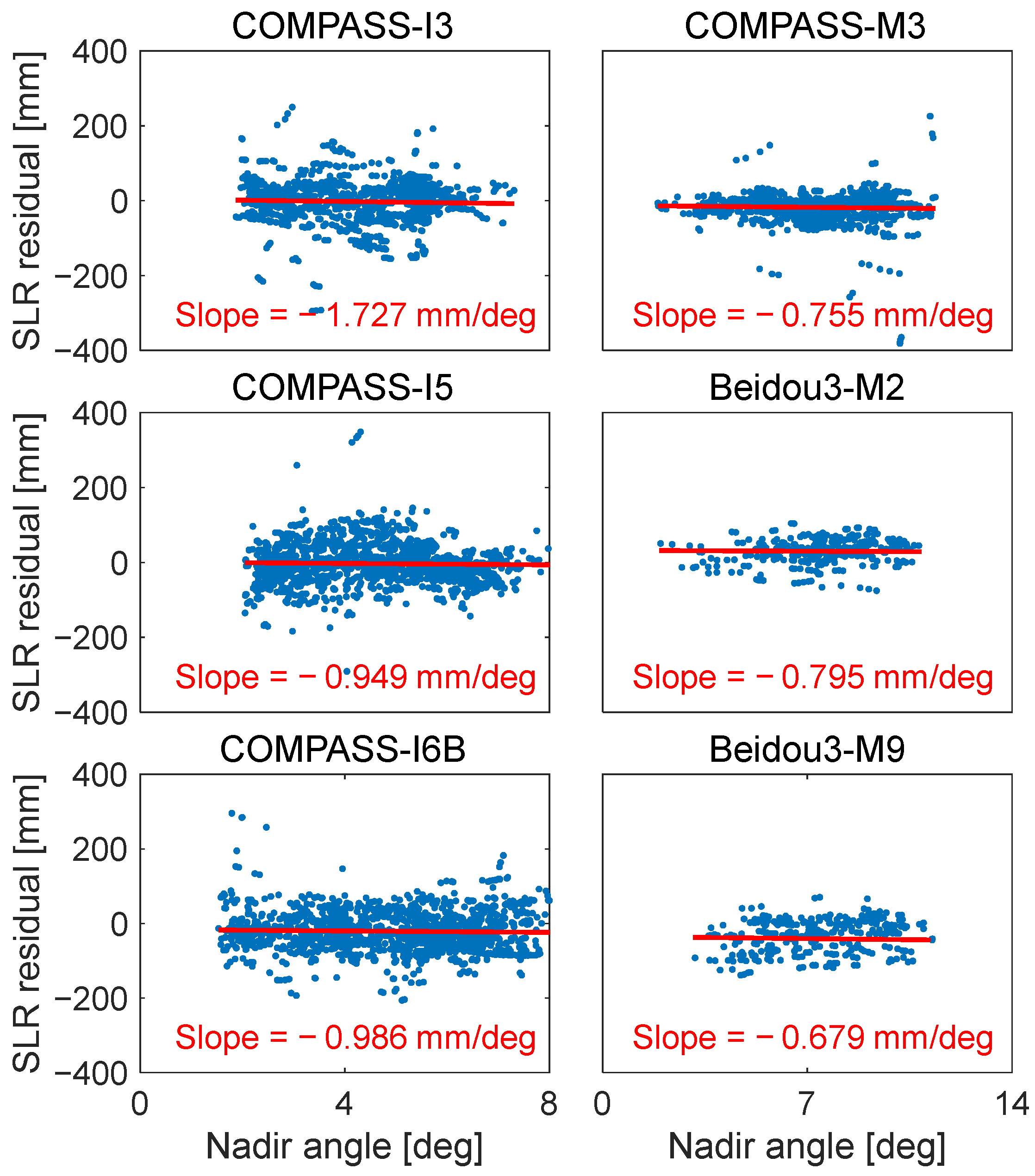
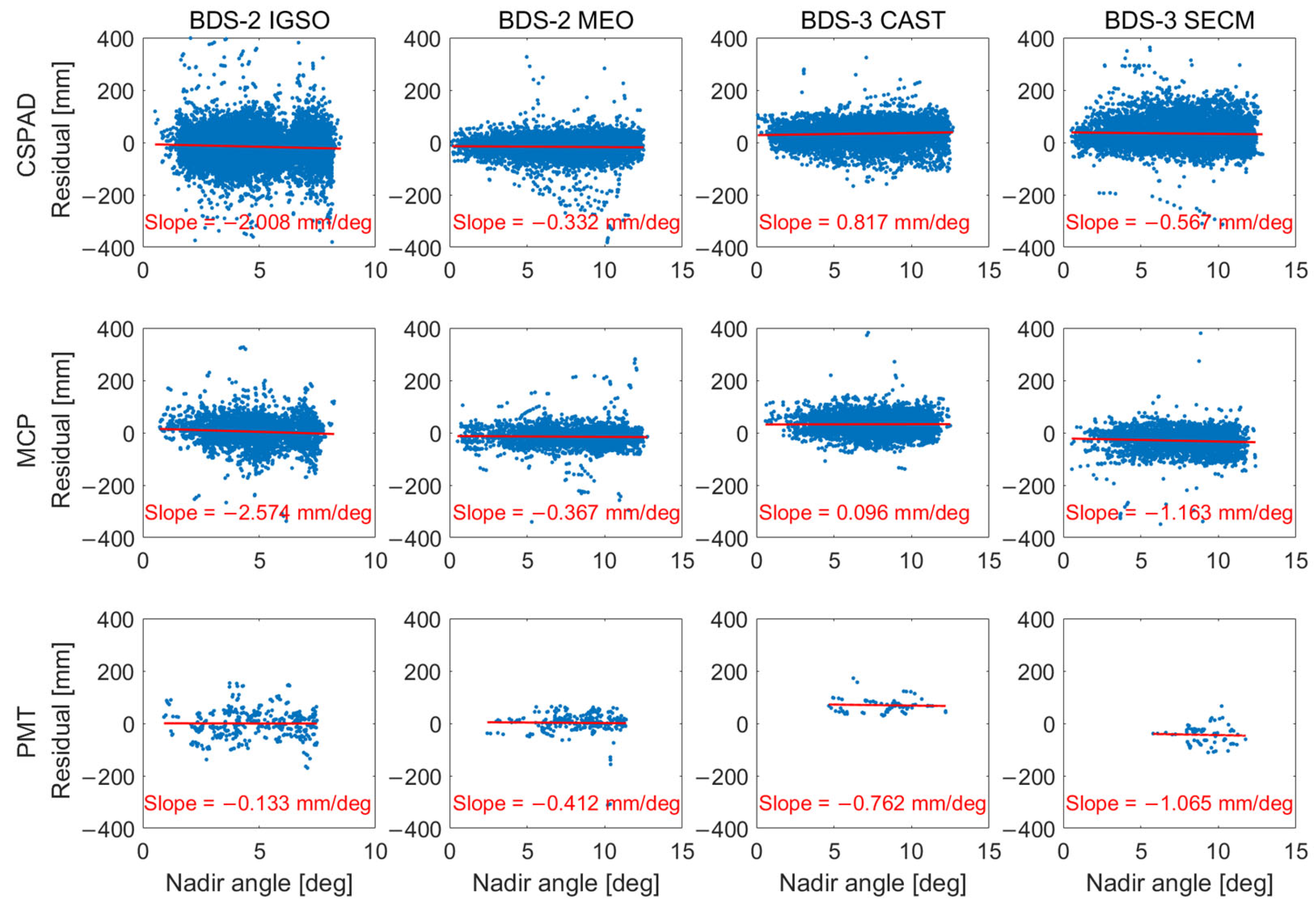
3.1. Satellite Signature Effect of BDS
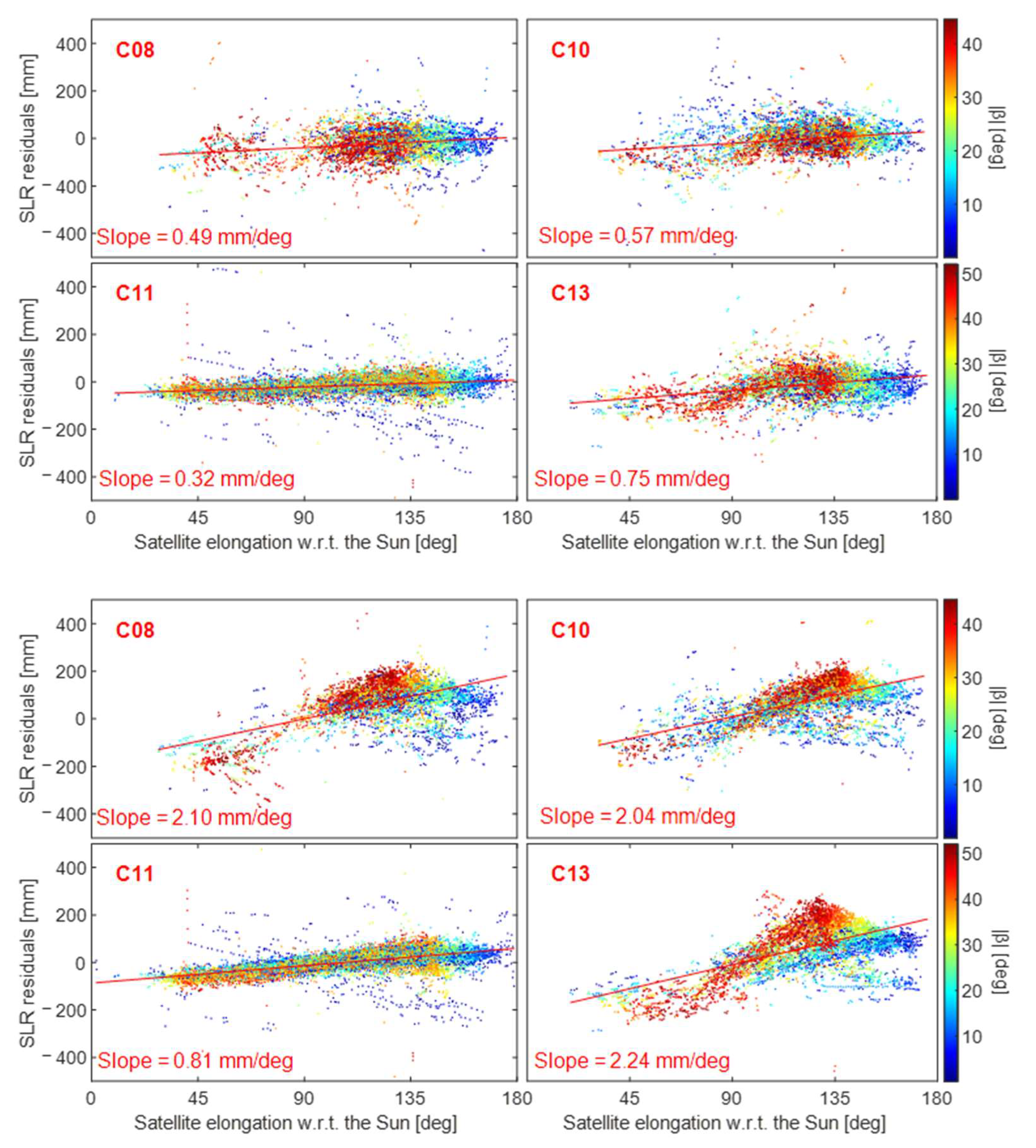
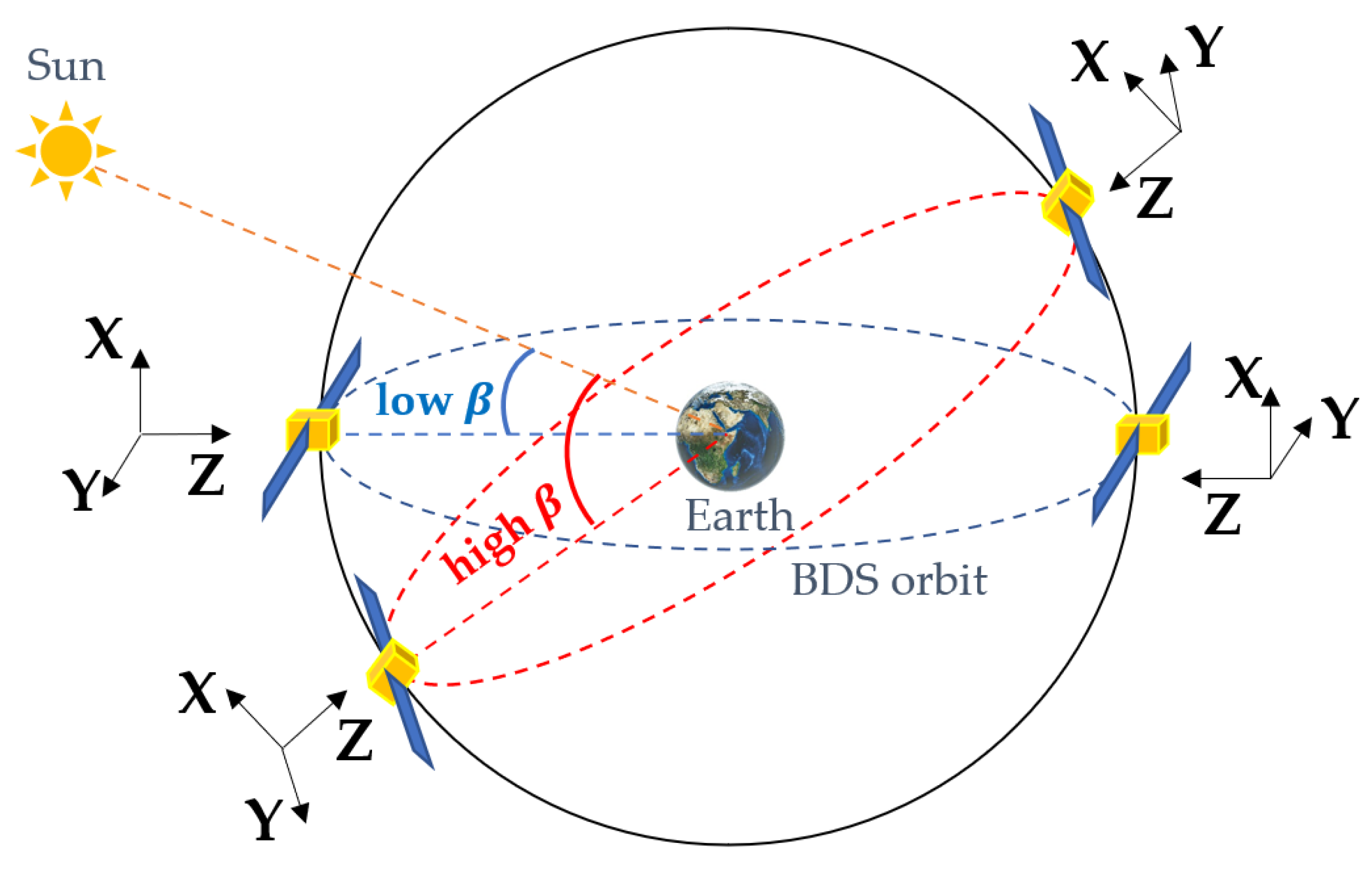
3.2. Non-Conservative Force Modeling Effect of BDS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Tang, J.; Montenbruck, O. Chinese Navigation Satellite Systems. In Springer Handbook of Global Navigation Satellite Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 273–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSNO TARC Test and Assessment Research Center of China Satellite Navigation Office. Available online: http://csno-tarc.cn/system/constellation (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Montenbruck, O.; Rizos, C.; Weber, R.; Weber, G.; Neilan, R.; Hugentobler, U. Getting a grip on multi-GNSS: The international GNSS service MGEX campaign. GPS World 2013, 24, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Uhlemann, M.; Gendt, G.; Ramatschi, M.; Deng, Z. GFZ Global Multi-GNSS Network and Data Processing Results//IAG 150 Years. In Proceedings of the IAG Scientific Assembly, Postdam, Germany, 1–6 September 2013; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, T.A.; Otten, M.; Flohrer, C. Spreading the Usage of NAPEOS, the ESA Tool for Satellite Geodesy. In EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts; EGU: Vienna, Austria, 2012; p. 7099. [Google Scholar]
- Prange, L.; Dach, R.; Lutz, S.; Schaer, S.; Jaggi, A. The CODE MGEX Orbit and Clock Solution//IAG 150 Years. In Proceedings of the IAG Scientific Assembly, Postdam, Germany, 1–6 September 