Abstract
This paper introduces a fast backprojection synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imaging algorithm based on wavenumber-domain spectral splicing. The traditional fast backprojection (FBP) algorithm establishes the polar coordinate system with the center of the sub-aperture as the origin. Therefore, the coordinates of the image obtained from each sub-aperture are different. Sub-aperture images must be projected to a uniform coordinate system before they can be coherently superimposed to form the final image, which requires a large amount of calculation. In order to deal with this problem, this paper proposes a novel imaging method, which uses the same polar coordinate system for each sub-aperture. The sub-aperture images are then spliced in the wavenumber-domain, and directly added after upsampling. This method avoids the projection from each sub-aperture to the uniform coordinate system, thus improving the imaging accuracy and efficiency. At the same time, the algorithm is suitable for various configurations, and can achieve good imaging results for bistatic forward-looking SAR and high-speed mobile platform. Finally, simulations are presented to demonstrate the effectiveness of the algorithm.
1. Introduction
SAR utilizes the movement of a flight carrier to form a virtual array of antenna to obtain high azimuth resolution. SAR has unique advantages over optical sensors in terms of all-day and all-weather imaging capabilities, which is widely used in military and civil fields. Current research on SAR includes bistatic SAR imaging [1,2], spaceborne SAR [3,4,5], and moving target recognition [6,7,8], to name a few.
During the past decades, SAR imaging algorithms have been continuously developing, which can be mainly divided into time domain and frequency domain methods. Frequency domain imaging algorithms process the echo data in the frequency domain, which improves the computational efficiency. Typical frequency domain algorithms include range-Doppler (RD) algorithm [9], chirp scaling (CS) [10], and algorithm. However, each algorithm has its own scope of application [11], and various approximations are introduced in the calculation process, which reduces the imaging accuracy [12,13]. The representative time-domain imaging algorithm is the backprojection (BP) algorithm. For each pixel in the imaging grid, the coherent integration along the range migration trajectory is carried out to realize the focusing of scattering points [14]. BP has simple structure and high robustness, which can be applied to different SAR configurations. However, its computational efficiency is low compared with frequency domain imaging methods. Yegulalp proposed an FBP algorithm [15], which divides the full aperture into multiple sub-apertures, and transforms the imaging coordinate system from Cartesian coordinates to polar coordinates. The sub-images are obtained by using the sub-aperture, respectively. In the process of coherent superposition of sub-images, the angular resolution is continuously improved. Finally, a full-resolution image is obtained by integrating all of the sub-images [16]. On the basis of the FBP algorithm, fast factorized backprojection based on aperture factorization (FFBP) is proposed [17] to further increase the calculation speed. However, the coordinate system still needs to be re-established during sub-aperture fusion [18,19], and multiple searches and projections are required, which results in a large amount of computation.
The purpose of studying various imaging algorithms is to serve different SAR configurations. Under various configurations [20,21], the ultimate goal is to obtain high-quality SAR images. However, limited by the imaging mechanism, in the forward-looking area [22], the equal delay line and equal Doppler line of monostatic SAR are approximately parallel, so the forward-looking area is the imaging blind area of monostatic SAR. The transmitting and receiving stations of the bistatic SAR system are placed on different platforms. Under the reasonable configuration setting, it is an effective technical way to solve the forward-looking inability of monostatic SAR [23]. At the same time, bistatic SAR has good electromagnetic concealment. The receiving platform only needs to carry the receiving station with small volume and weight. It can not only realize the ground measurement and imaging, but also obtain the observation information different from monostatic SAR. In order to speed up BP algorithm, fine-tuned algorithms for GPUs are presented. Communication between processors is overlapped with GPU calculation to reduce communication time [24]. However, it does not fundamentally solve the problem of high complexity of BP algorithm. A precise topography accommodation algorithm is proposed in document [25]. The images computed over the different sub-apertures are displayed in an advantageous elliptical coordinate system capable of incorporating the topographic information of the imaged scene in an analogous manner as topography-dependent monostatic SAR algorithms do. However, the algorithm is still based on the framework of FFBP algorithm [26]. A new FFBP based on orthogonal elliptical polar (OEP) coordinate is proposed for bistatic forward-looking SAR imaging in [27]. The algorithm reduces the computational burden to a certain extent, but still needs a lot of interpolation operations.
In this paper, a fast backprojection algorithm based on wavenumber-domain spectral splicing (WFBP) is presented. First, a polar coordinate system is established with the center of the full aperture as the origin. After the image in this coordinate system is obtained, the angular domain is upsampled. Then, according to the moving rule of the wavenumber-domain spectrum, the wavenumber-domain spectrum is stitched together to obtain a high-resolution image. Compared with the FBP algorithm, it reduces the number of searches and projections during sub-aperture fusion, and greatly improves the computational efficiency.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces the radar echo model. In Section 3, the WFBP algorithm is introduced in detail and the complexity of the WFBP algorithm is analyzed. In Section 3.2 and Section 4, the imaging results of WFBP algorithm for point target and area target are analyzed, respectively, and the speed comparison with the FBP algorithm is analyzed. In addition, this paper is concluded in Section 6.
2. Radar Echo Model
As shown in Figure 1, it is assumed that the radar is flying at a constant speed v along the positive direction of X-axis, and there is a target in the scene [28]. is the polar diameter of the target; is the polar angle. Therefore, the instantaneous range history from the radar to the target can be expressed as
where x is the distance traveled by the aircraft. The total length of the synthetic aperture is L, then . Assume the radar transmits a linear frequency modulation (LFM) signal:
where T is the pulse width of LFM, K is the linear frequency rate slope, is the carrier frequency, and is the fast time. After the echo signal is range-compressed, we obtain
where is a constant amplitude, B is the bandwidth of the transmitted signal, i.e., , and , the time angular frequency is the derivative of radians with respect to time, i.e., , and the wave number (i.e., the spatial angular frequency) is the derivative of the distance in radians, i.e., .
