Environmental and Biophysical Effects of the Bowen Ratio over Typical Farmland Ecosystems in the Loess Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
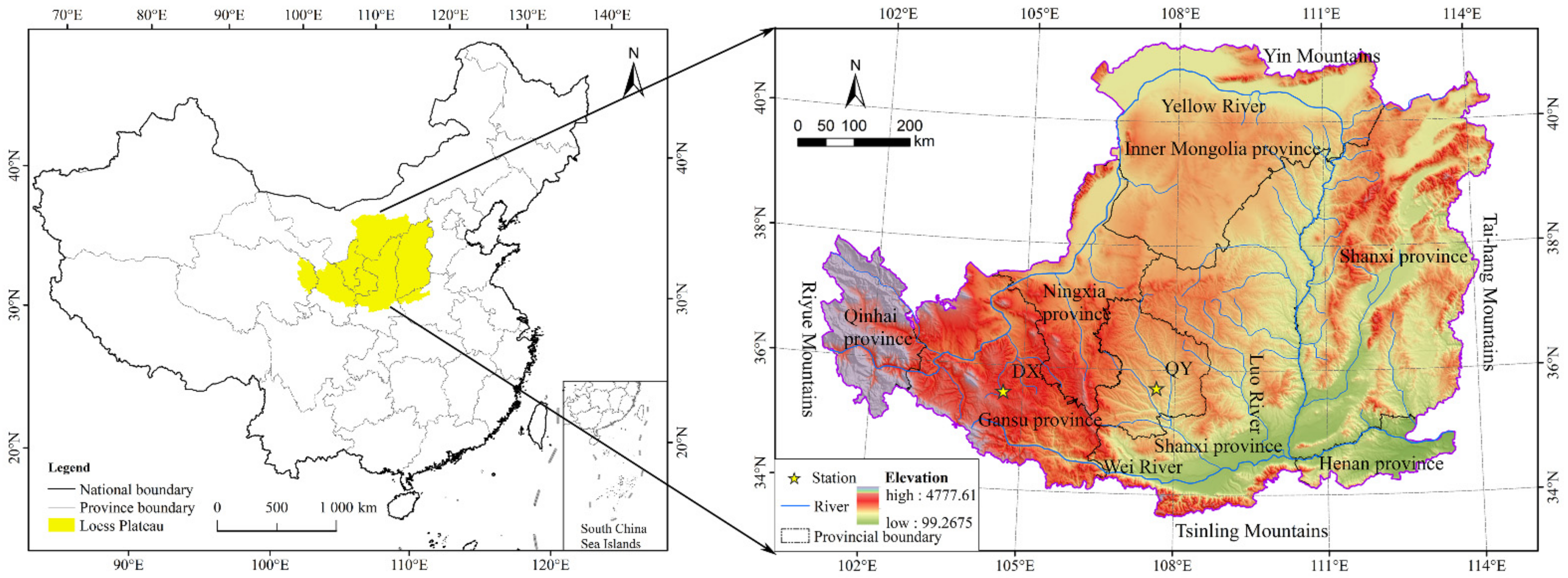
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Observation Method and Data Processing
2.3. Energy Balance
2.4. Soil Heat Flux Correction
2.5. Bowen Ratio
2.6. Overall Land Surface Parameters
3. Results
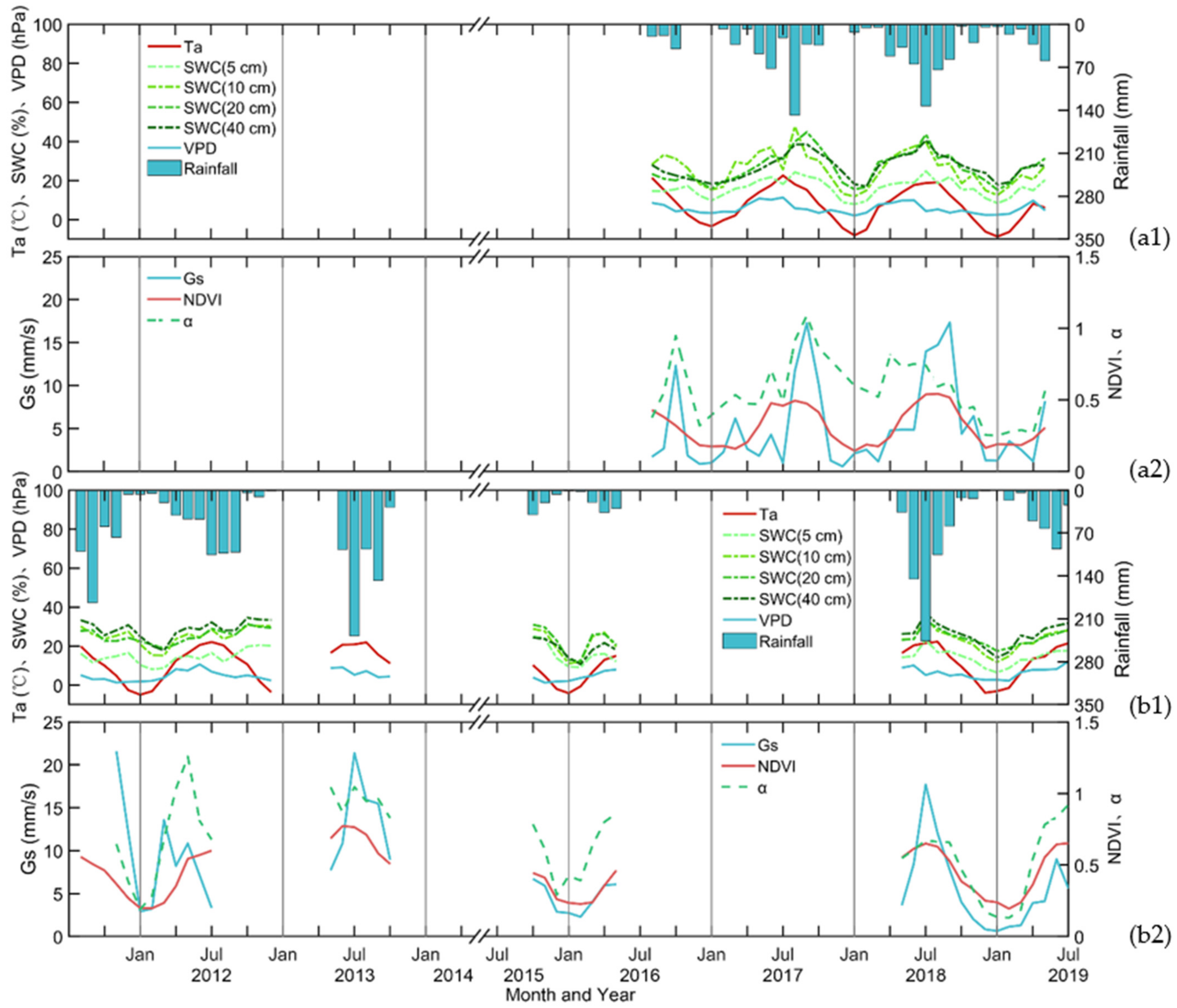
3.1. Environmental Factor Variations
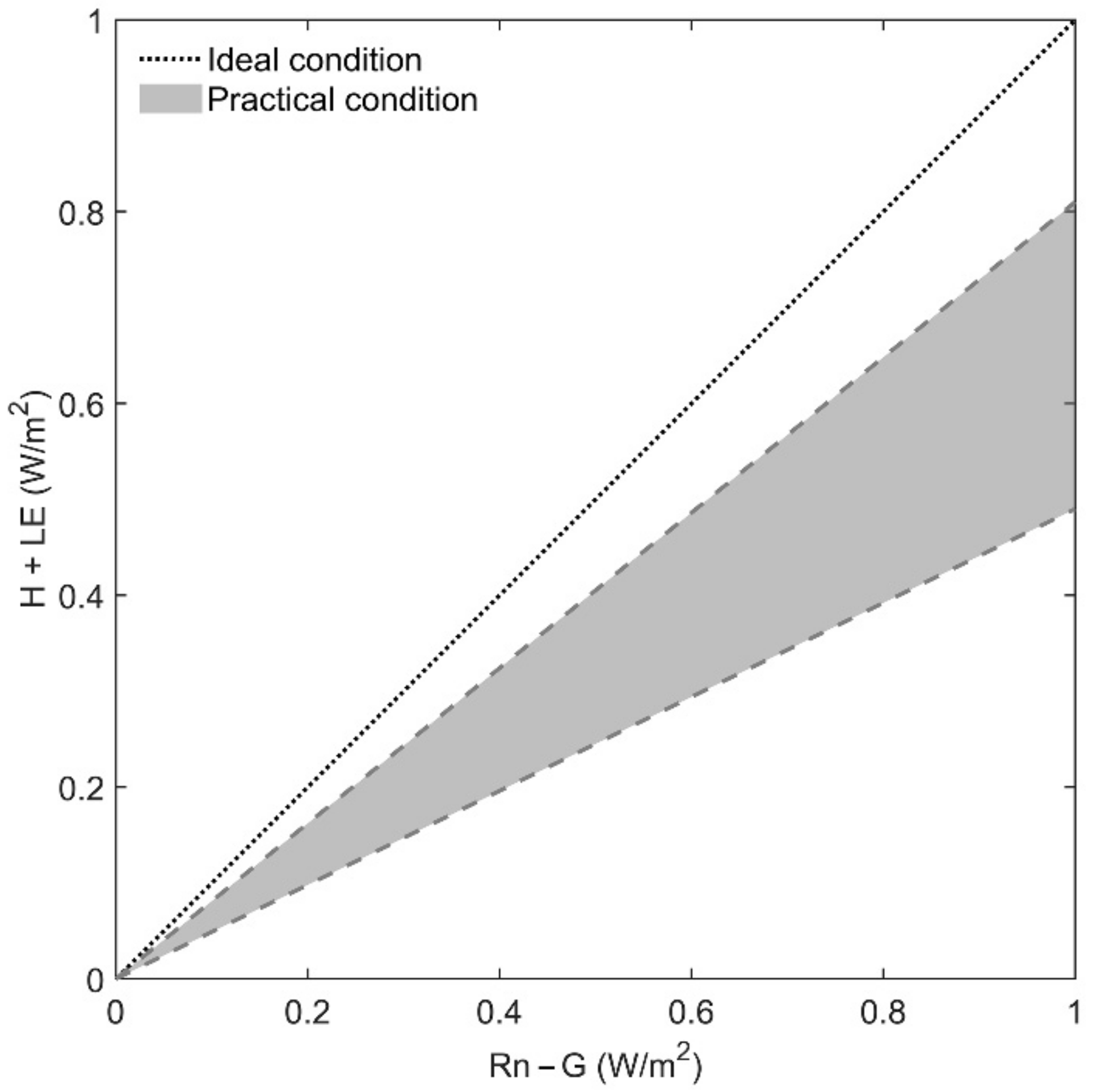
3.2. Energy Balance Characteristics
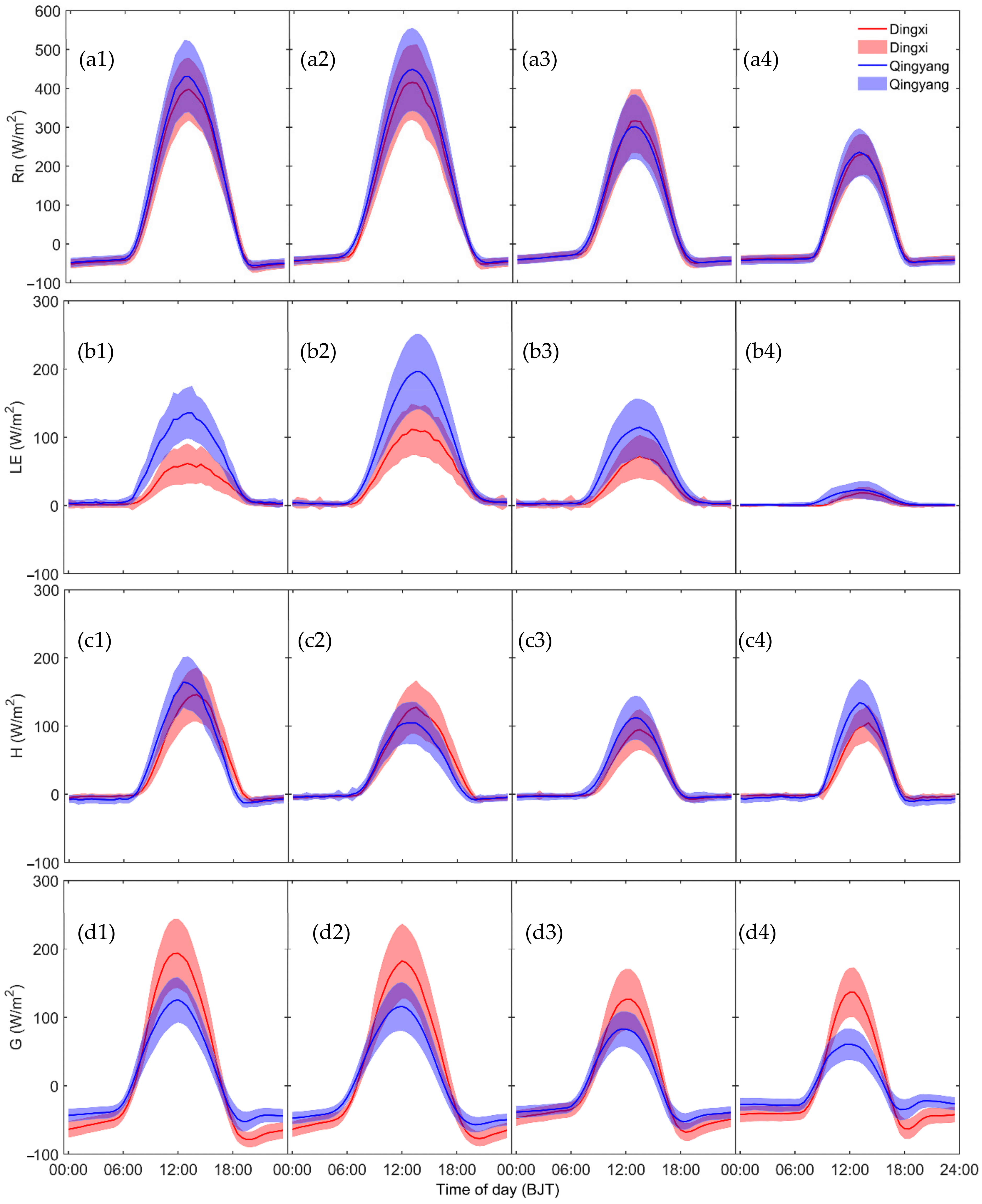
3.3. Diurnal Cycle and Seasonal Variation in Energy Flux
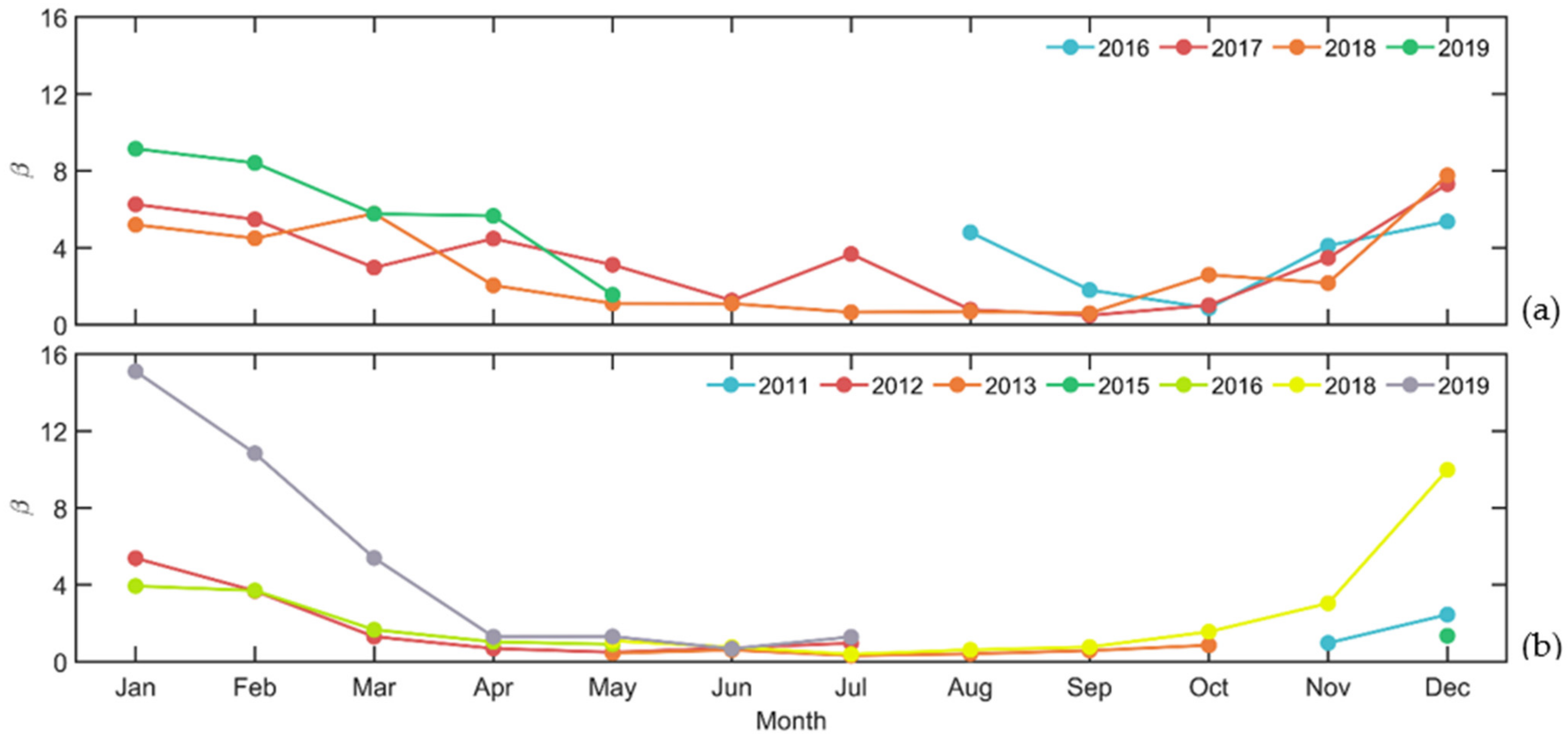
3.4. Bowen Ratio Variation
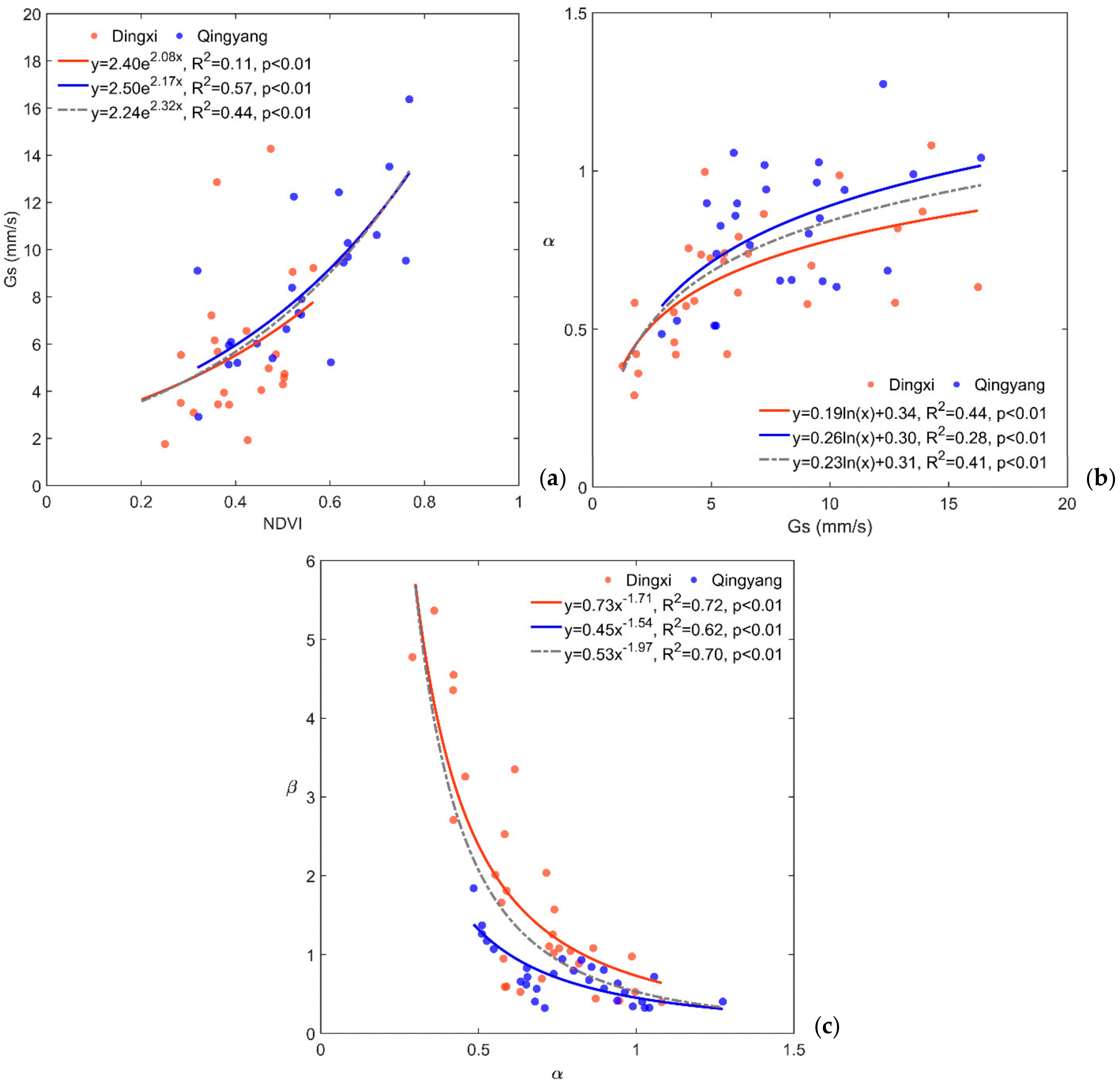
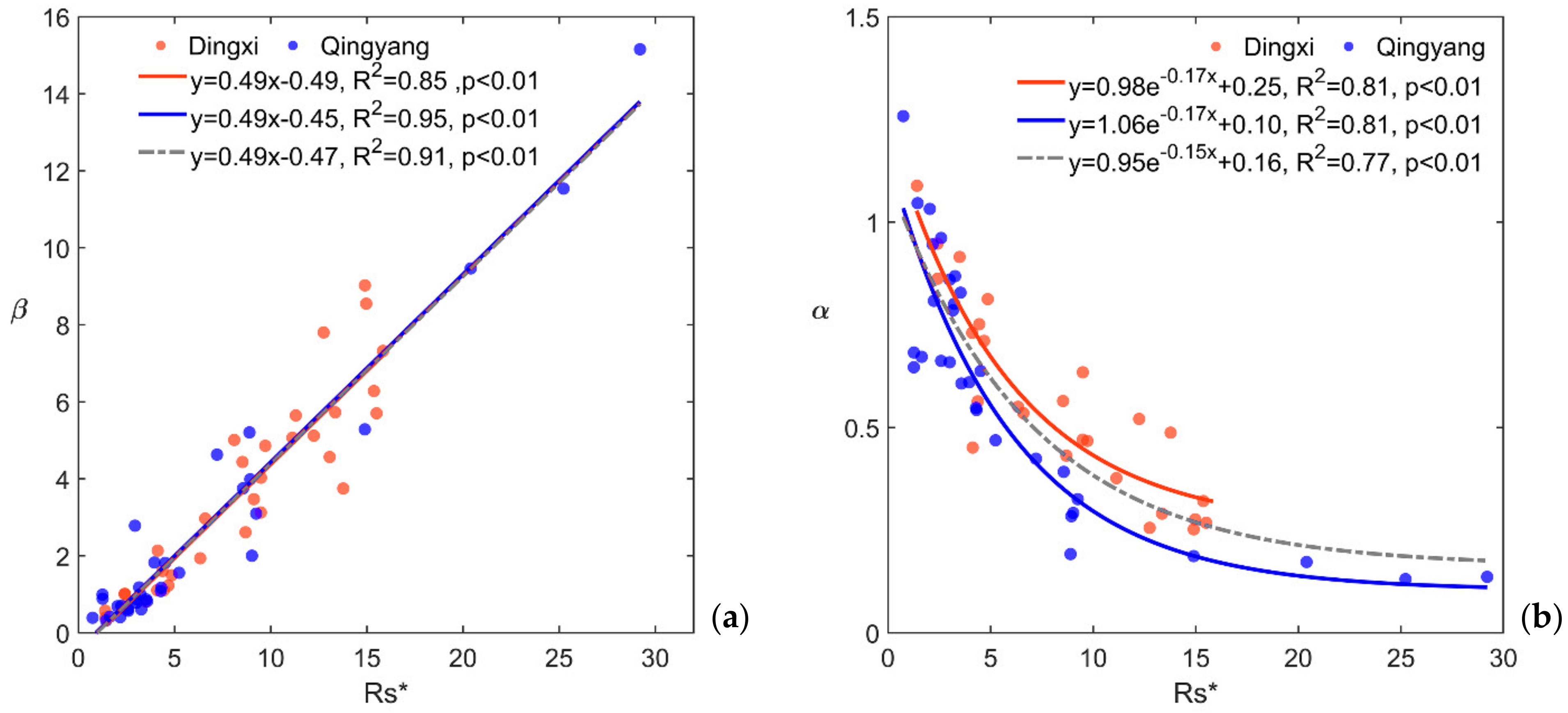
3.5. Environmental and Ecological Controls on Bowen Ratio
4. Discussion
4.1. Bowen Ratio Variation
4.2. Influence of Environmental and Ecological Factors on the Bowen Ratio
4.3. Biometeorological Controls on the Bowen Ratio
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rana, G.; Katerji, N.; Mastrorilli, M.; El Moujabber, M.; Brisson, N. Validation of a model of actual evapotranspiration for water stressed soybeans. Agric. For. Meteor. 1997, 86, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.B.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Aubinet, M.; Berbigier, P.; Bernhofer, C.; Dolman, H.; Falge, E.; Field, C.; Goldstein, A.; Granier, A.; et al. Energy partitioning between latent and sensible heat flux during the warm season at FLUXNET sites. Water Res. Res. 2002, 38, 30-1–30-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.P.; Chen, J.Q.; Lin, G.H.; Zhang, W.L.; Miao, H.X.; Wei, L.; Huang, J.H.; Han, X.G. Energy balance and partition in Inner Mongolia steppe ecosystems with different land use types. Agric. For. Meteor. 2009, 149, 1800–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biudes, M.S.; Vourlitis, G.L.; Machado, N.G.; Arruda, P.H.Z.D.; Nogueira, J.D.S. Patterns of energy exchange for tropical ecosystems across a climate gradient in Mato Grosso, Brazil. Agricu. For. Meteor. 2015, 202, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milly, P.C.D.; Dunne, K.A. A Hydrologic Drying Bias in Water-Resource Impact Analyses of Anthropogenic Climate Change. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2017, 53, 822–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf Vaghefi, S.; Mousavi, S.J.; Abbaspour, K.C.; Srinivasan, R.; Yang, H. Analyses of the impact of climate change on water resources components, drought and wheat yield in semiarid regions: Karkheh River Basin in Iran. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 2018–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, N.; Bhave, A.G.; Mishra, A.; Singh, R. Impact of human intervention and climate change on natural flow regime. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lama, G.F.C.; Sadeghifar, T.; Azad, M.T.; Sihag, P.; Kisi, O. On the Indirect Estimation of Wind Wave Heights over the Southern Coasts of Caspian Sea: A Comparative Analysis. Water 2022, 14, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowska, M.B. Effect of water–air heat transfer on the spread of thermal pollution in rivers. Acta Geophys. 2019, 67, 597–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jodar-Abellan, A.; Valdes-Abellan, J.; Pla, C.; Gomariz-Castillo, F. Impact of land use changes on flash flood prediction using a sub-daily SWAT model in five Mediterranean ungauged watersheds (SE Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1578–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.H.; Zhang, L.; Liang, J.N.; Cao, X.J.; Liu, H.; Yang, Z.H. Understanding the partitioning of the available energy over the semi-arid areas of the Loess Plateau, China. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahmana, M.M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, K. Assessment on surface energy imbalance and energy partitioning using ground and satellite data over a semi-arid agricultural region in north China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.M.; Yang, D.W. Interannual and seasonal variability in evapotranspiration and energy partitioning over an irrigated cropland in the North China Plain. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.S.; Kang, S.Z.; Li, F.S.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Tong, L. Evapotranspiration measurement and estimation using modified Priestley–Taylor model in an irrigated maize field with mulching. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 168, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.J.; Liu, C.W.; Cui, N.B.; Wu, Y.J.; Wang, Z.C.; Li, G. Evapotranspiration estimation using a modified Priestley-Taylor model in a rice-wheat rotation system. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 224, 105755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lama, G.F.C.; Crimaldi, M.; Pasquino, V.; Padulano, R.; Chirico, G.B. Bulk drag predictions of riparian arundo donax stands through UAV-acquired multispectral images. Water 2021, 13, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez-Nicolás, M.; García-López, S.; Barbero, L.; Ruiz-Ortiz, V.; Sánchez-Bellón, Á. Applications of unmanned aerial systems (UASs) in hydrology: A review. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, P.; Zhang, Q.; Ren, X.Y.; Yang, Z.S.; Li, H.Y.; Yang, Y. Environmental and biophysical effects of evapotranspiration in semiarid grassland and maize cropland ecosystems over the summer monsoon transition zone of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 264, 107462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, P.J.; Castellvi, F.; Martínez-Cob, A. A simple model for estimating the Bowen ratio from climatic factors for determining latent and sensible heat flux. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Noormets, A.; Fang, X.; Zha, T.; Zhou, J.; Sun, G.; McNulty, S.G.; Chen, J. Energy partitioning and surface resistance of a poplar plantation in northern China. Biogeoscience 2015, 12, 4245–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Yu, Y.; Chen, J.B.; Zhang, T.T.; Li, Z.C. Seasonal and interannual variation of radiation and energy fluxes over a rain-fed cropland in the semi-arid area of Loess Plateau, northwestern China. Atmos. Res. 2016, 176, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Gong, D.Z.; Mei, X.R.; Hao, W.P.; Tang, D.H.; Cui, N.B. Energy balance and partitioning in partial plastic mulched and non-mulched maize fields on the Loess Plateau of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 191, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.S.; Zhang, Q.; Hao, X.C. Environmental and biological controls on monthly and annual evapotranspiration in China’s Loess Plateau. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2019, 137, 1675–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Oki, T.; Yeh, P.J.F.; Kim, W.; Kanae, S.; Otsuki, K. On the relationship between the Bowen ratio and the near-surface air temperature. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2012, 108, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Q.; Kueppers, L.M. Surface energy partitioning over four dominant vegetation types across the United States in a coupled regional climate model (Weather Research and Forecasting Model 3–Community Land Model 3.5). J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2012, 117, D06111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, K.B.; Baldocchi, D.D. Seasonal and interannual variability of energy fluxes over a broadleaved temperate deciduous forest in North American. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 100, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wever, L.A.; Flanagan, L.B.; Carlson, P.J. Seasonal and interannual variation in evapotranspiration, energy balance and surface conductance in a northern temperate grassland. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2002, 112, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, P.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.L.; Hao, X.C.; Sun, X.Y. Seasonal and inter-annual variability of the Bowen smith ratio over a semi-arid grassland in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 252, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Q. Synergistic effects of climatic factors and drought on maize yield in the east of Northwest China against the background of climate change. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2020, 143, 1017–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wen, J.; Wei, Z.G.; Tian, H.