Review of Land Surface Albedo: Variance Characteristics, Climate Effect and Management Strategy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Analysis of Surface Albedo
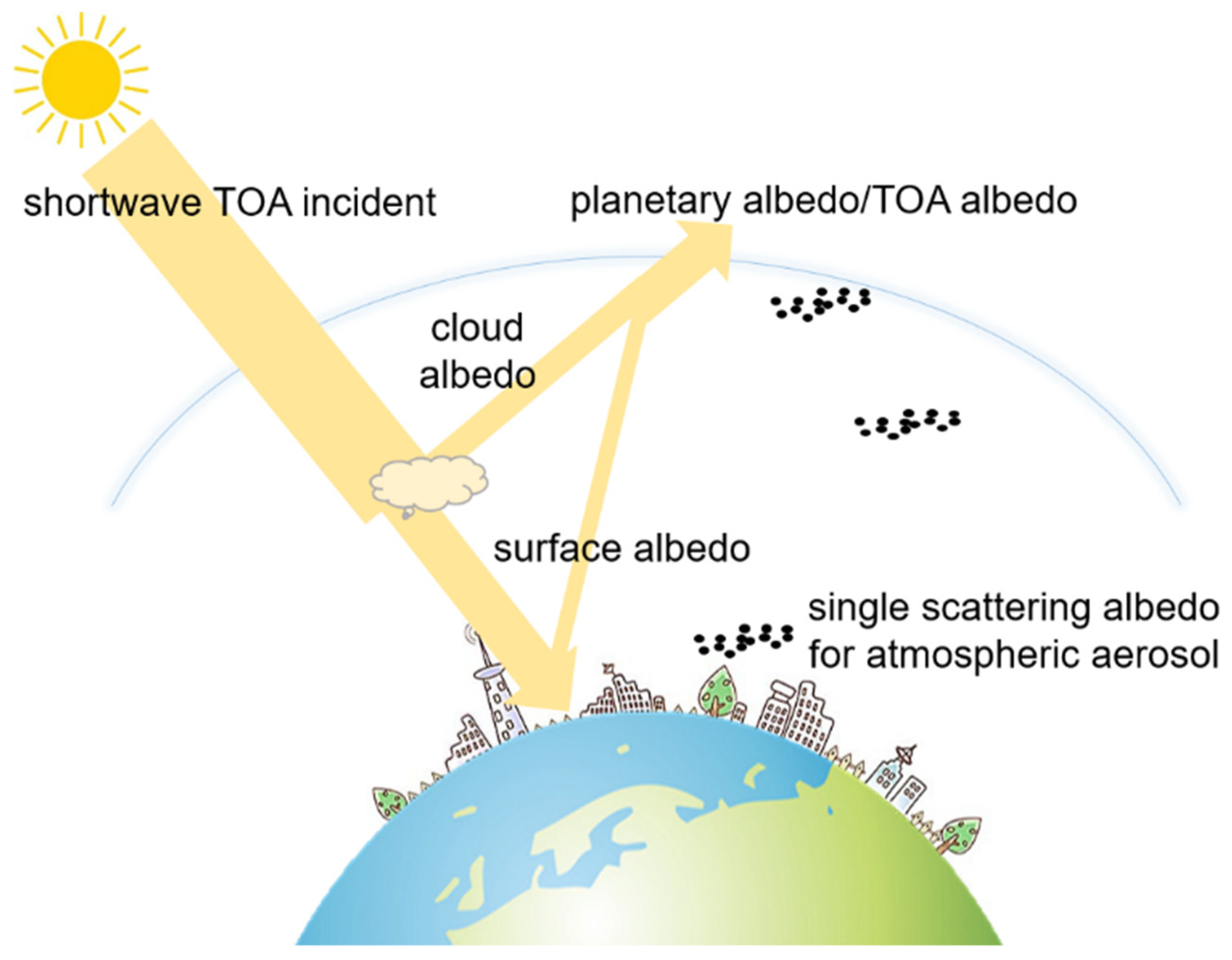
2.1. Definition Distinction
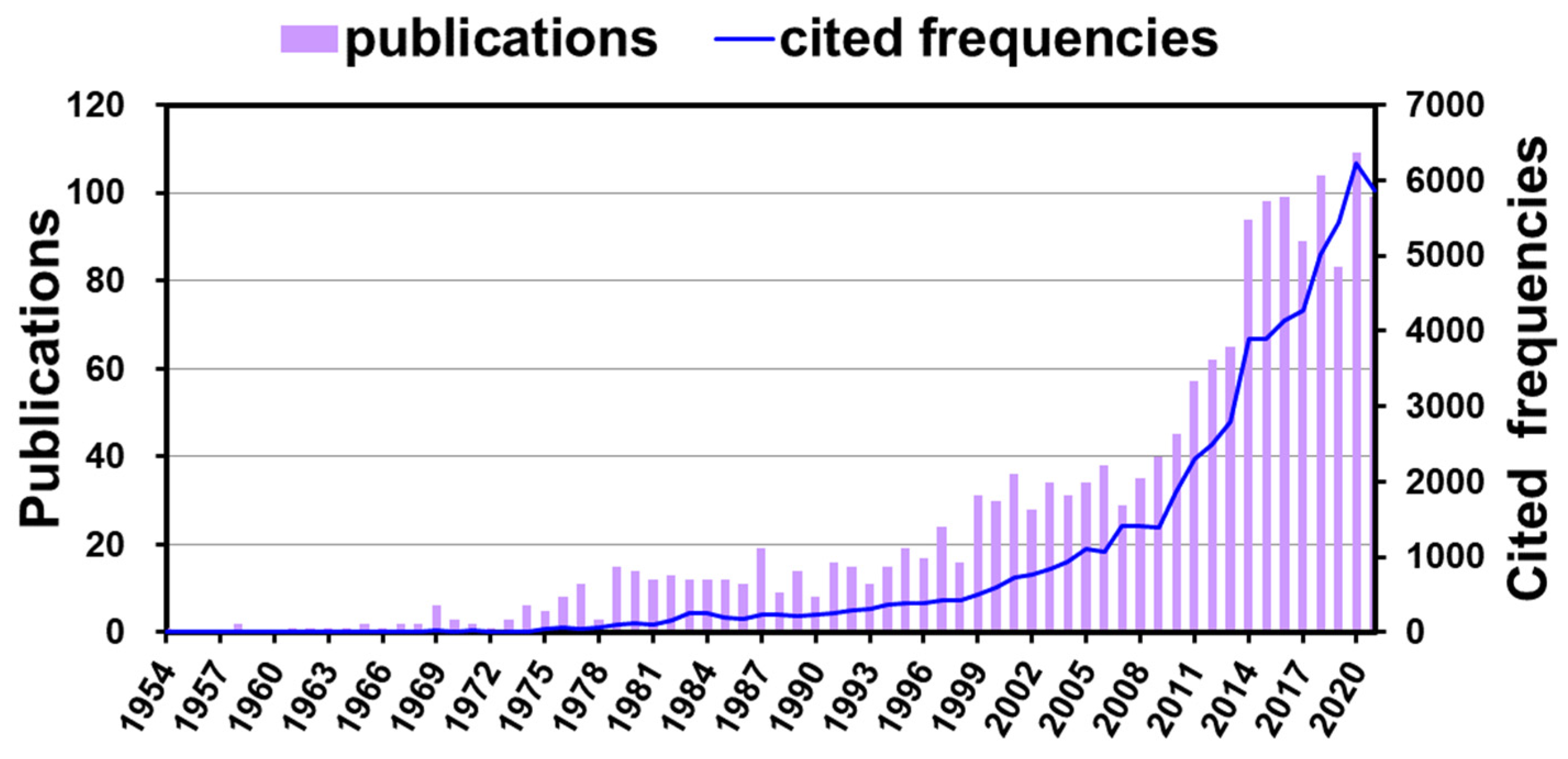
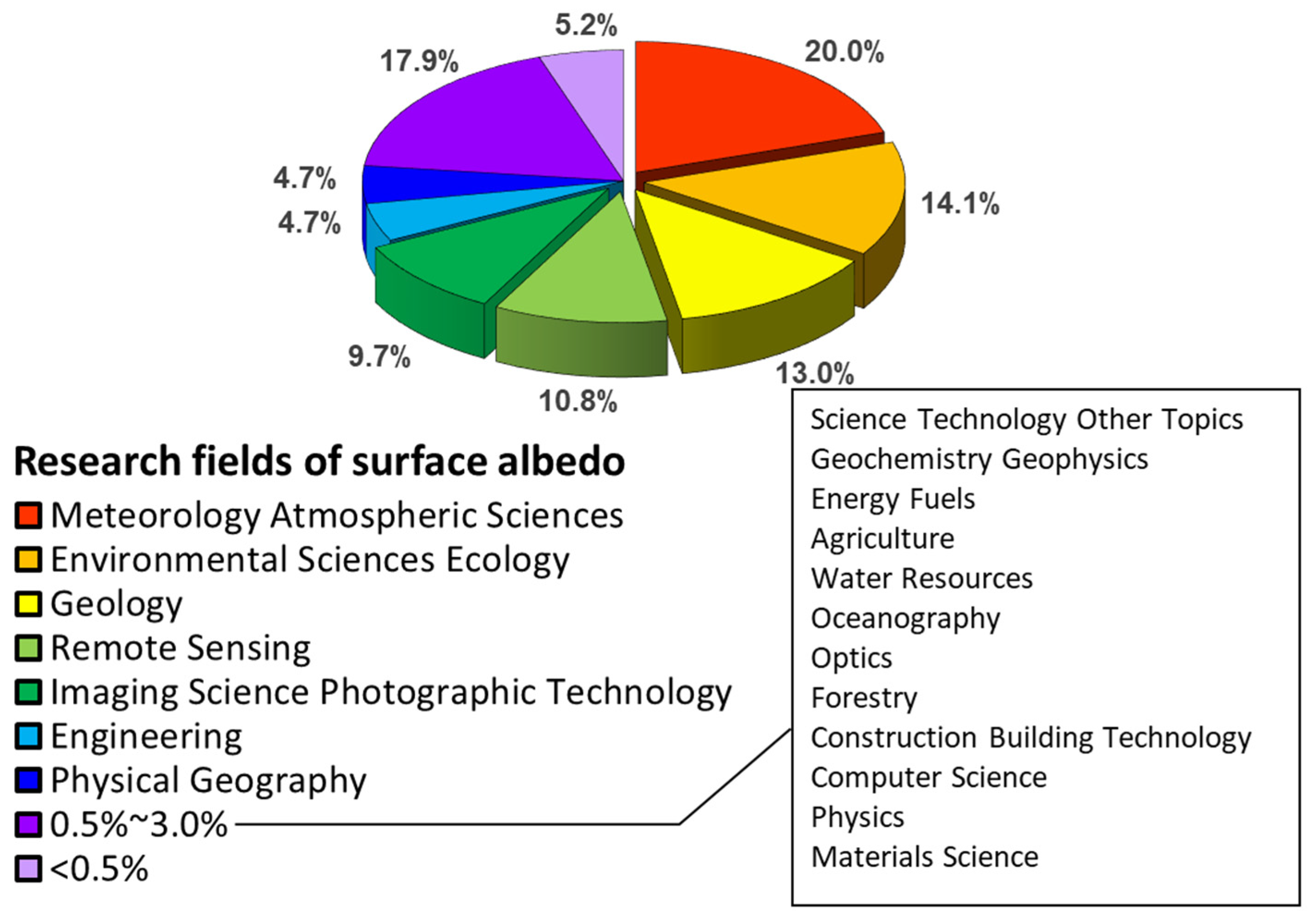
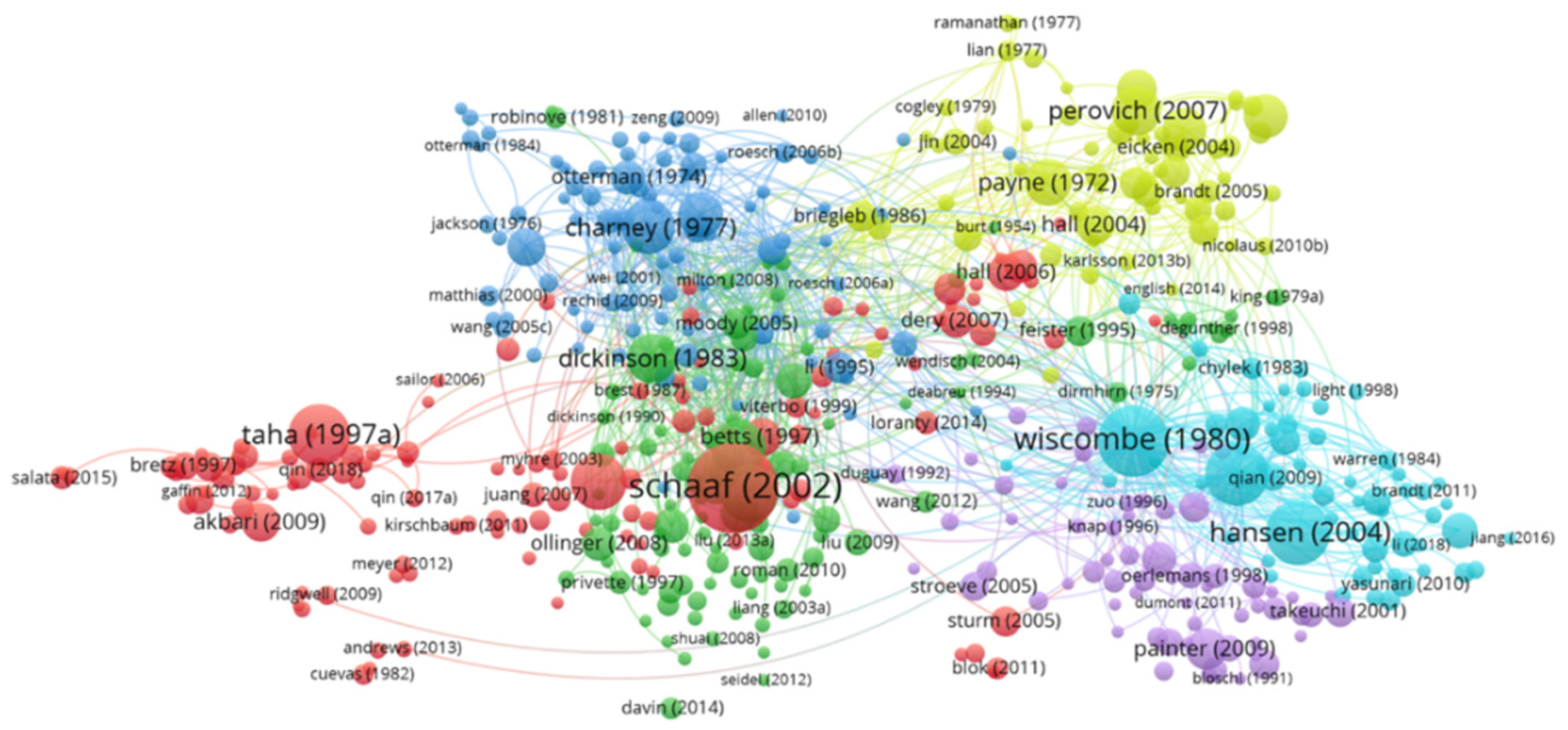
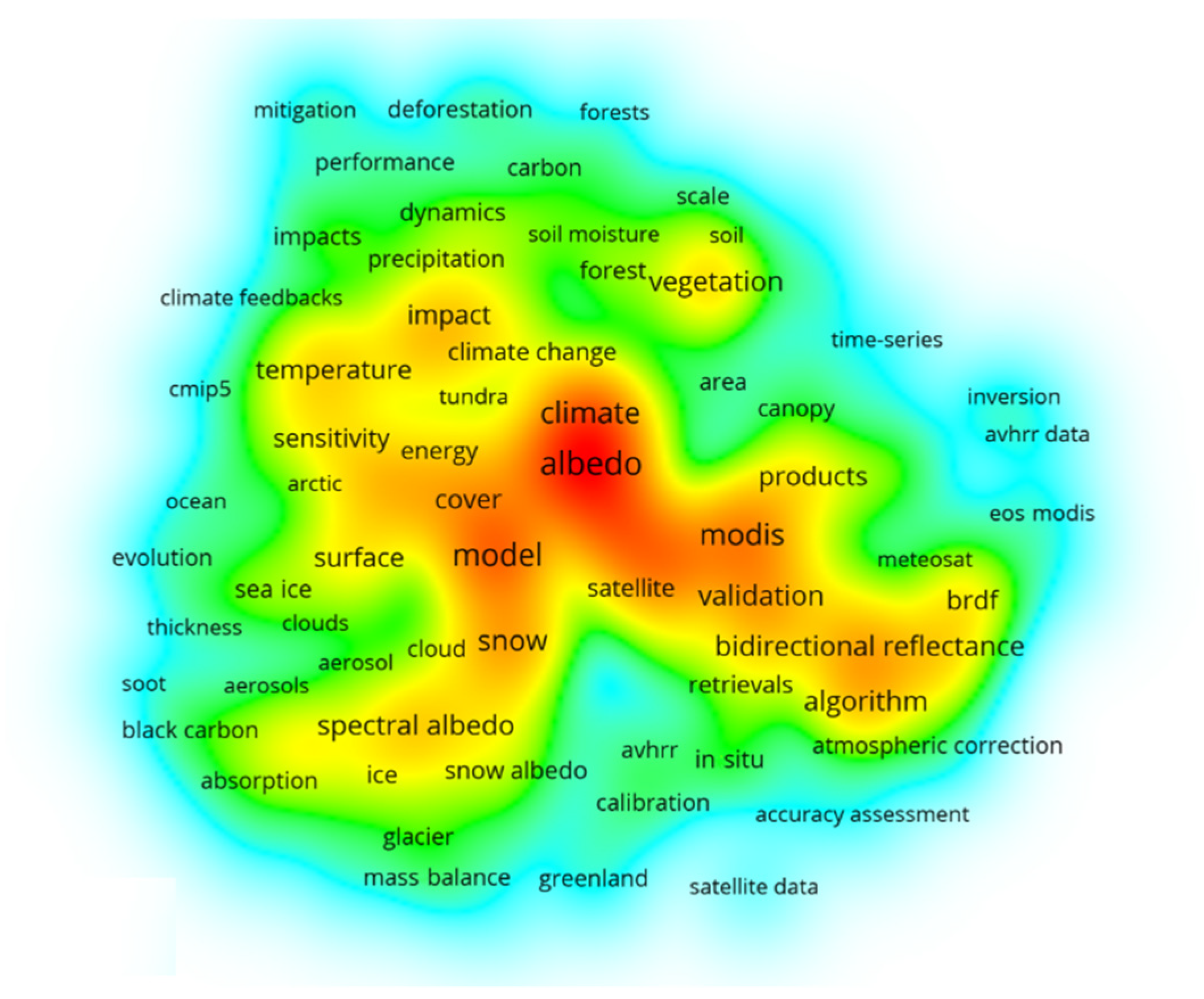
2.2. Literature Analysis
3. Variance Characteristics of Surface Albedo for Essential Land Types and Scales
3.1. Albedo Variances for Typical Land Types
3.1.1. Soil Albedo
3.1.2. Vegetation Albedo
3.1.3. Snow, Ice and Water Albedos
3.1.4. Urban Albedo
3.2. Albedo Variances for Mixed Land Types
3.3. Albedo Variances for Special Objects
3.4. Discussion of Albedo Variances Characteristics
4. Climate Feedback and Management Strategy for Surface Albedo
4.1. Monitoring Short-to-Long-Term Albedo Change and Climate Effects
4.1.1. Relationships between Surface Albedo Variance and Climate Feedback
4.1.2. Albedo Variances Induced by Anthropogenic Land Use
4.1.3. Application in Ecology and Climate Simulations
4.2. Economic Cost and Management Strategy for Surface Albedo
4.3. Discussion of Albedo-Induced Climate Feedback and Albedo Management Methods
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- A more specific term, “surface albedo”, is recommended for inclusion in titles and keywords instead of “albedo” to avoid confusion (e.g., planetary albedo), and the high frequency of the word “climate” indicates many efforts have been made in dealing with climate problems using surface albedo data. Although many albedo management strategies have been proposed in recent years [20], their quantity and influence are still limited and need to be further developed.
