Varying Amplitude Vibration Phase Suppression Algorithm in ISAL Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. ISAL Turntable Imaging Model
2.1. Imaging Geometry
2.2. Signal Model of ISAL Imaging
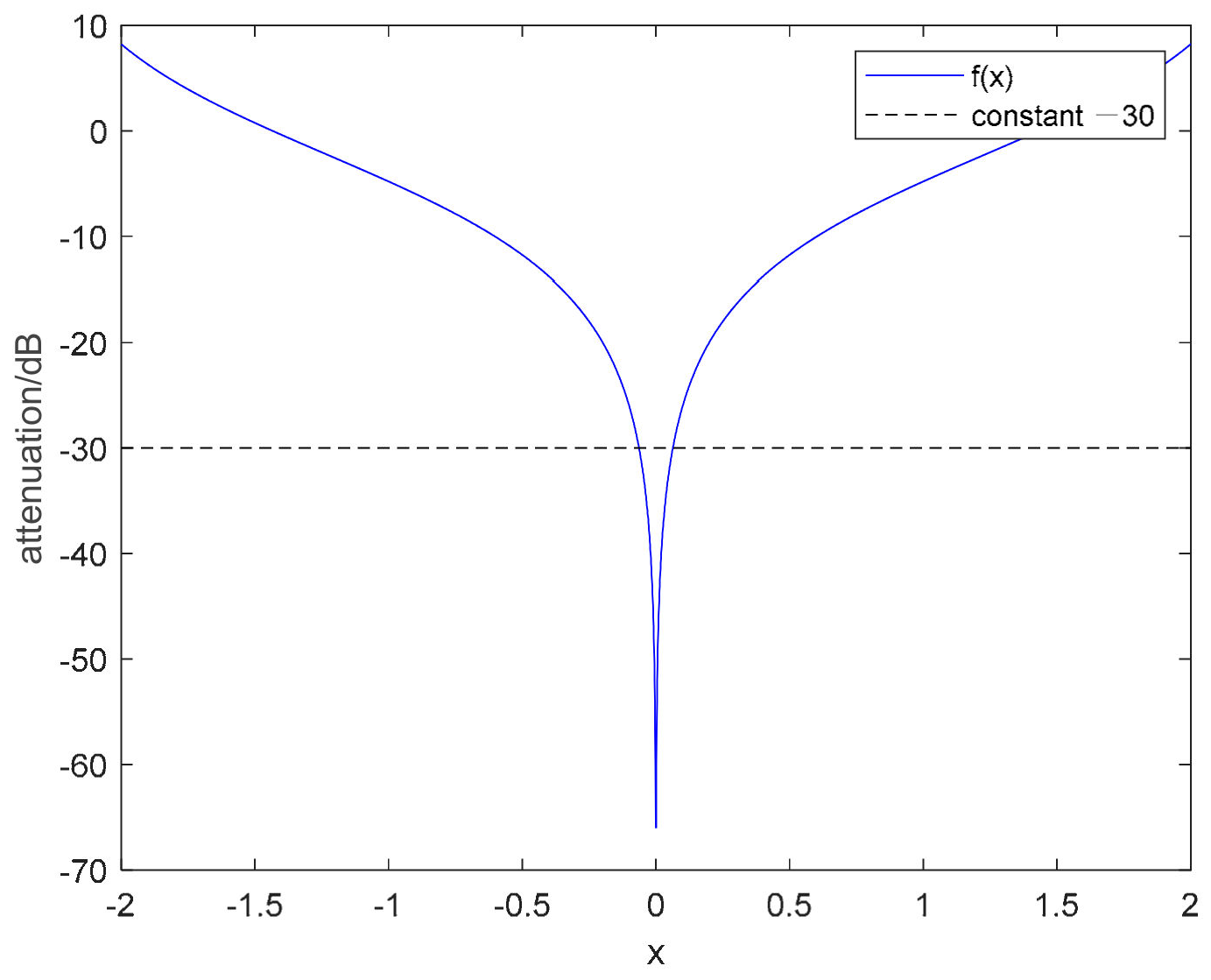