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.Z.; Shi, X.G.; Zhang, T.T.; Liu, R.; Zhang, J.H. Study on water deficit of the topsoil over the Chinese Loess Plateau mesa region. Plateau Meteorol. 2009, 28, 530–538. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Zhang, L.Y.; Wang, W.Y.; Sha, S. Spatial distribution of surface energy fluxes over the Loess Plateau in China and its relationship with climate and the environment. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 2135–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, S. On land surface processes and its experimental study in Chinese Loess Plateau. Adv. Earth Sci. 2008, 23, 167–173. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yue, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Wei, W.; Yang, Z.S.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, S.; Sun, X.Y. Biometeorological effects on carbon dioxide and water-use efficiency within a semiarid grassland in the Chinese Loess Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Dong, Q.G.; Jiao, M.Y.; Zhao, X.N.; Gao, X.R.; Wu, P.T.; Wang, A. Estimation of Actual Evapotranspiration in a Semiarid Region Based on GRACE Gravity Satellite Data—A Case Study in Loess Plateau. Remote. Sens. 2018, 10, 2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.R.; Sun, M.; Luan, Q.H.; Zhao, X.N.; Wang, J.C.; He, G.H.; Zhao, Y. The spatial and temporal evolution of the actual evapotranspiration based on the remote sensing method in the Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falge, E.; Baldocchi, D.; Olson, R.; Anthoni, P.; Aubinet, M.; Bernhofer, C.; Burba, G.; Ceulemans, G.; Clement, R.; Dolman, H.; et al. Gap filling strategies for long term energy flux data sets. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2001, 107, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavigne, M.B.; Ryan, M.G.; Anderson, D.E.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Crill, P.M.; Fitzjarrald, D.R.; Goulden, M.L.; Gower, S.T.; Massheder, J.M.; McCaughey, J.H.; et al. Comparing nocturnal eddy covariance measurements to estimates of ecosystem respiration made by scaling chamber measurements at six coniferous boreal sites. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 28977–29985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahrt, L. Stratified atmospheric boundary layers. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1999, 90, 375–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, B.E.; Goldstein, A.H.; Anthoni, P.M.; Unsworth, M.H.; Panek, J.A.; Bauer, M.R.; Fracheboud, J.M.; Hultman, N. Carbon dioxide and water vapor exchange by young and old ponderosa pine ecosystems during a dry summer. Tree Physiol. 2001, 21, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aubinet, M.; Grelle, A.; Ibrom, A.; Rannik, Ü.; Moncrieff, J.; Foken, T.; Kowalski, A.S.; Martin, P.H.; Berbigier, P.; Bernhofer, C.; et al. Estimates of the Annual Net Carbon and Water Exchange of Forests: The EUROFLUX Methodology. Adv. Ecol. Res. 1999, 30, 114–175. [Google Scholar]