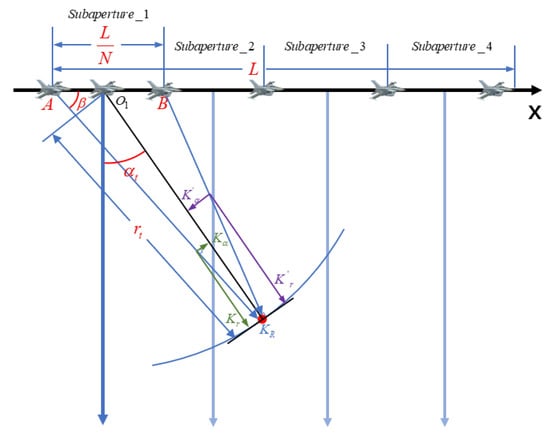
Figure 1.
Rules for coordinate system establishment in FBP algorithms.
3. Fast Backprojection Based on Wavenumber-Domain Spectral Splicing
3.1. Principle of WFBP
We briefly introduce the FBP algorithm. First, the full aperture is divided into several sub-apertures, and the polar coordinate system is established with the center of each sub-aperture as the coordinate origin. The polar coordinate system generally points to the beam direction of the radar, as shown in Figure 1.
The whole aperture is divided into N sub-apertures on average; the length of each sub-aperture is . The polar angular division rule of the sub-aperture is , where is the maximum electromagnetic frequency. After sub-images are coherently superimposed, a full-aperture image is finally obtained. Each sub-aperture image of the FBP algorithm has a different coordinate system, so it must be projected into a uniform coordinate system before the sub-images are overlaid. This is computationally intensive and can result in reduced image accuracy.
Next, we will analyze the sub-aperture image from the wavenumber-domain. Under spotlight SAR configuration, when the polar coordinates are established in the above-mentioned manner, the wavenumber-domain spectrum of the sub-aperture image will always be roughly located in the center of the entire spectrum band. We give an analysis from the support domain of the wavenumber-domain spectrum, as shown in Figure 1.
When the aircraft is at both ends of sub-aperture K, that is, point A and point B, , is projected in the polar direction, and the wave number and in the polar direction can be obtained
where . When the aircraft is at the center position of the sub-aperture, as shown in Figure 1, at this time, the direction of is perpendicular to the direction of , so .
In summary, for the Kth sub-aperture, the support domain of the wavenumber-domain spectrum is , as shown in Figure 2.
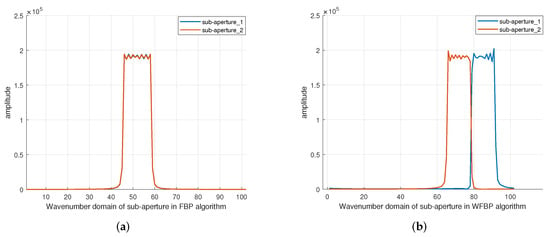
Figure 2.
Wavenumber-domain spectrum of WFBP and FBP algorithm: (a) FBP; (b) WFBP.
The wavenumber-domain spectra obtained by FBP and WFBP algorithms for the same target are drawn together. The blue and red lines are the wavenumber-domain spectra of sub-apertures 1 and 2. Figure 2a is the wavenumber-domain spectrum in FBP. Sub-aperture 1 and 2 have the same spectral positions and coincide. The position of the wavenumber-domain spectrum does not change with the movement of the sub-aperture.
Now, we directly establish a polar coordinate system with the center of the entire aperture as the origin, as shown in Figure 3. When the target is on the left side of the polar axis, . Similarly, when the aircraft is at the left end point A of the sub-aperture K,
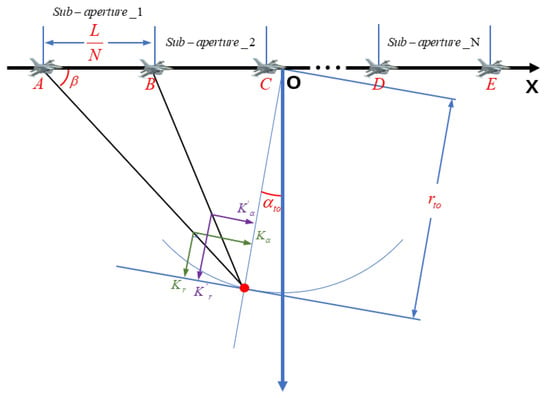
Figure 3.
Rules for coordinate system establishment in WFBP algorithms.
Therefore, at this time, the support domain of the wavenumber-domain in the polar angle direction of the target is .
Similarly, in sub-aperture 2, the BC section, , the support domain of the wavenumber-domain in the polar angle direction of the target is . By analogy, the wavenumber-domain spectrum of the target in the sub-image will move with the movement of the sub-aperture, which results in the target’s wavenumber-domain spectrum not in the center of the entire spectrum band, as shown in Figure 2b. In the new coordinate system establishment mode, considering the accuracy of the final image, the polar resolution in the sub-aperture imaging grid is slightly less than the azimuth resolution. Azimuth resolution can be expressed as:
The grid spacing in polar angle direction shall meet the following formula:
Although the above content is derived based on spotlight mode, the WFBP algorithm is also applicable to strip mode because the WFBP algorithm backprojects to the imaging grid pulse by pulse, and the process of backprojection is not affected by the imaging mode. In the strip mode, the synthetic aperture length is no longer the total length of flight, but the flight length of each target illuminated by the beam.