3. Vibration Phase Estimation and Compensation
4. Experimental Results and Analyses
4.1. Processing Results of Simulated Data
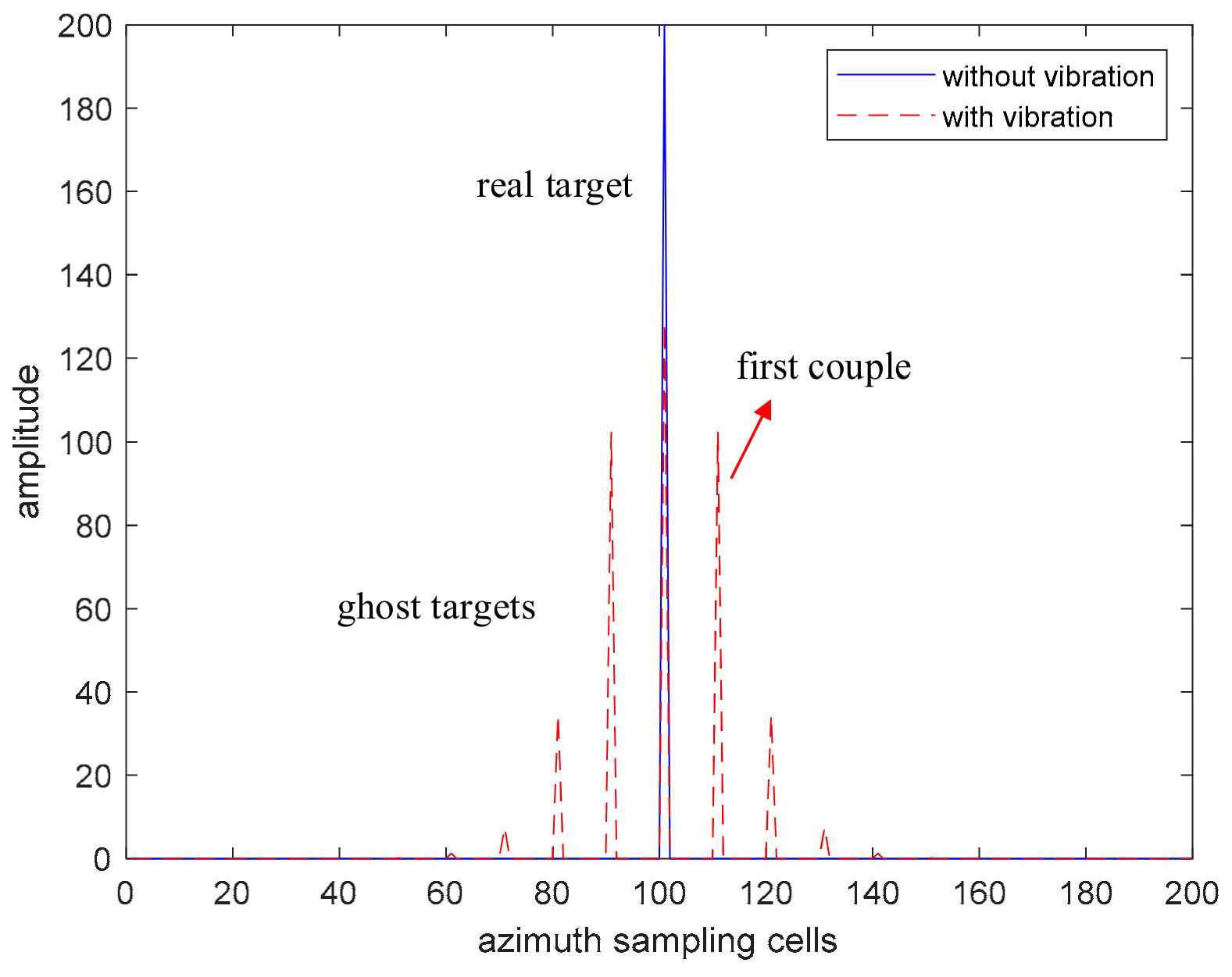
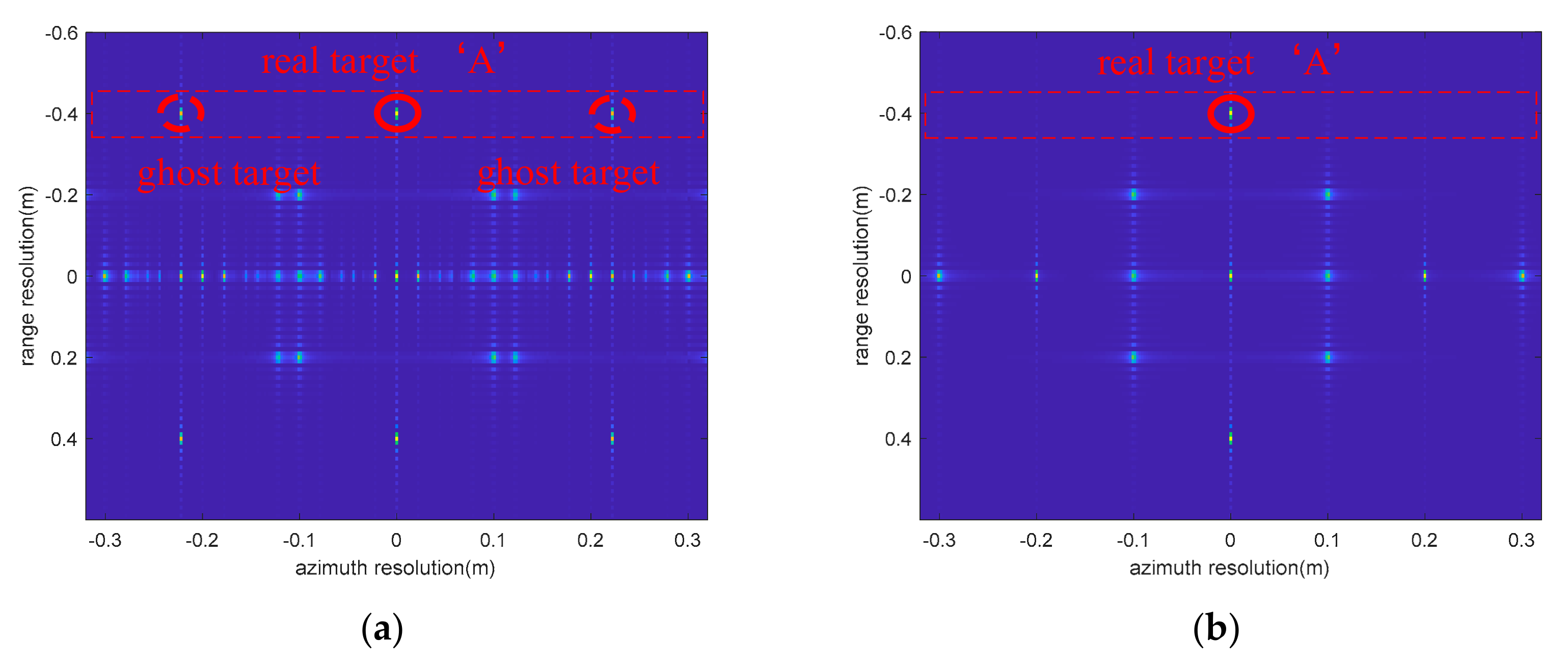
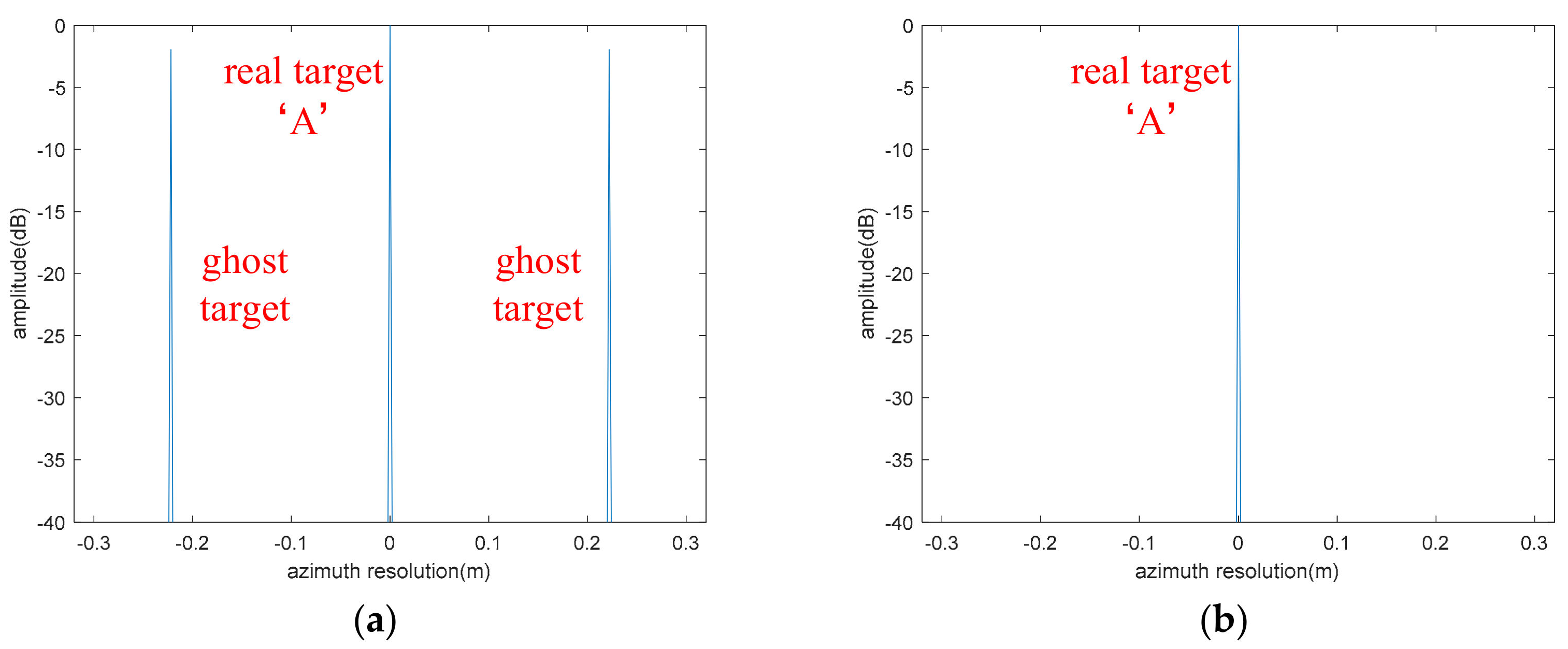
