Modeling Post-Sunset Equatorial Spread-F Occurrence as a Function of Evening Upward Plasma Drift Using Logistic Regression, Deduced from Ionosondes in Southeast Asia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Modeling ESF Occurrence with Logistic Regression
- 1.
- Setting the initial value of ,where t = 0 indicates the initial set of values of . In this study, we set the initial value of each regression coefficient to zero.
- 2.
- Computing the cost function (error) between the predicted and actual outputs based on logistic regression; hence, the cost function is given by:where J is the cost function, i represents the number of observation data in the training set ranging from 1 to m (number of observations), is the actual output of the post-sunset ESF occurrence from the observations, and is the predicted output of the post-sunset ESF occurrence obtained from Equation (1).
- 3.
- Computing the gradient of the cost function for each coefficient .
- 4.
- Finding the minimum J and to obtain the optimum using the fminunc function in the optimization toolbox of the MATLAB software. The function fminunc is used to find a local minimum of J with a value of very close to zero.
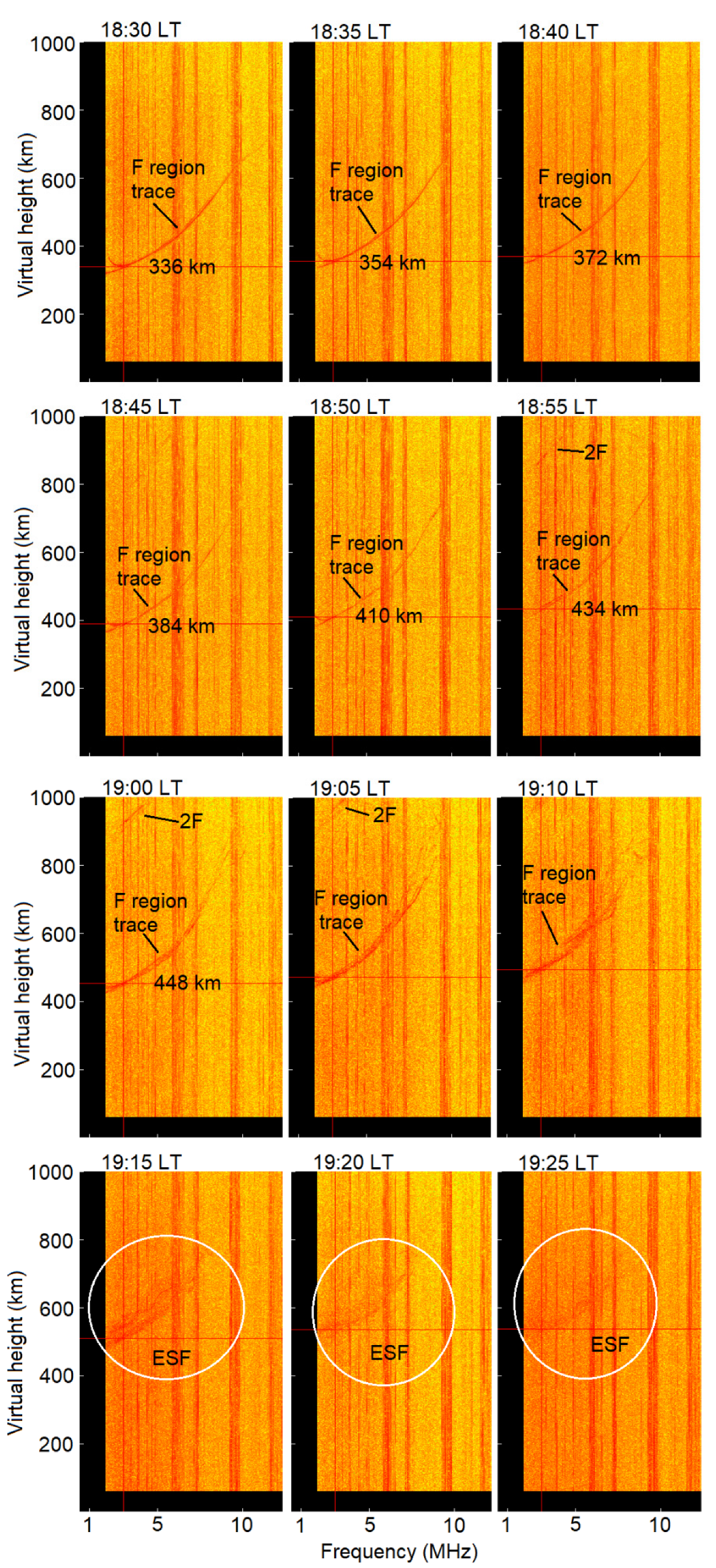
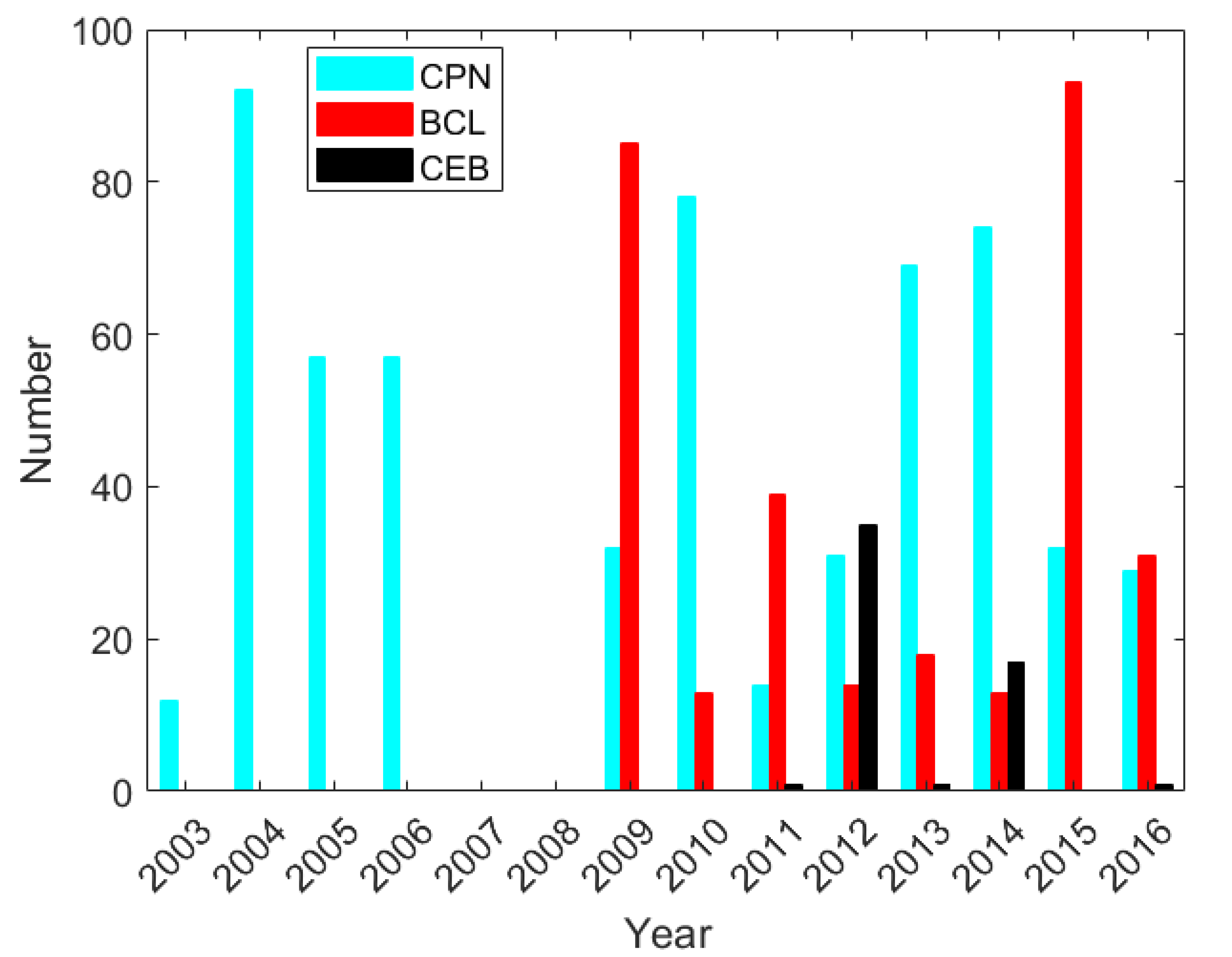
2.2. Data Used
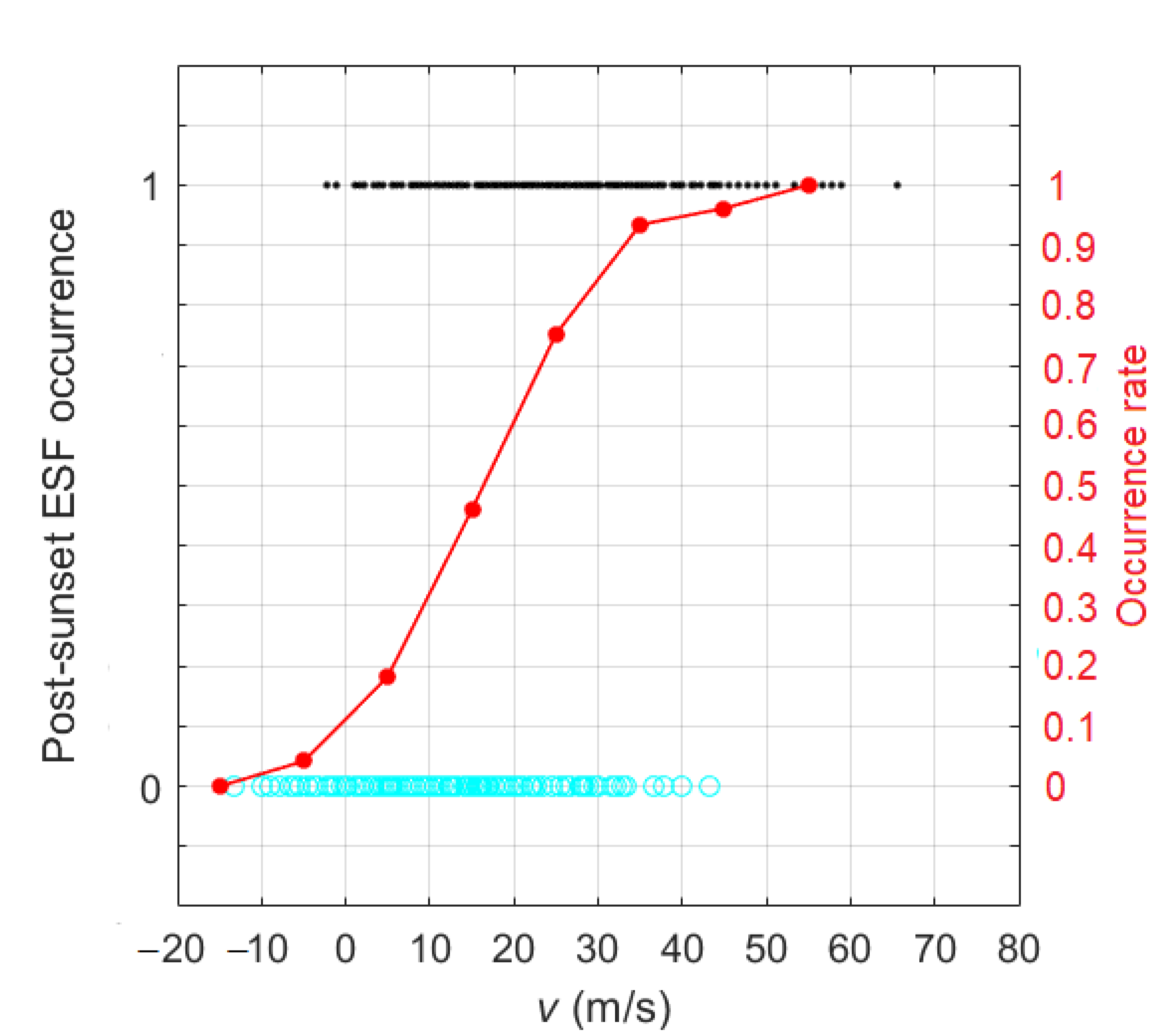
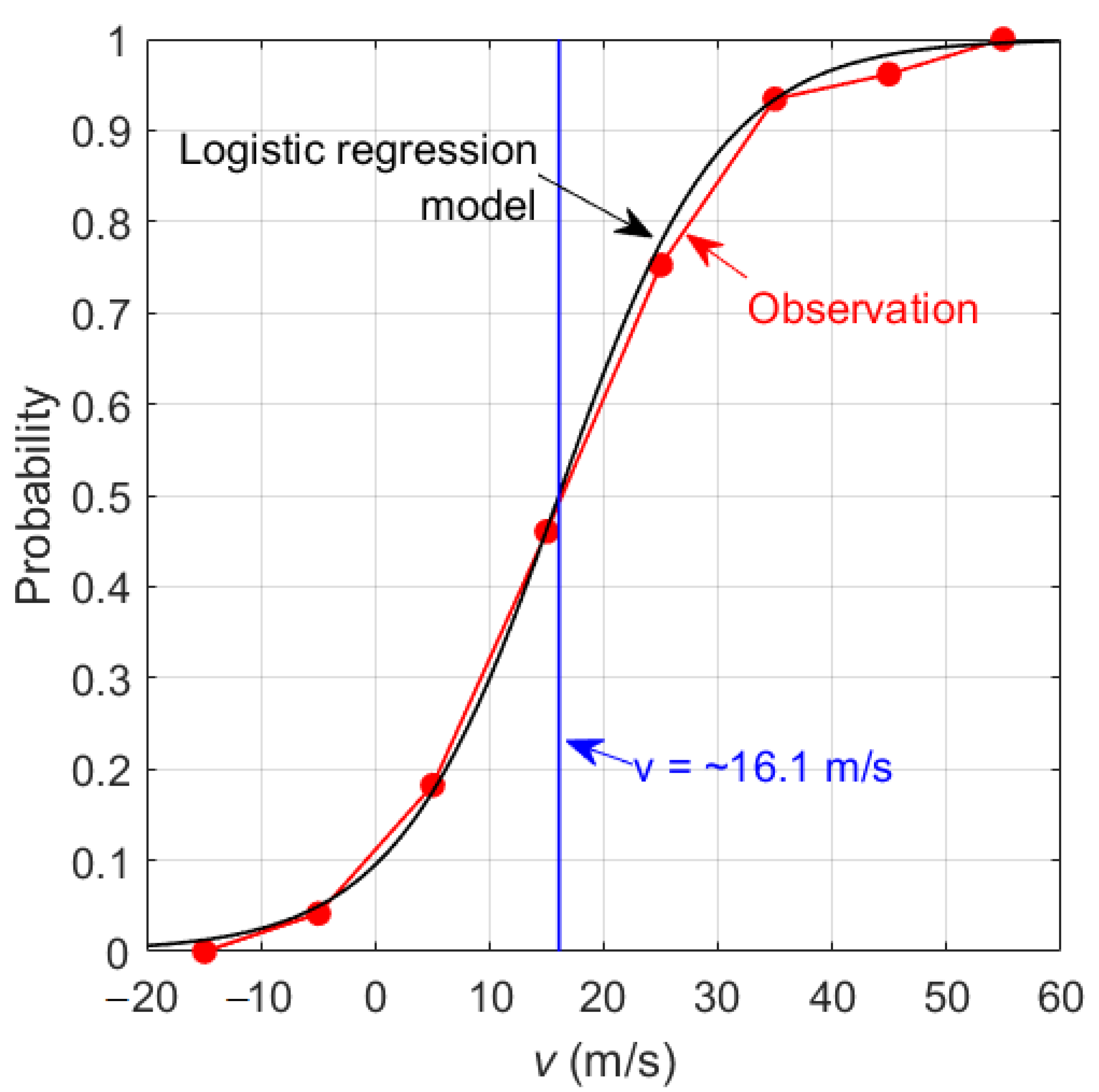
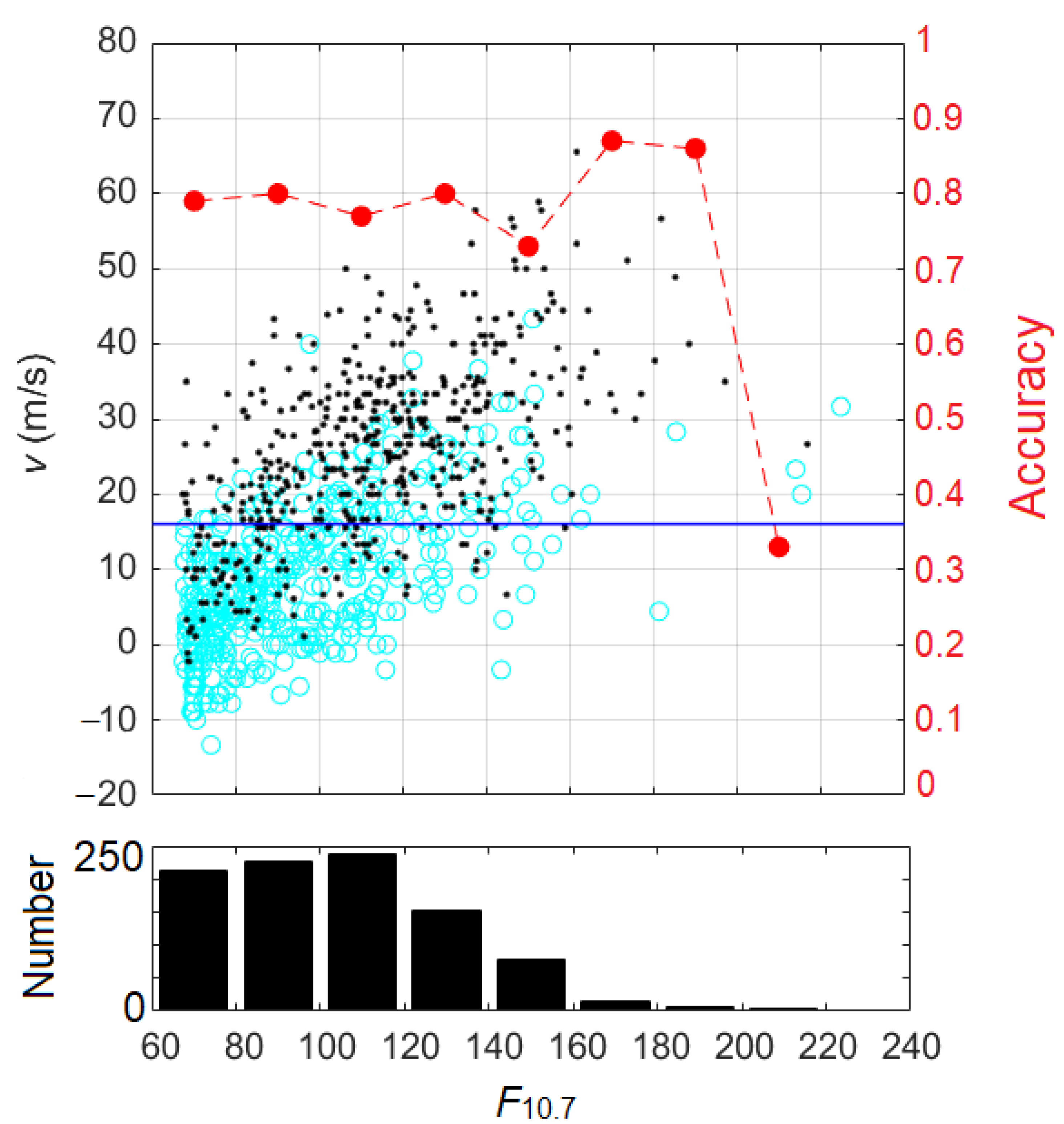
3. Results and Discussion
4. Summary and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Booker, H.G.; Wells, H.W. Scattering of radio waves by the F region of the ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1938, 43, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, M.C.; Makela, J.J.; Paxton, L.J.; Kamalabadi, F.; Comberiate, J.M.; Kil, H. The first coordinated ground- and space-based optical observations of equatorial plasma bubbles. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Stolle, C.; Lühr, H. The Swarm satellite loss of GPS signal and its relation to ionospheric plasma irregularities. Space Weather 2016, 14, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aa, E.; Zou, S.; Eastes, R.; Karan, D.K.; Zhang, S.