Next, the formula is deduced and the principle of the wavenumber-domain spectrum movement of the sub-aperture is quantitatively analyzed. The model in Figure 3 is used to establish the polar coordinate system with the center point of the full aperture as the origin. The position of the target in the polar coordinate system is . The Kth sub-aperture is processed. The phase compensation of the range-compressed echo is based on the slant distance from the radar to the polar coordinate pixel, and the impulse response function (IRF) in the azimuth direction (i.e., the polar angle direction) can be obtained after the integration, as shown in Formula (11).
where is the data after range compression, and is the compensated phase. The range of x can be expressed as . Where , , , bring into . After simplification, we can obtain
where . Perform a second-order Taylor expansion of x to obtain
When the radar is far from the imaging scene, . Therefore, ignoring the quadratic term, we can obtain: . Inputting into Formula (12) and integrating, the following expression can be written as
The wavenumber-domain expression is obtained by taking the fast Fourier transform (FFT) of the impulse response function of the point target in the azimuth direction.
where , after intergration, we can obtain
where , is related to the position of the sub-aperture.
Thus, the wavenumber-domain spectrum of the point target in the sub-image will move with the position of the sub-aperture, as shown in Figure 2b, and the flow chart of the algorithm is shown in Figure 4.
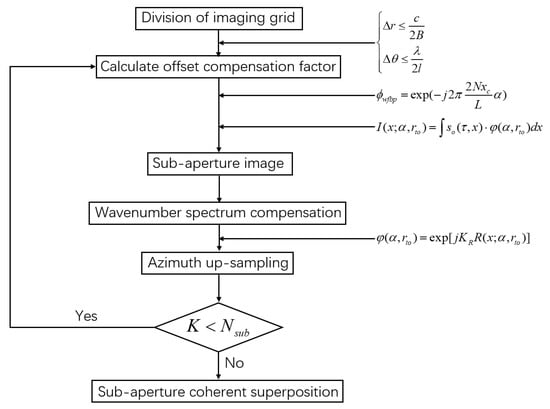
Figure 4.
Flowchart of the WFBP algorithm.
3.2. Application in Bistatic Forward-Looking SAR
Bistatic forward-looking SAR has many advantages. However, for a high-speed platform, its high-speed mobility and irregular trajectory bring great challenges to imaging. The high-speed mobile platform invalidates the “stop and go” model widely used in the traditional echo model, and the echo presents the characteristics of large time delay migration, large Doppler bandwidth, and strong spatial variability of parameters. It is necessary to study and design a new efficient and high-precision imaging algorithm.
The imaging algorithm of monostatic SAR can not be used directly on bistatic SAR, and the frequency domain algorithm is highly dependent on the imaging geometry and observation direction. The traditional range-Doppler imaging algorithm can not correct the two-dimensional space variability when it is strong. The two-dimensional frequency domain algorithm also has great limitations. The two-dimensional frequency domain algorithm requires the time-delay migration and Doppler parameters of the echo to change along the track. Therefore, this kind of algorithm is not suitable for bistatic forward-looking SAR on a high-speed mobile platform. The WFBP algorithm proposed in this paper can be applied to various complex configurations, it has strong robustness, and it can obtain better imaging results.
The configuration of bistatic forward-looking SAR of a high-speed mobile platform is shown in Figure 5:
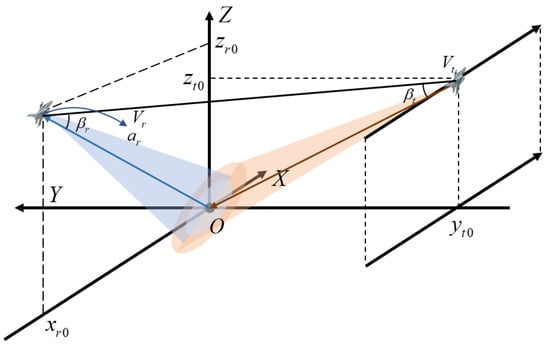
Figure 5.
Bistatic forward-looking SAR for a high-speed mobile platform.
The position of the receiving station is , the acceleration is , and the speed of the receiving station at the initial time is set as . Then, at time t, the speed of the receiving station is , where , , , where t represents the slow time:
where is the pulse repetition period, represents the total number of pulses, the position of the receiving station is , where ; similarly, can be obtained, and the receiving station flies at high speed towards point O along the curved track. At time t, the position of the transmitting station is , and the transmitting station flies along the positive direction of axis X at speed .
In the WFBP algorithm, the echo signal needs phase compensation before focusing can be completed, and finally the azimuth high-resolution image can be obtained. Therefore, the distance history from the transmitting station and receiving station to the target is very important. However, as a new system SAR, the high-speed mobile platform bistatic forward-looking SAR is quite different from the traditional SAR in configuration and platform motion characteristics, which leads to the failure of the important assumption of “stop and go” in the traditional SAR and causes great difficulties in imaging.
The pulse propagation delay is related to the following three types of motion of the platform:
- The motion of the transmitting station and the receiving station in the slow time t, that is, the movement of the transmitting station and the receiving station in each pulse repetition period.
- After the transmitting station transmits the pulse, the displacement generated before receiving the pulse because of the too-fast speed of the receiving station.
- The movement of the receiving station in the fast time , that is, the movement of the receiving station in the pulse propagation period.
In the traditional SAR pulse radar echo model, generally speaking, the speed of the moving platform is low, which is far lower than the speed of light. It can be considered that after the transmitting station transmits the echo, it will be received by the receiving station immediately, and the duration of the transmitted pulse is short, so it ignores the two and three kinds of motion, and only considers the influence of the first kind of motion on the pulse propagation delay, that is, the “stop and go” model. However, when the speed of the receiving platform is too high, the influence of the second kind of motion on the pulse propagation delay increases gradually. If the second kind of motion is still ignored, it will have a great impact on the azimuth focusing, as shown in Figure 6.