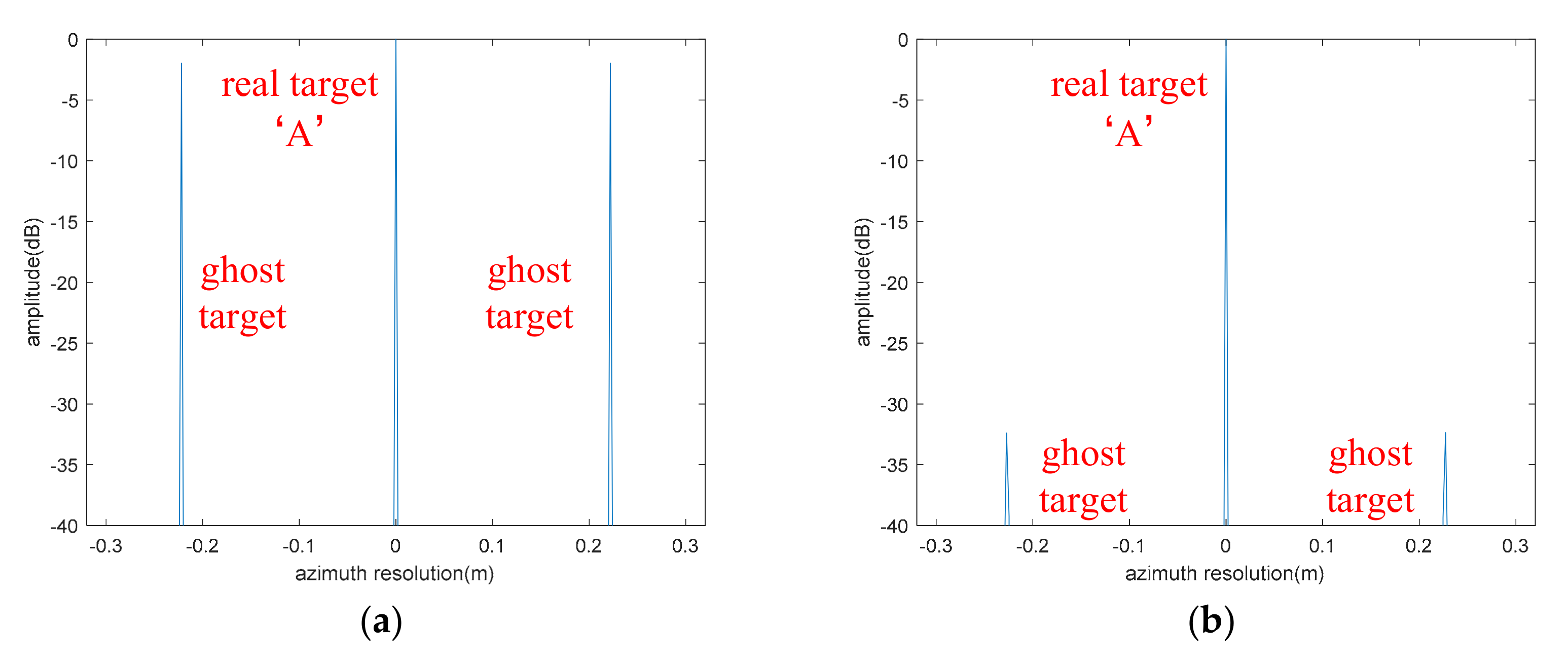
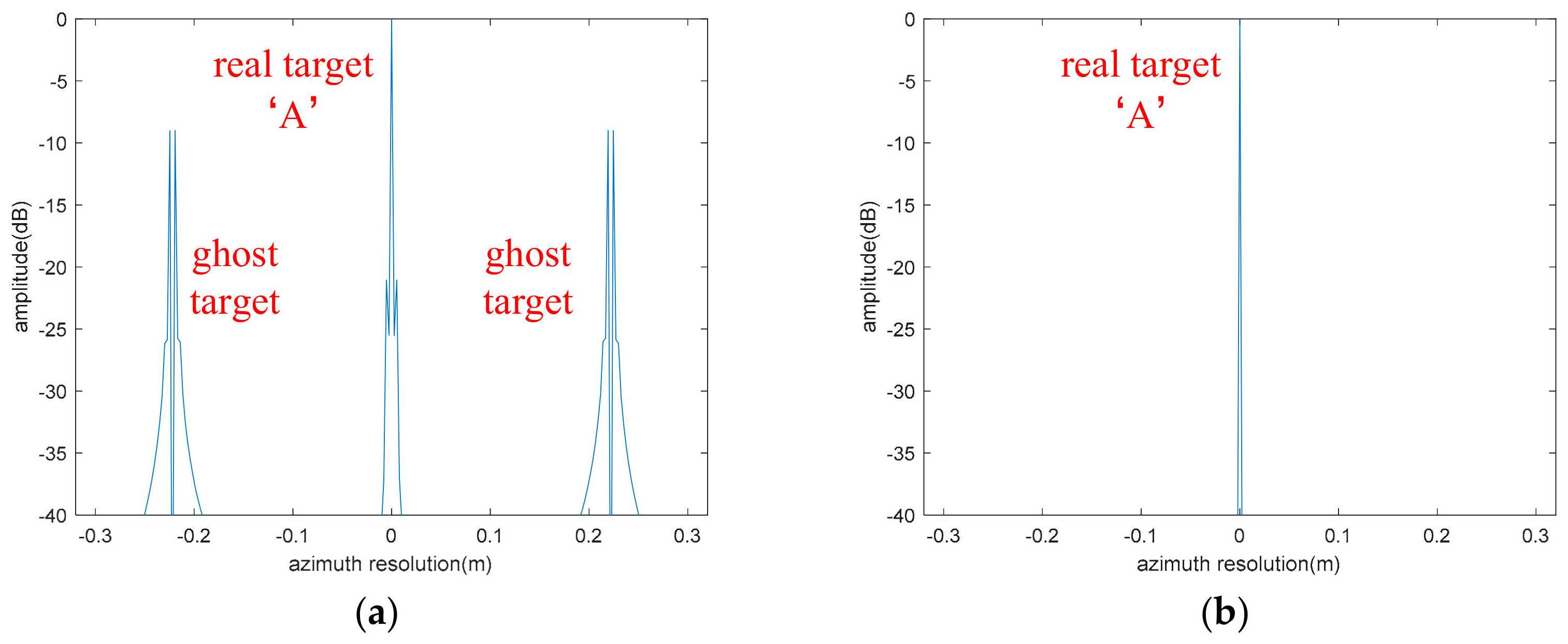
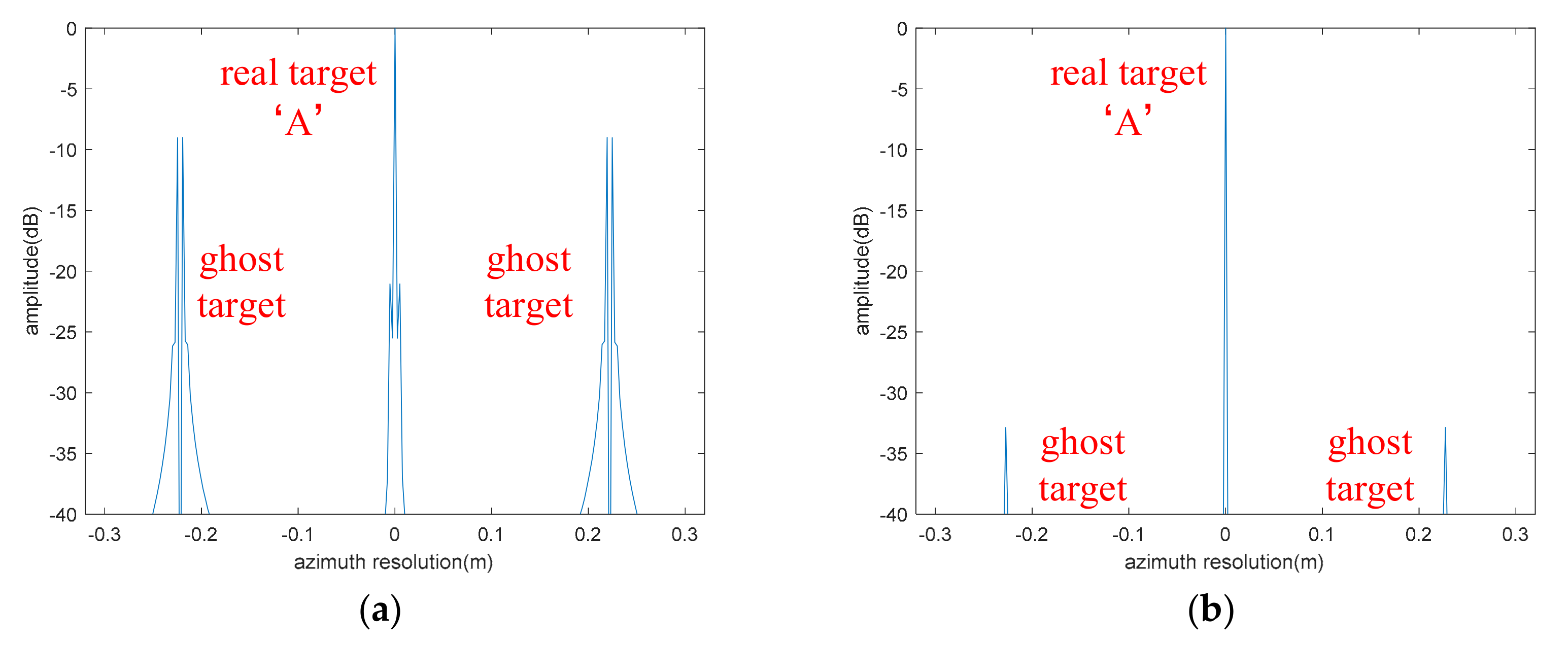
4.1.1. The Compensation Results of Fixed Amplitude Vibration Phase
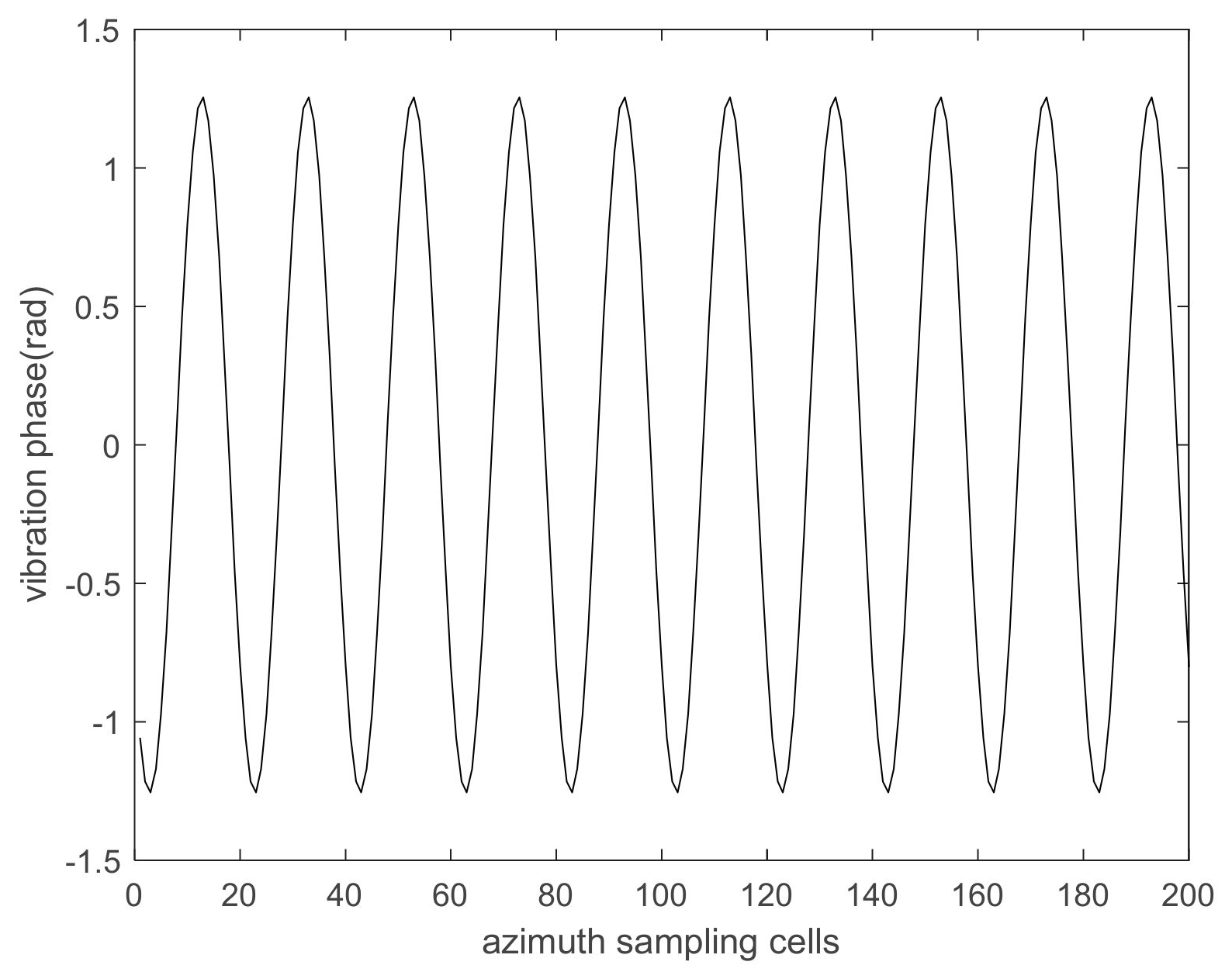
