Exploring the Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of China’s Four Major Urban Agglomerations in the Luminous Remote Sensing Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. Night-Time Light
2.2.2. Baidu Search Index
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Night Light Data Correction
- Ridgeline sampling regression
- Improved data correction combined with the Hadamard matrix
2.3.2. Methods of Urban Spatial Expansion Analysis
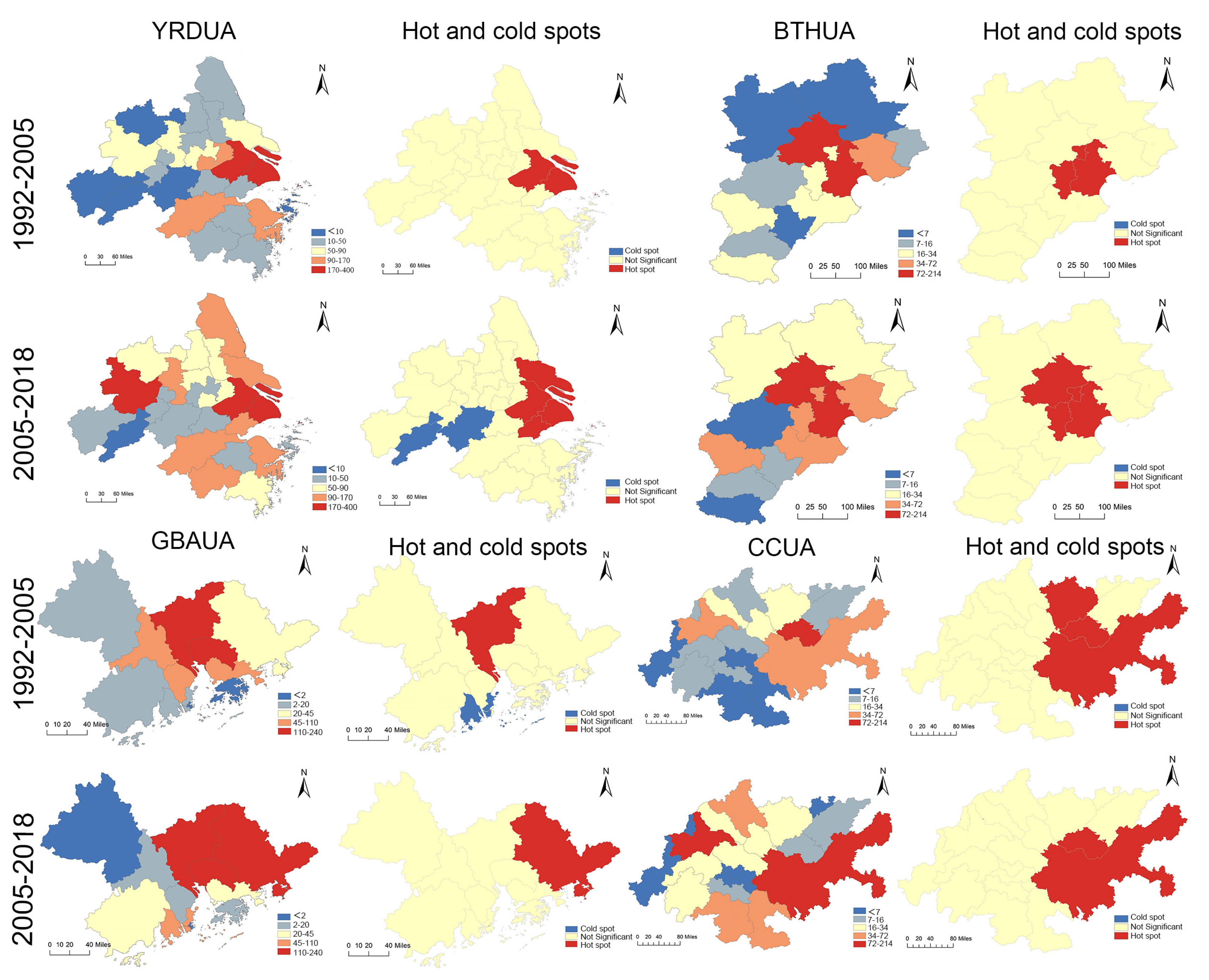
- Hot and cold spot extraction for built-up areas based on Getis–Ord Gi*
- Analysis of Built-up Area Expansion Index
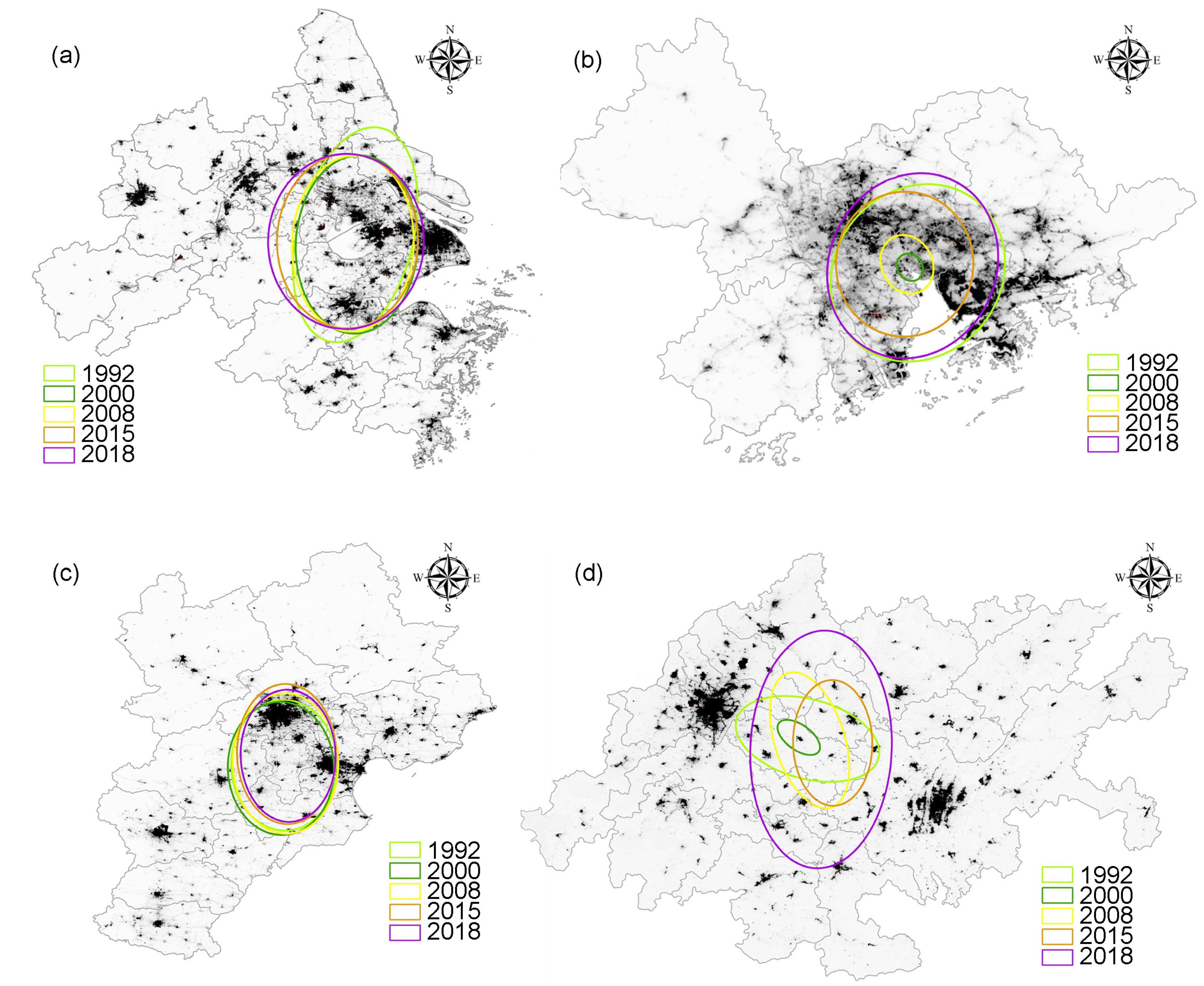
- Directional evolution of UAs using SDE
- Center of gravity index
2.3.3. City Connection Based on the Baidu Search Index
3. Results
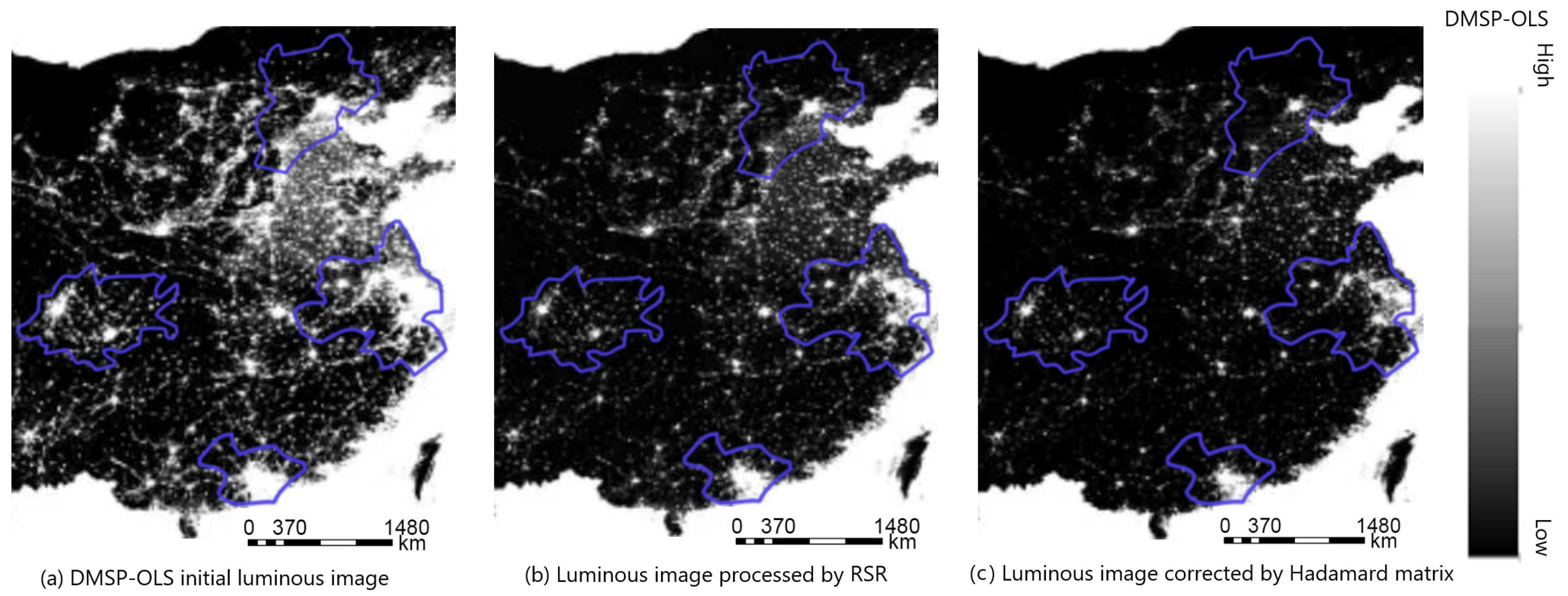