- (2)
- A significant surface albedo-induced climate feedback has been observed, and many studies focus on enhanced glacier, ice and snow melt in the Arctic and Antarctic induced by increasing global temperature, high albedo loss and albedo reduction due to impurities. However, there are some inconsistent and even controversial analyses at multiple spatiotemporal scales simulated from many climate models [109,187]. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the suitable spatiotemporal scale for different subjects, and improvements of surface albedo product and climate models are also required for accurate climate evaluation [29].
- (3)
- In addition, a series of effective management schemes regarding surface albedo show the potential to mitigate global warming, which provide practical suggestions for achieving CO2 emission peaks and carbon-neutral goals worldwide. The LCA method should be used for surface albedo-induced climate feedback analysis to avoid inconsistencies in conclusions [106], and more coordinated research among terrestrial ecologists, resource managers, and coupled climate modellers is needed to support the making of climate policies [24]. Through the improvements to the spatiotemporal resolution of satellite observations and remote sensing from airborne observations, surface albedo monitoring at finer levels would help better understand environmental and climate dynamic processes as well as facilitate interventions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviations | Full Name |
| ABCD | Albedo, Building Green, Control of Global Warming and Desertification |
| AOD | Aerosol Optical Depth |
| BRDF | Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function |
| BSA | Black-Sky Albedo |
| CCSM | Community Climate System Model |
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| CMIP | Coupled Model Intercomparison Project |
| EBM | Energy Balance Model |
| ECV | Essential Climate Variable |
| FVC | Fractional Vegetation Cover |
| GCOS | Global Climate Observing System |
| GLASS | Global Land Surface Satellite |
| GPP | Gross Primary Productivity |
| GWP | Global Warming Potential |
| IGBP | International Geosphere-Biosphere Program |
| IPCC | Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change |
| LAI | Leaf Area Index |
| LCA | Life Cycle Assessment |
| MODIS | Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer |
| MUST | Model for Urban Surface Temperature |
| NIR | Near-Infrared |
| PISM | Parallel Ice Sheet Model |
| RAA | Relative Azimuth Angle |
| RRM | Retroreflective Materials |
| SAF | Snow Albedo Feedback |
| SDG | Sustainable Development Goals |
| SIAF | Sea-Ice Albedo Feedback |
| SSA | Single Scattering Albedo |
| SZA | Solar Zenith Angle |
| TOA | Top of Atmosphere |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| UHI | Urban Heat Island |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| VZA | View Zenith Angle |
| WMO | World Meteorological Organization |
| WRF | Weather Research and Forecasting |
| WSA | White-Sky Albedo |
References
- Dickinson, R.E. Land Surface Processes and Climate-Surface Albedos and Energy Balance. Adv. Geophys. 1983, 25, 305–353. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson-Sellers, A.; Wilson, M.F. Surface Albedo Data for Climatic Modeling. Rev. Geophys. 1983, 21, 1743–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, R.E. Land Processes in Climate Models. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 51, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wang, D.; He, T.; Yu, Y. Remote Sensing of Earth’s Energy Budget: Synthesis and Review. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2019, 12, 737–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, P.; Katavouta, A.; Roussenov, V.M.; Foster, G.L.; Rohling, E.J.; Williams, R.G. Pathways to 1.5 Degrees C and 2 Degrees C Warming Based on Observational and Geological Constraints. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, R.J.; Fuglestvedt, J.S.; Friedlingstein, P.; Rogelj, J.; Grubb, M.J.; Matthews, H.D.; Skeie, R.B.; Forster, P.M.; Frame, D.J.; Allen, A.R. Emission Budgets and Pathways Consistent with Limiting Warming to 1.5 °C. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, F.E.L.; Frame, D.J.; Otto, A.; Allen, M.R. Embracing Uncertainty in Climate Change Policy. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson-Delmotte, V.; Zhai, P.; Pirani, A.; Connors, S.L.; Péan, C.; Berger, S.; Caud, N.; Chen, Y.; Goldfarb, L.; Gomis, M.I.; et al. IPCC, 2021: Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Taalas, P. The Global Observing System for Climate: Implementation Needs; GCOS: Guayaquil, Ecuador, 2016; pp. 1–325. [Google Scholar]
- Corner, S.P. The Sixth Major IPCC Assessment Report and its Implications: 15 September 2021. Weather 2022, 77, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaaf, C.B.; Gao, F.; Strahler, A.H.; Lucht, W.W.; Li, X.W.; Tsang, T.; Strugnell, N.C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Jin, Y.F.; Muller, J.P.; et al. First Operational BRDF, Albedo Nadir Reflectance Products from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.L. Narrowband to Broadband Conversions of Land Surface Albedo I Algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 213–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Liang, S.; Liu, Q.; He, T.; Liu, S.; Li, X. Mapping Surface Broadband Albedo from Satellite Observations: A Review of Literatures on Algorithms and Products. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 990–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.L.; Zhao, X.; Liu, S.H.; Yuan, W.P.; Cheng, X.; Xiao, Z.Q.; Zhang, X.T.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, J.; Tang, H.R.; et al. A Long-Term Global LAnd Surface Satellite (GLASS) Data-Set for Environmental Studies. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2013, 6, 5–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Schaaf, C.B.; Sun, Q.; Shuai, Y.; Roman, M.O. Capturing Rapid Land Surface Dynamics with Collection V006 MODIS BRDF/NBAR/Albedo (MCD43) Products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 207, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birchfield, G.E.; Wertman, J. Topography, Albedo-Temperature Feedback, and Climate Sensitivity. Science 1983, 219, 284–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, V.; Manninen, T.; Riihela, A. High Temporal Resolution Estimations of the Arctic Sea Ice Albedo during the Melting and Refreezing Periods of the Years 2003-2011. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shi, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y. An Overview of Snow Albedo Sensitivity to Black Carbon Contamination and Snow Grain Properties Based on Experimental Datasets across the Northern Hemisphere. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2020, 6, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravitz, B.; Rasch, P.J.; Wang, H.; Robock, A.; Gabriel, C.; Boucher, O.; Cole, J.N.S.; Haywood, J.; Ji, D.; Jones, A.; et al. The Climate Effects of Increasing Ocean Albedo: An Idealized Representation of Solar Geoengineering. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 13097–13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotana, F.; Rossi, F.; Filipponi, M.; Coccia, V.; Pisello, A.L.; Bonamente, E.; Petrozzi, A.; Cavalaglio, G. Albedo Control as an Effective Strategy to Tackle Global Warming: A Case Study. Appl. Energy 2014, 130, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueymard, C.A.; Lara-Fanego, V.; Sengupta, M.; Xie, Y. Surface Albedo and Reflectance: Review of Definitions, Angular and Spectral Effects, and Intercomparison of Major Data Sources in Support of Advanced Solar Irradiance Modeling over the Americas. Sol. Energy. 2019, 182, 194–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wen, J.; Tang, Y.; Ma, M.; You, D.; Dou, B.; Wu, X.; Zhu, X.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Q. A Web-Based Land Surface Remote Sensing Products Validation System (LAPVAS): Application to Albedo Product. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2018, 11, 308–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loew, A.; Bennartz, R.; Fell, F.; Lattanzio, A.; Doutriaux-Boucher, M.; Schulz, J. A Database of Global Reference Sites to Support Validation of Satellite Surface Albedo Datasets (SAVS 1.0). Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2016, 8, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, R.M.; Zhao, K.; Jackson, R.B.; Cherubini, F. Quantifying Surface Albedo and Other Direct Biogeophysical Climate Forcings of Forestry Activities. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 3246–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Kaloush, K.E. Environmental Impacts of Reflective Materials: Is High Albedo a ‘Silver Bullet’ for Mitigating Urban Heat Island? Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2015, 47, 830–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotaling, S.; Lutz, S.; Dial, R.J.; Anesio, A.M.; Benning, L.G.; Fountain, A.G.; Kelley, J.L.; McCutcheon, J.; Skiles, S.M.; Takeuchi, N.; et al. Biological Albedo Reduction on Ice Sheets, Glaciers, and Snowfields. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 220, 103728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thackeray, C.W.; Fletcher, C.G. Snow Albedo Feedback: Current Knowledge, Importance, Outstanding Issues and Future Directions. Prog. Phys. Geogr.-Earth Environ. 2016, 40, 392–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Takeuchi, N. Unmasking Photogranulation in Decreasing Glacial Albedo and Net Autotrophic Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 6391–6404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, R.M.; Lund, M.T. CO2-equivalence Metrics for Surface Albedo Change Based on the Radiative Forcing Concept: A Critical Review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 9887–9907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.; Parisi, A.V. Ultraviolet Radiation Albedo and Reflectance in Review: The Influence to Ultraviolet Exposure in Occupational Settings. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divine, D.V.; Granskog, M.A.; Hudson, S.R.; Pedersen, C.A.; Karlsen, T.I.; Divina, S.A.; Renner, A.H.H.; Gerland, S. Regional Melt-Pond Fraction and Albedo of Thin Arctic First-Year Drift Ice in Late Summer. Cryosphere 2015, 9, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thackeray, C.W.; Hall, A. An Emergent Constraint on Future Arctic Sea-Ice Albedo Feedback. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicodemus, F.E.; Richmond, J.C.; Hsia, J.J.; Ginsberg, I.W.; Limperis, T. Geometrical Considerations and Nomenclature for Reflectance; National Bureau of Standards: Washington, DC, USA, 1977; pp. 1–52.