-R.; Erickson, P.J.; Coster, A.J. Coordinated ground-based and space-based observations of equatorial plasma bubbles. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2020, 125, e2019JA027569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Burns, A.G.; Wang, W.; Coster, A.; Qian, L.; Liu, J.; Solomon, S.C.; Eastes, R.W.; Daniell, R.E.; McClintock, W.E. Comparison of GOLD nighttime measurements with total electron content: Preliminary results. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2020, 125, e2019JA027767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO). Manual on Space Weather Information in Support of International Air Navigation (Doc 10100); ICAO Publication: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2018; pp. 2-1–2-6.
- Alfonsi, L.; Spogli, L.; Pezzopane, M.; Romano, R.; Zuccheretti, E.; De Franceschi, G.; Cabrera, M.A.; Ezquer, R.G. Comparative analysis of spread-F signature and GPS scintillation occurrences at Tucuman, Argentina. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2013, 118, 4483–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Walter, T.; Chiou, T.Y.; Enge, P. Characteristics of deep GPS signal fading due to ionospheric scintillation for aviation receiver design. Radio Sci. 2009, 44, RS0A16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ning, B.; Otsuka, Y.; Abdu, M.A.; Abadi, P.; Liu, Z.; Spogli, L.; Wan, W. Challenges to Equatorial Plasma Bubble and Ionospheric Scintillation Short-Term Forecasting and Future Aspects in East and Southeast Asia. Surv. Geophys. 2021, 42, 201–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinagawa, H.; Jin, H.; Miyoshi, Y.; Fujiwara, H.; Yokoyama, T.; Otsuka, Y. Daily and seasonal variations in the linear growth rate of the Rayleigh-Taylor instability in the ionosphere obtained with GAIA. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2018, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, B.A.; Yizengaw, E.; Retterer, J.M.; Francis, M.; Terkildsen, M.; Marshall, R.; Norman, R.; Zhang, K. An analysis of the quiet time day-to-day variability in the formation of postsunset equatorial plasma bubbles in the Southeast Asian region. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 3206–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.S.; Hairston, M.R. The postsunset vertical plasma drift and its effects on the generation of equatorial plasma bubbles observed by the C/NOFS satellite. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2015, 120, 2263–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fejer, B.G.; Scherliess, L.; de Paula, E.R. Effects of the vertical plasma drift velocity on the generation and evolution of equatorial spread F. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1999, 104, 19859–19869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabas, R.S.; Singh, L.; Lakshmi, D.R.; Subramanyam, P.; Chopra, P.; Garg, S.C. Evolution and dynamics of equatorial plasma bubbles: Relationships to ExB drift, postsunset total electron content enhancements, and equatorial electrojet strength. Radio Sci. 2003, 38, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, P.; Otsuka, Y.; Liu, H.X.; Hozumi, K.; Martinigrum, D.R.; Jamjareegulgarn, P.; Thanh, L.T.; Otadoy, R. Roles of thermospheric neutral wind and equatorial electrojet in pre-reversal enhancement, deduced from observations in Southeast Asia. Earth Planet. Phys. 2021, 5, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, J.A.; Barnett, A.G. An Introduction to Generalized Linear Model, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 149–174. [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, T.; Kawamura, M.; Saito, S.; Nozaki, K.; Kato, H.; Hemmakorn, N.; Boonchuk, T.; Komolmis, T.; Ha Duyen, C. Low latitude ionosphere-thermosphere dynamics studies with ionosonde chain in Southeast Asia. Ann. Geophys. 2007, 25, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nozaki, K. FMCW ionosonde for the SEALION project. J. Natl. Inst. Inf. Commun. Technol. 2009, 56, 287–298. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, W.J.; Huang, C.Y.; Gentile, L.C.; Bauer, L. Seasonal-longitudinal variability of equatorial plasma bubbles. Ann. Geophys. 2004, 22, 3089–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piggott, W.R.; Rawer, K. URSI Handbook of Ionogram Interpretation and Reduction; Rep. UAG-23A, World Data Cent. for Sol.Terr. Phys.; NOAA: Boulder, CO, USA, 1972.
