Multi-Temporal Variations in Surface Albedo on Urumqi Glacier No.1 in Tien Shan, under Arid and Semi-Arid Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
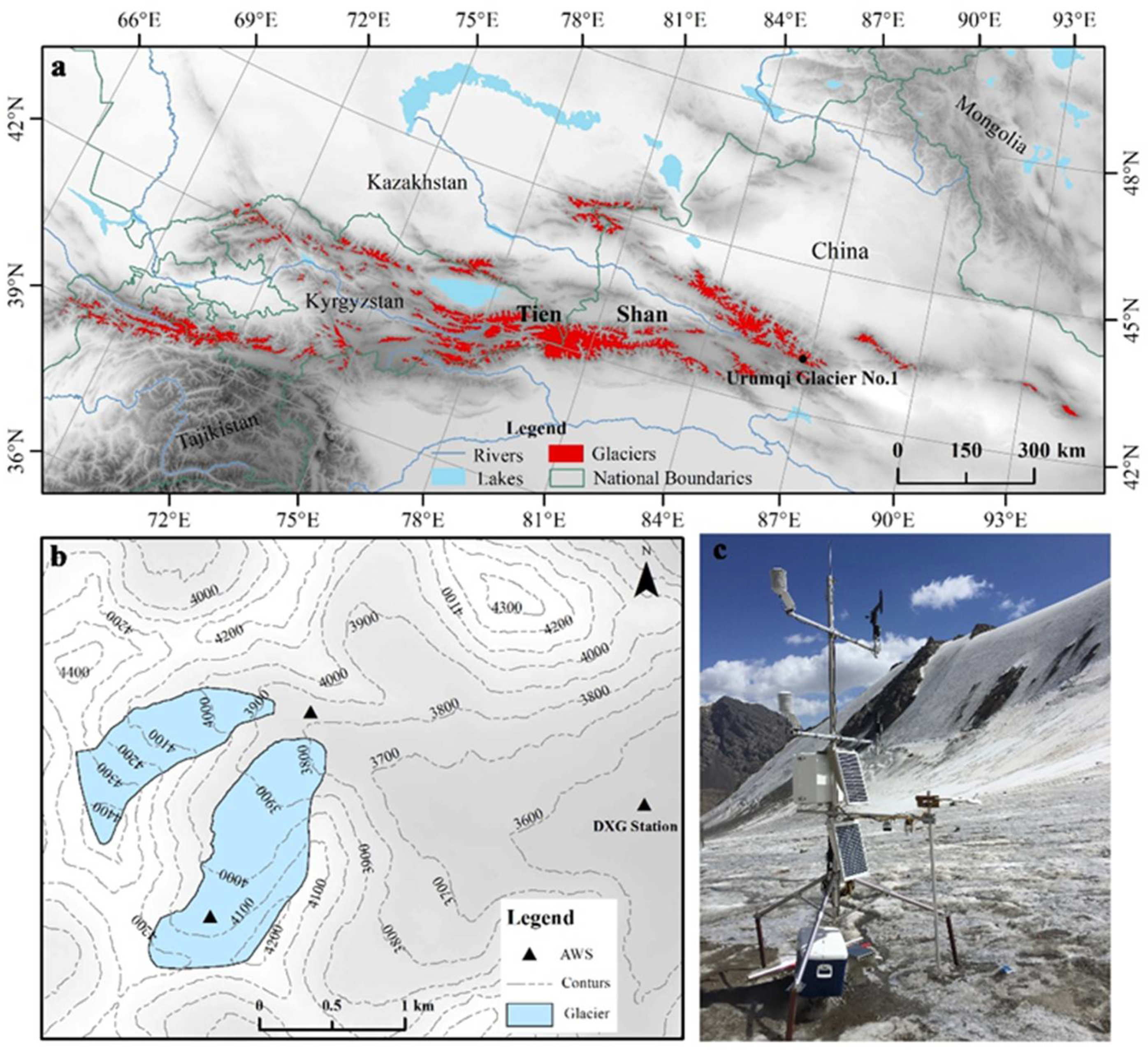
2. Study Site
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Broadband Albedo Derived from Satellite Data
3.1.1. MOD10A1 Products
3.1.2. Landsat Data
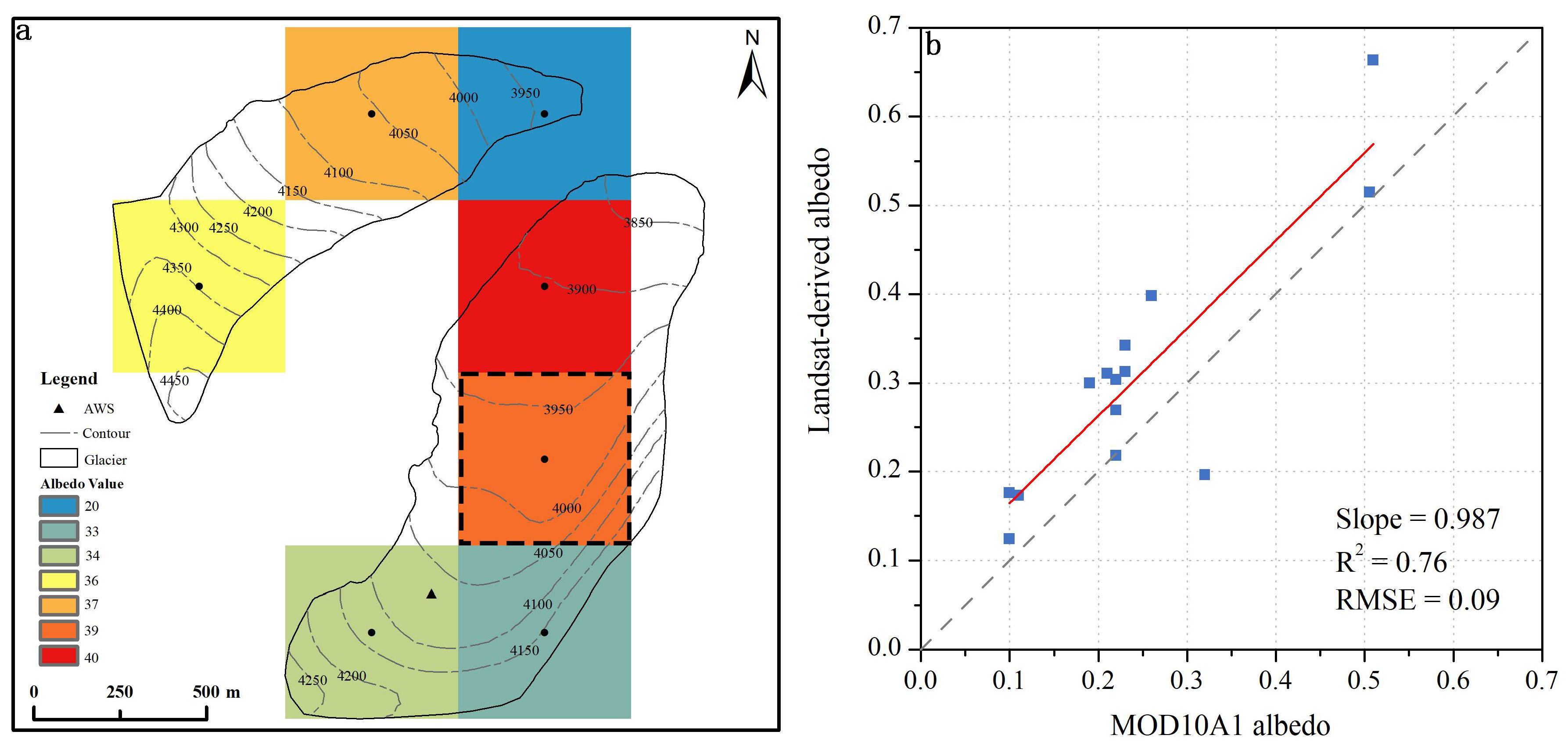
3.2. Field Measurements
3.3. Uncertainties in the Data
4. Results
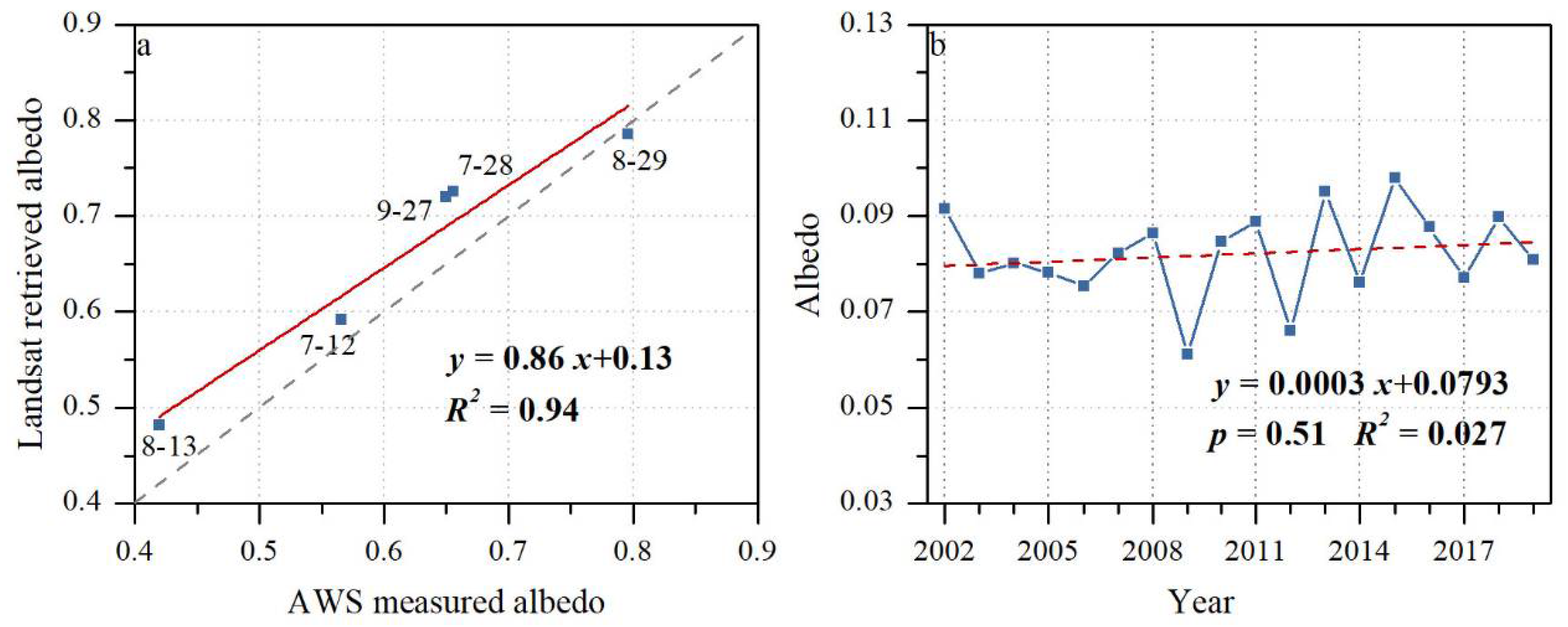
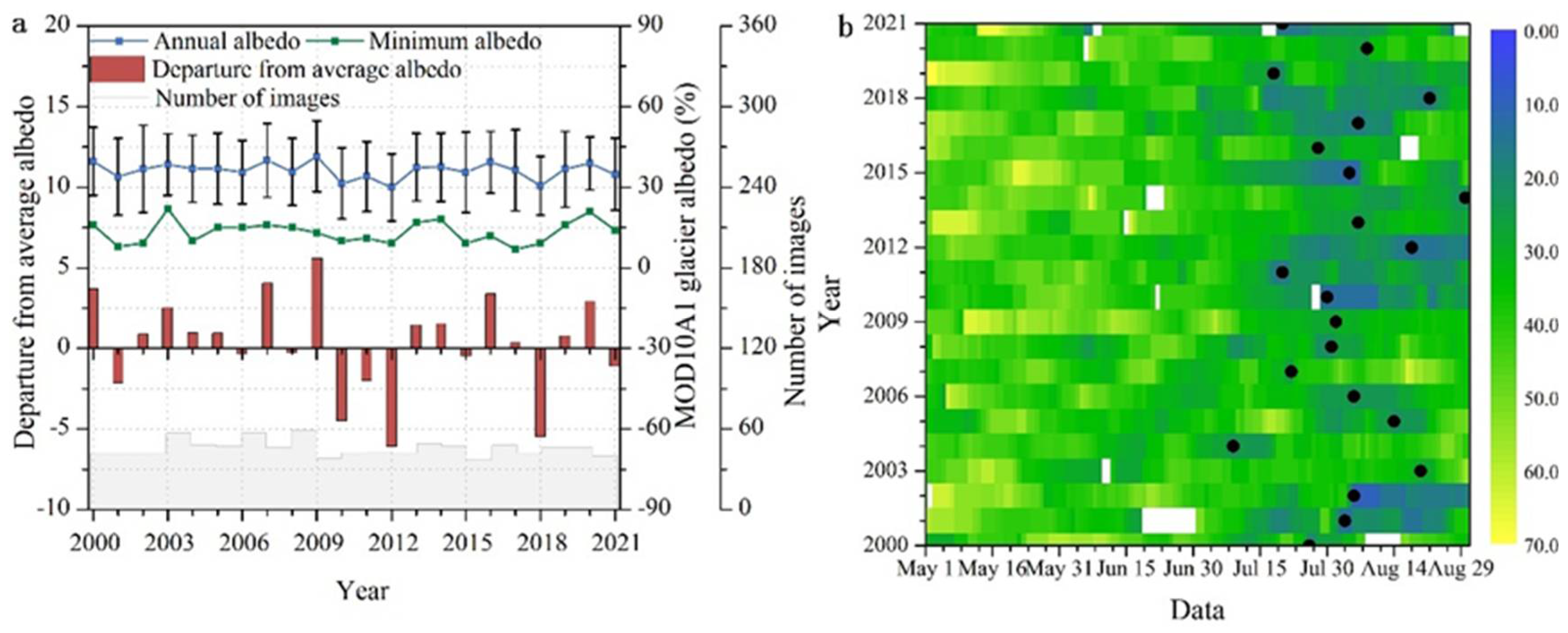
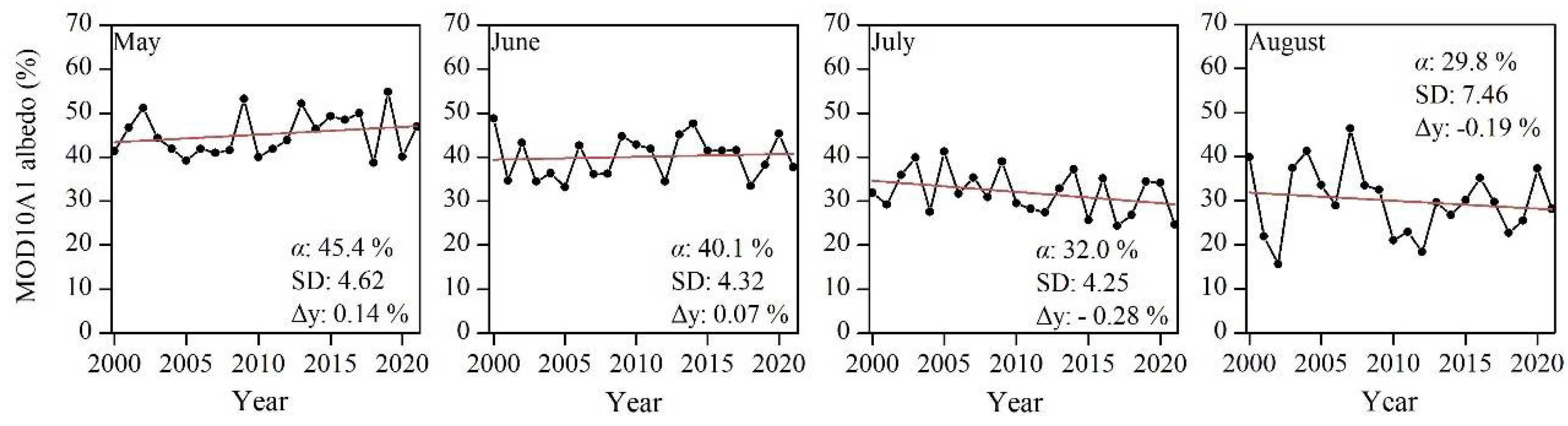
4.1. Interannual Variability of Glacier Albedo from MOD10A1 Products
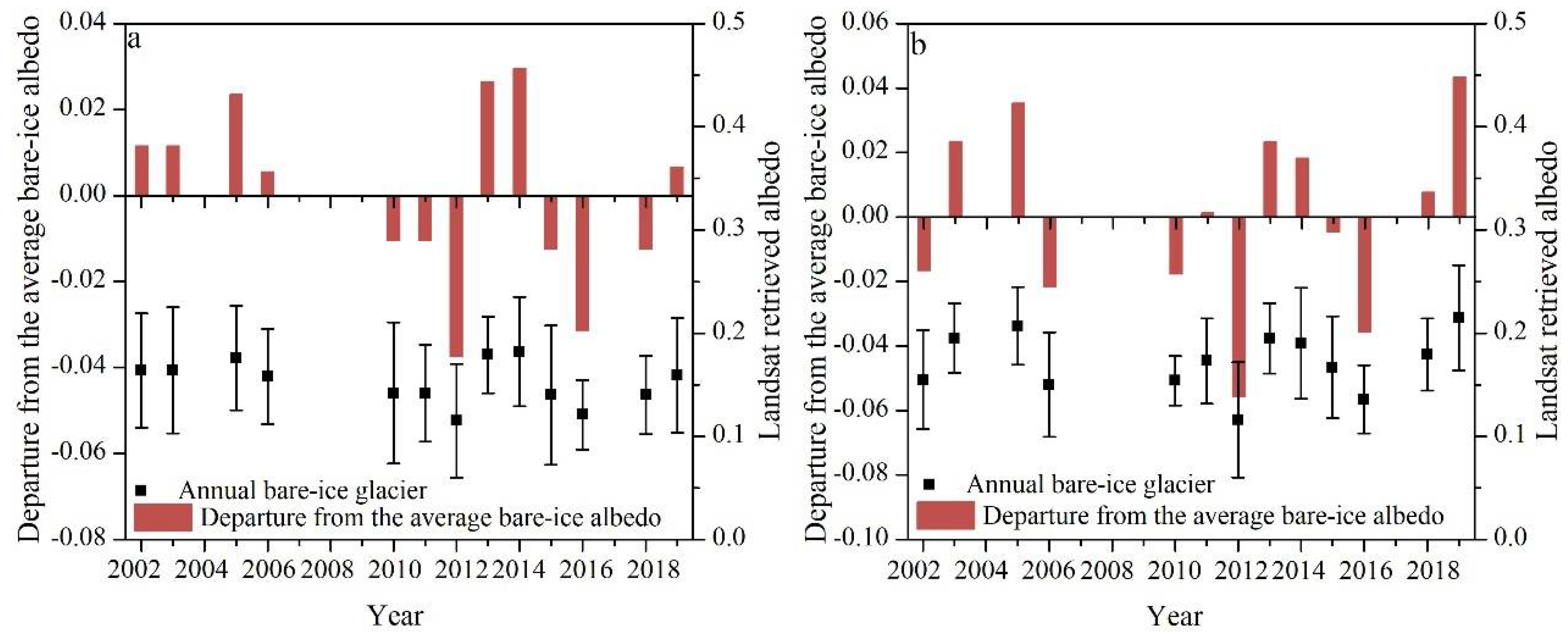
4.2. Multi-Year Variability of the Bare-Ice Albedo Retrieved from Landsat Imagery
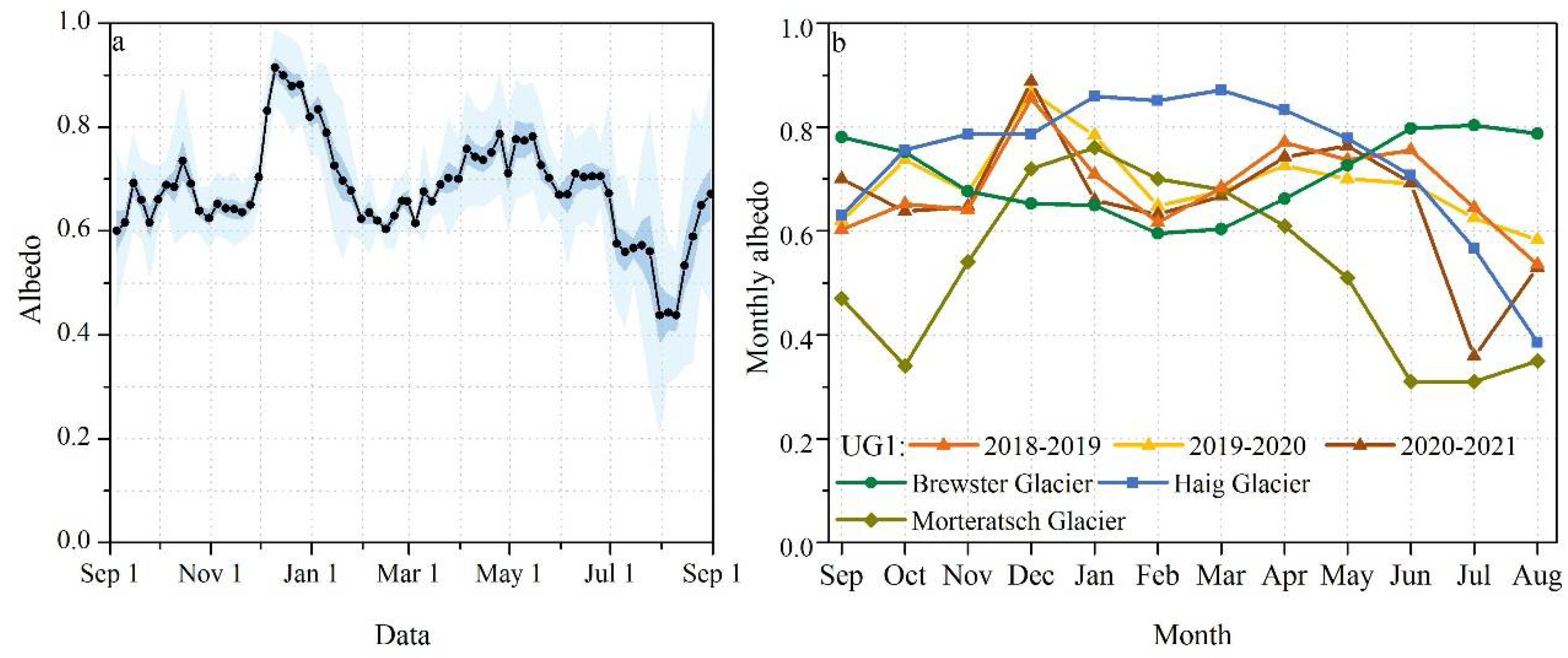
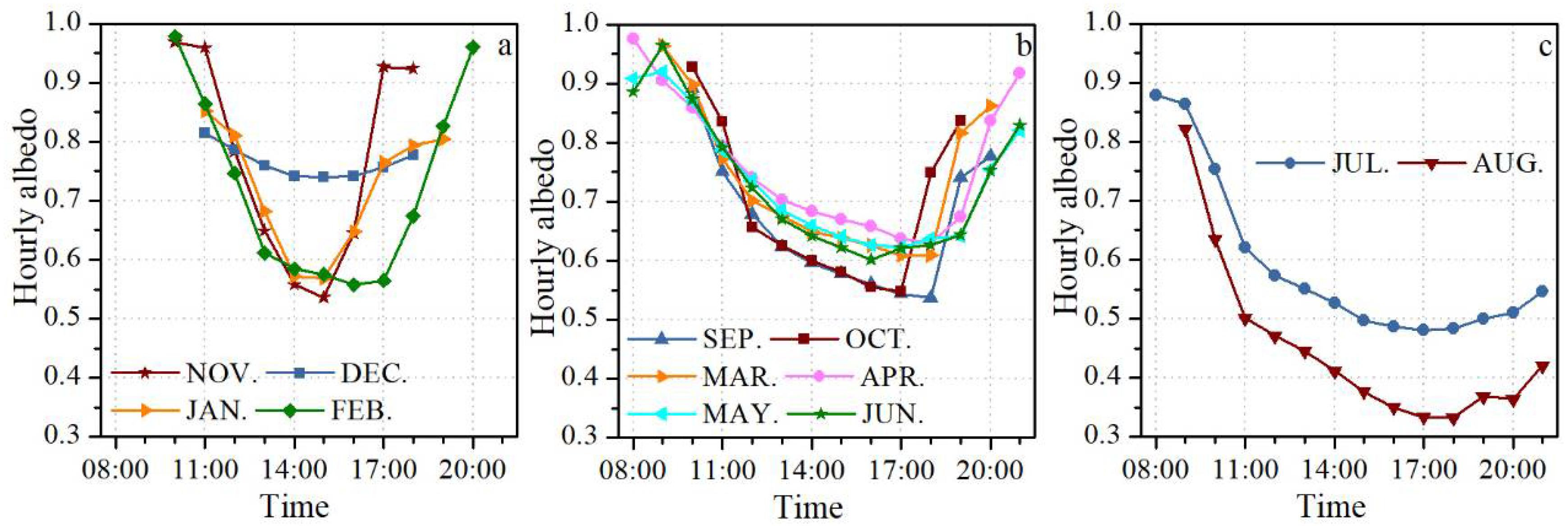
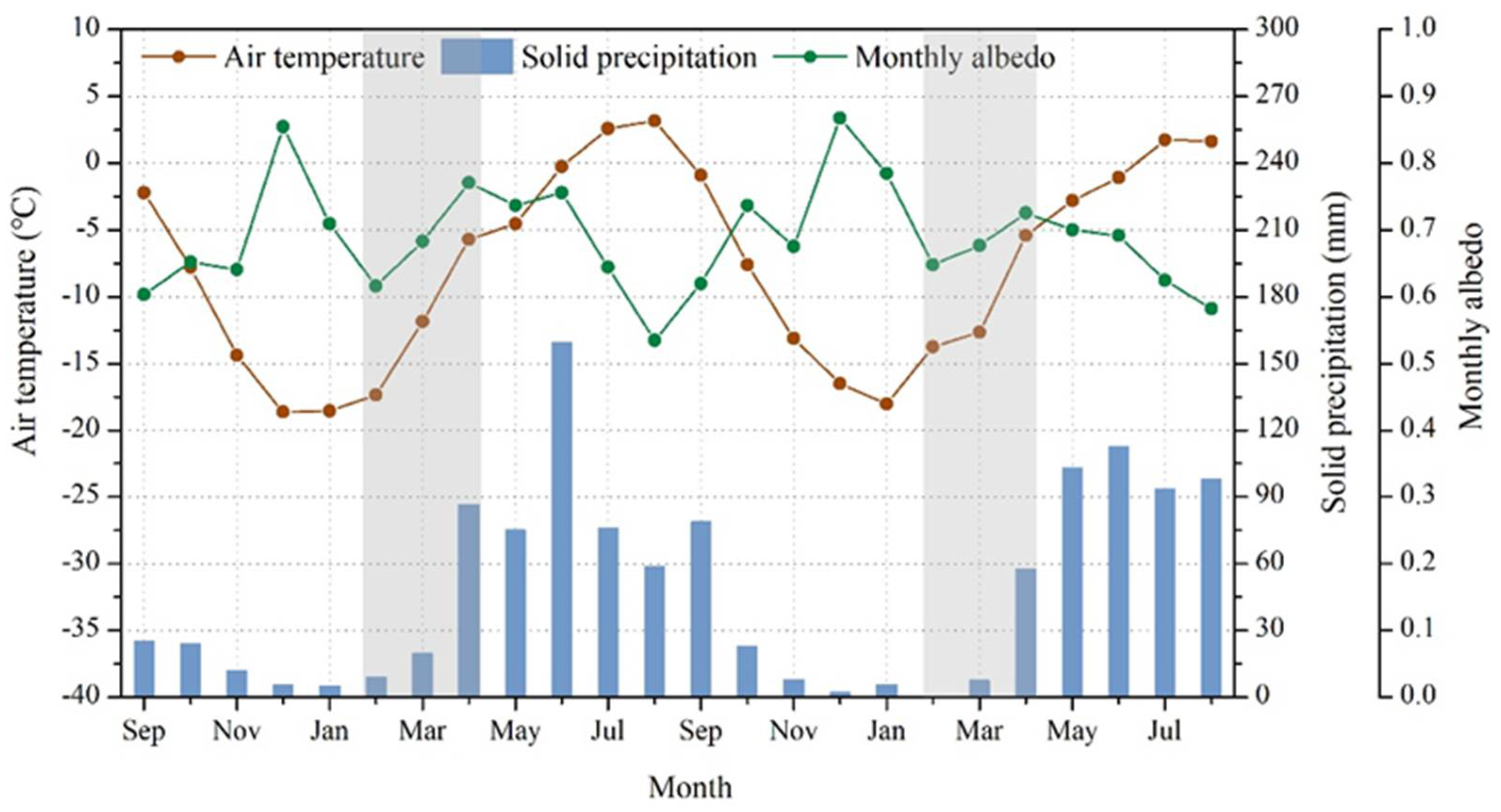
4.3. Seasonal Variations in Average Albedo Measured by AWS near the ELA
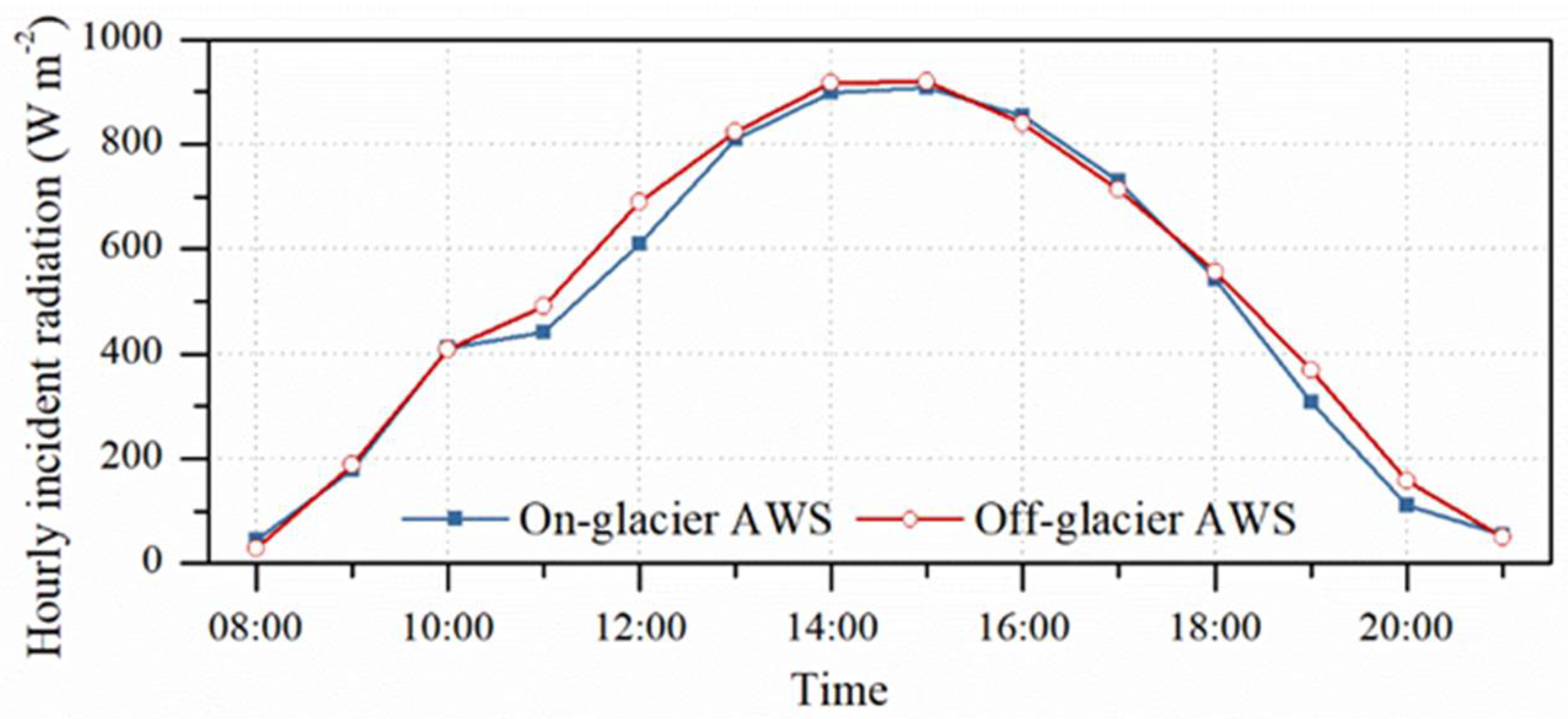
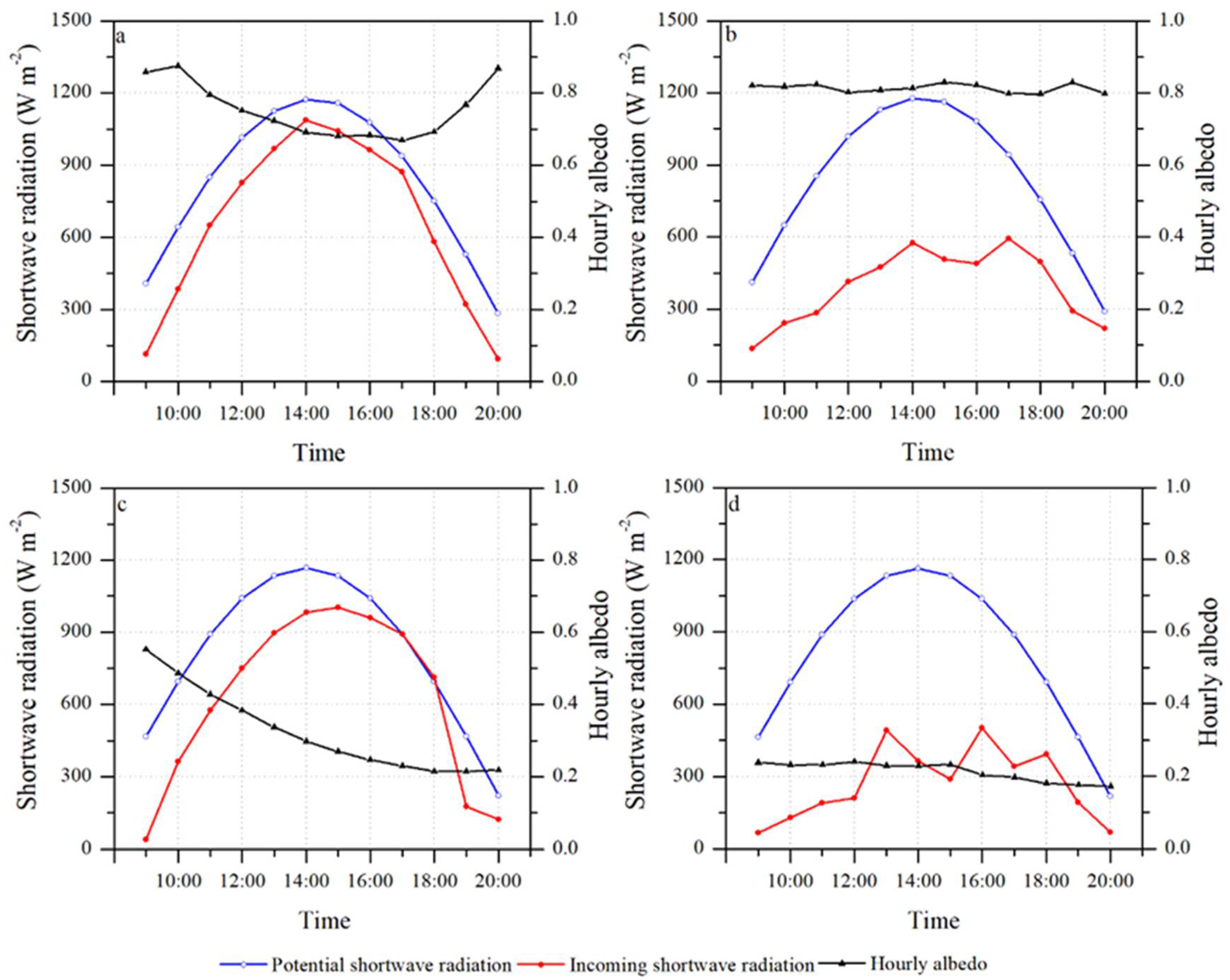
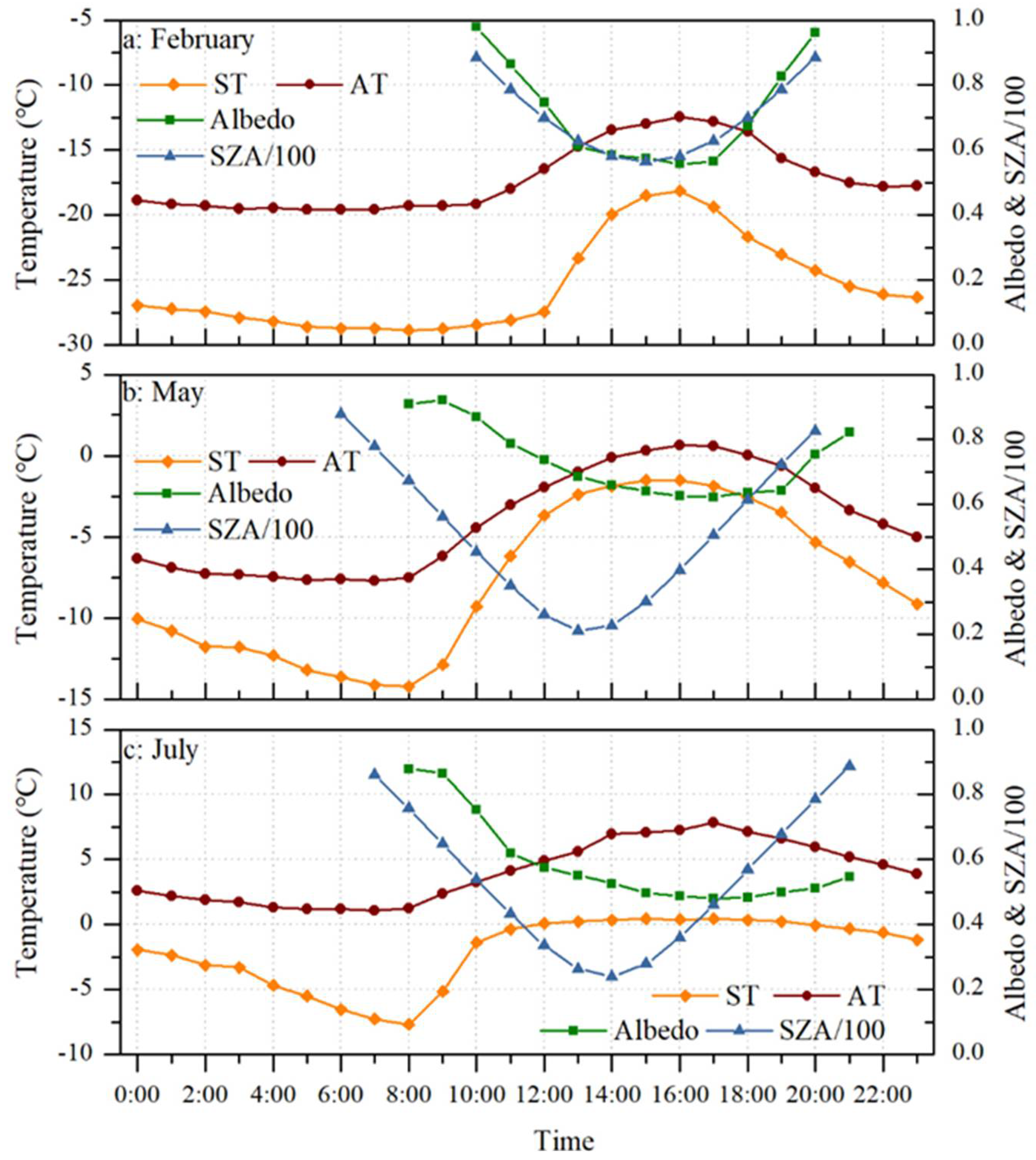
4.4. The Diurnal Cycles in the Surface Albedo Measured by AWS near the ELA
5. Discussions
5.1. Influence of Air Temperature and Precipitation on Glacier Albedo
5.2. Possible Causes of Diurnal Cycle of Surface Albedo
5.3. Absorbed Shortwave Radiation Difference
5.4. Potential Impact of Albedo Variation on Glacier Melting
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, D.; Zhou, B.; Xiao, C. Progress in studies of cryospheric changes and their impacts on climate of China. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2014, 72, 869–879. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné, K.; Rasmussen, M.B.; Orlove, B. Glaciers and society: Attributions, perceptions, and valuations. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2014, 5, 793–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, K.; Wang, L. Study on recent glacier changes and their impact on water resources in Xinjiang, North Western China. Quat. Sci. 2010, 30, 96–106. [Google Scholar]