3.1. Results of Night Light Data Correction
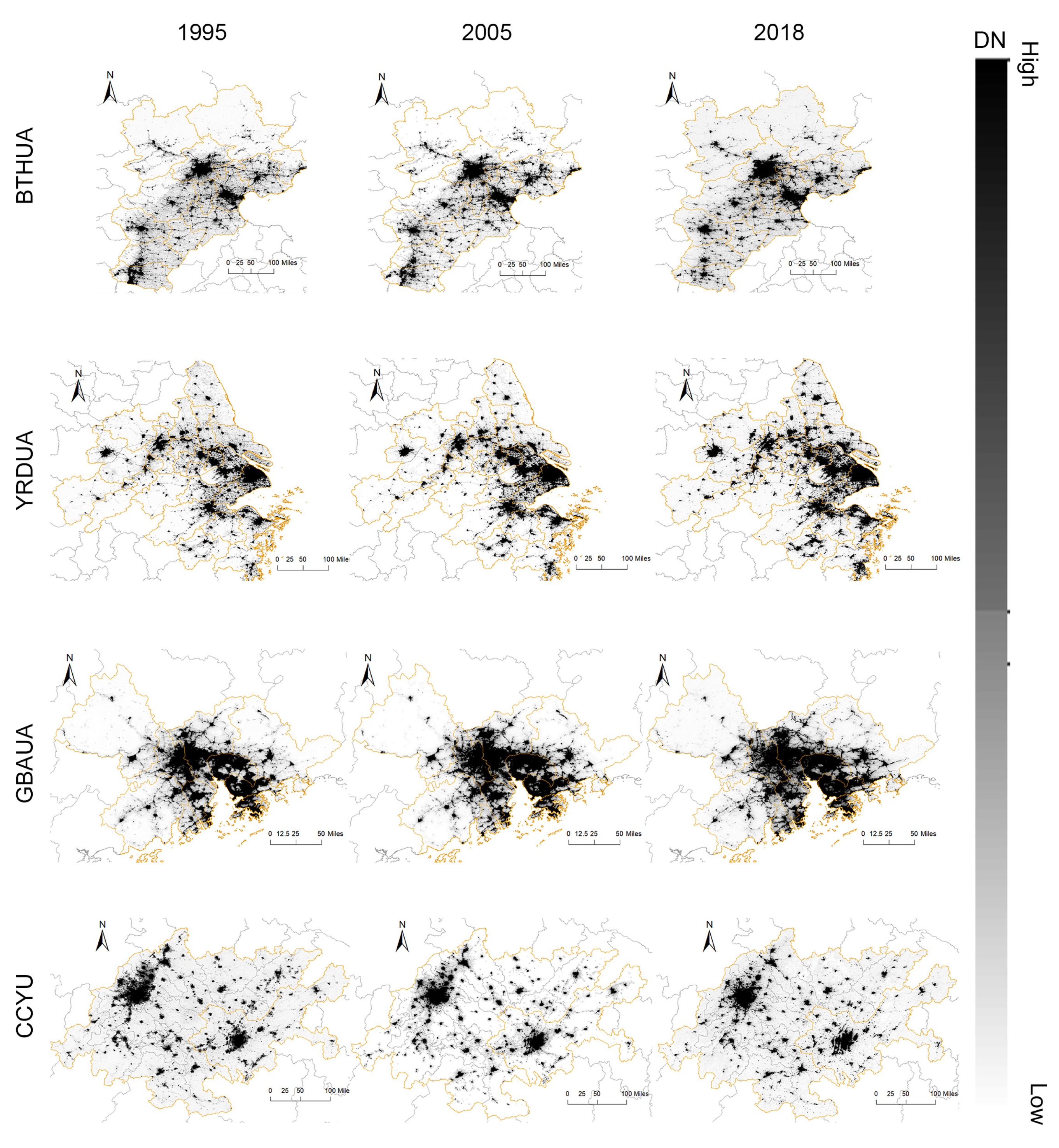
3.2. Urban Evolution of FMUAs under Night Light
4. Discussion
4.1. Relationship between Population, DEM, and Luminous Growth
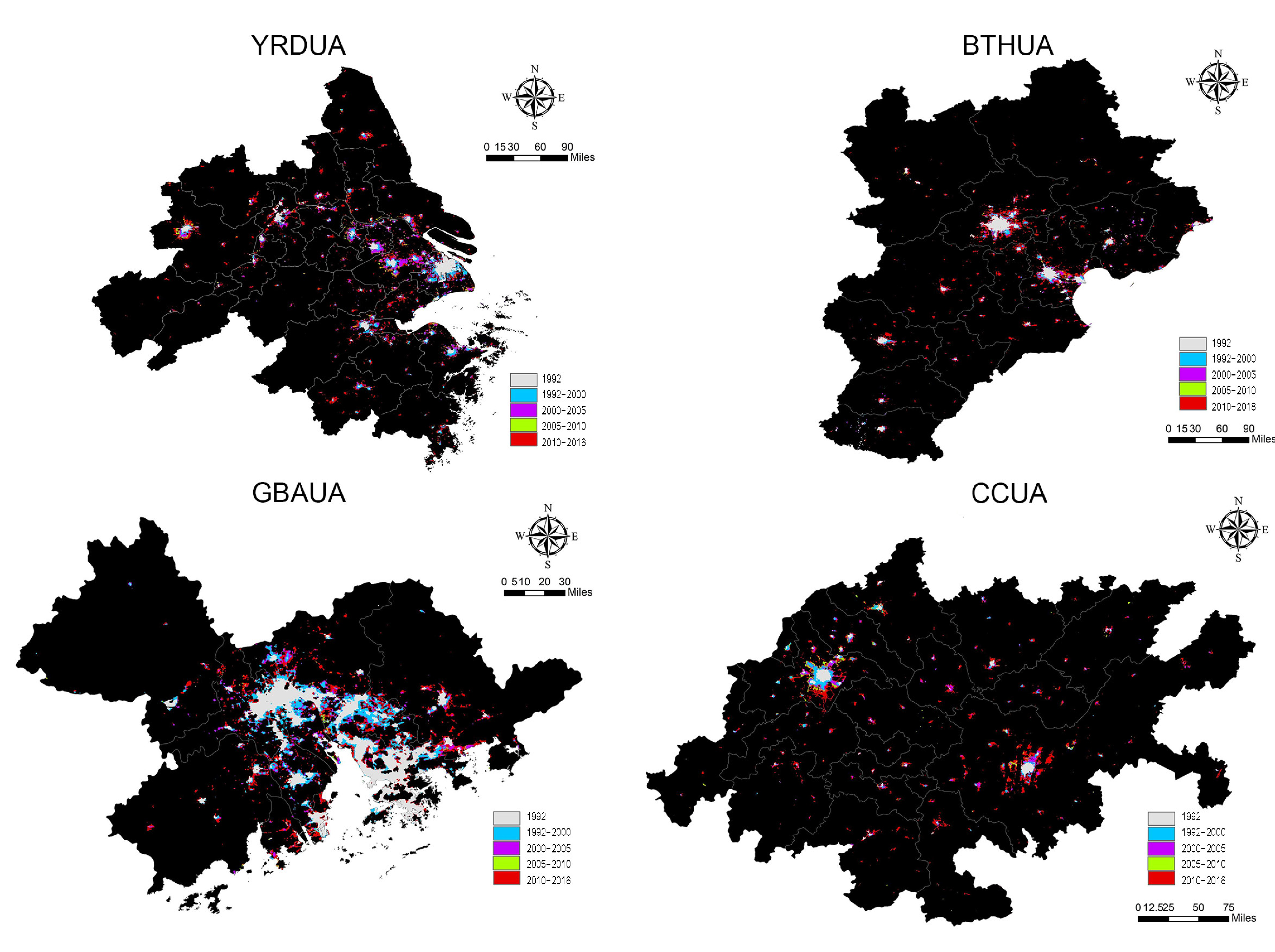
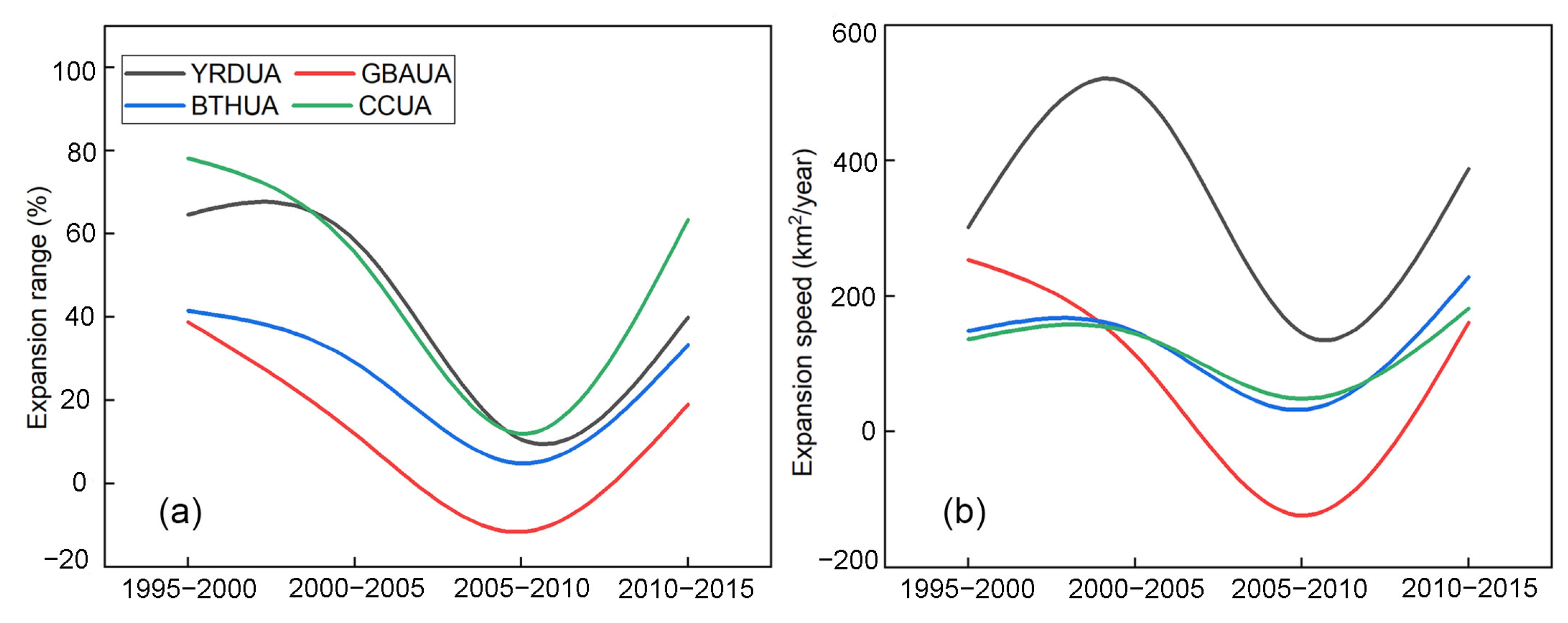
4.2. Evolution of Built-Up Area Expansion in UAs
4.3. SDE Directional Evolution of UAs
4.4. Development Planning of UAs Using the Luminous Correlation Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, M.; Guo, S.; Guan, Y.; Cai, D.; Zhang, C.; Fraedrich, K.; Liao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Z. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity Analysis of Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration: Evidence from Nighttime Light Data (2001–2019). Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Mertes, C.M.; Tatem, A.J.; Tan, B.; Sulla-Menashe, D.; Graves, S.J.; Patel, N.N.; Horton, J.A.; Gaughan, A.E.; Rollo, J.T.; et al. A new urban landscape in East–Southeast Asia, 2000–2010. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 034002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2019 Revision; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019.