2013; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prange, L.; Orliac, E.; Dach, R.; Arnold, D.; Beutler, G.; Schaer, S.; Jaggi, A. CODE’s five-system orbit and clock solution—The challenges of multi-GNSS data analysis. J. Geod. 2017, 91, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J. Precise orbit determination for quad-constellation satellites at Wuhan University: Strategy, result validation, and comparison. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, K.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, G.; Xiong, Y. Precise orbit and clock products of Galileo, BDS and QZSS from MGEX since 2018: Comparison and PPP validation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Hugentobler, U. Enhanced solar radiation pressure modeling for Galileo satellites. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlis, E.C. Comparison of GPS S/C orbits determined from GPS and SLR tracking data. Adv. Space Res. 1995, 16, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urschl, C.; Beutler, G.; Gurtner, W.; Hugentobler, U.; Schaer, S. Contribution of SLR tracking data to GNSS orbit determination. Adv. Space Res. 2007, 39, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, J.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, K. Galileo and QZSS precise orbit and clock determination using new satellite metadata. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1123–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajdel, R.; Sośnica, K.; Bury, G. A new online service for the validation of multi-GNSS orbits using SLR. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleby, G.; Rodríguez, J.; Altamimi, Z. Assessment of the accuracy of global geodetic satellite laser ranging observations and estimated impact on ITRF scale: Estimation of systematic errors in LAGEOS observations 1993–2014. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 1371–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sośnica, K.; Thaller, D.; Dach, R.; Steigenberger, P.; Beutler, G.; Arnold, D.; Jaggi, A. Satellite laser ranging to GPS and GLONASS. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 725–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sośnica, K.; Prange, L.; Kaźmierski, K.; Bury, G.; Drożdżewski, M.; Zajdel, R.; Hadas, T. Validation of Galileo orbits using SLR with a focus on satellites launched into incorrect orbital planes. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ILRS Study Group. LARGE: Laser Ranging to GNSS s/c Experiment Expanded SLR Tracking of GNSS Satellites. Available online: https://ilrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/2014/GNSS_Pilot_Project_v2_20140311.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Lin, X.; Baojun, L.; Yingchun, L.; Sujie, X.; Tao, B. Satellite Geometry and Attitude Mode of BDS-3 MEO Satellites Developed by SECM. In Proceedings of the 31st International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2018), Miami, FL, USA, 24–28 September 2018; pp. 1268–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, B.C.; Harris, I.B.; Beckman, T.J.; Reed, D.A.; Cook, D.A. Design and performances of laser retro-reflector arrays for Beidou navigation satellites and SLR observations. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 54, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, G.; Koidl, F. Maximizing the Output of SLR Station Graz: Tracking 140 Targets. In Proceedings of the 2015 ILRS Technical Workshop, Matera, Italy, 26–30 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pearlman, M.R.; Degnan, J.J.; Bosworth, J.M. The international laser ranging service. Adv. Space Res. 2002, 30, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsubo, T.; Appleby, G.M. System-dependent center-of-mass correction for spherical geodetic satellites. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2003, 108, 2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Assessment of precise orbit and clock products for Galileo, BeiDou, and QZSS from IGS Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX). GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IERS. IERS Conventions 2010: IERS Technical Note 36; Petit, G., Luzum, B., Eds.; Verlag des Bundesamts für Kartographie und Geodäsie: Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, D.; Meindl, M.; Beutler, G.; Dach, R.; Schaer, S.; Lutz, S.; Prange, L.; Sośnica, K.; Mervart, L.; Jäggi, A. CODE’s new solar radiation pressure model for GNSS orbit determination. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altamimi, Z.; Rebischung, P.; Métivier, L.; Collilieux, X. ITRF2014: A new release of the International Terrestrial Reference Frame modeling nonlinear station motions. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2016, 121, 6109–6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, V.B.; Prates, G.; Pavlis, E.C.; Pavlis, D.E.; Langley, R.B. Improved mapping functions for atmospheric refraction correction in SLR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 53-1–53-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, V.B.; Pavlis, E.C. High-accuracy zenith delay prediction at optical wavelengths. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L14602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ILRS International Laser Ranging Service. Available online: https://ilrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/2012/COMPASS-I3_RRA_information.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- ILRS International Laser Ranging Service. Available online: https://ilrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/2012/COMPASS-M3_RRA_information.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- ILRS International Laser Ranging Service. Available online: https://ilrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/2015/ilrsmsr_1604_retro_v2-Compass-MS1.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- Dong, X.; Han, X.; Fan, C.; Song, Q. Improvements of Changchun SLR Station. In Proceedings of the 20th International Workshop on Laser Ranging, Potsdam, Germany, 9–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Solano, C.; Hugentobler, U.; Steigenberger, P. Adjustable box-wing model for solar radiation pressure impacting GPS satellites. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 49, 1113–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Lyu, Y.; Xu, X.; Yang, C.; Li, J. Precise orbit determination for BDS satellites. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Solano, C.J. Impact of Albedo Modelling on GPS Orbits; Technische Universität München: München, Germany, 2009; Available online: https://mediatum.ub.tum.de/doc/1368717/document.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- Montenbruck, O.; Schmid, R.; Mercier, F.; Steigenberger, P.; Noll, C.; Fatkulin, R.; Kogure, S.; Ganeshan, A. GNSS satellite geometry and attitude models. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 56, 1015–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Satellite Navigation Office. CSNO Satellite Information of BDS. Available online: http://en.beidou.gov.cn/SYSTEMS/Officialdocument/201912/P020200103556125703019.rar (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Fritsche, M.; Sośnica, K.; Rodriguez-Solano, C.J.; Steigenberger, P.; Wang, K.; Dietrich, R.; Dach, R.; Hugentobler, U.; Rothacher, M. Homogeneous reprocessing of GPS, GLONASS and SLR observations. J. Geod. 2014, 88, 625–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

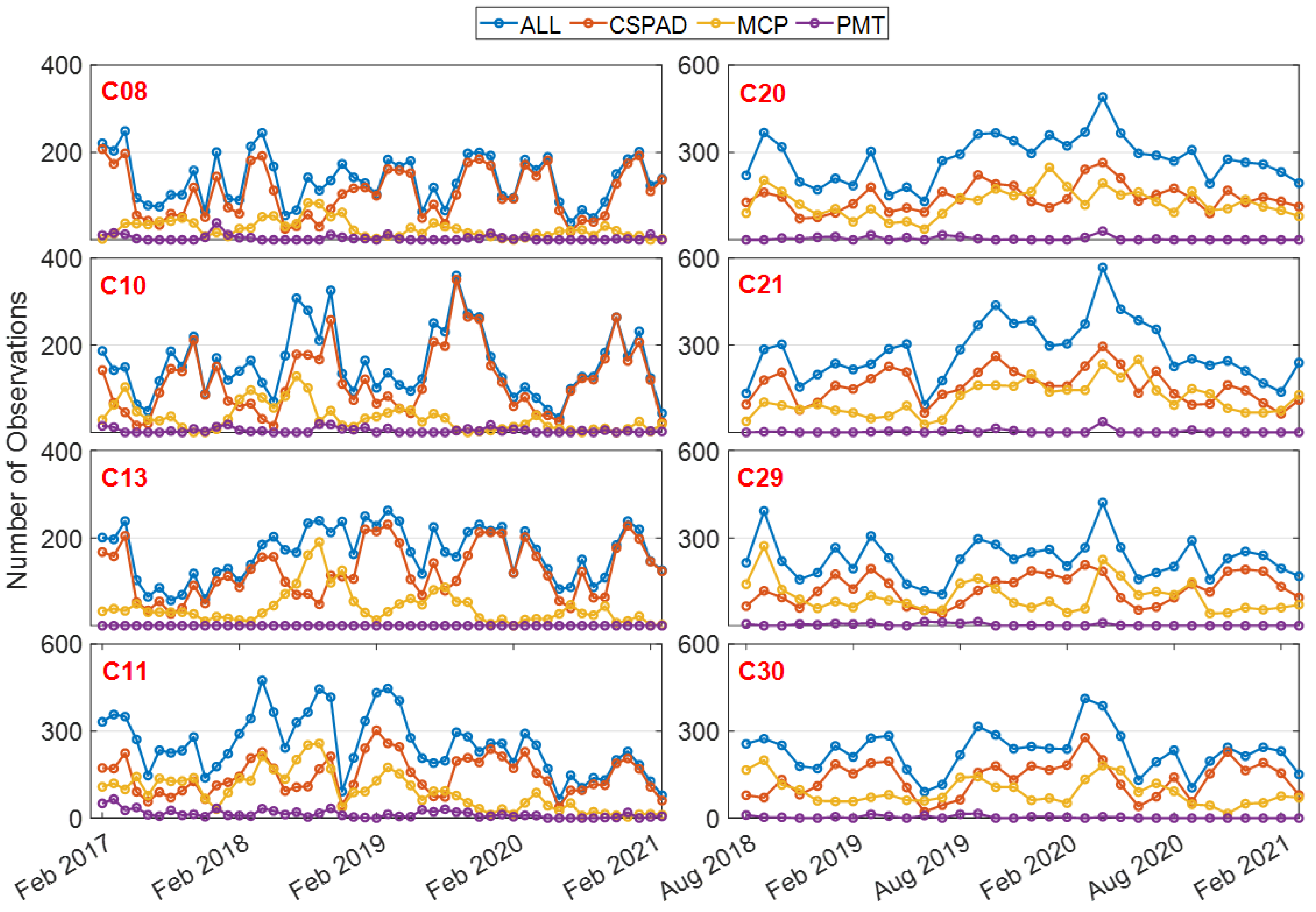
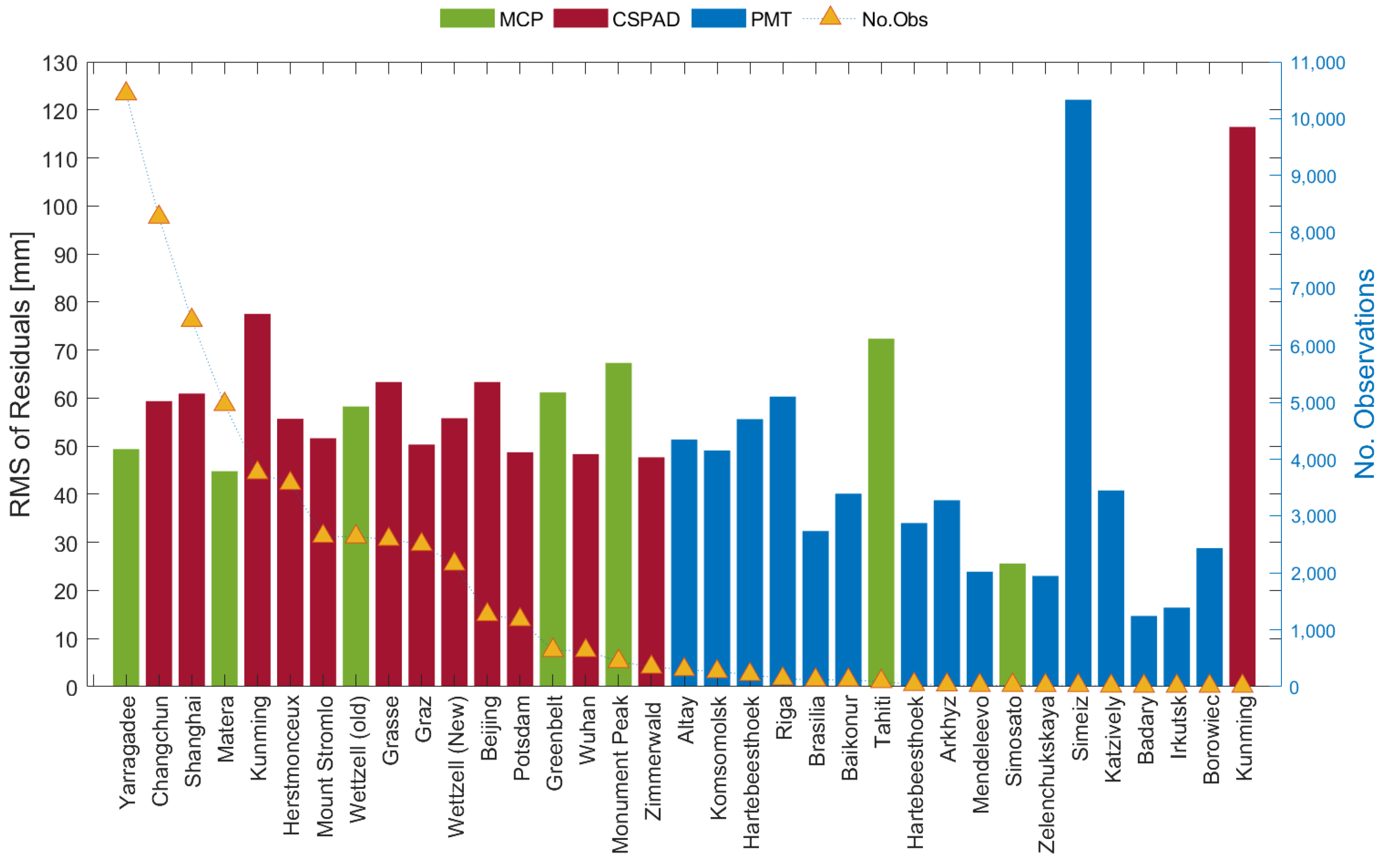

| Items | MEO (SHAO) | GEO/IGSO (SHAO) | MEO (NCRIEO) |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. corner cube | 42 | 90 | 38 |
| Diameter of each cube | 33 mm | 33 mm | 33 mm |
| Height of each cube | 24.0 mm | 24.0 mm | 23.3 mm |
| Dihedral offset | 0.6″ | 0.5″ | 1.1″ |
| Satellites (Tracking by ILRS only) | COMPASS-M3 (PRN: C11) BeiDou3-M9 (PRN: C29) BeiDou3-M10 (PRN: C30) | COMPASS-G1 (PRN: C01) COMPASS-I3 (PRN: C08) COMPASS-I5 (PRN: C10) COMPASS-I6B (PRN: C13) | BeiDou3-M2 (PRN: C20) BeiDou3-M3 (PRN: C21) |
| Detector Type | Monument | Code | Location Name | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMT | 1868 | KOML | Komsomolsk | Russia |
| 1873 | SIML | Simeiz | Ukraine | |
| 1874 | MDVS | Mendeleevo | Russia | |
| 1879 | ALTL | Atlay | Russia | |
| 1884 | RIGL | Riga | Latvia | |
| 1886 | ARKL | Arkhyz | Russia | |
| 1887 | BAIL | Baikonur | Kazakhstan | |
