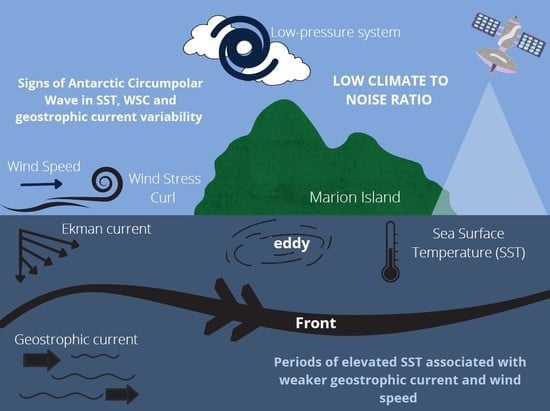
Long-Term Trends and Interannual Variability of Wind Forcing, Surface Circulation, and Temperature around the Sub-Antarctic Prince Edward Islands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
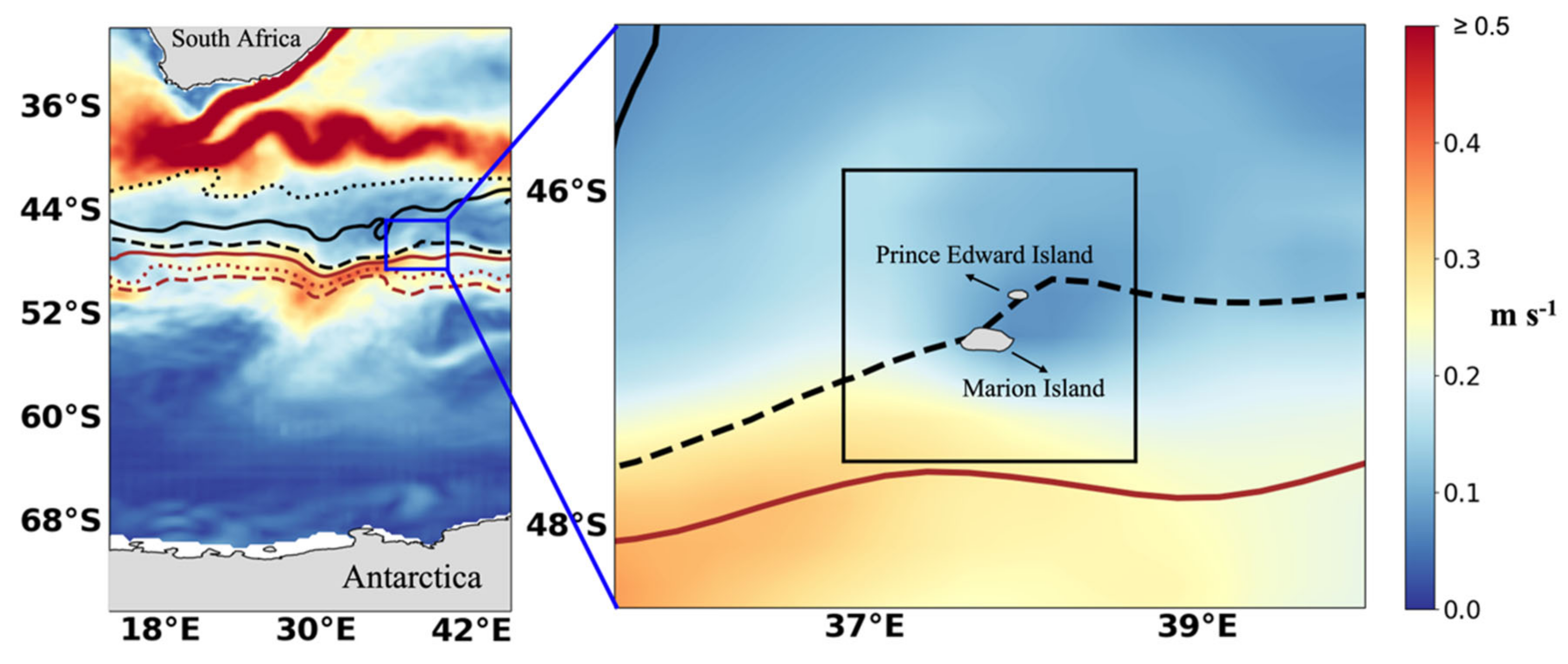
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Product Information
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
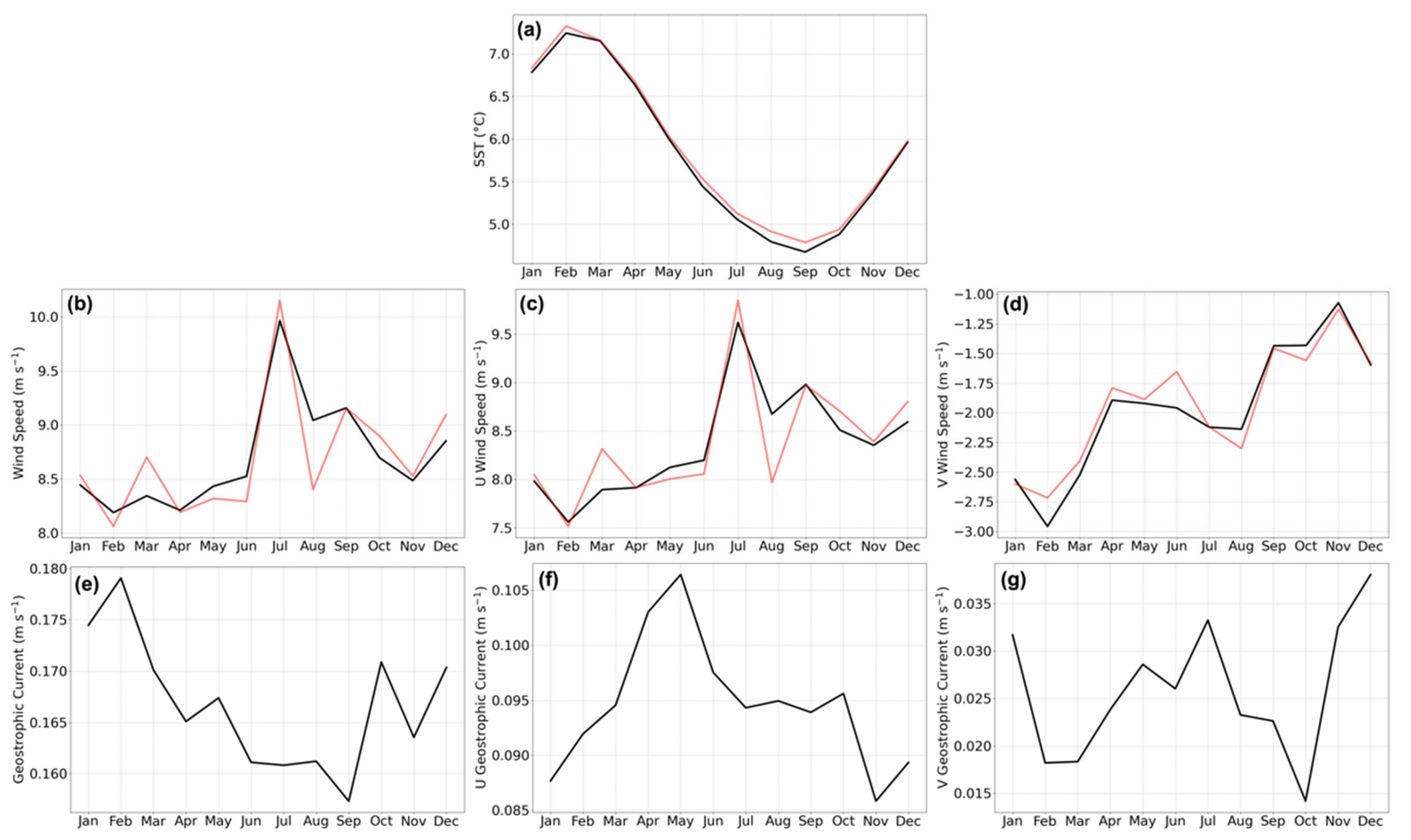
3.1. Seasonal Variations
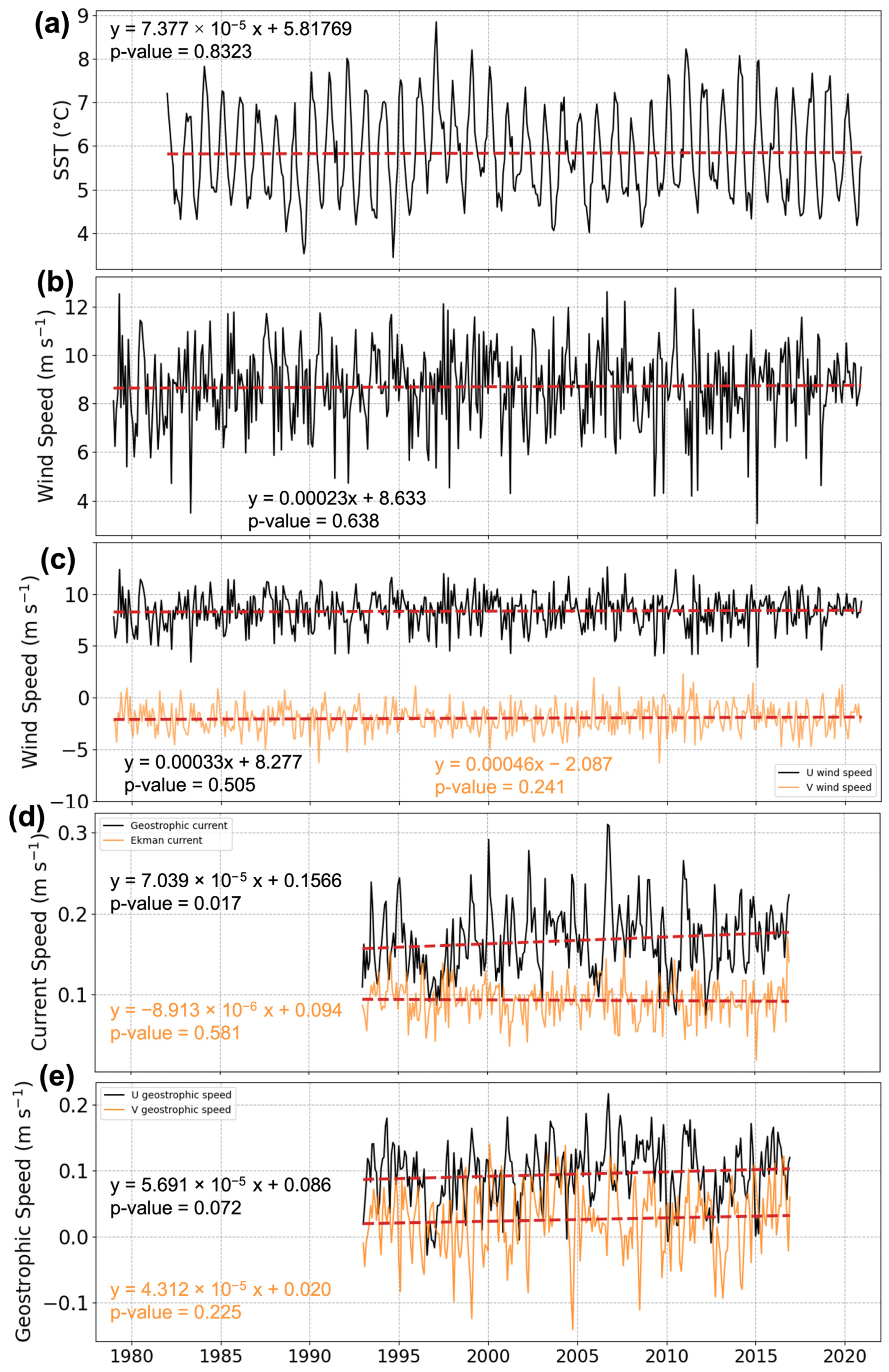
3.2. Long-Term Trends
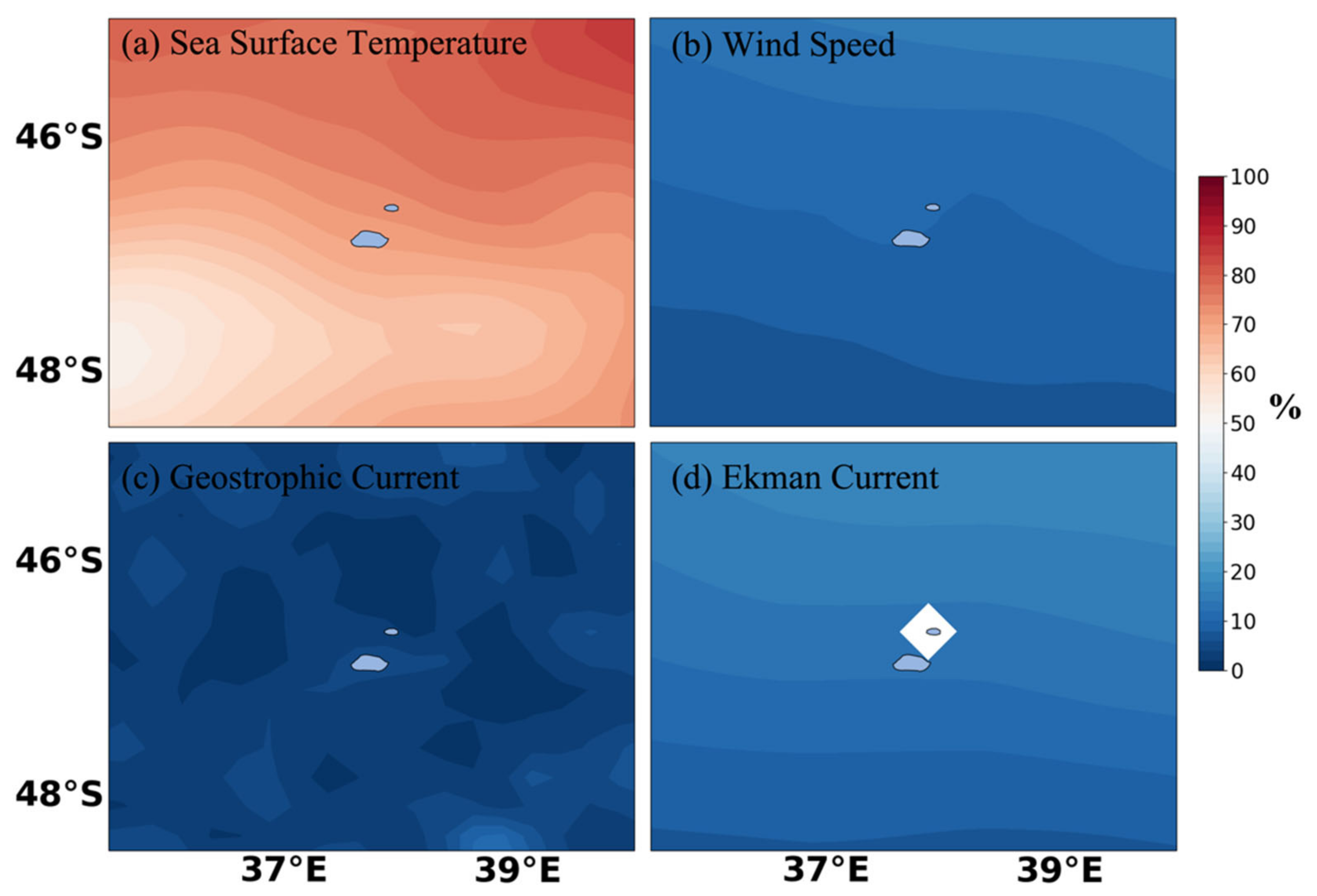
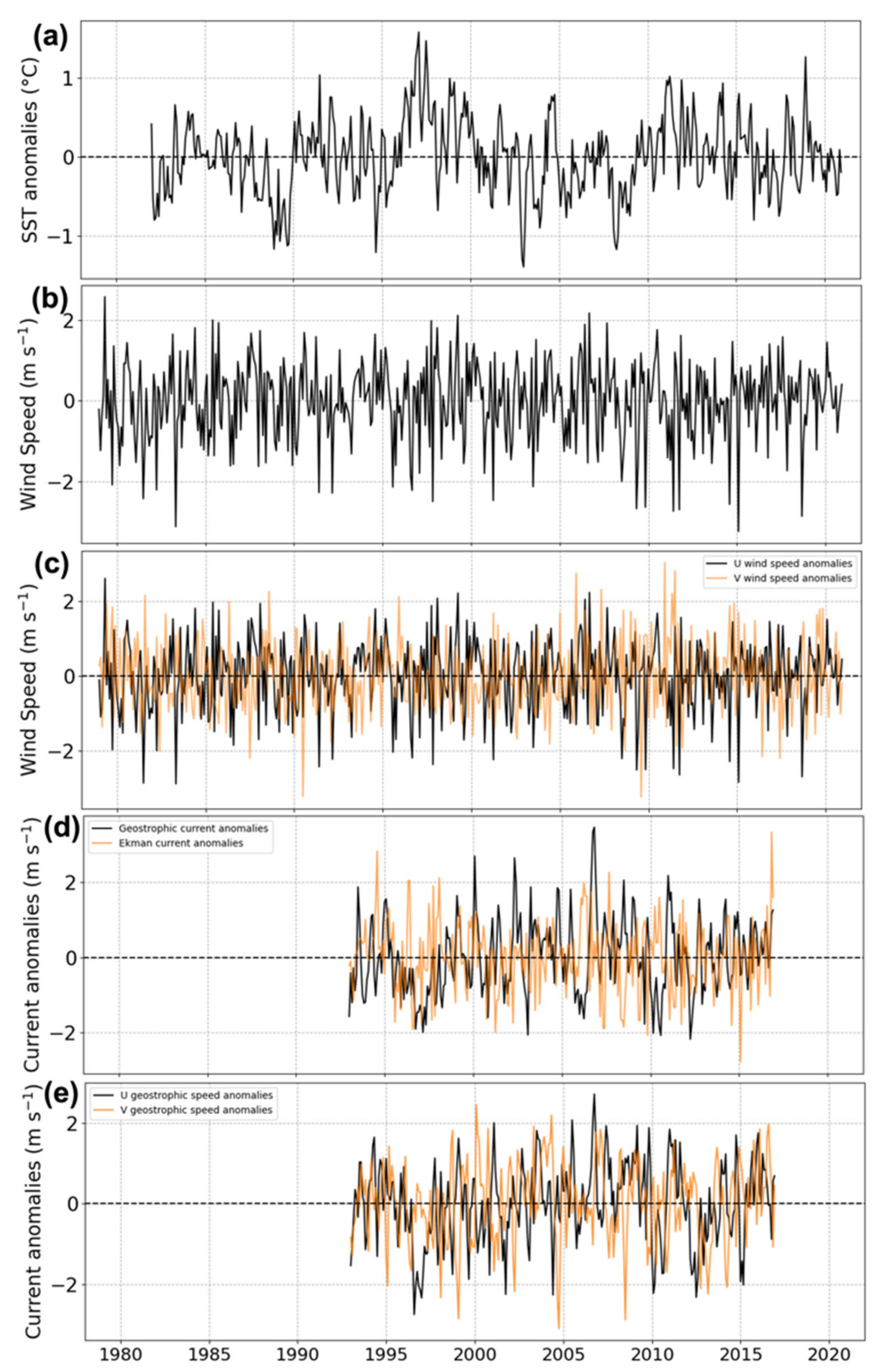
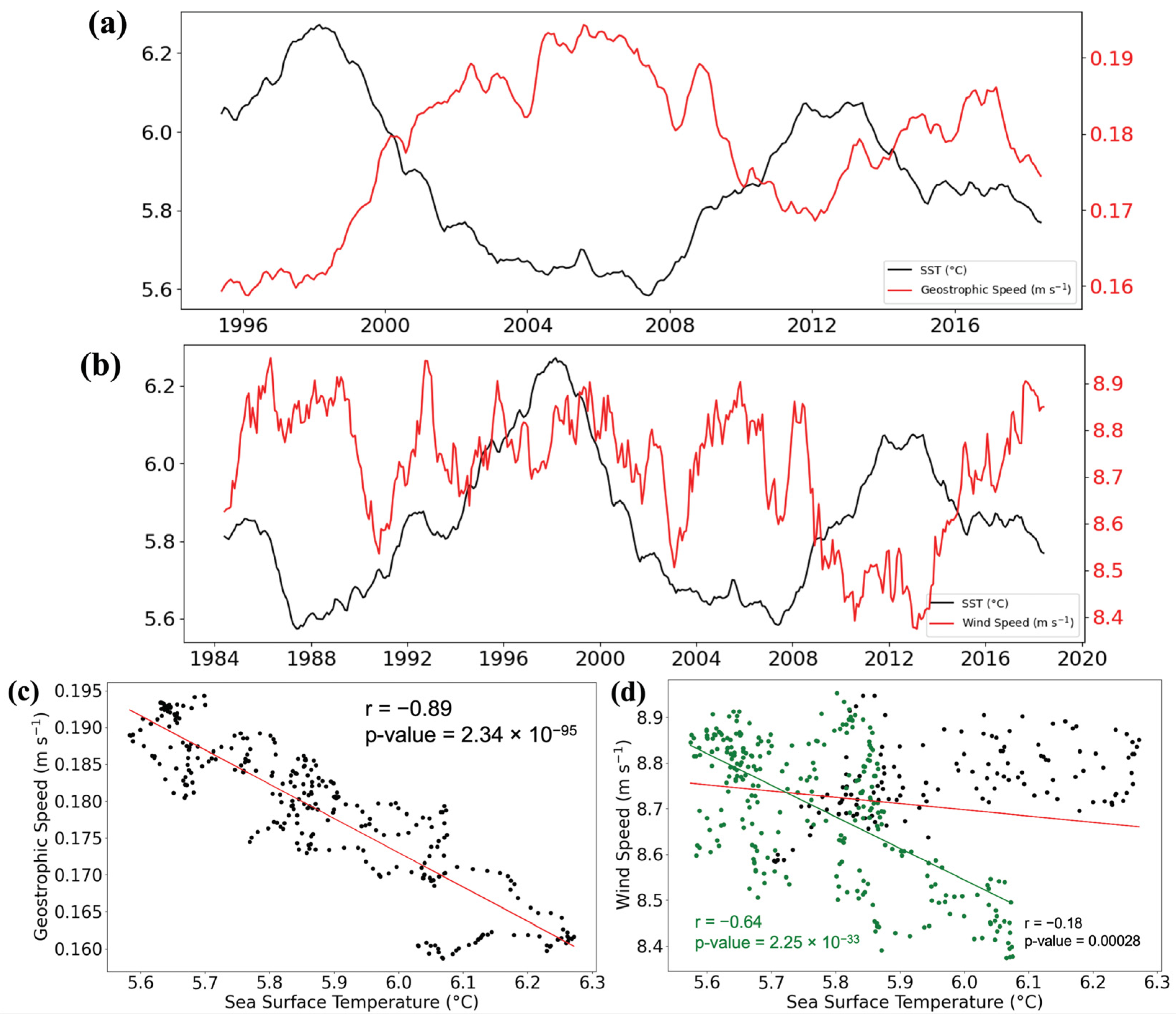
3.3. Interannual Variations
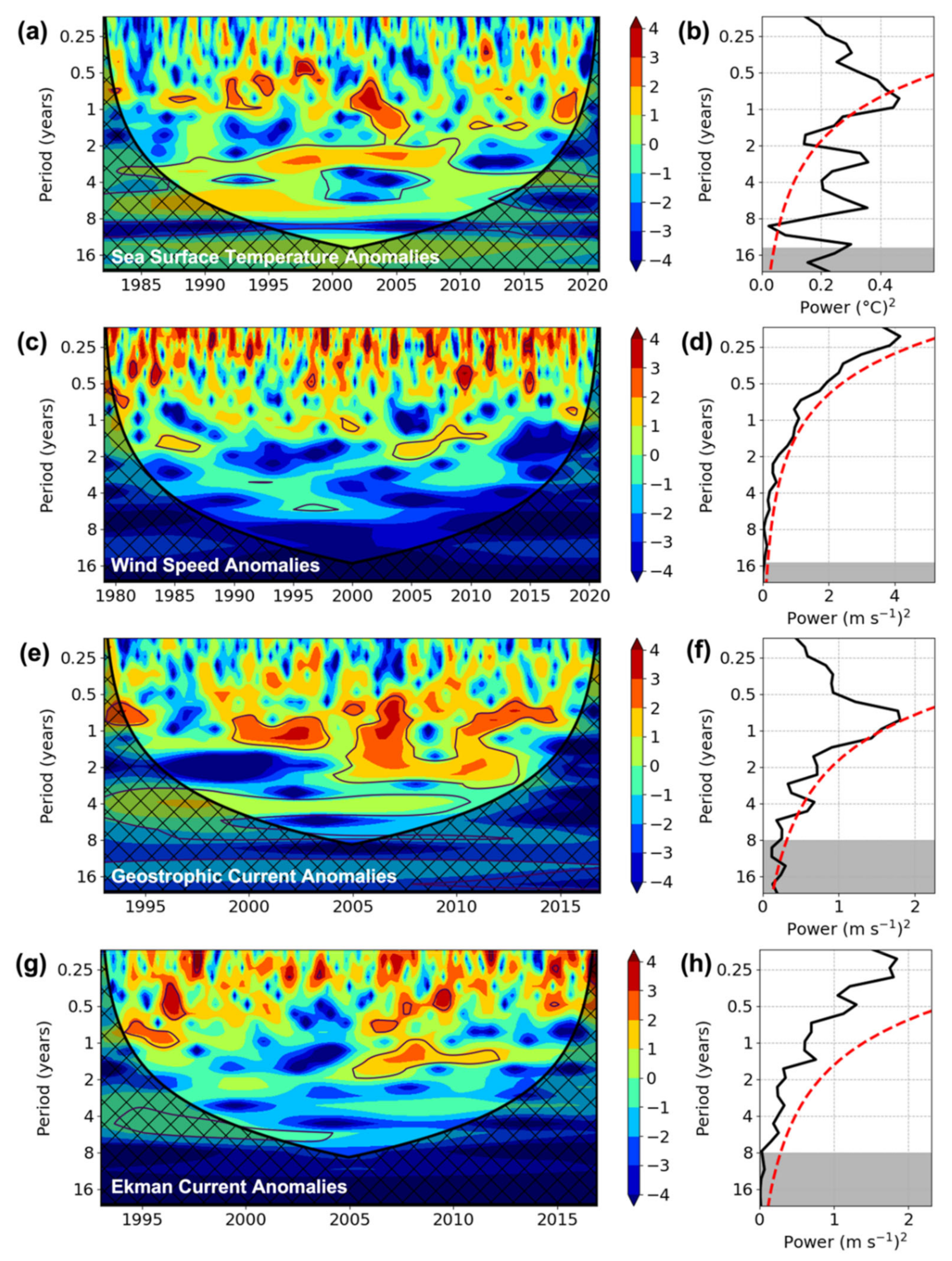
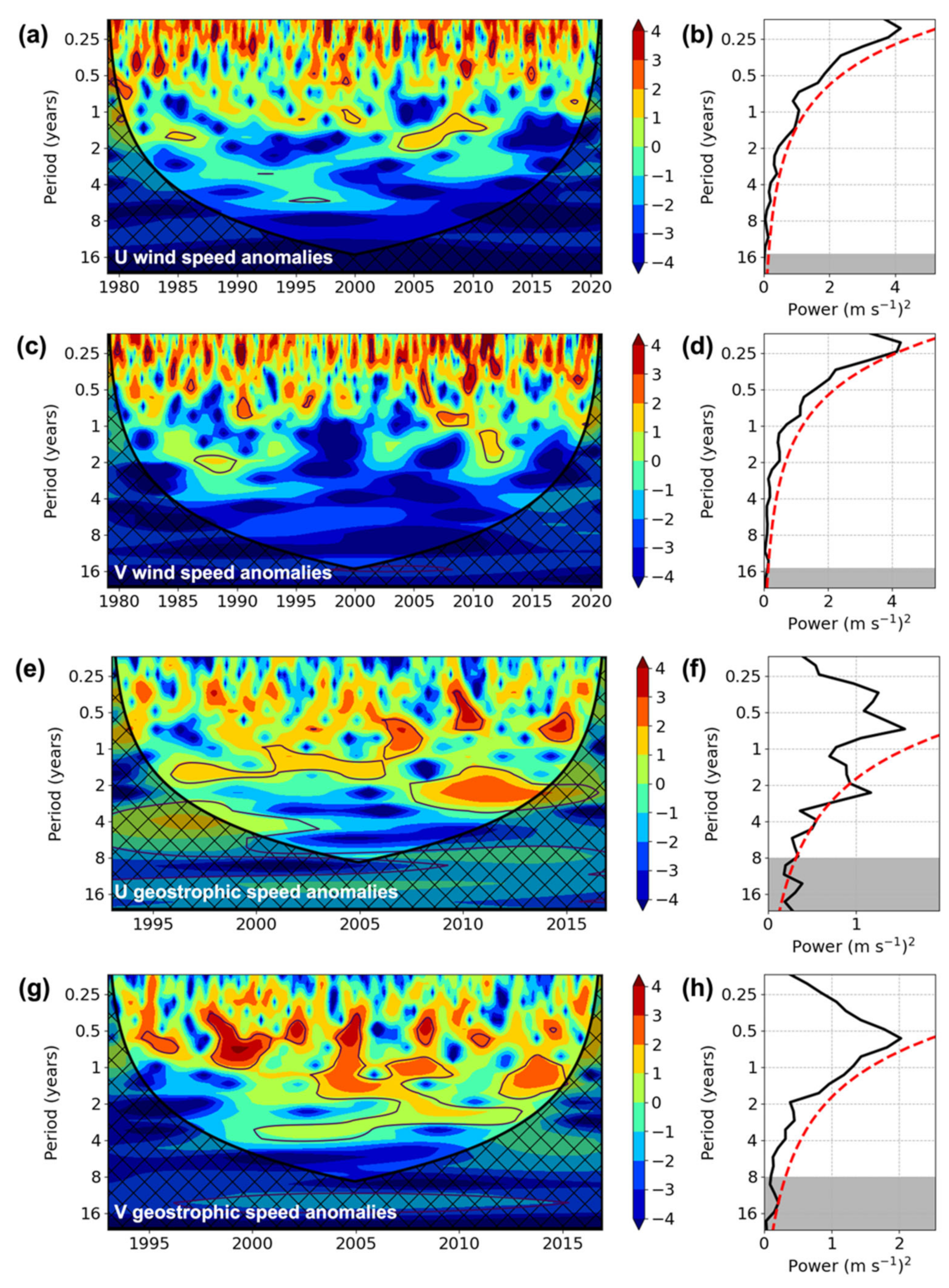
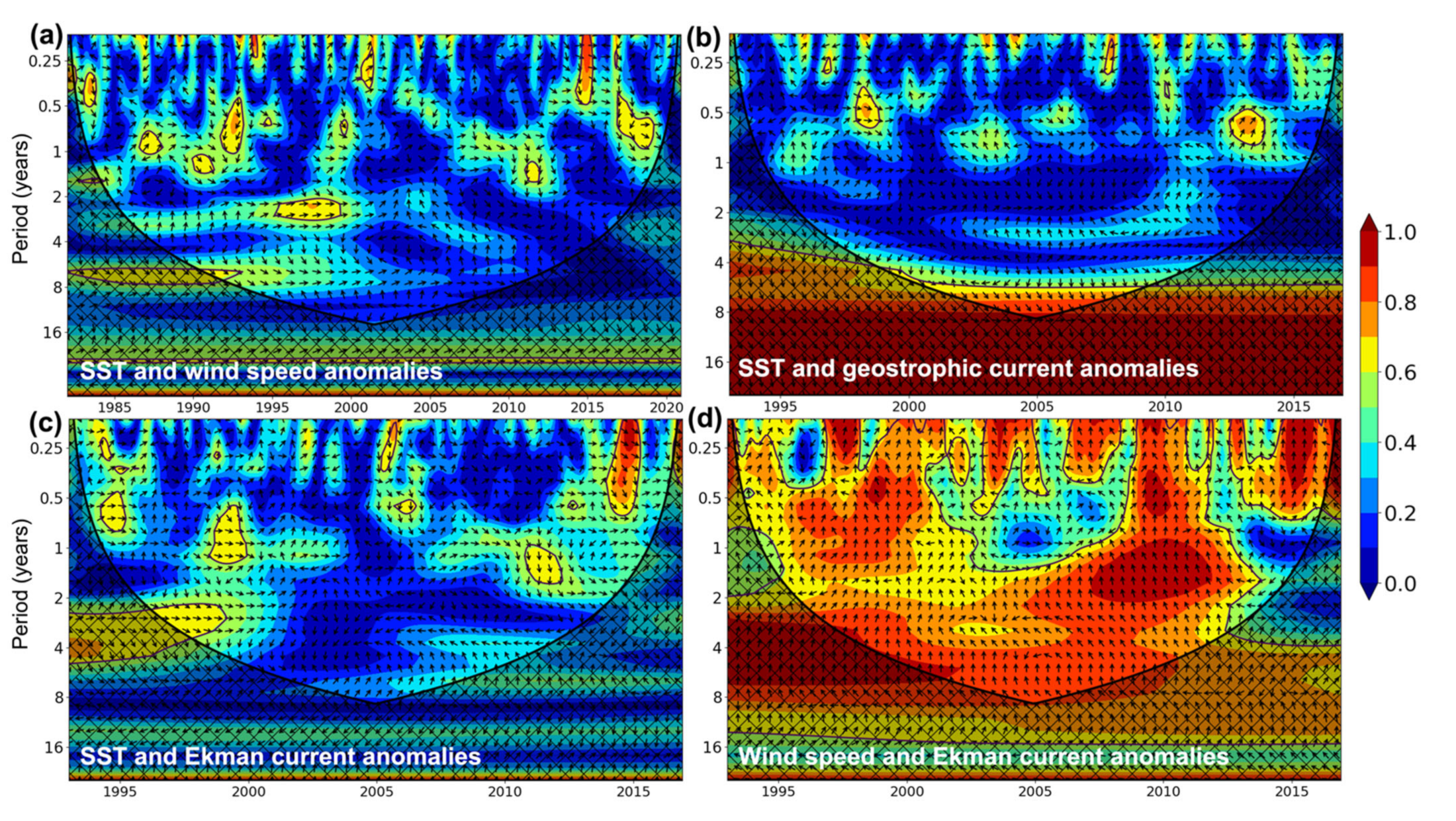
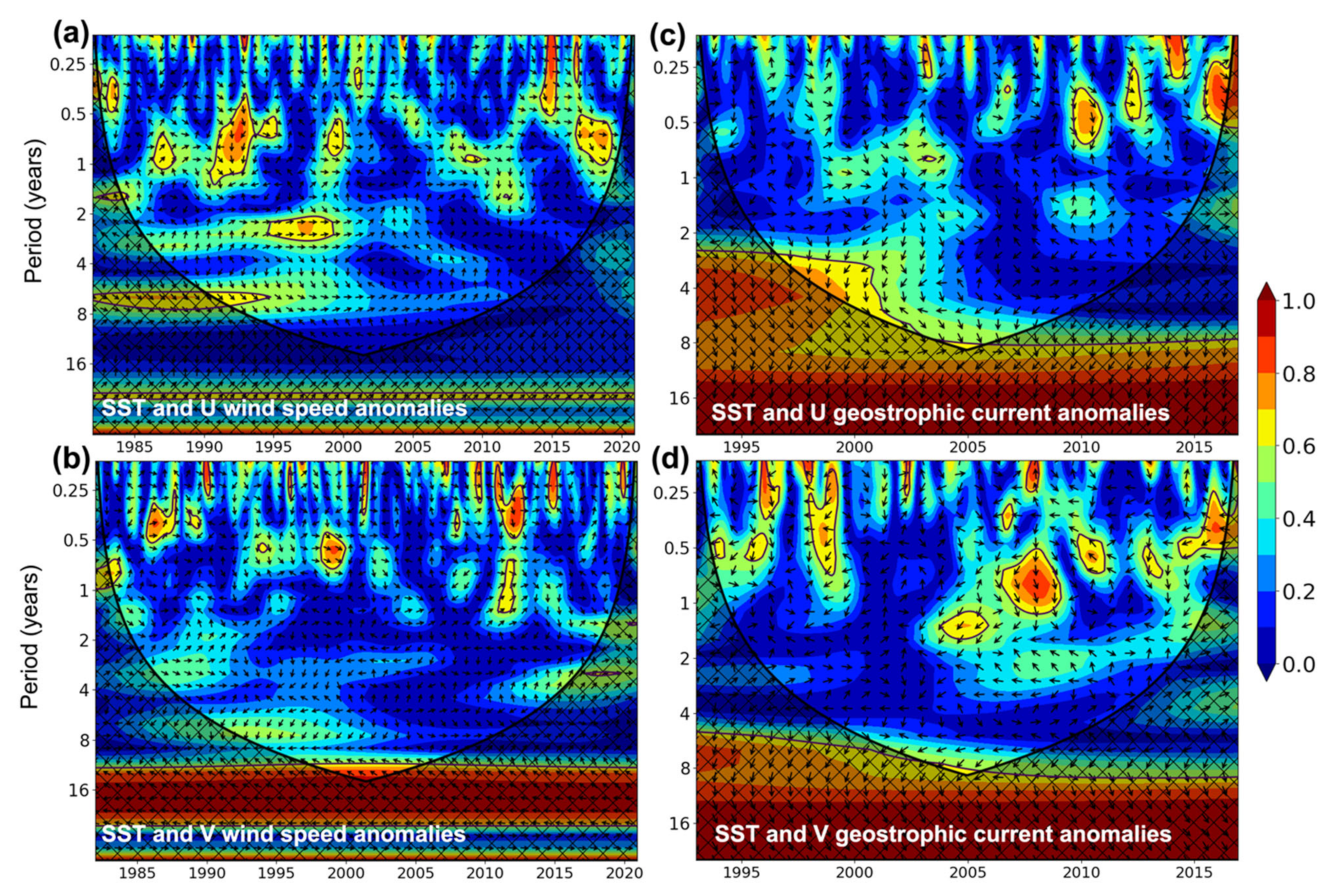
3.4. Wavelet Analyses
3.5. Wavelet Coherence
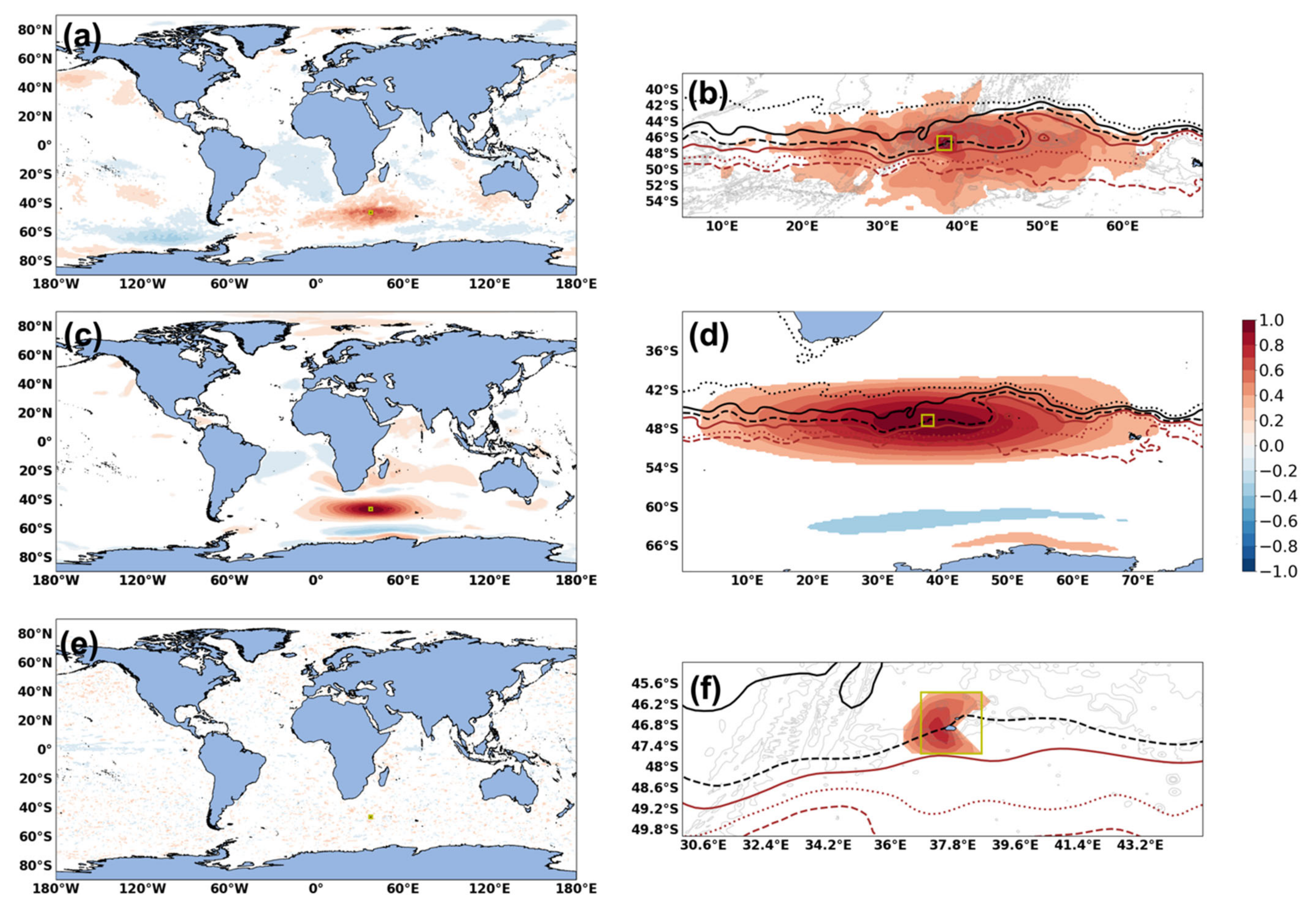
3.6. Spatial Correlations
4. Discussion
4.1. Seasonal Changes and Long-Term Trends
4.2. Interannual and Decadal-scale Variations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masson-Delmotte, Z.P.; Pirani, A.; Connors, S.L.; Péan, C.; Berger, S.; Caud, N.; Chen, Y.; Goldfarb, L.; Gomis, M.; Huang, M.; et al. IPCC, 2021: Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Swart, N.C.; Gille, S.T.; Fyfe, J.C.; Gillett, N.P. Recent Southern Ocean warming and freshening driven by greenhouse gas emissions and ozone depletion. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogt, R.L.; Marshall, G.J. The Southern Annular Mode: Variability, trends, and climate impacts across the Southern Hemisphere. WIREs Clim. Change 2020, 11, e652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perren, B.B.; Hodgson, D.A.; Roberts, S.J.; Sime, L.; Van Nieuwenhuyze, W.; Verleyen, E.; Vyverman, W. Southward migration of the Southern Hemisphere westerly winds corresponds with warming climate over centennial timescales. Commun. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambri, B.; Solomon, S.; Thompson, D.W.J.; Fu, Q. Emergence of Southern Hemisphere stratospheric circulation changes in response to ozone recovery. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallée, J.-B. Southern Ocean Warming. Oceanography 2018, 31, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kostov, Y.; Marshall, J.; Hausmann, U.; Armour, K.C.; Ferreira, D.; Holland, M.M. Fast and slow responses of Southern Ocean sea surface temperature to SAM in coupled climate models. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 48, 1595–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogers, A.; Frinault, B.; Barnes, D.; Bindoff, N.; Downie, R.; Ducklow, H.; Friedlaender, A.; Hart, T.; Hill, S.; Hofmann, E.; et al. Antarctic Futures: An Assessment of Climate-Driven Changes in Ecosystem Structure, Function, and Service Provisioning in the Southern Ocean. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2020, 12, 87–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ansorge, I.J.; Durgadoo, J.V.; Treasure, A.M. Sentinels to climate change. The need for monitoring at South Africa’s Subantarctic laboratory. South Afr. J. Sci. 2014, 110, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansorge, I.J.; Lutjeharms, J.R.E. Direct observations of eddy turbulence at a ridge in the Southern Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgadoo, J.V.; Ansorge, I.J.; Lutjeharms, J.R. Oceanographic observations of eddies impacting the Prince Edward Islands, South Africa. Antarct. Sci. 2010, 22, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, T.; van den Berg, M.A. Mesoscale eddies influencing the sub-Antarctic Prince Edward Islands Archipelago: Origin, pathways, and characteristics. Cont. Shelf Res. 2020, 210, 104257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, T.; van den Berg, M.A. Mesoscale eddies influencing the sub-Antarctic Prince Edward Islands archipelago: Temporal variability and impact. Cont. Shelf Res. 2020, 212, 104309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bost, C.; Cotté, C.; Bailleul, F.; Cherel, Y.; Charrassin, J.; Guinet, C.; Ainley, D.; Weimerskirch, H. The importance of oceanographic fronts to marine birds and mammals of the southern oceans. J. Mar. Syst. 2009, 78, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stukel, M.R.; Aluwihare, L.I.; Barbeau, K.; Chekalyuk, A.M.; Goericke, R.; Miller, A.; Ohman, M.D.; Ruacho, A.; Song, H.; Stephens, B.; et al. Mesoscale ocean fronts enhance carbon export due to gravitational sinking and subduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1252–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carpenter-Kling, T.; Reisinger, R.R.; Orgeret, F.; Connan, M.; Stevens, K.L.; Ryan, P.G.; Makhado, A.; Pistorius, P.A. Foraging in a dynamic environment: Response of four sympatric sub-Antarctic albatross species to interannual environmental variability. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 11277–11295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, P.G.; Bester, M.N. Pelagic predators. In The Prince Edward Islands. Land-Sea Interactions in a Changing Ecosystem; Chown, S.L., Froneman, P.W., Eds.; African Sun Media: Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2008; pp. 121–164. ISBN 978-1-920109-85-1. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, E.L.; Froneman, W.; Durgadoo, J.; McQuaid, C.; Ansorge, I.J.; Richoux, N. Critical indirect effects of climate change on sub-Antarctic ecosystem functioning. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 2994–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hofmeyr, G.J.G.; Bester, M.N.; Makhado, A.B.; Pistorius, P.A. Population changes in Subantarctic and Antarctic fur seals at Marion Island: Research article. S. Afr. J. Wildl. Res. 2006, 36, 55–68. [Google Scholar]
- Mélice, J.-L.; Lutjeharms, J.R.E.; Rouault, M.; Ansorge, I.J. Sea-surface temperatures at the sub-Antarctic islands Marion and Gough during the past 50 years. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2003, 99, 363–366. [Google Scholar]
- Mélice, J.-L.; Lutjeharms, J.R.E.; Goosse, H.; Fichefet, T.; Reason, C.J.C. Evidence for the Antarctic circumpolar wave in the sub-Antarctic during the past 50 years. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouault, M.; Mélice, J.; Reason, C.J.C.; Lutjeharms, J.R.E. Climate variability at Marion Island, Southern Ocean, since 1960. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richard, Y.; Rouault, M.; Pohl, B.; Crétat, J.; Duclot, I.; Taboulot, S.; Reason, C.J.C.; Macron, C.; Buiron, D. Temperature changes in the mid- and high- latitudes of the Southern Hemisphere. Int. J. Clim. 2013, 33, 1948–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangheta, A.L. Long Term Climate Variability at the Prince Edward Islands in the Southern Ocean. Master’s Thesis, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, V.R. Climate Change in the Sub-Antarctic: An Illustration from Marion Island. Clim. Change 2002, 52, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roux, P.C.; McGeoch, M.A. Changes in climate extremes, variability and signature on sub-Antarctic Marion Island. Clim. Change 2008, 86, 309–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, T.; Tutt, G.; Barlow, R. Phytoplankton biomass and photophysiology at the sub-Antarctic Prince Edward Islands ecosystem in the Southern Ocean. J. Mar. Syst. 2022, 226, 103699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, T.; van den Berg, M.A.; Tutt, G.C.O.; Ansorge, I.J. Impact of deep-ocean eddies and fronts on the shelf seas of a sub-Antarctic Archipelago: The Prince Edward Islands. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 177, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toolsee, T.; Lamont, T.; Rouault, M.; Ansorge, I. Characterising the seasonal cycle of wind forcing, surface circulation and temperature around the sub-Antarctic Prince Edward Islands. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2021, 43, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toolsee, T. Interannual Variability and Long-Term Trends of Surface Hydrography around the Prince Edward Island Archipelago, Southern Ocean. Master’s Thesis, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 2021, unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI); US National Climatic Data Center (NCDC). GHRSST Level 4 AVHRR_OI Global Blended Sea Surface Temperature Analysis from NCEI (GDS versions 1 and 2). NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information. Dataset. 2007. Available online: https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/archive/accession/GHRSST-AVHRR_OI-NCEI-L4-GLOB (accessed on 3 September 2021).
- Reynolds, R.W.; Smith, T.M.; Liu, C.; Chelton, D.B.; Casey, K.S.; Schlax, M.G. Daily High-Resolution-Blended Analyses for Sea Surface Temperature. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 5473–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentz, F.J.; Gentemann, C.; Smith, D.; Chelton, D. Satellite Measurements of Sea Surface Temperature Through Clouds. Science 2000, 288, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horanyi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, L.W.; Chelton, D.B.; Esbensen, S.K. Observations of SST-Induced Perturbations of the Wind Stress Field over the Southern Ocean on Seasonal Timescales. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 2340–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Risien, C.M.; Chelton, D.B. A Global Climatology of Surface Wind and Wind Stress Fields from Eight Years of QuikSCAT Scatterometer Data. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2008, 38, 2379–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, M.-H.; Mulet, S.; Picot, N. Beyond GOCE for the ocean circulation estimate: Synergetic use of altimetry, gravimetry, and in situ data provides new insight into geostrophic and Ekman currents. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 8918–8925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taburet, G.; Sanchez-Roman, A.; Ballarotta, M.; Pujol, M.-I.; Legeais, J.