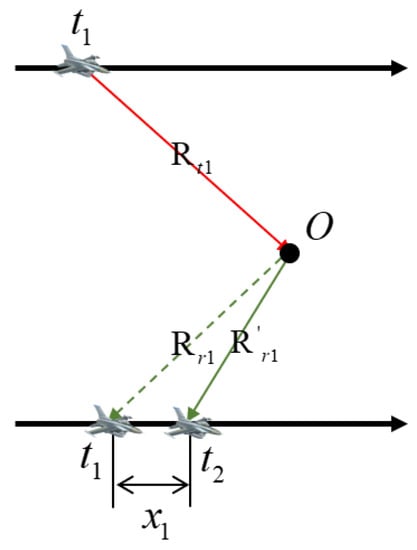
Figure 6.
Non-“stop and go” mode.
At time , the transmitting station transmits signal to the target point O. At this time, the positions of the transmitting station and the receiving station are shown in Figure 6. However, when the reflected signal of the target reaches the receiving station, there will be a displacement because of the receiving station moving fast, which will influence the calculation of pulse propagation delay and distance history between the transmitting station and the receiving station.
It is very important to accurately calculate the slant distances and from the transmitting station and receiving station to the target. At time , the coordinate of the transmitting station is , and each position component can be obtained from . Setting the position of the target point as , the slant distance from the transmitting station to the target is
The main difficulty is to calculate the slant range when the receiving station receives the echo from the target. At , the coordinate of the receiving station is , and the velocity is . The velocity component in each direction can be calculated by . Assuming that the time when the receiving station receives the echo is and the coordinate is , the following equations can be obtained:
By solving the simultaneous equation, the time and coordinate of the echo received by the receiving station can be obtained. Under the “non stop and go” mode, the pulse propagation delay is
At this time, the echo model can be expressed as
Another key problem of the WFBP algorithm is to establish the polar coordinate system at the appropriate position and calculate the two-dimensional resolution according to the configuration, to divide the imaging area into polar coordinate grids. When focusing in azimuth, the WFBP algorithm needs to calculate the distance from each azimuth time to each pixel in the imaging coordinate system and make phase compensation. Therefore, the number of pixels in the imaging coordinate system has a great impact on the operation speed. It is very important to divide the imaging grid according to the appropriate sampling rate. The denser the meshing, the higher the resolution, but the slower it runs. Moreover, when the theoretical resolution is exceeded, the imaging effect will not be improved, resulting in data redundancy. If the mesh generation is sparse and lower than the resolution of the actual imaging, it is equivalent to not using all the information and losing the resolution. The final result cannot describe the actual effect of the algorithm. Therefore, the imaging grid should be reasonably divided according to the actual resolution. The delay ground resolution and the doppler ground resolution can be obtained by gradient method [29], as shown in the following expressions.
Among these, stands for the angle between the line-of-sights of transmitting station and the receiving station to point O, which is called the bistatic angle, and is the projection angle of the delay resolution to the ground.
where is the projection angle of the Doppler resolution direction to the ground, while stands for the bistatic SAR synthetic rotation. consists of a stacking of transceiver stations that are mutually enhanced or offset depending on different modes and geometries [30].
Therefore, when dividing the sub-aperture grid, the resolution should meet the following requirements:
where is the grid point spacing in the polar diameter direction and is the grid point spacing in the polar angle direction.
After the imaging grid is divided according to the theoretical resolution, the delay of each imaging grid point at each azimuth time of the transmitting and receiving platform is accurately calculated to compensate, as shown in Figure 7.
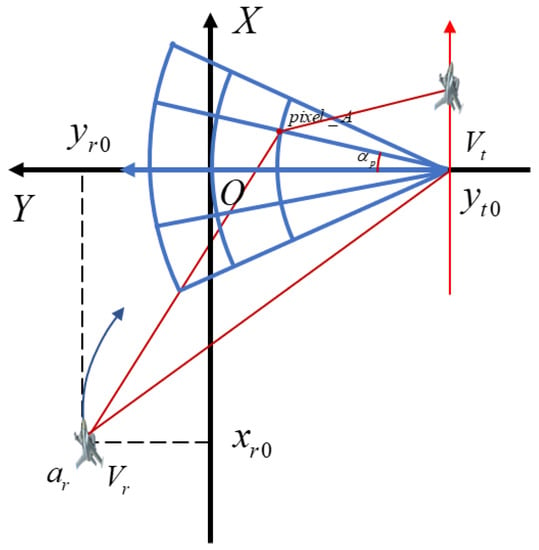
Figure 7.
Slant range from transceiver platform to imaging grid point.
Suppose that the transmitting station transmits a beam of signal at , the position is , and the receiving station receives the echo at , and the position is . and can be obtained from Formula (19). Suppose that the position of a pixel point in the imaging area is , where is the polar angle and is the polar diameter, then the instantaneous slant range from the transmitting station to a pixel point in the imaging scene when transmitting the signal is
When the receiving station receives the signal, the instantaneous slant range to pixel in the scene is
where . Therefore, the time delay migration trajectory is
In azimuth focusing, the compensated phase factor is
The image of sub-aperture is
3.3. Computational Efficiency Analysis
In the WFBP algorithm, it is assumed that the imaging area is divided by pixels, azimuthal pulses for the return matrix. Assuming that the echo data has been pulse-compressed and the number of azimuthal pulses in the sub-aperture is m, a total of sub-apertures are divided. Radial pixel points in the sub-aperture imaging grid are approximately N; letting , polar angle has m pixels, so the pixel points in the sub-aperture imaging grid are . Each step of the algorithm is computed as follows, where steps 2(a) and 2(b) are required for each sub-aperture.
- Establish sub-aperture coordinate system; this requires times complex matrix multiplication.
- (a)
- Backprojection on the sub-aperture polar grid; this requires times complex matrix multiplication.
- (b)
- Polar angle interpolation of sub-aperture coordinate system; this requires times complex matrix multiplication.