- Che, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Wei, Y.; Nan, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Su, B. Energy balance model of mass balance and its sensitivity to meteorological variability on Urumqi River Glacier No.1 in the Chinese Tien Shan. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, W.; Qin, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Du, W.; Zhang, T.; Huai, B. The response of surface mass and energy balance of a continental glacier to climate variability, western Qilian Mountains, China. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 50, 3557–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, N.; He, J.; Wu, X.; Song, G. A distributed surface energy and mass balance model and its application to a mountain glacier in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 2079–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Yao, T.; Yang, W.; Maussion, F.; Huintjes, E.; Li, S. Energy- and mass-balance comparison between Zhadang and Parlung No. 4 glaciers on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Glaciol. 2015, 61, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brock, B.W.; Willis, I.C.; Sharp, M.J. Measurement and parameterization of albedo variations at Haut Glacier d’Arolla, Switzerland. J. Glaciol. 2000, 46, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, Y. Mechanisms and Simulation of Accelerated Shrinkage of Continental Glaciers a Case Study of Urumqi Glacier No. 1 in Eastern Tianshan, Central Asia. J. Earth Sci. 2011, 22, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuffey, K.M.; Paterson, W.S.B. The Physics of Glaciers, 4th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 145–146. [Google Scholar]
- Oerlemans, J.; Giesen, R.H.; Van den Broeke, M.R. Retreating alpine glaciers increased melt rates due to accumulation of dust (Vadret da Morteratsch, Switzerland). J. Glaciol. 2009, 55, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Ye, B.; Cui, Y.; He, X.; Yang, G. Spatial and temporal variations of albedo on nine glaciers in western China from 2000 to 2011. Hydrol. Processes 2014, 28, 3454–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.; Kim, H.C.; Huh, M.; Yeom, J.M.