Smoothing Linear Multi-Target Tracking Using Integrated Track Splitting Filter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Target and Sensor Models
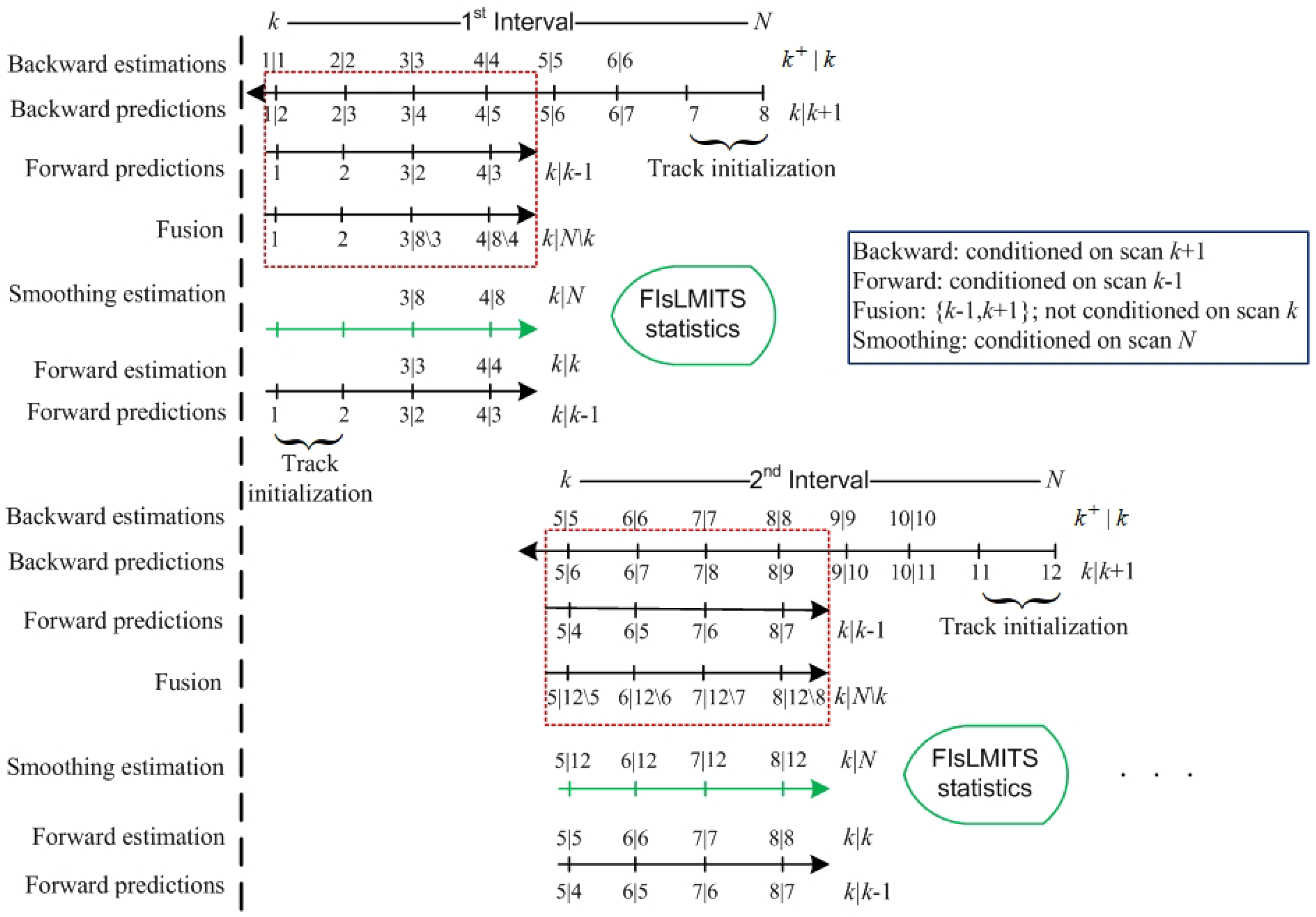
3. Fixed Interval Smoothing in Linear Multi-Target Based on ITS (FIsLMITS)
- Calculate the backward multi-tracks multi-components state estimations from scan N up to scan k based on the measurements received in each scan (where subscript on indicates the backward-time scan).