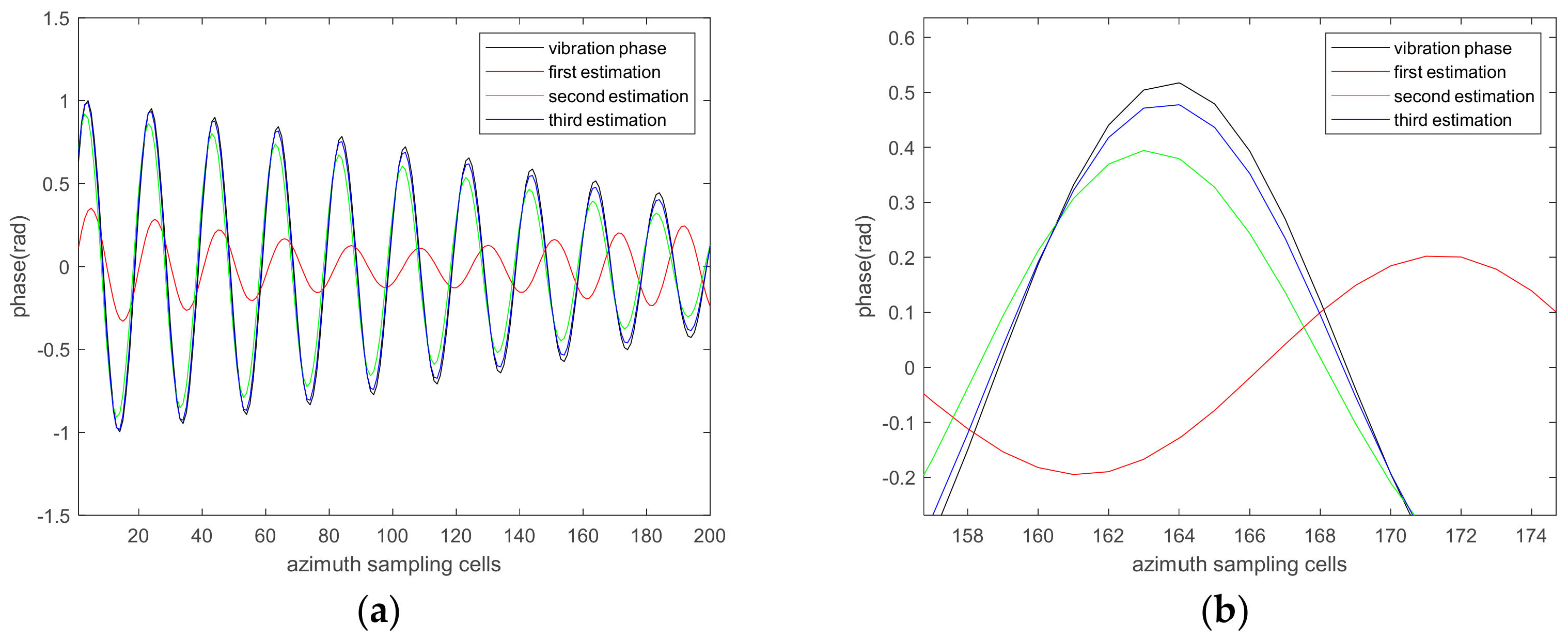
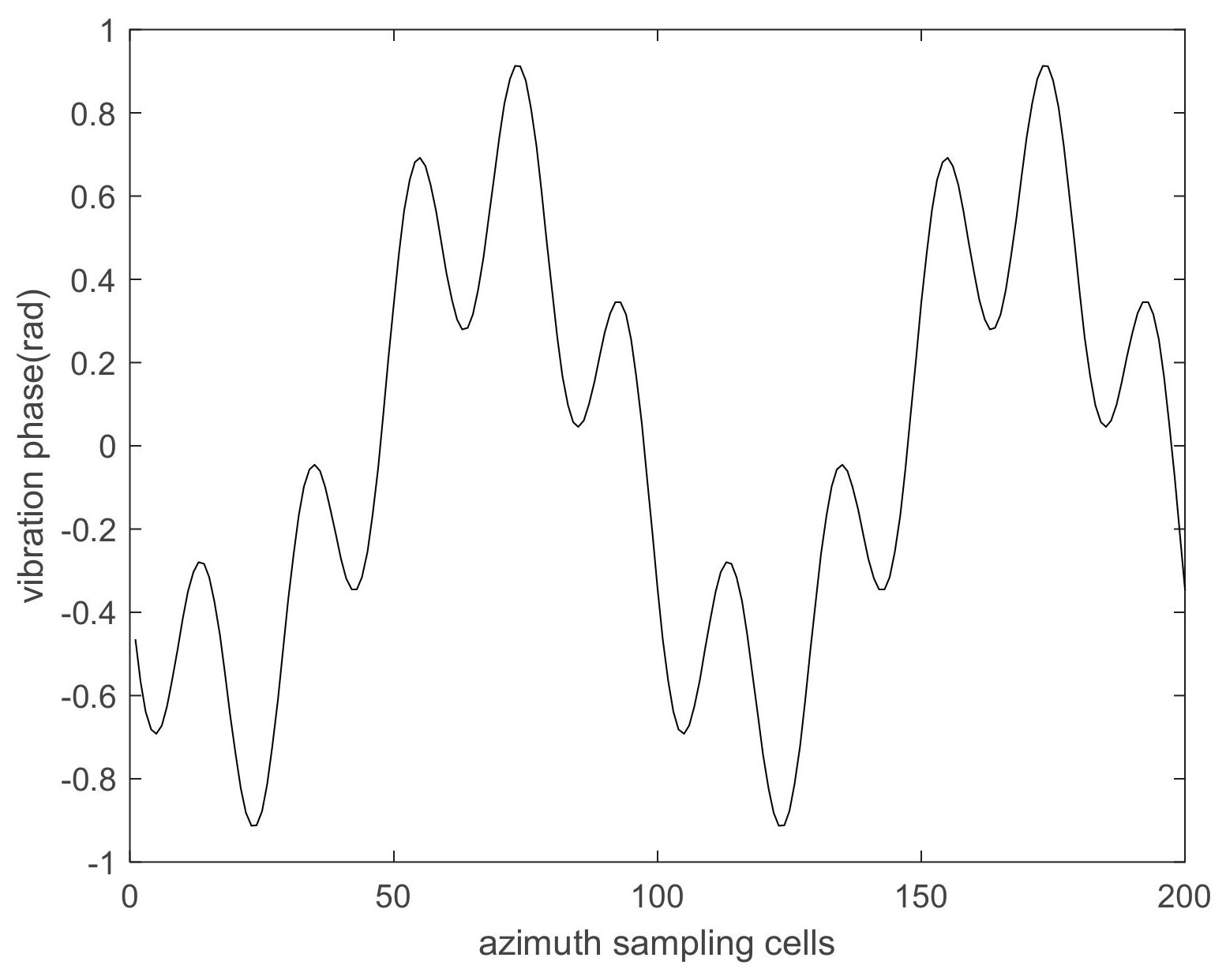
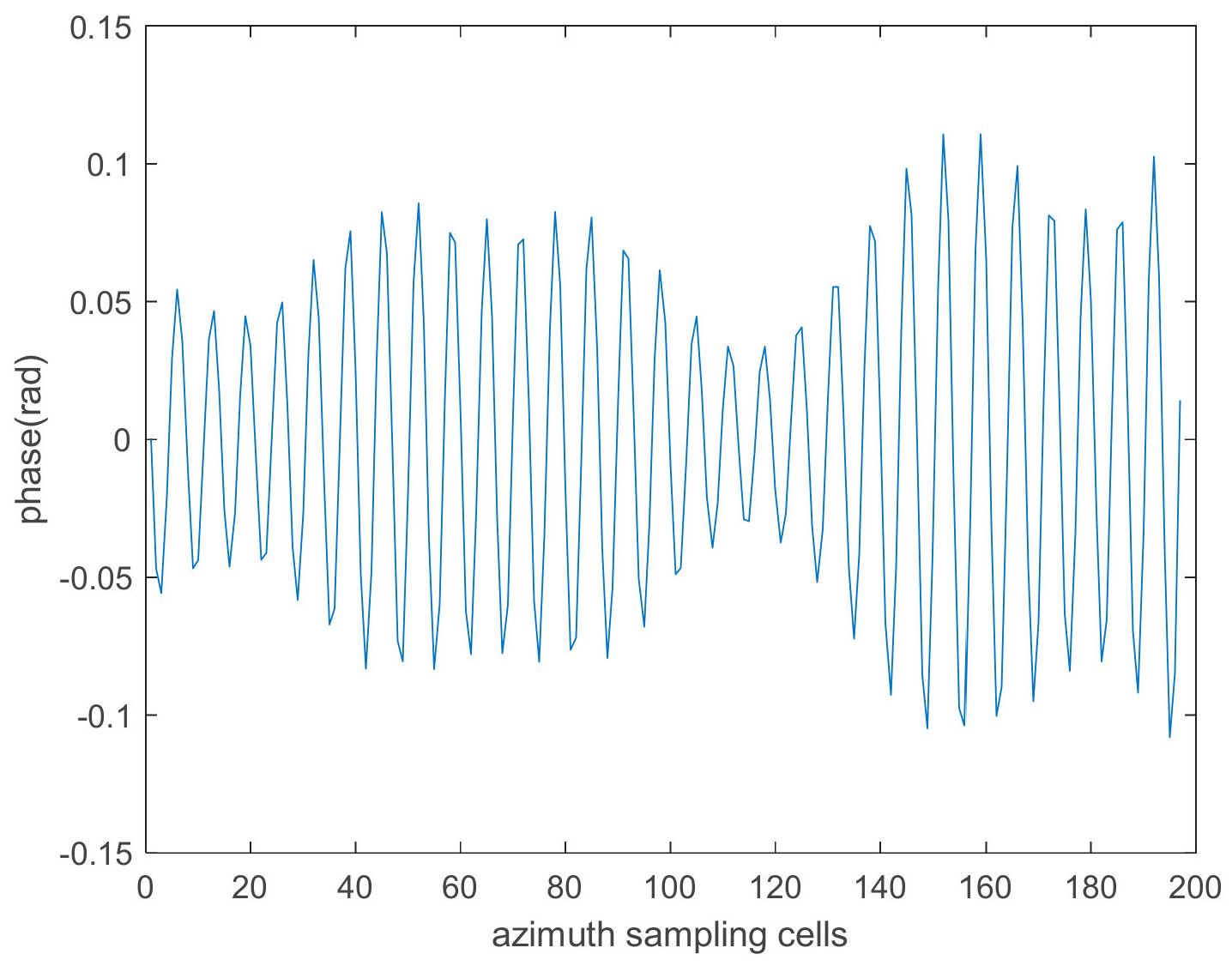
4.1.2. The Compensation Results of Varying Amplitude Vibration Phase
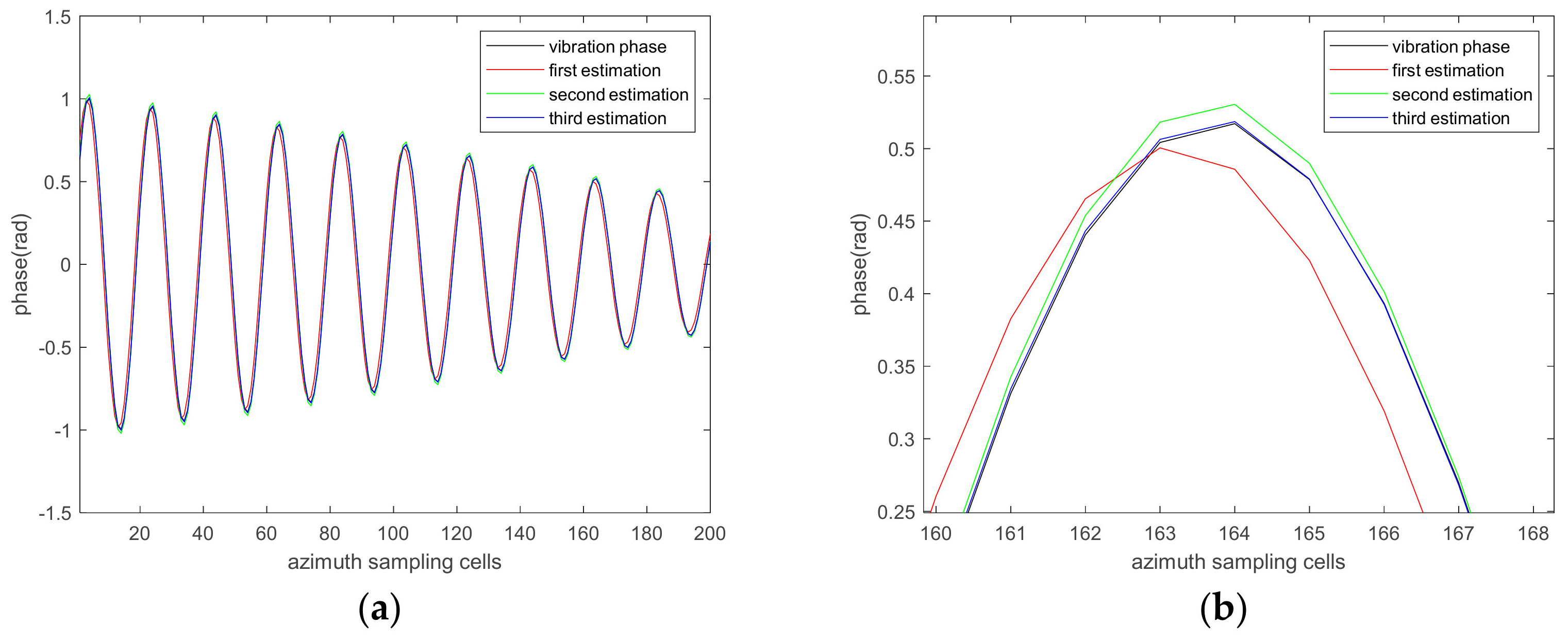
