Convective Entrainment Rate over the Tibetan Plateau and Its Adjacent Regions in the Boreal Summer Using SNPP-VIIRS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
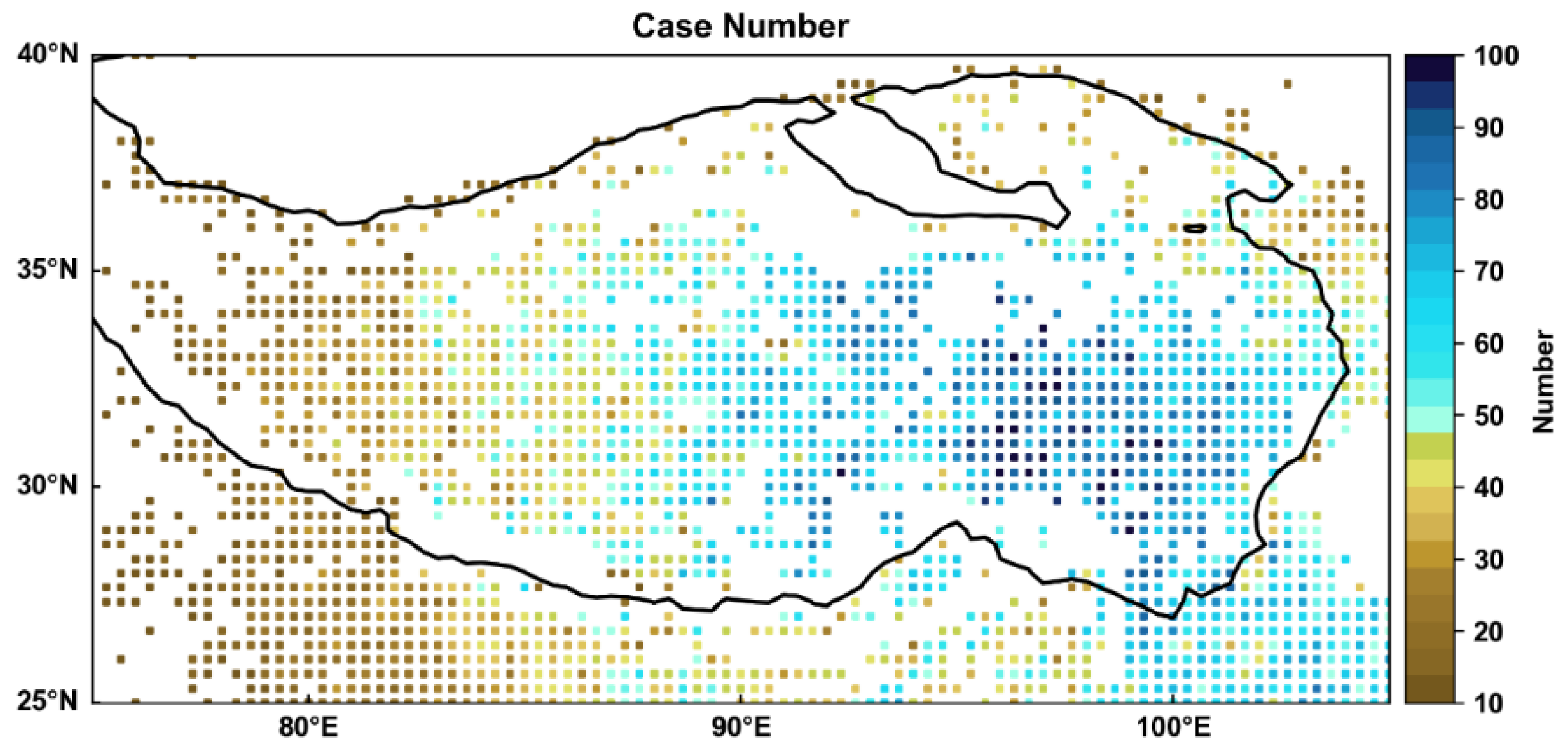
2. Method
3. Result
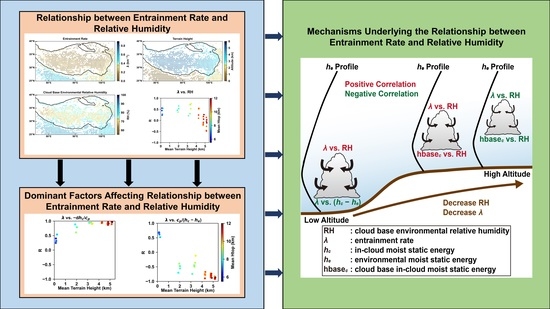
3.1. Relationship between Entrainment Rate and Relative Humidity
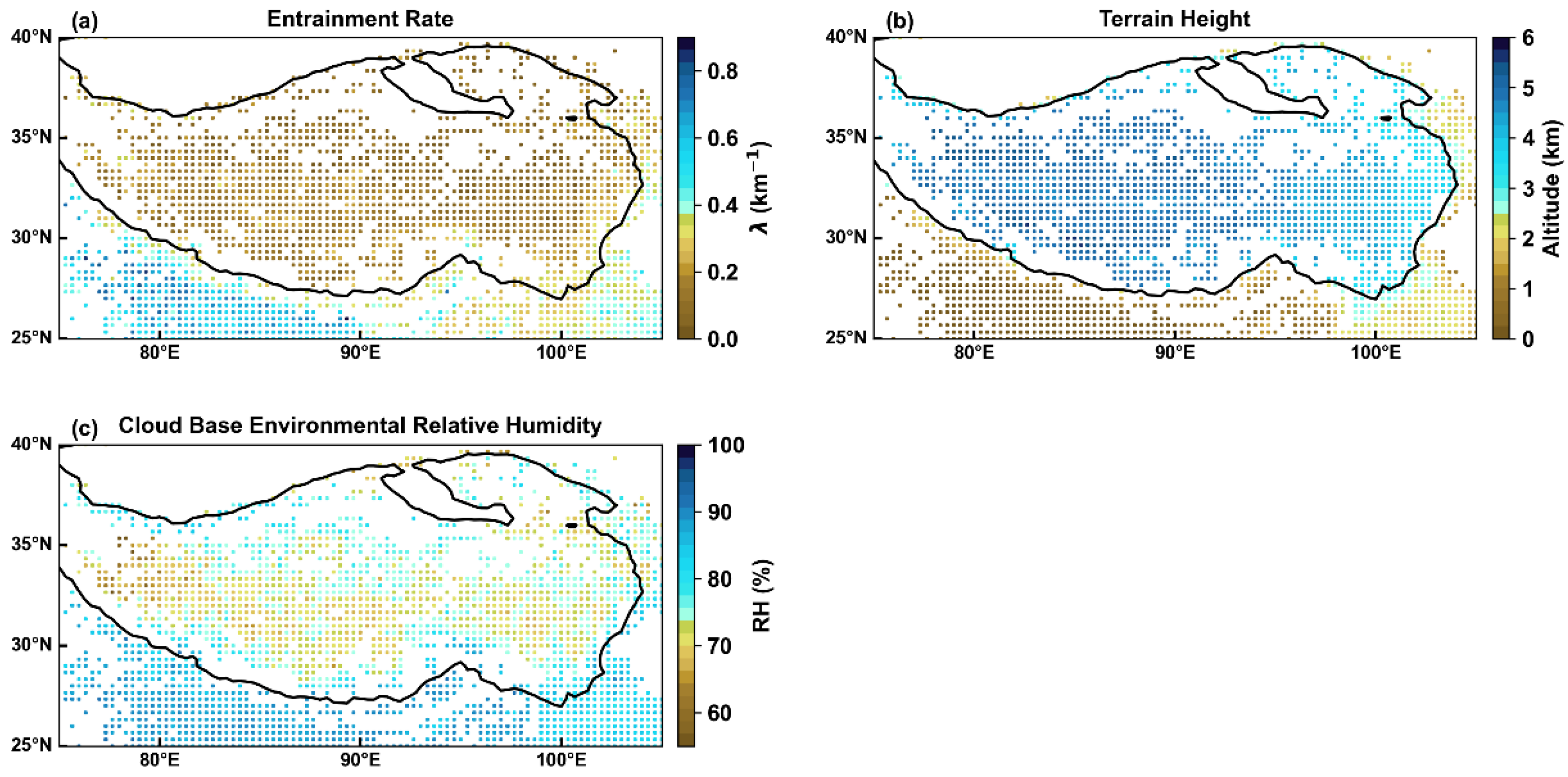
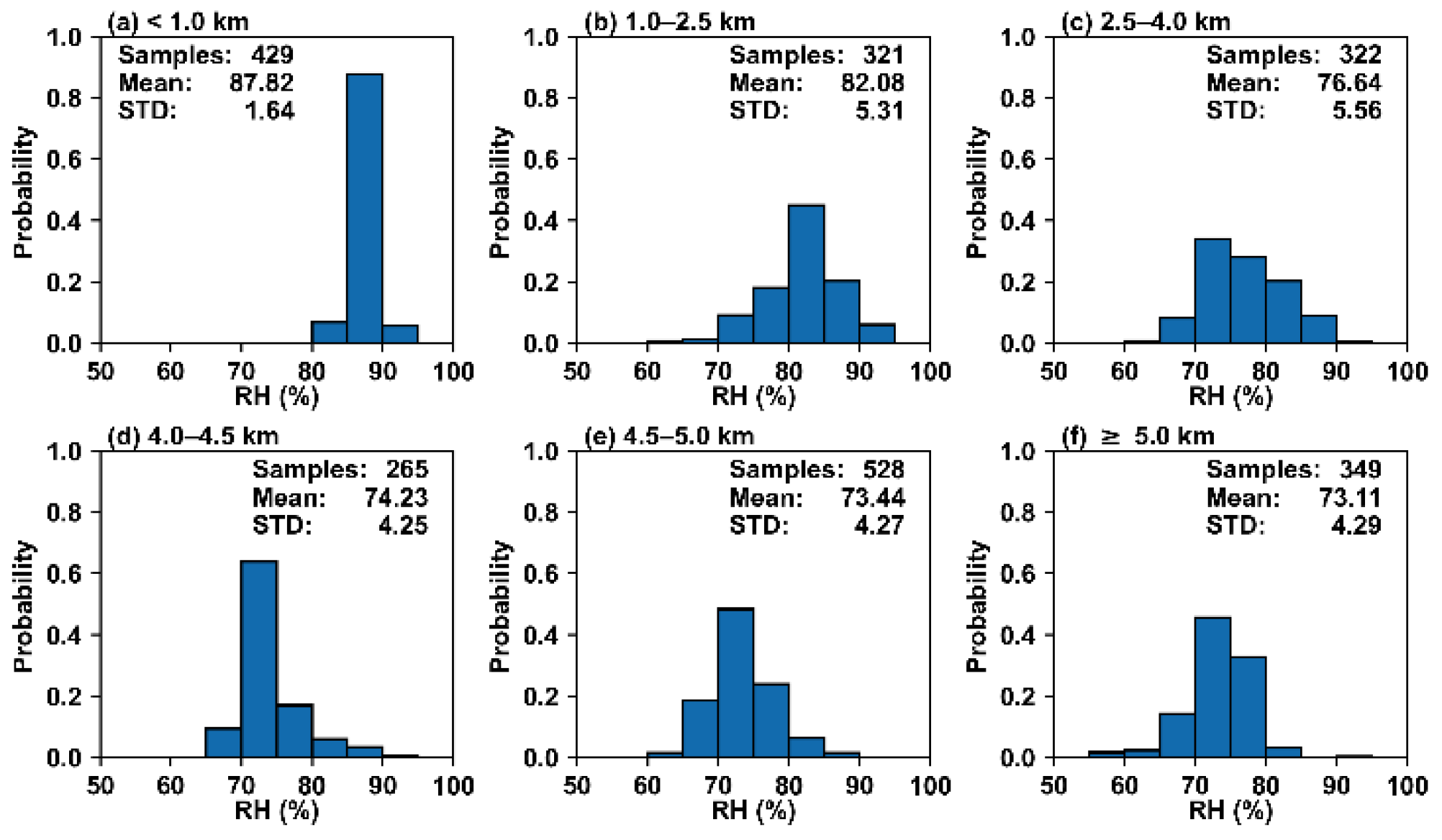
3.1.1. Effects of Terrain Height on Entrainment Rate and Relative Humidity
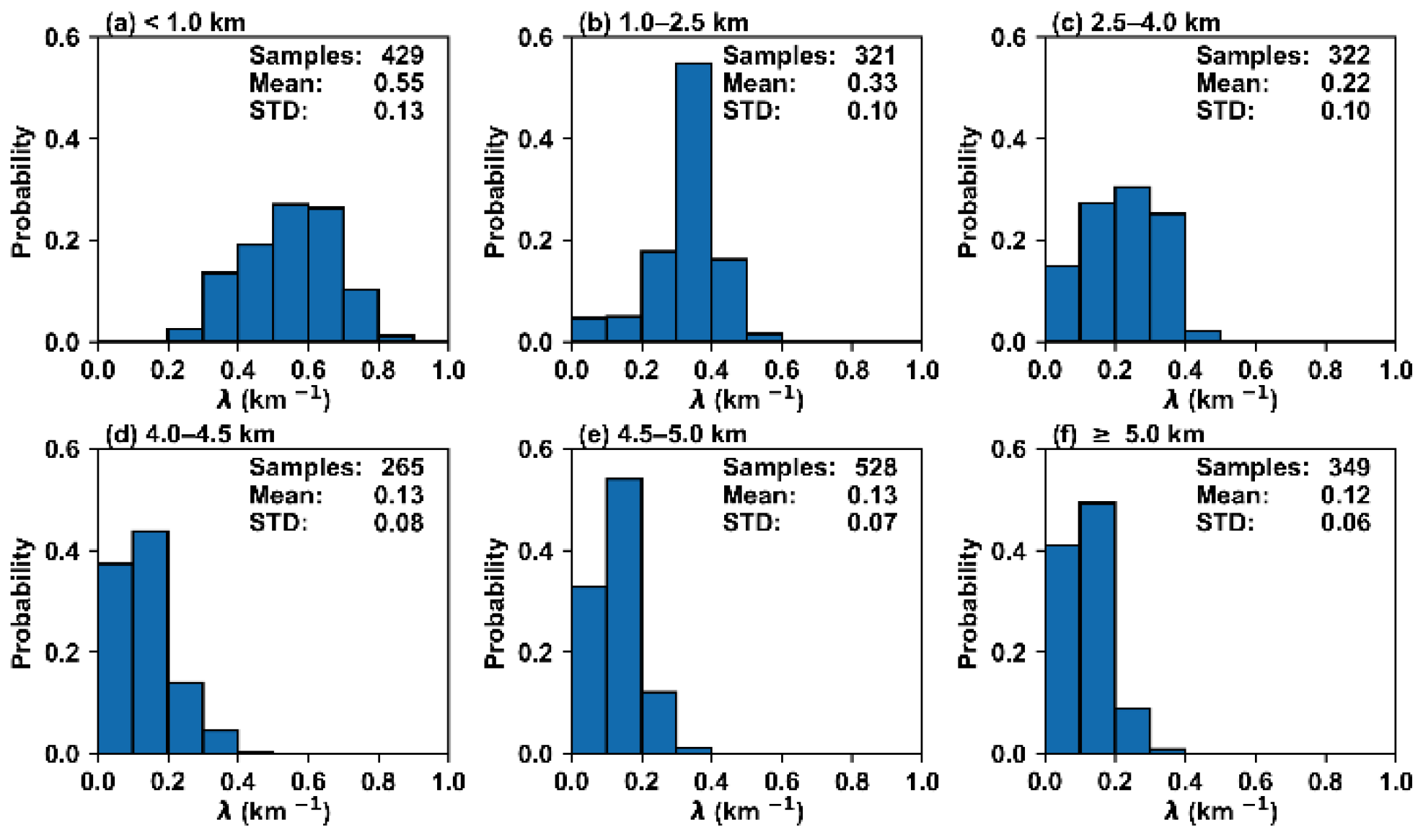
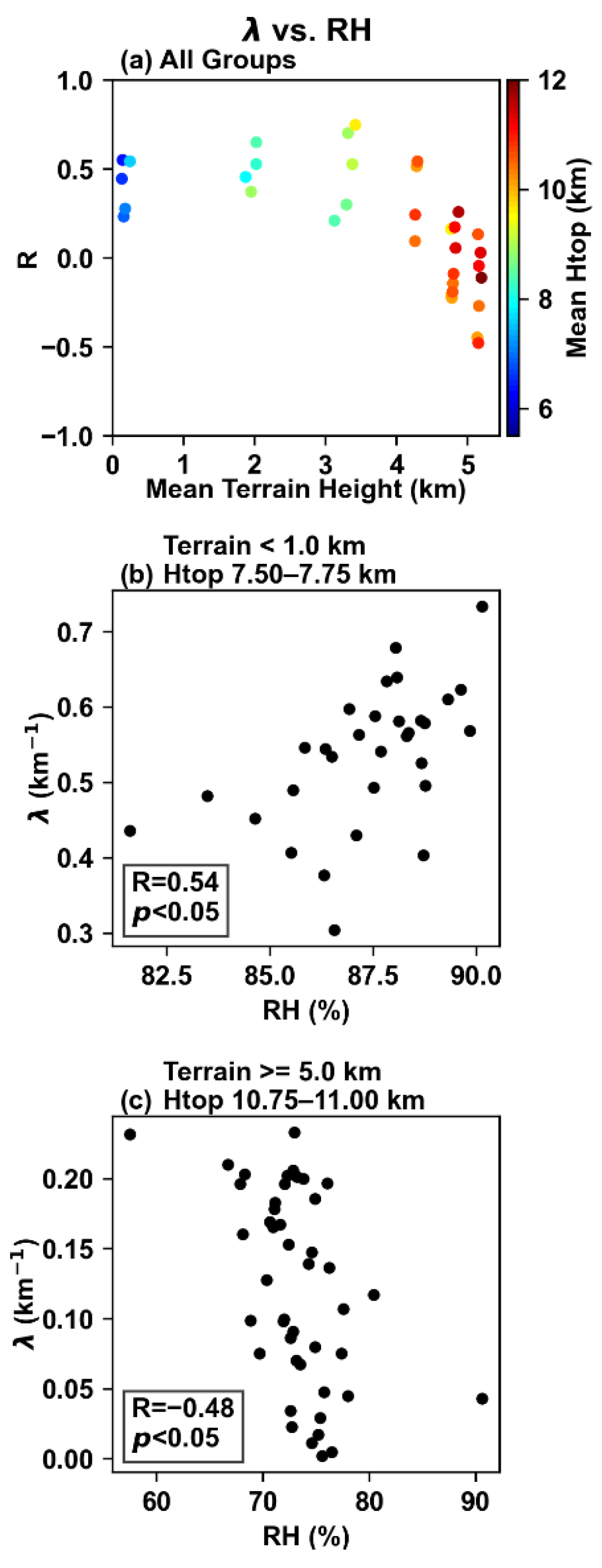
3.1.2. Quantitative Relationships between Entrainment Rate and Relative Humidity in Different Terrain Height Ranges
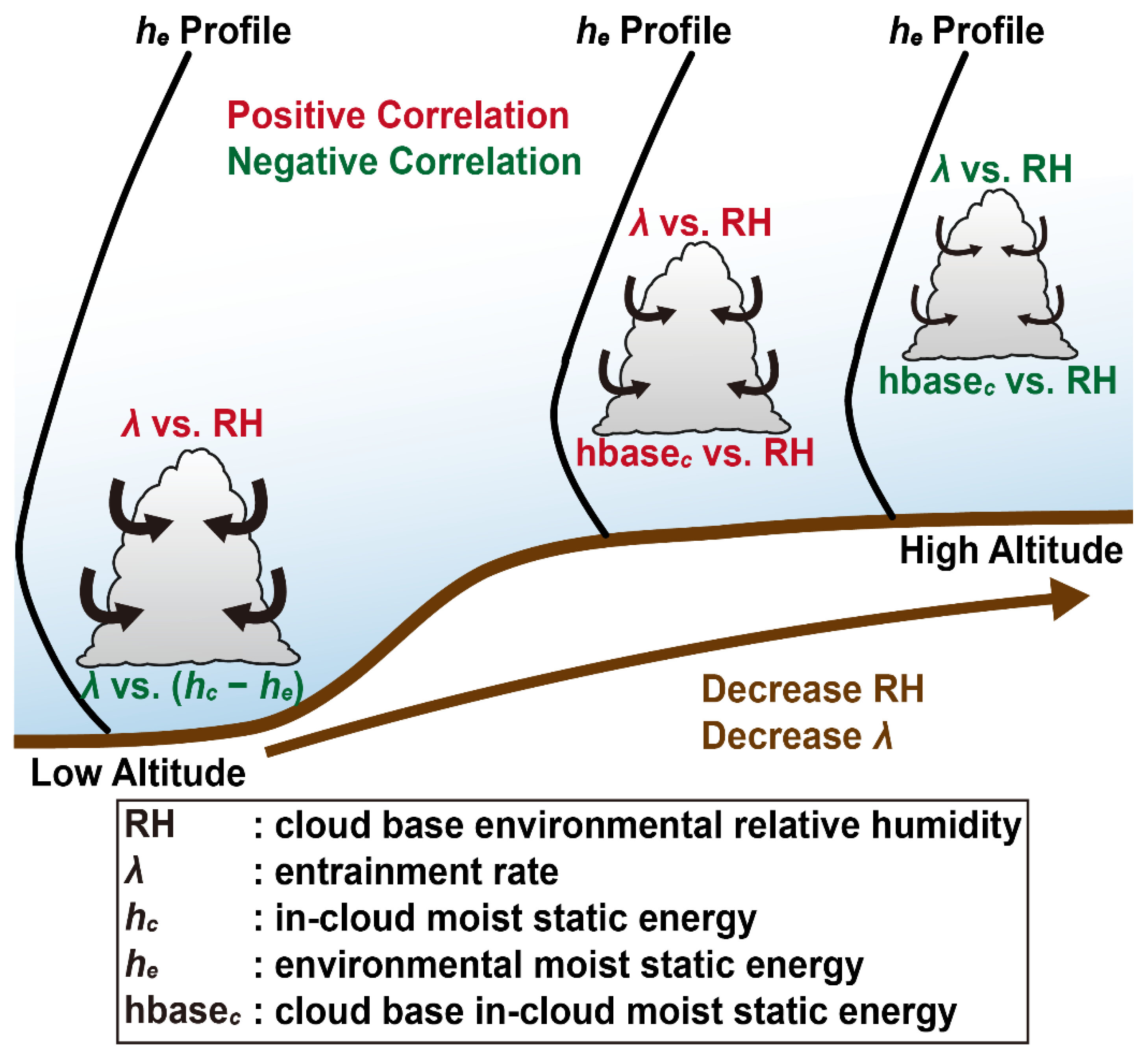
3.2. Physical Mechanisms of Relative Humidity Affecting Entrainment Rate
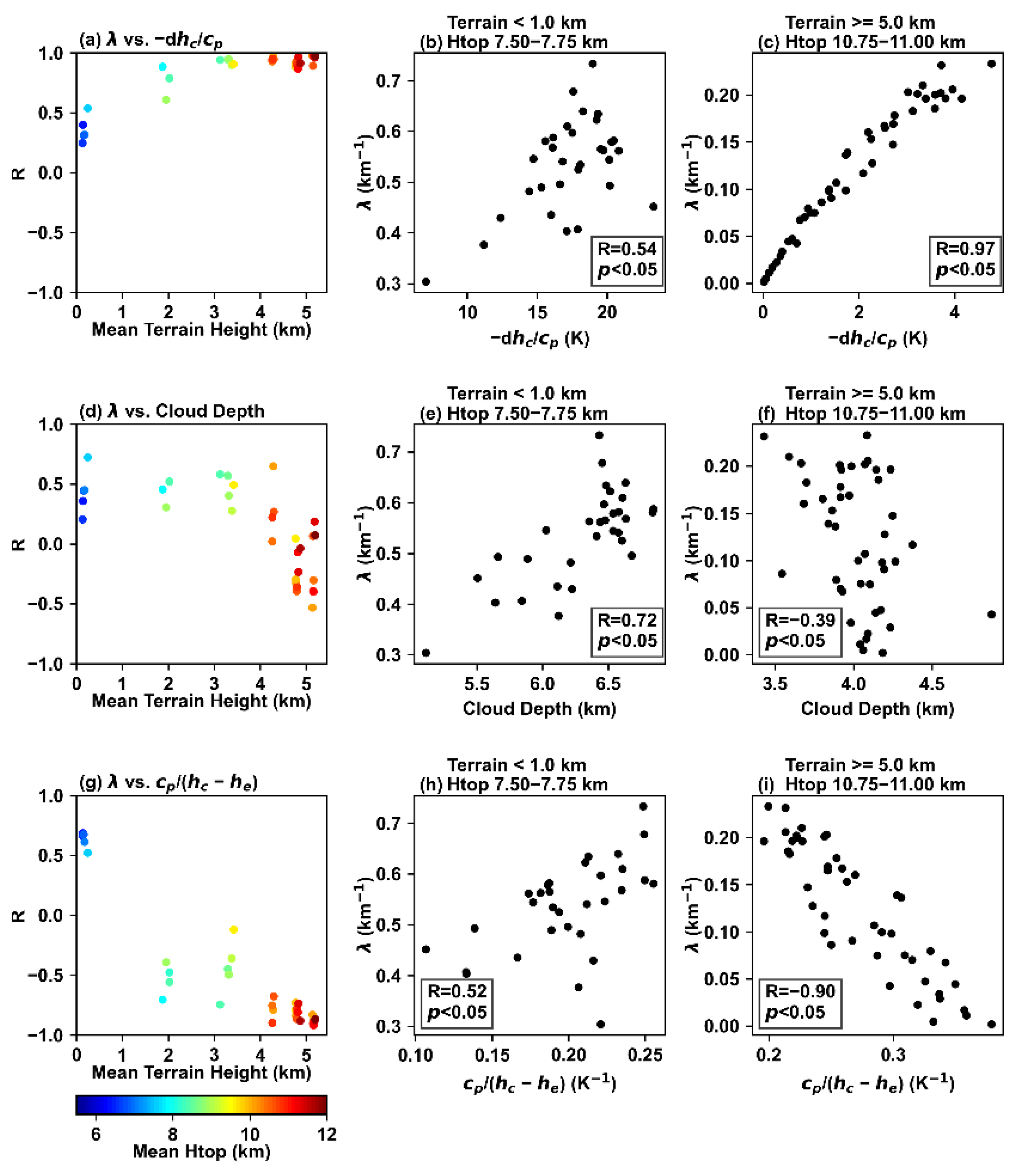
3.2.1. Dominant Factors Affecting Relationships between Entrainment Rate and Relative Humidity
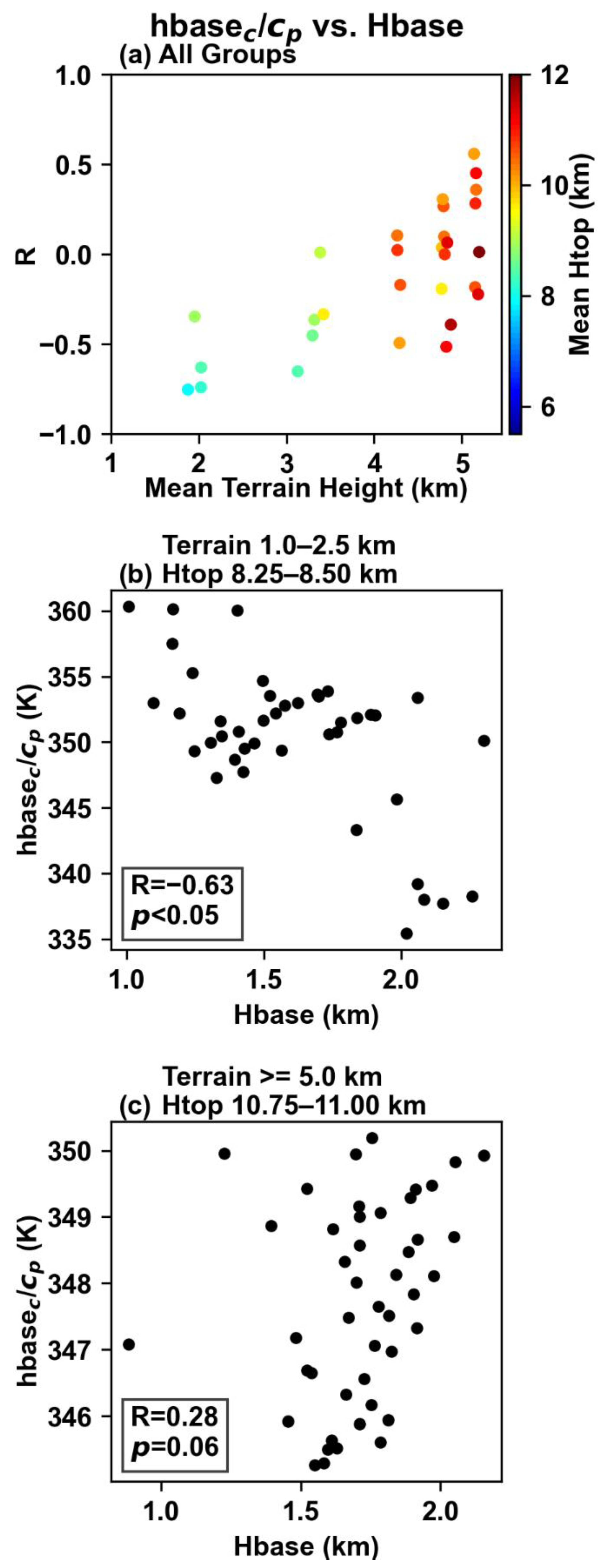
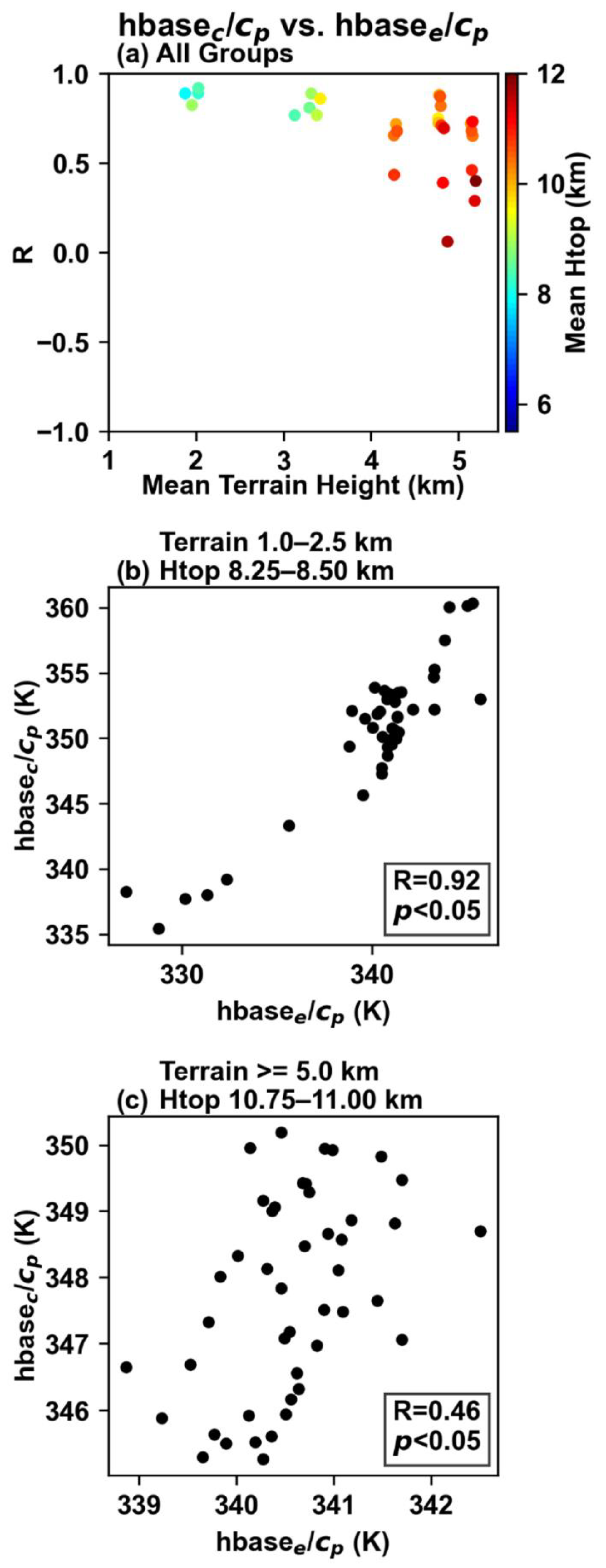
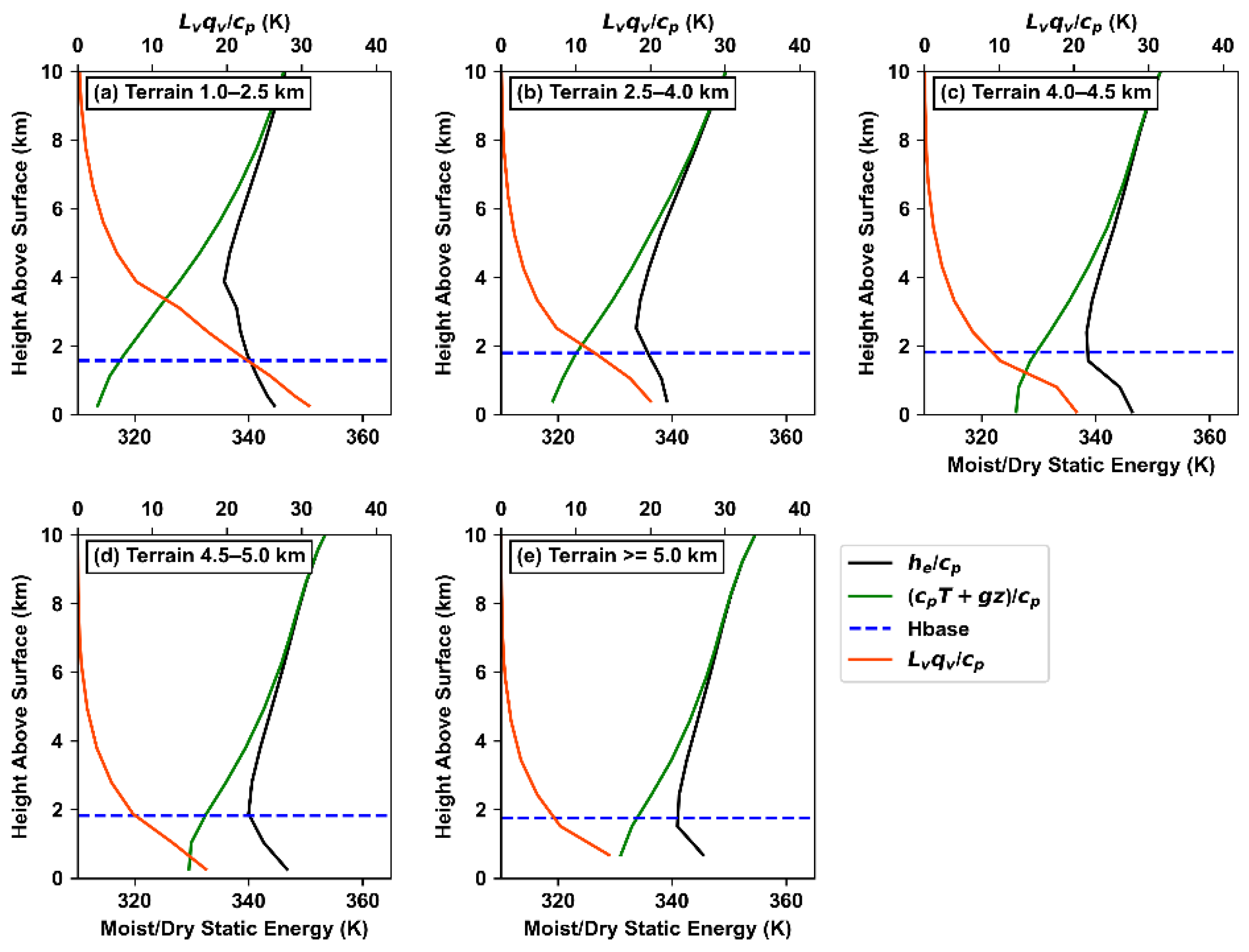
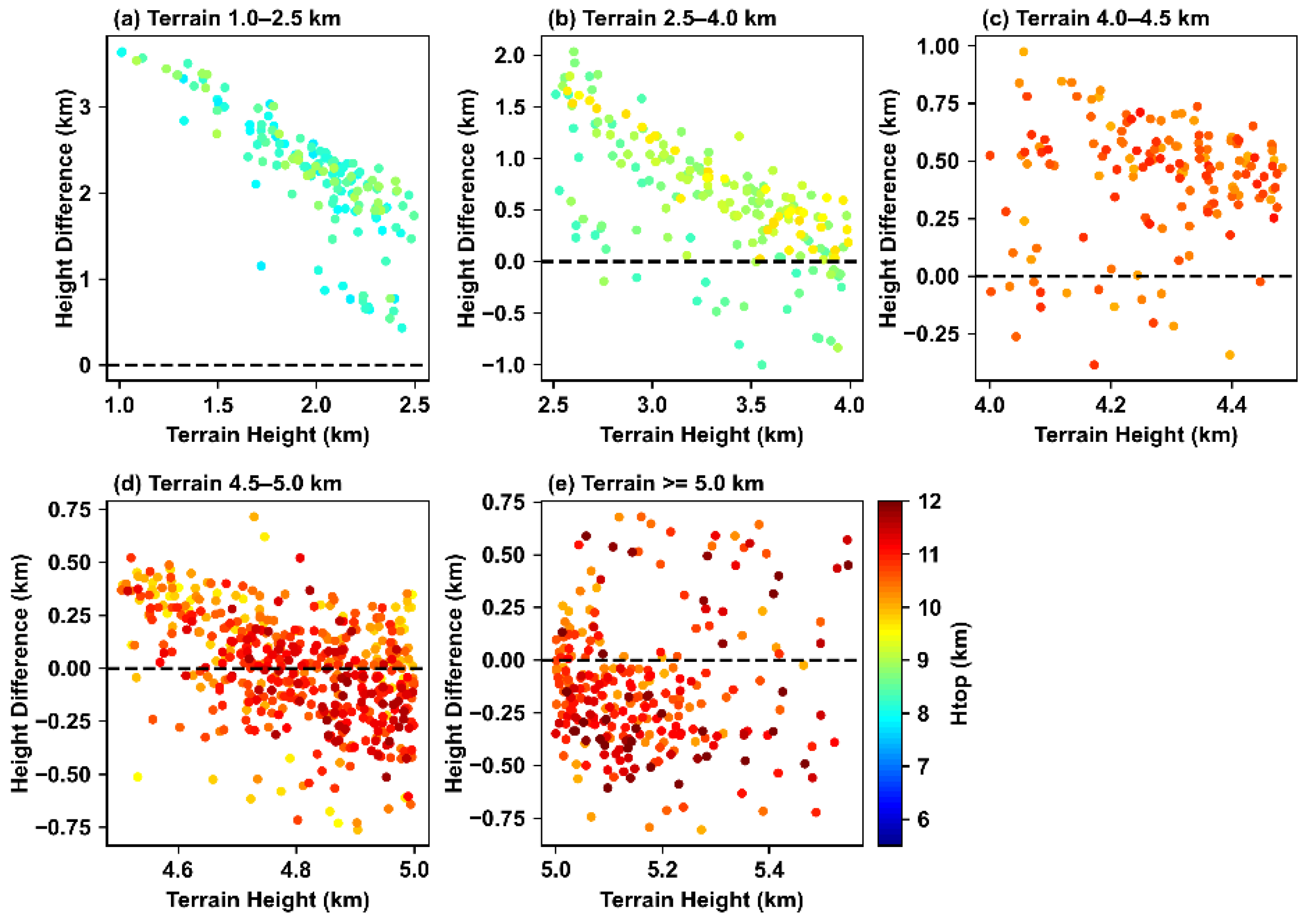
3.2.2. Critical Factor: MSE Turning Point versus Cloud Base Height
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yanai, M.; Wu, G. Effects of the tibetan plateau. In The Asian Monsoon; Wang, B., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 513–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Duan, A. Relative contributions of the Tibetan Plateau thermal forcing and the Indian Ocean Sea surface temperature basin mode to the interannual variability of the East Asian summer monsoon. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 2697–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, M.; Yang, H.; Duan, A.; He, B.; Yang, S.; Wu, G. Land–atmosphere–ocean coupling associated with the Tibetan Plateau and its climate impacts. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 534–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Li, W.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Guo, J. The uncertainties of residual diagnosis of atmospheric diabatic heating from ERA40 and NCEP reanalysis over Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Hu, Y.; Wright, J.S.; Jiang, J.H.; Dickinson, R.E.; Chen, M.; Filipiak, M.; Read, W.G.; Waters, J.W.; Wu, D.L. Short circuit of water vapor and polluted air to the global stratosphere by convective transport over the Tibetan Plateau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, G.; Zhang, Y. Tibetan Plateau forcing and the timing of the monsoon onset over South Asia and the South China Sea. Mon. Weather Rev. 1998, 126, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, T.; Lu, C.; Guo, Y.; Chen, B.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Shi, X. An important mechanism sustaining the atmospheric “water tower” over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 11287–11295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Yin, Y.; Xiao, H. Characteristics of heat sources and clouds over eastern China and the Tibetan Plateau in boreal summer. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 7279–7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, R.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. Effects of convection over the Tibetan Plateau on rainstorms downstream of the Yangtze River Basin. Atmos. Res. 2019, 219, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhong, L.; Yang, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, C.; Xu, X.; Yang, K.; Xu, X.; Liu, L.; et al. Land surface processes and summer cloud-precipitation characteristics in the Tibetan Plateau and their effects on downstream weather: A review and perspective. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 500–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Vogel, J.M.; Lin, Y.; Pan, B.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, X.; Jiang, J.H.; Yung, Y.L.; Zhang, R. Aerosol microphysical and radiative effects on continental cloud ensembles. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 35, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Yang, X.; Dong, Z.; Wang, M. Diurnal variations of global clouds observed from the CATS spaceborne lidar and their links to large-scale meteorological factors. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 57, 2637–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cess, R.D.; Jing, X. Concerning the interpretation of enhanced cloud shortwave absorption using monthly-mean Earth Radiation Budget Experiment/Global Energy Balance Archive measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 25899–25905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leung, L.R.; Bader, D.C.; Taylor, M.A.; McCoy, R.B. An Introduction to the E3SM Special Collection: Goals, Science Drivers, Development, and Analysis. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2020, 12, e2019MS001821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Liou, K.-N.; Bi, L.; Liu, C.; Yi, B.; Baum, B.A. On the radiative properties of ice clouds: Light scattering, remote sensing, and radiation parameterization. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 32, 32–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Yin, Y.; Huang, Q.; Xiao, H. Characteristics of cloud systems over the Tibetan Plateau and East China during boreal summer. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 3117–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Yin, Y.; Lu, C. Large-scale circulation environment and microphysical characteristics of the cloud systems over the Tibetan Plateau in boreal summer. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2020EA001154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, R.; Wang, G.; Zhaxi, S. Cloud vertical structure measurements from a ground-based cloud radar over the southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Res. 2021, 258, 105629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, M. Cumulus over the Tibetan Plateau in the Summer Based on CloudSat–CALIPSO Data. J. Clim. 2015, 29, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Xu, X.; Welty, J.; Lenschow, D.H.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, Y. Why are there more summer afternoon low clouds over the Tibetan Plateau compared to eastern China? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL089665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zheng, J.; Ruan, Z.; Cui, Z.; Hu, Z.; Wu, S.; Dai, G.; Wu, Y. Comprehensive Radar Observations of Clouds and Precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau and Preliminary Analysis of Cloud Properties. J. Meteorol. Res. 2015, 29, 546–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lu, J. Cloud vertical structure, precipitation, and cloud radiative effects over Tibetan Plateau and its neighboring regions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 5864–5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y.; Gao, W.