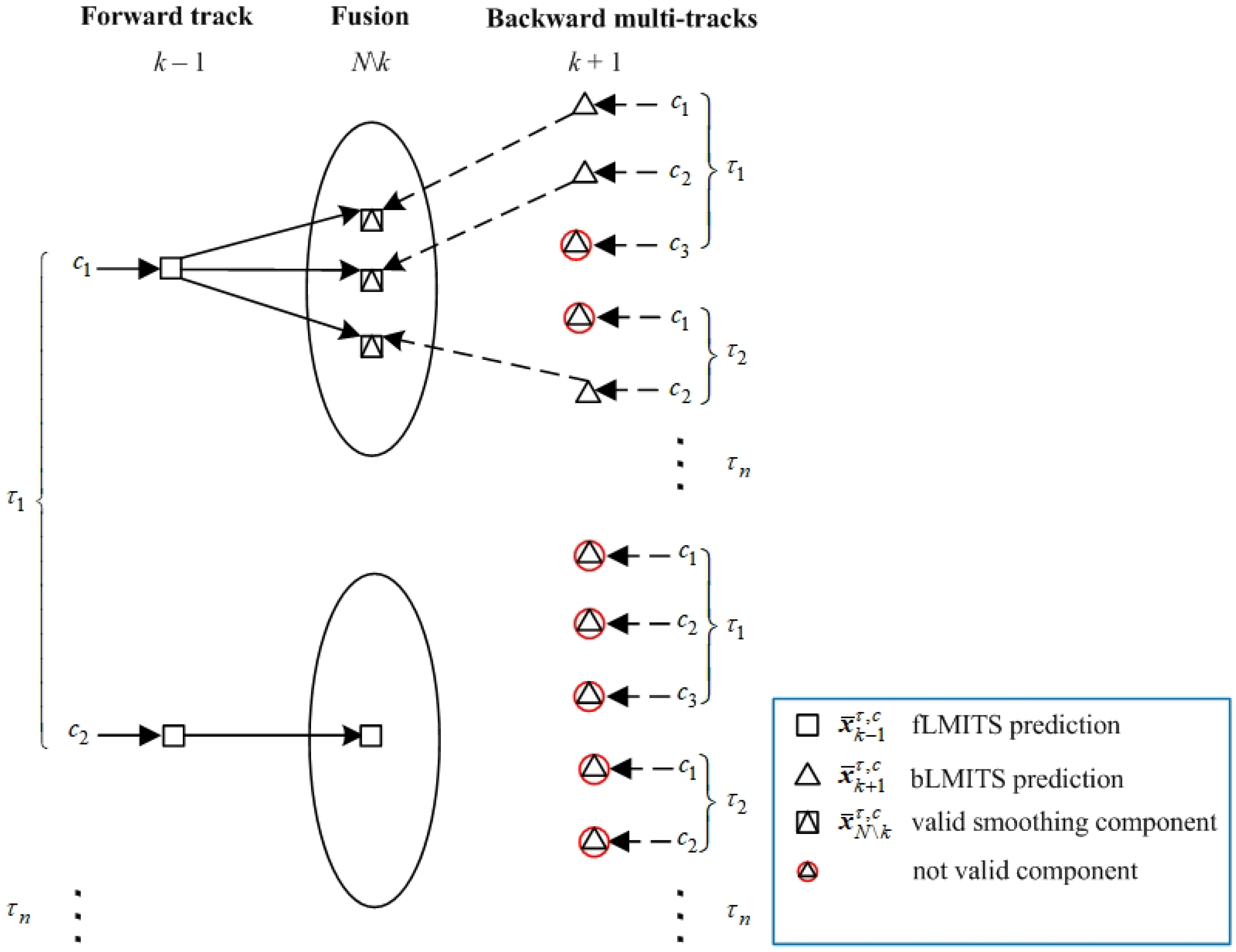
- After the arrival of the backward multi-tracks at first scan k of an interval, the forward multi-tracks are initialized using the corresponding component pdf measured by the sensor measurements. Each forward track forms a validation gate based on the backward multi-track-multi-components predictions. In the validation gate, each forward component prediction fuses with the associated backward multi-components predictions to obtain the smoothing multi-components predictions in each scan k (for example, ).