4.1.3. The Influence of the Number of Iterations on the Estimation Accuracy
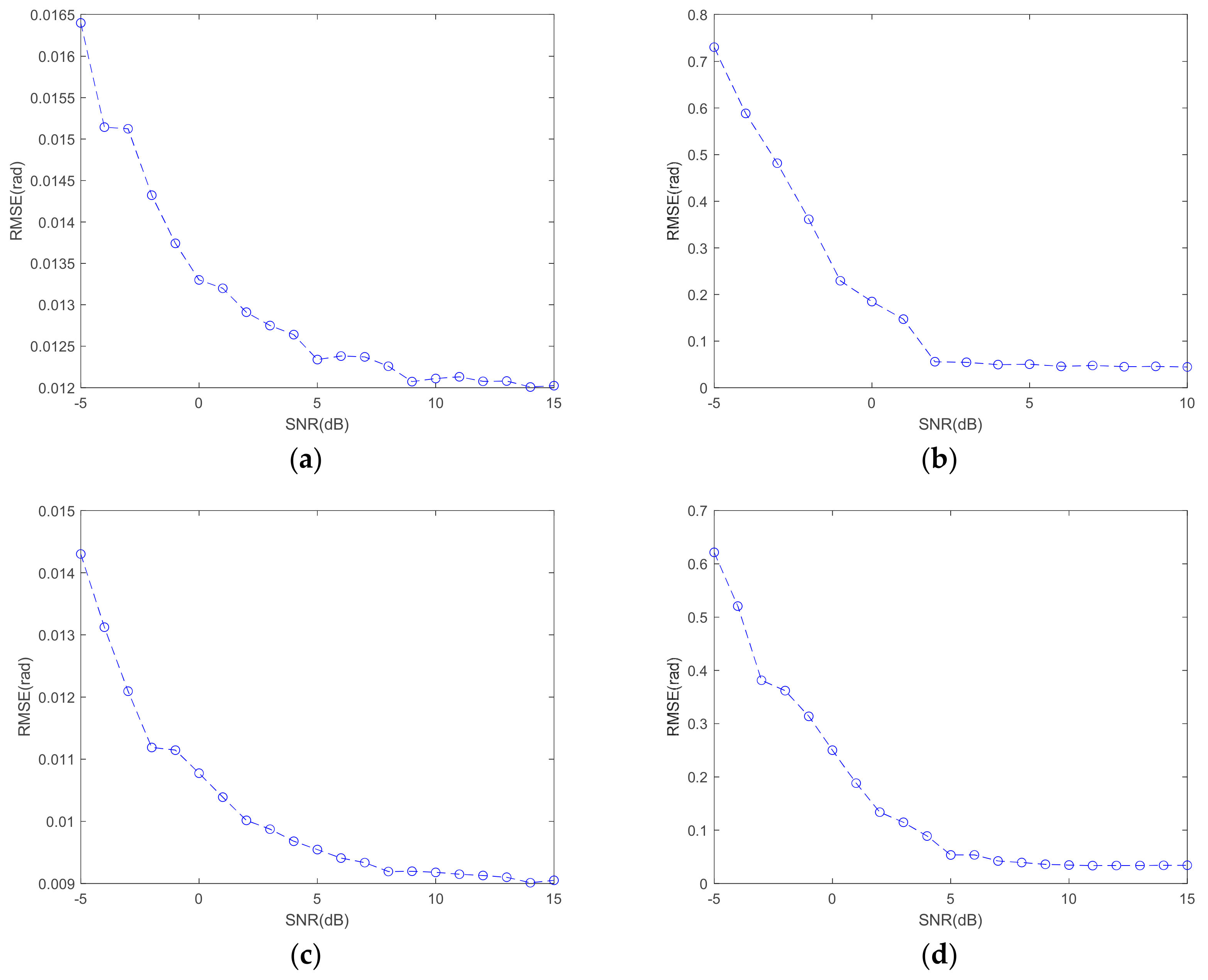
4.1.4. The Influence of SNR on the Estimation Accuracy
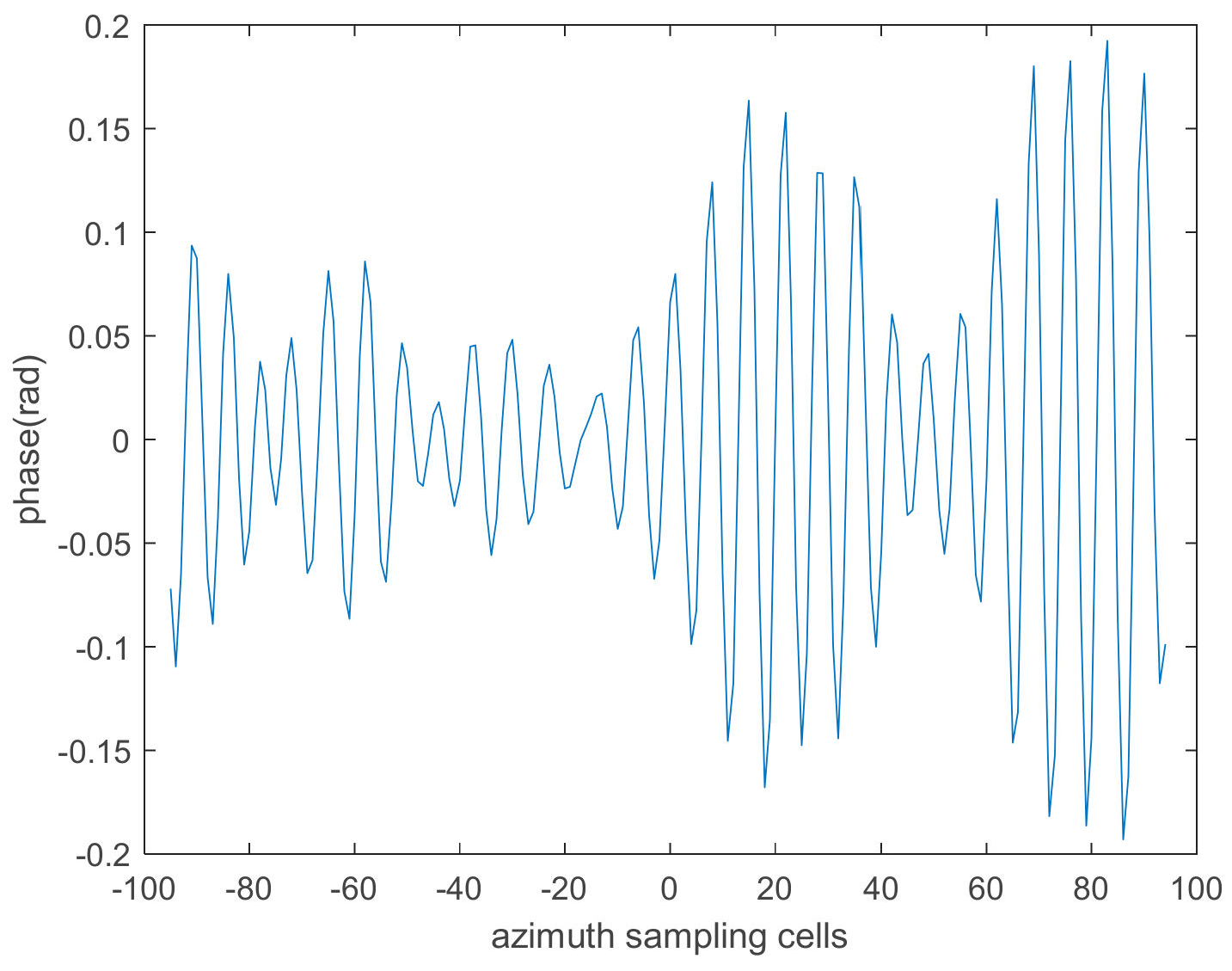