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global Change and the Ecology of Cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, J. The effects of human movements on urban climate over Eastern China. npj Urban Sustain. 2021, 1, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Zhan, W.; Voogt, J.; Quan, J.; Huang, F.; Zhou, J.; Bechtel, B.; Hu, L.; Wang, K.; Cao, C.; et al. Meteorological controls on daily variations of nighttime surface urban heat islands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 253, 112198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, T.; Shi, Y.; Gilbert, K.M.; Liu, X. Spatiotemporal variations of air pollutants based on ground observation and emission sources over 19 Chinese urban agglomerations during 2015–2019. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ferrier, R.C.; Jenkins, A.; Yuan, J.; Bailey, M.J.; et al. Forty years of reform and opening up: China’s progress toward a sustainable path. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau9413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Nian, M.; Li, L. China’s Strategies and Policies for Regional Development During the Period of the 14th Five-Year Plan. Chin. J. Urban Environ. Stud. 2020, 8, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, J. Efficiency evaluation and influencing factors of energy saving and emission reduction: An empirical study of China’s three major urban agglomerations from the perspective of environmental benefits. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, S.; Zheng, Y.; Xiao, X. Integrated regional development: Comparison of urban agglomeration policies in China. Land Use Policy 2022, 114, 105939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. Statistics, China City Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Li, X.; Lu, Z. Quantitative measurement on urbanization development level in urban Agglomerations: A case of JJJ urban agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahtta, R.; Fragkias, M.; Güneralp, B.; Mahendra, A.; Reba, M.; Wentz, E.A.; Seto, K.C. Urban land expansion: The role of population and economic growth for 300+ cities. npj Urban Sustain. 2022, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Du, S.; Bai, L.; Liu, B. Mapping Annual Urban Evolution Process (2001–2018) at 250 m: A normalized multi-objective deep learning regression. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 278, 113088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Balz, T. Beijing Land Subsidence Revealed Using PS-InSAR with Long Time Series TerraSAR-X SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Lv, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Li, N. Common fate of sister lakes in Hulunbuir Grassland: Long-term harmful algal bloom crisis from multi-source remote sensing insights. J. Hydrol. 2021, 594, 125970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; He, T.; Liang, S.; Roujean, J.-L.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, X. Multi-decadal analysis of high-resolution albedo changes induced by urbanization over contrasted Chinese cities based on Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; He, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, H. Quantitative Evaluation of Urban Expansion using NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light and Landsat Spectral Data. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 76, 103338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Elvidge, C.D. Night on Earth: Mapping decadal changes of anthropogenic night light in Asia. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 22, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, C.; Haynie, S.; Pei, T.; Xu, T. Night-time light derived estimation of spatio-temporal characteristics of urbanization dynamics using DMSP/OLS satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, W.; Li, M.; Huang, K. Building a Series of Consistent Night-Time Light Data (1992–2018) in Southeast Asia by Integrating DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 58, 1843–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, X. A harmonized global nighttime light dataset 1992–2018. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, X. Harmonization of DMSP and VIIRS Nighttime Light Data from 1992–2021 at the Global Scale. Figshare. Dataset. 2022. Available online: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/Harmonization_of_DMSP_and_VIIRS_nighttime_light_data_from_1992-2018_at_the_global_scale/9828827/7 (accessed on 11 February 2023).