- Calculate the smoothing and forward estimates using the step 2 in each scan k, for example, and , respectively.
3.1. Backward Multi-Track State Estimation
3.2. Backward Multi-Track State Fusion in a Forward Track
3.3. Forward Track State Estimation Using Smoothing Multi-Target Data Association
4. Numerical and Technical Analysis Using Simulations
4.1. Technical Considerations
4.2. Simulation Parameters and Scenario
- nCases: It is the number of CTTs following a potential target that was counted in scan 15;
- nOk: The number of CTTs that keep pursuing the original target (without switching to other target track) in scan 30;
- nSwitched: It counts the number of CTTs that swapped the original target and are now pursuing a different target in scan 30;
- nLost: The number of CTTs accounted from nCases that are not pursuing any target in scan 30 because they were terminated due to low track TEP or low track component existence probabilities or they became confirmed false tracks;
- nResult: It counts the number of CTTs that is retained until the last scan .
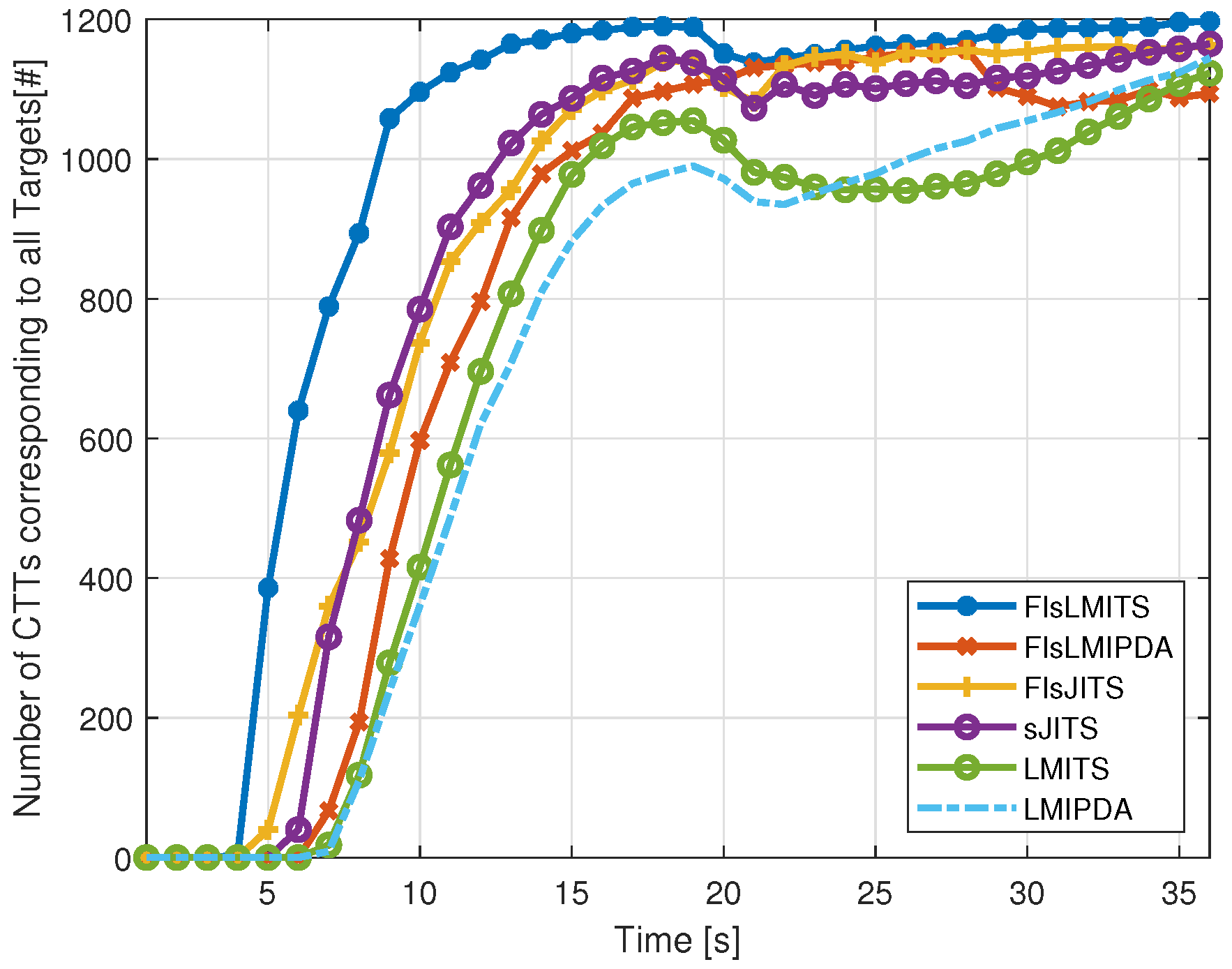
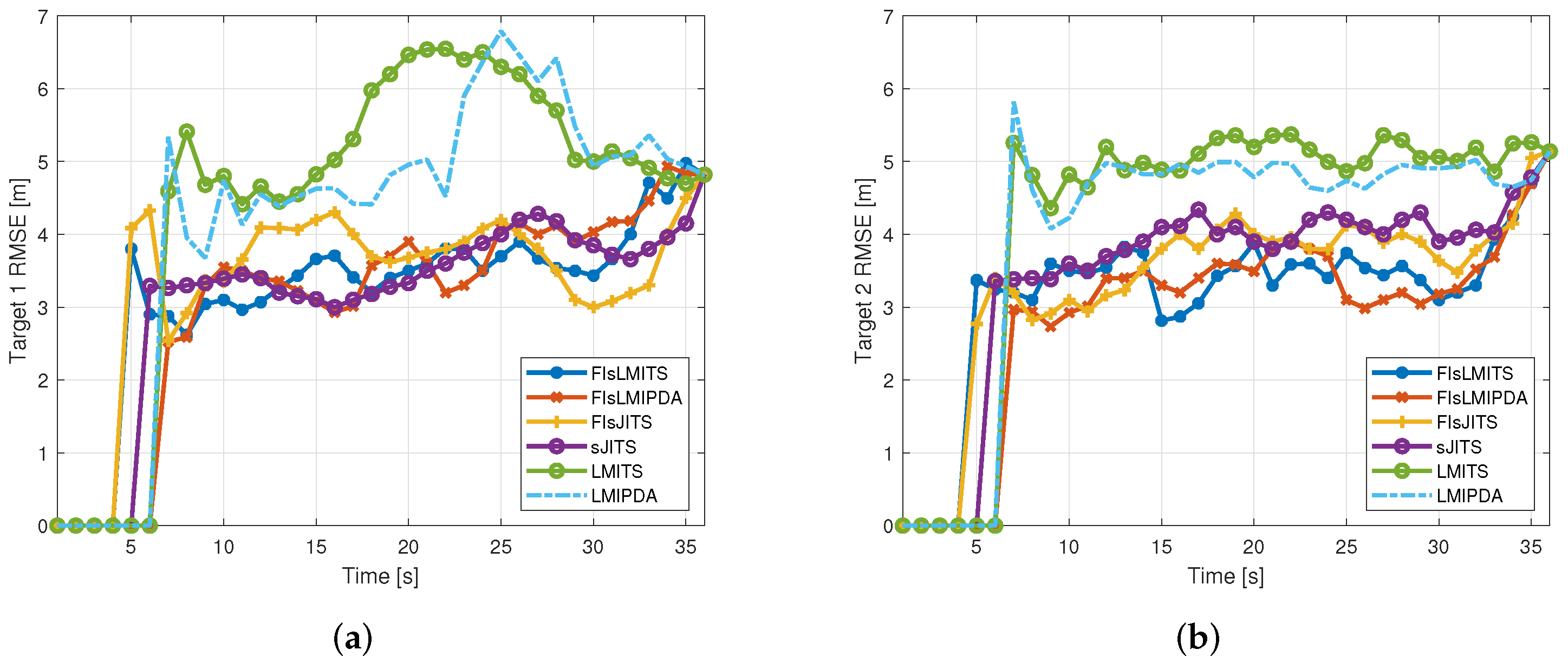
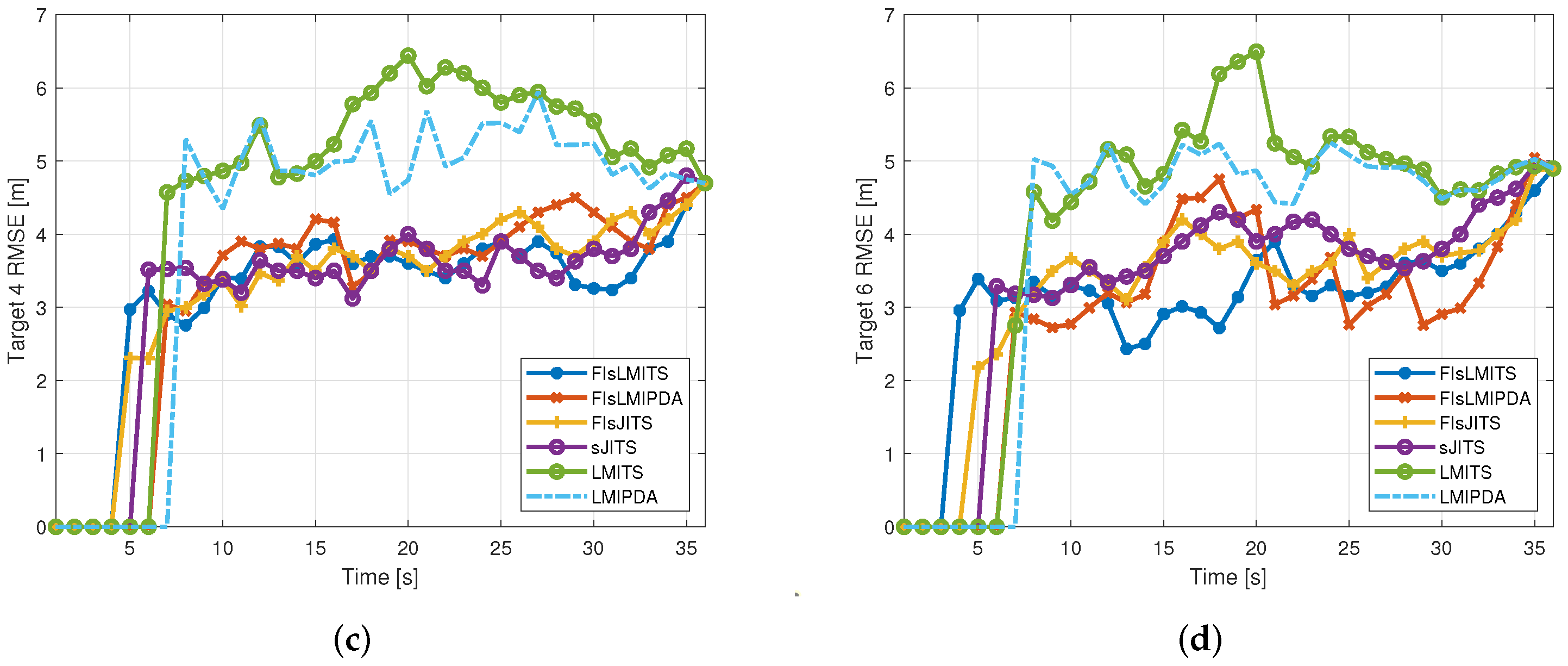
4.3. Illustrative Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FTD | False track discrimination |
| TEP | Target existence probability |
| MTT | Multi-target tracking |
| STT | Single target tracking |
| LM | Linear multi-target |
| IPDA | Integrated probabilistic data association |
| ITS | Integrated track splitting |
| JIPDA | Joint integrated probabilistic data association |
| JITS | Joint integrated track splitting |
