The Cross-Border Transport of PM2.5 from the Southeast Asian Biomass Burning Emissions and Its Impact on Air Pollution in Yunnan Plateau, Southwest China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ground-Based Observation Data
2.2. MODIS Remote Sensing Products
2.3. Model Configuration
2.3.1. WRF-Chem Model

| Options | Schemes |
|---|---|
| Microphysics | Morrison 2-moment scheme (Morrison) |
| Longwave radiation | Rapid Radiative Transfer Model for GCMs (RRTMG) |
| Shortwave radiation | Rapid Radiative Transfer Model for GCMs (RRTMG) |
| Land-surface | Noah Land Surface Model (Noah) |
| Boundary layer | Yonsei University scheme (YSU) |
| Cumulus | Improved version of the Grell–Devenyi ensemble scheme (Grell 3-D) |
| Photolysis | Madronich photolysis scheme (Madronich) |
| Chemistry | The regional acid deposition model, version 2 (RADM2) |
| Aerosol particles | The Modal Aerosol Dynamics Model for Europe (MADE/SORGAM) |
| Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Name | Xishuangbanna | Puer | Lincang | Yuxi | Honghe | Wenshan |
| Number | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Name | Dehong | Baoshan | Dali | Chuxiong | Kunming | Qujing |
| Name | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | ||
| Number | Nujiang | Diqing | Lijiang | Zhaotong |
2.3.2. Air Pollutant Emission Inventories
2.3.3. Numerical Experiments
2.3.4. FLEXPART-WRF Models
2.4. WRF-Chem Modeling Validation
3. Results and Discussion
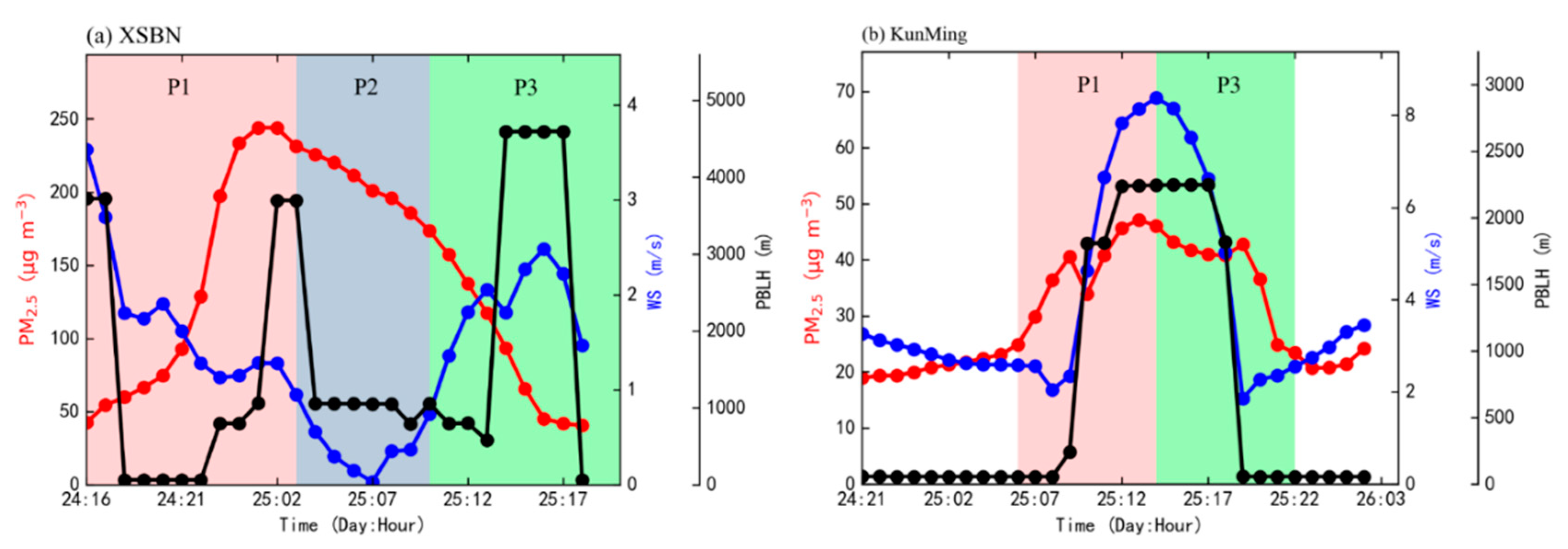
3.1. A Springtime Air Pollution Event Observed in YP
3.2. Correlation between Wind Speeds and PM2.5 Concentrations
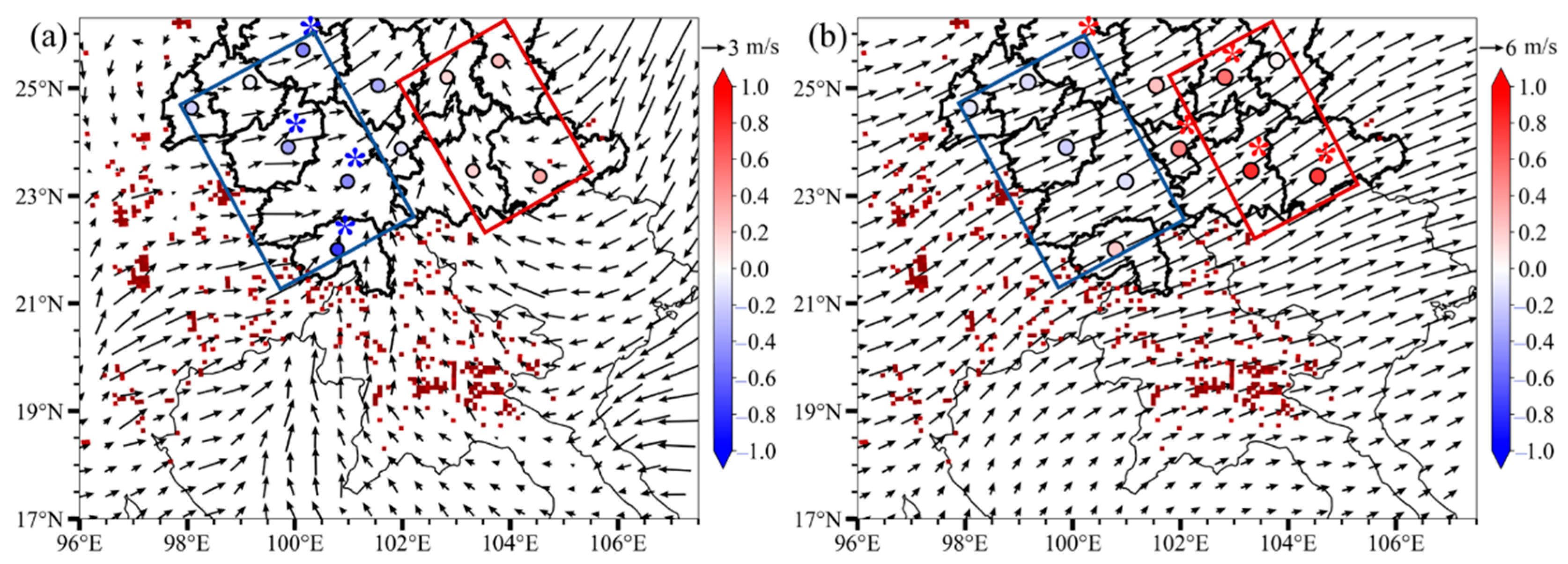
3.3. The Different Mechanisms of PM2.5 Pollution in SR and RR
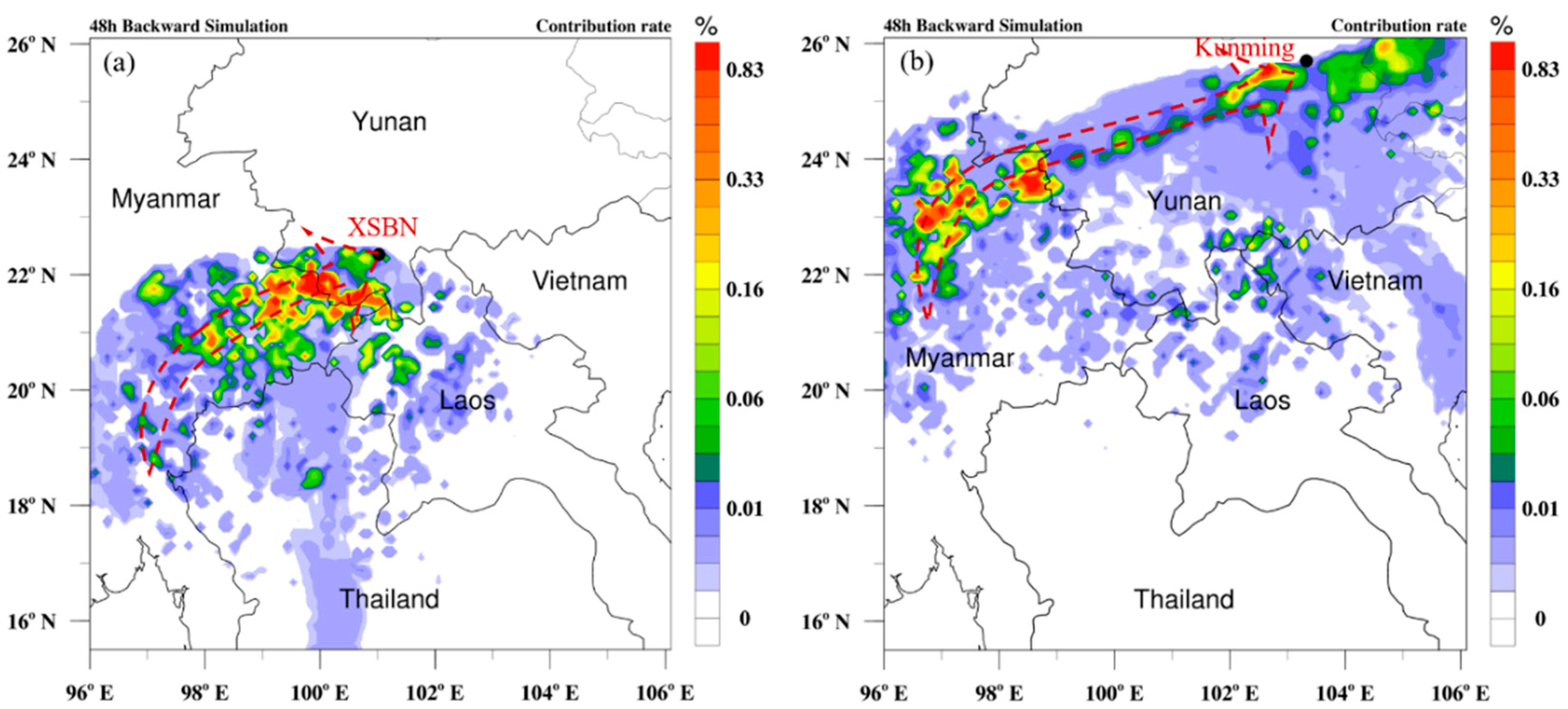
3.4. Patterns of Regional PM2.5 Transport to Different YP Sites
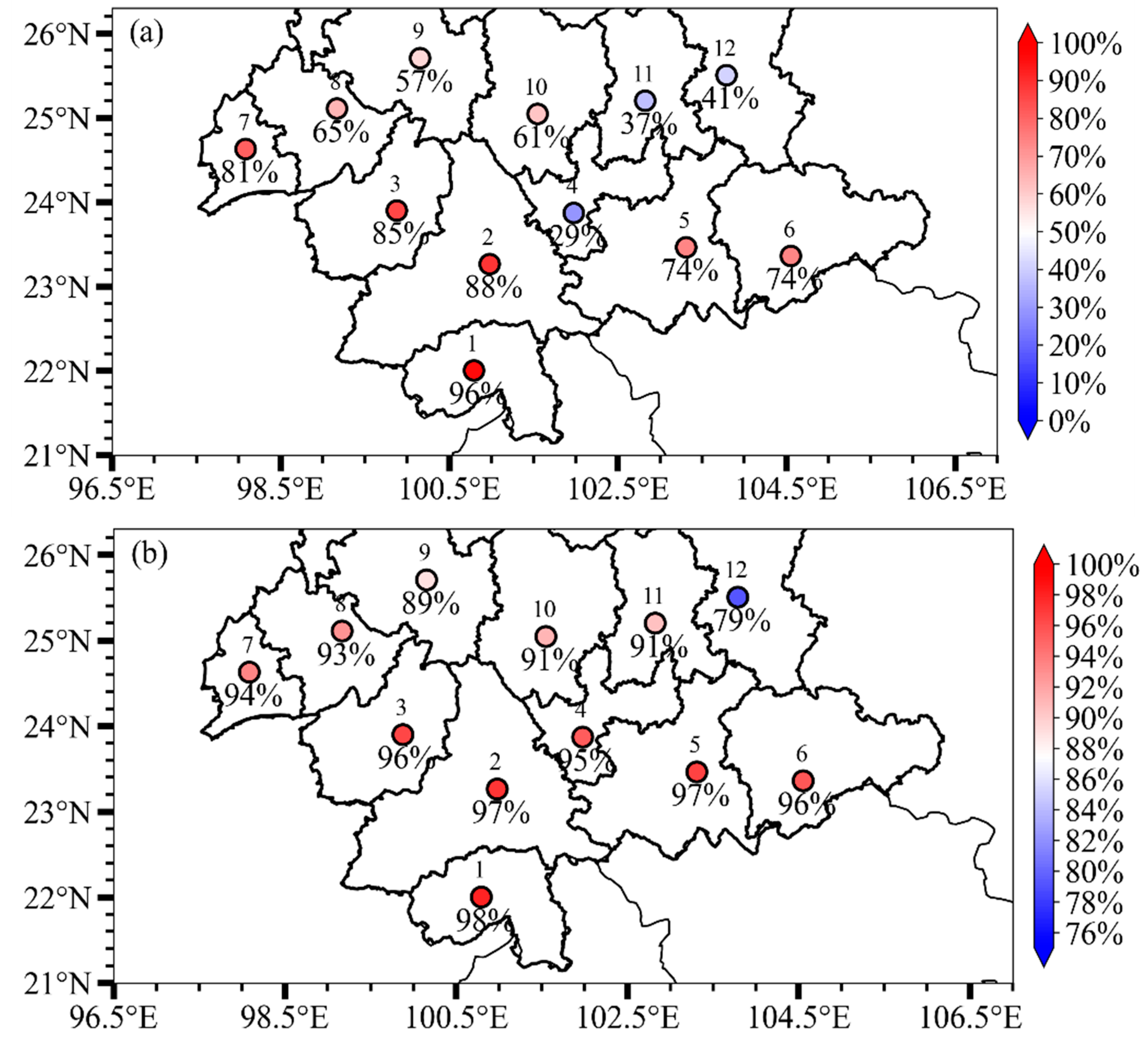
3.5. Contribution of BB Emissions to PM2.5 Concentrations over YP
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zheng, R.; Li, S.; Barnett, A.G.; Zhang, S.; Zou, X.; Huxley, R.R.; Chen, W.; Williams, G. Lung cancer incidence and ambient air pollution in China: A spatial age–period cohort study 1990–2009. Lancet 2015, 386, S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, J.P.; Adams, P.J.; Pandis, S.N. Sensitivity of PM 2.5 to climate in the Eastern US: A modeling case study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 4295–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Q.; Zhuang, G.; Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Huang, K.; Li, J.; Hou, B.; Lu, T.; Streets, D.G. Mechanism of formation of the heaviest pollution episode ever recorded