- Projection to Cartesian coordinate system after sub-aperture coherent overlay; this requires times complex matrix multiplication.
The total amount of calculation to obtain the final image is
For the FBP algorithm [31], each sub-aperture needs to perform step 1. The projection relationship from each sub-aperture coordinate system to the final rectangular coordinate system is different and needs to be calculated separately, so the total amount of operation for FBP algorithm is
Therefore, compared with the FBP algorithm, the WFBP algorithm reduces times multiplication operation. Moreover, in practice, the coefficient is usually much larger than m, so the WFBP algorithm greatly reduces the amount of computation.
4. Simulation Results
The WFBP algorithm can be used in monostatic and bistatic SAR configurations, and is suitable for mobile platforms such as satellites and aircraft. Next, we apply the WFBP algorithm to monostatic SAR and bistatic forward-looking SAR imaging. Then, the WFBP and FBP algorithms are compared from two aspects of imaging quality and speed.
4.1. Simulation Results of Monostatic SAR
Next, we validate the effectiveness and efficiency of the WFBP algorithm through simulation. The simulation parameters are shown in Table 1. The spatial distribution of the point targets are illustrated in Figure 8. A total of 25 ideal point targets are evenly distributed in the plane with 200 m distance between adjacent targets both in x and y directions. The scene size is assumed to be 800 m both in azimuth and range directions.

Table 1.
Simulation parameters of monostatic SAR.
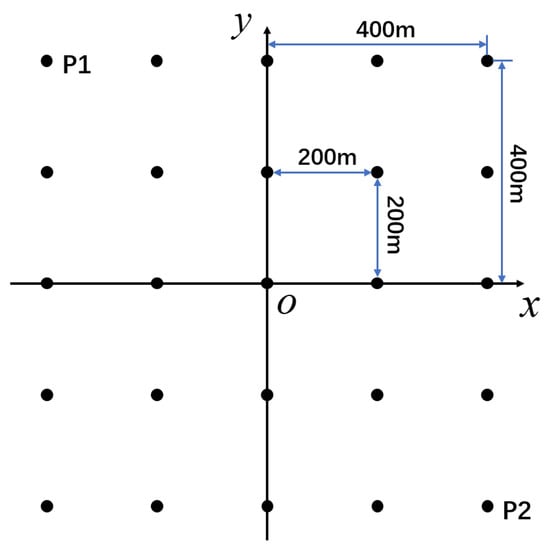
Figure 8.
Spatial distribution of point targets.
The image result obtained by the WFBP algorithm is shown in Figure 9, where zoomed-in results of the targets O, P1, and P2 are given on the right. It can be seen that the targets are well focused in the 800 m × 800 m scene.
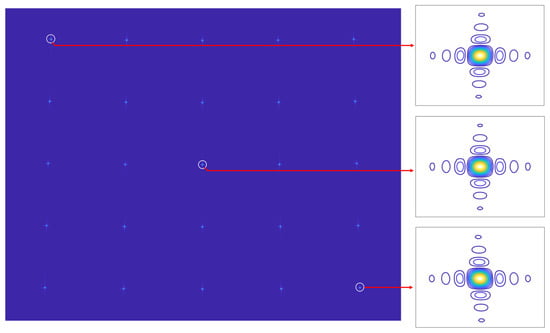
Figure 9.
Imaging result of point targets.
In order to further analyze the imaging results of the WFBP and FBP algorithm, the azimuth and range slices of the three selected targets, i.e., O, P1, and P2, are shown in Figure 10, with measured imaging matrices. It can be seen that the measured PSLR and ISLR are close to the theoretical values.
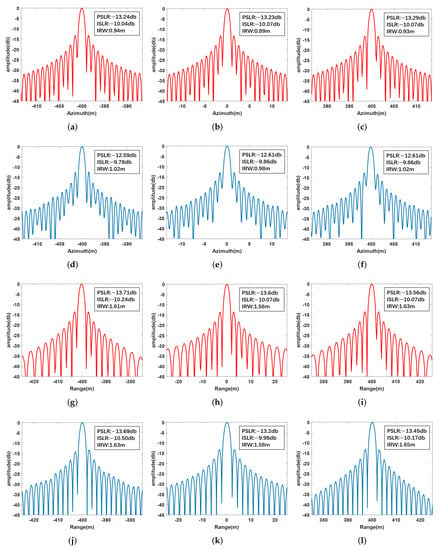
Figure 10.
Detailed imaging results by WFBP and FBP algorithm. (a) Azimuth slice of Target P1 by WFBP algorithm. (b) Azimuth slice of Target O by WFBP algorithm. (c) Azimuth slice of Target P2 by WFBP algorithm. (d) Azimuth slice of Target P1 by FBP algorithm. (e) Azimuth slice of Target O by FBP algorithm. (f) Azimuth slice of Target P2 by FBP algorithm. (g) Range slice of Target P1 by WFBP algorithm. (h) Range slice of Target O by WFBP algorithm. (i) Range slice of Target P2 by WFBP algorithm. (j) Range slice of Target P1 by FBP algorithm. (k) Range slice of Target O by FBP algorithm. (l) Range slice of Target P2 by FBP algorithm.
As can be seen from Figure 10, the PSLR of the azimuth slice of the target by the WFBP algorithm is reduced by about 0.7 db compared with FBP algorithm, ISLR is decreased by about 0.3 db, and IRW is reduced by about 0.1 m. The imaging results obtained by the WFBP algorithm have higher accuracy because the sub-aperture images of the WFBP algorithm and FBP algorithm are reconstructed in the imaging grid with high range resolution and low azimuth resolution. In the process of sub-image superposition, the azimuth resolution is continuously improved while the range resolution is unchanged, so the range resolution is almost the same in the imaging results obtained by the two algorithms.