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, K.S.; Choi, S.; Han, K.S. Long-Term variability of surface albedo and its correlation with climatic variables over Antarctica. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oerlemans, J.; Knap, W.H. A 1 year record of global radiation and albedo in the ablation zone of Morteratschgletscher, Switzerland. J. Glaciol. 1998, 44, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marshall, S.J.; Miller, K. Seasonal and interannual variability of melt-season albedo at Haig Glacier, Canadian Rocky Mountains. Cryosphere 2020, 14, 3249–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsell, U.; Hock, R.; Holmgren, B. Spatial and temporal variations in albedo on Storglaciaren, Sweden. J. Glaciol. 2003, 49, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Zender, C.S. Arctic and Antarctic diurnal and seasonal variations of snow albedo from multiyear Baseline Surface Radiation Network measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, F0Shaw08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fugazza, D.; Senese, A.; Azzoni, R.S.; Maugeri, M.; Maragno, D.; Diolaiuti, G.A. New evidence of glacier darkening in the Ortles-Cevedale group from Landsat observations. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2019, 178, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naegeli, K.; Huss, M.; Hoelzle, M. Change detection of bare-ice albedo in the Swiss Alps. Cryosphere 2019, 13, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.; Kang, S.; Wu, H.; Yuan, X. Detection of spatio-temporal variability of air temperature and precipitation based on long-term meteorological station observations over Tianshan Mountains, Central Asia. Atmos. Res. 2018, 203, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, N.; Li, Z. Characteristics of Surface Dust on Ürümqi Glacier No. 1 in the Tien Shan Mountains, China. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2008, 40, 744–750. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, J.; Fan, J.; Takeuchi, N.; Wang, L. Variations in albedo and relationship with surface dust at Urumqi Glacier No.1 in Tien Shan, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinotti, D.; Longuevergne, L.; Moholdt, G.; Duethmann, D.; Mölg, T.; Bolch, T.; Vorogushyn, S.; Güntner, A. Substantial glacier mass loss in the Tian Shan over the past 50 years. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Kang, E.; Felix, B. Characteristics of precipitation in the source area of the Urumqi River Basin. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 1992, 14, 258–266. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, A.G.; Stroeve, J. Development and validation of a snow albedo algorithm for the MODIS Instrument. Ann. Glaciol. 2002, 34, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A. MODIS/Terra Snow Cover Daily L3 Global 500 m SIN Grid, [2000–2021], Version 61; NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Stamnes, K.; Tsay, S.C.; Wiscombe, W.; Jayaweere, K. Numerically stable algorithm for discrete-ordinate-method radiative transfer in multiple scattering and emitting layered media. Appl. Opt. 1988, 27, 2502–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Schaaf, C.B.; Chopping, M.J.; Strahler, A.H.; Wang, J.; Román, M.O.; Rocha, A.V.; Woodcock, C.E.; Shuai, Y. Evaluation of Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) snow albedo product (MCD43A) over tundra. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 264–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, C.A.; Martin, S. Spatiotemporal variability of Canadian High Arctic glacier surface albedo from MODIS data. Cryosphere 2018, 12, 701–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunnarsson, A.; Gardarsson, S.M.; Pálsson, F.; Jóhannesson, T.; Sveinsson, Ó.G.B. Annual and inter-annual variability and trends of albedo of Icelandic glaciers. Cryosphere 2021, 15, 547–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachikawa, T.; Kaku, M.; Iwasaki, A.; Gesch, D.; Oimoen, M.; Zhang, Z.; Danielson, J.; Krieger, T.; Curtis, B.; Haase, J.; et