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Luo, S.; Van Weverberg, K. Effects of Cloud Liquid-Phase Microphysical Processes in Mixed-Phase Cumuli Over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD033371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Wan, G.; Chen, X.; Liang, X. Simulation Influences of Summer Precipitation by Two Cumulus Parameterization Schemes over Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Plateau Meteorol. 2014, 33, 313–322. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, K.; Wang, Y. Implementation of a turbulent orographic form drag scheme in WRF and its application to the Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 50, 2443–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Furtado, K.; Zhou, T.; Chen, H.; Li, J. Convection-permitting modelling improves simulated precipitation over the central and eastern Tibetan Plateau. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2021, 147, 341–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.J.; Wu, X.; Zeng, X.; Mitovski, T. Estimation of convective entrainment properties from a cloud-resolving model simulation during TWP-ICE. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 47, 2177–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, M.; Zhang, G.J.; Guo, Z.; Qian, Y.; Huang, A.; Zhang, Y. Simulated Precipitation Diurnal Variation With a Deep Convective Closure Subject to Shallow Convection in Community Atmosphere Model Version 5 Coupled With CLUBB. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2020, 12, e2020MS002050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. A Method for a Direct Measure of Entrainment and Detrainment. Mon. Weather Rev. 2020, 148, 3329–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T. A mass-flux cumulus parameterization scheme for large-scale models: Description and test with observations. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 38, 725–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blyth, A.M. Entrainment in Cumulus Clouds. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1993, 32, 626–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Huang, X.; Liang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Xu, S.; Huang, W.; Xu, F.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Y.; et al. Community Integrated Earth System Model (CIESM): Description and Evaluation. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2020, 12, e2019MS002036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.J.; Craig, G.C. Stochastic convective parameterization improving the simulation of tropical precipitation variability in the NCAR CAM5. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 6612–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, J.; Kuang, Z. Responses of Shallow Cumulus Convection to Large-Scale Temperature and Moisture Perturbations: A Comparison of Large-Eddy Simulations and a Convective Parameterization Based on Stochastically Entraining Parcels. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 69, 1936–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Hendon, H.H. Role of large-scale moisture advection for simulation of the MJO with increased entrainment. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 2127–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, G.J. Improving the Simulation of Tropical Convective Cloud-Top Heights in CAM5 with CloudSat Observations. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 5189–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donner, L.J.; O’Brien, T.A.; Rieger, D.; Vogel, B.; Cooke, W.F. Are atmospheric updrafts a key to unlocking climate forcing and sensitivity? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 12983–12992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, Y.; Kuang, Z. Dependence of entrainment in shallow cumulus convection on vertical velocity and distance to cloud edge. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 4056–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, J.M.; Morrison, H.; Varble, A.C.; Hannah, W.M.; Giangrande, S.E. Thermal Chains and Entrainment in Cumulus Updrafts. Part II: Analysis of Idealized Simulations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 77, 3661–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagan, G.; Koren, I.; Altaratz, O.; Feingold, G. Feedback mechanisms of shallow convective clouds in a warmer climate as demonstrated by changes in buoyancy. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 054033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Small, J.D.; Chuang, P.Y.; Feingold, G.; Jiang, H. Can aerosol decrease cloud lifetime? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L16806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helfer, K.C.; Nuijens, L.; de Roode, S.R.; Siebesma, A.P. How Wind Shear Affects Trade-wind Cumulus Convection. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2020, 12, e2020MS002183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Sun, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.J.; Lin, Y.; Gao, W.; Niu, S.; Yin, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Jin, L. Observational Relationship Between Entrainment Rate and Environmental Relative Humidity and Implications for Convection Parameterization. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 13495–13504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, S.; Prabha, T.V. Parameterization of Entrainment Rate and Mass Flux in Continental Cumulus Clouds: Inference from Large Eddy Simulation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 13127–13139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neggers, R.A.J.; Siebesma, A.P.; Jonker, H.J.J. A Multiparcel Model for Shallow Cumulus Convection. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 1655–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.J.; Wu, X.; Endo, S.; Cao, L.; Li, Y.; Guo, X. Improving Parameterization of Entrainment Rate for Shallow Convection with Aircraft Measurements and Large-Eddy Simulation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 73, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawe, J.T.; Austin, P.H. Direct entrainment and detrainment rate distributions of individual shallow cumulus clouds in an LES. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7795–7811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.; Feingold, G. Effect of aerosol on warm convective clouds: Aerosol-cloud-surface flux feedbacks in a new coupled large eddy model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D01202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Xue, H.; Teller, A.; Feingold, G.; Levin, Z. Aerosol effects on the lifetime of shallow cumulus. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L14806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, H.; Feingold, G. Large-Eddy Simulations of Trade Wind Cumuli: Investigation of Aerosol Indirect Effects. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 63, 1605–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, L.; Lu, C.; Yan, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.J.; Mei, F.; Zhu, B.; Fast, J.D.; Matthews, A.; Pekour, M.S. A New Approach for Simultaneous Estimation of Entrainment and Detrainment Rates in Non-Precipitating Shallow Cumulus. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL093817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirling, A.J.; Stratton, R.A. Entrainment processes in the diurnal cycle of deep convection over land. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 138, 1135–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Axelsen, S.L. The Role of Relative Humidity on Shallow Cumulus Dynamics; Results from a Large Eddy Simulation Model; Utrecht University: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 65–66. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, M.P.; Del Genio, A.D. Factors Limiting Convective Cloud-Top Height at the ARM Nauru Island Climate Research Facility. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 2105–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Jensen, M.P.; D’Iorio, J.A.; Jozef, G.; Giangrande, S.E.; Johnson, K.L.; Luo, Z.J.; Starzec, M.; Mullendore, G.L. An Observational Comparison of Level of Neutral Buoyancy and Level of Maximum Detrainment in Tropical Deep Convective Clouds. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD032637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; McFarquhar, G.M. Modeling aerosol effects on shallow cumulus convection under various meteorological conditions observed over the Indian Ocean and implications for development of mass-flux parameterizations for climate models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D20201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stanfield, R.E.; Su, H.; Jiang, J.H.; Freitas, S.R.; Molod, A.M.; Luo, Z.J.; Huang, L.; Luo, M. Convective Entrainment Rates Estimated from Aura CO and CloudSat/CALIPSO Observations and Comparison with GEOS-5. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 9796–9807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbyshire, S.H.; Maidens, A.V.; Milton, S.F.; Stratton, R.A.; Willett, M.R. Adaptive detrainment in a convective parametrization. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 1856–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtold, P.; Köhler, M.; Jung, T.; Doblas-Reyes, F.; Leutbecher, M.; Rodwell, M.J.; Vitart, F.; Balsamo, G. Advances in simulating atmospheric variability with the ECMWF model: From synoptic to decadal time-scales. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 134, 1337–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Golaz, J.C.; Held, I.M.; Guo, H.; Balaji, V.; Benson, R.; Chen, J.H.; Chen, X.; Donner, L.J.; Dunne, J.P.; et al. The GFDL Global Atmosphere and Land Model AM4.0/LM4.0: 2. Model Description, Sensitivity Studies, and Tuning Strategies. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2018, 10, 735–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böing, S.J.; Siebesma, A.P.; Korpershoek, J.D.; Jonker, H.J.J. Detrainment in deep convection. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L20816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernandez-Deckers, D.; Sherwood, S.C. On the Role of Entrainment in the Fate of Cumulus Thermals. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 75, 3911–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissner, J.M.; Mechem, D.B.; Jensen, M.P.; Giangrande, S.E. Factors Governing Cloud Growth and Entrainment Rates in Shallow Cumulus and Cumulus Congestus During GoAmazon2014/5. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2021JD034722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Luo, Z.J.; Stephens, G. Revisiting the Entrainment Relationship of Convective Plumes: A Perspective from Global Observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL092349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Roode, S.R.; Duynkerke, P.G.; Siebesma, A.P. Analogies between Mass-Flux and Reynolds-Averaged Equations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2000, 57, 1585–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, C.; Siebesma, A.P. A New Subcloud Model for Mass-Flux Convection Schemes: Influence on Triggering, Updraft Properties, and Model Climate. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 2765–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rooy, W.C.; Pier Siebesma, A. Analytical expressions for entrainment and detrainment in cumulus convection. Quart. J. R.. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 136, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Sun, C.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.J.; Chen, Q. Factors Affecting Entrainment Rate in Deep Convective Clouds and Parameterizations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2021JD034881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C. Some Bulk Properties of Cumulus Ensembles Simulated by a Cloud-Resolving Model. Part II: Entrainment Profiles. J. Atmos. Sci. 1999, 56, 3736–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Salzen, K.; McFarlane, N.A. Parameterization of the Bulk Effects of Lateral and Cloud-Top Entrainment in Transient Shallow Cumulus Clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 1405–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Rooy, W.C.; Yano, J.I.; Bechtold, P.; Böing, S.J. Entrainment and detrainment formulations for mass-flux parameterization. In Parameterization of Atmospheric Convection; Plant, R., Yano, J.I., Eds.; Imperial College Press: Singapore, 2016; pp. 273–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Lu, C.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, G.J.; Liu, Y. An Observational Study of Entrainment Rate in Deep Convection. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1362–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Lu, C.; Wu, X. Impacts of TIPEX-III Rawinsondes on the Dynamics and Thermodynamics Over the Eastern Tibetan Plateau in the Boreal Summer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD032635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Xu, X.; Chen, F.; Guo, X.; Zheng, X.; Liu, L.; Hong, Y.; Li, Y.; La, Z.; Peng, H. The Third Atmospheric Scientific Experiment for Understanding the Earth–Atmosphere Coupled System over the Tibetan Plateau and Its Effects. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 757–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.J.; Liu, G.Y.; Stephens, G.L. Use of A-Train data to estimate convective buoyancy and entrainment rate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L09804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Yin, Y.; Lu, C.; Xiao, H.; Huang, Q.; Deng, L. Thermal Effects of the Surface Heat Flux on Cloud Systems over the Tibetan Plateau in Boreal Summer. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 4699–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillger, D.; Kopp, T.; Lee, T.; Lindsey, D.; Seaman, C.; Miller, S.; Solbrig, J.; Kidder, S.; Bachmeier, S.; Jasmin, T.; et al. First-Light Imagery from Suomi NPP VIIRS. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Rosenfeld, D.; Liu, G.; Dai, J.; Yu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Hashimshoni, E.; Xu, X.; Hui, Y.; Lauer, O. Automated Mapping of Convective Clouds (AMCC) Thermodynamical, Microphysical, and CCN Properties from SNPP/VIIRS Satellite Data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2019, 58, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Yu, X.; Liu, G.; Dai, J.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, X.; Hui, Y.; Chen, C. Microphysical Properties of Convective Clouds in Summer over the Tibetan Plateau from SNPP/VIIRS Satellite Data. J. Meteorol. Res. 2019, 33, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Rosenfeld, D.; Yu, X.; Liu, G.; Dai, J.; Xu, X. Satellite retrieval of convective cloud base temperature based on the NPP/VIIRS Imager. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 1308–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.; Simmons, A.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Zhang, F. Evaluation of NCEP–CFSR, NCEP–NCAR, ERA-Interim, and ERA-40 reanalysis datasets against independent sounding observations over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, X.; Zhang, F. How accurate are modern climate reanalyses for the data-sparse Tibetan Plateau region? J. Clim. 2019, 32, 7153–7172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans, H.; Bell, W.; Berrisford, P.; Andras, H.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Raluca, R.; Dinand, S.; Adrian, S.; Cornel, S.; et al. Global reanalysis: Goodbye ERA-Interim, hello ERA5. ECMWF Newsl. 2019, 159, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- NOAA/NCEP. NCEP FNL Operational Model Global Tropospheric Analyses, Continuing from July 1999. 2000. Available online: https://rda.ucar.edu/datasets/ds083.2/ (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- Han, J.; Pan, H.-L. Revision of Convection and Vertical Diffusion Schemes in the NCEP Global Forecast System. Weather Forecast. 2011, 26, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Chen, Q.; Sun, J. Modification of cumulus convection and planetary boundary layer schemes in the GRAPES global model. J. Meteorol. Res. 2015, 29, 806–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, C.J.; Held, I.M. Detailed Investigation of the Self-Aggregation of Convection in Cloud-Resolving Simulations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 69, 2551–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, M.; Rosenfeld, D.; Zhu, Y.; Bai, H.; Cao, Y.; Liang, Y. Evaluation of Cloud and Precipitation Response to Aerosols in WRF-Chem With Satellite Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD033108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rooy, W.C.; Siebesma, A.P. A Simple Parameterization for Detrainment in Shallow Cumulus. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 560–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Hua, S.; Luo, R.; Zhu, Q. Features of the Cloud Base Height and Determining the Threshold of Relative Humidity over Southeast China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Rosenfeld, D. Linear relation between convective cloud base height and updrafts and application to satellite retrievals. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 6485–6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Zheng, Y.; Hashimshoni, E.; Pöhlker, M.L.; Jefferson, A.; Pöhlker, C.; Yu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, G.; Yue, Z.; et al. Satellite retrieval of cloud condensation nuclei concentrations by using clouds as CCN chambers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X.; Bao, X.; Chen, D.; Kim, H.M.; Lai, H.-W.; Leung, L.R.; Ma, X.; Meng, Z.; et al. Development and Evaluation of an Ensemble-Based Data Assimilation System for Regional Reanalysis Over the Tibetan Plateau and Surrounding Regions. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2019, 11, 2503–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Genio, A.D.; Wu, J. The Role of Entrainment in the Diurnal Cycle of Continental Convection. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 2722–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeley, J.T.; Romps, D.M. Why does tropical convective available potential energy (CAPE) increase with warming? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 10429–10437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yanai, M.; Esbensen, S.; Chu, J.-H. Determination of bulk properties of tropical cloud clusters from large-scale heat and moisture budgets. J. Atmos. Sci. 1973, 30, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, A.; Schubert, W.H. Interaction of a Cumulus Cloud Ensemble with the Large-Scale Environment, Part I. J. Atmos. Sci. 1974, 31, 674–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mokhov, I.I.; Akperov, M.G. Tropospheric lapse rate and its relation to surface temperature from reanalysis data. Izve. Atmos. Ocean. Phy. 2006, 42, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshbaum, D.J.; Lamer, K. Climatological Sensitivities of Shallow-Cumulus Bulk Entrainment in Continental and Oceanic Locations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 78, 2429–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Guo, X. Characteristics of convective cloud and precipitation during summer time at Naqu over Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 1706–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Yue, Z.; Lu, C.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Xu, X.; Luo, S.; Zhu, L.; Wu, S.; Wang, F.; et al. Convective Entrainment Rate over the Tibetan Plateau and Its Adjacent Regions in the Boreal Summer Using SNPP-VIIRS. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092073
Li J, Yue Z, Lu C, Chen J, Wu X, Xu X, Luo S, Zhu L, Wu S, Wang F, et al. Convective Entrainment Rate over the Tibetan Plateau and Its Adjacent Regions in the Boreal Summer Using SNPP-VIIRS. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(9):2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092073
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Junjun, Zhiguo Yue, Chunsong Lu, Jinghua Chen, Xiaoqing Wu, Xiaoqi Xu, Shi Luo, Lei Zhu, Shiying Wu, Fan Wang, and et al. 2022. "Convective Entrainment Rate over the Tibetan Plateau and Its Adjacent Regions in the Boreal Summer Using SNPP-VIIRS" Remote Sensing 14, no. 9: 2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092073
APA StyleLi, J., Yue, Z., Lu, C., Chen, J., Wu, X., Xu, X., Luo, S., Zhu, L., Wu, S., Wang, F., & He, X. (2022). Convective Entrainment Rate over the Tibetan Plateau and Its Adjacent Regions in the Boreal Summer Using SNPP-VIIRS. Remote Sensing, 14(9), 2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092073