-F.; Fournier, F.; Faugere, Y.; Dibarboure, G. DUACS DT2018: 25 years of reprocessed sea level altimetry products. Ocean Sci. 2019, 15, 1207–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, J.; Jung, Y. Local climate impacts of dipole-like sea surface temperature oscillations in the Southern Hemisphere. J. Water Clim. Change 2021, 12, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferster, B.S.; Subrahmanyam, B.; Macdonald, A.M. Confirmation of ENSO-Southern Ocean Teleconnections Using Satellite-Derived SST. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, G.; Gommers, R.; Waselewski, F.; Wohlfahrt, K.; O’Leary, A. PyWavelets: A Python package for wavelet analysis. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, X.S.; Weisberg, R.H. Rectification of the Bias in the Wavelet Power Spectrum. J. Atmospheric Ocean. Technol. 2007, 24, 2093–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinsted, A.; Moore, J.C.; Jevrejeva, S. Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2004, 11, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, M.; Jha, S.; Chakraborty, P. Indian Ocean wind speed variability and global teleconnection patterns. Oceanologia 2020, 62, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.J.; Trathan, P.N.; Watkins, J.L.; Reid, K.; Meredith, M.P.; Forcada, J.; Thorpe, S.; Johnston, N.M.; Rothery, P. Climatically driven fluctuations in Southern Ocean ecosystems. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2007, 274, 3057–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomalla, S.J.; Fauchereau, N.; Swart, S.; Monteiro, P.M.S. Regional scale characteristics of the seasonal cycle of chlorophyll in the Southern Ocean. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 2849–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luis, A.J.; Pandey, P.C. Seasonal variability of QSCAT-derived wind stress over the Southern Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L13304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, M.P.; Murphy, E.J.; Hawker, E.J.; King, J.C.; Wallace, M.I. On the interannual variability of ocean temperatures around South Georgia, Southern Ocean: Forcing by El Niño/Southern Oscillation and the Southern Annular Mode. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2008, 55, 2007–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hogg, R.V.; McKean, J.; Craig, A.T. Introduction to Mathematical Statistics, 7th ed.; Pearson Education: Harlow, UK, 2014; ISBN 978-1-292-02499-8. [Google Scholar]