| LMIPDA | Linear multi-target integrated probabilistic data association |
| LMITS | Linear multi-target integrated track splitting |
| FIsJIPDA | Fixed interval smoothing joint integrated probabilistic data association |
| sJITS | Smoothing joint integrated track splitting |
| FIsJITS | Fixed interval smoothing joint integrated track splitting |
| FIsLMIPDA | Fixed interval smoothing Linear multi-target integrated probabilistic data association |
| FIsLMITS | Fixed interval smoothing Linear multi-target integrated track splitting |
References
- Khaleghi, B.; Khamis, A.; Karray, F.O.; Razavi, S.N. Multisensor data fusion: A review of the state-of-the-art. Inf. Fusion 2013, 14, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challa, S.; Evans, R.; Morelande, M.; Mušicki, D. Fundamentals of Object Tracking; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mušicki, D.; Evans, R.; Stankovic, S. Integrated probabilistic data association. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1994, 39, 1237–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.L.; Mušicki, D. Target tracking with target state dependent detection. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mušicki, D.; Evans, R. JIPDA: Automatic target tracking avoiding track coalescence. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2015, 51, 962–974. [Google Scholar]
- Song, T.L.; Mušicki, D.; Yong, K. Multi-target tracking with state dependent detection. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2015, 9, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyan, T.; Chin, T.; Arulampalam, S.; Suter, D. A Multiple Hypothesis Tracker for Multitarget Tracking with Multiple Simultaneous Measurements. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2013, 7, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mušicki, D.; Scala, B.L. Multi-target tracking in clutter without measurement assignment. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2008, 44, 877–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mušicki, D.; Song, T.L.; Lee, H. Linear multitarget finite resolution tracking in clutter. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2014, 50, 1798–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Shalom, Y.; Li, X.R.; Kirubarajan, T. Estimation with Applications to Tracking and Navigation: Theory Algorithms and Software; Wiley and Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jason, S.; Travis, B.; Mark, R.; Jason, B.; Moriba, J.; Keric, H. Joint Probabilistic Data Association and Smoothing Applied to Multiple Space Object Tracking. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2017, 41, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Nagappa, S.; Delande, E.D.; Clark, D.E.; Houssineau, J. A Tractable Forward– Backward CPHD Smoother. IEEE Trans. Aeorsp. Electron. Syst. 2017, 53, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, W. Fixed-interval retrodiction approach to Bayesian IMM-MHT for maneuvering multiple targets. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2000, 36, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, S.A.; Kim, M.; Shin, M.; Daudpoto, J.; Pathan, D.M.; Son, H. Extended Smoothing Joint Data Association for Multi-target Tracking in Cluttered Environments. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2020, 14, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, S.; Song, T.L.; Kim, T.H. Smoothing Data Association for Target Trajectory Estimation in Cluttered Environments. Eurasip J. Adv. Signal Process. 2016, 21, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Memon, S.A.; Song, T.L.; Memon, K.H.; Ullah, I.; Khan, U. Modified Smoothing Data Association for Target Tracking in Clutter. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 141, 112969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Mušicki, D.; Song, T.L.; Lee, C.M. Smoothing joint integrated probabilistic data association. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2015, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, D.; Potter, J. The optimum linear smoother as a combination of two optimum linear filters. IEEE Trans. Automat. Cont. 1969, 14, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Song, T.L. Multi-target multi-scan smoothing in clutter. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2016, 10, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, S.A.; Kim, M.; Son, H. Tracking and Estimation of Multiple Cross-over Targets in Clutter. Sensors 2019, 19, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Memon, S.A.; Ullah, I. Detection and tracking of the trajectories of dynamic UAVs in restricted and cluttered environment. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 183, 115309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, S.A.; Kim, W.