- Vermote, E.F.; Tanre, D.; Deuze, J.L.; Herman, M.; Morcette, J. Second Simulation of the Satellite Signal in the Solar Spectrum, 6S: An overview. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucht, W.W.; Schaaf, C.B.; Strahler, A.H. An Algorithm for the Retrieval of Albedo from Space Using Semiempirical BRDF Models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 977–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Liang, S.L.; Wang, D.D.; Cao, Y.F.; Gao, F.; Yu, Y.Y.; Feng, M. Evaluating Land Surface Albedo Estimation from Landsat MSS, TM, ETM Plus, and OLI Data Based on the Unified Direct Estimation Approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiao, Z.; Dong, Y.; He, T.; Ding, A.; Yin, S.; Zhang, H.; Cui, L.; Chang, Y.; Guo, J.; et al. Development of the Direct-Estimation Albedo Algorithm for Snow-Free Landsat TM Albedo Retrievals Using Field Flux Measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 2020, 58, 1550–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.S.; Schaaf, C.B.; Strahler, A.H.; Chopping, M.J.; Roman, M.O.; Shuai, Y.M.; Woodcock, C.E.; Hollinger, D.Y.; Fitzjarrald, D.R. Evaluation of MODIS Albedo Product (MCD43A) over Grassland, Agriculture and Forest Surface Types during Dormant and Snow-Covered Periods. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, S.; Yu, Y.; Wang, D. Developing Land Surface Directional Reflectance and Albedo Products from Geostationary GOES-R and Himawari Data: Theoretical Basis, Operational Implementation, and Validation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, C.; Istomina, L.; Tietsche, S.; Jkel, E.; Heygster, G. Broadband Albedo of Arctic Sea Ice from MERIS Optical Data. Cryosphere 2020, 14, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendergrass, A.G.; Conley, A.; Vitt, F.M. Surface and Top-of-Atmosphere Radiative Feedback Kernels for CESM-CAM5. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, R.M.; O’Halloran, T.L. Developing a Monthly Radiative Kernel for Surface Albedo Change from Satellite Climatologies of Earth’s Shortwave Radiation Budget: CACK V1.0. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 3975–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, H.A.; Bryn, A.; Hofgaard, A.; Karstensen, J.; Kvalevag, M.M.; Peters, G.P. Climate Warming Feedback from Mountain Birch Forest Expansion: Reduced Albedo Dominates Carbon Uptake. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2344–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, G.L.; O’Brien, D.; Webster, P.J.; Pilewski, P.; Kato, S.; Li, J. The Albedo of Earth. Rev. Geophys. 2015, 53, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, D.J.; Feingold, G.; Jacobson, A.R.; Loeb, N. Detection Limits of Albedo Changes Induced by Climate Engineering. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.Z. Global Direct Radiative Forcing Due to Multicomponent Anthropogenic and Natural Aerosols. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2001, 106, 1551–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, S.E. Are Global Cloud Albedo and Climate Controlled by Marine-Phytoplankton. Nature 1988, 336, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, R.J.; Lovelock, J.E.; Andreae, M.O.; Warren, S.G. Oceanic Phytoplankton, Atmospheric Sulfur, Cloud Albedo and Climate. Nature 1987, 326, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carder, K.L.; Liu, C.C.; Lee, Z.P.; English, D.C.; Patten, J.; Chen, F.R.; Ivey, J.E.; Davis, C.O. Illumination and Turbidity Effects on Observing Faceted Bottom Elements with Uniform Lambertian Albedos. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, B.; Liu, W.C.; Grumpe, A.; Woehler, C. Construction of Pixel-Level Resolution DEMs from Monocular Images by Shape and Albedo from Shading Constrained with Low-Resolution DEM. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2018, 140, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, N.K.; Cook, T.A.; Wilton, K.P.; Chakrabarti, S.; France, K.; Gordon, K.D. Far-Ultraviolet Dust Albedo Measurements in the Upper Scorpius Cloud Using the Spinr Sounding Rocket Experiment. Astrophys. J. 2009, 706, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luszik-Bhadra, M.; Zimbal, A.; Busch, F.; Eichelberger, A.; Engelhardt, J.; Figel, M.; Frasch, G.; Guenther, K.; Jordan, M.; Martini, E.; et al. Albedo Neutron Dosimetry in Germany: Regulations and Performance. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2014, 162, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmet, T. Albedo Factor Determination of some Selected 3D Alloy Samples. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2021, 169, 109505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabasari, I.; Pettolino, F.; Liao, M.; Bacic, A. Pectic Polysaccharides from Mature Orange (Citrus Sinensis) Fruit Albedo Cell Walls: Sequential Extraction and Chemical Characterization. Carbohyd. Polym. 2011, 84, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, A.; Meadows, A.J. Long-Term Variations in Albedo and Surface-Temperature of Earth. Nature 1975, 254, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohoe, A.; Battisti, D.S. Atmospheric and Surface Contributions to Planetary Albedo. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 4402–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.G.; Crutzen, P.J. Was Breaking the Taboo on Research on Climate Engineering via Albedo Modification a Moral Hazard, or a Moral Imperative? Earths Future 2017, 5, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfield, E. From the Science of Science to Scientometrics Visualizing the History of Science with HistCite Software. J. Informetr. 2009, 3, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, H. Urban Climates and Heat Islands: Albedo, Evapotranspiration, and Anthropogenic Heat. Energy Build. 1997, 25, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, R.A. Offset of the Potential Carbon Sink from Boreal Forestation by Decreases in Surface Albedo. Nature 2000, 408, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charney, J.; Quirk, W.J.; Chow, S.H.; Kornfield, J. Comparative-Study of Effects of Albedo Change on Drought in Semi-Arid Regions. J. Atmos. Sci. 1977, 34, 1366–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perovich, D.K.; Light, B.; Eicken, H.; Jones, K.F.; Runciman, K.; Nghiem, S.V. Increasing Solar Heating of the Arctic Ocean and Adjacent Seas, 1979-2005: Attribution and Role in the Ice-Albedo Feedback. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L19505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, R.E. Albedo of Sea-Surface. J. Atmos. Sci. 1972, 29, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.; Nazarenko, L. Soot Climate Forcing Via Snow and Ice Albedos. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiscombe, W.J.; Warren, S.G. A Model for the Spectral Albedo of Snow 1. Pure Snow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1980, 37, 2712–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiao, Z.; Zhao, C.; Guo, J.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Yin, S.; Zhang, H.; Cui, L.; et al. Evaluation of BRDF Information Retrieved from Time-Series Multiangle Data of the Himawari-8 AHI. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Breon, F.M.; Dong, Y.; Schaaf, C.B.; Roman, M.O.; Wang, Z.; Cui, L.; Yin, S.; Ding, A.; et al. The Influence of Spatial Resolution on the Angular Variation Patterns of Optical Reflectance as Retrieved from MODIS and POLDER Measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cereceda-Balic, F.; Vidal, V.; Florencia Ruggeri, M.; Gonzalez, H.E. Black Carbon Pollution in Snow and its Impact on Albedo near the Chilean Stations on the Antarctic Peninsula: First Results. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardi, S.; Magnani, F.; Nole, A.; Van Noije, T.; Borghetti, M. A Global Assessment of Forest Surface Albedo and its Relationships with Climate and Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moody, E.G.; King, M.D.; Schaaf, C.B.; Hall, D.K.; Platnick, S. Northern Hemisphere Five-Year Average (2000–2004) Spectral Albedos of Surfaces in the Presence of Snow: Statistics Computed from Terra MODIS Land Products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 111, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.G.; Donald, K.P. Seasonal and Spatial Evolution of Albedo in a Snow-Ice-Land-Ocean Environment. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2004, 109, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, J.; Chang, D.Y.; Lelieveld, J.; Pozzer, A.; Kim, J.; Yum, S.S. Empirical Evidence of a Positive Climate Forcing of Aerosols at Elevated Albedo. Atmos. Res. 2019, 229, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, S.E.; Menon, S. Aerosol Direct, Indirect, Semidirect, and Surface Albedo Effects from Sector Contributions Based on the IPCC AR5 Emissions for Preindustrial and Present-Day Conditions. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2012, 117, D1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Hu, Y.; Chen, N.; Wang, D.; Huang, J.; Stamnes, K. High Cloud Coverage over Melted Areas Dominates the Impact of Clouds on the Albedo Feedback in the Arctic. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.; Ma, H.; Liang, S.; He, T. Extension of the Hapke Model to the Spectral Domain to Characterize Soil Physical Properties. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widlowski, J.L.; Mio, C.; Disney, M.; Adams, J.; Andredakis, I.; Atzberger, C.; Brennan, J.; Busetto, L.; Chelle, M.; Ceccherini, G.; et al. The Fourth Phase of the Radiative Transfer Model Intercomparison (RAMI) Exercise: Actual Canopy Scenarios and Conformity Testing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 418–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokhanovsky, A.A.; Zege, E.P. Scattering Optics of Snow. Appl. Optics 2004, 43, 1589–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, T.; Aoki, T.; Fukabori, M.; Hachikubo, A.; Tachibana, Y.; Nishio, F. Effects of Snow Physical Parameters on Spectral Albedo and Bidirectional Reflectance of Snow Surface. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2000, 105, 10219–10236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Ding, A.; Kokhanovsky, A.; Schaaf, C.; Breon, F.