| 1889 | ZELL | Zelenchukskya | Russia | |
| 1890 | BADL | Badray | Russia | |
| 1891 | IRKL | Irkutsk | Russia | |
| 1893 | KTZL | Katzively | Ukraine | |
| 7407 | BRAL | Brasilia | Brazil | |
| 7501 | HARL | Brasilia | Brazil | |
| 7503 | HRTL | Hartebeesthoek | South Africa | |
| 7811 | BORL | Borowiec | Poland | |
| MCP | 7090 | YARL | Yarragadee | Australia |
| 7105 | GODL | Greenbelt | United States of America | |
| 7110 | MONL | Monument Peak | United States of America | |
| 7124 | THTL | Tahiti | French Polynesia | |
| 7838 | SISL | Simosato | Japan | |
| 7941 | MATM | Matera | Italy | |
| CSPAD | 7237 | CHAL | Changchun | China |
| 7249 | BEIL | Beijing | China | |
| 7396 | JFNL | Wuhan | China | |
| 7810 | ZIML | Hartebeesthoek | South Africa | |
| 7819 | KUN2 | Kunming | China | |
| 7821 | SHA2 | Shanghai | China | |
| 7825 | STL3 | Mt Stromlo | Australia | |
| 7827 | SOSW | Wettzell | Germany | |
| 7839 | GRZL | Graz | Austria | |
| 7840 | HERL | Herstmonceux | United Kingdom | |
| 7841 | POT3 | Potsdam | Germany | |
| 7845 | GRSM | Grasse | France (LLR) | |
| 8834 | WETL | Wettzell | Germany (WLRS) |
| AC | SAT | High-Performing | All | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (mm) | RMS (mm) | Mean (mm) | RMS (mm) | ||
| CODE | BDS-2 IGSO | −6.2 | 58.3 | −0.2 | 59.3 |
| BDS-2 MEO | −23.0 | 39.8 | −18.1 | 40.9 | |
| GFZ | BDS-2 IGSO | 2.7 | 55.5 | 4.3 | 57.2 |
| BDS-2 MEO | −24.9 | 52.6 | −18.5 | 53.6 | |
| BDS-3 CAST | 30.3 | 50.3 | 28.7 | 50.5 | |
| BDS-3 SECM | −48.5 | 61.5 | −52.3 | 65.5 | |
| WU | BDS-2 IGSO | −3.8 | 50.5 | −5.4 | 50.9 |
| BDS-2 MEO | −13.7 | 49.5 | −13.1 | 50.3 | |
| BDS-3 CAST | 7.2 | 47.4 | 3.0 | 48.2 | |
| BDS-3 SECM | −12.7 | 51.5 | −10.2 | 52.9 | |