- McGloin, R.; Šigut, L.; Fischer, M.; Foltýnová, L.; Chawla, S.; Trnka, M.; Pavelka, M.; Marek, M.V. Available energy partitioning during drought at two Norway spruce forests and a European Beech forest in Central Europe. J. Geophys. Res-Atmos. 2019, 124, 3726–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCaughey, J.H. Energy balance storage terms in a mature mixed forest at Petawawa, Ontario—A case study. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1985, 31, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.J. Frequency response corrections for eddy correlation systems. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1986, 37, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Q.; Yu, G.R.; Wen, X.F.; Zhang, L.M.; Ren, C.Y.; Fu, Y.L. Energy balance closure at ChinaFLUX sites. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2005, 48, 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, W.; Wang, R.Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.Y.; Shi, J.S.; Hao, X.C. Influence of environmental factors on land-surface water and heat exchange during dry and wet periods in the growing season of semiarid grassland on the Loess Plateau. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 2002–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wang, J.M. A temperature prediction-correction method for estimating surface soil heat flux from soil temperature and moisture data. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 2008, 51, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, T.; Saitoh, T.M.; Sato, Y.; Morooka, T.; Manfroi, O.J.; Kuraji, K.; Suzuki, M. Transpiration, canopy conductance and the decoupling coefficient of a lowland mixed dipterocarp forest in Sarawak, Borneo: Dry spell effects. J. Hydrol. 2004, 287, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, M.S.; Mano, M.; Miyata, A.; Baten, M.A.; Hiyama, T. Surface energy partitioning and evapotranspiration over a double-cropping paddy field in Bangladesh. Hydrol. Proc. 2012, 26, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arain, M.A.; Black, T.A.; Barr, A.G.; Griffis, T.J.; Morgenstern, K.; Nesic, Z. Year-round observations of the energy and water vapour fluxes above a boreal black spruce forest. Hydrol. Proc. 2003, 17, 3581–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.R.; Vourlitis, G.L.; Lobo, F.D.; de Oliveira, R.G.; Nogueira, J.D. Seasonal variation in energy balance and canopy conductance for a tropical savanna ecosystem of south central Mato Grosso, Brazil. J. Geophys. Res.-Biogeosci. 