Improved GM-PHD Filter with Birth Intensity and Spawned Intensity Estimation Based on Trajectory Situation Feedback Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- The target trajectories are formed on the basis of the discrete state estimation of GM-PHD, which is conducive to further analysis of the target’s behavior in the scenario.
- (2)
- In the process of the proposed GM-PHD filtering, the birth intensity is adjusted adaptively according to the trajectory initiation of Gaussian components, which facilitates the accurate tracking of the unknown and time-varying birth targets.
- (3)
- Through the analysis and feedback of the trajectory situation, the proposed GM-PHD filter improves the identification of the intersected targets by enhancing spawned intensity, and maintains the target’s state during the intersection period.
2. Problem Formulation
2.1. Traditional PHD Filter
2.2. GM-PHD Filter
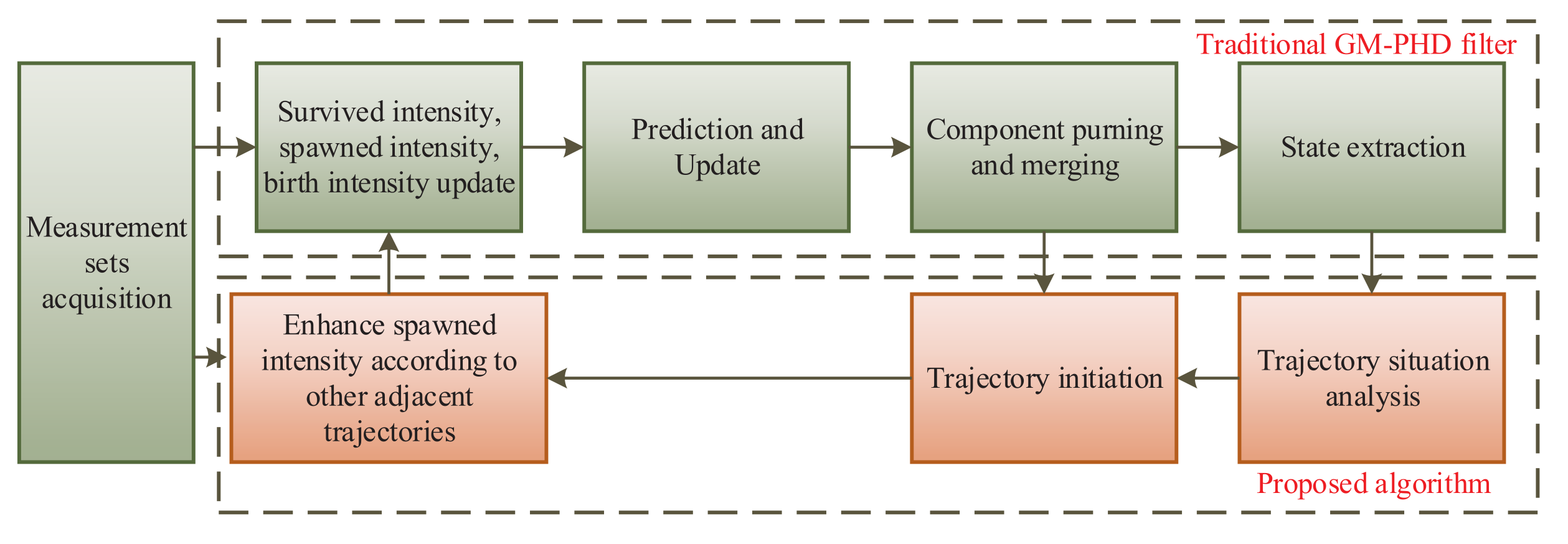
3. GM-PHD Filter Based on Trajectory Situation Feedback Control
3.1. Birth Intensity Estimation Method
| Algorithm 1 Pseudo-code for the birth intensity estimation. |
| Input:, minimum rate of status change , maximum rate of status change , interval time t and deviation threshold . Set: , and . Step 1. initiation.
|
3.2. Spawned Intensity Estimation Method
| Algorithm 2 Pseudo-code for the spawned intensity estimation. |
| Input:, the closeness of trajectories , the measurement-trajectory threshold U, the trajectory closeness threshold T. Set: , and . Step 1. prediction for birth and existing targets (details omitted, as seen in Algorithm 1 and Ref. [10]). Step 2. prediction for spawned targets.
Step 4. component pruning (details omitted, as seen in Ref. [10]).