4.1.5. The Compensation Results of the Data Containing Multiple Vibration Components
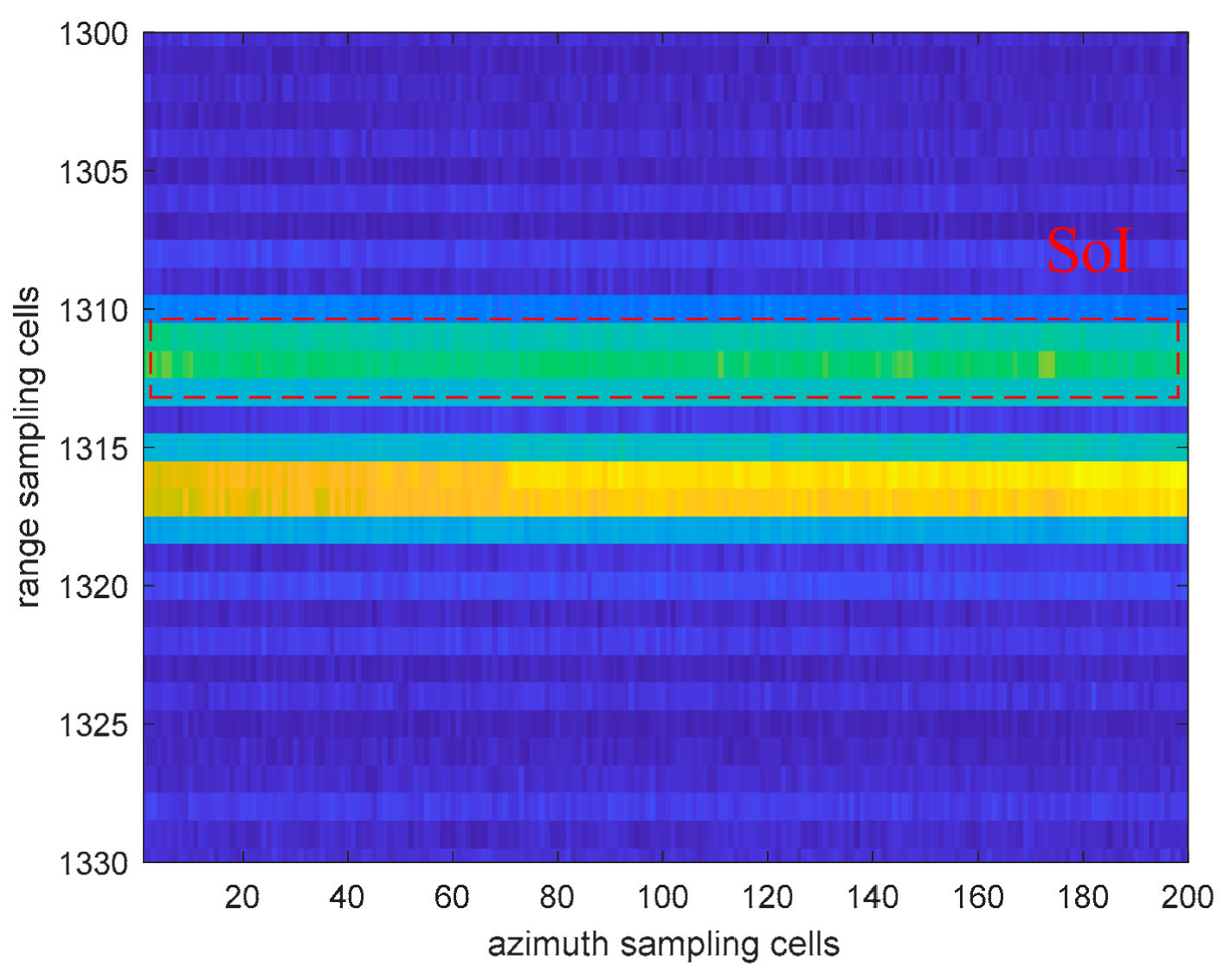
4.2. Processing Result of Real Data
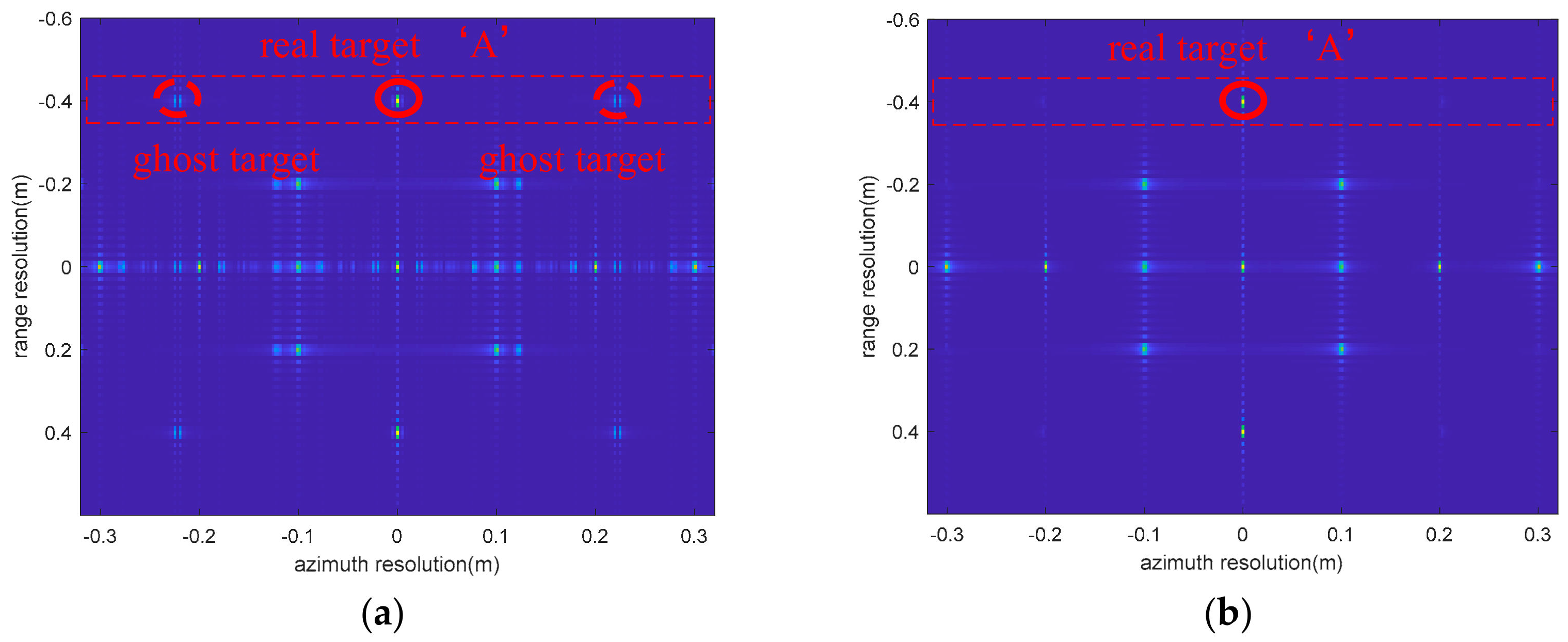
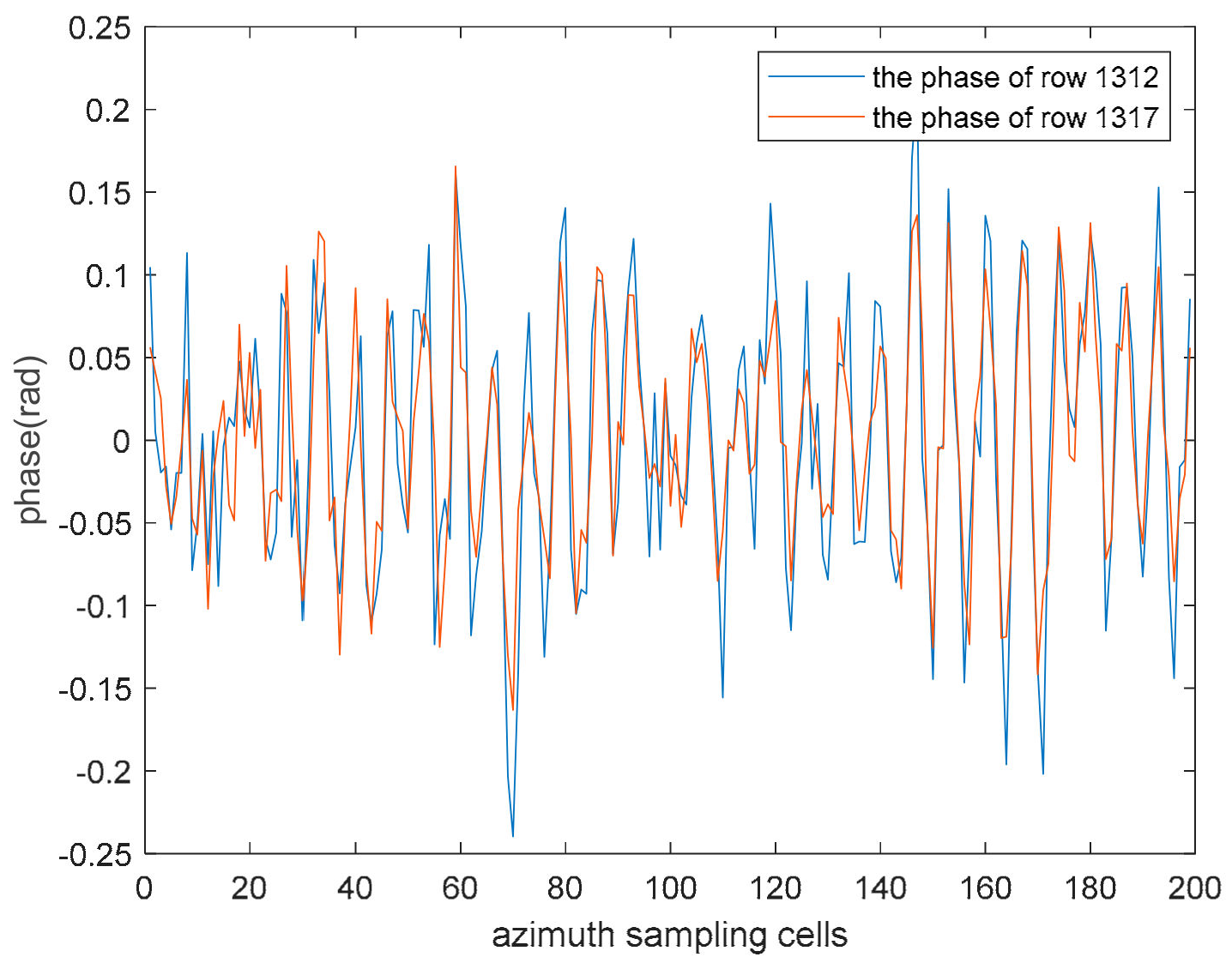