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yin, S.; et al. Development of a Snow Kernel to Better Model the Anisotropic Reflectance of Pure Snow in a Kernel-Driven BRDF Model Framework. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Q.; Tang, Y.; Dou, B. An Improved Land-Surface Albedo Algorithm with DEM in Rugged Terrain. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 11, 883–887. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J. Diurnal Asymmetry in Surface Albedo. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1998, 92, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, M.O.; Gatebe, C.K.; Schaaf, C.B.; Poudyal, R.; Wang, Z.S.; King, M.D. Variability in Surface BRDF at Different Spatial Scales (30 M-500 M) over a Mixed Agricultural Landscape as Retrieved from Airborne and Satellite Spectral Measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2184–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguntunde, P.G.; Ajayi, A.E.; van de Giesen, N. Tillage and Surface Moisture Effects on Bare-Soil Albedo of a Tropical Loamy Sand. Soil Till. Res. 2006, 85, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cierniewski, J.; Karnieli, A.; Kazmierowski, C.; Krolewicz, S.; Piekarczyk, J.; Lewinska, K.; Goldberg, A.; Wesolowski, R.; Orzechowski, M. Effects of Soil Surface Irregularities on the Diurnal Variation of Soil Broadband Blue-Sky Albedo. IEEE J.-STARS 2015, 8, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kala, J.; Evans, J.P.; Pitman, A.J.; Schaaf, C.B.; Decker, M.; Carouge, C.; Mocko, D.; Sun, Q. Implementation of a Soil Albedo Scheme in the CABLEv1.4B Land Surface Model and Evaluation Against MODIS Estimates over Australia. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 2121–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Mejia, Z.M.; Papuga, S.A.; Swetish, J.B.; Van Leeuwen, W.J.D.; Szutu, D.; Hartfield, K. Quantifying the Influence of Deep Soil Moisture on Ecosystem Albedo: The Role of Vegetation. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 4038–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimaki, H.; Shiozawa, S.; Inoue, M. Effect of Salty Crust on Soil Albedo. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2003, 118, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Bowker, M.A. Moss-Biocrusts Strongly Decrease Soil Surface Albedo, Altering Land-Surface Energy Balance in a Dryland Ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usowicz, B.; Lipiec, J.; Lukowski, M.; Marczewski, W.; Usowicz, J. The Effect of Biochar Application on Thermal Properties and Albedo of Loess Soil under Grassland and Fallow. Soil Till. Res. 2016, 164, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzi, E.; Genesio, L.; Toscano, P.; Pieri, M.; Miglietta, F. Mimicking Biochar-Albedo Feedback in Complex Mediterranean Agricultural Landscapes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 84014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, S.; Bright, R.M.; Fischer, D.; Schulz, H.; Glaser, B. Albedo Impact on the Suitability of Biochar Systems to Mitigate Global Warming. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12726–12734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Mikami, M.; Yamazaki, A.; Yabuki, S.; Yamada, Y.; Ishizuka, M.; Zeng, F.J.; Gao, W.D.; Sun, J.Y.; Liu, L.C.; et al. Spectral Albedo of Desert Surfaces Measured in Western and Central China. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2005, 83, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, R.M.; Bogren, W.; Bernier, P.; Astrup, R. Carbon-Equivalent Metrics for Albedo Changes in Land Management Contexts: Relevance of the Time Dimension. Ecol. Appl. 2016, 26, 1868–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollinger, S.V.; Richardson, A.D.; Martin, M.E.; Hollinger, D.Y.; Frolking, S.E.; Reich, P.B.; Plourde, L.C.; Katul, G.G.; Munger, J.W.; Oren, R.; et al. Canopy Nitrogen, Carbon Assimilation, and Albedo in Temperate and Boreal Forests: Functional Relations and Potential Climate Feedbacks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19336–19341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halim, M.A.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Thomas, S.C. Stand Age and Species Composition Effects on Surface Albedo in a Mixedwood Boreal Forest. Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 4357–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Wang, S.; Dai, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Shugart, H.H. Forest Greening Increases Land Surface Albedo during the Main Growing Period between 2002 and 2019 in China. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020J–e33582J. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibakhshi, S.; Naimi, B.; Hovi, A.; Crowther, T.W.; Rautiainen, M. Quantitative Analysis of the Links between Forest Structure and Land Surface Albedo on a Global Scale. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 246, 111854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukes, P.; Stenberg, P.; Rautiainen, M. Relationship between Forest Density and Albedo in the Boreal Zone. Ecol. Model. 2013, 261, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuusinen, N.; Tomppo, E.; Shuai, Y.; Berninger, F. Effects of Forest Age on Albedo in Boreal Forests Estimated from MODIS and Landsat Albedo Retrievals. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridgwell, A.; Singarayer, J.S.; Hetherington, A.M.; Valdes, P.J. Tackling Regional Climate Change by Leaf Albedo Bio-Geoengineering. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollinger, D.Y.; Ollinger, S.V.; Richardson, A.D.; Meyers, T.P.; Dail, D.B.; Martin, M.E.; Scott, N.A.; Arkebauer, T.J.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Clark, K.L.; et al. Albedo Estimates for Land Surface Models and Support for a New Paradigm Based on Foliage Nitrogen Concentration. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 696–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riihela, A.; Manninen, T. Measuring the Vertical Albedo Profile of a Subarctic Boreal Forest Canopy. Silva Fenn. 2008, 42, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautiainen, M.; Mottus, M.; Yanez-Rausell, L.; Homolova, L.; Malenovsky, Z.; Schaepman, M.E. A Note on Upscaling Coniferous Needle Spectra to Shoot Spectral Albedo. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhao, G.; Dong, J.; Ge, Q.; Tao, J.; Zhang, X.; Qi, Y.; Doughty, R.B.; Xiao, X. Spatial, Temporal, and Spectral Variations in Albedo Due to Vegetation Changes in China’s Grasslands. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2019, 152, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira, M.; Weiss, M.; Baret, F.; Courault, D.; Hagolle, O.; Gallego-Elvira, B.; Olioso, A. The MODIS (Collection V006) BRDF/albedo Product MCD43D: Temporal Course Evaluated over Agricultural Landscape. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 170, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Wang, J.; Feng, Y.; Wang, M.; Qin, Z.; Dunn, J.B. Consideration of Land Use Change-Induced Surface Albedo Effects in Life-Cycle Analysis of Biofuels. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 2855–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loranty, M.M.; Goetz, S.J.; Beck, P.S.A. Tundra Vegetation Effects on pan-Arctic Albedo. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 24014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Lu, H.; Yin, C.; Xue, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Kang, Y.; He, L.; Heiskanen, J. Vegetation Response to Climate Zone Dynamics and its Impacts on Surface Soil Water Content and Albedo in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teuling, A.J.; Seneviratne, S.I. Contrasting Spectral Changes Limit Albedo Impact on Land-Atmosphere Coupling during the 2003 European Heat Wave. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iler, A.M.; Walwema, A.S.; Steltzer, H.; Blázquez-Castro, A. Can Flowers Affect Land Surface Albedo and Soil Microclimates? Int. J. Biometeorol. 2021, 65, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, S.G.; Wiscombe, W.J. A Model for the Spectral Albedo of Snow 2. Snow Containing Atmospheric Aerosols. J. Atmos. Sci. 1980, 37, 2734–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, S.; Oglesby, R.J. An Improved Snow Hydrology for GCMs 1. Snow Cover Fraction, Albedo, Grain-Size, and Age. Clim. Dyn. 1994, 10, 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Marks, A.A.; King, M.D. The Effect of Snow/Sea Ice Type on the Response of Albedo and Light Penetration Depth (E-Folding Depth) to Increasing Black Carbon. Cryosphere 2014, 8, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallet, J.; Domine, F.; Arnaud, L.; Picard, G.; Savarino, J. Vertical Profile of the Specific Surface Area and Density of the Snow at Dome C and on a Transect to Dumont D’Urville, Antarctica—Albedo Calculations and Comparison to Remote Sensing Products. Cryosphere 2011, 5, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhermitte, S.; Abermann, J.; Kinnard, C. Albedo over Rough Snow and Ice Surfaces. Cryosphere 2014, 8, 1069–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huovinen, P.; Ramirez, J.; Gomez, I. Remote Sensing of Albedo-Reducing Snow Algae and Impurities in the Maritime Antarctica. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 146, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, T.; Kang, S.; Shangguan, D.; Luo, X. Albedo Reduction as an Important Driver for Glacier Melting in Tibetan Plateau and its Surrounding Areas. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 220, 103735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadley, O.L.; Kirchstetter, T.W. Black-Carbon Reduction of Snow Albedo. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riihela, A.; Manninen, T.; Laine, V. Observed Changes in the Albedo of the Arctic Sea-Ice Zone for the Period 1982-2009. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 895–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Liang, S.L.