|
4. Simulation Results and Discussion
4.1. Target Birth Scenario
4.2. Target Intersection Scenario
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Mao, D.; Niu, J.; Wu, Q.M.; Ji, Y. Continuous Tracking of Targets for Stereoscopic HFSWR Based on IMM Filtering Combined with ELM. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Q. Modified Multi-Mode Target Tracker for High-Frequency SurfaceWave Radar. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Huang, H.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, X.; Yin, X. Adaptive Unscented Kalman Filter for Target Tracking in the Presence of Nonlinear Systems Involving Model Mismatches. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Yu, H.; Lan, J.; Fu, Z.; He, Z.; Pu, J. Tracking of Multiple Maneuvering Random Hypersurface Extended Objects Using High Resolution Sensors. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, D.B. An algorithm for tracking multiple targets. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1979, 24, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortmann, T.E.; Bar-Shalom, Y.; Scheffe, M. Sonar tracking of multiple targets using joint probabilistic data association. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2003, 8, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahler, R.P.S. Multitarget Bayes filtering via first-order multi-target moments. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2003, 39, 1152–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, B.N.; Singh, S.; Doucet, A. Sequential Monte Carlo methods for multi-target filtering with random finite sets. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2005, 41, 1224–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wang, W.; Kirubarajan, T.; Sun, J.; Lei, P. PHD and CPHD Filtering With Unknown Detection Probability. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 3784–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, B.N.; Ma, W.K. The Gaussian mixture probability hypothesis density filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 4091–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, B.T.; Vo, B.N.; Cantoni, A. Analytic implementations of the cardinalized probability hypothesis density filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2007, 55, 3553–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zou, H.; Ji, K. Probability hypothesis density filter with adaptive estimation of target birth intensity. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2016, 10, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, T.; Pan, J.; Bao, Q. The Modified Probability Hypothesis Density Filter With Adaptive Birth Intensity Estimation for Multi-Target Tracking in Low Detection Probability. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 43690–43710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Park, S.; Kim, E. A newborn track detection and state estimation algorithm using Bernoulli random finite sets. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 2660–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Xie, L.; Su, H. Estimations of time-varying birth cardinality distribution and birth intensity in Gaussian mixture CPHD filter for multi-target tracking. Signal Process. 2022, 190, 108321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Ji, H.; Liu, L. Adaptive target birth intensity multi-Bernoulli filter with noise-based threshold. Sensors 2019, 19, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Meng, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Collaborative penalized Gaussian mixture PHD tracker for close target tracking. Signal Process. 2014, 102, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Ji, H.; Zhang, Y. A standard PHD filter for joint tracking and classification of maneuvering extended targets using random matrix. Signal Process. 2018, 144, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Li, X.R. Tracking of extended object or target group using random ma- trix: New model and approach. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2016, 52, 2973–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Xu, N.; Xu, L.P.; Li, M.; Cheng, P. An improved partitioning algorithm based on FCM algorithm for extended target tracking in PHD filter. Digit. Signal Process. 2019, 90, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wang, D.; Sun, H.; Zhang, T. Radiation intensity Gaussian mixture PHD filter for close target tracking. Signal Process. 2021, 7, 108196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Wang, W.; Naqvi, S.M.; Chambers, J. Adaptive Retrodiction Particle PHD Filter for Multiple Human Tracking. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 1592–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arenas-Garca, J.; Azpicueta-Ruiz, L.A.; Sliva, M.T.M.; Nascimento, V.H.; Sayed, A.H. Combinations of adaptive filters. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2016, 33, 120–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, Á.F.; Svensson, L. Trajectory PHD and CPHD Filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2019, 67, 5702–5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, B.A. CPHD filter birth modeling using the probabilistic admissible region. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 1456–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, K.; Zhang, Q.; An, W.; Jiang, Y.; Ping, X.; Chen, P. Iterative RANSAC based adaptive birth intensity estimation in GM-PHD filter for multi-target tracking. Signal Process. 2017, 131, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, Y.F.; He, B. Entropy distribution and coverage rate based birth intensity estimation in GM-PHD filter for multi-target visual tracking. Signal Process. 2014, 94, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, A.F.; Vo, B.-N. Derivation of the PHD and CPHD filters based on direct Kullback-Leibler divergence minimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 5812–5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhmacher, D.; Vo, B.T.; Vo, B.N. A consistent metric for performance evaluation of multi-object filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2008, 56, 3447–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

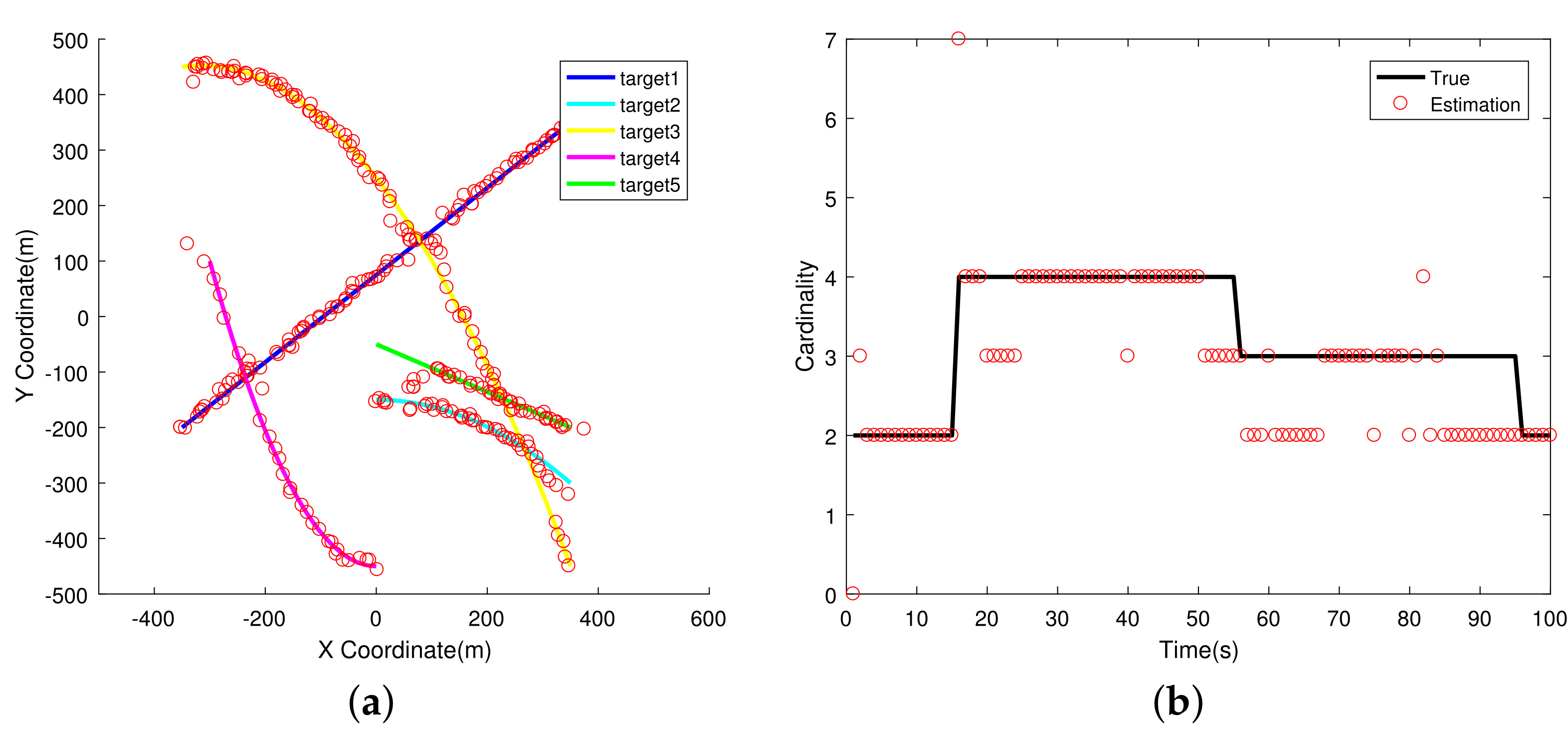