2014, 119, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.Q.; Yang, P.J.; Hu, H.C.; Liu, H. Energy balance and canopy conductance for a cotton field under film mulched drip irrigation in an arid region of northwestern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foken, T.; Wimmer, F.; Mauder, M.; Thomas, C.; Liebethal, C. Some aspects of the energy balance closure problem. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 4395–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Twine, T.E.; Kustas, W.P.; Norman, J.M.; Cook, D.R.; Houser, P.R.; Meyers, T.P.; Prueger, J.H.; Starks, P.J.; Wesely, M.L. Correcting eddy-covariance flux underestimates over a grassland. Agric. For. Meteor. 2000, 103, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez, J.M.; Caselles, V.; Rubio, E.M. Analysis of the energy balance closure over a FLUXNET boreal forest in Finland. Hydrol. Earth System Sci. 2010, 14, 1487–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majozi, N.P.; Mannaerts, C.M.; Ramoelo, A.; Mathieu, R.; Nickless, A.; Verhoef, W. Analysing surface energy balance closure and partitioning over a semi-arid savanna FLUXNET site in Skukuza, Kruger National Park, South Africa. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 3401–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, P.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, S.J.; Cheng, H.; Wang, X.Y. Effects of the soil heat flux estimates on surface energy balance closure over a semi-arid grassland. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2011, 25, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Xiao, H.B.; Qi, D.L. Features of land surface process over wetland at Tibetan Plateau during soil freezing and thawing periods. Acta. Meteor. Sin. 2017, 75, 481–491. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, Z.X.; Wang, S. Analysis of Variation Regularity of Land-Surface Physical Quantities Over the Dingxi Region of the Loess Plateau. Chin. J. Geophys. 2011, 54, 436–447. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Hao, X.; Yue, P. Conversion features of evapotranspiration responding to climate warming in transitional climate regions in northern China. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 3891–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.P.; Yu, H.P.; Guan, X.D.; Wang, G.Y.; Guo, R.X. Accelerated dryland expansion under climate change. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.S.; Zhang, Q.; Hao, X.C.; Yue, P. Changes in evapotranspiration over global semiarid regions 1984–2013. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2019, 124, 2946–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdogan, M.; Rodell, M.; Beaudoing, H.K.; Toll, D.L. Simulating the Effects of Irrigation over the United States in a Land Surface Model Based on Satellite-Derived Agricultural Data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanken, P.D.; Black, T.A.; Yang, P.C.; Neumann, H.H.; Nesic, Z.; Staebler, R.; Hartog, G.D.; Noval, M.D.; Lee, X. Energy balance and canopy conductance of a boreal aspen forest: Partitioning overstory and understory components. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 1997, 102, 28915–28927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mchaughton, K.G.; Spriggs, T.W. A mixed-layer model for regional evaporation. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1986, 34, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraedrich, K.; Kleidon, A.; Lunkeit, F. A green planet versus a desert world: Estimating the effect of vegetation extremes on the atmosphere. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 3156–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Instrument | Type | Installation Height | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dingxi | Qingyang | ||
| Open Path CO2/H2O Gas Analyzer | Li-7500, Li-Cor (Lincoln, NE, USA) | 2.5 m | 3 m |
| Three-dimensional (3D) sonic anemometer | CSAT-3, Campbell (Logan, UT, USA) | 2.5 m | 3 m |
| Temperature and relative humidity probe | HMP45C-L, Vaisala (Vantaa, Finland) | 1, 2, 4, 10, and 16 m | 2, 4, 8, and 18 m |
| Net radiometer | CNR4, Kipp and Zoned (Delft, The Netherlands) | 1.5 m | 1.5 m |
| Self-calibrating heat flux sensor | HFP01SC-L50, Hukseflux (Delft, The Netherlands) | 2, 5, and 10 cm | 1, 2.5 and 5 cm |
| Soil temperature profile sensor | STP01-L50, Hukseflux | 0, 5, 10, 20, 40, 50, and 80 cm | 0, 5, 10, 20, 40, 60, and 90 cm |
| Water content reflectometer | CS616-L, Campbell | 5, 10, 20, 40, 50, and 80 cm | 5, 10, 20, 40, 60, and 90 cm |
| Site | Midday | Night | All Day | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Numbers | OLS | EBR | Sample Numbers | OLS | EBR | Sample Numbers | OLS | EBR | ||||
| Slope | R2 | Slope | R2 | Slope | R2 | |||||||
| Dingxi | 10,516 | 0.65 | 0.68 | 0.89 | 11,190 | 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 40,350 | 0.76 | 0.81 | 0.68 |
| Qingyang | 5149 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.81 | 7773 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.49 | 24,064 | 0.73 | 0.85 | 0.60 |
| Site | Rn (W/m2) | LE (W/m2) | H (W/m2) | G (W/m2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak | Mean | Peak | Mean | Peak | Mean | Peak | Mean | |
| Dingxi | 334.10 | 67.29 | 64.14 | 20.95 | 120.29 | 28.98 | 157.88 | 6.08 |
| Qingyang | 348.37 | 71.74 | 125.83 | 41.41 | 122.32 | 28.50 | 96.93 | 1.62 |
| Energy Component (W/m2) | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dingxi | Qingyang | Dingxi | Qingyang | Dingxi | Qingyang | Dingxi | Qingyang | ||
| Rn | Peak | 345.02 | 376.71 | 440.16 | 460.16 | 362.38 | 348.03 | 226.45 | 240.88 |
| Mean | 67.73 | 77.14 | 109.87 | 119.84 | 78.76 | 75.02 | 25.34 | 26.20 | |
| LE | Peak | 39.31 | 82.61 | 103.10 | 169.41 | 101.19 | 168.67 | 22.55 | 21.63 |