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.J.; Feng, Y.B.; Liu, S.H. Estimating Arctic Sea-Ice Shortwave Albedo from MODIS Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.; Lee, C.S.; Kim, H.; Huh, M.; Han, K. Relationship between Sea Ice Concentration and Sea Ice Albedo over Antarctica. Korean J. Remote Sens. 2015, 31, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applegate, P.J.; Keller, K. How Effective is Albedo Modification (Solar Radiation Management Geoengineering) in Preventing Sea-Level Rise from the Greenland Ice Sheet? Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 84018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yallop, M.L.; Anesio, A.M.; Perkins, R.G.; Cook, J.; Telling, J.; Fagan, D.; MacFarlane, J.; Stibal, M.; Barker, G.; Bellas, C.; et al. Photophysiology and Albedo-Changing Potential of the Ice Algal Community on the Surface of the Greenland Ice Sheet. ISME J. 2012, 6, 2302–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greuell, W.; Knap, W.H. Remote Sensing of the Albedo and Detection of the Slush Line on the Greenland Ice Sheet. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2000, 105, 15567–15576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leidman, S.Z.; Rennermalm, A.K.; Muthyala, R.; Guo, Q.; Overeem, I. The Presence and Widespread Distribution of Dark Sediment in Greenland Ice Sheet Supraglacial Streams Implies Substantial Impact of Microbial Communities on Sediment Deposition and Albedo. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, L88444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedstone, A.J.; Cook, J.M.; Williamson, C.J.; Hofer, S.; McCutcheon, J.; Irvine-Fynn, T.; Gribbin, T.; Tranter, M. Algal Growth and Weathering Crust State Drive Variability in Western Greenland Ice Sheet Ice Albedo. Cryosphere 2020, 14, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leshkevich, G.A. Machine Classification of Fresh-Water Ice Types from Landsat-1 Digital Data Using Ice Albedos as Training Sets. Remote Sens. Environ. 1985, 17, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Lepparanta, M.; Cheng, B.; Li, Z. Influence of Melt-Pond Depth and Ice Thickness on Arctic Sea-Ice Albedo and Light Transmittance. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2016, 124, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carns, R.C.; Brandt, R.E.; Warren, S.G. Salt Precipitation in Sea Ice and its Effect on Albedo, with Application to Snowball Earth. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2015, 120, 7400–7412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, R.; Dagsson-Waldhauserova, P.; Moeller, M.; Kukla, P.A.; Schneider, C.; Gudmundsson, M.T. Persistent Albedo Reduction on Southern Icelandic Glaciers Due to Ashfall from the 2010 Eyjafjallajokull Eruption. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbi, J.; Huss, M.; Bauder, A.; Cao, F.; Schwikowski, M. The Impact of Saharan Dust and Black Carbon on Albedo and Long-Term Mass Balance of an Alpine Glacier. Cryosphere 2015, 9, 1385–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, S.N.; Menounos, B. The Influence of Forest Fires Aerosol and Air Temperature on Glacier Albedo, Western North America. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 267, 112732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Qu, Y.; Liang, S. Estimation of the Ocean Water Albedo from Remote Sensing and Meteorological Reanalysis Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 850–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seferian, R.; Baek, S.; Boucher, O.; Dufresne, J.; Decharme, B.; Saint-Martin, D.; Roehrig, R. An Interactive Ocean Surface Albedo Scheme (OSAv1.0): Formulation and Evaluation in ARPEGE-Climat (V6.1) and LMDZ (V5A). Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnett, G.; Feddersen, F. The Competing Effects of Breaking Waves on Surfzone Heat Fluxes: Albedo versus Wave Heating. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2018, 123, 7172–7184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, J.A.; Jackson, L.S.; Forster, P.M. Can Increasing Albedo of Existing Ship Wakes Reduce Climate Change? J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2016, 121, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlfahrt, G.; Tomelleri, E.; Hammerle, A. The Albedo-Climate Penalty of Hydropower Reservoirs. Nature Energy 2021, 6, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argaman, E.; Keesstra, S.D.; Zeiliguer, A. Monitoring the Impact of Surface Albedo on a Saline Lake in SW Russia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2012, 23, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, A.; Moore, R.D. Influence of Turbidity and Aeration on the Albedo of Mountain Streams. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 4477–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groleau, D.; Mestayer, P.G. Urban Morphology Influence on Urban Albedo: A Revisit with the SOLENE Model. Bound.-Lay. Meteorol. 2013, 147, 301–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, Y. The Impact of Building Density and Building Height Heterogeneity on Average Urban Albedo and Street Surface Temperature. Build. Environ. 2015, 90, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morini, E.; Castellani, B.; Presciutti, A.; Anderini, E.; Filipponi, M.; Nicolini, A.; Rossi, F. Experimental Analysis of the Effect of Geometry and Facade Materials on Urban District’s Equivalent Albedo. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Farnham, C.; Emura, K. Development of a Retro-Reflective Material as Building Coating and Evaluation on Albedo of Urban Canyons and Building Heat Loads. Energy Build. 2015, 103, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, R.; Egolf, M.; Chen, S.; Berdahl, P. Experimental Comparison of Pyranometer, Reflectometer, and Spectrophotometer Methods for the Measurement of Roofing Product Albedo. Sol. Energy 2020, 206, 826–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurthy, P.; Sun, T.; Rule, K.; Bou-Zeid, E. The Joint Influence of Albedo and Insulation on Roof Performance: An Observational Study. Energy Build. 2015, 93, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, J.; Hou, S.; Liu, M. Field and Laboratory Measurement of Albedo and Heat Transfer for Pavement Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 202, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Roesler, J. Aging Albedo Model for Asphalt Pavement Surfaces. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 117, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, C.; Jonas, T. Influence of Canopy Shading and Snow Coverage on Effective Albedo in a Snow-Dominated Evergreen Needleleaf Forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 214, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manninen, T.; Stenberg, P. Simulation of the Effect of Snow Covered Forest Floor on the Total Forest Albedo. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.; Lindgren, B.S.; Jackson, P. Rock Albedo and Monitoring of Thermal Conditions in Respect of Weathering: Some Expected and some Unexpected Results. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 2005, 30, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.D.; Davis, F.J.; Badiee, A.; Hadley, P.; Twitchen, C.; Pearson, S.; Gargan, K. Optical and Thermal Properties of Commercial Polymer Film, Modeling the Albedo Effect. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, e50581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Ramamoorthi, R. Interactive Albedo Editing in Path-Traced Volumetric Materials. ACM Trans. Graph. 2013, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.T.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Y.D.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, Q.; Li, X.W. An Algorithm for Retrieval of Surface Albedo from Small View-Angle Airborne Observations through the Use of BRDF Archetypes as Prior Knowledge. IEEE J.-STARS 2015, 8, 3279–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canisius, F.; Wang, S.; Croft, H.; Leblanc, S.G.; Russell, H.A.J.; Chen, J.; Wang, R. A UAV-Based Sensor System for Measuring Land Surface Albedo: Tested over a Boreal Peatland Ecosystem. Drones 2019, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H.; Shao, H. Albedo Indicating Land Degradation Around the Badain Jaran Desert for Better Land Resources Utilization. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, S.; Solvik, K.; Erb, A.; Goetz, S.J.; Johnstone, J.F.; Mack, M.C.; Randerson, J.T.; Roman, M.O.; Schaaf, C.L.; Turetsky, M.R.; et al. Climate Change Decreases the Cooling Effect from Postfire Albedo in Boreal North America. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 1592–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lintunen, J.; Rautiainen, A. On Physical and Social-Cost-Based CO2 Equivalents for Transient Albedo-Induced Forcing. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 190, 107204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschbaum, M.U.F.; Whitehead, D.; Dean, S.M.; Beets, P.N.; Shepherd, J.D.; Ausseil, A.G.E. Implications of Albedo Changes following Afforestation on the Benefits of Forests as Carbon Sinks. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 3687–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, H.; Menon, S.; Rosenfeld, A. Global Cooling: Increasing World-Wide Urban Albedos to Offset CO2. Clim. Chang. 2009, 94, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otterman, J. Baring High-Albedo Soils by Overgrazing—Hypothesized Desertification Mechanism. Science 1974, 186, 531–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.D.; Idso, S.B. Surface Albedo and Desertification. Science 1975, 189, 1012–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Novillo, C.J.; Arrogante-Funes, P.; Vazquez-Jimenez, R.; Berdugo, M.; Maestre, F.T. Remotely Sensed Albedo Allows the Identification of Two Ecosystem States Along Aridity Gradients in Africa. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1502–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courel, M.F.; Kandel, R.S.; Rasool, S.I. Surface Albedo and the Sahel Drought. Nature 1984, 307, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, G.; Govaerts, Y.; Haywood, J.M.; Berntsen, T.K.; Lattanzio, A. Radiative Effect of Surface Albedo Change from Biomass Burning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L20812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, F.; Visser, M.D.; Shiklomanov, A.; Dietze, M.C.; Guzman, J.A.Q.; Sanchez-Azofeifa, G.A.; De Deurwaerder, H.P.T.; Moorthy, S.M.K.; Schnitzer, S.A.; Marvin, D.C.; et al. Liana Optical Traits Increase Tropical Forest Albedo and Reduce Ecosystem Productivity. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanner, M.G.; Shell, K.M.; Barlage, M.; Perovich, D.K.; Tschudi, M.A. Radiative Forcing and Albedo Feedback from the Northern Hemisphere Cryosphere between 1979 and 2008. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Erb, A.M.; Schaaf, C.B.; Sun, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shuai, Y.; Casey, K.A.; Roman, M.O. Early Spring Post-Fire Snow Albedo Dynamics in High Latitude Boreal Forests Using Landsat-8 OLI Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Loboda, T.V.; He, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, S. Strong Cooling Induced by Stand-Replacing Fires through Albedo in Siberian Larch Forests. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, S.C.; Ceppi, P.; Croci-Maspoli, M.; Appenzeller, C. Snow-Albedo Feedback and Swiss Spring Temperature Trends. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2012, 110, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molotch, N.P.; Bales, R.C. Comparison of Ground-Based and Airborne Snow Surface Albedo Parameterizations in an Alpine Watershed: Impact on Snowpack Mass Balance. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, S.N.; Copland, L.; Thomson, L.; Burgess, D. Comparing Simple Albedo Scaling Methods for Estimating Arctic Glacier Mass Balance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 246, 111858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenaerts, J.T.M.; Lhermitte, S.; Drews, R.; Ligtenberg, S.R.M.; Berger, S.; Helm, V.; Smeets, C.J.P.P.; Van den Broeke, M.R.; Van de Berg, W.J.; Van Meijgaard, E.; et al. Meltwater Produced by Wind-Albedo Interaction Stored in an East Antarctic Ice Shelf. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.J.; Zender, C.S. Effects of Continental-Scale Snow Albedo Anomalies on the Wintertime Arctic Oscillation. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2010, 115, D23105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, G.; Domine, F.; Krinner, G.; Arnaud, L.; Lefebvre, E. Inhibition of the Positive Snow-Albedo Feedback by Precipitation in Interior Antarctica. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riihela, A.; Bright, R.M.; Anttila, K. Recent Strengthening of Snow and Ice Albedo Feedback Driven by Antarctic Sea-Ice Loss. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, P.S.A.; Goetz, S.J.; Mack, M.C.; Alexander, H.D.; Jin, Y.; Randerson, J.T.; Loranty, M.M. The Impacts and Implications of an Intensifying Fire Regime on Alaskan Boreal Forest Composition and Albedo. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 2853–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanamoorthy, P.; Song, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Sha, L.; Fan, Z.; Burman, P.K.D. Altered Albedo Dominates the Radiative Forcing Changes in a Subtropical Forest Following an Extreme Snow Event. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 6192–6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderhoof, M.Y.; Williams, C.A.; Shuai, Y.; Jarvis, D.; Kulakowski, D.; Masek, J. Albedo-Induced Radiative Forcing from Mountain Pine Beetle Outbreaks in Forests, South-Central Rocky Mountains: Magnitude, Persistence, and Relation to Outbreak Severity. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craft, K.M.; Horel, J.D. Variations in Surface Albedo Arising from Flooding and Desiccation Cycles on the Bonneville Salt Flats, Utah. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2019, 58, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphree, J.S.; Anger, C.D. An Empirical-Method for Determining Albedo Contribution to Satellite Photometer Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1980, 9, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallner, S.; Kocifaj, M. Impacts of Surface Albedo Variations on the Night Sky Brightness—A Numerical and Experimental Analysis. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2019, 239, 106648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Hou, M.; Zhao, C.; Zhen, X.; Yao, L.; Xu, Y. Human-Induced Changes of Surface Albedo in Northern China from 1992-2012. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 79, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambelluca, T.W.; Holscher, D.; Bastos, T.X.; Frazao, R.R.; Nullet, M.A.; Ziegler, A.D. Observations of Albedo and Radiation Balance over Postforest Land Surfaces in the Eastern Amazon Basin. J. Clim. 1997, 10, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, R.M.; Stromman, A.H.; Peters, G.P. Radiative Forcing Impacts of Boreal Forest Biofuels: A Scenario Study for Norway in Light of Albedo. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7570–7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreidenweis, U.; Humpenoeder, F.; Stevanovic, M.; Bodirsky, B.L.; Kriegler, E.; Lotze-Campen, H.; Popp, A. Afforestation to Mitigate Climate Change: Impacts on Food Prices under Consideration of Albedo Effects. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 85001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.Y.; Pulliainen, J.; Menard, C.B.; Johansen, B.; Oksanen, L.; Luojus, K.; Ikonen, J. Effect of Reindeer Grazing on Snowmelt, Albedo and Energy Balance Based on Satellite Data Analyses. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 135, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, G.; Kvalevag, M.M.; Schaaf, C.B. Radiative Forcing Due to Anthropogenic Vegetation Change Based on MODIS Surface Albedo Data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L21410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Lv, M.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Qu, Y. Reconstruction of Historical Land Surface Albedo Changes in China from 850 to 2015 Using Land Use Harmonization Data and Albedo Look-Up Maps. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2021EA001799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Luo, M.; Liu, Z.; Sun, J.; Wu, K.; Lin, H. The Roles of Leaf Area Index and Albedo in Vegetation Induced Temperature Changes across China Using Modelling and Observations. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, T.; Jiang, B.; Wu, D.; Tang, B. Assessing the Impacts of Urbanization on Albedo in Jing-Jin-Ji Region of China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trlica, A.; Hutyra, L.R.; Schaaf, C.L.; Erb, A.; Wang, J.A. Albedo, Land Cover, and Daytime Surface Temperature Variation across an Urbanized Landscape. Earths Future 2017, 5, 1084–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susca, T. Enhancement of Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) Methodology to Include the Effect of Surface Albedo on Climate Change: Comparing Black and White Roofs. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 163, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Lu, Q. Estimation of Albedo Effect in Pavement Life Cycle Assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 64, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, T.; Riehl, B.; Fuchs, A. Effects of Albedo and Thermal Inertia on Pavement Surface Temperatures with Convective Boundary Conditions–A CFD Study. Processes 2021, 9, 2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrijvers, P.J.C.; Jonker, H.J.J.; de Roode, S.R.; Kenjeres, S. The Effect of Using a High-Albedo Material on the Universal Temperature Climate Index within a Street Canyon. Urban Clim. 2016, 17, 284–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, G.; Masson, S.; Durand, F.; Terray, P.; Berthet, S.; Jullien, S. Roles of Land Surface Albedo and Horizontal Resolution on the Indian Summer Monsoon Biases in a Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Tropical-Channel Model. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 48, 1571–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covey, C.; Taylor, K.E.; Dickinson, R.E. Upper Limit for Sea Ice Albedo Feedback Contribution to Global Warming. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 1991, 96, 9169–9174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanova, V.; Lohmann, G.; Grosfeld, K. Effect of Land Albedo, CO2, Orography, and Oceanic Heat Transport on Extreme Climates. Clim. Past 2006, 2, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willeit, M.; Ganopolski, A. The Importance of Snow Albedo for Ice Sheet Evolution over the Last Glacial Cycle. Clim. Past 2018, 14, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraedrich, K. Catastrophes and Resilience of a Zero-Dimensional Climate System with Ice-Albedo and Greenhouse Feedback. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1979, 105, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graversen, R.G.; Wang, M. Polar Amplification in a Coupled Climate Model with Locked Albedo. Clim. Dyn. 2009, 33, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graversen, R.G.; Langen, P.L.; Mauritsen, T. Polar Amplification in CCSM4: Contributions from the Lapse Rate and Surface Albedo Feedbacks. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 4433–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitz, M.; Reese, R.; Beckmann, J.; Krebs-Kanzow, U.; Winkelmann, R. Impact of the Melt-Albedo Feedback on the Future Evolution of the Greenland Ice Sheet with PISM-dEBM-simple. Cryosphere 2021, 15, 5739–5764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, A.J.; Ackland, G.J.; Lenton, T.M. Mutation of Albedo and Growth Response Produces Oscillations in a Spatial Daisyworld. J. Theor. Biol. 2006, 242, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landry, J.; Parrott, L.; Price, D.T.; Ramankutty, N.; Matthews, H.D. Modelling Long-Term Impacts of Mountain Pine Beetle Outbreaks on Merchantable Biomass, Ecosystem Carbon, Albedo, and Radiative Forcing. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 5277–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abell, J.T.; Pullen, A.; Lebo, Z.J.; Kapp, P.; Gloege, L.; Metcalf, A.R.; Nie, J.; Winckler, G. A Wind-Albedo-Wind Feedback Driven by Landscape Evolution. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, H. Modeling the Impacts of Large-Scale Albedo Changes on Ozone Air Quality in the South Coast Air Basin. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Emura, K.; Farnham, C. Is Urban Albedo or Urban Green Covering More Effective for Urbanmicro Climate Improvement?: A Simulation for Osaka. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 32, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, P.; Aghlmand, S.; Fadaei, A.; Gachkar, S.; Gachkar, D.; Karimi, A. Evaluating the Role of the Albedo of Material and Vegetation Scenarios along the Urban Street Canyon for Improving Pedestrian Thermal Comfort Outdoors. Urban Clim. 2021, 40, 100993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falasca, S.; Ciancio, V.; Salata, F.; Golasi, I.; Rosso, F.; Curci, G. High Albedo Materials to Counteract Heat Waves in Cities: An Assessment of Meteorology, Buildings Energy Needs and Pedestrian Thermal Comfort. Build. Environ. 2019, 163, 106242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandaghian, Z.; Berardi, U. Analysis of the Cooling Effects of Higher Albedo Surfaces during Heat Waves Coupling the Weather Research and Forecasting Model with Building Energy Models. Energy Build. 2020, 207, 109627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhan, X.; Zheng, Y.; Hain, C.R.; Ek, M.; Wen, J.; Fang, L.; Liu, J. Improving Noah Land Surface Model Performance Using near Real Time Surface Albedo and Green Vegetation Fraction. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 218, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussetta, S.; Balsamo, G.; Dutra, E.; Beljaars, A.; Albergel, C. Assimilation of Surface Albedo and Vegetation States from Satellite Observations and their Impact on Numerical Weather Prediction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 163, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, M.; Eickhout, B.; Hoogwijk, M.; Strengers, B.; van Vuuren, D.; Leemans, R.; Opsteegh, T. CO2 and Albedo Climate Impacts of Extratropical Carbon and Biomass Plantations. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2006, 20, B2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thackeray, C.W.; Hall, A.; Zelinka, M.D.; Fletcher, C.G. Assessing Prior Emergent Constraints on Surface Albedo Feedback in CMIP6. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 3889–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamborg, F.S.E.; Brovkin, V.; Claussen, M. Background Albedo Dynamics Improve Simulated Precipitation Variability in the Sahel Region. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2014, 5, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, A.; Stevens, B.; Bader, J.; Mauritsen, T. Compensation of Hemispheric Albedo Asymmetries by Shifts of the ITCZ and Tropical Clouds. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 1029–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrett, C.F. Phanerozoic Land Sea and Albedo Variations as Climate Controls. Nature 1982, 296, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamborg, F.S.E.; Brovkin, V.; Claussen, M. The Effect of a Dynamic Background Albedo Scheme on Sahel/Sahara Precipitation during the mid-Holocene. Clim. Past 2011, 7, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Peltier, W.R.; Hu, Y. The Initiation of Modern “Soft Snowball” and “Hard Snowball” Climates in CCSM3. Part I: The Influences of Solar Luminosity, CO2 Concentration, and the Sea Ice/Snow Albedo Parameterization. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 2711–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienert, H.; Feulner, G.; Petoukhov, V. Albedo and Heat Transport in 3-D Model Simulations of the Early Archean Climate. Clim. Past 2013, 9, 1841–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, F.W.; Haywood, A.M.; Dowsett, H.J.; Pickering, S.J. Sensitivity of Pliocene Arctic Climate to Orbital Forcing, Atmospheric CO2 and Sea Ice Albedo Parameterisation. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 441, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, D.A.; Howarth, R.B. The Price of Snow: Albedo Valuation and a Case Study for Forest Management. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 64013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favero, A.; Sohngen, B.; Huang, Y.; Jin, Y. Global Cost Estimates of Forest Climate Mitigation with Albedo: A New Integrative Policy Approach. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 125002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautiainen, A.; Lintunen, J.; Uusivuori, J. Market-Level Implications of Regulating Forest Carbon Storage and Albedo for Climate Change Mitigation. Agric. Resour. Econ. Rev. 2018, 47, 239–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, J.; Zhang, J.; Reid, J.S.; Roberts, D.C. Albedo Impacts of Changing Agricultural Practices in the United States through Space-Borne Analysis. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewry, D.T.; Kumar, P.; Long, S.P. Simultaneous Improvement in Productivity, Water Use, and Albedo through Crop Structural Modification. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 1955–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davin, E.L.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Ciais, P.; Olioso, A.; Wang, T. Preferential Cooling of Hot Extremes from Cropland Albedo Management. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9757–9761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtsmark, B. A Comparison of the Global Warming Effects of Wood Fuels and Fossil Fuels Taking Albedo into Account. GCB Bioenergy 2015, 7, 984–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraha, M.; Chen, J.; Hamilton, S.K.; Sciusco, P.; Lei, C.; Shirkey, G.; Yuan, J.; Robertson, G.P. Albedo-Induced Global Warming Impact of Conservation Reserve Program Grasslands Converted to Annual and Perennial Bioenergy Crops. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 84059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cereceda-Balic, F.; Vidal, V.; Moosmuller, H.; Lapuerta, M. Reduction of Snow Albedo from Vehicle Emissions at Portillo, Chile. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2018, 146, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschnaller, S. The Albedo Loss from the Melting of the Greenland Ice Sheet and the Social Cost of Carbon. Clim. Chang. 2020, 163, 2201–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, H.I.; Golden, J.S. Spatial Superposition Method via Model Coupling for Urban Heat Island Albedo Mitigation Strategies. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2012, 51, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, R.S.; Garg, V.; Ram, V.V.; Bhatia, A. Optimizing Roof Insulation for Roofs with High Albedo Coating and Radiant Barriers in India. J. Build. Eng. 2015, 2, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.L.; Wong, N.H.; Tan, P.Y.; Jusuf, S.K.; Chiam, Z.Q. Impact of Plant Evapotranspiration Rate and Shrub Albedo on Temperature Reduction in the Tropical Outdoor Environment. Build. Environ. 2015, 94, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekemeche, A.; Beghdad, M. Impact of the Environmental Effective Albedo on the Performance of PERC plus Solar Cells. Silicon-Neth. 2021, 13, 3991–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, A.; Luque, A.; Eguren, J.; Delalamo, J. 50-Percent More Output Power from an Albedo-Collecting Flat Panel Using Bifacial Solar-Cells. Sol. Energy 1982, 29, 419–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Thanh, T.T.; Park, J.; Duy, P.P.; Lee, S.; Huy, B.D.; Nam, N.D.; Vinh-Ai, D.; Kim, J.; Yi, J. Over 30% Efficiency Bifacial 4-Terminal Perovskite-Heterojunction Silicon Tandem Solar Cells with Spectral Albedo. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Nakano, N. Bifacial Heterojunction Back Contact Solar Cell: 29-MW/cm(2) Output Power Density in Standard Albedo Condition. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2021, 68, 5645–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fartaria, T.O.; Pereira, M.C. Simulation and Computation of Shadow Losses of Direct Normal, Diffuse Solar Radiation and Albedo in a Photovoltaic Field with Multiple 2-Axis Trackers Using Ray Tracing Methods. Sol. Energy 2013, 91, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Fan, D.; Kong, M. Reliability Assessment on PV Backsheets with and without Considering Spectral UV Albedo Effects: A Theoretical Comparison. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2021, 230, 111230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzio, A.; Schulz, J.; Matthews, J.; Okuyama, A.; Theodore, B.; Bates, J.J.; Knapp, K.R.; Kosaka, Y.; Schueller, L. Land Surface Albedo from Geostationary Satellites: A Multiagency Collaboration within SCOPE-CM. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Jiao, Z.; Zhao, C.; Qu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Tong, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Guo, J.; et al. Review of Land Surface Albedo: Variance Characteristics, Climate Effect and Management Strategy. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061382
Zhang X, Jiao Z, Zhao C, Qu Y, Liu Q, Zhang H, Tong Y, Wang C, Li S, Guo J, et al. Review of Land Surface Albedo: Variance Characteristics, Climate Effect and Management Strategy. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(6):1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061382
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaoning, Ziti Jiao, Changsen Zhao, Ying Qu, Qiang Liu, Hu Zhang, Yidong Tong, Chenxia Wang, Sijie Li, Jing Guo, and et al. 2022. "Review of Land Surface Albedo: Variance Characteristics, Climate Effect and Management Strategy" Remote Sensing 14, no. 6: 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061382
APA StyleZhang, X., Jiao, Z., Zhao, C., Qu, Y., Liu, Q., Zhang, H., Tong, Y., Wang, C., Li, S., Guo, J., Zhu, Z., Yin, S., & Cui, L. (2022). Review of Land Surface Albedo: Variance Characteristics, Climate Effect and Management Strategy. Remote Sensing, 14(6), 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061382