al. ASTER Global Digital Elevation Model Version 2—Summary of Validation Results; NASA Land Processes; NASA Distributed Ac-tive Archive Center/Joint Japan–US ASTER Science Team: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Klok, E.J.; Greull, W.; Oerlemans, J. Temporal and spatial variation of the surface albedo of Morteratschgletscher, Switzerland, as derived from 12 Landsat images. J. Glaciol. 2003, 49, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, M.; Fan, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, P. Spatial and temporal variations of the surface albedo and other factors influencing Urumqi Glacier No. 1 in Tien Shan, China. J. Glaciol. 2017, 63, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greuell, W.; De Ruyter de Wildt, M. Anisotropic reflection of melting glacier ice: Measurements and parameterizations. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 70, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijmer, C.H.; Bintanja, R.; Greuell, W. Surface albedo measurements over snow blue ice in thematic mapper bands 2 and 4 Dronning Maud Land, Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 9661–9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knap, W.H.; Reijmer, C.H.; Oerlemans, J. Narrowband to broadband conversion of Landsat TM glacier albedos. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 2091–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugazza, D.; Senese, A.; Azzoni, R.S.; Maugeri, M.; Diolaiuti, G.A. Spatial distribution of surface albedo at the Forni Glacier (Stelvio National Park, Central Italian Alpa). Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2016, 125, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knap, W.H.; Brock, B.W.; Oerlemans, J.; Willis, I.C. Comparison of Landsat TM-derived and ground-based albedos of Haut Glacier d’Arolla, Switzerland. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 3293–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abermann, J.; Kinnard, C.; Macdonell, S. Albedo variations and impact of cloud on glaciers in the Chilean semi-arid Andes. J. Glaciol. 