| Mean | 11.77 | 25.70 | 36.00 | 74.11 | 32.54 | 58.31 | 5.23 | 6.64 | |
| H | Peak | 148.75 | 162.54 | 143.10 | 112.81 | 107.21 | 110.68 | 93.27 | 118.66 |
| Mean | 34.85 | 34.02 | 41.31 | 30.49 | 28.59 | 25.33 | 17.93 | 21.93 | |
| G | Peak | 173.24 | 109.18 | 214.49 | 125.82 | 124.15 | 97.69 | 136.16 | 56.19 |
| Mean | 10.34 | 6.68 | 20.07 | 8.67 | 1.24 | −2.29 | −3.29 | −6.94 | |
| Environmental Factors | Equation Parameters | Dingxi | Qingyang | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Wet | Dry | Wet | ||
| Ts − Ta (℃) | |||||
| a | 1.27 | 0.78 | 0.39 | 0.26 | |
| b | 0.24 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.13 | |
| R2 | 0.36 | 0.59 | 0.51 | 0.58 | |
| p | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| VPD (kPa) | |||||
| a | 2.18 | 0.46 | 0.66 | 0.39 | |
| b | 1.62 | 1.45 | 1.76 | 0.65 | |
| R2 | 0.29 | 0.38 | 0.44 | 0.22 | |
| p | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | |
| Effective precipitation (mm) | |||||
| a | 4.25 | 1.27 | 2.16 | 1.05 | |
| b | −0.02 | −0.004 | −0.03 | −0.01 | |
| R2 | 0.37 | 0.27 | 0.80 | 0.60 | |
| p | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| SWC) | |||||
| a | 15.23 | 2.49 | 2.48 | 0.12 | |
| b | −11.08 | −4.24 | −5.92 | −1.10 | |
| R2 | 0.19 | 0.33 | 0.36 | 0.63 | |
| p | <0.05 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| Site | Correlation Effect | NDVI | Ta | VPD | SWC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dingxi | Direct | −0.68 | 0.42 | 0.11 | −0.21 |
| Indirect | 0.12 | −0.36 | 0.39 | −0.41 | |
| Total | −0.57 | 0.06 | 0.51 | −0.63 | |
| Qingyang | Direct | 0.33 | −0.90 | 0.54 | −0.35 |
| Indirect | −0.84 | 0.37 | −0.26 | −0.01 | |
| Total | −0.51 | −0.53 | 0.28 | −0.36 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yue, P.; Yang, J.; Wang, S. Environmental and Biophysical Effects of the Bowen Ratio over Typical Farmland Ecosystems in the Loess Plateau. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081897
Ren X, Zhang Q, Yue P, Yang J, Wang S. Environmental and Biophysical Effects of the Bowen Ratio over Typical Farmland Ecosystems in the Loess Plateau. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(8):1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081897
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Xueyuan, Qiang Zhang, Ping Yue, Jinhu Yang, and Sheng Wang. 2022. "Environmental and Biophysical Effects of the Bowen Ratio over Typical Farmland Ecosystems in the Loess Plateau" Remote Sensing 14, no. 8: 1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081897
APA StyleRen, X., Zhang, Q., Yue, P., Yang, J., & Wang, S. (2022). Environmental and Biophysical Effects of the Bowen Ratio over Typical Farmland Ecosystems in the Loess Plateau. Remote Sensing, 14(8), 1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081897