-G.; Park, M.; Attique, M. Rauch-Tung-Striebel Smoothing Linear Multi-Target Tracking in Clutter. IEEE Access 2021, 10, 3007–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.L.; Musicki, D. Adaptive clutter measurement density estimation for improved target tracking. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2011, 47, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Memon, S.A.; Shin, M.; Son, H. Dynamic based trajectory estimation and tracking in an uncertain environment. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 177, 114919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, M.S.; Andrews, A.P. Kalman filtering: Theory and Practice with MATLAB; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Memon, S.; Son, H.; Memon, A.A.; Ahmed, S. Track Split Smoothing for Target Tracking in Clutter. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering (ICASE), Islamabad, Pakistan, 14–16 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Memon, S.; Son, H.; Memon, K.H.; Ansari, A. Multi-scan smoothing for tracking manoeuvering target trajectory in heavy cluttered environment. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2017, 11, 1815–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, S.; Popoli, R. Design and Analysis of Modern Tracking Systems; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA; London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Salmond, D.J. Mixture Reduction Algorithms for Target Tracking in Clutter. SPIE 1990, 1305, 434–445. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, B.; Pham, K.; Blasch, E.; Shen, D.; Chen, G. Consensus-based auction algorithm for distributed sensor management in space object tracking. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 4–11 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
