The Roles of Sea Ice Export, Atmospheric and Oceanic Factors in the Seasonal and Regional Variability of Arctic Sea Ice during 1979–2020
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.1.1. Sea Ice Concentration
2.1.2. Sea Ice Thickness
2.1.3. Sea Ice Drift
2.1.4. Sea Ice Albedo
2.1.5. Weather Data
2.2. Methods
3. Results
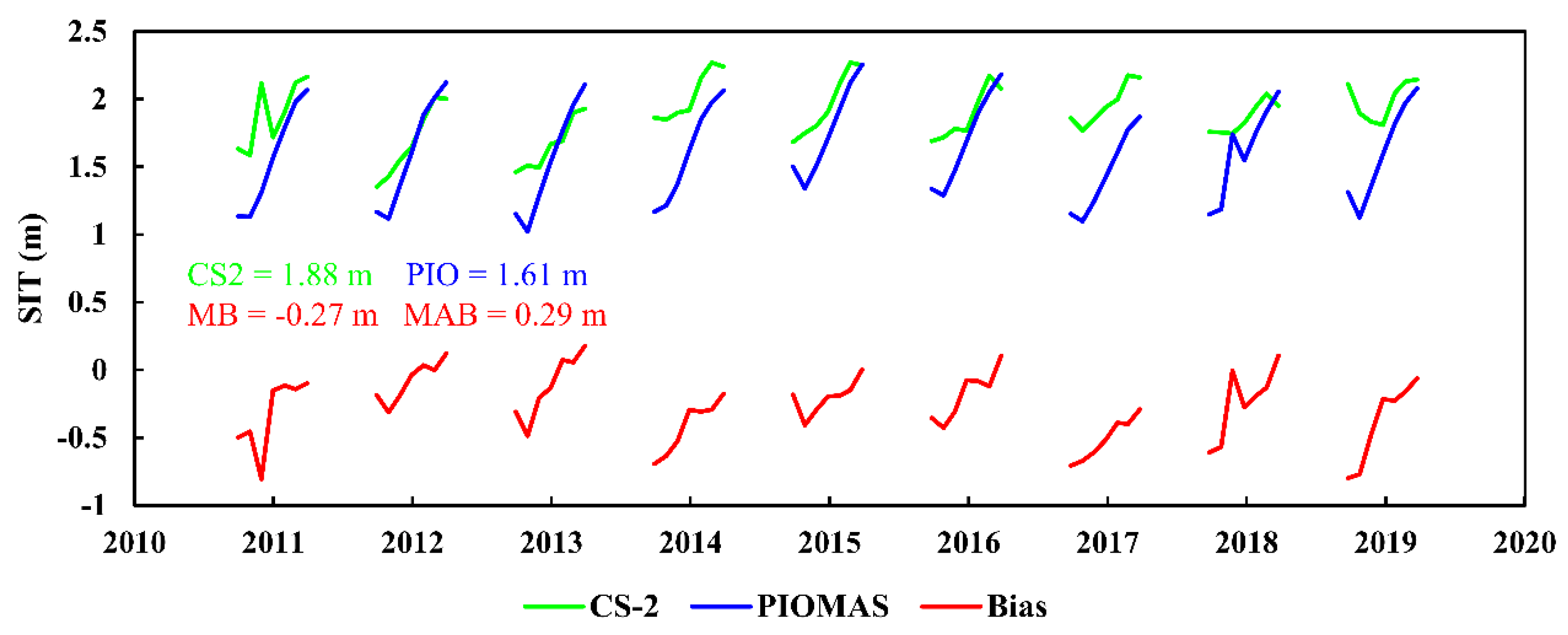
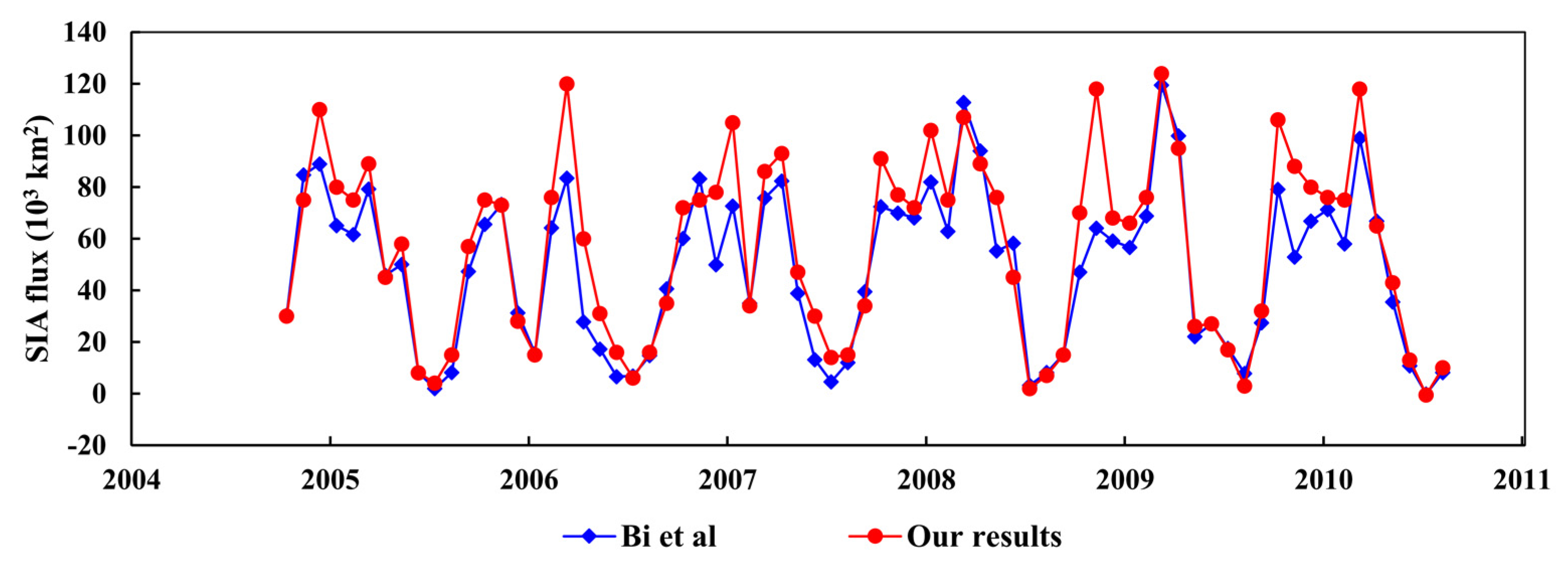
3.1. The Comparisons between PIOMAS and CS2
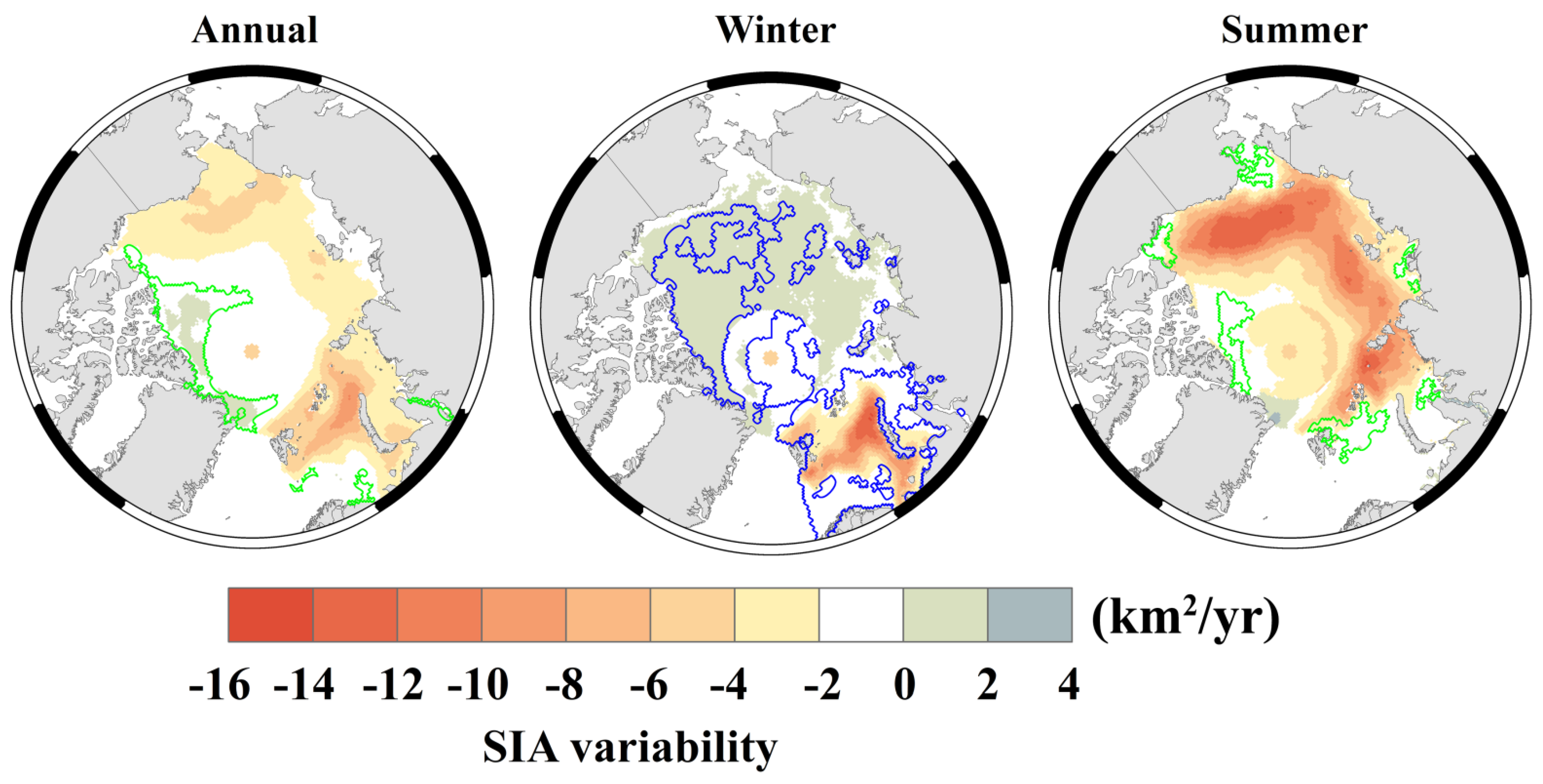
3.2. Seasonal and Regional Variability of Sea Ice Area
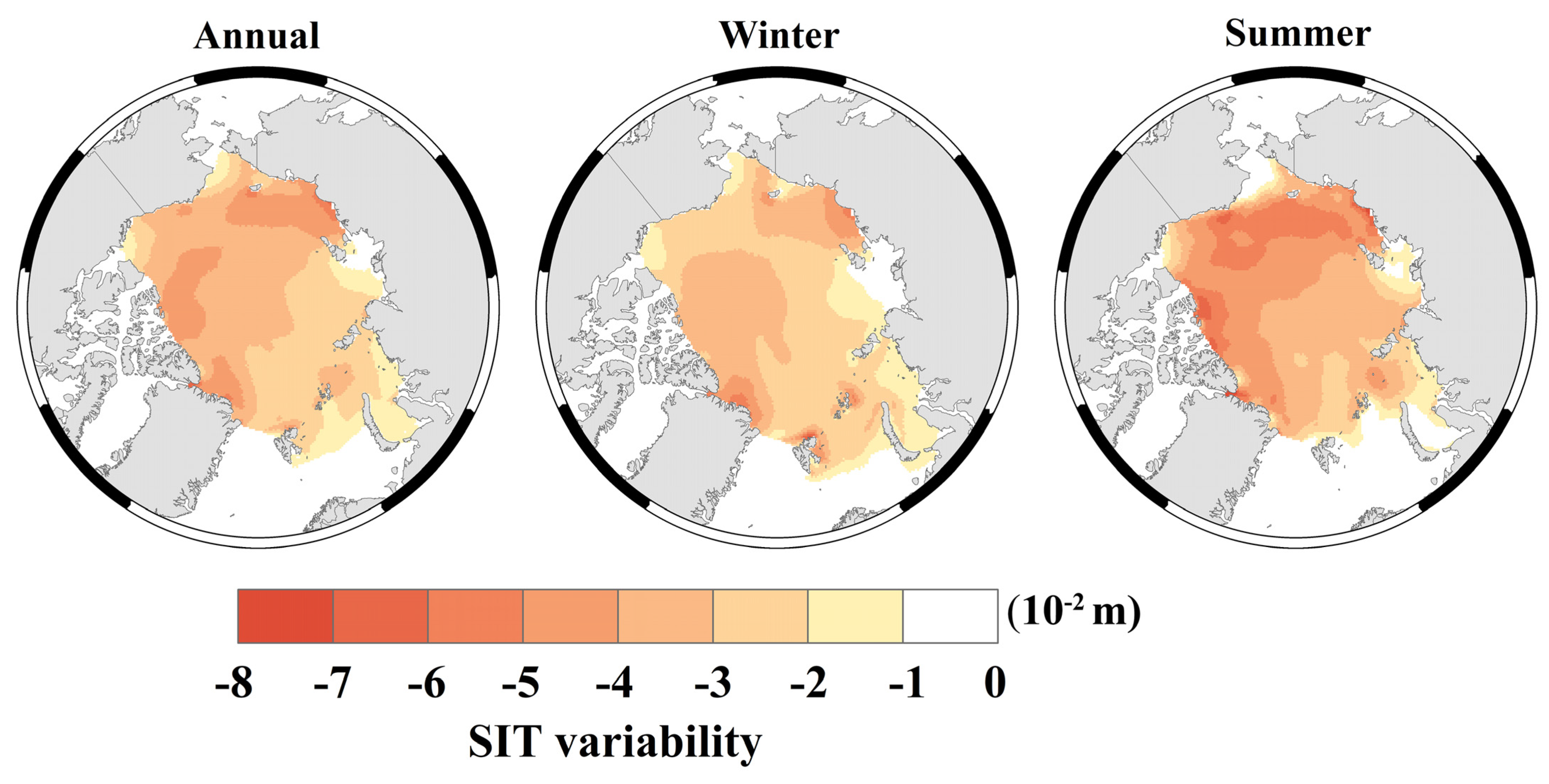
3.3. Seasonal and Regional Variability of Sea Ice Thickness
4. Discussion
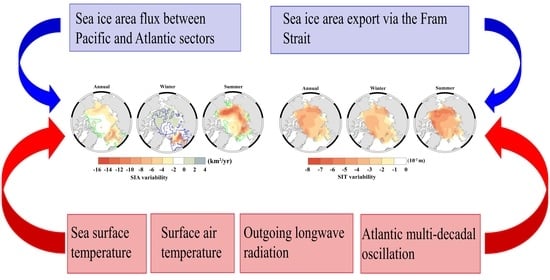
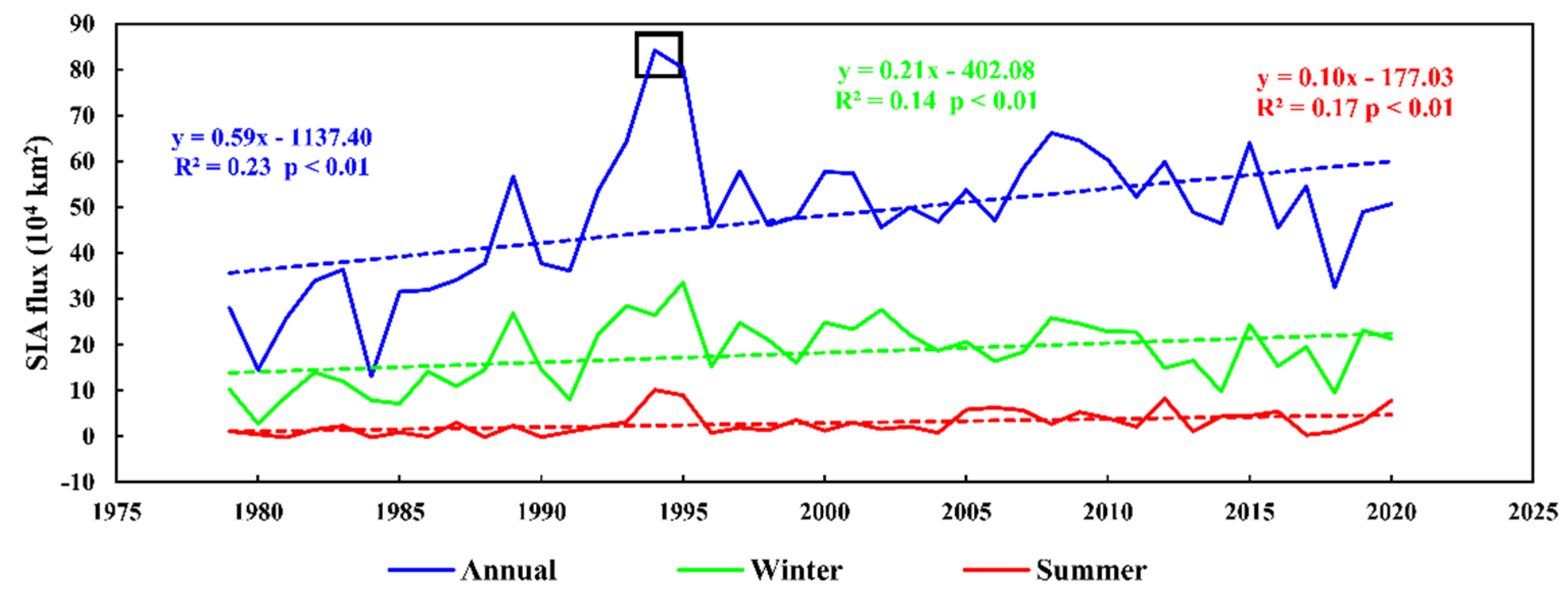
4.1. Role of Sea Ice Export in Sea Ice Loss
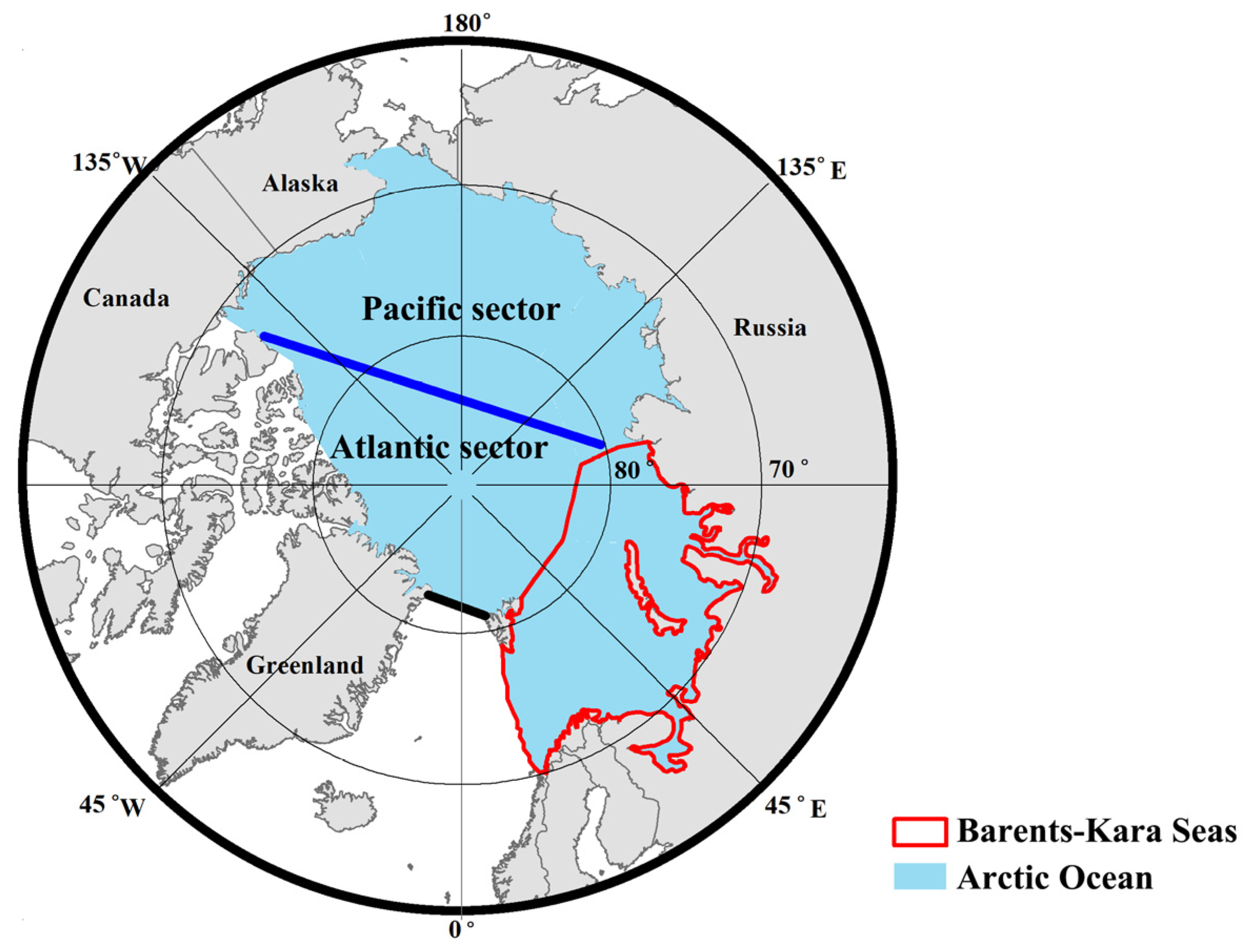
4.1.1. Impact of Sea Ice Area Flux between the Atlantic and Pacific Sectors on Sea Ice Loss
4.1.2. Impact of Sea Ice Area Outflow through the Fram Strait on Sea Ice Loss
4.2. Roles of Atmospheric and Oceanic Factors in Sea Ice Loss
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bi, H.; Yang, Q.; Liang, X. Contributions of advection and melting processes to the decline in sea ice in the Pacific sector of the Arctic Ocean. Cryosphere 2019, 13, 1423–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwok, R. Arctic sea ice thickness, volume, and multiyear ice coverage: Losses and coupled variability (1958–2018). Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 105005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R.; Rothrock, D. Decline in Arctic Sea ice thickness from submarine and ICESat records: 1958–2008. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L15501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krumpen, T.; Gerdes, R.; Haas, C.; Hendricks, S.; Herber, A.; Selyuzhenok, V.; Smedsrud, L.; Spreen, G. Recent summer sea ice thickness surveys in Fram Strait and associated ice volume fluxes. Cryosphere 2016, 10, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, W.C.; Magnusdottir, G. Year-to-year Variability in Arctic Minimum Sea Ice Extent and Its Preconditions in Observations and the CESM Large Ensemble Simulations. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rampal, P.; Weiss, J.; Marsan, D. Positive trend in the mean speed and deformation rate of Arctic sea ice, 1979–2007. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2009, 114, C05013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreen, G.; Kwok, R.; Menemenlis, D. Trends in Arctic sea ice drift and tole of wind forcing: 1992–2009. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L19501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, T.; Steele, M.; Zhang, J. Seasonality and long-term trend of Arctic Ocean surface stress in a model. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 1723–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, L.; Alexeev, V.A.; Walsh, J.E. Arctic Sea Ice Growth in Response to Synoptic- and Large-ScaleAtmospheric Forcing from CMIP5 Models. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 6083–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olonscheck, D.; Mauritsen, T.; Notz, D. Arctic sea-ice variability is primarily driven by atmospheric temperature fluctuations. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, L.; Vázquez, M.; Eiras-Barca, J.; Sorí, R.; Algarra, I.; Nieto, R. Atmospheric moisture transport and the decline in Arctic Sea ice. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2019, 10, e588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygård, T.; Naakka, T.; Vihma, T. Horizontal Moisture Transport Dominates the Regional Moistening Patterns in the Arctic. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 6793–6807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegyi, B.M.; Taylor, P.C. The regional influence of the Arctic Oscillation and Arctic Dipole on the wintertime Arctic surface radiation budget and sea ice growth. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 4341–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehder, Z.; Niederdrenk, A.L.; Kaleschke, L.; Kutzbach, L. Analyzing links between simulated Laptev Sea sea ice and atmospheric conditions over adjoining landmasses using causal-effect networks. Cryosphere 2020, 14, 4201–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Yadav, J.; Mohan, R. Global warming leading to alarming recession of the Arctic sea-ice cover: Insights from remote sensing observations and model reanalysis. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Screen, J.A.; Simmonds, I. The central role of diminishing sea ice in recent Arctic temperature amplification. Nature 2010, 464, 1334–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinault, J.L. The Moist Adiabat, Key of the Climate Response to Anthropogenic Forcing. Climate 2020, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steele, M.; Dickinson, S. The phenology of Arctic Ocean surface warming. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 6847–6861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R. Summer sea ice motion from the 18 GHz channel of AMSR-E and the exchange of sea ice between the Pacific and Atlantic sectors. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L03504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woodgate, R.A.; Weingartner, T.J.; Lindsay, R. Observed increases in Bering Strait oceanic fluxes from the Pacific to the Arctic from 2001 to 2011 and their impacts on the Arctic Ocean water column. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 2012GL054092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serreze, M.C.; Crawford, A.D.; Stroeve, J.C.; Barrett, A.P.; Woodgate, R.A. Variability, trends, and predictability of seasonal sea ice retreat and advance in the Chukchi Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 7308–7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudels, B. Arctic Ocean circulation, processes and water masses: A description of observations and ideas with focus on the period prior to the International Polar Year 2007–2009. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 132, 22–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Ke, C.-Q.; Shen, X.; Cheng, B.; Li, H. Investigation of the Arctic Sea ice volume from 2002 to 2018 using multi-source data. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 2509–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onarheim, I.H.; Eldevik, T.; Smedsrud, L.H.; Stroeve, J.C. Seasonal and regional manifestation of Arctic sea ice loss. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 4917–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Yadav, J.; Mohan, R. Spatio-temporal change and variability of Barents-Kara sea ice, in the Arctic: Ocean and atmospheric implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 753, 142046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenigk, T.; Caian, M.; Nikulin, G.; Schimanke, S. Regional Arctic sea ice variations as predictor for winter climate conditions. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 317–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Screen, J.A. Simulated atmospheric response to regional and pan-Arctic sea ice loss. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 3945–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Labe, Z.; Magnusdottir, G.; Stern, H. Variability of Arctic Sea Ice Thickness Using PIOMAS and the CESM Large Ensemble. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 3233–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R.; Cunningham, G.F.; Pang, S.S. Fram Strait sea ice outflow. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2004, 109, C01009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalieri, D.J.; Parkinson, C.L.; Gloersen, P.; Zwally, H.J. Sea Ice Concentrations from Nimbus-7 SMMR and DMSP SSM/I-SSMIS Passive Microwave Data, 1980–1999; Digital Media; National Snow and Ice Data Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Fetterer, F.; Knowles, K.; Meier, W.N.; Savoie, M.; Windnagel, A.K. Sea Ice Index, Version 3. [Indicate Subset Used]; National Snow and Ice Data Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Rothrock, D.A. Modeling Global Sea Ice with a Thickness and Enthalpy Distribution Model in Generalized Curvilinear Coordinates. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 845–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schweiger, A.; Lindsay, R.; Zhang, J.; Steele, M.; Stern, H.; Kwok, R. Uncertainty in Modeled Arctic Sea Ice Volume. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, C00D06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Key, J.; Kwok, R.; Zhang, J. Comparison of Arctic Sea ice thickness from satellites, aircraft, and PIOMAS data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurtz, N.T.; Galin, N.; Studinger, M. An improved CryoSat-2 sea ice freeboard retrieval algorithm through the use of waveform fitting. Cryosphere 2014, 8, 1217–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tschudi, M.A.; Meier, W.N.; Stewart, J.S. An enhancement to sea ice motion and age products at the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC). Cryosphere 2020, 14, 1519–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumata, H.; Gerdes, R.; Kauker, F.; Karcher, M. Empirical error functions for monthly mean Arctic sea-ice drift. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 120, 7450–7475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.T.; Ke, C.Q.; Shen, X.; Li, M.; Shao, Z.D. Summer albedo variations in the Arctic sea ice region from 1982 to 2015. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 3008–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Shea, D.J. Atlantic hurricanes and natural variability in 2005. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L12704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liebmann, B.; Smith, C.A. Description of a Complete (Interpolated) Outgoing Longwave Radiation Datasets. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 1275–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson, C.L.; Cavalieri, D.J. Arctic sea ice variability and trends, 1979–2006. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2008, 113, 1979–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Xie, H. Assessing Three Waveform Retrackers on Sea Ice Freeboard Retrieval from Cryosat-2 Using Operation IceBridge Airborne Altimetry Datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 204, 456–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ke, C.-Q.; Xie, H.; Miao, X.; Shen, X.; Xia, W. Arctic Sea ice thickness retrievals from CryoSat-2: Seasonal and interannual comparisons of three different products. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 152–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroeve, J.; Barrett, A.; Serreze, M.; Schweiger, A. Using records from submarine, aircraft and satellites to evaluate climate model simulations of Arctic sea ice thickness. Cryosphere 2014, 8, 1839–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lang, A.; Yang, S.; Kaas, E. Sea ice thickness and recent Arctic warming. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R.; Spreen, G.; Pang, S. Arctic sea ice circulation and drift speed: Decadal trends and ocean currents. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 2408–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haine, T.W.N.; Curry, B.; Gerdes, R.; Hansen, E.; Karcher, M.; Lee, C.; Rudels, B.; Spreen, G.; Steur, L.D.; Stewart, K.D.; et al. Arctic freshwater export: Status, mechanisms, and prospects. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2015, 125, 13–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bi, H.; Sun, K.; Zhou, X.; Huang, H.; Xu, X. Arctic Sea Ice Area Export Through the Fram Strait Estimated from Satellite-Based Data:1988–2012. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 3144–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedsrud, L.H.; Halvorsen, M.H.; Stroeve, J.C.; Zhang, R.; Kloster, K. Fram Strait sea ice export variability and September Arctic sea ice extent over the last 80 years. Cryosphere 2017, 11, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinje, T.; Kvambekk, Å.S. Barents Sea drift ice characteristics. Polar Res. 1991, 10, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauker, F. Variability of Arctic and North Atlantic sea ice: A combined analysis of model results and observations from 1978 to 2001. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2003, 108, 3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Lindsay, R.; Steele, M.; Schweiger, A. What drove the dramatic retreat of arctic sea ice during summer 2007? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L11505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smedsrud, L.H.; Sorteberg, A.; Kloster, K. Recent and future changes of the Arctic sea-ice cover. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L20503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Årthun, M.; Eldevik, T.; Smedsrud, L.H.; Skagseth, Q.; Ingvaldsen, R.B. Quantifying the influence of Atlantic heat on Barents Sea ice variability and retreat. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 4736–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Stegall, S.T.; Zhang, X. Wind–sea surface temperature–sea ice relationship in the Chukchi–Beaufort Seas during autumn. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 034008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perovich, D.K.; Polashenski, C. Albedo evolution of seasonal Arctic sea ice. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L08501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castruccio, F.S.; Ruprich-Robert, Y.; Yeager, S.G.; Danabasoglu, G.; Msadek, R.; Delworth, T.L. Modulation of Arctic Sea Ice Loss by Atmospheric Teleconnections from Atlantic Multidecadal Variability. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 1419–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhong, S.; Zhou, M.; Lenschow, D.H.; Sun, B. Revisiting the linkages between the variability of atmospheric circulations and arctic melt-season sea ice cover at multiple time scales. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 1461–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.J.; Hargreaves, J.C.; Annan, J.D.; Abe-Ouchi, A. Sources of multi-decadal variability in Arctic sea ice extent. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 034011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bathiany, S.; Notz, D.; Mauritsen, T.; Raedel, G.; Brovkin, V.; Bathiany, S.; Notz, D.; Mauritsen, T.; Raedel, G.; Brovkin, V. On the potential for abrupt Arctic winter sea ice loss. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 2703–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zampieri, L.; Goessling, H.F. Sea ice targeted geoengineering can delay Arctic sea ice decline but not global warming. Earth’s Future 2019, 7, 1296–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kashiwase, H.; Ohshima, K.I.; Nihashi, S.; Eicken, H. Evidence for ice-ocean albedo feedback in the Arctic Ocean shifting to a seasonal ice zone. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludescher, J.; Bunde, A.; Schellnhuber, H.J. Statistical significance of seasonal warming/cooling trends. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E2998–E3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, N.; Ding, M.; Ludescher, J.; Bunde, A. Increase of the Antarctic Sea Ice Extent is highly significant only in the Ross Sea. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bunde, A.; Ludescher, J.; Schellnhuber, H.J. How to determine the statistical significance of trends in seasonal records: Application to Antarctic temperatures. Clim. Dyn. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| SIC | SIT | SID | SIL | Weather data | ||||
| SST | SAT | OLR | AMO | |||||
| Temporal coverage | 1979–2020 | 1979–2020 | 1979–2020 | 1982–2018 | 1979–2020 | 1979–2020 | 1979–2020 | 1979–2020 |
| Spatial coverage | Pan-Arctic Ocean | - | ||||||
| Spatial resolution | 25 km | 25 km | 25 km | 25 km | 0.25° | 0.25° | 2.5° | - |
| Temporal resolution | monthly | |||||||
| Source | NSIDC | PSC | NSIDC | EUMETSATCM SAF | ECMWF | NCEP-NCAR | NOAA | |
| SIA | Annual | Winter | Summer |
|---|---|---|---|
| AS | −0.50 | −0.14 | −1.17 |
| PS | −1.73 | 0.08 (p = 0.07) | −4.57 |
| BKS | −1.33 | −1.31 | −0.79 |
| AO | −3.55 | −1.37 | −6.49 |