- Wang, C.; Zhan, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Fu, P.; Huang, F.; Lai, J.; Chen, J.; Hong, F.; et al. Satellite-based mapping of the Universal Thermal Climate Index over the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chan, P.; Deng, T.; Yang, H.-L.; Luo, H.-Y.; Xia, D.; He, Y.-Q. Review of advances in urban climate study in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area, China. Atmos. Res. 2021, 261, 105759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liang, L.; Sun, Z.; Wang, X. Spatiotemporal differentiation and the factors influencing urbanization and ecological environment synergistic effects within the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 243, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, C.; Jiao, L.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Y. Analysis on the spatial-temporal evolution of urban agglomeration resilience: A case study in Chengdu-Chongqing Urban Agglomeration, China. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 79, 103167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, C.N. Ciesin Thematic Guide to Night-Time Light Remote Sensing and Its Applications; Center for International Earth Science Information Network of Columbia University: Palisades, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pok, S.; Matsushita, B.; Fukushima, T. An easily implemented method to estimate impervious surface area on a large scale from MODIS time-series and improved DMSP-OLS nighttime light data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 133, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.-C.; Baugh, K. What is so great about nighttime VIIRS data for the detection and characterization of combustion sources? Proc. Asia-Pac. Adv. Netw. 2013, 35, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Zhen, F.; Wang, B.; Xi, G.L. The research of the Yangtze River Delta Core Area’s City network characteristics based on Baidu index. Econ. Geogr. 2013, 33, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wei, H.; Li, N.; Chen, S.; Qu, W.; Zhang, Y. Exploring the Spatial-Temporal Dynamics of the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration Based on Night-Time Light Remote Sensing Technology. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 5369–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, P.S. Image-Based Atmospheric Corrections—Revisited and Improved. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1996, 62, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Schott, J.R.; Salvaggio, C.; Volchok, W.J. Radiometric Scene Normalization Using Pseudoinvariant Features; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1988; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jing, W.; Yao, L.; Yue, X.; Zhao, X. A New Urban Index for Expressing Inner-City Patterns Based on MODIS LST and EVI Regulated DMSP/OLS NTL. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wu, J.; Li, W.; Peng, J.; Liu, H. Evaluating Saturation Correction Methods for DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data: A Case Study from China’s Cities. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9853–9872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Woodcock, C.E.; Seto, K.C.; Lenney, M.P.; Macomber, S.A. Classification and Change Detection Using Landsat TM Data: When and How to Correct Atmospheric Effects? Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 75, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Pandey, B.; Seto, K.C. A Robust Method to Generate a Consistent Time Series From DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data. IEEE Trans. Geoence Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 5821–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwitira, I.; Murwira, A.; Zengeya, F.M.; Shekede, M.D. Application of GIS to predict malaria hotspots based on Anopheles arabiensis habitat suitability in Southern Africa. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 64, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleasby, I.R.; Owen, E.; Wilson, L.; Wakefield, E.D.; O’Connell, P.; Bolton, M. Identifying important at-sea areas for seabirds using species distribution models and hotspot mapping. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 241, 108375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Huang, H. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Multiscale Urbanization Level in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region Using the Integration of DMSP/OLS and NPP/VIIRS Night Light Datasets. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, J.; Nie, P. Tracking the history of urban expansion in Guangzhou (China) during 1665–2017: Evidence from historical maps and remote sensing images. Land Use Policy 2022, 112, 105773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Jiang, F. Spatial and temporal distribution of population in urban agglomerations changes in China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Xia, R.; Li, Q.; Liu, H.; Shi, T.; Wu, G. Comparing hillside urbanizations of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, Yangtze River Delta and Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macau greater Bay area urban agglomerations in China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Hu, S. Ecological efficiency and its determining factors in an urban agglomeration in China: The Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration. Urban Clim. 2022, 41, 101071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Smith, S.J.; Zhao, K.; Imhoff, M.L.; Thomson, A.M.