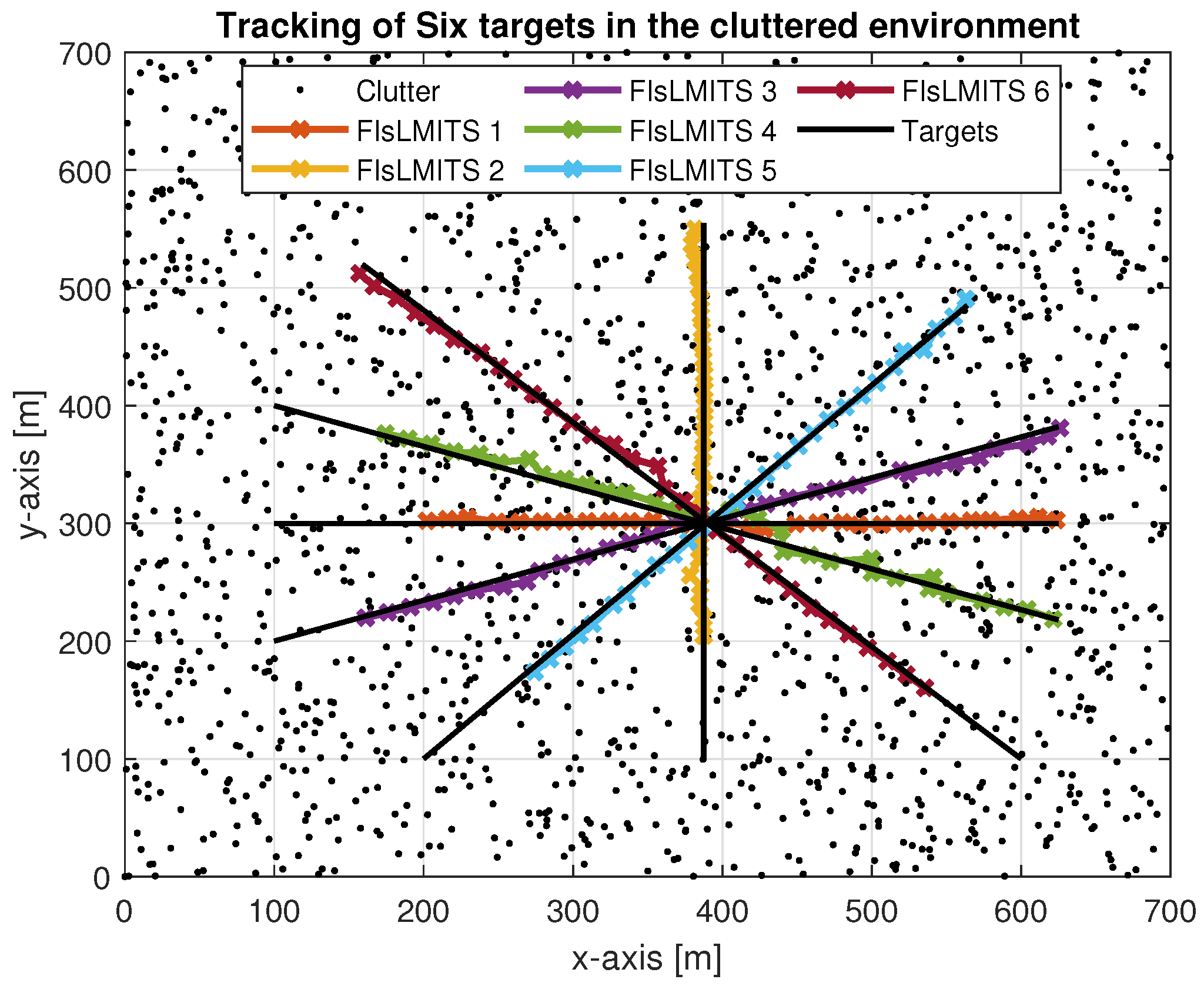
| Target No. | Position |
|---|---|
| 1 | [100; 300] |
| 2 | [387; 100] |
| 3 | [100; 200] |
| 4 | [100; 400] |
| 5 | [200; 100] |
| 6 | [600; 100] |
| Algorithm | nCases | nOk | nSwitched | nLost | nResult | Execution Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIsLMITS | 1185 | 978 | 192 | 15 | 1197 | 11.2 |
| FIsLMIPDA | 1090 | 720 | 260 | 110 | 1094 | 5.4 |
| FIsJITS | 1154 | 611 | 497 | 46 | 1163 | 16.3 |
| sJITS | 1119 | 648 | 390 | 81 | 1165 | 16.8 |
| LMITS | 996 | 595 | 197 | 204 | 1123 | 7.2 |
| LMIPDA | 1055 | 622 | 288 | 145 | 1145 | 0.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Memon, S.A.; Ullah, I.; Khan, U.; Song, T.L. Smoothing Linear Multi-Target Tracking Using Integrated Track Splitting Filter. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051289
Memon SA, Ullah I, Khan U, Song TL. Smoothing Linear Multi-Target Tracking Using Integrated Track Splitting Filter. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(5):1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051289
Chicago/Turabian StyleMemon, Sufyan Ali, Ihsan Ullah, Uzair Khan, and Taek Lyul Song. 2022. "Smoothing Linear Multi-Target Tracking Using Integrated Track Splitting Filter" Remote Sensing 14, no. 5: 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051289
APA StyleMemon, S. A., Ullah, I., Khan, U., & Song, T. L. (2022). Smoothing Linear Multi-Target Tracking Using Integrated Track Splitting Filter. Remote Sensing, 14(5), 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051289