| ESA | BDS-2 IGSO | 69.4 | 111.4 | 70.2 | 123.9 |
| BDS-2 MEO | −2.2 | 46.5 | 5.1 | 50.0 | |
| BDS-3 CAST | 46.8 | 51.2 | 45.4 | 51.3 | |
| BDS-3 SECM | −20.2 | 30.3 | −22.3 | 33.9 | |
| Model | CODE | GFZ | WU | ESA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRP | ECOM2 | ECOM | ECOM + PBW(BDS-3) | ECOM + estimated PBW |
| ERP | Not applied | Not applied | Applied in BDS-2 MEO | Applied |
| AT | Not applied | Not applied | Applied in BDS-2 | Not applied |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Liu, C.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, K. Current Status and Challenges of BDS Satellite Precise Orbit Products: From a View of Independent SLR Validation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2782. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112782
Li X, Liu C, Yuan Y, Zhang K. Current Status and Challenges of BDS Satellite Precise Orbit Products: From a View of Independent SLR Validation. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(11):2782. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112782
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xingxing, Chengbo Liu, Yongqiang Yuan, and Keke Zhang. 2023. "Current Status and Challenges of BDS Satellite Precise Orbit Products: From a View of Independent SLR Validation" Remote Sensing 15, no. 11: 2782. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112782
APA StyleLi, X., Liu, C., Yuan, Y., & Zhang, K. (2023). Current Status and Challenges of BDS Satellite Precise Orbit Products: From a View of Independent SLR Validation. Remote Sensing, 15(11), 2782. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112782