2014, 60, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brock, B.W. An analysis of short-term albedo variations at Haut Glacier d’Arolla, Switzerland. Geogr. Ann. 2004, 86, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.; Atsumu, O. Study on energy-water-mass balance and the hydrological flow model in a glacierized catchment of Tianshan mountain. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1993, 38, 925–929. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Schneider, C.; Li, H.; Hamm, A.; Jing, S.; Xu, C.; Li, H.; Yue, X.; Yang, M. A test study of an energy and mass balance model ap-plication to a site on Urumqi Glacier No. 1, Chinese Tian Shan. Water 2020, 12, 2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WGMS 2021. Global Glacier Change Bulletin No. 4 (2018–2019); Zemp, M., Nussbaumer, S.U., GärtnerRoer, I., Bannwart, J., Paul, F., Hoelzle, M., Eds.; World Glacier Monitoring Service; ISC(WDS)/IUGG(IACS)/UNEP/UNESCO/WMO: Zurich, Switzerland, 2021; p. 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Fang, H.; Chen, M.; Shuey, C.J.; Walthall, C.; Daughtry, C.; Morisette, J.; Schaaf, C.; Strahler, A. Validating MODIS land surface reflectance and albedo products: Methods and preliminary results. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, T.E.; Ulloa, G.; Farías-Barahona, D.; Fernandez, R.; Lattus, J.M.; McPhee, J. Glacier albedo reduction and drought effects in the extratropical Andes, 1986–2020. J. Glaciol. 2020, 12, 2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirguey, P.; Still, H.; Cullen, N.J.; Dumont, M.; Arnaud, Y.; Conway, J.P. Reconstructing the mass balance of Brewster Glacier, New Zealand, using MODIS-derived glacier-wide albedo. Cryosphere 2016, 10, 2465–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gardner, A.S.; Sharp, M.J. A review of snow and ice albedo and the development of a new physically based broadband albedo parameterization. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2010, 15, F01009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, M.; Gardelle, J.; Sirguey, P.; Guillot, A.; Six, D.; Rabatel, A.; Arnaud, Y. Linking glacier annual mass balance and glacier albedo retrieved from MODIS data. Cryosphere 2012, 6, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sirguey, P.; Mathieu, R.; Arnaud, Y. Subpixel monitoring of the seasonal snow cover with MODIS at 250 m spatial resolution in the Southern Alps of New Zealand: Methodology and accuracy assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 160–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilker, T.; Wulder, M.A.; Coops, N.C.; Seitz, N.; White, J.C.; Gao, F.; Masek, J.G.; Stenhouse, G. Generation of dense time series synthetic Landsat data through data blending with MODIS using a spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1988–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
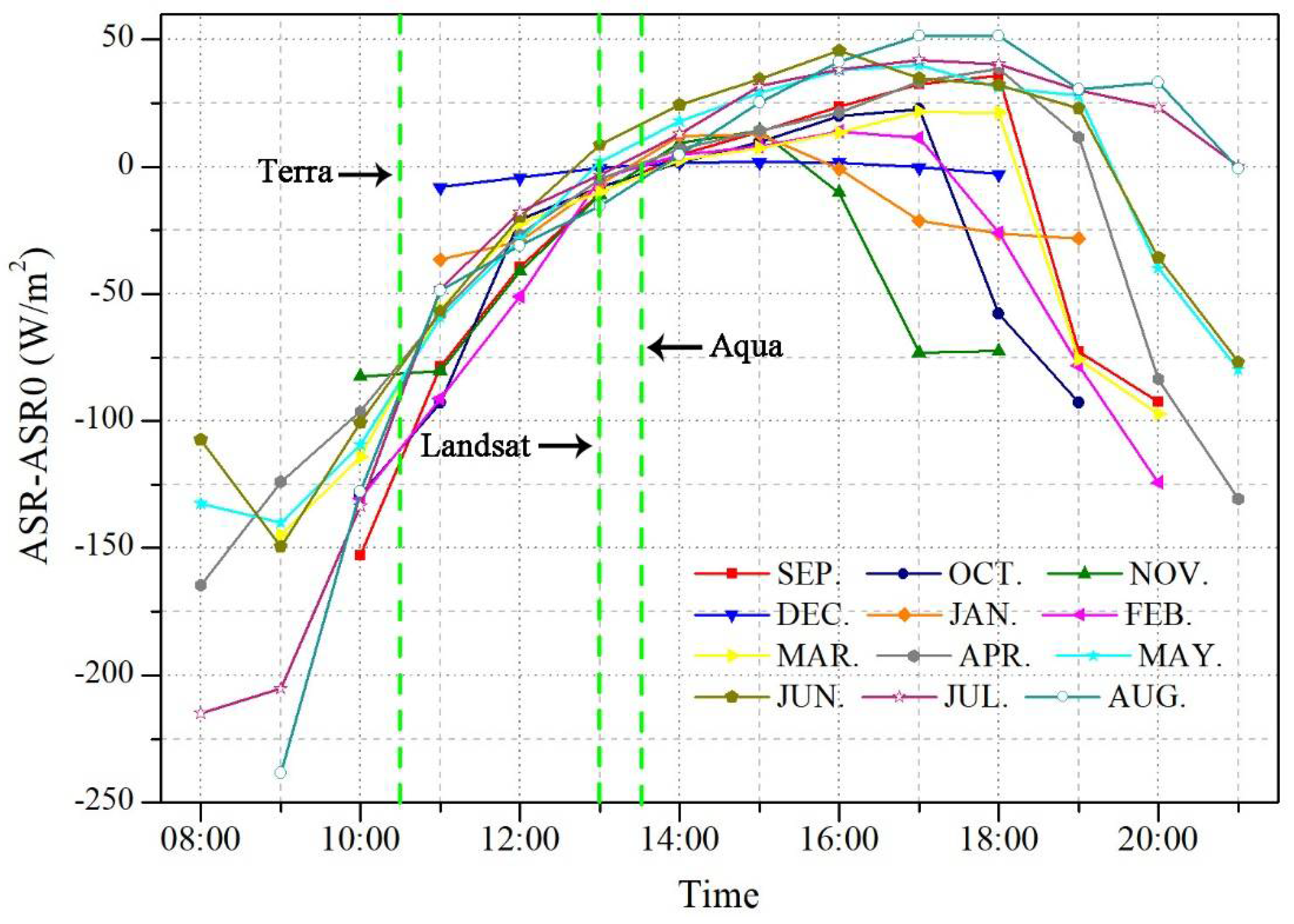
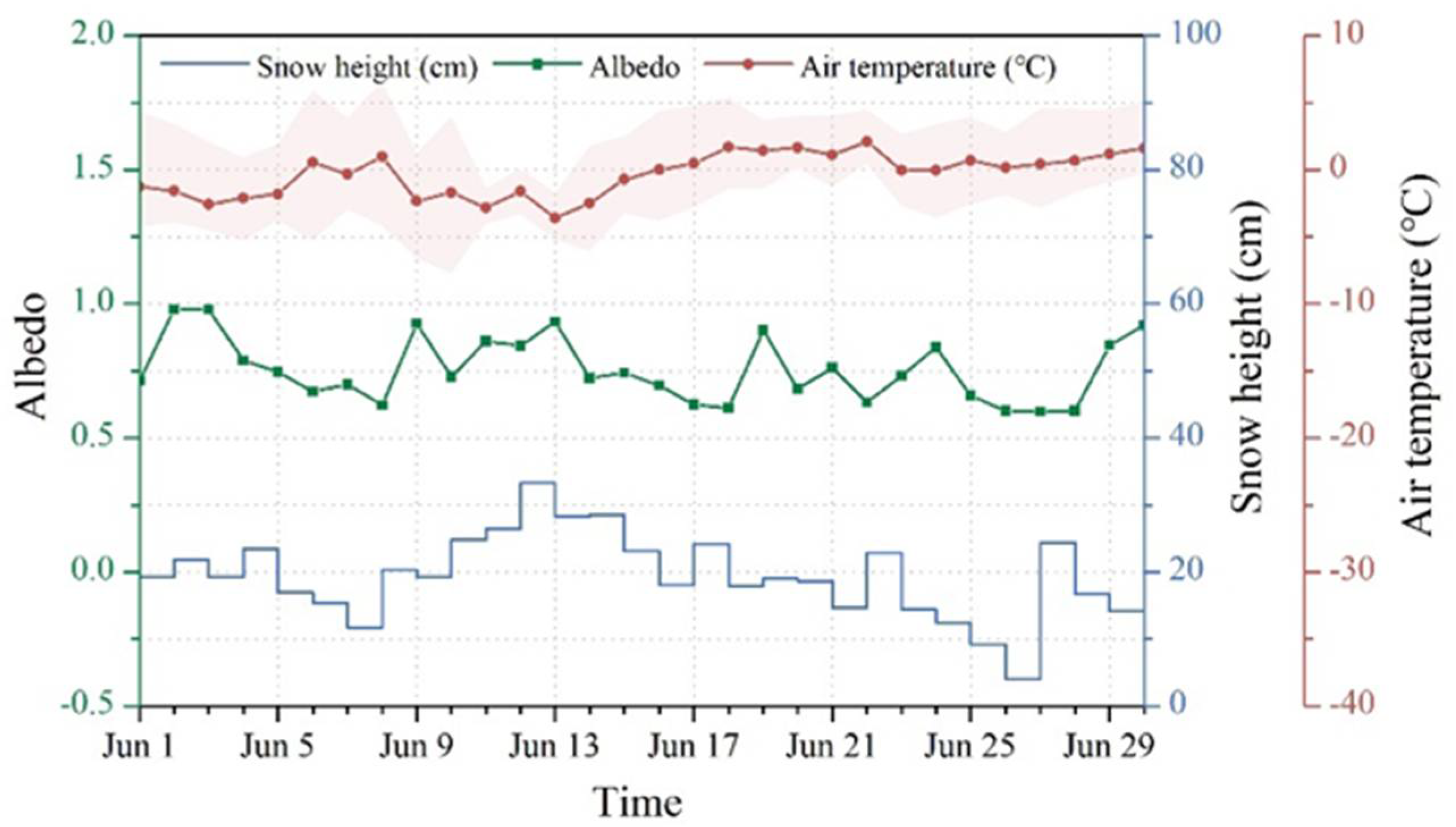
| Date YYYYMMDD | Landsat Sensor | Verify the MOD10A1 | Date YYYYMMDD | Landsat Sensor | Verify the MOD10A1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20020814 | TM5 | No | 20150826 | ETM+ | Yes |
| 20030817 | TM5 | Yes | 20160804 | OLI | Yes |
| 20050814 | ETM+ | Yes | 20180810 | OLI | Yes |
| 20060801 | ETM+ | Yes | 20180927 * | OLI | No |
| 20100804 | TM5 | Yes | 20190712 * | OLI | No |
| 20110807 | TM5 | Yes | 20190728 * | OLI | Yes |
| 20120902 | ETM+ | Yes | 20190813 * | OLI | Yes |
| 20130905 | ETM+ | Yes | 20190829 * | OLI | Yes |
| 20140831 | OLI | Yes |
| Observing Parameter | Sensors | Company | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air temperature (°C) | HC2-S3 | Rotronic | ±0.1 °C (23 °C) |
| Shortwave radiation (W m−2) | CNR4 | Kipp&Zonen | <20 W/m2 @ < 80° |
| Precipitation (mm) | T-200B | Geonor | ±0.1mm (−40 °C~60 °C) |
| Surface height (cm) | SR50A | Campbell | ±1.0 cm |
| Surface temperature (°C) | SI-111 | Campbell | ±0.2 °C @−10~65 °C ±0.5 °C @−40~70 °C |
| Data Sources | Time Scales | Solid Precipitation | Air Temperature | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.8 °C | 1.0 °C | |||