Next, the WFBP algorithm is used to image the area target. The imaging parameters are shown in Table 2, and the imaging results are shown in Figure 11; it can be seen that the WFBP algorithm also has good imaging results for area targets.

Table 2.
Area target simulation scene parameters.
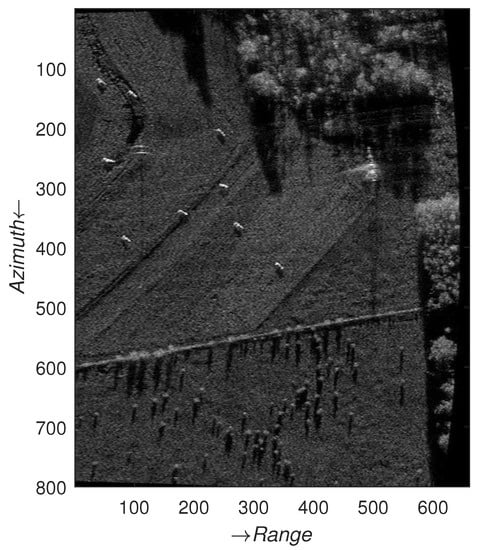
Figure 11.
Imaging result of area targets.
On the other hand, in the FBP algorithm, because each sub-aperture establishes its own coordinate system, when images from different sub-apertures are superimposed, it is difficult for pixels to correspond one by one. Therefore, it is necessary to introduce approximation to make the pixels in different coordinate systems correspond. Then, the pixels of the sub-image can be projected into the final imaging coordinate system. Inevitable errors are introduced during the mapping from the individual coordinate system to the final polar coordinate system by interpolation, which results in loss of accuracy of the final image, while WFBP always uses the same polar coordinate system, thus avoiding the loss of accuracy when sub-images are projected to the final coordinate system. Therefore, compared with the FBP algorithm, the WFBP algorithm is more accurate. In order to achieve a similar imaging accuracy, FBP needs higher interpolation precision, which will greatly reduce the computational efficiency.
4.2. Simulation Results of Bistatic Forward-Looking SAR
Next, we still use the point target in Figure 8 for simulation. The configuration is shown in Figure 5, and the new imaging parameter table is shown in Table 3:

Table 3.
Bistatic forward looking SAR simulation parameters.
The imaging results of bistatic forward-looking SAR obtained by the WFBP algorithm are shown in Figure 12. It can be seen that in the forward-looking mode of the high-speed mobile platform, the WFBP algorithm has achieved good results, for which the details of P1, O, and P2 are shown in Figure 13a,c,e. In order to compare the imaging quality of the WFBP algorithm and the FBP algorithm, the FBP algorithm is used for imaging under the same parameters and configuration. The imaging results of P1, O, and P2 are shown in Figure 13b,d,f. The quantitative results in terms of 3 dB main lobe and ratios, including peak sidelobe ratio (PSLR), integrated sidelobe ratio (ISLR), and impilse response width (IRW), are listed in Table 4. It can be seen that the accuracy of the WFBP algorithm is higher than that of the FBP algorithm.
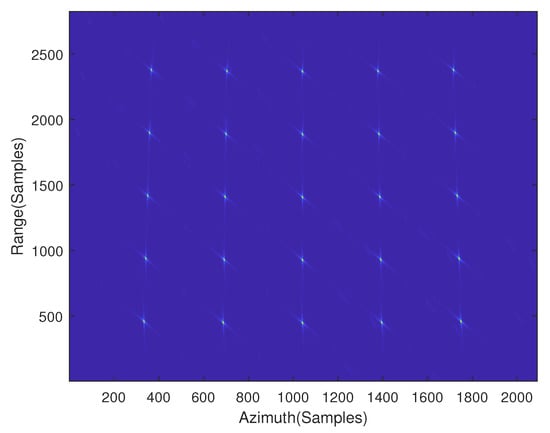
Figure 12.
Imaging results of the WFBP algorithm under the bistatic forward-looking model.
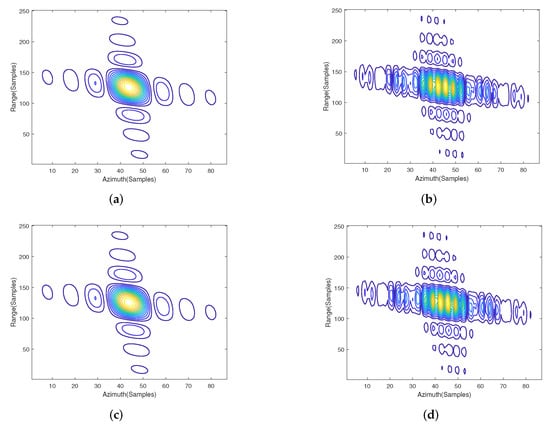
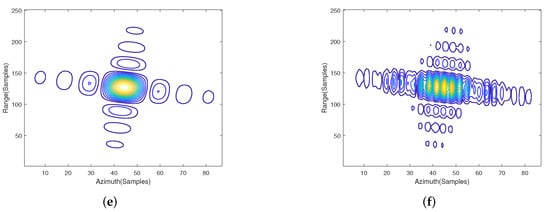
Figure 13.
Detailed imaging results by the WFBP and the FBP under the bistatic forward-looking model. (a) P1 point imaging results obtained by the WFBP algorithm; (b) P1 point imaging results obtained by the FBP algorithm; (c) O point imaging results obtained by the WFBP algorithm; (d) O point imaging results obtained by the FBP algorithm; (e) P2 point imaging results obtained by the WFBP algorithm; (f) P2 point imaging results obtained by the FBP algorithm.

Table 4.
Comparison of focusing results between the WFBP and FBP algorithms.
4.3. Imaging Results of Real Bistatic Forward-Looking SAR Experiment Data
In October 2020, we carried out the bistatic forward-looking SAR experiment in Yinchuan. In this section, the echo data obtained in the experiment will be used to further verify the effectiveness of WFBP algorithm. The bistatic forward-looking SAR system works in the X-band, and its configuration is shown in Figure 14.
