PSI Spatially Constrained Clustering: The Sibari and Metaponto Coastal Plains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mapping the Sibari and Metaponto Coastal Plains
2.1. Geography of the Region of Interest
2.2. The SPINUA Algorithm for Ground Displacement Evaluations
3. Assessment of Homogeneous and Anomalous Ground Displacements
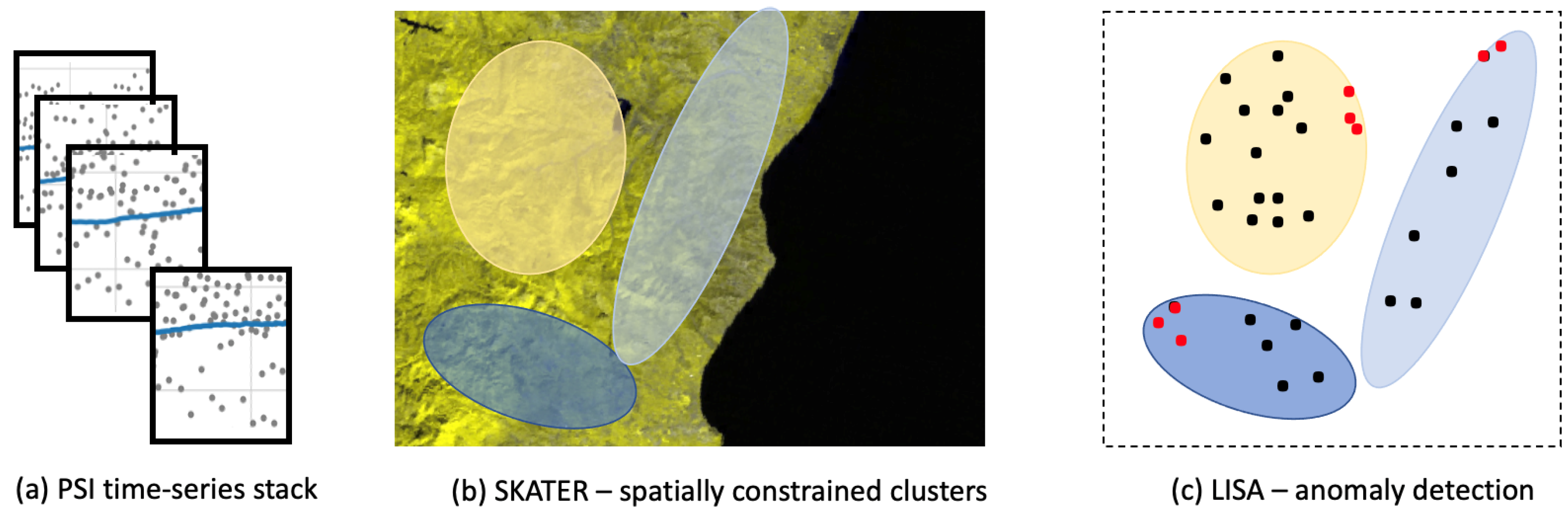
3.1. Methodological Overview
3.2. Spatially-Constrained Clustering Algorithm (SKATER)
3.3. LISA Outlier Detection
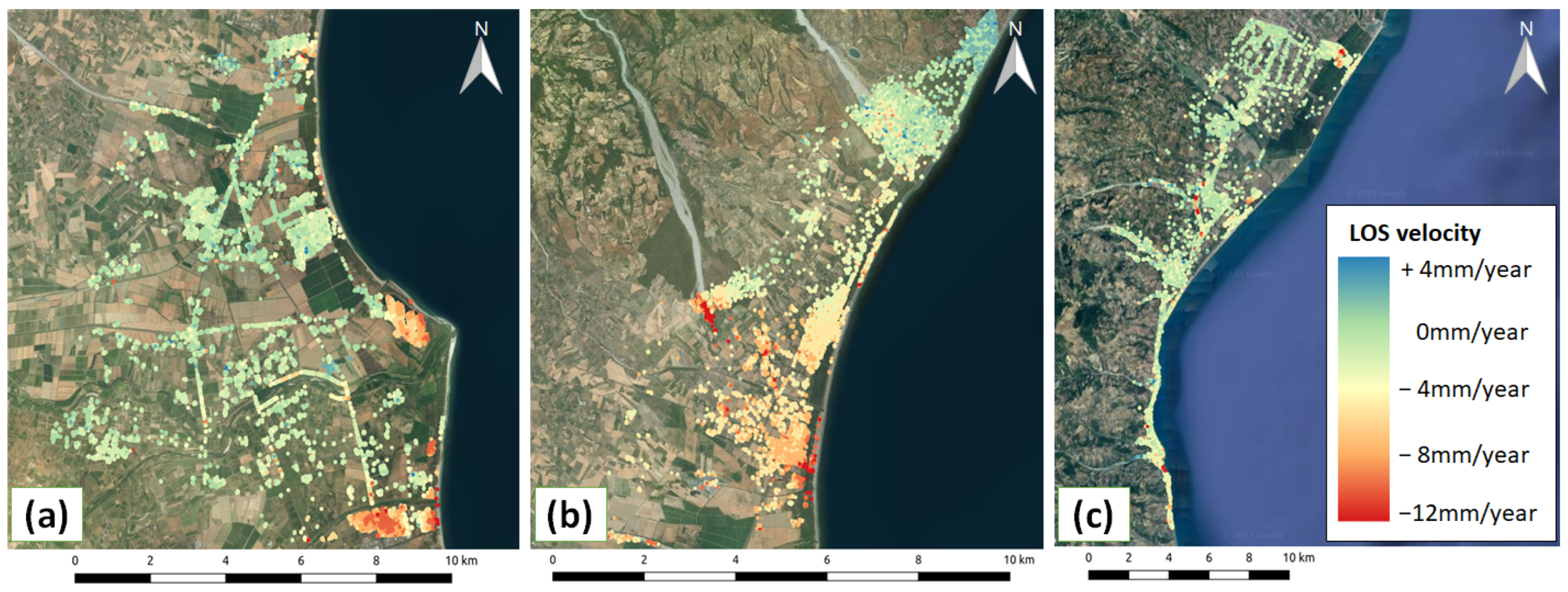
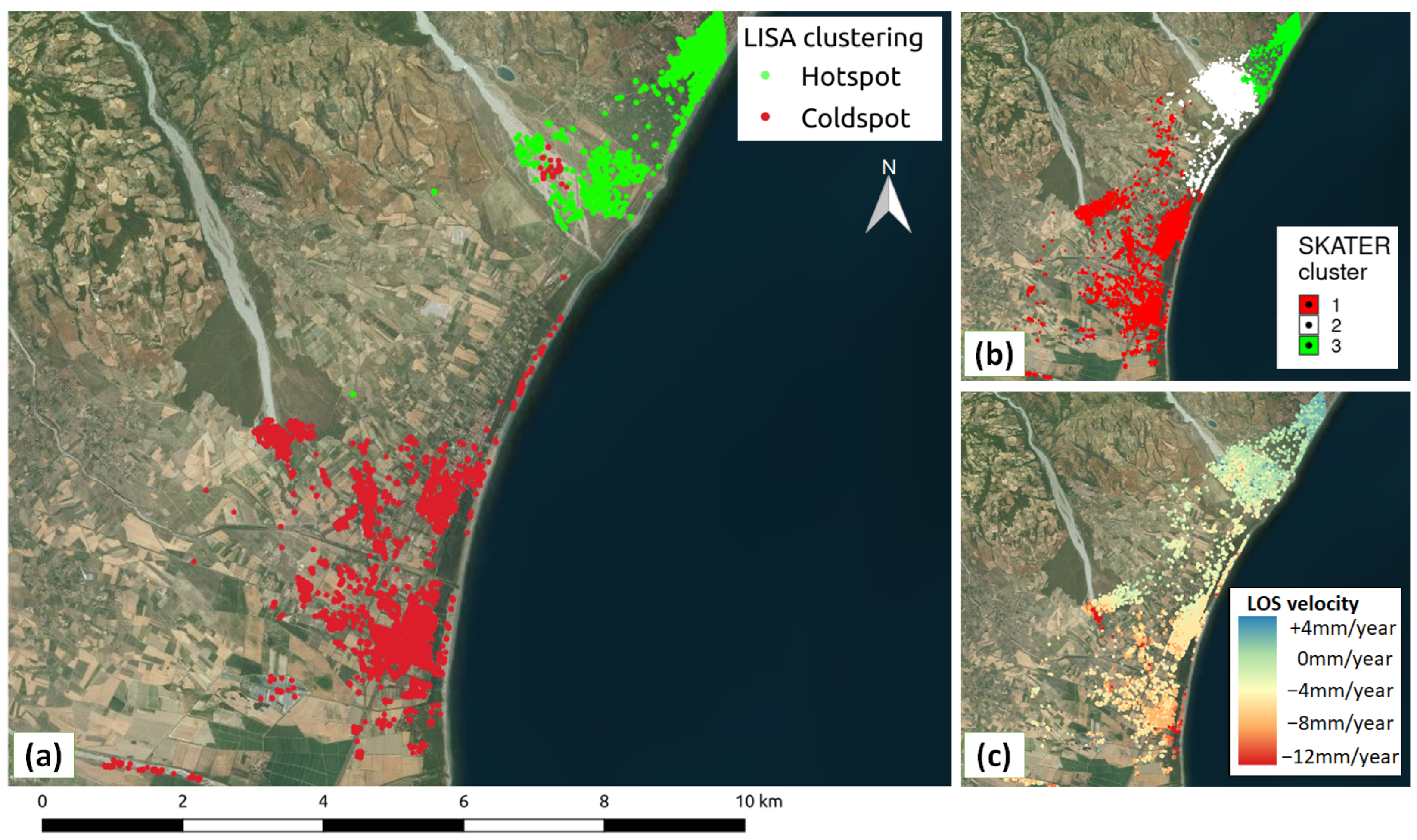
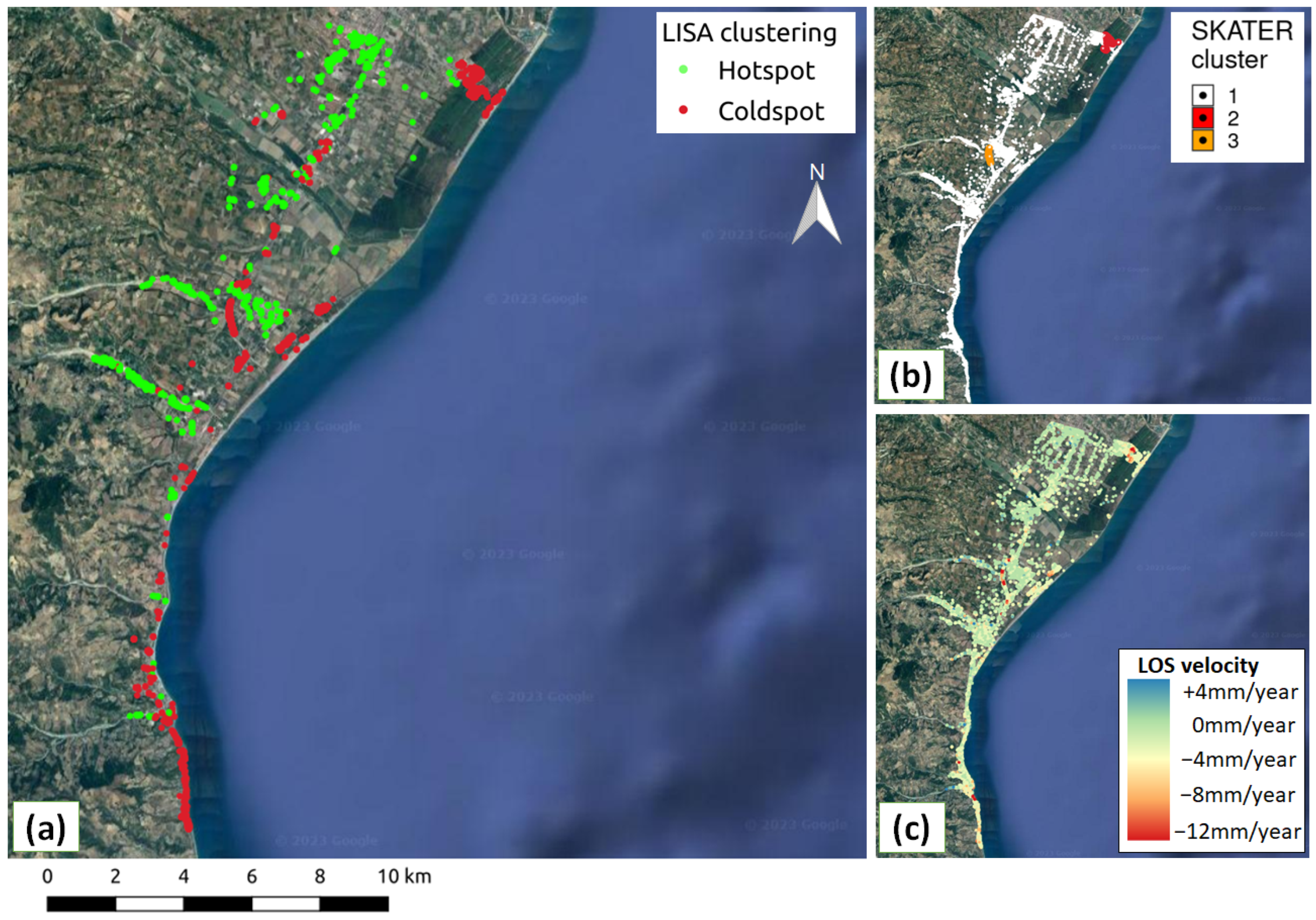
4. Results
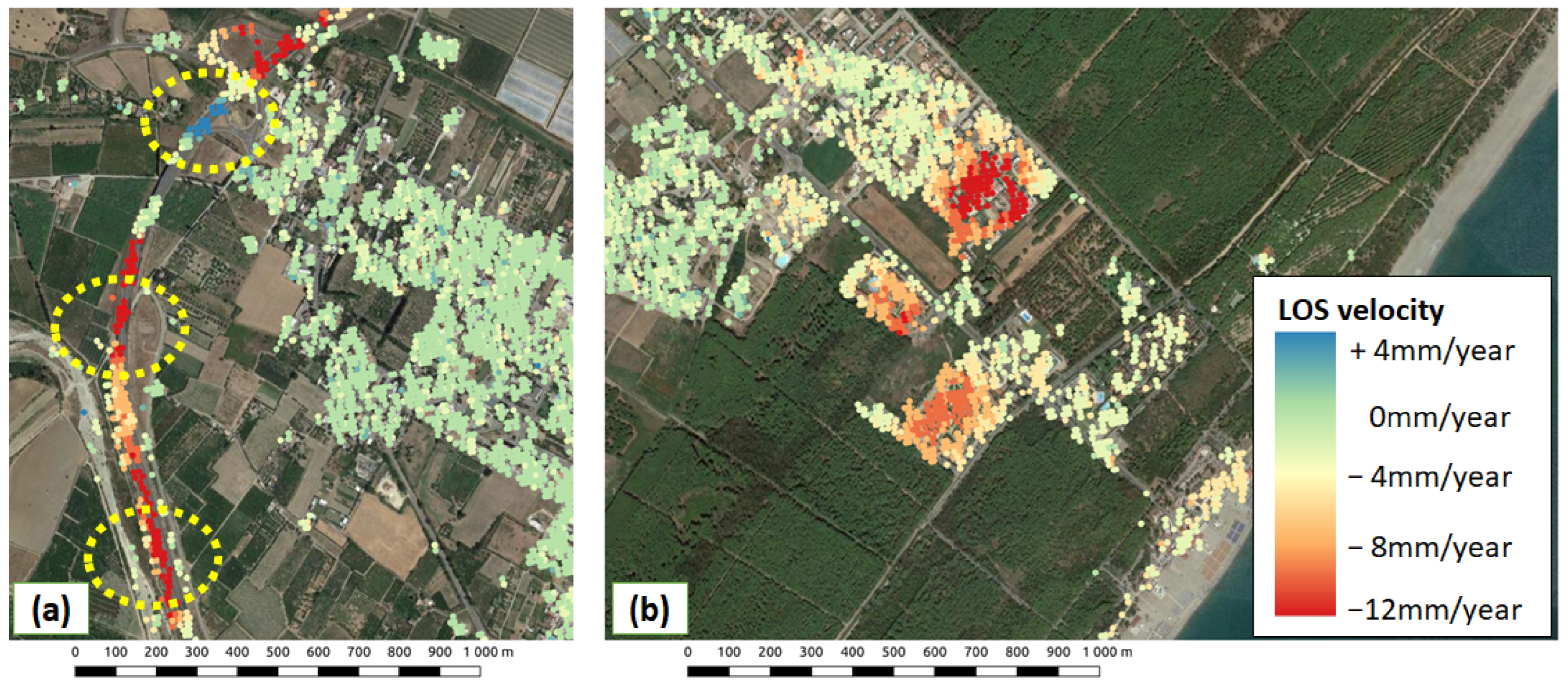
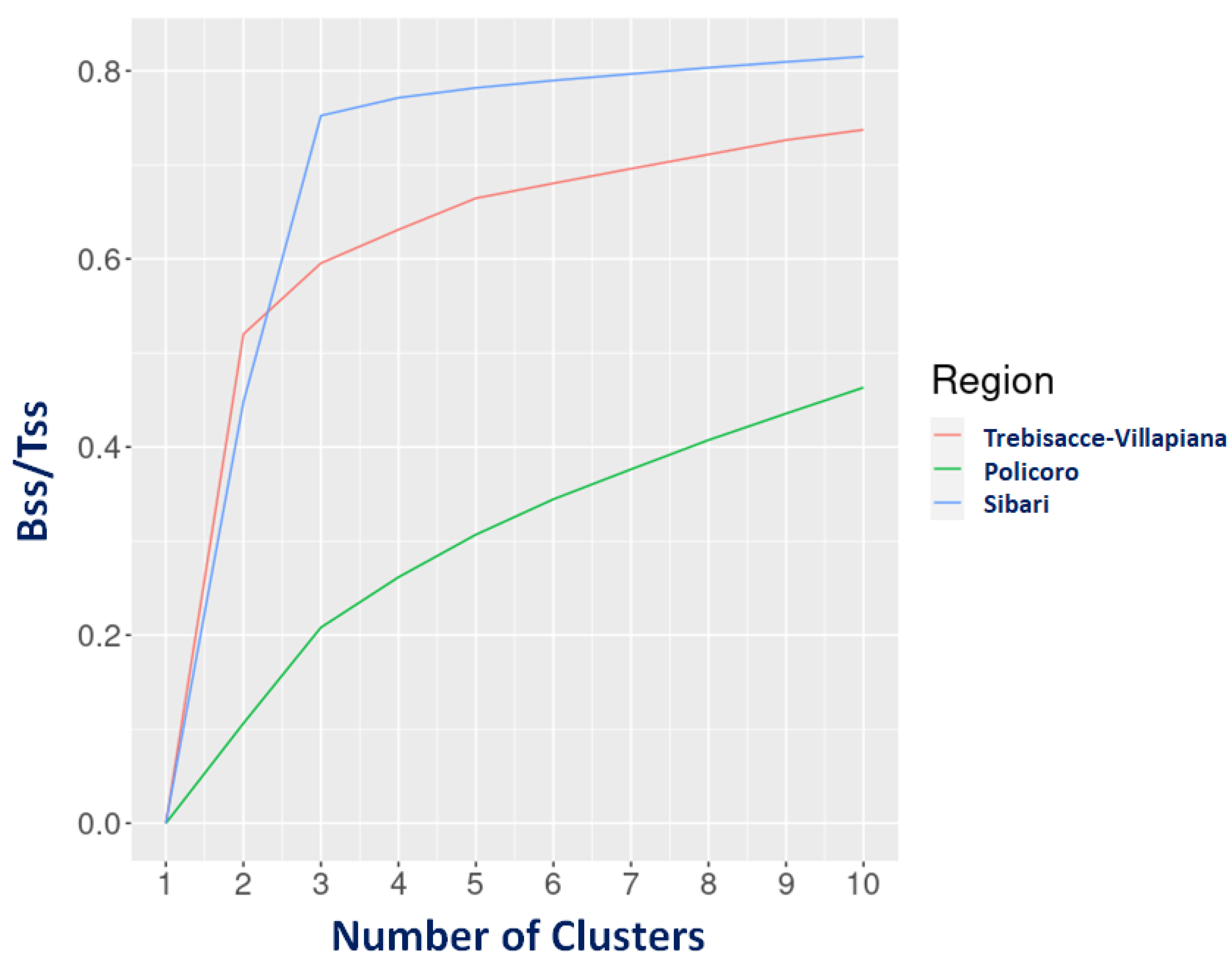
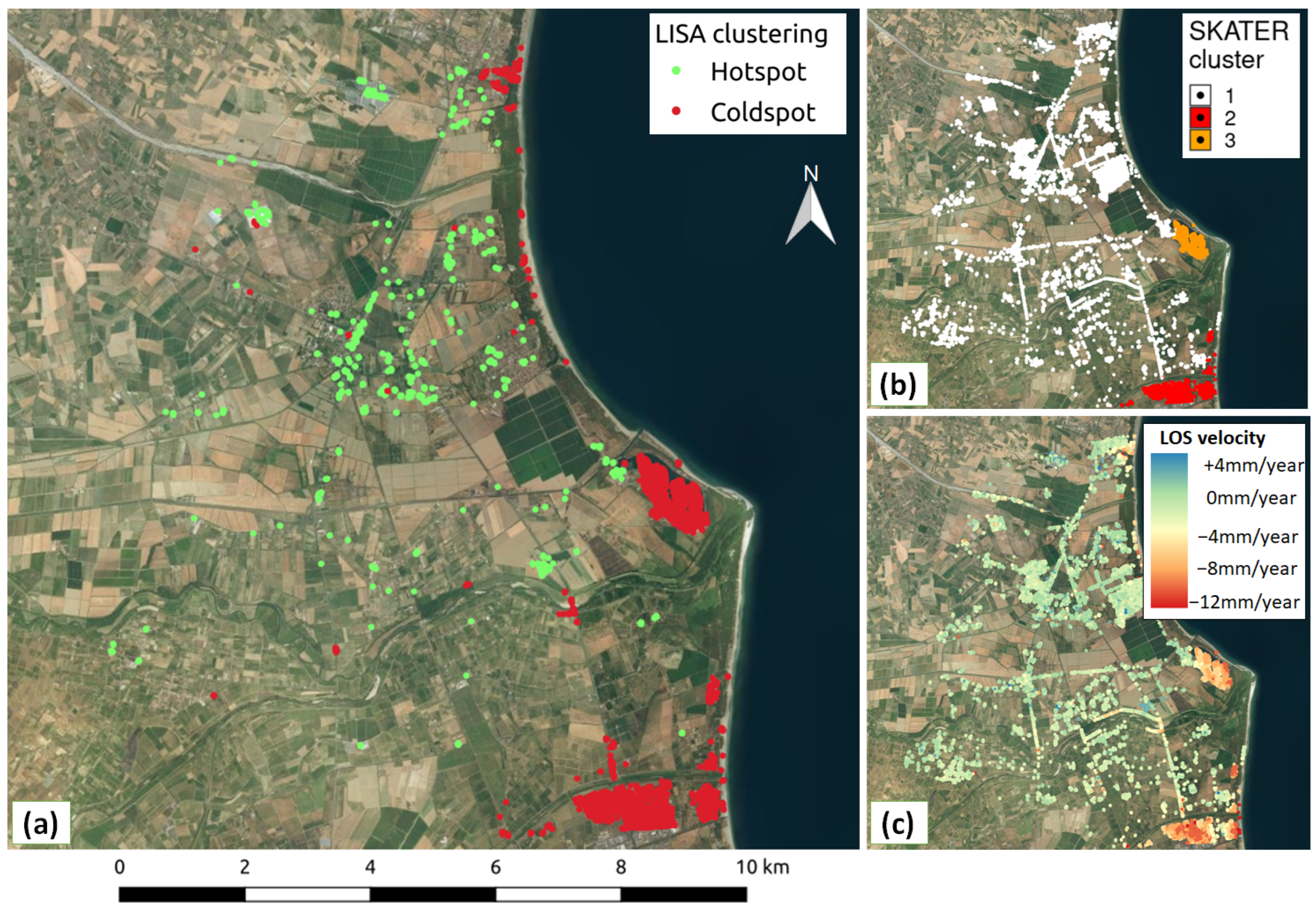
4.1. Revealing Homogeneous On-Ground Displacements with SKATER
4.2. Sibari
4.3. Trebisacce-Villapiana
4.4. Policoro
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D’Aranno, P.J.; Di Benedetto, A.; Fiani, M.; Marsella, M.; Moriero, I.; Palenzuela Baena, J.A. An application of persistent scatterer interferometry (psi) technique for infrastructure monitoring. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teatini, P.; Tosi, L.; Strozzi, T.; Carbognin, L.; Cecconi, G.; Rosselli, R.; Libardo, S. Resolving land subsidence within the Venice Lagoon by persistent scatterer SAR interferometry. Phys. Chem. Earth 2012, 40, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-González, M.; Devanthéry, N.; Crippa, B. Persistent scatterer interferometry: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; Ren, X.; Hussain, M.A.; Jan, M.Q. Monitoring Land Subsidence Using PS-InSAR Technique in Rawalpindi and Islamabad, Pakistan. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado Blasco, J.M.; Foumelis, M.; Stewart, C.; Hooper, A. Measuring urban subsidence in the Rome metropolitan area (Italy) with Sentinel-1 SNAP-StaMPS persistent scatterer interferometry. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, K.; Kumar, D.; Perissin, D. Assessment of subsidence in Delhi NCR due to groundwater depletion using TerraSAR-X and persistent scatterers interferometry. Imaging Sci. J. 2019, 67, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmanoğlu, B.; Dixon, T.H.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Jiang, Y. Mexico City subsidence observed with persistent scatterer InSAR. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nádudvari, Á. Using radar interferometry and SBAS technique to detect surface subsidence relating to coal mining in Upper Silesia from 1993–2000 and 2003–2010. Environ. Socio-Econ. Stud. 2016, 4, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solarski, M.; Machowski, R.; Rzetala, M.; Rzetala, M.A. Hypsometric changes in urban areas resulting from multiple years of mining activity. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawluszek-Filipiak, K.; Borkowski, A. Monitoring mining-induced subsidence by integrating differential radar interferometry and persistent scatterer techniques. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 54, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammirati, L.; Mondillo, N.; Rodas, R.A.; Sellers, C.; Di Martire, D. Monitoring land surface deformation associated with gold artisanal mining in the Zaruma City (Ecuador). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.C.; Kim, S.W.; Jung, H.S.; Min, K.D.; Won, J.S. Satellite observation of coal mining subsidence by persistent scatterer analysis. Eng. Geol. 2007, 92, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.A.; Chen, Z.; Shoaib, M.; Shah, S.U.; Khan, J.; Ying, Z. Sentinel-1A for monitoring land subsidence of coastal city of Pakistan using Persistent Scatterers In-SAR technique. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, R.; Deng, Y.; Ma, P.; Lin, H.; Wang, J. Mapping the Yellow River Delta land subsidence with multitemporal SAR interferometry by exploiting both persistent and distributed scatterers. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 148, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.H.M.; Ge, L.; Li, X.; Abidin, H.Z.; Andreas, H.; Zhang, K. Mapping land subsidence in Jakarta, Indonesia using persistent scatterer interferometry (PSI) technique with ALOS PALSAR. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 18, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassileva, M.; Al-Halbouni, D.; Motagh, M.; Walter, T.R.; Dahm, T.; Wetzel, H.U. A decade-long silent ground subsidence hazard culminating in a metropolitan disaster in Maceió, Brazil. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofani, V.; Raspini, F.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI) technique for landslide characterization and monitoring. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 1045–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. A new algorithm for processing interferometric data-stacks: SqueeSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Segall, P.; Zebker, H. Persistent scatterer interferometric synthetic aperture radar for crustal deformation analysis, with application to Volcán Alcedo, Galápagos. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, O.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Broquetas, A. Linear and nonlinear terrain deformation maps from a reduced set of interferometric SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2243–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M.; Falco, S.; Malvarosa, F.; Minati, F. A new method for identification and analysis of persistent scatterers in series of SAR images. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2008–2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 6–11 July 2008; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Bovenga, F.; Argentiero, I.; Refice, A.; Nutricato, R.; Nitti, D.O.; Pasquariello, G.; Spilotro, G. Assessing the Potential of Long, Multi-Temporal SAR Interferometry Time Series for Slope Instability Monitoring: Two Case Studies in Southern Italy. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovenga, F.; Nutricato, R.; Guerriero, A.R.L.; Chiaradia, M. SPINUA: A flexible processing chain for ERS/ENVISAT long term interferometry. In Proceedings of the 2004 Envisat & ERS Symposium (ESA SP-572), Salzburg, Austria, 6–10 September 2004; Volume 572. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, H.; Zhang, H.; Dai, H.; Wang, C.; Tang, W.; Zou, L.; Tang, Y. Landslide Identification and Gradation Method Based on Statistical Analysis and Spatial Cluster Analysis. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoroso, N.; Cilli, R.; Bellantuono, L.; Massimi, V.; Monaco, A.; Nitti, D.O.; Nutricato, R.; Samarelli, S.; Taggio, N.; Tangaro, S.; et al. PSI Clustering for the Assessment of Underground Infrastructure Deterioration. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, A.C. Classification of landslide activity on a regional scale using persistent scatterer interferometry at the moselle valley (Germany). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Casagli, N.; Catani, F.; Tofani, V. Persistent Scatterers Interferometry Hotspot and Cluster Analysis (PSI-HCA) for detection of extremely slow-moving landslides. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 466–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib, O.C.; Shimon, W.; Sarah, K.; Tonian, R. Detection of sinkhole activity in West-Central Florida using InSAR time series observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, A.; Vitiello, A.; Bonano, M.; Miano, A.; Lanari, R.; Acampora, G.; Prota, A. On the Joint Exploitation of Satellite DInSAR Measurements and DBSCAN-Based Techniques for Preliminary Identification and Ranking of Critical Constructions in a Built Environment. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struhár, J.; Rapant, P. Spatiotemporal Visualisation of PS InSAR Generated Space–Time Series Describing Large Areal Land Deformations Using Diagram Map with Spiral Graph. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajocco, S.; Dragoz, E.; Gitas, I.; Smiraglia, D.; Salvati, L.; Ricotta, C. Mapping Forest Fuels through Vegetation Phenology: The Role of Coarse-Resolution Satellite Time-Series. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, Y.; Gauthier, S.; Burton, P.; Vaillancourt, M.A. An alternative fire regime zonation for Canada. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2012, 21, 1052–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Shu, S.; Liu, H.; Song, W.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z. Object-based spatial cluster analysis of urban landscape pattern using nighttime light satellite images: A case study of China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 2328–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, W.; Liu, W. Regionalization and spatiotemporal variation of drought in China based on standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index (1961–2013). Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 950262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, J.P.; Assunção, R.M.; Reis, E.A. A minimal spanning tree algorithm applied to spatial cluster analysis. Electron. Notes Discret. Math. 2001, 7, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assunção, R.M.; Neves, M.C.; Câmara, G.; da Costa Freitas, C. Efficient regionalization techniques for socio-economic geographical units using minimum spanning trees. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2006, 20, 797–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, O.; Janikas, M.V.; Assunção, R.M.; Lee, T.H. A quantitative comparison of regionalization methods. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2021, 35, 2287–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K. Data clustering: 50 years beyond K-means. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Local Indicators of Spatial Association—LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianflone, G.; Tolomei, C.; Brunori, C.A.; Dominici, R. InSAR time series analysis of natural and anthropogenic coastal plain subsidence: The case of Sibari (Southern Italy). Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 16004–16023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, S.; Moretti, S. Analysis of recent ground subsidence in the Sibari plain (Italy) by means of satellite SAR interferometry-based methods. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 4550–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vespasiano, G.; Cianflone, G.; Romanazzi, A.; Apollaro, C.; Dominici, R.; Polemio, M.; De Rosa, R. A multidisciplinary approach for sustainable management of a complex coastal plain: The case of Sibari Plain (Southern Italy). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 109, 740–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maesano, F.E.; Tiberti, M.M.; Basili, R. The Calabrian Arc:Three-dimensional modelling of the subduction interface. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molin, P.; Pazzaglia, F.J.; Dramis, F. Geomorphic expression of active tectonics in a rapidly-deforming forearc, Sila massif, Calabria, southern Italy. Am. J. Sci. 2004, 304, 559–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, C.; Tortorici, L. Active faulting in the Calabrian arc and eastern Sicily. J. Geodyn. 2000, 29, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortorici, L.; Monaco, C.; Tansi, C.; Cocina, O. Recent and active tectonics in the Calabrian arc (Southern Italy). Tectonophysics 1995, 243, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.A. Advances in delta-subsidence research using satellite methods. Hydrogeol. J. 2016, 24, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastoria, B.; Bussettini, M.; Mariani, S.; Piva, F.; Braca, G. Rapporto sulle condizioni di pericolosità da alluvione in Italia e indicatori di rischio associati. Istituto Superiore per la Protezione e la Ricerca Ambientale, ISPRA. Report 353/2021. 