- Abadi, P.; Otsuka, Y.; Supriadi, S.; Olla, A. Probability of ionospheric plasma bubble occurrence as a function of pre-reversal enhancement deduced from ionosondes in Southeast Asia. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2226, 050001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, B.A.; Currie, J.L.; Dao, T.; Yizengaw, E.; Retterer, J.; Terkildsen, M.; Groves, K.; Caton, R. On the assessment of daily equatorial plasma bubble occurrence modeling and forecasting. Space Weather 2020, 18, e2020SW002555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabas, R.S.; Lakshmi, D.R.; Reddy, B.M. Day-to-day variability in the occurrence of equatorial and low-latitude scintillations in the Indian zone. Radio Sci. 1998, 33, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, M.A.; de Medeiros, R.T.; Bittencourt, J.A.; Batista, I.S. Vertical ionization drift velocities and range type spread F in the evening equatorial ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, R.T.; Yamamoto, M.; Tsugawa, T.; Hoang, T.L.; Tulasi Ram, S.; Thampi, S.V.; Chau, H.D.; Nagatsuma, T. On seeding, large scale wave structure, equatorial spread F, and scintillations over Vietnam. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L20102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Datasets | Performance | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | TPR | FPR | TSS | |
| Training (657 data points) | 0.78 | 0.79 | 0.22 | 0.57 |
| Testing (281 data points) | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.21 | 0.58 |
| Persistence technique (780 data points) | 0.65 | 0.68 | 0.38 | 0.30 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abadi, P.; Ahmad, U.A.; Otsuka, Y.; Jamjareegulgarn, P.; Martiningrum, D.R.; Faturahman, A.; Perwitasari, S.; Saputra, R.E.; Septiawan, R.R. Modeling Post-Sunset Equatorial Spread-F Occurrence as a Function of Evening Upward Plasma Drift Using Logistic Regression, Deduced from Ionosondes in Southeast Asia. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1896. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081896
Abadi P, Ahmad UA, Otsuka Y, Jamjareegulgarn P, Martiningrum DR, Faturahman A, Perwitasari S, Saputra RE, Septiawan RR. Modeling Post-Sunset Equatorial Spread-F Occurrence as a Function of Evening Upward Plasma Drift Using Logistic Regression, Deduced from Ionosondes in Southeast Asia. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(8):1896. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081896
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbadi, Prayitno, Umar Ali Ahmad, Yuichi Otsuka, Punyawi Jamjareegulgarn, Dyah Rahayu Martiningrum, Agri Faturahman, Septi Perwitasari, Randy Erfa Saputra, and Reza Rendian Septiawan. 2022. "Modeling Post-Sunset Equatorial Spread-F Occurrence as a Function of Evening Upward Plasma Drift Using Logistic Regression, Deduced from Ionosondes in Southeast Asia" Remote Sensing 14, no. 8: 1896. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081896
APA StyleAbadi, P., Ahmad, U. A., Otsuka, Y., Jamjareegulgarn, P., Martiningrum, D. R., Faturahman, A., Perwitasari, S., Saputra, R. E., & Septiawan, R. R. (2022). Modeling Post-Sunset Equatorial Spread-F Occurrence as a Function of Evening Upward Plasma Drift Using Logistic Regression, Deduced from Ionosondes in Southeast Asia. Remote Sensing, 14(8), 1896. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081896