| SIT | Annual | Winter | Summer |
|---|---|---|---|
| AS | −3.36 | −3.15 | −3.81 |
| PS | −3.25 | −2.58 | −3.90 |
| BK | −1.28 | −1.49 | −0.92 |
| AO | −2.77 | −2.46 | −3.10 |
| Correlation | SIT | SIA | SST | SAT | OLR | AMO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIT | 1 | |||||
| SIA | 0.59 | 1 | ||||
| SST | −0.80 | −0.43 | 1 | |||
| SAT | −0.58 | −0.34 | 0.43 | 1 | ||
| OLR | −0.40 | −0.31 | 0.38 | 0.44 | 1 | |
| AMO | −0.63 | −0.35 | 0.70 | 0.31 | 0.32 | 1 |
| Correlation | SIT | SIA | SST | SAT | OLR | AMO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIT | 1 | |||||
| SIA | 0.66 | 1 | ||||
| SST | −0.56 | −0.77 | 1 | |||
| SAT | −0.65 | −0.34 | 0.28 | 1 | ||
| OLR | −0.39 | −0.30 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 1 | |
| AMO | −0.56 | −0.44 | 0.41 | 0.39 | 0.36 | 1 |
| Correlation | SIT | SIA | SST | SAT | OLR | AMO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIT | 1 | |||||
| SIA | 0.84 | 1 | ||||
| SST | −0.67 | −0.62 | 1 | |||
| SAT | −0.64 | −0.64 | 0.56 | 1 | ||
| OLR | −0.43 | −0.48 | 0.25 | 0.42 | 1 | |
| AMO | −0.40 | −0.39 | 0.48 | 0.34 | 0.18 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Ke, C.; Cheng, B.; Shen, X.; He, Y.; Sha, D. The Roles of Sea Ice Export, Atmospheric and Oceanic Factors in the Seasonal and Regional Variability of Arctic Sea Ice during 1979–2020. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040904
Li M, Ke C, Cheng B, Shen X, He Y, Sha D. The Roles of Sea Ice Export, Atmospheric and Oceanic Factors in the Seasonal and Regional Variability of Arctic Sea Ice during 1979–2020. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(4):904. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040904
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Mengmeng, Changqing Ke, Bin Cheng, Xiaoyi Shen, Yue He, and Dexuan Sha. 2022. "The Roles of Sea Ice Export, Atmospheric and Oceanic Factors in the Seasonal and Regional Variability of Arctic Sea Ice during 1979–2020" Remote Sensing 14, no. 4: 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040904
APA StyleLi, M., Ke, C., Cheng, B., Shen, X., He, Y., & Sha, D. (2022). The Roles of Sea Ice Export, Atmospheric and Oceanic Factors in the Seasonal and Regional Variability of Arctic Sea Ice during 1979–2020. Remote Sensing, 14(4), 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040904