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; Asrar, G.R.; Zhang, X.; He, C.; Elvidge, C.D. A global map of urban extent from nightlights. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 0554011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gu, T.; Zeng, J. Urbanisation and ecosystem health in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River urban agglomerations, China: A U-curve relationship. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 318, 115565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, N.; Wong, S.W.; Ren, Y.; Shen, L. Regional Disparity in Urbanizing China: Empirical Study of Unbalanced Development Phenomenon of Towns in Southwest China. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2020, 146, 05020013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| A, B/% | YRDUA | GBAUA | BTHYA | CCUA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0−100 | 73.10, 90.44 | 43.31, 90.44 | 61.07, 97.19 | 0.01, 0 |
| 100−500 | 21.37, 4.95 | 14.28, 4.95 | 34.47, 2.8 | 55.24, 76.25 |
| 500−1000 | 5.15, 3.77 | 19.34, 3.77 | 4.26, 0.02 | 29.47, 23.4 |
| 1000−1500 | 0.37, 0.76 | 18.29, 0.76 | 0.2, 0 | 8.3, 0.29 |
| 1500−3000 | 0.01, 0.09 | 4.79, 0.09 | 0, 0 | 6.99, 0.06 |
| YRDUA | GBAUA | BTHYA | CCUA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Threshold | 19 | 12 | 12 | 11 |
| Statistical values | 7225.92 | 4536.63 | 3564.53 | 2367.67 |
| Extracted values | 7408.57 | 4626.38 | 3429.45 | 2271.75 |
| Error | −2.53% | −1.98% | 3.78% | 4.05% |
| Year | Threshold | Statistical Values | Extracted Values | Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1992 | 12 | 1510.83 | 1427.10 | 5.54% |
| 1993 | 12 | 1607.75 | 1485.80 | 7.58% |
| 1994 | 12 | 1664.54 | 1719.28 | −3.29% |
| 1995 | 12 | 1728.21 | 1790.62 | −3.61% |
| 1996 | 12 | 1755.34 | 1802.60 | −2.69% |
| 1997 | 12 | 1786.24 | 1798.09 | −0.66% |
| 1998 | 12 | 1787.06 | 1918.88 | −7.38% |
| 1999 | 12 | 1908.07 | 2072.96 | −8.64% |
| 2000 | 12 | 2336.87 | 2532.73 | −8.38% |
| 2001 | 12 | 2393.91 | 2488.83 | −3.96% |
| 2002 | 12 | 2570.63 | 2695.59 | −4.86% |
| 2003 | 12 | 2838.57 | 2585.71 | 8.91% |
| 2004 | 12 | 2930.39 | 2927.91 | 0.08% |
| 2005 | 12 | 3046.38 | 3269.71 | −7.33% |
| 2006 | 12 | 3211.18 | 3275.26 | −2.00% |
| 2007 | 12 | 3334.85 | 3368.78 | −1.02% |
| 2008 | 12 | 3479.79 | 3596.60 | −3.36% |
| 2009 | 12 | 3520.08 | 3598.72 | −2.23% |
| 2010 | 12 | 3564.53 | 3429.45 | 3.79% |
| 2011 | 12 | 3626.90 | 3809.62 | −5.04% |
| 2012 | 12 | 3722.25 | 3904.53 | −4.90% |
| 2013 | 12 | 3840.71 | 3911.39 | −1.84% |
| 2014 | 12 | 4015.68 | 3925.37 | 2.25% |
| 2015 | 12 | 4230.44 | 4516.27 | −6.76% |
| 2016 | 12 | 4483.57 | 4522.99 | −0.88% |
| 2017 | 12 | 4607.23 | 4540.50 | 1.45% |
| 2018 | 12 | 4709.88 | 4752.82 | −0.91% |
| UAs | Parameter | 1992 | 2000 | 2008 | 2015 | 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YRDUA | Azimuth | −4.0268 | −19.0200 | −22.7213 | −40.8104 | −51.1588 |
| Longitude | 120.3087 | 120.3296 | 120.2753 | 120.1984 | 120.1770 | |
| Latitude | 31.2796 | 31.1425 | 31.1539 | 31.1899 | 31.1845 | |
| Long axis | 0.8224 | 0.8602 | 0.8588 | 0.9942 | 1.0989 | |
| Short axis | 1.5508 | 1.2599 | 1.2434 | 1.2315 | 1.2357 | |
| GBAUA | Azimuth | −1.1683 | 1.3552 | 1.9412 | −18.1176 | −2.1185 |
| Longitude | 113.6484 | 113.5987 | 113.5802 | 113.5653 | 113.6160 | |
| Latitude | 22.7886 | 22.8238 | 22.8428 | 22.8435 | 22.8337 | |
| Long axis | 0.5241 | 0.0778 | 0.1610 | 0.4346 | 0.5276 | |
| Short axis | 0.5878 | 0.0913 | 0.1915 | 0.4591 | 0.5981 | |
| BTHUA | Azimuth | 34.0014 | 25.9257 | 33.4617 | 37.1724 | 35.4692 |
| Longitude | 116.4852 | 116.4326 | 116.5050 | 116.5219 | 116.5461 | |
| Latitude | 39.1014 | 39.0520 | 39.1301 | 39.2800 | 39.2506 | |
| Long axis | 0.8385 | 0.8402 | 0.8346 | 0.7848 | 0.7513 | |
| Short axis | 1.0332 | 1.0526 | 1.1097 | 1.1073 | 1.0455 | |
| CCUA | Azimuth | 0.2717 | 0.7145 | 3.0877 | 72.3169 | −21.7125 |
| Longitude | 105.0918 | 104.9962 | 105.1147 | 105.3669 | 105.2393 | |
| Latitude | 30.2869 | 30.3036 | 30.2734 | 30.2441 | 30.1756 | |
| Long axis | 0.4346 | 0.1380 | 0.3821 | 0.4329 | 0.7726 | |
| Short axis | 0.8043 | 0.2680 | 0.7715 | 0.6872 | 1.2974 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Min, S. Exploring the Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of China’s Four Major Urban Agglomerations in the Luminous Remote Sensing Perspective. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102546
Wang J, Chen J, Liu X, Wang W, Min S. Exploring the Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of China’s Four Major Urban Agglomerations in the Luminous Remote Sensing Perspective. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(10):2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102546
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiahan, Jiaqi Chen, Xiangmei Liu, Wei Wang, and Shengnan Min. 2023. "Exploring the Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of China’s Four Major Urban Agglomerations in the Luminous Remote Sensing Perspective" Remote Sensing 15, no. 10: 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102546
APA StyleWang, J., Chen, J., Liu, X., Wang, W., & Min, S. (2023). Exploring the Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of China’s Four Major Urban Agglomerations in the Luminous Remote Sensing Perspective. Remote Sensing, 15(10), 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102546