- Sokolov, S.; Rintoul, S. Circumpolar structure and distribution of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current fronts: 1. Mean circumpolar paths. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2009, 114, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Giannakis, D.; Slawinska, J. The Antarctic circumpolar wave and its seasonality: Intrinsic travelling modes and El Niño-Southern Oscillation teleconnections. Int. J. Clim. 2018, 39, 1026–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, R.S.C.; Eigenbrod, F.; Bates, A.E. Projected losses of global mammal and bird ecological strategies. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, M.; Dash, P.; Ignatov, A.; Banzon, V.; Beggs, H.; Brasnett, B.; Cayula, J.-F.; Cummings, J.; Donlon, C.; Gentemann, C.; et al. Group for High Resolution Sea Surface temperature (GHRSST) analysis fields inter-comparisons. Part 1: A GHRSST multi-product ensemble (GMPE). Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2012, 77, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, P.; Ignatov, A.; Martin, M.; Donlon, C.; Brasnett, B.; Reynolds, R.W.; Banzon, V.; Beggs, H.; Cayula, J.-F.; Chao, Y.; et al. Group for High Resolution Sea Surface Temperature (GHRSST) analysis fields inter-comparisons—Part 2: Near real time web-based level 4 SST Quality Monitor (L4-SQUAM). Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2012, 77-80, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henson, S.A.; Beaulieu, C.; Lampitt, R.S. Observing climate change trends in ocean biogeochemistry: When and where. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Auger, M.; Morrow, R.; Kestenare, E.; Sallée, J.-B.; Cowley, R. Southern Ocean in-situ temperature trends over 25 years emerge from interannual variability. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; University of California Riverside; Xie, S.-P. An Ocean View of the Global Surface Warming Hiat. Oceanography 2018, 31, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacka, T.H.; Budd, W.F.; Holder, A. A further assessment of surface temperature changes at stations in the Antarctic and Southern Ocean, 1949–2002. Ann. Glaciol. 2004, 39, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, J.L.; Waugh, D.W.; Gnanadesikan, A. Southern Hemisphere extratropical circulation: Recent trends and natural variability. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 5508–5515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liau, J.-R.; Chao, B.F. Variation of Antarctic circumpolar current and its intensification in relation to the southern annular mode detected in the time-variable gravity signals by GRACE satellite. Earth Planets Space 2017, 69, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Orsi, A.H. On the Variability of Antarctic Circumpolar Current Fronts Inferred from 1992–2011 Altimetry*. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2014, 44, 3054–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, A.E.; Gille, S.T.; Mecking, S.; Thompson, L. Properties of the Subantarctic Front and Polar Front from the skewness of sea level anomaly. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 5179–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapman, C.C. New Perspectives on Frontal Variability in the Southern Ocean. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2017, 47, 1151–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansorge, I.; Durgadoo, J.; Pakhomov, E. Dynamics of physical and biological systems of the Prince Edward Islands in a changing climate. Pap. Proc. R. Soc. Tasman. 2009, 143, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asdar, S. Climate Change Impact on Ecosystems of Prince Edward Islands: Role of Oceanic Mesoscale Processes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 2019, unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Bitz, C.M.; Polvani, L.M. Antarctic climate response to stratospheric ozone depletion in a fine resolution ocean climate model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L20705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meehl, G.A.; Hurrell, J.W.; Van Loon, H. A modulation of the mechanism of the semiannual oscillation in the Southern Hemisphere. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 1998, 50, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B.; Peterson, R.G. An Antarctic circumpolar wave in surface pressure, wind, temperature and sea-ice extent. Nature 1996, 380, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrone, D.; Fusco, G.; Cotroneo, Y.; Simmonds, I.; Budillon, G. The Antarctic Circumpolar Wave: Its Presence and Interdecadal Changes during the Last 142 Years. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6371–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B. Comments on “Synchronous Variability in the Southern Hemisphere Atmosphere, Sea Ice, and Ocean Resulting from the Annular Mode”. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 2249–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhang, W.; Turner, A.G.; Sun, J. How does El Niño-Southern Oscillation affect winter fog frequency over eastern China? Clim. Dyn. 2020, 54, 1043–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, J.; Cobb, K.M. A Review of Paleo El Niño-Southern Oscillation. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McPhaden, M.J. Genesis and Evolution of the 1997-98 El Niño. Science 1999, 283, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shabbar, A.; Yu, B. The 1998–2000 La Niña in the context of historically strong La Niña events. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2009, 114, 13105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deser, C.; Phillips, A.S. Atmospheric Circulation Trends, 1950–2000: The Relative Roles of Sea Surface Temperature Forcing and Direct Atmospheric Radiative Forcing. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 396–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fauchereau, N.; Trzaska, S.; Richard, Y.; Roucou, P.; Camberlin, P. Sea-surface temperature co-variability in the Southern Atlantic and Indian Oceans and its connections with the atmospheric circulation in the Southern Hemisphere. Int. J. Clim. 2003, 23, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.-R.; Talley, L.D.; Xie, S.-P.; Peng, Q.; Liu, W. Ocean warming and accelerating Southern Ocean zonal flow. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roemmich, D.; Church, A.J.; Gilson, J.; Monselesan, D.; Sutton, P.; Wijffels, S. Unabated planetary warming and its ocean structure since 2006. Nat. Clim. Change 2015, 5, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, E.; Frame, D.; Harrington, L.; Joshi, M.; King, A.; Rojas, M.; Sutton, R. Observed Emergence of the Climate Change Signal: From the Familiar to the Unknown. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2019GL086259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toolsee, T.; Lamont, T. Long-Term Trends and Interannual Variability of Wind Forcing, Surface Circulation, and Temperature around the Sub-Antarctic Prince Edward Islands. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061318
Toolsee T, Lamont T. Long-Term Trends and Interannual Variability of Wind Forcing, Surface Circulation, and Temperature around the Sub-Antarctic Prince Edward Islands. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(6):1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061318
Chicago/Turabian StyleToolsee, Tesha, and Tarron Lamont. 2022. "Long-Term Trends and Interannual Variability of Wind Forcing, Surface Circulation, and Temperature around the Sub-Antarctic Prince Edward Islands" Remote Sensing 14, no. 6: 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061318
APA StyleToolsee, T., & Lamont, T. (2022). Long-Term Trends and Interannual Variability of Wind Forcing, Surface Circulation, and Temperature around the Sub-Antarctic Prince Edward Islands. Remote Sensing, 14(6), 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061318