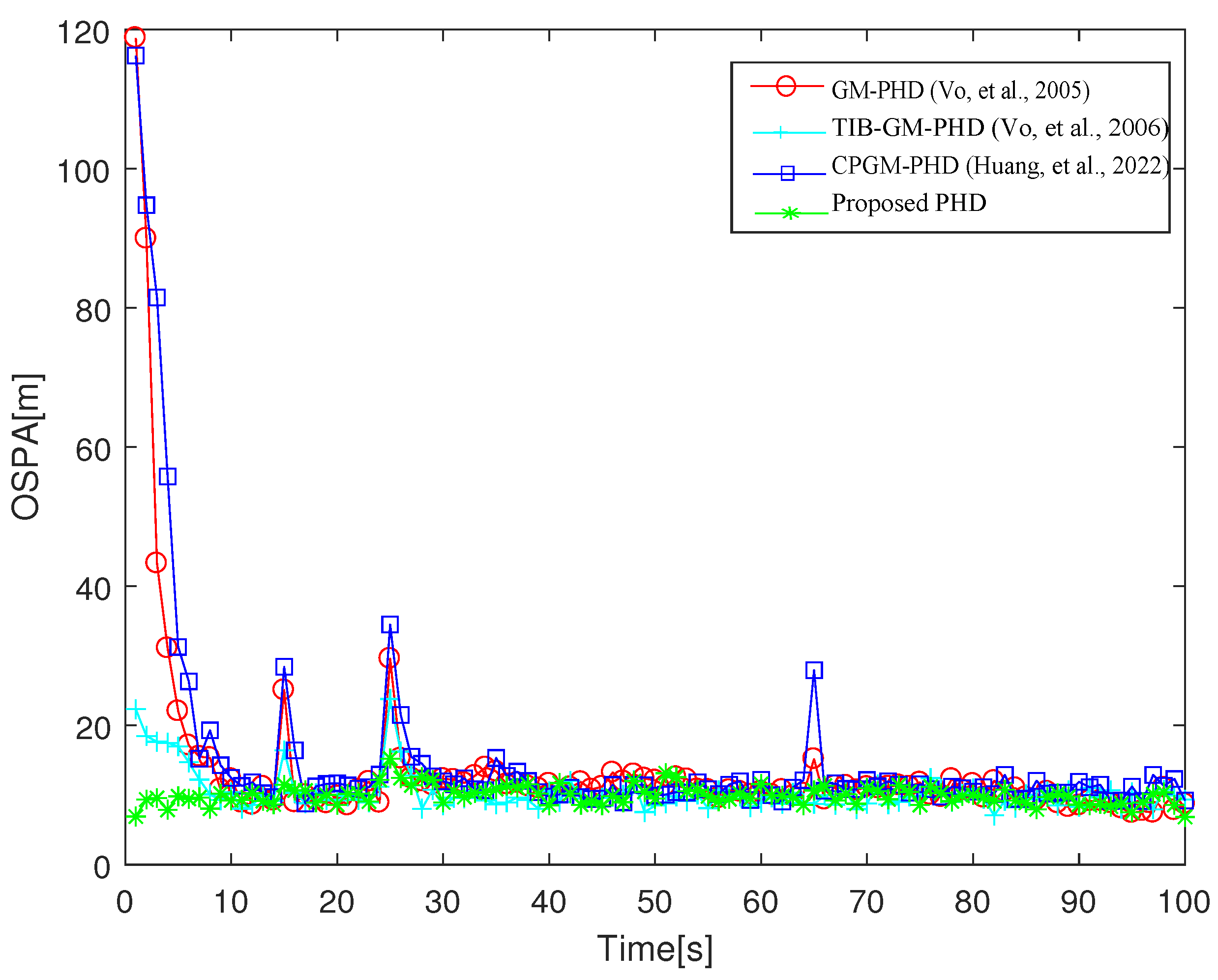

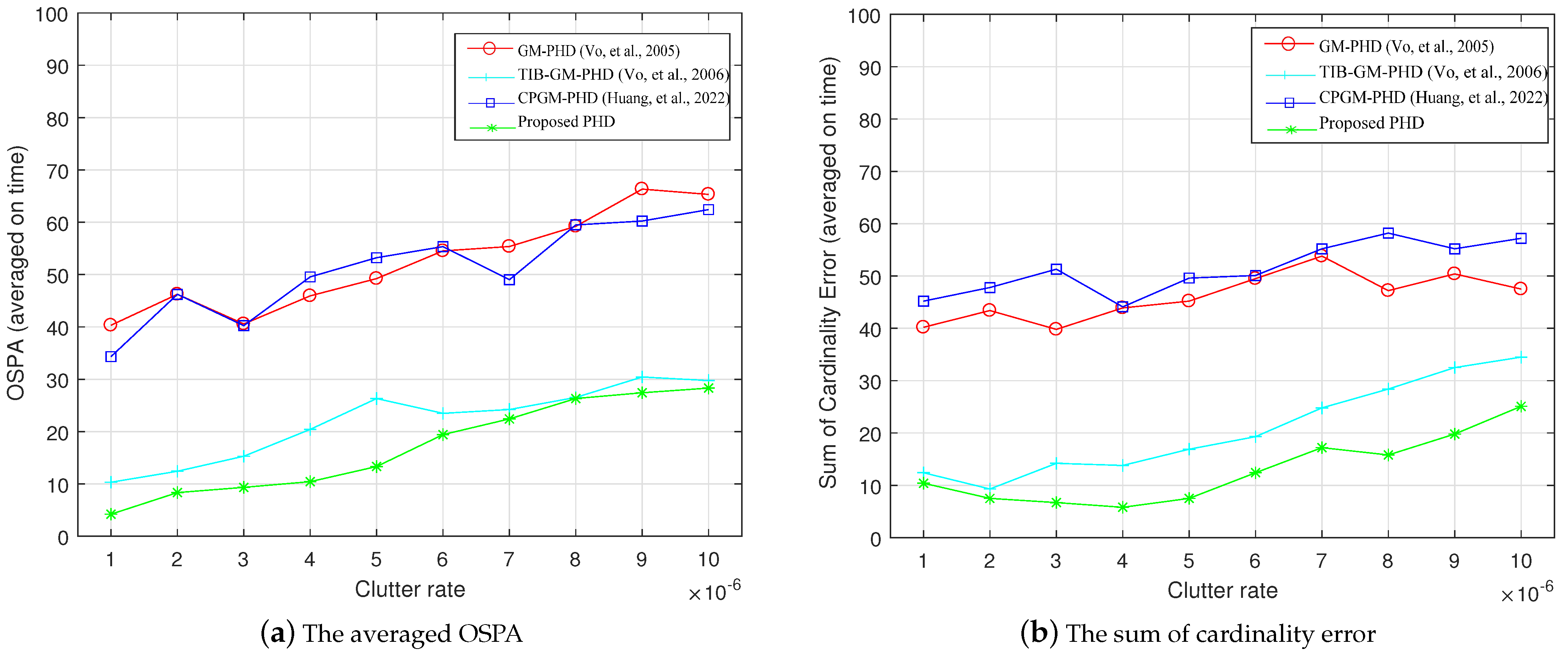
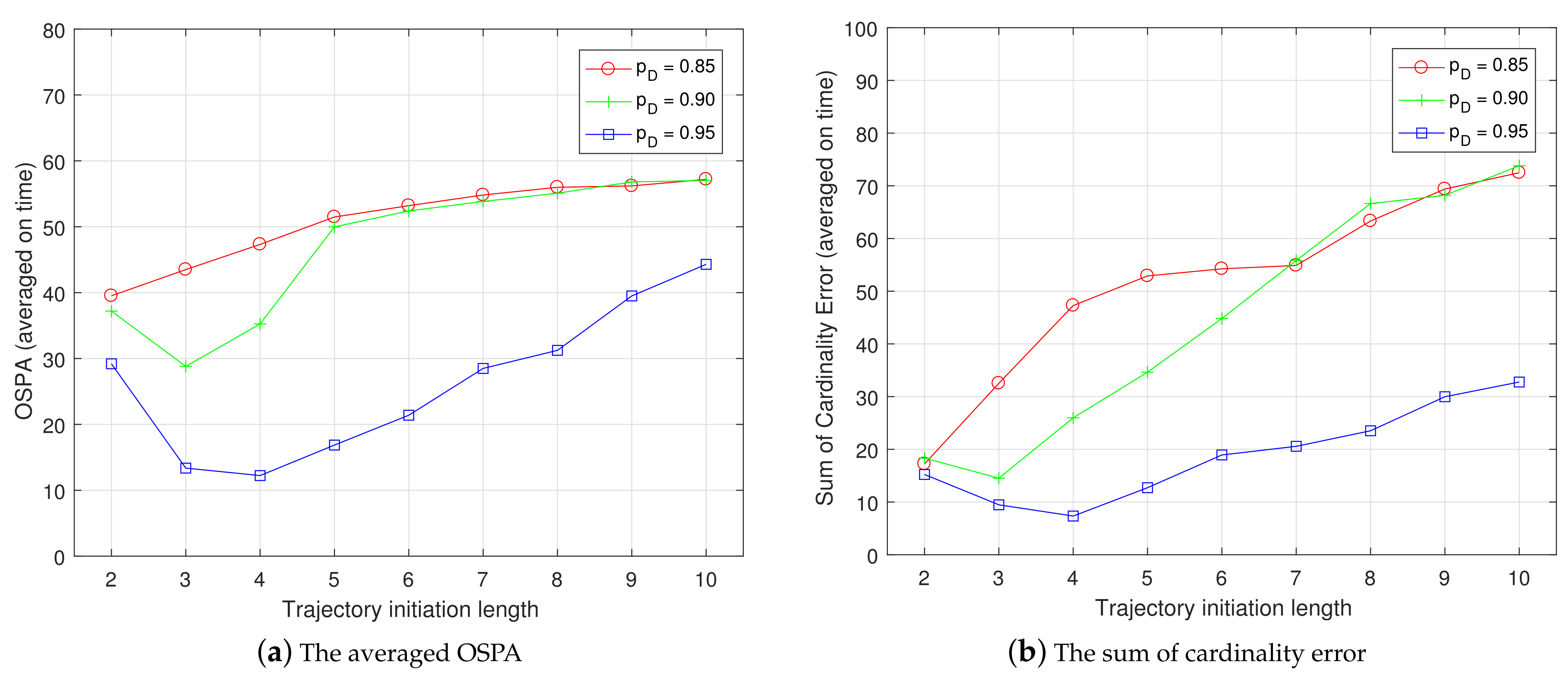
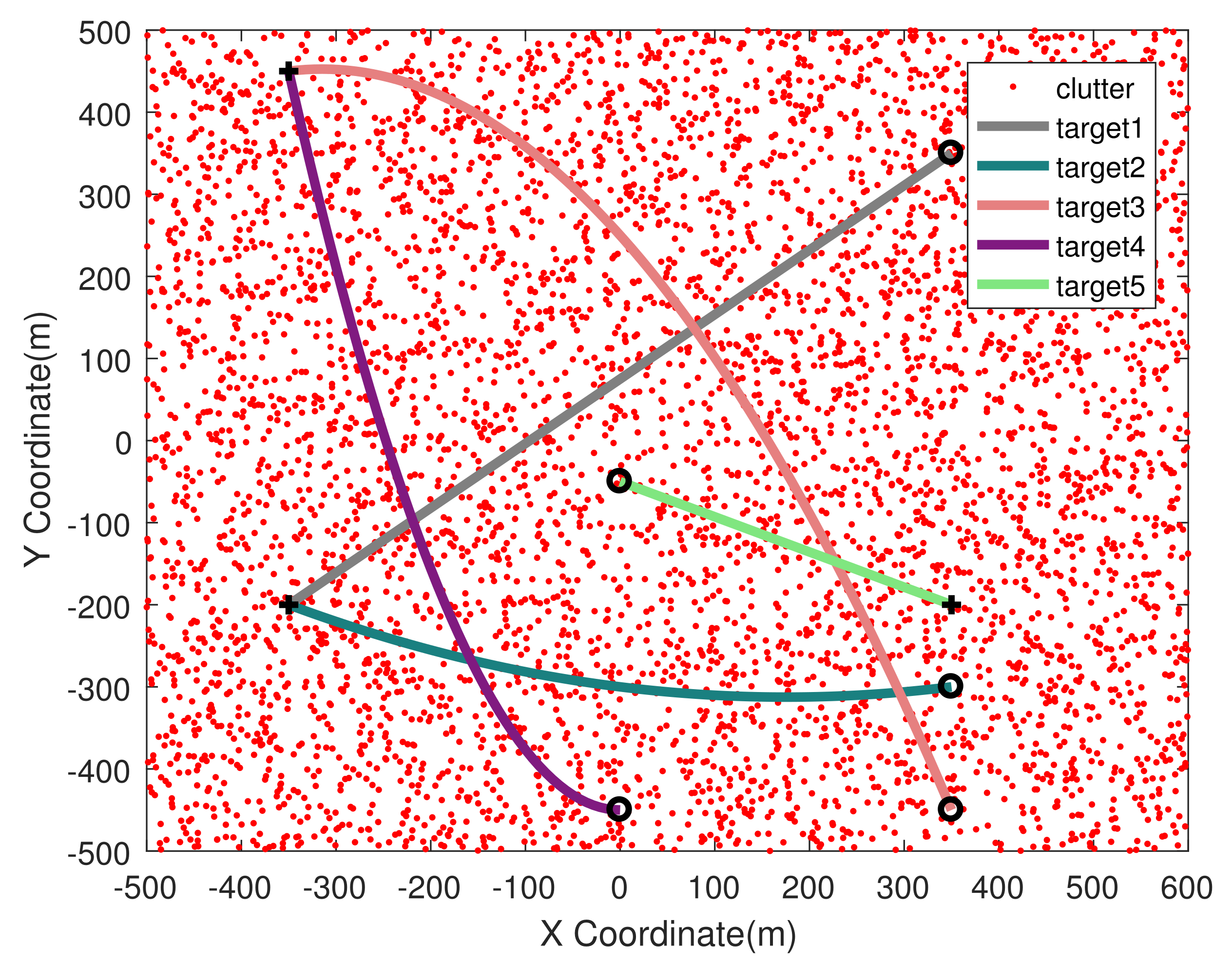
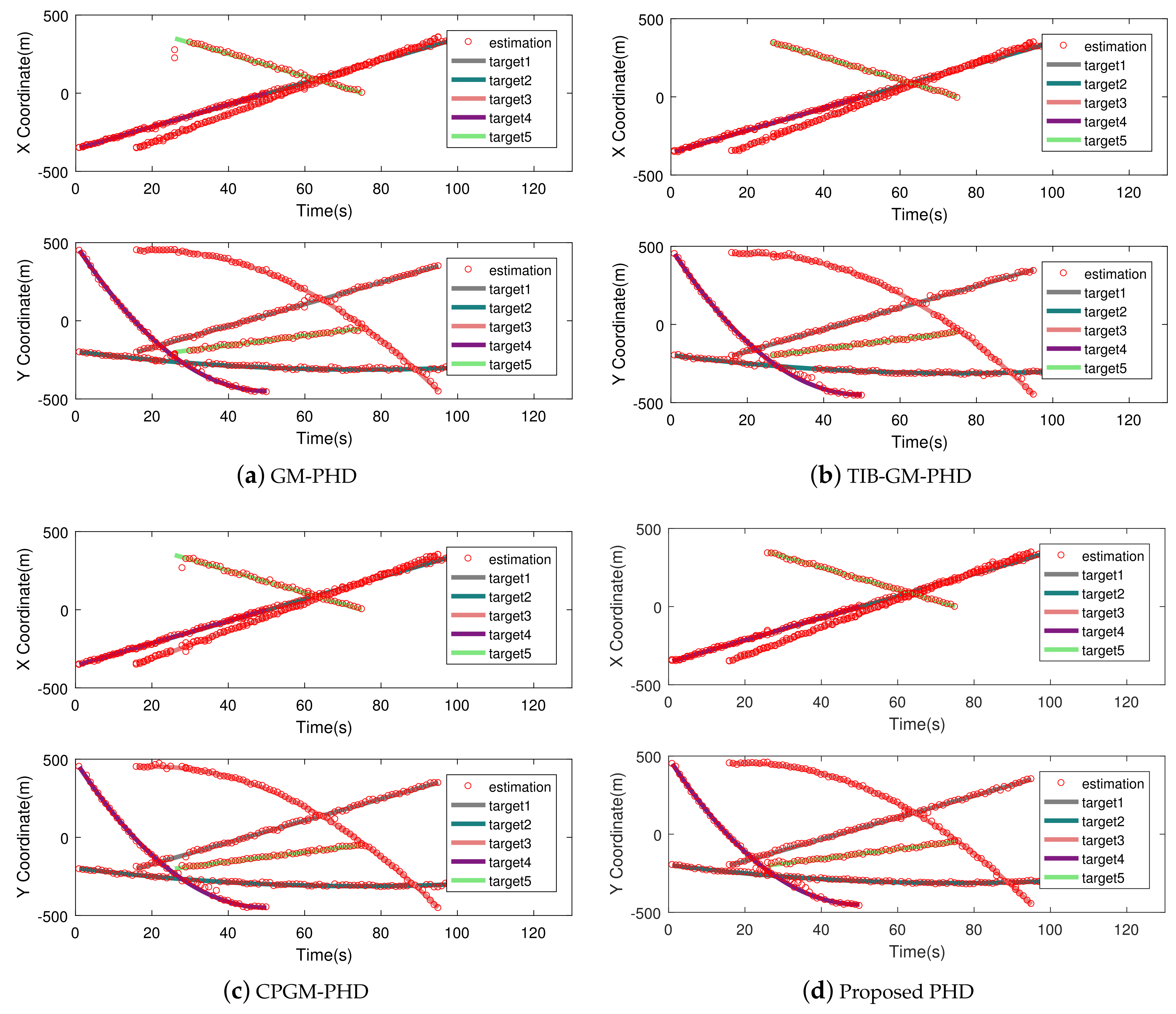

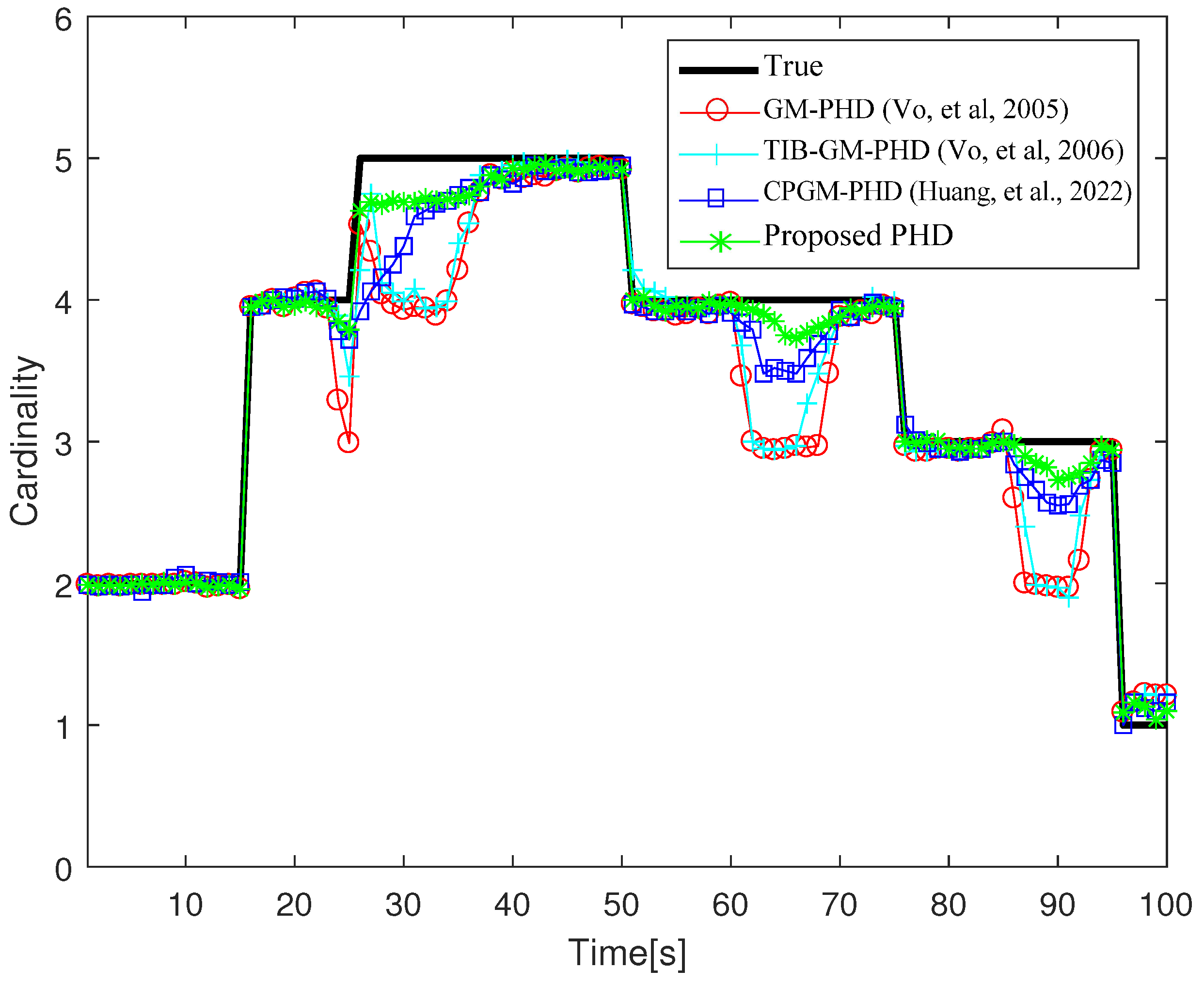
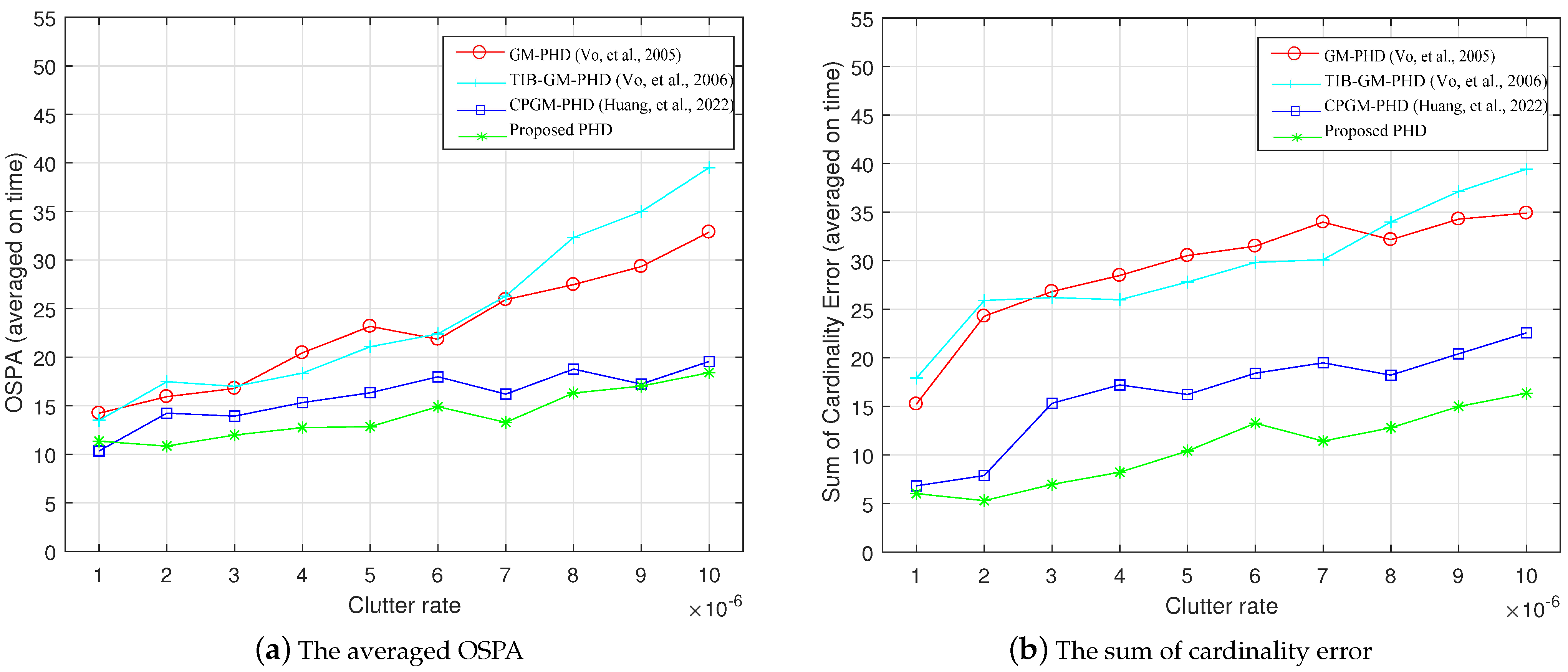
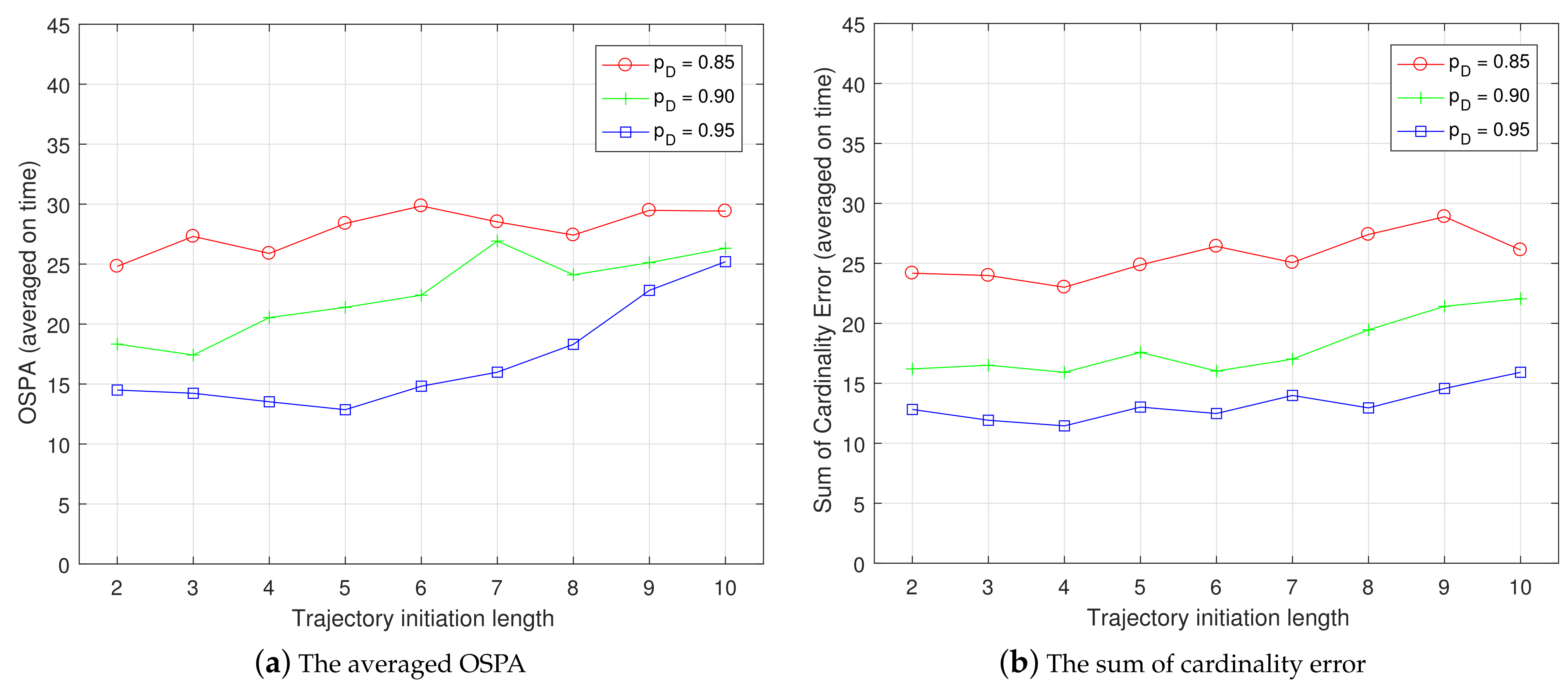
| Target Index | Initial Target State (m) | Appearing Time (s) | Disappearing Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [−350, −400, 1, 1] | 1 | 100 |
| 2 | [450, −450, −1, 1] | 25 | 44 |
| 3 | [350, −100, −1, −1] | 1 | 20 |
| 4 | [−400, 300, −1, 1] | 1 | 100 |
| 5 | [−400, 300, 1, 1] | 45 | 94 |
| 6 | [400, 100, 1, −1] | 15 | 64 |
| 7 | [−300, 200, 1, −1] | 35 | 84 |
| 8 | [−200, 100, 1, 1] | 65 | 74 |
| 9 | [−100, 50, 1, 0] | 1 | 30 |
| 10 | [0, −200, −1, 1] | 25 | 54 |
| Target Index | Initial Target State (m) | Appearing Time (s) | Disappearing Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [−350, −200, 1, 1] | 15 | 95 |
| 2 | [−350, −200, 1, −1] | 1 | 100 |
| 3 | [−350, 450, 1, −1] | 15 | 95 |
| 4 | [−350, 450, 1, −1] | 1 | 50 |
| 5 | [350, −200, −1, 1] | 25 | 75 |
| Standard | GM-PHD | TIB-GM-PHD | CPGM-PHD | Proposed PHD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSPA | 23.63 | 21.97 | 16.76 | 13.62 |
| Cardinality | 31.14 | 26.00 | 16.96 | 12.86 |
| Times (s) | 64.12 | 59.89 | 85.34 | 69.29 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Qin, T. Improved GM-PHD Filter with Birth Intensity and Spawned Intensity Estimation Based on Trajectory Situation Feedback Control. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071683
Zhang C, Li Z, Zhu Y, Luo Z, Qin T. Improved GM-PHD Filter with Birth Intensity and Spawned Intensity Estimation Based on Trajectory Situation Feedback Control. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(7):1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071683
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chao, Zhengzhou Li, Yong Zhu, Zefeng Luo, and Tianqi Qin. 2022. "Improved GM-PHD Filter with Birth Intensity and Spawned Intensity Estimation Based on Trajectory Situation Feedback Control" Remote Sensing 14, no. 7: 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071683
APA StyleZhang, C., Li, Z., Zhu, Y., Luo, Z., & Qin, T. (2022). Improved GM-PHD Filter with Birth Intensity and Spawned Intensity Estimation Based on Trajectory Situation Feedback Control. Remote Sensing, 14(7), 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071683