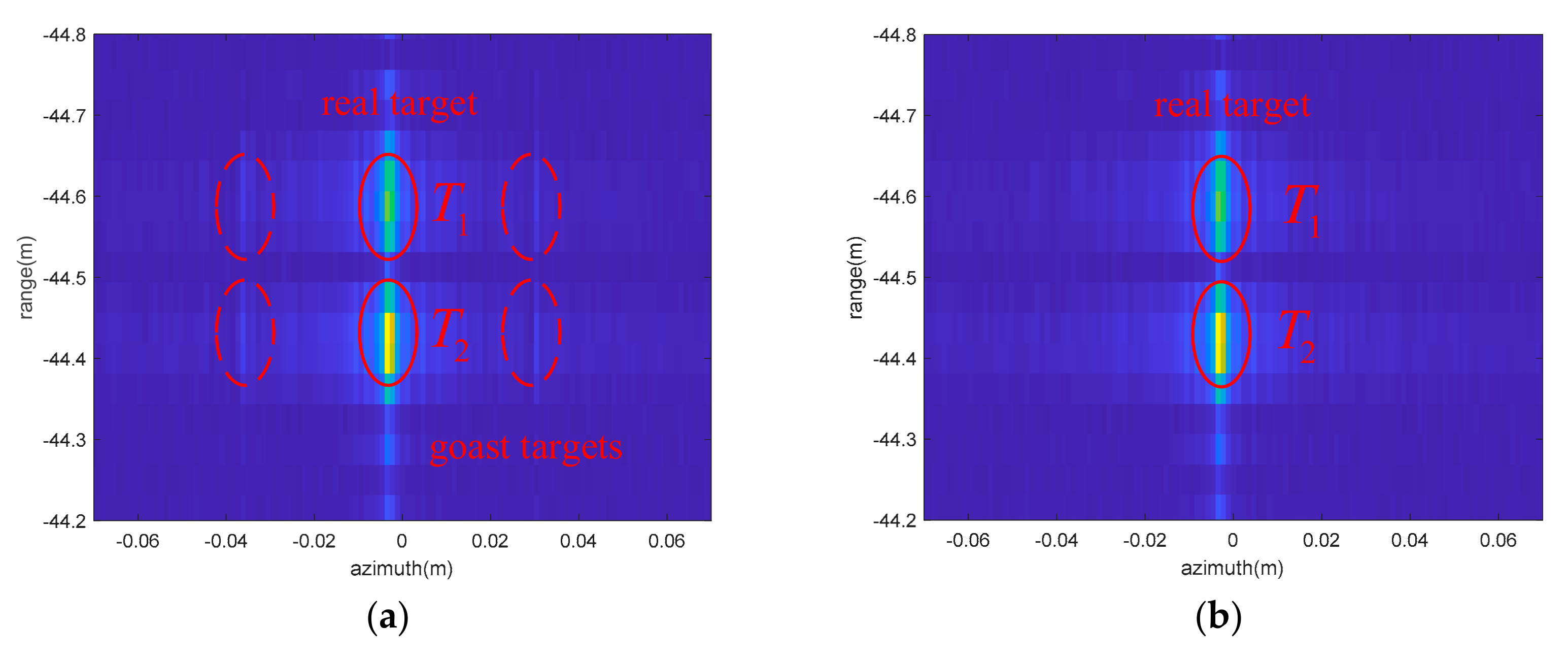
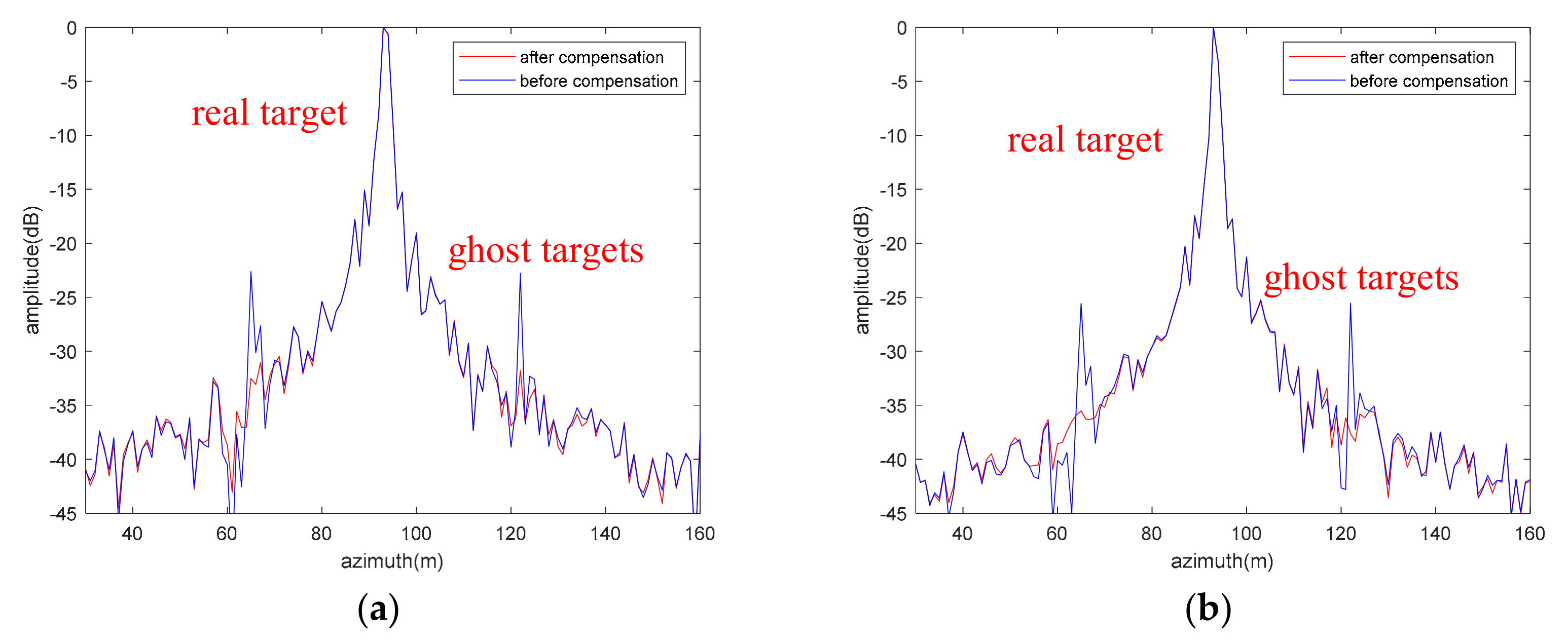
4.2.1. Stationary Point Targets
4.2.2. Rotating Point Targets
5. Discussion
- (1)
- The proposed algorithm can estimate the fixed and varying amplitude vibration phase.