| albedo from MOD10A1, climate variables from DXG weather station | mean ablation-period albedo vs. mean ablation-period climate variables | 0.441 * | 0.483 * | −0.455 * |
| mean ablation-period albedo vs. mean accumulation-period climate variables | 0.348 | 0.383 | 0.331 | |
| mean albedo in May vs. mean accumulation-period climate variables | 0.600 ** | 0.743 ** | 0.072 | |
| mean albedo in May vs. mean climate variables in May | 0.175 | 0.311 | −0.327 | |
| mean albedo in June vs. mean climate variables in June | 0.536 * | 0.543 * | −0.533 * | |
| mean albedo in July vs. mean climate variables in July | 0.212 | 0.334 | −0.556 * | |
| mean albedo in August vs. mean climate variables in August | 0.707 ** | 0.583 ** | −0.762 ** | |
| albedo and climate variables from the on-glacier AWS | mean monthly albedo vs. monthly climate variables | 0.292 | 0.252 | −0.571 * |
| mean daily albedo vs. daily climate variables | 0.182 ** | 0.240 ** | −0.386 ** | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, X.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, F.; Jin, S. Multi-Temporal Variations in Surface Albedo on Urumqi Glacier No.1 in Tien Shan, under Arid and Semi-Arid Environment. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040808
Yue X, Li Z, Li H, Wang F, Jin S. Multi-Temporal Variations in Surface Albedo on Urumqi Glacier No.1 in Tien Shan, under Arid and Semi-Arid Environment. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(4):808. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040808
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Xiaoying, Zhongqin Li, Huilin Li, Feiteng Wang, and Shuang Jin. 2022. "Multi-Temporal Variations in Surface Albedo on Urumqi Glacier No.1 in Tien Shan, under Arid and Semi-Arid Environment" Remote Sensing 14, no. 4: 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040808
APA StyleYue, X., Li, Z., Li, H., Wang, F., & Jin, S. (2022). Multi-Temporal Variations in Surface Albedo on Urumqi Glacier No.1 in Tien Shan, under Arid and Semi-Arid Environment. Remote Sensing, 14(4), 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040808