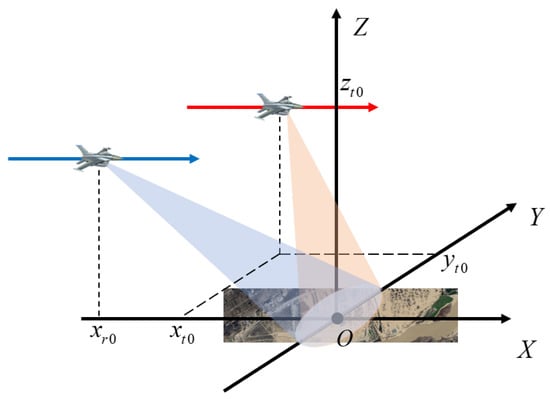
Figure 14.
Airborne bistatic forward-looking SAR configuration.
The transmitting station adopts oblique forward-looking mode, and the receiving station receives echo in forward-looking mode. The transmitted LFM signal bandwidth is 300 MHz and PRF is 3000 Hz. The initial positions of the transmitting station and the receiving station are (−1840, 1140, 2000) m and (−2860, 0, 2400) m. The speed of transceiver stations is equal, both of which are (100, 0, 0) m/s. The echo is processed by the WFBP algorithm, and the imaging results are shown in Figure 15. It can be seen that the WFBP algorithm obtains accurate imaging results.
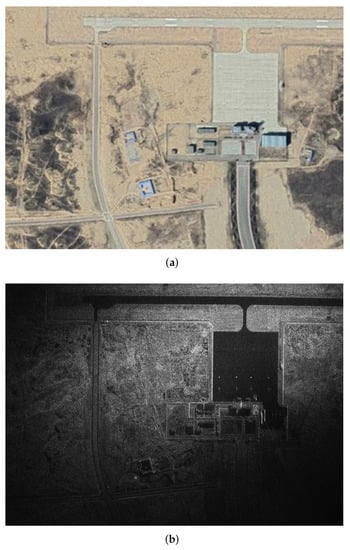
Figure 15.
Imaging results of the WFBP algorithm. (a) Optical image; (b) imaging results of real experiment data by the WFBP algorithm.
5. Discussion
In order to verify the efficiency of the proposed WFBP algorithm, the computation time of the WFBP algorithm is compared with that of the FBP algorithm under different number of sub-apertures. To ensure a fair comparison, the interpolation multiple of the FBP algorithm is finely tuned to achieve a similar imaging performance to the WFBP algorithm. In the actual imaging processing of the FBP algorithm, a suitable interpolation multiplier should be selected to strike a balance between the computational efficiency and processing accuracy. A too-long sinc interpolation kernel will increase the amount of calculation, and too short will affect the accuracy. The sinc function of the eight-point interpolation kernel is a tradeoff [32,33]. The simulation platform is an Intel® Core(TM) i5-9500 CPU @ 3.00 GHz processor. As shown in Table 5, the WFBP algorithm is faster than the FBP algorithm in each number of sub-apertures. When the number of sub-apertures is 12, the acceleration effect reaches 49.3%. Then, we compare the percentage acceleration of the two algorithms with regard to the BP algorithm with different number of sub-apertures, as shown in Figure 16. The acceleration effect of the WFBP is always more obvious than that of the FBP algorithm; the acceleration effect can reach up to 87.8%. It can be concluded that the FBP algorithm requires a higher interpolation multiple to obtain a similar accuracy to the WFBP algorithm, which results in lower computational efficiency.

Table 5.
Comparison of computation time between the WFBP and FBP algorithms.
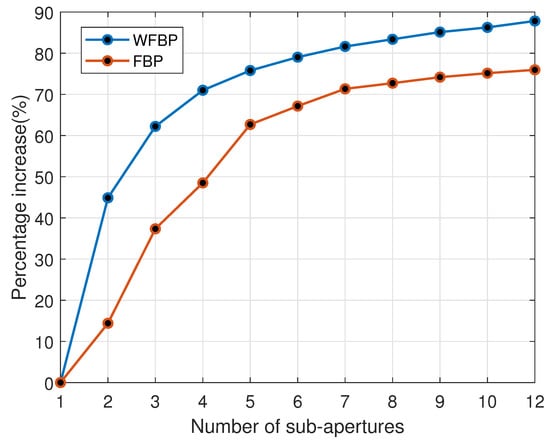
Figure 16.
Acceleration effect comparison between the WFBP and FBP algorithms.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, a fast backward-projection algorithm based on wavenumber-domain spectral splicing is presented, which uses a new sub-aperture polar coordinate construction method. It will reduce the steps of sub-image projection to the final coordinate system, which speeds up the operation and improves the accuracy. We also derive the movement principle of the sub-aperture wavenumber-domain spectrum, and verify the correctness and efficiency of the WFBP algorithm through simulation. Compared with the BP and FBP algorithms, the acceleration effect of the WFBP algorithm is further illustrated. The WFBP algorithm is suitable for many configurations. This paper verifies the effectiveness of the WFBP algorithm through simulation.