- (2)
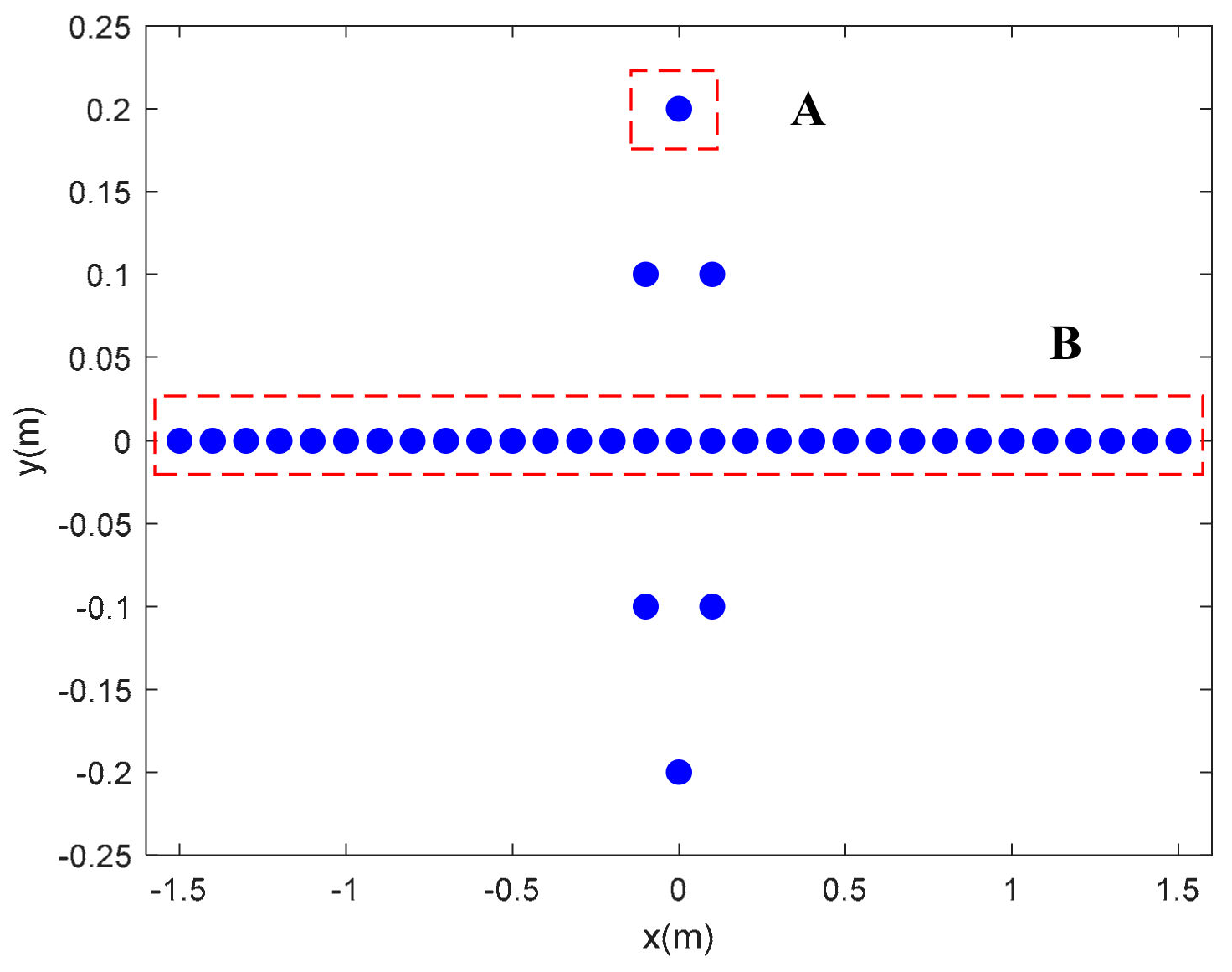
- The proposed algorithm is suitable for imaging scenes both with and without isolated points.
- (3)
- The residual vibration phase decreases as the number of iterations increases. In this paper, we operated three iterations for the vibration phase estimation.
- (4)
- Generally, the SNR of ISAL images is greater than 10 dB, so the proposed method has strong robustness to SNR.
- (5)
- The proposed algorithm can suppress ghost targets without introducing new phase error and without broadening the main lobe of targets.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beck, S.M.; Buck, J.R.; Buell, W.F.; Dickinson, R.P.; Kozlowski, D.A.; Marechal, N.J.; Wright, T.J. Synthetic-aperture imaging laser radar: Laboratory demonstration and signal processing. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 7621–7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Yin, H.F.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, J.F.; Zeng, X.D.; Tang, Y.; Xing, M.D. A novel sidelobe-suppression algorithm for airborne synthetic aperture imaging ladar. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 111, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Song, S.; Xu, W.; Hu, Y. Real-time inverse synthetic aperture ladar system based on continuous m-sequence phase modulation. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2021, 54, 072801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Yu, T.; Meng-dao, X.; Zheng, B. Experimentation system of synthetic aperture imaging lidar. J. Electron. 2009, 26, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouch, S.; Barber, Z.W. Laboratory demonstrations of interferometric and spotlight synthetic aperture ladar techniques. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 24237–24246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, J.F.; Luan, Z.; Wang, L.J.; Xu, Q.; Li, G.Y.; Zhang, G.; Liu, L.R. Airborne down-looking synthetic aperture imaging ladar field experiment and its flight testing. Chin. J. Lasers 2017, 44, 0110001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Z.; Wang, N.; Wang, R.; Zhang, K.S.; Wu, Y.R. Imaging method for airborne SAL data. Electron. Lett. 2017, 53, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, V.; Li, F.; Ho, S.S.; Wechsler, H. Micro-doppler effect in radar: Phenomenon, model, and simulation study. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2006, 42, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, P.; Astola, J.; Egiazarian, K.; Totsky, A. On Micro-Doppler Period Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2013 19th International Conference on Control Systems and Computer Science, Bucharest, Romania, 29–31 May 2013; pp. 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Paired echo suppression algorithm in helicopter-borne SAR imaging. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2017, 11, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, B.; Xu, L. Compensation for High-Frequency Vibration of Platform in SAR Imaging Based on Adaptive Chirplet Decomposition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 792–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Pepin, M.; Wright, A.; Dunkel, R.; Atwood, T.; Santhanam, B.; Gerstle, W.; Doerry, A.W.; Hayat, M.M. Reduction of vibration-induced artifacts in synthetic aperture radar imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 3063–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Pepin, M.; Beach, R.J.; Dunkel, R.; Atwood, T.; Santhanam, B.; Gerstle, W.; Doerry, A.W.; Hayat, M.M. SAR-Based Vibration Estimation Using the Discrete Fractional Fourier Transform. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 4145–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Setlur, P.; Amin, M.; Thayaparan, T. Micro-Doppler signal estimation for vibrating and rotating targets. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Symposium on Signal Processing and Its Applications, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 28–31 August 2005; pp. 639–642. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Lei, P.; Hong, W. SAR-based paired echo focusing and suppression of vibrating targets. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 7593–7605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, D.J. Vibration phases estimation based on multi-channel interferometry for ISAL. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 6481–6490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Wang, B.; Xiang, M.; Li, C.; Wang, S. Vibration compensation method based on instantaneous ranging model for triangular FMCW ladar signals. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 15918–15939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ash, J.; Ertin, E.; Potter, L.; Zelnio, E. Wide-angle synthetic aperture radar imaging: Models and algorithms for anisotropic scattering. IEEE Signal Processing Mag. 2014, 31, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

















| 1550 nm | 10°/s | ||
| Pulse width | 10 us | 1 km | |
| Band width | 15 GHz | Vibration frequency | 5 kHz |
| Fs | 250 MHz | Initial vibration phase | 1 rad |
| PRF | 100 kHz | The max vibration amplitude | /10 |
| Vibration frequency 1 | 5 kHz | Vibration frequency 2 | 1 kHz |
| Initial vibration phase 1 | 1 rad | Initial vibration phase 2 | 0.5 rad |
| Vibration amplitude 1 | /40 | Vibration amplitude 2 | /20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, H.; Guo, L.; Li, Y.; Han, L.; Xing, M.; Zeng, X. Varying Amplitude Vibration Phase Suppression Algorithm in ISAL Imaging. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051122
Yin H, Guo L, Li Y, Han L, Xing M, Zeng X. Varying Amplitude Vibration Phase Suppression Algorithm in ISAL Imaging. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(5):1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051122
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Hongfei, Liang Guo, Yachao Li, Liang Han, Mengdao Xing, and Xiaodong Zeng. 2022. "Varying Amplitude Vibration Phase Suppression Algorithm in ISAL Imaging" Remote Sensing 14, no. 5: 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051122
APA StyleYin, H., Guo, L., Li, Y., Han, L., Xing, M., & Zeng, X. (2022). Varying Amplitude Vibration Phase Suppression Algorithm in ISAL Imaging. Remote Sensing, 14(5), 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051122