in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2023–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Xia, J.; Wang, C.; Cao, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, L. Elevated 3D structures of PM 2.5 and impact of complex terrain-forcing circulations on heavy haze pollution over Sichuan Basin, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 9253–9268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.P.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, Q.H.; Li, C.C.; Shu, H.L.; Ying, Y.; Dai, Z.P.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.Y.; Liang, A.M. The impact of circulation patterns on regional transport pathways and air quality over Beijing and its surroundings. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 5031–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Mao, J.; Lau, K.-H.A.; Chen, J.-C.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhu, A.; Liu, G. Characteristics of distribution and seasonal variation of aerosol optical depth in eastern China with MODIS products. Chinese Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 2488–2495. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, T.; Chen, J. A climatology of aerosol optical depth over China from recent 10 years of MODIS remote sensing data. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ding, A.; Wang, Z.; Ding, K.; Gao, J.; Chai, F.; Fu, C. Amplified transboundary transport of haze by aerosol–boundary layer interaction in China. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, G.; Yan, Y.; He, J. Relay transport of aerosols to Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region by multi-scale atmospheric circulations. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 165, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Zhu, B.; Gao, J.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Su, J.; Pan, C.; Zhu, T.; Yu, B. Potential impacts of cold frontal passage on air quality over the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3673–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, M.; Tang, X.; Wang, Z.; Gbaguidi, A.; Liang, S.; Hu, K.; Wu, L.; Wu, H.; Huang, Z.; Shen, L. Source tagging modeling study of heavy haze episodes under complex regional transport processes over Wuhan megacity, Central China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Cheng, S.; Yao, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J. Multiple perspectives for modeling regional PM2. 5 transport across cities in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region during haze episodes. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 212, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squizzato, S.; Masiol, M.; Innocente, E.; Pecorari, E.; Rampazzo, G.; Pavoni, B. A procedure to assess local and long-range transport contributions to PM2. 5 and secondary inorganic aerosol. J. Aerosol Sci. 2012, 46, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.; Cheng, S.; Li, J.; Chen, D.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, X.; Han, L.; Wang, H. A monitoring and modeling study to investigate regional transport and characteristics of PM2. 5 pollution. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 943–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Li, G.; Cao, J.; Bei, N.; Wang, Y.; Feng, T.; Huang, R.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Tie, X. Contributions of trans-boundary transport to summertime air quality in Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2035–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Bao, S.; Wang, S.; Hu, Y.; Shi, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, B.; Jiang, J.; Zheng, M.; Wu, M. Local and regional contributions to fine particulate matter in Beijing during heavy haze episodes. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhao, T.; Bai, Y.; Kong, S.; Xiong, J.; Sun, X.; Yang, Q.; Gu, Y.; Lu, H. Importance of regional PM2. 5 transport and precipitation washout in heavy air pollution in the Twain-Hu Basin over Central China: Observational analysis and WRF-Chem simulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Liu, S.C.; Chou, C.C.K.; Liu, T.H.; Lee, C.-T.; Yuan, C.-S.; Shiu, C.-J.; Young, C.-Y. Long-range transport of Asian dust and air pollutants to Taiwan. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2004, 15, 759–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Ccoyllo, O.R.; de Fatima Andrade, M. The influence of meteorological conditions on the behavior of pollutants concentrations in São Paulo, Brazil. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 116, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, O.; Krusa, M.; Zencak, Z.; Sheesley, R.J.; Granat, L.; Engstrom, E.; Praveen, P.S.; Rao, P.; Leck, C.; Rodhe, H. Brown clouds over South Asia: Biomass or fossil fuel combustion? Science 2009, 323, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisen, F.; Meyer, C.P.M.; Keywood, M.D. Impact of biomass burning sources on seasonal aerosol air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 67, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.S.; Hsu, N.C.; Gao, Y.; Huang, K.; Li, C.; Lin, N.-H.; Tsay, S.-C. Evaluating the influences of biomass burning during 2006 BASE-ASIA: A regional chemical transport modeling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 3837–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Modeling the Impacts of Biomass Burning in Southeast Asia on PMover China in Spring. Res. Environ. Sci. 2016, 29, 952–962. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, D.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Boylan, J.W.; Zheng, M.; Russell, A.G. Assessment of biomass burning emissions and their impacts on urban and regional PM2. 5: A Georgia case study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Hsu, H.-M.; Lee, Y.H.; Kuo, C.H.; Sheng, Y.-F.; Chu, D.A. A new transport mechanism of biomass burning from Indochina as identified by modeling studies. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 7901–7911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsay, S.C.; Hsu, N.C.; Lau, W.K.; Li, C.; Gabriel, P.M.; Ji, Q.; Holben, B.N.; Judd Welton, E.; Nguyen, A.X.; Janjai, S. From BASE-ASIA toward 7-SEAS: A satellite-surface perspective of boreal spring biomass-burning aerosols and clouds in Southeast Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 78, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, X.; Tie, X.; Zhou, X.; Wu, D.; Zhong, L.; Tan, H.; Fei, L.; Huang, X.; Bi, X.; Tao, D. Effects of Southeast Asia biomass burning on aerosols and ozone concentrations over the Pearl River Delta (PRD) region. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8493–8501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.Y.; Chan, L.Y.; Harris, J.M.; Oltmans, S.J.; Zheng, X.D. Characteristics of biomass burning emission sources, transport, and chemical speciation in enhanced springtime tropospheric ozone profile over Hong Kong. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, ACH-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y. Yunnan Mountain Climate; Yunnan Science and Technology Press: Kunming, China, 2006. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Xia, X.; Che, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Duan, Y. Study of aerosol optical properties at Kunming in southwest China and long-range transport of biomass burning aerosols from North Burma. Atmos. Res. 2016, 169, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.S.P.; Huang, H.Y.; Lei, T.L.; Bui, T.T.; Wang, S.H.; Chi, K.H.; Sheu, G.R.; Lee, C.T.; Ou-Yang, C.F.; Lin, N.H. Characterizing a landmark biomass-burning event and its implication for aging processes during long-range transport. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 241, 117766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Fu, J.S.; Hsu, N.C.; Gao, Y.; Dong, X.; Tsay, S.C.; Lam, Y.F. Impact assessment of biomass burning on air quality in Southeast and East Asia during BASE-ASIA. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 78, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Song, W.; Zhang, Y.L.; Ponsawansong, P.; Prapamontol, T.; Wang, Y. Contribution of brown carbon to the light absorption and radiative effect of carbonaceous aerosols from biomass burning emissions in Chiang Mai, Thailand. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 260, 118544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Huang, X.; Ding, A.; Wang, M.; Su, H.; Kerminen, V.M.; Petäjä, T.; Tan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, D.; et al. Aerosol-boundary-layer-monsoon interactions amplify semi-direct effect of biomass smoke on low cloud formation in Southeast Asia. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, C.; Wang, J.; Reid, J.S. Mesoscale modeling of smoke transport over the Southeast Asian Maritime Continent: Coupling of smoke direct radiative effect below and above the low-level clouds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, A.; Xu, H.; Deng, J.; Ma, J.; Li, S. El Niño--Southern Oscillation (ENSO) effect on interannual variability in spring aerosols over East Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 5919–5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Fu, J.S.; Huang, K.; Zhu, Q.; Tipton, M. Regional climate effects of biomass burning and dust in East Asia: Evidence from modeling and observation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 11490–11499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Nazeer, M.; Qiu, Z.; Ding, X.; Wei, J. Global validation of MODIS C6 and C6. 1 merged aerosol products over diverse vegetated surfaces. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Xie, Y.; Fu, Q.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, K. Validation of MODIS aerosol optical depth retrieval over mountains in central China based on a sun-sky radiometer site of SONET. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grell, G.A.; Peckham, S.E.; Schmitz, R.; McKeen, S.A.; Frost, G.; Skamarock, W.C.; Eder, B. Fully coupled “online” chemistry within the WRF model. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6957–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A New Vertical Diffusion Package with an Explicit Treatment of Entrainment Processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 134, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrison, H.; Thompson, G.; Tatarskii, V. Impact of Cloud Microphysics on the Development of Trailing Stratiform Precipitation in a Simulated Squall Line: Comparison of One- and Two-Moment Schemes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2009, 137, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iacono, M.J.; Delamere, J.S.; Mlawer, E.J.; Shephard, M.W.; Collins, W.D. Radiative Forcing by Long-Lived Greenhouse Gases: Calculations with the AER Radiative Transfer Models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D13103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Dudhia, J. Coupling an Advanced Land Surface–Hydrology Model with the Penn State–NCAR MM5 Modeling System. Part I: Model Implementation and Sensitivity. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stockwell, W.R.; Middleton, P.; Chang, J.S.; Tang, X. The second generation regional acid deposition model chemical mechanism for regional air quality modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1990, 95, 16343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Kurokawa, J.I.; Woo, J.H.; He, K.; Lu, Z.; Ohara, T.; Song, Y.; Streets, D.G.; Carmichael, G.R. MIX: A mosaic Asian anthropogenic emission inventory under the international collaboration framework of the MICS-Asia and HTAP. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 935–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guenther, A.; Karl, T.; Harley, P.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Palmer, P.I.; Geron, C. Estimates of global terrestrial isoprene emissions using MEGAN (Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3181–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiedinmyer, C.; Akagi, S.K.; Yokelson, R.J.; Emmons, L. The Fire INventory from NCAR (FINN): A high resolution global model to estimate the emissions from open burning. Geosci. Model Dev. 2011, 4, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freitas, S.R.; Longo, K.M.; Chatfield, R.; Latham, D.; Dias, M.S.; Andreae, M.O.; Prins, E.; Santos, J.C.; Gielow, R.; Carvalho, J.A. Including the sub-grid scale plume rise of vegetation fires in low resolution atmospheric transport models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freitas, S.R.; Longo, K.M.; Trentmann, J.; Latham, D. Technical Note: Sensitivity of 1-D smoke plume rise models to the inclusion of environmental wind drag. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stohl, A. A backward modeling study of intercontinental pollution transport using aircraft measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A.; Forster, C.; Frank, A.; Seibert, P.; Wotawa, G. Technical note: The Lagrangian particle dispersion model FLEXPART version 6.2. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 2461–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brioude, J.; Arnold, D.; Stoh, A.; Cassiani, M.; Morton, D.; Seibert, P.; Angevine, W.; Evan, S.; Dingwell, A.; Fast, J.D. The Lagrangian particle dispersion model FLEXPART-WRF version 3.1. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 1889–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sauvage, B.; Fontaine, A.; Eckhardt, S.; Auby, A.; Boulanger, D.; Petetin, H.; Paugam, R.; Athier, G.; Cousin, J.M.; Darras, S. Source attribution using FLEXPART and carbon monoxide emission inventories: SOFT-IO version 1.0. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 15271–15292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, C.; Zhao, T.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chang, J. Heavy air pollution with a unique “non-stagnant” atmospheric boundary layer in the Yangtze River middle basin aggravated by regional transport of PM2.5 over China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 7217–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Hu, W.; Zhao, T.; Bai, Y.; Wang, H.; Kong, S.; Zhu, Y. Changes in the Distribution Pattern of PM2.5 Pollution over Central China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, G.; Zhu, B.; Geng, F.; Chang, L. A method for fast quantification of air pollutant sources. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2017, 37, 2474–2481. [Google Scholar]
- Hanna, S.R.; Yang, R. Evaluations of Mesoscale Models’ Simulations of Near-Surface Winds, Temperature Gradients, and Mixing Depths. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.; Jacob, D.J.; Brewer, J.F.; Li, K.; Moch, J.M.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Lim, H.; Lee, H.C.; Kuk, S.K. Relating geostationary satellite measurements of aerosol optical depth (AOD) over East Asia to fine particulate matter (PM 2.5): Insights from the KORUS-AQ aircraft campaign and GEOS-Chem model simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 16775–16791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boylan, J.W.; Russell, A.G. PM and light extinction model performance metrics, goals, and criteria for three-dimensional air quality models. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 4946–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.-F.; Ma, Z.-Y.; Ha, X.-Z. Spatial-temporal patterns of PM2. 5 concentrations for 338 Chinese cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leeuw, G.; Sogacheva, L.; Rodriguez, E.; Kourtidis, K.; Georgoulias, A.K.; Alexandri, G.; Amiridis, V.; Proestakis, E.; Marinou, E.; Xue, Y. Two decades of satellite observations of AOD over mainland China using ATSR-2, AATSR and MODIS/Terra: Data set evaluation and large-scale patterns. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 1573–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Cheng, T.; Shi, S.; Guo, H.; Han, Z. Evaluating the impacts of burning biomass on PM2.5 regional transport under various emission conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Cai, X.; Wang, J.; Song, Y.; Zhu, T. Climatological study of the Boundary-layer air Stagnation Index for China and its relationship with air pollution. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 7573–7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, T.; Liu, F.; Gong, S.L.; Kristovich, D.; Lu, C.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Ding, G. Climate modulation of the Tibetan Plateau on haze in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
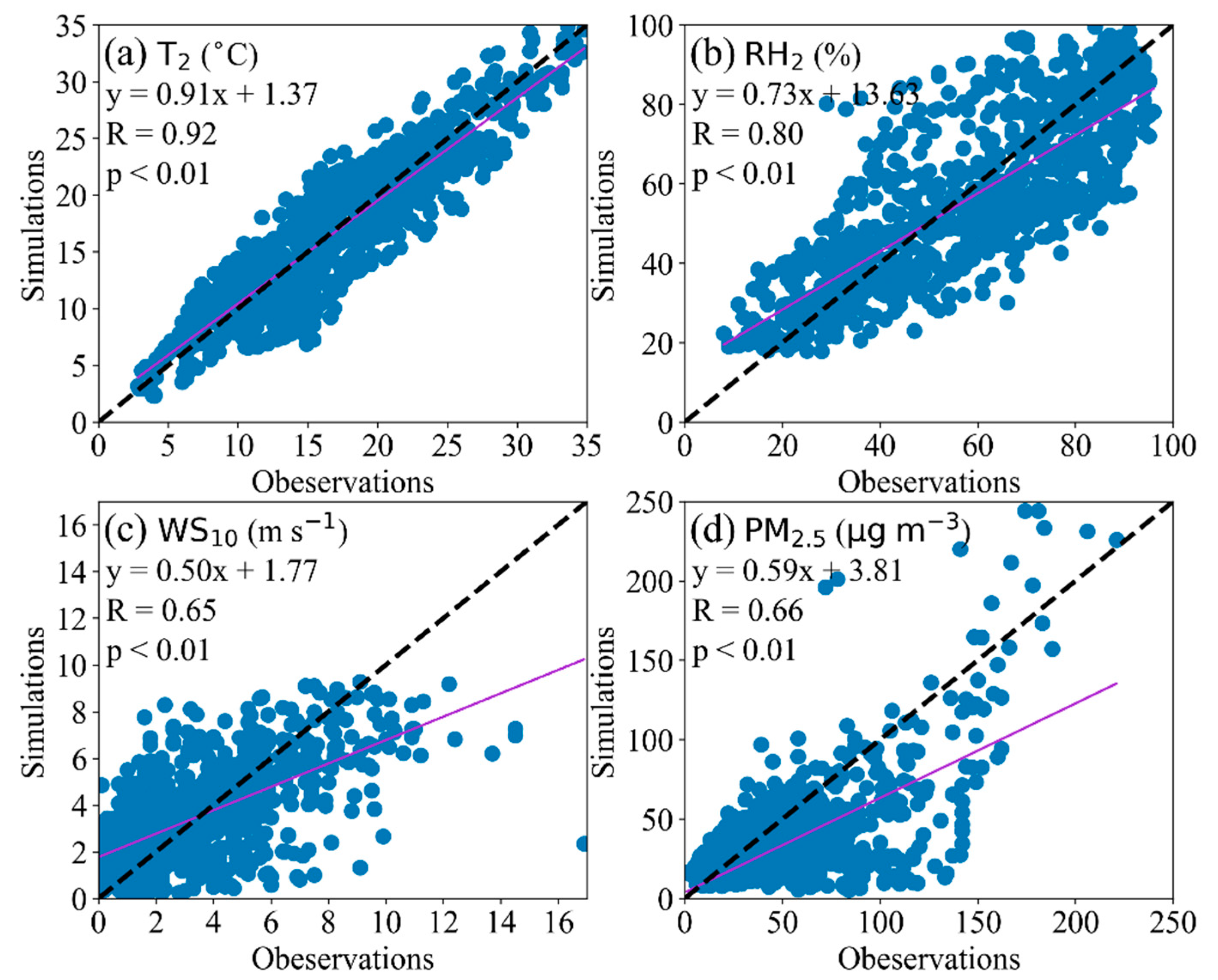
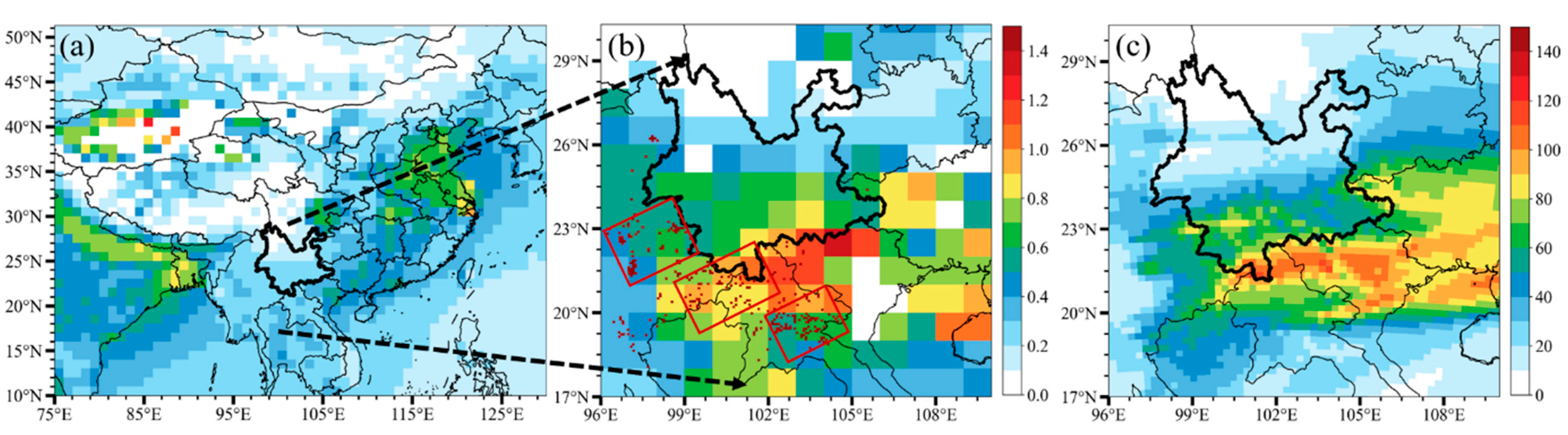
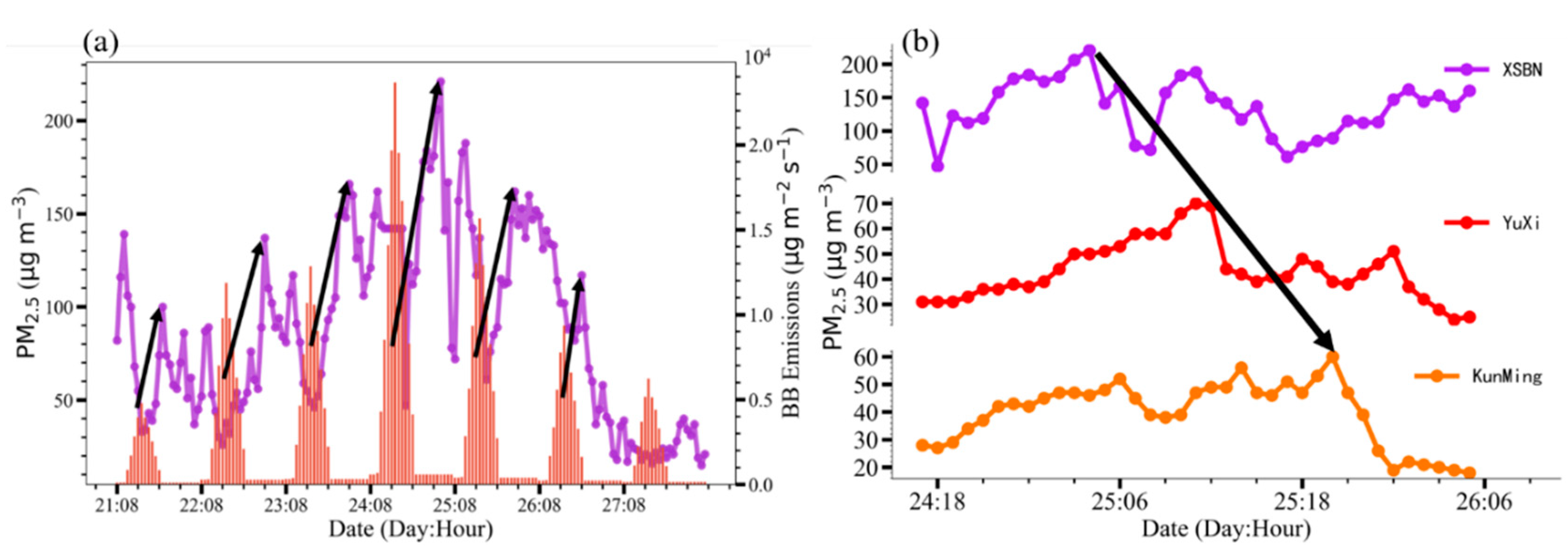
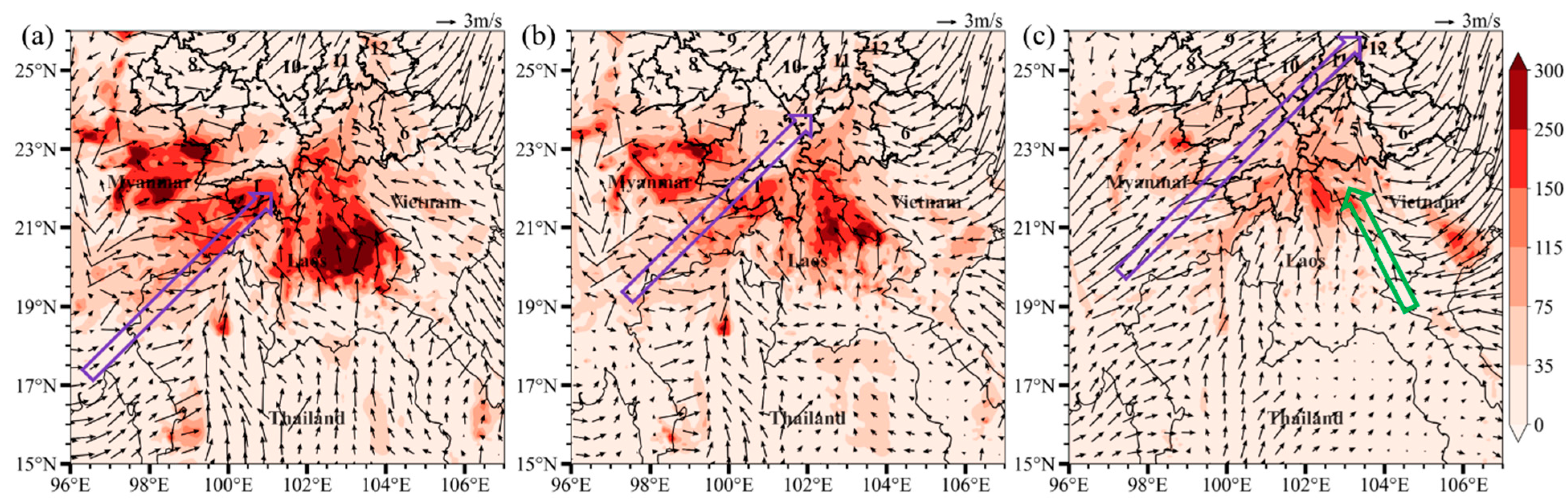
| R | RMSE | MB | ME | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2 (°C) | 0.92 * | 2.71 | −0.25 | 2.16 |
| WS10 (m s−1) | 0.65 * | 2.03 | 0.10 | 1.51 |
| RH2 (%) | 0.80 * | 14.11 | −1.31 | 11.10 |
| R | RMSE (μg m−3) | MFB (%) | MFE (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 0.66 * | 31.09 | −21.30 | 33.26 |
| SR | RR | |
|---|---|---|
| Surface | 79% | 56% |
| 700 hPa | 94% | 90% |
| Increments | 16% | 34% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Q.; Zhao, T.; Tian, Z.; Kumar, K.R.; Chang, J.; Hu, W.; Shu, Z.; Hu, J. The Cross-Border Transport of PM2.5 from the Southeast Asian Biomass Burning Emissions and Its Impact on Air Pollution in Yunnan Plateau, Southwest China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081886
Yang Q, Zhao T, Tian Z, Kumar KR, Chang J, Hu W, Shu Z, Hu J. The Cross-Border Transport of PM2.5 from the Southeast Asian Biomass Burning Emissions and Its Impact on Air Pollution in Yunnan Plateau, Southwest China. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(8):1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081886
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Qingjian, Tianliang Zhao, Zhijie Tian, Kanike Raghavendra Kumar, Jiacheng Chang, Weiyang Hu, Zhuozhi Shu, and Jun Hu. 2022. "The Cross-Border Transport of PM2.5 from the Southeast Asian Biomass Burning Emissions and Its Impact on Air Pollution in Yunnan Plateau, Southwest China" Remote Sensing 14, no. 8: 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081886
APA StyleYang, Q., Zhao, T., Tian, Z., Kumar, K. R., Chang, J., Hu, W., Shu, Z., & Hu, J. (2022). The Cross-Border Transport of PM2.5 from the Southeast Asian Biomass Burning Emissions and Its Impact on Air Pollution in Yunnan Plateau, Southwest China. Remote Sensing, 14(8), 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081886