Author Contributions
H.S. proposed the main idea, designed the experiment, and wrote the manuscript. Z.S. participated in the design experiment, wrote the manuscript, and modified the manuscript. T.C. and Y.M. helped complete the matlab code. J.W. and J.Y. reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61901088, Grant 61922023, Grant 61771113, and Grant 61801099; in part by the Postdoctoral Innovation Talent Support Program under Grant BX20180059; and in part by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant 2020M683292, Grant 2019M65338, and Grant 2019TQ0052.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yang, J.; Huang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wu, J.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Yang, X. A first experiment of airborne bistatic forward-looking SAR—Preliminary results. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium—IGARSS, Melbourne, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; pp. 4202–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yen, G.G.; Wu, J.; Ren, H.; An, H.; Yang, J. Mission Planning for Energy-Efficient Passive UAV Radar Imaging System Based on Substage Division Collaborative Search. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Dong, X.; Chen, Z.; Hu, C.; Tian, W. A Long-Time Coherent Integration STAP for GEO Spaceborne-Airborne Bistatic SAR. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; An, H.; He, X. Geosynchronous Spaceborne-Airborne Bistatic SAR Data Focusing Using a Novel Range Model Based on One-Stationary Equivalence. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 1214–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wu, J.; Pei, J.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J. Inclined Geosynchronous Spaceborne–Airborne Bistatic SAR: Performance Analysis and Mission Design. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, W.; Zheng, M.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, Z.X. Phase Mismatch Calibration for Dual-Channel Sliding Spotlight SAR-GMTI. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Quan, H.; Cao, Z.; Xu, S.; Wu, J. SAR Target CFAR Detection Via GPU Parallel Operation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 4884–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Sun, Z.; An, H.; Wu, J.; Yang, J. BeiDou-Based Passive Multistatic Radar Maritime Moving Target Detection Technique via Space-Time Hybrid Integration Processing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5802313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Numerical Simulation of SAR Image for Sea Surface. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, H.; Véstias, M.; Monteiro, J.; Neto, H.; Duarte, R.P. A Review of Synthetic-Aperture Radar Image Formation Algorithms and Implementations: A Computational Perspective. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Fu, Z.; Chang, J.; Wu, L.; Li, N. A Novel High-Squint Spotlight SAR Raw Data Simulation Scheme in 2-D Frequency Domain. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.Y.; Wu, C. A SAR correlation algorithm which accommodates large-range migration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1984, GE-22, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Q.; Xiao, Y.; An, H.; Yang, H.; Wu, J.; Yang, J. Hybrid SAR-ISAR Image Formation via Joint FrFT-WVD Processing for BFSAR Ship Target High-Resolution Imaging. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5215713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Xu, Z.; Wang, F.; Yang, D.; Guo, G. An Improved Back-Projection Algorithm for GNSS-R BSAR Imaging Based on CPU and GPU Platform. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yegulalp, A. Fast backprojection algorithm for synthetic aperture radar. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE Radar Conference. Radar into the Next Millennium (Cat. No.99CH36249), Waltham, MA, USA, 22 April 1999; pp. 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Bresler, Y. Error analysis and performance optimization of fast hierarchical backprojection algorithms. IEEE Trans. Image Process. Publ. IEEE Signal Process. Soc. 2001, 10, 1103–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulander, L.; Hellsten, H.; Stenstrom, G. Synthetic-aperture radar processing using fast factorized back-projection. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2003, 39, 760–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Qiao, Z.; Xu, Z. A Fast BP Algorithm with Wavenumber Spectrum Fusion for High-Resolution Spotlight SAR Imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1460–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Góes, J.A.; Castro, V.; Sant’Anna Bins, L.; Hernandez-Figueroa, H.E. Spiral SAR Imaging with Fast Factorized Back-Projection: A Phase Error Analysis. Sensors 2021, 21, 5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Ren, H.; Yen, G.G.; Chen, T.; Wu, J.; An, H.; Yang, J. An Evolutionary Algorithm with Constraint Relaxation Strategy for Highly Constrained Multiobjective Optimization. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, Z.; Yang, H.; Wu, J.; Yang, J. Bistatic Forward Looking SAR MP-DPCA Method for Space Time Extension Clutter Suppression. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 6565–6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.T.; Sjögren, T.K.; Pettersson, M.I. SAR imaging in ground plane using Fast Backprojection for mono- and bistatic cases. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Radar Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 7–11 May 2012; pp. 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Fan, Y.; Pi, Y. Analysis and Improvement of a Fast Backprojection Algorithm for Stripmap Bistatic SAR Imaging. In Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2–5 June 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wijayasiri, A.; Banerjee, T.; Ranka, S.; Sahni, S.; Schmalz, M. Dynamic Data-Driven SAR Image Reconstruction Using Multiple GPUs. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 4326–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Cassola, M.; Prats, P.; Krieger, G.; Moreira, A. Efficient Time-Domain Image Formation with Precise Topography Accommodation for General Bistatic SAR Configurations. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2011, 47, 2949–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ran, L.; Liu, Z.; Xie, R.; Zhang, L. Focusing High-Squint Synthetic Aperture Radar Data Based on Factorized Back-Projection and Precise Spectrum Fusion. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, S.; Yang, L.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Chen, L.; Xing, M. A New Fast Factorized Back Projection Algorithm for Bistatic Forward-Looking SAR Imaging Based on Orthogonal Elliptical Polar Coordinate. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 1508–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.T.; Pettersson, M.I. Fast Backprojection Algorithms Based on Subapertures and Local Polar Coordinates for General Bistatic Airborne SAR Systems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 2706–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardillo, G. On the use of the gradient to determine bistatic SAR resolution. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation Society, Merging Technologies for the 90’s, Dallas, TX, USA, 7–11 May 1990; Volume 2, pp. 1032–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. (Ed.) Chapter 2—Bistatic SAR imaging theory. In Bistatic Synthetic Aperture Radar; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 77–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorham, L.; Majumder, U.K.; Buxa, P.; Backues, M.J.; Lindgren, A.C. Implementation and analysis of a fast backprojection algorithm. Proc. SPIE 2006, 6237, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Yang, L. A New Fast Factorized Back-Projection Algorithm with Reduced Topography Sensibility for Missile-Borne SAR Focusing with Diving Movement. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tang, J.; Wang, R.; Deng, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, N. An Accelerated Backprojection Algorithm for Monostatic and Bistatic SAR Processing. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).