2021. Available online: https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/it/pubblicazioni/rapporti/rapporto-sulle-condizioni-di-pericolosita-da-alluvione-in-italia-e-indicatori-di-rischio-associati (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Comerci, V.; Blumetti, A.M.; Di Manna, P.; Fiorenza, D.; Guerrieri, L.; Lucarini, M.; Serva, L.; Vittori, E. ITHACA Project and capable faults in the Po Plain (northern Italy). Ing. Sismica 2013, 30, 36–50. [Google Scholar]
- de Musso, N.M.; Capolongo, D.; Refice, A.; Lovergine, F.P.; D’Addabbo, A.; Pennetta, L. Spatial evolution of the December 2013 Metaponto plain (Basilicata, Italy) flood event using multi-source and high-resolution remotely sensed data. J. Maps 2018, 14, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfredi, M.; Coppola, R.; Simoniello, T.; Coluzzi, R.; D’Emilio, M.; Imbrenda, V.; Macchiato, M. Early identification of land degradation hotspots in complex bio-geographic regions. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8154–8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucci, L. Raised marine terraces in the Northern Calabrian Arc (Southern Italy): A ∼600 kyr-long geological record of regional uplift. Ann. Geophys. 2004. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2122/838 (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Muzzillo, R.; Zuffianò, L.E.; Rizzo, E.; Canora, F.; Capozzoli, L.; Giampaolo, V.; De Giorgio, G.; Sdao, F.; Polemio, M. Seawater Intrusion Proneness and Geophysical Investigations in the Metaponto Coastal Plain (Basilicata, Italy). Water 2020, 13, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Anselin, L. rgeoda: R Library for Spatial Data Analysis. 2022. Available online: https://github.com/geodacenter/rgeoda/; https://geodacenter.github.io/rgeoda/ (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Westaway, R. Quaternary uplift of southern Italy. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1993, 98, 21741–21772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbau, C.; Greco, M.; Martino, G.; Olivo, E.; Simeoni, U. Assessment of the Vulnerability of the Lucana Coastal Zones (South Italy) to Natural Hazards. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, M.; Martino, G. Vulnerability assessment for preliminary flood risk mapping and management in coastal areas. Nat. Hazards 2016, 82, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| ROI | Orbit | No. of Images | No. of PSs | Time Span |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sibari | Asc | 248 | 38,386 | 2 January 2017 to 22 February 2021 |
| Trebisacce-Villapiana | Asc | 190 | 24,574 | 1 April 2015 to 15 February 2019 |
| Policoro | Asc | 204 | 38,265 | 1 April 2015 to 5 March 2019 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amoroso, N.; Cilli, R.; Nitti, D.O.; Nutricato, R.; Iban, M.C.; Maggipinto, T.; Tangaro, S.; Monaco, A.; Bellotti, R. PSI Spatially Constrained Clustering: The Sibari and Metaponto Coastal Plains. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102560
Amoroso N, Cilli R, Nitti DO, Nutricato R, Iban MC, Maggipinto T, Tangaro S, Monaco A, Bellotti R. PSI Spatially Constrained Clustering: The Sibari and Metaponto Coastal Plains. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(10):2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102560
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmoroso, Nicola, Roberto Cilli, Davide Oscar Nitti, Raffaele Nutricato, Muzaffer Can Iban, Tommaso Maggipinto, Sabina Tangaro, Alfonso Monaco, and Roberto Bellotti. 2023. "PSI Spatially Constrained Clustering: The Sibari and Metaponto Coastal Plains" Remote Sensing 15, no. 10: 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102560
APA StyleAmoroso, N., Cilli, R., Nitti, D. O., Nutricato, R., Iban, M. C., Maggipinto, T., Tangaro, S., Monaco, A., & Bellotti, R. (2023). PSI Spatially Constrained Clustering: The Sibari and Metaponto Coastal Plains. Remote Sensing, 15(10), 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102560













